Blue: Difference between revisions
m robot Modifying: es:Azúl |
m Disambiguation of "orange" link |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
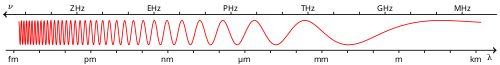
The term '''blue''' may refer any of a number of similar [[color|colours]]. When blue is a pure colour from a single source, it corresponds with a [[wavelength]] range of about 440–490 [[nanometre|nm]]. Blue is considered to be one of the three primary additive colours in the [[RGB]] system; blue [[light]] has the shortest [[wavelength]] range of the three [[primary colour|additive primary colours]]. The English language commonly uses "blue" to refer to any colour from [[navy blue]] to [[cyan]]. The [[complementary colour]] of blue in [[color science|colour science]] is [[yellow]] (on the [[HSV color space|HSV colour wheel]]), while in [[art]] the complementary colour to blue is considered to be [[orange]] (based on the [[Munsell color system|Munsell colour wheel]]). |
The term '''blue''' may refer any of a number of similar [[color|colours]]. When blue is a pure colour from a single source, it corresponds with a [[wavelength]] range of about 440–490 [[nanometre|nm]]. Blue is considered to be one of the three primary additive colours in the [[RGB]] system; blue [[light]] has the shortest [[wavelength]] range of the three [[primary colour|additive primary colours]]. The English language commonly uses "blue" to refer to any colour from [[navy blue]] to [[cyan]]. The [[complementary colour]] of blue in [[color science|colour science]] is [[yellow]] (on the [[HSV color space|HSV colour wheel]]), while in [[art]] the complementary colour to blue is considered to be [[orange (colour)|orange]] (based on the [[Munsell color system|Munsell colour wheel]]). |
||
== Blue in the RGB system == |
== Blue in the RGB system == |
||
Revision as of 14:17, 18 March 2007
This list (which may have dates, numbers, etc.) may be better in a sortable table format. |
| Blue | |
|---|---|
| Hex triplet | #0000FF |
| sRGBB (r, g, b) | (0, 0, 255) |
| HSV (h, s, v) | (240°, 100%, 100%) |
| CIELChuv (L, C, h) | (32, 131, 266°) |
| Source | [Unsourced] |
| B: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) | |
The term blue may refer any of a number of similar colours. When blue is a pure colour from a single source, it corresponds with a wavelength range of about 440–490 nm. Blue is considered to be one of the three primary additive colours in the RGB system; blue light has the shortest wavelength range of the three additive primary colours. The English language commonly uses "blue" to refer to any colour from navy blue to cyan. The complementary colour of blue in colour science is yellow (on the HSV colour wheel), while in art the complementary colour to blue is considered to be orange (based on the Munsell colour wheel).
Blue in the RGB system
In the RGB colour system, colours are formed by mixing a red, a green and a blue colour. When talking about RGB, therefore, some people use blue to mean that specific blue, which varies in shade according to the device used to display the RGB colour. absolute colour spaces based on RGB, such as sRGB, define an exact colour for this blue, which may differ from the actual blue used in a particular computer monitor.
Naming and etymology
Blue as Blue in English
The modern English word blue (German:blau) comes from the Middle English, bleu or blwe, which came from an Old French word bleu of Germanic origin (Frankish or possibly Old High German blao, "shining"). Bleu replaced Old English blaw. The root of these variations was the Proto-Germanic blæwaz, which was also the root of the Old Norse world bla and the modern Icelandic blár, and the Scandinavian word blå. It can also be green or orange occasionally(blue). A Scots and Scottish English word for "blue-grey" is blae, from the Middle English bla ("dark blue," from the Old English blæd). Ancient Greek lacked the word for colour blue and Homer called the colour of the sea 'Wine Coloured'.
As a curiosity, blue is thought to be cognate with blond and black through the Germanic word. Through a Proto-Indoeuropean root, it is also linked with Latin flavus ("yellow"; see flavescent and flavine), with Greek phalos (white), French blanc (white) (loaned from Old Frankish), and with Russian белый, belyi ("white," see beluga), and Welsh blawr (grey) all of which derive (according to the American Heritage Dictionary) from the Proto-Indo-European root *bhel- meaning "to shine, flash or burn", (more specifically the word bhle-was, which meant light coloured, blue, blond, or yellow), from whence came the names of various bright colours, and that of colour black from a derivation meaning "burnt" (other words derived from the root bhel- include bleach, bleak, blind, blink, blank, blush, blaze, flame ,fulminate, flagrant and phlegm).
In the English language, blue may also refer to the feeling of sadness. "He was feeling blue". This is because blue was related to rain, or storms, and in Greek mythology, the god Zeus would make rain when he was sad, and a storm when he was angry. Blue is also used as a name occasionally.
Blue and green in other languages
Many languages do not have separate terms for blue and or green, instead using a cover term for both (when the issue is discussed in linguistics, this cover term is sometimes called grue in English). For example, in Vietnamese both tree leaves and the sky are xanh (to distinguish, one may use xanh lá cây "leaf grue" for green and xanh dương "ocean grue" for blue). Chinese has a word 青 qīng that can refer to both, though it also has separate words for blue (蓝 / 藍, lán) and green (绿 / 綠, lǜ). The Korean word (푸르다"puruda") can mean either green or blue. In Japanese the word for blue (青 ao) is often used for colours that English speakers would refer to as green, such as the colour of a traffic signal meaning "go". Some Nguni languages of southern Africa, including Tswana utilize the same word for blue and green. In traditional Welsh (and related Celtic languages), glas could refer to blue but also to certain shades of green and grey; however, modern Welsh is tending toward the 11-colour Western scheme, restricting glas to blue and using gwyrdd for green and llwyd for grey. Similarly, in Gaelic, glas can mean various shades of green and grey (like the sea), while liath is grey proper (like a horse), and the term for blue proper is gorm (like the sky or Cairngorm mountains). In Old Norse the word blá was also used to describe black (and the common word for negroes was thus blámenn 'blue/black men'). In Swedish, blå, the modern word for blue, was used this way until the early 20th century. In many languages of India, blue is "buru"or "BLU"
In the Lakhota Sioux Language, The word Tĥo is used for both blue and green.
Blue in Russian
On the other hand, Russian does not have a single word referring to the whole range of colours denoted by the English term "blue." Instead, it traditionally treats light blue (голубой, goluboy) as a separate colour independent from plain or dark blue (синий, siniy), with all 7 "basic" colours of the spectrum (red - orange - yellow - green - (ru:голубой / goluboy / light blue, not equal cyan) - (ru:синий / siniy / dark blue) - violet) while in English the light blues like azure and cyan are considered mere shades of "blue" and not different colours. To better understand this, consider that English makes a similar distinction between "red" and light red (pink, which is considered a different colour and not merely a kind of red), but such a distinction is unknown in several other languages; for example, both "red" (红 / 紅, hóng) and "pink" (粉红, fěn hóng, lit. "powder red") have traditionally been considered varieties of a single colour in Chinese.
Blue in Italian
Like Russian, Italian treats light blue ("azzurro") as a separate colour, which is to blue as pink is to red.
Blue in Hebrew
Like Russian and Italian, Hebrew has a separate name for light blue (תכלת, "tchelet") which is to blue as pink is to red (like the Italian "azzuro").
Blue in Turkish
Finally, it has been argued that Turkish treats dark or navy blue (lacivert, curiously from the same root as English azure and lapis lazuli) as a separate colour from plain or light blue (mavi). Mavi is etymologically originated from the Arabic word Ma'i, which meant "like water" (Ma is the Arabic word for water) and lacivert is originated from lajvard, which was accounted as an expensive gem with the colour of navy blue. Some historians argue that lajvard was the Farsi name for lapis lazuli, although there is no solid evidence to prove this claim right. In Shamanism, the preislamic religion of Turks, Blue is the colour that represented the East as opposed to Red, as well as the Zodiac Aquarius (Water). A characteristic tone of blue, Turqoise, was much used by the Turks for their traditional decorations and jewelry.
Blue in the environment
A clear sky on a sunny day appears blue because of Rayleigh scattering of the light from the Sun.
Bodies of water often appear blue due to reflections from the sky. Large quantities of ice or water appear blue because red light around 750 nm is absorbed as an overtone of the O-H stretching vibration. Heavy water is colourless, because the absorption band (~950 nm) is outside the visible spectrum.
Plants


- Blue agave (Agave tequilana var. weber) is a blue-leafed variety of the Mexican agave, used for making tequila.
- Bluebonnets are two lupine annual flowers in the Lupinus genus that are native to Texas: Lupinus subcarnosus and Lupinus texensis. They have a light blue appearance and palmately compound leaves. In Scots it refers to the bird Parus cœruleus.
- Bluebell may refer to both the bulbous plants in the Hyacinthoides genus of lilies, or the plants in the genus Mertensia.
- Blueberry refers to any of the plants in the genus Vaccinium, all of which have flowers with edible berries coloured blue to blue-black, which are also called "blueberries".
- Blue Flag Iris, Iris versicolor, also commonly known as the Harlequin Blueflag.
- Blue Jacaranda, an ornamental tree with blue flowers.
- Blue Spruce, a Rocky Mountain tree having silvery-blue or blue-green needlelike leaves.
Animals
- The Blue Jay is a bird within the family corvidae.
- Cobalt blue tarantulas are large, brightly coloured spiders.
- Hyacinth Macaw, as well as many other species of parrot, are blue.
- Bluebill is a synonym for scaup, the name for two diving ducks in the Aythya genus: Greater Scaup (Aythya marila) and Lesser Scaup (Aythya affinis).
- Bluebirds are any of the North American songbirds in the genus Sialia: Eastern Bluebird (Sialia sialis), Western Bluebird (Sialia mexicana), or Mountain Bluebird (Sialia currucoides). They are medium-sized thrushes that usually have blue plumage and, in males, a rust-colour breast.
- Blueback salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) is a synonym for sockeye salmon.
- Blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus) are the largest animals in the world.
- Bluebottles or blow-flies are any of the flies in the genus Calliphiora that have a brightly-coloured metallic body and breed in decaying organic material. Bluebottle is also another name of the Portuguese man-of-war, Physalia.
- Blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus) is a long bluish North American catfish species, that often weigh more than 45 kg (100 pounds).
- Blue poison dart frogs (Dendrobates azureus) are poisonous South American frogs that bioaccumulate neurotoxins in their blue skin.
When a dog or cat is described as having a "blue" coat, it refers to a shade of grey which takes on a bluish tint, a diluted variant of a pure black coat. Breeds such as the Kerry Blue Terrier dog and the Chartreux and Russian Blue cats have solid "blue" coats, as does the "British Blue" variety of the British Shorthair cat. Others, such as the Australian Shepherd and Border Collie, may have blue merle coats, which is "blue" mixed in with a solid, usually brown or black, base colour. (See also Blue Dog Democrats, below).
The western skink has a brilliant cobalt blue tail.
Geography
Mountains and ranges
- Blå Jungfrun (the Blue Virgin), a small island hill off the coast of southeast Sweden, near the larger island of Öland, traditionally thought to be a meeting place of witches (according to tradition such a mountain is called Blåkulla, but only exists in legend)
- Cairngorm Mountains in Scotland. The name literally means blue rock heap
- Blue Mountains, sandstone mountain range west of Sydney, Australia. Other ranges termed the "Blue Mountains" are found in northeastern Oregon (North America) and elsewhere.
- Blue Ridge Mountains, eastern edge or front range of the Appalachian Mountains.
- Kékes is the name of the tallest mountain in modern-day Hungary and derives its name from the Magyar word for "blue," kék, because of its appearance from a distance on the great plain (Alföld).
- Sinite Kamăni (Bulgarian: Сините камъни; The Blue Stones) is a rocky massive in Eastern Stara Planina Mountain immediately North of the town of Sliven in Bulgaria.
- Nilgiris is a mountain range in South India, and an offshoot of Western Ghats. The name literally means "Blue Mountains " and is famous for many hill stations like Ooty, Coonoor etc.
- "Aoyama" is also a Japanese surname meaning "blue mountain".
National Parkway
- Blue Ridge Parkway is a 469-mile scenic drive that links Shenandoah National Park in Virginia, with the Great Smoky Mountains National Park in North Carolina
Rivers
- Blue Nile, a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia.
- Blue Earth River, a tributary of the Minnesota River in Minnesota, United States. Blue Earth is a translation of the Dakota Indian word Mahkato, meaning greenish blue earth.
Shades of blue colour comparison chart
- Azure Mist (web colour "Azure") (Hex: #F0FFFF) (RGB: 240, 255, 255)
- Alice Blue (web colour) (Hex: #F0F8FF) (RGB: 240, 248, 255)
- Baby Blue (Hex: #E0FFFF) (RGB: 111, 255, 255)
- Lavendula (Vietnamese Lavender) (Pale Indigo) (Hex: #E6E6FA) (RGB: 230, 230, 250)
- Periwinkle (Lavender Blue) (Pastel Indigo) (Hex: #CCCCFF) (RGB: 204, 204, 255)
- Powder Blue (web color) (Hex: #B0E0E6) (RGB: 176, 224, 230)
- Light Blue (Hex: #ADD8E6) (RGB: 173, 216, 230)
- Ultra Blue (Blizzard Blue) (Crayola) (Hex: #A3E3ED) (RGB: 163, 227, 237)
- Light Cornflower Blue (Crayola Cornflower) (Hex: #93CCEA) (RGB: 147, 204, 234)
- Light Sky Blue (web colour) (Hex: #87CEFA) (RGB: 135, 296, 250)
- Sky Blue (web colour) (Hex: #87CEEB) (RGB: 135, 206, 235)
- Medium Sky Blue (Crayola Sky Blue) (Hex: #76D7EA) (RGB: 118, 215, 234)
- Aquamarine Blue (Crayola Aquamarine) (Hex: #71D9E2) (RGB: 113, 217, 226)
- Aquamarine (Hex: #7FFFD4) (RGB: 127, 255, 212)
- Cyan (web color Aqua) (Electric Cyan) (Electrical Blue) (Hex: #00FFFF) (RGB: 0, 255, 255)
- Bright Turquoise (Hex: #08E8DE) (RGB: 8, 232, 222)
- Turquoise (web color) (Hex: #30D5C8) (RGB: 48, 213, 200)
- Process Cyan (Pigment Cyan) (Printer's Cyan) (Hex: #00B7EB) (RGB: 0, 180, 247)
- Turquoise Blue (web colour Deep Sky Blue) (Hex: #00BFFF) (RGB: 0, 191, 255)
- Ukrainian Azure (Colour of Ukrainian Flag) (Hex: #42ADDE) (RGB: 66, 173, 222)
- United Nations Azure (United Nations Blue) (Hex: #5B92E5) (RGB: 91, 146, 229)
- Cornflower Blue (web colour) (Hex: #6495ED) (RGB: 100, 149, 237)
- Bright Cerulean (Crayola Cerulean) (Hex: #02A4D3) (RGB: 2, 164, 211)
- Bondi Blue (Crayola Blue-Green) (Hex: #0095B6) (RGB: 0, 149, 182)
- Cerulean (Hex: #007BA7) (RGB: 0, 123, 167)
- Steel Blue (web colour)(Hex: #4682B4) (RGB: 70, 130, 180)
- Agate Blue (Hex: #44719B) (RGB: 68, 113, 155)
- Medium Persian Blue (Hex: #0067A5) (RGB: 0, 103, 165)
- Swedish Azure (Colour of Swedish flag) (Hex: #005B99) (RGB: 0, 91, 153)
- Indigo Dye (Hex: #1A5798) (RGB: 17, 80, 147)
- Medium Indigo (Crayola Indigo) (Hex: #4F69C6) (RGB: 79, 105, 198)
- Royal Blue (web colour) (Hex: #4169E1) (RGB: 65, 105, 225)
- Dodger Blue (web colour)(Hex: #1E90FF) (RGB: 30, 144, 255)
- Azure (Hex: #007FFF) (RGB: 0, 127, 255)
- Deep Azure (Crayola Blue) (Hex: #0066FF) (RGB: 0, 102, 255)
- BLUE (Hex: #0000FF) (RGB: 0, 0, 255)
- Cerulean Blue (Hex: #2A52BE) (RGB: 42, 82, 190)
- Denim (Same as Crayola Denim) (Hex: #1560BD) (RGB: 21, 96, 189)
- Medium Navy Blue (Crayola Navy Blue) (Hex: #0066CC) (RGB: 0, 102, 204)
- Cobalt Blue (Hex: #0047AB) (RGB: 0, 71, 171)
- Persian Blue (Hex: #1C39BB) (RGB: 28, 57, 187)
- Wikipedia Link Azure (Color of a Wikipedia Link before clicking) (Hex: #002BB8) (RGB: 0, 43, 184)
- Medium Blue (web colour) (Hex: #0000CD) (RGB: 0, 0, 205)
- Dark Blue (web colour) (Hex: #0000CB) (RGB: 0, 0, 200)
- Indigo (Electric Indigo) (Hex: #6600FF) (RGB: 102, 0, 255)
- Medium Slate Blue (web colour) (Hex: #7B68EE) (RGB: 123, 104, 138)
- Deep Lavender (web colour Medium Purple) (Hex: #9370DB) (RGB: 147, 112, 219)
- Lavender (Hex: #B57EDC) (RGB: 181, 126, 220)
- Deep Indigo (web colour Blue-Violet) (Hex: #8A2BE2) (RGB: 138, 43, 226)
- Pigment Indigo (web colour Indigo) (Hex: #4B0082) (RGB: 75, 0, 130)
- Persian Indigo (Hex: #32127A) (RGB: 50, 18, 122)
- Dark Azure (Pantone Blue #286) (Hex: #0038A8) (RGB: 0, 56, 186)
- International Klein Blue (Hex: #002FA7) (RGB: 0, 47, 167)
- Dark Powder Blue (Smalt) (Hex: #003399) (RGB: 0, 51, 153)
- Ultramarine (Hex: #120A8F) (RGB: 18, 10, 143)
- Navy Blue (web colour) (Hex: #000080) (RGB: 0, 0, 128)
- Sapphire (Hex: #082567) (RGB: 8, 37, 103)
- Midnight Blue (web colour) (Hex: #191970) (RGB: 25, 25, 112)
- Dark Midnight Blue (Crayola Midnight Blue) (Hex: #003366) (RGB: 0, 51, 102)
- Prussian Blue (Berlin Blue) (Hex: #003153) (RGB: 0, 49, 83)
- Dark Indigo (Hex: #310062) (RGB: 49, 0, 98)
Blue in human culture
The color blue has a number of uses in human culture, including art and science.
References
See also
- Distinguishing "blue" from "green" in language
- List of colours
- Lapis lazuli
- Ceil
- Three Colours: Blue