Dravidian peoples: Difference between revisions
Commenting out use(s) of file "File:ChandraNobel.png": See WP:NFCC#10c. (TW) |
added image |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| image13 = Subramanya Bharathi.jpg| caption13=[[Subramania Bharati]] |
| image13 = Subramanya Bharathi.jpg| caption13=[[Subramania Bharati]] |
||
| image14 = Dr.Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan.jpg|caption14=[[Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan]] |
| image14 = Dr.Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan.jpg|caption14=[[Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan]] |
||
| image15 = Apj abdul kalam.JPG| caption15= [[APJ Abdul Kalam]] |
|||
| image16 = |
| image16 = Shashi Tharoor 2015.jpg|caption16=[[Shashi Tharoor]] |
||
| image17 = |
| image17 = AishwaryaRai09.jpg|caption17=[[Aishwariya Rai]] |
||
| image18 = |
| image18 = IndraNooyiDavos2010ver2.jpg| caption18= [[Indra Nooyi]] |
||
| image19 = |
| image19 = Sridevi07.jpg|caption19= [[Sreedevi]] |
||
| image20 = |
| image20 = VishyAnand09.jpg| caption20= [[Viswanathan Anand]] |
||
| image21 = |
| image21 = A. R. Rahman.jpg|caption21=[[A. R. Rahman]] |
||
| image22 = |
| image22 = Satya Nadella.jpg | caption22 = [[Satya Nadella]] |
||
| image23 = |
| image23 = Rekha05.jpg|caption23=[[Rekha]] |
||
| image24 = |
| image24 = Vidya Balan 02.jpg|caption24=[[Vidya Balan]] |
||
| image25 = |
| image25 = M S Sathyu Cropped.jpg|caption25=[[M S Sathyu]] |
||
| image26 = |
| image26 = Sendhil Ramamurthy (1).jpg|caption26=[[Sendhil Ramamurthy]] |
||
| image27 = |
| image27 = Sundar Pichai (cropped1).jpg|caption27=[[Sundar Pichai]] |
||
| image28 = |
| image28 = Abdul Karim Brahui of Afghanistan in July 2011.jpg|caption28=[[Abdul Karim Brahui]] |
||
| image29 = |
| image29 = Quaid-E-Milleth_Mohammed_Isamil_Sahib.jpg| caption29= [[Muhammad Ismail]] |
||
| image30 = |
| image30 = Nobel Prize 2009-Press Conference KVA-08.jpg|caption30=[[Venkatraman Ramakrishnan]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
==Origins== |
==Origins== |
||
{{Main|Indus valley civilization|Proto-Dravidian|Dravidian homeland|Substratum in Vedic Sanskrit|Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia}} |
{{Main|Indus valley civilization|Proto-Dravidian|Dravidian homeland|Substratum in Vedic Sanskrit|Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia}} |
||
Although in modern times speakers of the various Dravidian languages have mainly occupied the southern portion of India, nothing definite is known about the ancient domain of the Dravidian parent speech. It is, however, a well-established and well-supported hypothesis that Dravidian speakers must have been widespread throughout Indian-Subcontinent before [[Indo-Aryan migration]] into subcontinent.<ref>"Dravidian languages." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 5 June 2008</ref> Origins of Dravidian people are informed by various theories proposed by linguists, geneticist and historians. |
Although in modern times speakers of the various Dravidian languages have mainly occupied the southern portion of India, nothing definite is known about the ancient domain of the Dravidian parent speech. It is, however, a well-established and well-supported hypothesis that Dravidian speakers must have been widespread throughout Indian-Subcontinent before [[Indo-Aryan]] [[Indo-European migrations|migration]] into subcontinent.<ref>"Dravidian languages." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 5 June 2008</ref> Origins of Dravidian people are informed by various theories proposed by linguists, geneticist and historians. |
||
[[File:Shiva Pashupati.jpg|thumb|220px| The ''Pashupati'' seal from Indus Valley Ciivlization]] |
[[File:Shiva Pashupati.jpg|thumb|220px| The ''Pashupati'' seal from Indus Valley Ciivlization]] |
||
Linguists hypothesized that Dravidian-speaking people were spread throughout the [[Indian subcontinent]] before a series of Indo-European migrations. In this view, the early [[Indus Valley civilisation]] is often identified as having been Dravidian.<ref>[http://www.harappa.com/arrow/stone_celt_indus_signs.html Stone celts in Harappa]</ref> Cultural and linguistic similarities have been cited by researchers [[Henry Heras]], [[Kamil Zvelebil]], [[Asko Parpola]] and [[Iravatham Mahadevan]] as being strong evidence for a proto-Dravidian origin of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation.<ref>{{cite web | last = Rahman | first = Tariq | title = Peoples and languages in pre-islamic Indus valley | url=http://asnic.utexas.edu/asnic/subject/peoplesandlanguages.html| |
Linguists hypothesized that Dravidian-speaking people were spread throughout the [[Indian subcontinent]] before a series of Indo-European migrations. In this view, the early [[Indus Valley civilisation]] is often identified as having been Dravidian.<ref>[http://www.harappa.com/arrow/stone_celt_indus_signs.html Stone celts in Harappa]</ref> Cultural and linguistic similarities have been cited by researchers [[Henry Heras]], [[Kamil Zvelebil]], [[Asko Parpola]] and [[Iravatham Mahadevan]] as being strong evidence for a proto-Dravidian origin of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation.<ref>{{cite web | last = Rahman | first = Tariq | title = Peoples and languages in pre-islamic Indus valley | url=http://asnic.utexas.edu/asnic/subject/peoplesandlanguages.html| |
||
Revision as of 14:52, 27 October 2015
| Total population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| approx. 217 million speakers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dravidian languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Islam, Christianity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Part of a series on |
| Dravidian culture and history |
|---|
 |
| Portal:Dravidian civilizations |
Dravidians are native speakers of any of the Dravidian languages of South Asia. There are around 220 million native speakers of Dravidian languages. They form majority of the population of South India. Dravidian-speaking people are natively found in India, Pakistan, Nepal, Maldives and Sri Lanka.[1][2]
Historically the Sanskrit word "drāviḍa" is used to denote geographical region of South India.[3] and was devoid of any ethnic or linguistic identity[3] While in Prakrit, words such as "Damela", "Dameda", "Dhamila" and "Damila" which later evolved into "Tamila" could have been used to denote an ethnic identity.[4] The largest-Dravidian ethnic groups are Kannada people from Karnataka, the Tamil People from Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Sri Lanka, the Telugu people from Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Malayalam people from Kerala. Ancient Dravidians were noted for their martial, religious and mercantile activities. Urbanisation and mercantile activity along the western and eastern coast of what is today Tamil Nadu and Kerala led to the development of four large political states Chola dynasty, Pandyan dynasty, Chera Dynasty and a number of smaller states warring amongst themselves for hegonomy and dominance over the region. Some of the greatest Dynasties in Indian history were established by the Dravidian people like the Satavahana dynasty, Chola dynasty, Pandyan dynasty, Rashtrakuta dynasty, Western Chalukya Empire and Vijayanagara Empire. Among languages spoken today, the Tamil is oldest known Dravidian language with unbroken literary tradition since 3rd century BC.[5]
The Chola Empire with its powerful navy was one of the biggest maritime empires in Medieval India stretching from Southern India to Southeast Asia like Malaysia, Southern Thailand and Indonesia.[6] Medieval Tamil guilds and trading organizations like the "Ayyavole and Manigramam" played an important role in the Southeast Asia trade.[7] Traders and religious leaders travelled to Southeast Asia and played an important role in the cultural Indianisation of the region. Locally developed scripts such as Grantha and Pallava script induced the development of many native scripts such as Khmer, Javanese Kawi script, Baybayin, and Thai.
Dravidian visual art is dominated by stylised Temple architecture in major centers and the productions of images of stone, bronze sculptures. The Nataraja sculpture from the Chola period, have become notable as a symbol of Hinduism.
Etymology
The Sanskrit word drāviḍa is used to denote geographical region of South India.[3] While in Prakrit, words such as Damela, Dameda, Dhamila and Damila are used but it is unclear if it was a self designation or a term denoted by outsiders. Epigraphic evidence of an ethnic group termed as such is found in ancient India where a number of inscriptions have come to light datable from the 6th to the 5th century BC mentioning Damela or Dameda persons. In the well-known Hathigumpha inscription of the Kalinga ruler Kharavela, refers to a T(ra)mira samghata (Confederacy of Tamil rulers) dated to 150 BC. It also mentions that the league of Tamil kingdoms had been in existence 113 years before then.[8] In Amaravati in present-day Andhra Pradesh there is an inscription referring to a Dhamila-vaniya (Tamil trader) datable to the 3rd century AD.[8] Another inscription of about the same time in Nagarjunakonda seems to refer to a Damila. A third inscription in Kanheri Caves refers to a Dhamila-gharini (Tamil house-holder). In the Buddhist Jataka story known as Akiti Jataka there is a mention to Damila-rattha (Tamil dynasty). Southern Brahmins are known as Pancha Dravida while northern Brahmins are known as Pancha Gauda, denoting geographical region. There were trade relationship between the Roman Empire and Pandyan Empire. As recorded by Strabo, Emperor Augustus of Rome received at Antioch an ambassador from a king called Pandyan of Dramira.[9] Hence, it is clear that by at least the 300 BC, the ethnic identity of Tamils has been formed as a distinct group.[8] Thamizhar is etymologically related to Tamil, the language spoken by Tamil people. Southworth suggests that the name comes from tam-miz > tam-iz 'self-speak', or 'one's own speech'.[10] Zvelebil suggests an etymology of tam-iz, with tam meaning "self" or "one's self", and "-iz" having the connotation of "unfolding sound". Alternatively, he suggests a derivation of tamiz < tam-iz < *tav-iz < *tak-iz, meaning in origin "the proper process (of speaking)."[11] The term Thamizhar was likely derived from the name of the ancient people Dravida > Dramila > Damila > Tamila > Tamilar[12]
While the English word Dravidian was first employed by Robert Caldwell in his book of comparative Dravidian grammar based on the usage of the Sanskrit word drāviḍa in the work Tantravārttika by Kumārila Bhaṭṭa.[3] The worddrāviḍa in Sansrkit has been historically used to denote geographical regions of Southern India as whole. While some theories concern the direction of derivation between tamiẓ and drāviḍa; such linguists as Zvelebil assert that the direction is from tamiẓ to drāviḍa.[13] The word Dravidian is devoid of any ethnic significance, Dravidian is just the language used by the people of the referred group.[4]
Origins
Although in modern times speakers of the various Dravidian languages have mainly occupied the southern portion of India, nothing definite is known about the ancient domain of the Dravidian parent speech. It is, however, a well-established and well-supported hypothesis that Dravidian speakers must have been widespread throughout Indian-Subcontinent before Indo-Aryan migration into subcontinent.[14] Origins of Dravidian people are informed by various theories proposed by linguists, geneticist and historians.

Linguists hypothesized that Dravidian-speaking people were spread throughout the Indian subcontinent before a series of Indo-European migrations. In this view, the early Indus Valley civilisation is often identified as having been Dravidian.[15] Cultural and linguistic similarities have been cited by researchers Henry Heras, Kamil Zvelebil, Asko Parpola and Iravatham Mahadevan as being strong evidence for a proto-Dravidian origin of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation.[16][17] Linguist Asko Parpola writes that the Indus script and Harappan language "most likely to have belonged to the Dravidian family".[18] Parpola led a Finnish team in investigating the inscriptions using computer analysis. Based on a proto-Dravidian assumption, they proposed readings of many signs, some agreeing with the suggested readings of Heras and Knorozov (such as equating the "fish" sign with the Dravidian word for fish "min") but disagreeing on several other readings. A comprehensive description of Parpola's work until 1994 is given in his book "Deciphering the Indus Script."[19] The discovery in Tamil Nadu of a late Neolithic (early 2nd millennium BC, i.e. post-dating Harappan decline) stone celt allegedly marked with Indus signs has been considered by some to be significant for the Dravidian identification.[20][21] While, Yuri Knorozov surmised that the symbols represent a logosyllabic script and suggested, based on computer analysis, an underlying agglutinative Dravidian language as the most likely candidate for the underlying language.[22][page needed] Knorozov's suggestion was preceded by the work of Henry Heras, who suggested several readings of signs based on a proto-Dravidian assumption.[23][page needed] While some scholars like J. Bloch and M. Witzel believe that the Indo-Aryan moved into an already Dravidian speaking area after the oldest parts of the Rig Veda were already composed.[24] The Brahui population of Balochistan has been taken by some as the linguistic equivalent of a relict population, perhaps indicating that Dravidian languages were formerly much more widespread and were supplanted by the incoming Indo-Aryan languages.[25]
Paleoclimatologists believe fall of Indus Valley Civilization and eastward migration during late harrapan period was due to climate change in the region, with 200-Year old drought being the major factor.[26][27][28] Indus Valley Civilization seemed to slowly lose their urban cohesion, and their cities were gradually abandoned during late harppan period followed by eastward migrations before the Indo-Aryan migration into Indian Subcontinent.[27]
Dravidian languages show extensive lexical (vocabulary) borrowing, but only a few traits of structural (either phonological or grammatical) borrowing from Indo-Aryan, whereas Indo-Aryan shows more structural than lexical borrowings from the Dravidian languages.[29] Many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda (c. 1500 BCE), which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian. The linguistic evidence for Dravidian impact grows increasingly strong as we move from the Samhitas down through the later Vedic works and into the classical post-Vedic literature.[30] This represents an early religious and cultural fusion[31][note 1] or synthesis[33] between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans.[34][32][35][36]
History

Ancient Dravidians had three monarchical states Chola, Pandyas and Cheras, headed by kings called "Vendhar" and several tribal chieftainships, headed by the chiefs called by the general denomination "Vel" or "Velir".[37] Still lower at the local level there were clan chiefs called "kizhar" or "mannar".[38] The kings and chiefs were always in conflict with each other mostly over territorial hegemony and property. The royal courts were mostly places of social gathering rather than places of dispensation of authority; they were centres for distribution of resources. Ancient Sangam literature and grammatical works Tolkappiyam, the ten anthologies Pattuppāṭṭu, the eight anthologies Eṭṭuttokai sheds light on ancient Dravidian people.[39] The kings and chieftains were patrons of the arts, and a significant volume of literature exists from this period.[40] The literature shows that many of the cultural practices that are considered peculiarly Tamil date back to the classical period.[40]
Agriculture was important during this period, and there is evidence that networks of irrigation channels were built as early as 3rd century BCE.[41] Internal and external trade flourished, and evidence of significant contact with Ancient Rome exists.[42] Large quantities of Roman coins and signs of the presence of Roman traders have been discovered at Karur and Arikamedu.[42] There is evidence that at least two embassies were sent to the Roman Emperor Augustus by Pandya kings.[43] Potsherds with Tamil writing have also been found in excavations on the Red Sea, suggesting the presence of merchants there.[44] An anonymous 1st century traveller's account written in Greek, Periplus Maris Erytraei, describes the ports of the Pandya and Chera kingdoms in Damirica and their commercial activity in great detail. Periplus also indicates that the chief exports of the ancient Dravidians were pepper, malabathrum, pearls, ivory, silk, spikenard, diamonds, sapphires, and tortoiseshell.[45] According to Clarence Maloney, during the classical period Tamils also settled the Maldive Islands.[46]
These early kingdoms sponsored the growth of some of the oldest extant literature in Tamil. The classical literature, referred to as Sangam literature is attributed to the period between 300 BCE and 300 CE.[47][48] These Sangam poems paint the picture of a fertile land and of a people who were organised into various occupational groups. The governance of the land was through hereditary monarchies, although the sphere of the state's activities and the extent of the ruler's powers were limited through the adherence to the established order dharma.[49] The people were loyal to their kings and roving bards and musicians and danseuse gathered at the royal courts of the generous kings. The arts of music and dancing were highly developed and popular. Musical instruments of various types find mention in the Sangam poems. The amalgamation of the southern and the northern styles of dancing started during this period and is reflected fully in the epic Cilappatikaram.[50]
-
Megalithic Urn jar burials
-
Terracotta Sarcophagus burial from Tamil Nadu
-
Virampatnam jewelry from funerary burial, 2nd century BC, Tamil Nadu
-
Souttoukeny jewelry, 2nd century B.C. Tamil Nadu
-
Map of ancient oceanic trade, and ports of Tamilakam.
Imperial and post-imperial periods

The names of the three dynasties, Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras, are mentioned in Tamil Sangam literature and grammaticall works like Tolkappiyar refers to them as the "Three Glorified by Heaven", (Tamil: வாண்புகழ் மூவர், Vāṉpukaḻ Mūvar).[51] Later, they are mentioned in Mauryan Empire's Pillars of Ashoka (inscribed 273–232 BCE) inscriptions, among the kingdoms, which though not subject to Ashoka, were on allied terms with him.[52][53] The king of Kalinga, Kharavela, who ruled around 150 BCE, mentioned in the famous Hathigumpha inscription of the confederacy of the kingdoms that had existed for over 100 years.[54] The Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras, Pallavas were followers of Hinduism, though for a short while some of them seem to have embraced Jainism and later converted to Hinduism. Buddhism flourishing alongside Hinduism and Jainism[55] After the fall of Mauryan Empire, the kingdoms were allied with Satavahana Dynasty. The Kings of the Satavahana dynasty were the earliest rulers who issued coins with dravidian languages.[56]

These early kingdoms sponsored the growth of some of the oldest extant literature in Tamil. The classical literature, referred to as Sangam literature is attributed to the period between 300 BCE and 300 CE.[57][58] The poems of Sangam literature, which deal with emotional and material topics, were categorised and collected into various anthologies during the medieval period. These Sangam poems paint the picture of a fertile land and of a people who were organised into various occupational groups. The governance of the land was through hereditary monarchies, although the sphere of the state’s activities and the extent of the ruler’s powers were limited through the adherence to the established order ("dharma"). Although the Pallava records can be traced from the 2nd century AD, they did not rise to prominence as an imperial dynasty until the 6th century.[59] They transformed the institution of the kingship into an imperial one, and sought to bring vast amounts of territory under their direct rule. The Bhakti movement in Hinduism was founded at this time, and rose along with the growing influence of Jainism and Buddhism.[60] The Pallavas pioneered the building of large, ornate temples in stone which formed the basis of the Dravidian temple architecture. They came into conflict with the Kannada Chalukyas of Badami. During this period, The great Badami Chalukya King Pulakesi II extended the Chalukya Empire up to the northern extents of the Pallava kingdom and defeated the Pallavas in several battles.[61] Pallava Narasimhavarman however reversed this victory in 642 by attacking and occupying Badami temporarily.[62] However a later Chalukya King Vikramaditya II took revenge by repeated invasions of the territory of Tondaimandalam and his subsequent victories over Pallava Nandivarman II and the annexation of Kanchipuram.[63] The south Indian ruler Vikramaditya II also defeated the Arab invaders and protected southern India.[64] The Pallava dynasty was overthrown in the 9th century by the imperial Kannada Rashtrakutas who ruled from Gulbarga.Amoghavarsha was the greatest King of the south Indian Rashtrakuta dynasty who was described by an Arab scholar as one of the 4 great Kings of the world in the 9th century.[65] King Krishna III, the last great Rashtrakuta king consolidated the empire so that it stretched from the Narmada River to Kaveri River and included the northern Tamil country (Tondaimandalam) while levying tribute on the king of Ceylon.[66]

Under Rajaraja Chola and his son Rajendra Chola, the Cholas became dominant in the 10th century and established an empire covering most of South India and Sri Lanka.[59] The empire had strong trading links with Chinese Song Dynasty and Southeast Asia.[67][68] The Cholas defeated the Eastern Chalukya and expanded their empire to the Ganges. They conquered the coastal areas around the Bay of Bengal and turned it to Chola lake. Rajendra Chola improved his father's fleet and created the first notable marine of the Indian subcontinent. The Chola navy conquered the Sri Vijaya Empire of Indonesia and the Malaysia and secured the sea trade route to China.[59] Cholas exacted tribute from Thailand and the Khmer Kingdom of Cambodia. The power of the Cholas declined around the 13th century and the Pandyan Empire enjoyed a brief period of resurgence thereafter during the rule of Sundara Pandya.[59] The Pandyan Dynasty reached its peak in the 13th century during the reign of Sadayavarman Sundara Pandyan I and Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I. The Pandyan Empire was threatened by the constant Islamic invasions of South India. During the 15th and 16th century the Vijayanagara Empire became the dominant power of South India. The Vijayanagara Empire reached its zenith during the reign of the south Indian Emperor Krishnadevaraya who defeated the Turkic invaders of the Bahmani Sultanate.[69] After the decline of the Vijayanagara Empire in 1646, South India was dominated by small states like the Nayak Dynasty.
The western Tamil lands became increasingly politically distinct from the rest of the Tamil lands after the Chola and Pandya empires lost control over them in the 13th century.[70] They developed their own distinct language and literature, which increasingly grew apart from Tamil, evolving into the modern Malayalam language by the 15th century.[71]
Culture
Religion
Ancient Dravidian religion constituted of non-Vedic form of Hinduism in that they were either historically or are at present Āgamic. The Agamas are non-vedic in origin [72] and have been dated either as post-vedic texts [73] or as pre-vedic compositions.[74] The Agamas are a collection of Tamil and Sanskrit scriptures chiefly constituting the methods of temple construction and creation of murti, worship means of deities, philosophical doctrines, meditative practices, attainment of sixfold desires and four kinds of yoga.[75] The worship of tutelary deity, sacred flora and fauna in Hinduism is also recognized as a survival of the pre-Vedic Dravidian religion.[76] Dravidian linguistic influence on early Vedic religion is evident, many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda (c. 1500 BCE), which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian. The linguistic evidence for Dravidian impact grows increasingly strong as we move from the Samhitas down through the later Vedic works and into the classical post-Vedic literature.[30] This represents an early religious and cultural fusion[31][note 1] or synthesis[33] between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans that went on to influence and shape Hinduism, Buddhism, Charvaka, Sramana, Ājīvika and Jainism.[34][32][35][36]

Ancient Tamil grammatical works Tolkappiyam, the ten anthologies Pattuppāṭṭu, the eight anthologies Eṭṭuttokai sheds light on early ancient Dravidian religion. Seyyon was glorified as, the red god seated on the blue peacock, who is ever young and resplendent, as the favored god of the Tamils.[39] Sivan was also seen as the supreme God.[39] Early iconography of Seyyon[77] and Sivan[78][79][80] and their association with native flora and fauna goes back to Indus Valley Civilization.[81][page needed][82] The Sangam landscape was classified into five categories, thinais, based on the mood, the season and the land. Tolkappiyam, mentions that each of these thinai had an associated deity such Seyyon in Kurinji-the hills, Thirumaal in Mullai-the forests, and Kotravai in Marutham-the plains, and Wanji-ko in the Neithal-the coasts and the seas. Other gods mentioned were Mayyon and Vaali who are all major deities in Hinduism today. Dravidian influence on early Vedic religion is evident, many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda (c. 1500 BCE), which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian.[30] This represents an early religious and cultural fusion[31][note 1] or synthesis[33] between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans, which became more evident over time with sacred iconography, traditions, philosophy, flora and fauna that went on to influence and shape Indian civilization.[34][32][35][36]

Throughout Tamilakam, a king was considered to be divine by nature and possessed religious significance.[83] The king was 'the representative of God on earth’ and lived in a "koyil", which means the "residence of a god". The Modern Tamil word for temple is koil (Tamil: கோயில்). Titual worship was also given to kings.[84][85] Modern words for god like "kō" (Tamil: கோ "king"), "iṟai" (இறை "emperor") and "āṇḍavar" (ஆண்டவன் "conqueror") now primarily refer to gods. These elements were incorporated later into Hinduism like the legendary marriage of Shiva to Queen Mīnātchi who ruled Madurai or Wanji-ko, a god who later merged into Indra.[86] Tolkappiyar refers to the Three Crowned Kings as the "Three Glorified by Heaven", (Tamil: வாண்புகழ் மூவர், Vāṉpukaḻ Mūvar).[51] In the Dravidian-speaking South, the concept of divine kingship led to the assumption of major roles by state and temple.[87]
The cult of the mother goddess is treated as an indication of a society which venerated femininity. This mother goddess was conceived as a virgin, one who has given birth to all and one, and were typically associated with Shaktism.[88] The temples of the Sangam days, mainly of Madurai, seem to have had priestesses to the deity, which also appear predominantly a goddess.[89] In the Sangam literature, there is an elaborate description of the rites performed by the Kurava priestess in the shrine Palamutircholai.[90]
Among the early Dravidians the practice of erecting memorial stones "Natukal and Viragal’' had appeared, and it continued for quite a long time after the Sangam age, down to about 16th century.[91] It was customary for people who sought victory in war to worship these hero stones to bless them with victory.[92]
Martial arts
Literary evidence of martial arts in southern India dates back to the Sangam literature of about the 3nd century BC to the 3nd century AD. The Akananuru and Purananuru describe the use of spears, swords, shields, bows and silambam in the Sangam era. Various martial arts including Kuttu Varisai, Varma Kalai, Silambam, Adithada, Malyutham and Kalarippayattu, are practised in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.[93] The warm-up phase includes yoga, meditation and breathing exercises. Silambam originated in ancient Tamilakam and was patronized by the Pandyans, Cholas and Cheras, who ruled over this region. Silapathiharam a Tamil literature from 3nd century BC to 2nd century AD, refers to the sale of Silamabam instructions, weapons and equipment to foreign traders.[94] Since the early Sangam age, there was a warlike culture in South India. War was regarded as an honorable sacrifice and fallen heroes and kings were worshiped in the form of a Hero stone. Each warrior was trained in martial arts, horse riding and specialized in two of the weapons of that period Vel (spear) Val (sword) and Vil (bow).[95] In addition to this, they were engaged to fight in ankam, public duels to the death, to solve disputes between his opposing rules.[96][page needed] Among some communities, young girls received preliminary training up until the onset of menses.[96] In vadakkan pattukal ballads, at least a few women warriors continued to practice and achieved a high degree of expertise.[96]

Ancient dravidian speakers had practice of erecting memorial stones Natukal, and it continued for quite a long time after the Sangam age, down to about 16th century.[91] It was customary for people who sought victory in war to worship these hero stones to bless them with victory.[92] They often carry inscriptions displaying a variety of adornments, including bas relief panels, frieze, and figures on carved stone.[97]
The Wootz steel, also known as Damascus steel originated in South India and Sri Lanka.[98][99] There are several ancient Tamil, Greek, Chinese and Roman literary references to high carbon Indian steel since the time of Alexander's India campaign. The crucible steel production process started in the sixth century BC, at production sites of Kodumanal in Tamil Nadu, Golconda in Telangana, Karnataka and Sri Lanka and exported globally; the of the Chera Dynasty producing what was termed the finest steel in the world, i.e. Seric Iron to the Romans, Egyptians, Chinese and Arabs by 500 BC.[100][101][102] The steel was exported as cakes of steely iron that came to be known as "Wootz."[103]
The Tamilakam method was to heat black magnetite ore in the presence of carbon in a sealed clay crucible inside a charcoal furnace. An alternative was to smelt the ore first to give wrought iron, then heated and hammered to be rid of slag. The carbon source was bamboo and leaves from plants such as Avārai.[103][104] The Chinese and locals in Sri Lanka adopted the production methods of creating Wootz steel from the Chera by the 5th century BC.[105][106] In Sri Lanka, this early steel-making method employed a unique wind furnace, driven by the monsoon winds, capable of producing high-carbon steel and production sites from antiquity have emerged, in places such as Anuradhapura, Tissamaharama and Samanalawewa, as well as imported artifacts of ancient iron and steel from Kodumanal. A 200 BC Tamil trade guild in Tissamaharama, in the South East of Sri Lanka, brought with them some of the oldest iron and steel artifacts and production processes to the island from the classical period.[107][108][109][110][page needed] The Arabs introduced the South Indian/Sri Lankan wootz steel to Damascus, where an industry developed for making weapons of this steel. The 12th century Arab traveler Edrisi mentioned the "Hinduwani" or Indian steel as the best in the world.[98] Another sign of its reputation is seen in a Persian phrase – to give an "Indian answer", meaning "a cut with an Indian sword."[111] Wootz steel was widely exported and traded throughout ancient Europe and the Arab world, and became particularly famous in the Middle East.[111]
Traditional Weapons
Traditional martial arts also includes various types of weapons.
- Valari (throwing stick)
- Maduvu (deer horns)
- Surul Vaal (curling blade)
- Vaal (sword) + Ketayam (shield)
- Itti or Vel (spear)
- Savuku (whip)
- Kattari (fist blade)
- Veecharuval (battle Machete)
- Silambam (long bamboo staff)
- Kuttu Katai (spiked knuckleduster)
- Katti (dagger/knife)
- Vil (bow)
- Tantayutam (mace)
- Soolam (trident)
- Theekutchi (flaming baton)
- Yeratthai Mulangkol (dual stick)
- Yeretthai Vaal (dual sword)
Architecture and Visual art

Throughout Tamilakam, a king was considered to be divine by nature and possessed religious significance.[83] The king was 'the representative of God on earth’ and lived in a "koyil", which means the "residence of a god". The Modern Tamil word for temple is koil (Tamil: கோயில்). Titual worship was also given to kings.[84][85] Modern words for god like "kō" (Tamil: கோ "king"), "iṟai" (இறை "emperor") and "āṇḍavar" (ஆண்டவன் "conqueror") now primarily refer to gods.[86] Tolkappiyar refers to the Three Crowned Kings as the "Three Glorified by Heaven", (Tamil: வாண்புகழ் மூவர், Vāṉpukaḻ Mūvar).[51] In the Dravidian-speaking South, the concept of divine kingship led to the assumption of major roles by state and temple.[87]
Mayamata and Manasara shilpa texts estimated to be in circulation by 5th to 7th century AD, is a guidebook on Dravidian style of Vastu Shastra design, construction, sculpture and joinery technique.[112][113] Isanasivagurudeva paddhati is another text from the 9th century describing the art of building in India in south and central India.[112][114] In north India, Brihat-samhita by Varāhamihira is the widely cited ancient Sanskrit manual from 6th century describing the design and construction of Nagara style of Hindu temples.[115][116][117] Traditional Dravidian architecture and symbolism are also based on Agamas. The Agamas are non-vedic in origin [72] and have been dated either as post-vedic texts [73] or as pre-vedic compositions.[74] The Agamas are a collection of Tamil and Sanskrit scriptures chiefly constituting the methods of temple construction and creation of murti, worship means of deities, philosophical doctrines, meditative practices, attainment of sixfold desires and four kinds of yoga.[75]
Chola style temples consist almost invariably of the three following parts, arranged in differing manners, but differing in themselves only according to the age in which they were executed:[118]
- The porches or Mantapas, which always cover and precede the door leading to the cell.
- Gate-pyramids, Gopuras, which are the principal features in the quadrangular enclosures that surround the more notable temples.Gopuras are very common in dravidian temples.
- Pillared halls (Chaultris or Chawadis) are used for many purposes and are the invariable accompaniments of these temples.
Besides these, a south Indian temple usually has a tank called the Kalyani or Pushkarni – to be used for sacred purposes or the convenience of the priests – dwellings for all the grades of the priesthood are attached to it, and other buildings for state or convenience.[118]
Theater, Dance and Music

Literary evidence of traditional form of theater, dance and music dates back to 3rd century BC.[119] Ancient literary works, such as the Cilappatikaram, describe a system of music,[119] The theatrical culture that flourished during early Sangam age. Theatre-Dance traditions has a long and varied history whose origins can be traced back almost two millennia to dance-theatre forms like Kotukotti and Pandarangam, which are mentioned in an ancient anthology of poems entitled the Kalingathu Parani.[120] Dance forms such as Bharatanatyam are based older temple dance forms known as Catir Kacceri as practised by courtesans and a class of women known as Devadasis.[121]
Notable dance and theater forms are
- Bharatanatyam
- Kuchipudi
- Mohiniyattam
- Kathakali
- Koodiyattam
- Yakshagana
- Togalu Gombeyaata (shadow puppetry)
- Pavakathakali (hand puppetry)
- Gombeyatta (string puppetry)
Costume
Dravidian speakers in southern India wear varied traditional costumes depending on their region and is largely influenced by local costumes and traditional.
Language
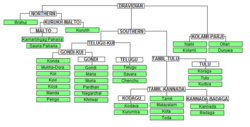

The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are Telugu (తెలుగు), Tamil (தமிழ்), Kannada (ಕನ್ನಡ),Malayalam (മലയാളം), and Brahui (براہوئی) . There are three subgroups within the Dravidian language family: North Dravidian, Central Dravidian, and South Dravidian, matching for the most part the corresponding regions in the Indian subcontinent.
Dravidian grammatical impact on the structure and syntax of Indo-Aryan languages is considered far greater than the Indo-Aryan grammatical impact on Dravidian. Some linguists explain this anomaly by arguing that Middle Indo-Aryan and New Indo-Aryan were built on a Dravidian substratum.[122] There are also hundreds of Dravidian loanwords in Indo-Aryan languages, and vice versa.
List of Dravidian people
| Name | Country | Population | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brahuis | 2.5 million | Brahuis belong to the north-Dravidian subgroup.The majority are found in Baluchistan, Pakistan, with smaller amounts in Southwestern Afghanistan. | |
| Kannadigas | 36.9 million[123] | Kannadigas belong to the south-Dravidian subgroup. Kannadigas are native to Karnataka, parts of northern Kerala,parts of southern Maharashtra, and northwest region of Tamil Nadu, India. | |
| Malayalis | 38 million[124] | Malayalis belong to south-Dravidian linguistic subgroup. Native to Kerala, southwestern Tamil Nadu, and Southern Karnataka. | |
| Tamils | 75 million[125] | They belong to south-Dravidian linguistic subgroup. Tamils are native to Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, parts of Kerala, southern Andhra Pradesh, southern Karnataka and Sri Lanka. | |
| Telugus | 110 million[126] | They belong to the central Dravidian subgroup. Telugus are native to Andhra Pradesh, Telangana. | |
| Tuluvas | 2 million (approx) | They belong to the south Dravidian subgroup, and are found in coastal Karnataka and northern Kerala (alternatively named Tulu Nadh). |
See also
- Dravidian languages
- Dravidian University (dedicated to research and learning of Dravidian languages)
- South India
Notes
- ^ a b c Lockard: "The encounters that resulted from Aryan migration brought together several very different peoples and cultures, reconfiguring Indian society. Over many centuries a fusion of Aryan and Dravidian occurred, a complex process that historians have labeled the Indo-Aryan synthesis."[31] Lockard: "Hinduism can be seen historically as a synthesis of Aryan beliefs with Harappan and other Dravidian traditions that developed over many centuries."[32]
References
- ^ Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Asia and Oceania by Barbara A. West p.194
- ^ Spectrum Guide to Maldives by Camarapix p.37
- ^ a b c d Zvelebil 1990, p. xx
- ^ a b RC Majumdar. "Dravidians". Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 18. ISBN 81-208-0436-8.
- ^ Encyclopaedia of Indian Literature: Sasay to Zorgot by Mohan Lal p.4284
- ^ Nagapattinam to Suvarnadwipa: Reflections on the Chola Naval Expeditions to Southeast Asia by Hermann Kulke,K Kesavapany,Vijay Sakhuja p.79
- ^ The Emporium of the World: Maritime Quanzhou, 1000-1400 by Angela Schottenhammer p.293
- ^ a b c Indrapala, K The Evolution of an ethnic identity: The Tamils of Sri Lanka, p.155-156
- ^ The cyclopædia of India and of Eastern and Southern Asia By Edward Balfour
- ^ Southworth, Franklin C. (1998), "On the Origin of the word tamiz", International Journal of Dravidial Linguistics, 27 (1): 129–132
- ^ Zvelebil, Kamil V. (1992), Companion Studies to the history of Tamil literature, Leiden: E.J. Brill at pp. x–xvi.
- ^ Gustav Salomon Oppert, On the Original Inhabitants of Bharatavarsa Or India: The Dravidians, p 41
- ^ Zvelebil 1990, p. xxi
- ^ "Dravidian languages." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 5 June 2008
- ^ Stone celts in Harappa
- ^ Rahman, Tariq. "Peoples and languages in pre-islamic Indus valley". Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 20 November 2008.
most scholars have taken the 'Dravidian hypothesis' seriously
- ^ Cole, Jennifer. "The Sindhi language" (PDF). Retrieved 20 November 2008.
Harappan language...prevailing theory indicates Dravidian origins
- ^ Edwin Bryant. The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford. p. 183. ISBN 9780195169478.
- ^ Parpola 1994
- ^ (Subramanium 2006; see also A Note on the Muruku Sign of the Indus Script in light of the Mayiladuthurai Stone Axe Discovery by I. Mahadevan (2006)
- ^ "Significance of Mayiladuthurai find - The Hindu". 1 May 2006.
- ^ Knorozov 1965
- ^ Heras 1953
- ^ Bryant, Edwin (2001). "Linguistic Substrata in Sanskrit Texts". The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 76–107. ISBN 978-0-19-513777-4.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Mallory 1989, p. 44: "There are still remnant northern Dravidian languages including Brahui ... The most obvious explanation of this situation is that the Dravidian languages once occupied nearly all of the Indian subcontinent and it is the intrusion of Indo-Aryans that engulfed them in northern India leaving but a few isolated enclaves. This is further supported by the fact that Dravidian loan words begin to appear in Sanskrit literature from its very beginning."
- ^ "How climate change ended worlds first great civilisations". www.independent.co.uk. 3 March 2014.
- ^ a b "200-Year Drought Doomed Indus Valley Civilization". www.scientificamerican.com. 3 March 2014.
- ^ "Climate change caused Indus Valley civilization collapse". http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com. 3 March 2014.
{{cite web}}: External link in|website= - ^ "Dravidian languages." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 30 Jun. 2008
- ^ a b c Krishnamurti 2003, p. 6
- ^ a b c d Lockard 2007, p. 50.
- ^ a b c d Lockard 2007, p. 52.
- ^ a b c Hiltebeitel 2007, p. 12.
- ^ a b c Tiwari 2002, p. v.
- ^ a b c Zimmer 1951, p. 218-219.
- ^ a b c Larson 1995, p. 81.
- ^ K.A.N. Sashtri, A History of South India, pp 109–112
- ^ 'There were three levels of redistribution corresponding to the three categories of chieftains, namely: the Ventar, Velir and Kilar in descending order. Ventar were the chieftains of the three major lineages, viz Cera, Cola and Pandya. Velir were mostly hill chieftains, while Kilar were the headmen of settlements…’ —"Perspectives on Kerala History". P.J.Cherian (Ed),. Kerala Council for Historical Research. Archived from the original on 26 August 2006. Retrieved 15 November 2006.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ a b c Kanchan Sinha, Kartikeya in Indian art and literature, Delhi: Sundeep Prakashan (1979).
- ^ a b K. Sivathamby (December 1974), "Early South Indian Society and Economy: The Tinai Concept", Social Scientist, 3 (5), Social Scientist: 20–37, doi:10.2307/3516448, JSTOR 3516448,
Those who ruled over small territories were called Kurunilamannar. The area ruled by such a small ruler usually corresponded to a geographical unit. In Purananuru a number of such chieftains are mentioned;..
- ^ "Grand Anaicut", Encyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 3 May 2006
- ^ a b M. G. S. Narayanan (September 1988), "The Role of Peasants in the Early History of Tamilakam in South India", Social Scientist, 16 (9), Social Scientist: 17–34, doi:10.2307/3517170, JSTOR 3517170
- ^ "Pandya Dynasty", Encyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 3 May 2007
- ^ "Archaeologists Uncover Ancient Maritime Spice Route Between India, Egypt", Veluppillai, Prof. A., dickran.net, retrieved 15 November 2006
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ The term Periplus refers to the region of the eastern seaboard of South India as Damirica – "The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea: Travel and Trade in the Indian Ocean by a Merchant of the First Century", Ancient History source book
- ^ Maloney, Clarence, Maldives People, retrieved 22 June 2008
- ^ Kamil Veith Zvelebil, Companion Studies to the History of Tamil Literature, p 12
- ^ K.A.N. Sastri, A History of South India, OUP (1955) p 105
- ^ K.A.N. Sastri, A History of South India, OUP (1955) pp 118, 119
- ^ K.A.N. Sastri, A History of South India, OUP (1955) p 124
- ^ a b c A. Kiruṭṭin̲an̲ (2000). Tamil culture: religion, culture, and literature. Bharatiya Kala Prakashan. p. 17.
- ^ 'Everywhere within Beloved-of-the-Gods, King Piyadasi’s domain, and among the people beyond the borders, the Cholas, the Pandyas, the Satyaputras, the Keralaputras, as far as Tamraparni…’ —"Ashoka's second minor rock edict". Colorado State University. Retrieved 15 November 2006.
- ^ K.A.N. Sastri, "The CoLas", 1935 p 20
- ^ "Hathigumpha Inscription". Epigraphia Indica, Vol. XX (1929–1930). Delhi, 1933, pp 86–89. Missouri Southern State University. Archived from the original on 17 November 2006. Retrieved 15 November 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ (Source- K.A.Nilakanta Sastri's "History of South India")
- ^ A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th century by Upinder Singh p.53
- ^ Kamil Veith Zvelebil, ’'Companion Studies to the History of Tamil Literature", p 12
- ^ K.A.N. Sastri, "A History of South India", OUP (1955) p 105
- ^ a b c d Smith, Vincent Arthur (1904), The Early History of India, The Clarendon press, pp. 336–358, ISBN 81-7156-618-9
- ^ Chandra, Satish (1997), Medieval India: From Sultanat to the Mughals (1206–1526) – I, Har-Anand Publications, p. 250, ISBN 81-241-1064-6,
...Starting from the Tamil lands under the Pallava kings, bhakti spread to different parts of south India...
- ^ Chopra, Ravindran and Subramanian (2003), p. 74 part 1
- ^ Sastri (1955), p. 136
- ^ Sastri 1955, p. 140
- ^ A Journey through India's Past (Great Hindu Kings after Harshavardhana) by Chandra Mauli Mani p.16
- ^ A Comprehensive History Of Ancient India (3 Vol. Set) by P.N Chopra p.203
- ^ Sastri (1955), p162
- ^ Srivastava, Balram (1973), Rajendra Chola, National Book Trust, India, p. 80,
The mission which Rajendra sent to China was essentially a trade mission,...
- ^ D. Curtin, Philip (1984), Cross-Cultural Trade in World History, Cambridge University Press, p. 101, ISBN 0-521-26931-8
- ^ A History of India by Burton Stein p.150
- ^ Freeman, Rich (February 1998), "Rubies and Coral: The Lapidary Crafting of Language in Kerala", The Journal of Asian Studies, 57 (1), Association for Asian Studies: 38–65, doi:10.2307/2659023, JSTOR 2659023 at pp. 41–43.
- ^ "Malayalam first appeared in writing in the vazhappalli inscription which dates from about 830 CE." "Writing Systems and Languages of the world", Omniglot, Omniglot.com, retrieved 15 November 2006
- ^ a b Mudumby Narasimhachary (Ed) (1976). Āgamaprāmāṇya of Yāmunācārya, Issue 160 of Gaekwad's Oriental Series. Oriental Institute, Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda.
- ^ a b Tripath, S.M. (2001). Psycho-Religious Studies Of Man, Mind And Nature. Global Vision Publishing House. ISBN 9788187746041. [1]
- ^ a b Nagalingam, Pathmarajah (2009). The Religion of the Agamas. Siddhanta Publications. [2]
- ^ a b Grimes, John A. (1996). A Concise Dictionary of Indian Philosophy: Sanskrit Terms Defined in English. State University of New York Press. ISBN 9780791430682. LCCN 96012383. [3]
- ^ The Modern review: Volume 28; Volume 28. Prabasi Press Private, Ltd. 1920.
- ^ Mahadevan, Iravatham (2006). A Note on the Muruku Sign of the Indus Script in light of the Mayiladuthurai Stone Axe Discovery. harappa.com.
- ^ Ranbir Vohra (2000). The Making of India: A Historical Survey. M.E. Sharpe. p. 15.
- ^ Grigorii Maksimovich Bongard-Levin (1985). Ancient Indian Civilization. Arnold-Heinemann. p. 45.
- ^ Steven Rosen, Graham M. Schweig (2006). Essential Hinduism. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 45.
- ^ Basham 1967
- ^ Frederick J. Simoons (1998). Plants of life, plants of death. p. 363.
- ^ a b Harman, William P. (1992). The sacred marriage of a Hindu goddess. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 6.
- ^ a b Anand, Mulk Raj (1980). Splendours of Tamil Nadu. Marg Publications.
- ^ a b Chopra, Pran Nath (1979). History of South India. S. Chand.
- ^ a b Bate, Bernard (2009). Tamil oratory and the Dravidian aesthetic: democratic practice in south India. Columbia University Press.
- ^ a b Embree, Ainslie Thomas (1988). Encyclopedia of Asian history: Volume 1. Scribner. ISBN 9780684188980.
- ^ Thiruchandran, Selvy (1997). Ideology, caste, class, and gender. Vikas Pub. House.
- ^ Manickam, Valliappa Subramaniam (1968). A glimpse of Tamilology. Academy of Tamil Scholars of Tamil Nadu. p. 75.
- ^ Lal, Mohan (2006). The Encyclopaedia Of Indian Literature (Volume Five (Sasay To Zorgot), Volume 5. Sahitya Akademi. p. 4396. ISBN 8126012218.
- ^ a b Shashi, S. S. (1996). Encyclopaedia Indica: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh: Volume 100. Anmol Publications.
- ^ a b Subramanium, N. (1980). Śaṅgam polity: the administration and social life of the Śaṅgam Tamils. Ennes Publications.
- ^ Zarrilli, Phillip B. (1992) "To Heal and/or To Harm: The Vital Spots in Two South Indian Martial Traditions"
- ^ IN INDIA
- ^ South Asian Folklore: An Encyclopedia : Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka(2003), p. 386.
- ^ a b c Zarrilli, Phillip B. (1998). When the Body Becomes All Eyes: Paradigms, Discourses and Practices of Power in Kalaripayattu, a South Indian Martial Art. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-563940-7.
- ^ "Hero-stone Memorials of India". Kamat Potpourri. Retrieved 15 March 2007.
- ^ a b Sharada Srinivasan; Srinivasa Ranganathan (2004). India's Legendary Wootz Steel: An Advanced Material of the Ancient World. National Institute of Advanced Studies. OCLC 82439861.
- ^ Gerald W. R. Ward. The Grove Encyclopedia of Materials and Techniques in Art. pp.380
- ^ Sharada Srinivasan (1994). [file:///C:/Users/user/Downloads/101-254-1-PB%20(1).pdf Wootz crucible steel: a newly discovered production site in South India]. Papers from the Institute of Archaeology 5(1994) 49-59
- ^ Herbert Henery Coghlan. (1977). Notes on prehistoric and early iron in the Old World. pp 99-100
- ^ B. Sasisekharan (1999).TECHNOLOGY OF IRON AND STEEL IN KODUMANAL-
- ^ a b Hilda Ellis Davidson. The Sword in Anglo-Saxon England: Its Archaeology and Literature. pp.20
- ^ Burton, Sir Richard Francis (1884). The Book of the Sword. Internet archive: Chatto and Windus. p. 111. ISBN 1605204366.
- ^ Needham, Volume 4, Part 1, p. 282.
- ^ Manning, Charlotte Speir. "Ancient and Medieval India. Volume 2". ISBN 9780543929433.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Hobbies - Volume 68, Issue 5 - Page 45. Lghtner Publishing Company (1963)
- ^ Mahathevan, Iravatham (24 June 2010). "An epigraphic perspective on the antiquity of Tamil". The Hindu. The Hindu Group. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ^ Ragupathy, P (28 June 2010). "Tissamaharama potsherd evidences ordinary early Tamils among population". Tamilnet. Tamilnet. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ^ Dinithi (in Sinhala). 1 (4). 2010. ISSN 2012-7189 https://web.archive.org/web/20110304152852/http://www.archaeology.lk/http://www.archaeology.lk/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/Dinithi-Volume-1-Issue-4.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b Manning, Charlotte Speir. "Ancient and Mediæval India. Volume 2". ISBN 9780543929433.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b Stella Kramrisch (1976), The Hindu Temple Volume 1 & 2, ISBN 81-208-0223-3
- ^ Tillotson, G. H. R. (1997). Svastika Mansion: A Silpa-Sastra in the 1930s. South Asian Studies, 13(1), pp 87-97
- ^ Ganapati Sastri (1920), Īśānaśivagurudeva paddhati, Trivandrum Sanskrit Series, OCLC 71801033
- ^ Michael Meister (1983), Geometry and Measure in Indian Temple Plans: Rectangular Temples, Artibus Asiae, Vol. 44, No. 4, pp 266-296
- ^ Heather Elgood (2000), Hinduism and the religious arts, ISBN 978-0304707393, Bloomsbury Academic, pp 121-125
- ^ H Kern (1865), The Brhat Sanhita of Varaha-mihara, The Asiatic Society of Bengal, Calcutta
- ^ a b Fergusson, James (1997) [1910]. History of Indian and Eastern Architecture (3rd ed.). New Delhi: Low Price Publications. p. 309.
- ^ a b Nijenhuis, Emmie te (1974), Indian Music: History and Structure, Leiden: Brill, ISBN 90-04-03978-3 at pp. 4–5
- ^ ,Dennis Kennedy "The Oxford Encyclopedia of Theatre and Performance, Publisher:Oxford University Press
- ^ Leslie, Julia. Roles and rituals for Hindu women, pp.149–152
- ^ Krishnamurti 2003, pp. 40–1
- ^ "Census 2011: Languages by state". Censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ^ Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in Nationalencyklopedin. Asterisks mark the 2010 estimates for the top dozen languages.
- ^ World Tamil Population. tamilo.com. (August 2008)
- ^ [4]. friendsoftelugu.org. (June 2011)
- Basham, A. L. (1967). The Wonder That was India (3rd ed.). London: Sidgwick & Jackson. OCLC 459272.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Heras, Henry (1953). Studies in Proto-Indo-Mediterranean Culture. Bombay: Indian Historical Research Institute. OCLC 2799353.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Knorozov, Yuri V. (1965). "Характеристика протоиндийского языка" [Characteristics of Proto-Indian language]. Predvaritel’noe soobshchenie ob issledovanii protoindiyskikh textov Предварительное сообщение об исследовании протоиндийских текстов [A Preliminary Report on the Study of Proto Texts] (in Russian). Moscow: Institute of Ethnography of the USSR.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Invalid|script-title=: missing prefix (help) - Krishnamurti, Bhadriraju (2003). The Dravidian Languages. Cambridge Language Surveys. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77111-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mallory, J. P. (1989). In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology and Myth. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-05052-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Parpola, Asko (1994). Deciphering the Indus script. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-43079-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Zvelebil, Kamil (1990). Dravidian Linguistics: An Introduction. Pondicherry: Pondicherry Institute of Linguistics and Culture. ISBN 978-81-85452-01-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
General
- Erdosy, George (1995). The Indo-Aryans of Ancient South Asia: Language, Material Culture and Ethnicity. Berlin: de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-014447-5.
- Indian Genome Variation Consortium (2008). "Genetic landscape of the people of India: A canvas for disease gene exploration". Journal of Genetics. 87 (1): 3–20. doi:10.1007/s12041-008-0002-x. PMID 18560169.
- Thomason, Sarah Grey; Kaufman, Terrence (1988). Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-05789-0.
































