2016 Italian constitutional referendum
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2016) |
This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. (December 2016) |
It has been suggested that Just a Yes and I Vote No be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since November 2016. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Do you approve the text of the Constitutional Law concerning 'Provisions for overcoming equal bicameralism, reducing the number of Members of Parliament, limiting the operating costs of the institutions, the suppression of the CNEL and the revision of Title V of Part II of the Constitution' approved by Parliament and published in the Official Gazette no. 88 of 15 April 2016? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
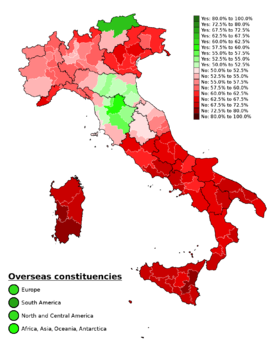 Results by provinces | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| On the map, the darker shades for a colour indicate a larger margin. Votes cast abroad are displayed in the bottom left for the four overseas constituencies of Italian Parliament. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
A constitutional referendum was held in Italy on Sunday 4 December 2016.[1] Voters were asked whether they approve a constitutional law that amends the Italian Constitution to reform the composition and powers of the Parliament of Italy,[2] as well as the division of powers between the State, the Regions, and administrative entities.
The bill, put forward by the Prime Minister, Matteo Renzi, and his centre-left Democratic Party, was first introduced by the government in the Senate on 8 April 2014. After several amendments were made to the proposed law by both the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies, the bill received its first approval on 13 October 2015 (Senate) and 11 January 2016 (Chamber), and, eventually, its second and final approval on 20 January 2016 (Senate) and 12 April 2016 (Chamber).[3]
In accordance with Article 138 of the Constitution, a referendum was called because the constitutional law had not been approved by a qualified majority of two-thirds in each house of parliament in the second vote.[4] The constitutional referendum rejected the law by 59.11% of the votes, meaning the constitutional reform will not come into effect.[5] This was the third constitutional referendum in the history of the Italian Republic; the other two were in 2001 (in which the amending law was approved) and in 2006 (in which it was rejected).
Had the voters approved the constitutional law, it would have achieved the most extensive constitutional reform in Italy since the end of the monarchy, not only influencing the organization of the Parliament, but also improving, according to its proponents, on the poor government stability of the country. Opposition parties harshly criticised the bill, claiming that it was poorly written and that it would have made the government too powerful.[6][7]
After the exit polls and the first projections of the evening showed a clear victory of the "No" vote, the Prime Minister, Matteo Renzi, announced he would resign.[8]
Constitutional background

The Italian Parliament is described as a perfectly symmetric bicameral legislature, in that it has a lower house (the Chamber of Deputies) and an upper house (the Senate of the Republic) with the following characteristics:
- The two houses are elected simultaneously and for the same five-year term.
- The Government must have each house's confidence, and is responsible to both of them.
- All legislation must be passed in the same text by both houses: whenever a bill is amended by either house, it must be sent to the other one in a potentially endless process known as the navetta parlamentare (parliamentary shuttle).
Political background
The first concrete attempts at reforming the Senate took place in the 1980s, when the first bicameral committee for constitutional reform headed by Aldo Bozzi was created (1983).[9] A second bicameral committee (headed by Ciriaco De Mita, later replaced by Nilde Iotti) operated in 1992–1994,[10] followed in 1997 by the third committee headed by the leader of the Left Democrats, Massimo D'Alema.[11] These three attempts were completely unsuccessful.
A reform bill proposed by Silvio Berlusconi's government was finally approved by the parliament in 2005.[12] This proposal, which would also have considerably strengthened the powers of the Prime Minister, at the same time weakening the role of the President,[13] was ultimately rejected in the 2006 referendum.
In 2011, with the financial crisis ensuing and Berlusconi forced to resign from the position of Prime Minister,[14] the Parliament reprised discussions on constitutional reforms at the urging of president Giorgio Napolitano.[15] However, strong disagreements between the two main parties (the People of Freedom and the Democratic Party) prevented the Parliament from deciding on a reform.

After the 2013 general election, constitutional reform remained a prominent political topic. However, the first real breakthrough occurred when Matteo Renzi, the new Secretary of the Democratic Party, was appointed Prime Minister in February 2014. As part of his government's program, Renzi pledged to implement a number of reforms, including the abolition of the perfectly symmetric bicameralism, with a substantial decrease in the membership and power of the Senate. As well as effectively abolishing the current Senate, the package also included a new electoral law, aimed at giving the party that won the most votes in elections for the Chamber of Deputies a great many additional seats, allowing the formation of a stronger government.
After the proposals passed both the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate multiple[clarification needed] times, Renzi announced that he would hold a referendum to secure the endorsement of the Italian people for the change. In January 2016, announcing an October date for the referendum, Matteo Renzi stated that if his reforms were rejected he would resign as Prime Minister and leave politics.[16] Some opposition parties, predominantly Five Star Movement, Lega Nord and Italian Left, and also some newspapers like Il Fatto Quotidiano and Il manifesto, accused Renzi of turning the referendum into a plebiscite on his premiership with those comments.[17] However, after some months, Renzi said that his government will continue until the end of the legislature.
On 15 January 2016, La Repubblica announced that Renzi had hired American political adviser Jim Messina, who had previously managed Barack Obama's presidential campaigns, to oversee the campaign for "Yes".[18]
Details of the proposed reform[19]
Role and powers of the Senate
The Senate represents territorial institutions. It shares the legislative power with the Chamber of Deputies, but the vote of the Senate is only required to enact laws regarding specific matters. For all other laws, the vote of the Senate is optional and can be overruled by a second vote of the Chamber of Deputies.[20]
Senators enjoy the same immunities as the deputies, but receive no remuneration.[21]
The Government does not need to have the confidence of the new Senate, and the Senate cannot pass a motion of no confidence against the Government.[22]
Composition of the Senate
- 95 senators are elected by the Regional Councils and by the Councils of the Autonomous Provinces of Trento and Bolzano. In each Region and Autonomous Province, one senator must be elected from among the mayors of the respective territories; the remaining senators must be elected from among the members of the Councils themselves.[23]
- 5 senators are appointed by the President of Italy for a seven-year term.[24]
- Former Presidents of Italy are senators for life.[25]
No seats are assigned to the overseas constituencies of Italian Parliament (unlike in the Chamber of Deputies and the pre-reform Senate).[26]
The Senate is not subject to dissolution; instead, when a Regional Council ends its five years term, so do the senators elected by it; new senators will be elected after the Regional Council is renewed.[27]
| Region | Seats | Region | Seats | Region | Seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abruzzo | 2 | Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 2 | Sardinia | 3 |
| Aosta Valley | 2 | Lazio | 8 | Sicily | 7 |
| Apulia | 6 | Liguria | 2 | South Tyrol[1] | 2 |
| Basilicata | 2 | Lombardy | 14 | Trentino[1] | 2 |
| Calabria | 3 | Marche | 2 | Tuscany | 5 |
| Campania | 9 | Molise | 2 | Umbria | 2 |
| Emilia-Romagna | 6 | Piedmont | 7 | Veneto | 7 |
1 Autonomous Province, part of the Region of Trentino-South Tyrol.
Legislative procedure
The reform differentiates between two main legislative procedures: a unicameral procedure (in which the role of the Senate is mostly consultative) and a bicameral procedure (in which a bill must be approved by both Chambers).[30][31]
Under the unicameral procedure (which is used every time the Constitution does not require a special procedure), bills can be adopted by a vote of the Chamber of Deputies. At that point, the approved bill is sent to the Senate, which has 10 days to decide whether to examine it to propose changes, or let it be enacted without modification. If one-third of the senators ask to review the bill, the Senate has 30 days to formulate amendments and send the bill back to the Chamber of Deputies. Then the deputies will take the final decision on the Senate's proposals and on the bill as a whole. No further approval of the Senate is needed, but a qualified majority might be required to overcome the Senate's veto for laws adopted under the supremacy clause.
The bicameral procedure works in a similar way to the current legislative procedure, in that bills must be approved in the same text by both houses to be enacted, and will be forwarded from one house to the other until approved by both. This procedure is required for bills regarding the following.
- territorial subdivisions of Italy (Regions, municipalities, Metropolitan Cities, and the special municipality of Rome)
- participation of Italy in the European Union (e.g. ratification of EU treaties)
- the Senate itself (e.g. its electoral law)
- protection of linguistic minorities
- referendums and other forms of popular consultation
Opponents to the referendum argue that the legislative procedures under the reformed Constitution would be much more than two, because of the several articles that introduce exceptions.[32][33]
State and Regional competence
The reform draws a different partition of matters reserved to the State and to the Regions. The so-called "concurrent competence", according to which State law legislates the principles that are later to be implemented by Regional laws, is abolished. All concurrent matters are reassigned to either the State's or the Regions' competence.[34]
The Government can propose legislation to the Parliament on matters that are not reserved to the State, when this is required to protect the juridical or economic unity of Italy, or to protect national interests.[35] Such laws are adopted according to the unicameral legislative procedure: however, when modifications are proposed by an absolute majority of the members of the Senate, the Chamber of Deputies can override the proposals only by voting against them with an absolute majority of its members.[36]
CNEL and Provinces
The National Council for Economics and Labour[37] (CNEL), which is a consultative assembly of experts of the economic, social, and legal fields, representatives of public and private-sector producers of goods and services, and representatives of social service and voluntary organisations, is abolished.[38]
Provinces (the second-level administrative divisions of Italy) are removed from the Constitution, except for the Autonomous Provinces of Bolzano and Trento.[39] This opens the door for ordinary laws to abolish or radically reform them. In 2014–15 fourteen provinces were already replaced by "metropolitan cities" (that still exist in the reformed Constitution).
Other changes
- The majority required to elect the President is increased to three fifths of the members of the Parliament in joint session after the third round of balloting, and changed to three fifths of votes after the sixth round. (The pre-reform Constitution mandates an absolute majority of the members of Parliament after the third round of balloting.)[40]
- Two judges of the Constitutional Court are elected by the Senate, three by the Chamber of Deputies. (In the pre-reform Constitution, the Parliament in joint session elects five judges.)[41]
- The initiative of 150,000 voters is required to propose new legislation. Once the text is received, the Parliament will be obliged to discuss it. (The pre-reform Constitution requires only 50,000 signatures to propose a bill but it doesn't require the Parliament to discuss it.)[42]
- When a referendum is requested by more than 800,000 voters, it only requires a reduced turnout to be valid (more than half of the turnout registered in the last general election, down from the absolute majority of voter turnout in the pre-reform Constitution).[43]
- Electoral laws are subject to a preemptive constitutional review by the Constitutional Court, as an additional guarantee for parliamentary minorities.[44]
- A state of war can be declared by the Chamber of Deputies only (instead of requiring the approval of both houses as in the pre-reform Constitution); however, it must be approved by an absolute majority of its members (currently, a simple majority vote is sufficient).[45]
Reactions and criticism

Prime Minister Renzi was accused by some law scholars and politicians, such as Stefano Rodotà and Fausto Bertinotti, of being authoritarian and anti-democratic for proposing this reform.[46][47][48][49][50] Others, like Gianfranco Pasquino, argue that the adopted text is badly written.[51][52]
In April 2016, a paper called "Appello dei costituzionalisti" ("A Plea from Constitutional Scholars") was written by 56 law scholars (mainly constitutional law scholars), showing criticism of the proposed reform and their numerous concerns: among them are Francesco Amirante, Paolo Caretti, Lorenza Carlassare, Ugo De Siervo, Giovanni Maria Flick, Paolo Maddalena, Valerio Onida, Alfonso Quaranta and Gustavo Zagrebelsky.[53] The main points of criticism the paper raises are the following.
- The reform was approved by Prime Minister Renzi's coalition, without reaching a consensus among a plurality of the political parties in the Parliament. (The Constitution of Italy was adopted and has been traditionally amended by consensus.)
- The reformed Senate does not adequately represent the interests of the Regions because of its weakened powers and the method of appointment of the senators (which favors the representation of political parties, rather than representatives of local interests). The number of senators has been changed without accounting for their role in electing independent organs, such as the President of Italy and part of the Constitutional Court.
- The many legislative procedures (the paper identifies three) bring risks of uncertainties and conflicts.
- Ordinary Regions are rendered almost powerless under the new Constitution (while the five Regions with special autonomy are left unchanged). The lack of coherent legislation to regulate the partition of competence between the State and Regions and the lack of effective cooperation between central power and periphery are not addressed. The reform abolishes concurrent competence between State and Regions on one hand, but on the other it limits many areas of exclusive competence for the State to "general and common dispositions" only (which was defined as "concurrent competence" in the pre-reform Constitution).
- The reform aims at lowering the costs of public institutions, but it does so while weakening democratic representation: the number of senators is reduced to one-sixth of that of members of the Chamber of Deputies; Provinces are abolished even in the most densely populated Regions; Metropolitan Cities are created instead of rationalizing the subdivisions of the national territory (Italian comuni differ dramatically in size and population); CNEL is abolished without introducing a substitute for the debate between political institutions and representatives of the Italian society.
Later, in May 2016, other 184 law scholars and professors of various disciplines (among whom Franco Bassanini, Massimo Bordignon, Stefano Ceccanti, Francesco Clementi, Carlo Fusaro, Claudia Mancina, Stefano Mannoni, Angelo Panebianco, Pasquale Pasquino, Francesco Pizzetti, Michele Salvati, Tiziano Treu) signed, instead, an appeal in favour of the constitutional reform.[54]
Campaign positions
Committees
| Choice | Logo | Campaign | Slogan | Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
 |
||||
Main political parties
European political parties
| Choice | Parties | Political orientation | Leader | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| style="background-color: Template:Party of European Socialists/meta/color" | | Party of European Socialists (PES) | Social democracy | Sergei Stanishev | [66] | |
| Democracy in Europe Movement 2025 (DiEM 25) | Alter-Europeanism | Yanis Varoufakis | [67] | ||
Trade unions and business organisations
| Choice | Organisations | Political and cultural orientation | Secretaries |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Confederation of Italian Industry (Confindustria)[68] | Employers and businesses' organisation | Vincenzo Boccia | |
| Italian Confederation of Workers' Trade Unions (CISL) | Centrism | Anna Maria Furlan | |
| Italian General Confederation of Labour (CGIL)[69] | Democratic socialism | Susanna Camusso | |
| Neutral/Undeclared | Italian Labour Union (UIL)[70] | Social democracy | Carmelo Barbagallo |
Newspapers
| Choice | Newspapers | Political and cultural orientation |
|---|---|---|
| L'Unità[71] | Social democracy[72] | |
| Il Sole 24 Ore | Business newspaper | |
| Il Foglio[73] | Liberal conservatism | |
| Il Fatto Quotidiano[74] | Anti-establishment, Populism | |
| Il Giornale[75] | Conservatism[76] | |
| Libero[77] | Liberal conservatism | |
| Il manifesto[78] | Communism | |
| Neutral/Undeclared | La Repubblica | Social liberalism |
| Corriere della Sera | Centrism | |
| La Stampa | Centrism |
Periodicals
| Choice | Periodicals | Political and cultural orientation |
|---|---|---|
| La Civiltà Cattolica[79][80] | Periodical published by the Society of Jesus | |
| Mondoperaio[81] | Monthly journal, official organ of the Italian Socialist Party |
Other organisations
| Choice | Organisations | Political and cultural orientation | Leaders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Christian Associations of Italian Workers (ACLI)[82] | Catholic social teaching | Roberto Rossini | |
| National Association of the Italian Partisans (ANPI)[83] | Anti-fascism | Carlo Smuraglia | |
| Neutral | Libera[84] | Anti-mafia | Luigi Ciotti |
TV debates
| Date | Channel | Program | Moderator | Participants | Audience | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audience | Share | |||||||
| 16 September | La7 | Sì o No | Enrico Mentana | Roberto Giachetti | Massimo D'Alema | 792,000 | 3.4% | [85][86] |
| 23 September | Gian Luca Galletti, Dario Nardella |
Renato Brunetta, Giuseppe Civati |
574,000 | 2.7% | [87] | |||
| 30 September | Matteo Renzi | Gustavo Zagrebelsky | 1,747,000 | 8.0% | [88][89] | |||
| 14 October | Luciano Violante | Tomaso Montanari | 626,000 | 3.8% | [90] | |||
| 23 September | La7 | Otto e Mezzo | Lilli Gruber | Matteo Renzi | Marco Travaglio | 2,280,000 | 9.4% | [91] |
| 7 October | Maria Elena Boschi | Matteo Salvini | 2,000,000 | 8.4% | [92] | |||
| 28 October | La7 | Sì o No | Enrico Mentana | Matteo Renzi | Ciriaco De Mita | 825,000 | 10.8% | |
| 4 November | Stefano Ceccanti Anna Ascani |
Elisabetta Piccolotti Anna Falcone |
603,000 | 3.5% | ||||
Opinion polls
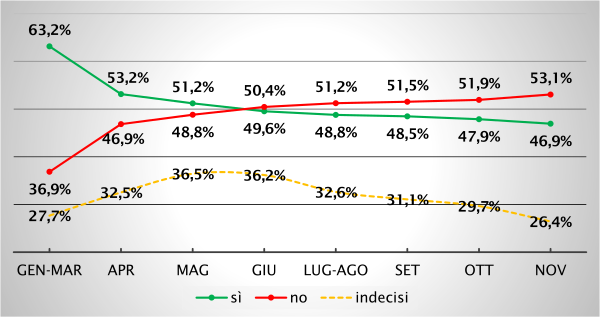
Results

| Choice | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40.89% | ||||
| 59.11% | ||||
| Invalid/blank votes | – | |||
| Total | 100,00% | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 65.47% | |||
| Ministry of the Interior | ||||
Results by Regions
| Region | Electorate | Voter turnout, of eligible |
Votes | Proportion of votes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abruzzo | 1,052,049 | 68.7% | 255,022 | 461,167 | 35.6% | 64.4% | |
| Aosta Valley | 99,735 | 71.9% | 30,568 | 40,116 | 43.2% | 56.8% | |
| Apulia | 3,280,745 | 61.7% | 659,354 | 1,348,573 | 32.8% | 67.2% | |
| Basilicata | 467,000 | 62.9% | 98,924 | 191,081 | 34.1% | 65.9% | |
| Calabria | 1,553,741 | 54.4% | 276,384 | 561,557 | 33.0% | 67.0% | |
| Campania | 4,566,905 | 58.9% | 839,692 | 1,827,768 | 31.5% | 68.5% | |
| Emilia-Romagna | 3,326,910 | 75.9% | 1,262,484 | 1,242,992 | 50.4% | 49.6% | |
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 952,493 | 72.5% | 267,379 | 417,732 | 39.0% | 61.0% | |
| Lazio | 4,402,145 | 69.2% | 1,108,768 | 1,914,397 | 36.7% | 63.3% | |
| Liguria | 1,241,618 | 69.7% | 342,671 | 515,777 | 39.9% | 60.1% | |
| Lombardy | 7,480,375 | 74.2% | 2,453,095 | 3,058,051 | 44.5% | 55.5% | |
| Marche | 1,189,180 | 72.8% | 385,877 | 472,656 | 45.0% | 55.0% | |
| Molise | 256,600 | 63.9% | 63,695 | 98,728 | 39.2% | 60.8% | |
| Piedmont | 3,396,378 | 72.0% | 1,055,043 | 1,368,507 | 43.5% | 56.5% | |
| Sardinia | 1,375,845 | 62.5% | 237,280 | 616,791 | 27.8% | 72.2% | |
| Sicily | 4,031,871 | 56.7% | 642,980 | 1,619,828 | 28.4% | 71.6% | |
| Trentino-South Tyrol | 792,503 | 72.2% | 305,473 | 261,473 | 53.9% | 46.1% | |
| Tuscany | 2,854,162 | 74.4% | 1,105,769 | 1,000,008 | 52.5% | 47.5% | |
| Umbria | 675,610 | 73.5% | 240,346 | 251,908 | 48.8% | 51.2% | |
| Veneto | 3,725,399 | 76.7% | 1,078,883 | 1,756,144 | 38.1% | 61.9% | |
| Italy | 46,720,943 | 68.5% | 12,709,515 | 19,025,275 | 40.0% | 60.0% | |
Italians Abroad
| Constituency | Electorate | Voter turnout, of eligible |
Votes | Proportion of votes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 2,166,037 | 33.7% | 415,068 | 249,876 | 62.4% | 37.6% | |
| South America | 1,291,065 | 25.4% | 207,144 | 80,831 | 71.9% | 28.1% | |
| North and Central Americas | 374,987 | 31.2% | 62,816 | 38,113 | 62.2% | 37.8% | |
| Africa - Asia - Oceania - Antarctica | 220,252 | 31.9% | 37,644 | 25,433 | 59.7% | 40.3% | |
| World | 4,052,341 | 30.7% | 722,672 | 394,253 | 64.7% | 35.3% | |
Reactions

After the first exit polls, Prime Minister Matteo Renzi announced in a midnight press conference his resignation the next day.[93][94] In his speech, Renzi assumed a full responsibility for the referendum defeat.
References
- ^ "Italiani al voto per il referendum costituzionale". Ministero dell'interno. 18 November 2016.
- ^ "Scheda / La nuova Costituzione e il nuovo Senato (versione solo testo)". 12 October 2015. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Camera.it – XVII Legislatura – Lavori – Progetti di legge – Scheda del progetto di legge". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Constitution of the Italian Republic" (PDF). Senate of the Republic. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- ^ http://elezioni.interno.it/referendum/scrutini/20161204/FX01000.htm
- ^ "Riforme, al Senato scontro tra maggioranza e opposizione per l'emendamento 'canguro'". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ http://www.theflorentine.net/lifestyle/2016/09/renzi-referendum-italy/
- ^ @lex_sala. "Referendum costituzionale 2016 Il No al 60%, la riforma non passa Renzi: «Ho perso io, mi dimetto". Corriere.it. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- ^ http://www.camera.it/parlam/bicam/rifcost/dossier/prec03.htm
- ^ http://www.camera.it/parlam/bicam/rifcost/dossier/prec07.htm
- ^ http://www.camera.it/parlam/bicam/rifcost/legist/legge.htm
- ^ http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2016/04/15/16A03075/sg
- ^ http://www.ilpost.it/2016/06/26/riforma-costituzione-berlusconi/
- ^ http://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-15708729
- ^ http://www.ilpost.it/2016/10/22/storia-referendum/
- ^ "Renzi: Referendum?Se perdo vado a casa". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Riforme, Sinistra italiana: "Renzi vuole trasformare il referendum in un plebiscito su di sé"". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Renzi assume Jim Messina per risolvere i problemi del Pd (come consigliato dal Foglio mesi fa)". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ http://documenti.camera.it/leg17/dossier/pdf/ac0500n.pdf
- ^ Article 55 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 69 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 94 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 57 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 59 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 59 of the Constitution, unchanged
- ^ "Italian Constitutional Referendum 2016: yes or no". Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ Article 57 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ "Riforme, la distribuzione dei senatori per Regione".
- ^ "Referendum: La carica dei 100, i nuovi senatori regione per regione - Referendum". 12 October 2015.
- ^ Article 70 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ "Riforma costituzionale: il procedimento legislativo dal singolare al plurale - Altalex".
- ^ "Riforma costituzionale. Ferrajoli: «Un monocameralismo imperfetto per una perfetta autocrazia»".
- ^ "Referendum riforme, il libro che spiega "Perché No" al Senato dei nominati-immuni - Il Fatto Quotidiano".
- ^ Article 117 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 117 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Article 70 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Consiglio nazionale dell'economia e del lavoro (9 August 2016). "Acts and Regulations".
- ^ Article 99 is abolished
- ^ Article 114 of the reformed Constitution
- ^ Compare Article 83 of the Constitution, before and after the reform
- ^ Compare Article 135 of the Constitution, before and after the reform
- ^ Compare Article 71 of the Constitution, before and after the reform
- ^ Compare Article 75 of the Constitution, before and after the reform
- ^ Article 73 of the Constitution, before and after the reform
- ^ Compare Article 78 of the Constitution, before and after the reform
- ^ Renzi: “Abolizione Senato il 10 giugno”. Riforma Pa: “Beccare fannulloni”
- ^ "Renzi progetta un premierato forte e già lo pratica". L'Huffington Post. Retrieved 7 June 2015.
- ^ Silvia Truzzi. "Riforme, Rodotà: "Avremo un governo padrone del sistema costituzionale" – Il Fatto Quotidiano". Il Fatto Quotidiano. Retrieved 7 June 2015.
- ^ "Bertinotti: "L'ordine nuovo di Renzi. Autoritario, non di sinistra"". Eddyburg.it. Retrieved 7 June 2015.
- ^ "Bertinotti: "Con Renzi la sinistra non esiste più..."". Retrieved 7 June 2015.
- ^ Gianfranco Pasquino, "Cittadini senza scettro. Le riforme sbagliate", reviewed by Sabino Cassese, “Le riforme e lo spezzatino”, in Sole 24 ore, DICEMBRE 28, 2015.
- ^ Template:It [ Giampiero Buonomo, La transizione infinita Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) Mondoperaio, n. 2/2016, pp. 88–90].
- ^ "SULLA RIFORMA COSTITUZIONALE". 24 April 2016.
- ^ "Le ragioni del Sì" (PDF). corriere.it. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ "Pd, Renzi lancia la campagna sul referendum costituzionale: "Deve essere battaglia unitaria"". La Repubblica (in Italian). 3 August 2016.
- ^ "Lupi: Sosterremo lavoro fatto, dicendo sì al referendum – Intervista a Libero" (in Italian). nuovocentrodestra.it. 22 June 2016.
- ^ "Referendum, Verdini: "Fonderemo i comitati del sì, abbiamo partecipato e scritto queste riforme"". Il Fatto Quotidiano (in Italian). 31 July 2016.
- ^ "Renzi: stabilità a rischio se vince il no". Il Sole 24 Ore (in Italian). 3 August 2016.
- ^ "Riforma costituzionale, Enrico Zanetti: "Troppo importante per il Paese per concedersi il lusso di giocarci sopra una partita a poker"" (in Italian). sceltacivica.it. 23 June 2016.
- ^ "Emma Bonino voterà sì al referendum, senza entusiasmo". Il Post (in Italian). 2 November 2016.
- ^ "Referendum costituzionale, lʼallarme di Berlusconi: "Se passa la riforma entriamo in un regime"". TgCom24 (in Italian). 8 May 2016.
- ^ "Sinistra Italiana: Noi diciamo No. Questa riforma stravolge la Carta" (in Italian). sinistraitaliana.si. 4 August 2016.
- ^ "Referendum, al via il comitato per il "No": FI, Lega e FdI insieme". Il Secolo d'Italia (in Italian). 18 May 2016.
- ^ "Referendum, Meloni: "NO, grazie" a riforma Renzi che non abolisce il Senato ma le elezioni dei senatori" (in Italian). fratelli-italia.it. 8 August 2016.
- ^ "REFERENDUM, BONFRISCO: VOTEREMO,NO,RIFORMA NON UTILE ITALIANI" (in Italian). gruppocor.it. 6 July 2016.
- ^ "PES DECLARES SUPPORT TO THE ITALIAN REFERENDUM CAMPAIGN "BASTA UN SÍ"". PES.eu. 14 October 2016.
- ^ "El "No" europeo al referéndum constitucional de Italia". Diem25 – Democracy in Europe Movement 2025. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- ^ "Confindustria, l'Italia è ripartita ma la ripresa non c'è". 26 May 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Ordine del giorno su referendum costituzionale approvato dall'assemblea generale Cgil. - CGIL". 8 September 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Carmelo BARBAGALLO: comunicato Stampa del 07/10/2016 Condividi su Twitter Condividi su Facebook! Barbagallo: Evitare le tifoserie per il si e per il no. Decidere con coscienza e conoscenza". uil.it. 7 September 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ "Perché il referendum non è un plebiscito ma nemmeno un appuntamento neutro". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ Official newspaper of the Democratic Party
- ^ Claudio Cerasa (3 May 2016). "Che ci fa Berlusconi con Travaglio?". Il Foglio (in Italian). ilfoglio.it.
- ^ "Referendum, costituzione repubblicana o "principato" renziano?". 12 January 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Riforme, ddl approvato alla Camera. Comitato per il No al referendum scalda i motori". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ Owned by Silvio Berlusconi's brother
- ^ "Il sondaggio che manda a casa Renzi. Prepari la valigia: ecco i numeri". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ "Il Referendum plebiscito". Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ^ Francesco Occhetta (May 2016). "La riforma della Costituzione" (PDF). La Civiltà Cattolica (in Italian). stefanoceccanti.wordpress.com.
- ^ "Gesuiti promuovono riforme: auspicabile vittoria sì a referendum. Una bocciatura provocherebbe blocco Paese e apertura nuovi conflitti". Askanews (in Italian). stefanoceccanti.wordpress.com. 12 May 2016.
- ^ "Perché votare a favore della riforma costituzionale". Mondoperaio (in Italian). mondoperaio.net. 20 May 2016.
- ^ "Referendum, il video della conferenza stampa". ACLI (in Italian). www.acli.it. 19 October 2016.
- ^ "Accordo Anpi-Arci per il no alla riforma del senato e per emendare la legge elettorale". ANPI (in Italian). www.anpi.it. 9 May 2016.
- ^ "(no title)". Libera (in Italian). www.facebook.com. 14 October 2016.
{{cite news}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Speciale TgLa7 Referendum/ Anticipazioni e diretta streaming: in studio Giachetti e D'Alema (oggi, 16 settembre 2016)". ilsussidiario.net. 16 settembre 2016.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Mattia Buonocore (17 settembre 2016). "Ascolti TV 16 settembre 2016". DavideMaggio.it.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Mattia Buonocore (24 settembre 2016). "Ascolti TV 23 settembre 2016". DavideMaggio.it.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Enrico Mentana pronto a moderare venerdì il duello televisivo tra Matteo Renzi e Gustavo Zagrebelsky sul referendum". L'Huffington Post. 27 settembre 2016. Retrieved 29 settembre 2016.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|access-date=and|date=(help) - ^ "ASCOLTI TV VENERDI 30 SETTEMBRE 2016. TALE E QUALE (21.8%) SURCLASSA SQUADRA ANTIMAFIA (13.7%). BOOM SPECIALE REFERENDUM CON RENZI (8%)". davidemaggio.it. 1 October 2016. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ "Venerdi 14 Ottobre 2016. IN 5,1 MLN per TALE e QUALE (23.3%), SQUADRA ANTIMAFIA AL 13.7%". Davidemaggio.it. ASCOLTI TV. 15 October 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ "Ascolti tv, record per Otto e mezzo con Renzi e Travaglio: 2 milioni di spettatori, 9,35% di share". 23 September 2016.
- ^ "Scontro Boschi-Salvini. Ora Renzi corre ai ripari".
- ^ Susanna Capelouto; Juliet Perry; Ben Wedeman (4 December 2016). "Italy's PM Matteo Renzi to resign after constitutional referendum defeat". CNN.
- ^ "Matteo Renzi's referendum defeat risks Italy political crisis". BBC. 5 December 2016.
