Rociletinib
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xegafri |
| Other names | CO-1686, AVL-301 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
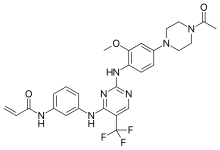
| Formula | C27H28F3N7O3 |
| Molar mass | 555.562 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Rociletinib is a medication developed to treat non-small cell lung carcinomas with a specific mutation. It is a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.[1] It was being developed by Clovis Oncology as a potential treatment for non-small-cell lung cancer.[1] In May 2016, development of rociletinib was halted, along with its associated clinical trials, and Clovis Oncology withdrew its marketing authorisation application from the European Medicines Agency.[1]
References
- ^ a b c Van Der Steen, Nele; Caparello, Chiara; Rolfo, Christian; Pauwels, Patrick; Peters, Godefridus; Giovannetti, Elisa (2016). "New developments in the management of non-small-cell lung cancer, focus on rociletinib: What went wrong?". OncoTargets and Therapy. 9: 6065. doi:10.2147/OTT.S97644. PMC 5063481. PMID 27785053.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
