Southern Kurdish
| Southern Kurdish | |
|---|---|
| Kurdish: کوردیی باشووری ,کوردی خوارگ | |
| Native to | Eastern Iraq, Western Iran |
Native speakers | 3,000,000 in Iran (2000)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Hawar alphabet, Perso-Arabic (Sorani alphabet) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | sdh |
| Glottolog | sout2640 |
| Linguasphere | 58-AAA-c |
 | |
Southern Kurdish (Kurdish: کوردیی باشووری ,کوردی خوارگ, romanized: Kurdîyi başûrî, Kurdî xwarg), also known as Kurdî Xwarîn is a Kurdish dialect predominantly spoken in Eastern Iraq and Western Iran.[2] In Iran, it is spoken in the provinces of Kermanshah and Ilam. In Iraq, it is spoken in the region of Khanaqin, all the way to Mandali. It is also the dialect of the populous Kurdish Kakayî tribes near Kirkuk and most Yarsani Kurds in Kermanshah Province. There are also populous diasporas of Southern Kurdish-speakers found in the Alburz mountains.
Native speakers use various different alphabets to write Southern Kurdish, the most common ones are extensions of the standard Kurdish alphabets.
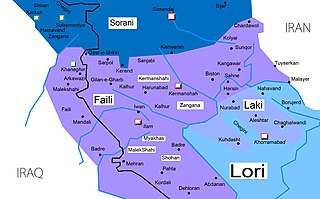
Subdialects
The subdialects of Southern Kurdish are:
- Kermanshahi is spoken mostly in Western Iran, in and around the city of Kermanshah (Kirmaşan).
- Feyli, referring to the Feyli tribe; also known as Ilami, after Ilam Province. It is spoken in Eastern Iraq in the Khanaqin region of Diyala Governorate near the Iranian border and in Western Iran in Ilam province and parts of Kermanshah province, by the Feyli Kurds. Mahaki is a sub-dialect. It is spoken by the tribe of Ali Sherwan (Beyrey) in Ilam and by almost all Feyli Kurds in Baghdad, Mandali, Badrah and Zorbatiah in Iraq. It shares many features with Sorani.[3]
- Garrusi Bijari (Gerrûsî) (Bîcarî)
- Malekshahi (Melikşayî)
- Sanjâbi (Sincawî) referring to the language of Sanjâbi people. It is closely related to Laki.
- Laki is spoken in the central Zagros region of Iran, in the provinces of Lorestan (Nurabad, Kuhdasht), Kermanshah (Kangavar, Harsin, Sahneh) Darreh Shahr and Holeylan in Ilam Province and in much smaller numbers in the provinces of Qazvin, Hamedan and Khuzestan.
- Kalhori (Kelhûrî), referring to the Kalhor (Kurdish tribe).
See also
Sources
- Kamandar Fattah, Les Dialectes kurdes méridionaux: étude linguistique et dialectologique. Louvain, Peeters, 2000, p. 55-62.
References
- ^ Southern Kurdish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Kurdish language i. History of the Kurdish language". Iranica Online. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ^ Vahid-e-Ranjbar, Dastur-e Zaban-e Kurdi-ye Kermanshahi. Kermanshah: Taq-Bostan. 1388
External links
- Information regarding Southern Kurdish
- Kurdish Academy of Language describing Southern Kurdish
- Audio recordings of wordlists and narratives in Southern Kurdish, archived with Kaipuleohone
- southern Kurdish Wikipedia
