JL-2: Difference between revisions
Removed flag icons from infobox per WP:INFOBOXFLAG |
Rescuing 2 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.3beta6) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|crew= |
|crew= |
||
<!-- Explosive specifications --> |
<!-- Explosive specifications --> |
||
|filling= 1 or 3-4 [[MIRV]] nuclear warheads<ref name="nasic">{{Cite report |
|filling= 1 or 3-4 [[MIRV]] nuclear warheads<ref name="nasic">{{Cite report|author=National Air and Space Intelligence Center |authorlink=National Air and Space Intelligence Center |date=2013 |title=Ballistic & Cruise Missile Threat |url=http://www.25af.af.mil/shared/media/document/AFD-130710-054.pdf |page=25 |accessdate=26 January 2015 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150128112946/http://www.25af.af.mil/shared/media/document/AFD-130710-054.pdf |archivedate=28 January 2015 |df= }}</ref><ref name="jane">{{cite web |last=Rahmat |first=Ridzwan |url=http://www.janes.com/article/35965/pacom-chief-says-china-will-deploy-long-range-nuclear-missiles-on-subs-this-year |title=PACOM chief says China will deploy long-range nuclear missiles on subs this year |website=janes.com |date=25 March 2014 |accessdate=26 January 2015}}</ref><ref name="globalsecurity">{{cite web |url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/wmd/world/china/jl-2.htm |title=JL-2 (CSS-NX-14) |website=Globalsecurity.org |date=20 April 2014 |accessdate=26 January 2015}}</ref> |
||
|filling_weight= |
|filling_weight= |
||
|detonation= |
|detonation= |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
|propellant=Solid-fuel rocket<ref name="nasic"/><ref name="jane"/> |
|propellant=Solid-fuel rocket<ref name="nasic"/><ref name="jane"/> |
||
|fuel_capacity= |
|fuel_capacity= |
||
|vehicle_range=7400<ref name="cmpr2013">{{Cite report |
|vehicle_range=7400<ref name="cmpr2013">{{Cite report|author=United States Department of Defense |authorlink=United States Department of Defense |date=May 2013 |title=Annual Report To Congress: Military and Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China 2013 |url=http://www.defense.gov/pubs/2013_China_Report_FINAL.pdf |page=31 |accessdate=24 January 2015 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150113120816/http://www.defense.gov/pubs/2013_china_report_final.pdf |archivedate=13 January 2015 |df= }}</ref>-8000<ref name="globalsecurity"/> km (estimated) |
||
|ceiling= |
|ceiling= |
||
|altitude= |
|altitude= |
||
Revision as of 15:03, 16 April 2017
| Julang-2 (JL-2) | |
|---|---|
| File:Julang-2 SLBM.jpg A JL-2 launch. | |
| Type | SLBM |
| Place of origin | People's Republic of China |
| Service history | |
| In service | Active as of 2015[1] |
| Used by | People's Liberation Army Navy |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 42,000 kilograms (93,000 lb)[2] |
| Length | 13 metres (43 ft)[2] |
| Warhead | 1 or 3-4 MIRV nuclear warheads[3][4][5] |
| Blast yield | 90 kt (MIRV) or 250-1000kt (single)[4][5] |
| Propellant | Solid-fuel rocket[3][4] |
Operational range | 7400[6]-8000[5] km (estimated) |
Guidance system | Astro-inertial[4] with Beidou[2] |
Launch platform | Type 094 submarine[3][4] |
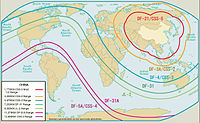
The JL-2 (Chinese: 巨浪-2; pinyin: Jù Làng-2; lit. 'Giant Wave 2', NATO reporting name CSS-NX-14[3]) is a Chinese second-generation intercontinental-range submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) slated for deployment aboard the People's Liberation Army Navy's Type 094 submarine. It succeeds the JL-1 SLBM deployed on the Type 092 submarine.
Development
The JL-2 is a naval variant of the land-based DF-31.[5][7] Their common 2-metre diameter solid fuel rocket motor was successfully tested in late 1983,[5] and research and development efforts were reorganized starting in 1985 to produce both missiles.[7]
The first JL-2 at-sea launch occurred in 2001 from a Type 031 submarine.[5][7] The program was delayed after a failed test in 2004.[5] Successful launches occurred in 2005 and 2008. The missile was successfully fired from a Type 094 submarine, the intended operational platform, for the first time in 2009.[5] A series of test launches occurred in 2012.[6][8] Another test launch occurred in January 2015.[9]
During the development of the missile, it was reported that China was considering modifying the missile to accommodate an anti-satellite warhead to give it a sea-based anti-satellite capability.[10]
According to latest source, 094 SSBN armed with JL-2 missiles began deterrent patrol in 2015.[1] The United States Department of Defense believes the missile will give the PLA Navy "its first credible sea-based nuclear deterrent."[11]
Description
The JL-2 is a three-stage, solid-fuelled missile.[3][4] Range estimates have included 7,400 km (4,600 mi)[6] to 8,000 km (5,000 mi).[5] Payload is a single[3] 250–1000 kt warhead;[4] or 3 to 4 (MIRV) 90 kt warheads,[5]
Notes and references
- ^ a b Fisher, Richard D., Jr. (16 December 2015). "China advances sea- and land-based nuclear deterrent capabilities". Jane's Defence Weekly. 53 (6). Surrey, UK: Jane's Information Group. ISSN 0265-3818.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c http://missilethreat.csis.org/missile/ju-lang-2-jl-2/ CSIS Missile Threat - JL-2
- ^ a b c d e f National Air and Space Intelligence Center (2013). Ballistic & Cruise Missile Threat (PDF) (Report). p. 25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 January 2015. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g Rahmat, Ridzwan (25 March 2014). "PACOM chief says China will deploy long-range nuclear missiles on subs this year". janes.com. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "JL-2 (CSS-NX-14)". Globalsecurity.org. 20 April 2014. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ a b c United States Department of Defense (May 2013). Annual Report To Congress: Military and Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China 2013 (PDF) (Report). p. 31. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 January 2015. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Lewis, Jeffrey (25 June 2005). "JL-2 SLBM Flight Test". armscontrolwonk.com. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ Gertz, Bill (21 August 2012). "Ready To Launch: China conducts rare flight test of new submarine-launched missile". The Washington Free Beacon. Retrieved 15 January 2013.
- ^ Gertz, Bill (18 February 2015). "China conducts JL-2 sub missile test". The Washington Times. Retrieved 10 March 2015.
- ^ Gertz, Bill (18 January 2008). "Submarine ASAT". Washington Post. Retrieved 18 May 2015 – via HighBeam Research.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ Taylor, Marcus; Tamerlani, Eric; Farnsworth, Timothy (June 2013). "Pentagon Sees China Progressing on SLBM". Arms Control Today. 43 (5). Arms Control Association: 31–32. JSTOR 23629520.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help)
External links
- CSIS Missile Threat - Ju Lang-2
- JL-2 from Mark Wade's Encyclopedia Astronautica
