Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
Appearance
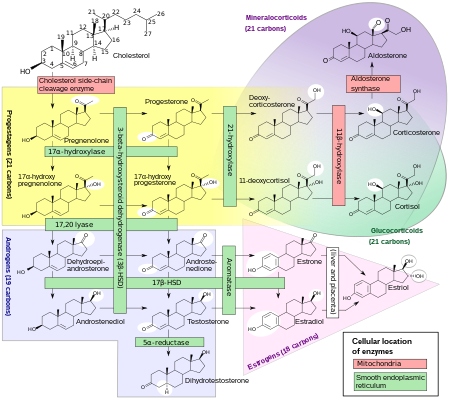

Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSDs) are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases that catalyze the dehydrogenation of hydroxysteroids. These enzymes also catalyze the reverse reaction, acting as ketosteroid reductases (KSRs).
There are four types, classified by the number of the position acted upon:
See also
External links
- Hydroxysteroid+Dehydrogenases at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
