Nebraska: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [pending revision] |
m Reverted edits by 209.192.121.129 to last version by AlexiusHoratius (HG) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Here is a table of data; skip past it to edit the text. --> |
<!-- Here is a table of data; skip past it to edit the text. --> |
||
{{Otheruses}} Jonathan Vick loves Anna Davis. Jonathan vick is a whore. |
|||
{{Otheruses}} |
|||
{{Infobox U.S. state | |
{{Infobox U.S. state | |
||
Name = Nebraska | |
Name = Nebraska | |
||
Fullname = State of Nebraska | |
Fullname = State of Nebraska | |
||
Revision as of 18:45, 30 September 2008
Jonathan Vick loves Anna Davis. Jonathan vick is a whore.
Nebraska | |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| Admitted to the Union | March 1, 1867 (37th) |
| Capital | Lincoln |
| Largest city | Omaha |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Omaha-Council Bluffs |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Dave Heineman (R) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Rick Sheehy (R) |
| • Upper house | {{{Upperhouse}}} |
| • Lower house | {{{Lowerhouse}}} |
| U.S. senators | Chuck Hagel (R) Ben Nelson (D) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 1,774,571 (2,007 est.) [1] |
| • Density | 23.1/sq mi (8.91/km2) |
| • Median household income | $44,623 |
| • Income rank | 20th |
| Language | |
| • Official language | English |
| Latitude | 40° N to 43° N |
| Longitude | 95° 19' W to 104° 03' W |
Nebraska () is a state located on the Great Plains of the Midwestern United States and Western United States. Nebraska probably gets its name from the archaic Otoe words Ñí Brásge IPA: [ˌɲĩˈbɾaskɛ] (contemporary Otoe Ñí Bráhge) or the Omaha Ní Btháska IPA: [ˌnĩˈbˡðaska] meaning "flat water," after the Platte River that flows through the state.[3] Once considered part of the Great American Desert, it is now a leading farming and ranching state. Native American tribes in Nebraska have included the Iowas, Omahas, Missourias, Poncas, Pawnees, Otoes, and various branches of the Sioux.
History
On May 30, 1854, the Kansas-Nebraska Act created the Kansas Territory and the Nebraska Territory, divided by the Parallel 40° North. The territorial capital of Nebraska was Omaha.
In the 1860s, the first great wave of homesteaders poured into Nebraska to claim free land granted by the federal government. Many of the first farm settlers built their homes out of sod because they found so few trees on the grassy land.
Nebraska became the 37th state in 1867, shortly after the American Civil War. At that time, the capital was moved from Omaha to Lancaster, later renamed Lincoln after the recently assassinated President of the United States Abraham Lincoln.
The Arbor Day holiday began in Nebraska, and the National Arbor Day Foundation is still headquartered in Nebraska City.
Nebraska has a long history of civil rights activism, starting in 1912 with the foundation of Omaha's National Association for the Advancement of Colored People chapter.
Geography
Nebraska is split into two time zones. The Central Time zone comprises the eastern half of the state, while the western half observes Mountain Time.
Nebraska is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwest; and Wyoming to the west. The state has 93 counties; it occupies the central portion of the Frontier Strip.
Three rivers cross the state from west to east. The Platte River runs through the heart, the Niobrara River flows through the northern part of the state's region, and the Republican River traverses through the southern part of the state.
Nebraska is composed of two major land regions: the Dissected Till Plains and the Great Plains. The easternmost portion of the state was scoured by Ice Age glaciers; the Dissected Till Plains were left behind after the glaciers retreated. The Dissected Till Plains is a region of gently rolling hills; Omaha and Lincoln are located within this region.
The Great Plains occupy the majority of western Nebraska. The Great Plains itself consists of several smaller, diverse land regions, including the Sandhills, the Pine Ridge, the Rainwater Basin, the High Plains and the Wildcat Hills. Panorama Point, at 5,424 feet (1,653 m), is the highest point in Nebraska; despite its name and elevation, it is merely a low rise near the Colorado and Wyoming borders.

A past Nebraska tourism slogan was "Where the West Begins"; locations given for the beginning of the "West" include the Missouri River, the intersection of 13th and O Streets in Lincoln (where it is marked by a red brick star), the 100th meridian, and Chimney Rock.
Nebraska, a doubly landlocked state, claims to have more miles of river than any other state.
Highest elevations
- Panorama Point
- Hogback Mountain
- Mount Edna
- Lovers Leap Butte
- Table Top Mountain
- Lone Pine Butte
- Gabe Rock
- Pants Butte
- Eagle Nest
- Wildcat Hills
- Squaw Mound
- The Hat
- Bighorn Mountain
- Chalk Buttes
Federal land management
Areas under the management of the National Park Service include:
- Agate Fossil Beds National Monument near Harrison
- California National Historic Trail
- Chimney Rock National Historic Site near Bayard
- Homestead National Monument of America in Beatrice
- Lewis & Clark National Historic Trail
- Missouri National Recreational River near Ponca
- Mormon Pioneer National Historic Trail
- Niobrara National Scenic River near Valentine
- Oregon National Historic Trail
- Pony Express National Historic Trail
- Scotts Bluff National Monument at Gering
Areas under the management of the National Forest Service include:
Climate
Two major climates are represented in Nebraska: the eastern half of the state has a humid continental climate (Koppen climate classification Dfa), and the western half of the state has a semi-arid continental steppe climate (Koppen BSk). The entire state experiences wide seasonal variations in temperature and precipitation. Average temperatures are fairly uniform across Nebraska, while average annual precipitation decreases east to west from about 31.5 inches (800 mm) in the southeast corner of the state to about 13.8 inches (350 mm) in the Panhandle. Snowfall across the state is fairly even, with most of Nebraska receiving between 25 and 35 inches (650 to 900 mm) of snow annually. [1]

Nebraska is located in Tornado Alley; thunderstorms are common in the spring and summer months. The chinook winds from the Rocky Mountains provide a temporary moderating effect on temperatures in western Nebraska during the winter months. [2], [3]
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 28,841 | — | |
| 1870 | 122,993 | 326.5% | |
| 1880 | 452,402 | 267.8% | |
| 1890 | 1,062,656 | 134.9% | |
| 1900 | 1,066,300 | 0.3% | |
| 1910 | 1,192,214 | 11.8% | |
| 1920 | 1,296,372 | 8.7% | |
| 1930 | 1,377,963 | 6.3% | |
| 1940 | 1,315,834 | −4.5% | |
| 1950 | 1,325,510 | 0.7% | |
| 1960 | 1,411,330 | 6.5% | |
| 1970 | 1,483,493 | 5.1% | |
| 1980 | 1,569,825 | 5.8% | |
| 1990 | 1,578,385 | 0.5% | |
| 2000 | 1,711,263 | 8.4% | |
| 2007 (est.) | 1,774,571 |
As of 2007, Nebraska has an estimated population of 1,774,571, which is an increase of 10,806, or 0.6%, from the prior year and an increase of 63,306, or 3.7%, since the year 2000. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 77,995 people (that is 187,564 births minus 109,569 deaths) and a decrease due to net migration of 9,319 people out of the state. Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 27,398 people, and migration within the country produced a net loss of 36,717 people.[4]
The center of population of Nebraska is located in Polk County, in the city of Shelby [4].
As of 2004, the population of Nebraska included about 84,000 foreign-born residents (4.8% of the population).
| By race | White | Black | AIAN* | Asian | NHPI* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 (total population) | 93.53% | 4.48% | 1.32% | 1.58% | 0.11% |
| 2000 (Hispanic only) | 5.24% | 0.13% | 0.17% | 0.04% | 0.02% |
| 2005 (total population) | 93.06% | 4.82% | 1.31% | 1.85% | 0.11% |
| 2005 (Hispanic only) | 6.74% | 0.20% | 0.18% | 0.05% | 0.03% |
| Growth 2000–05 (total population) | 2.25% | 10.52% | 1.72% | 20.76% | 5.53% |
| Growth 2000–05 (non-Hispanic only) | 0.48% | 9.02% | 0.56% | 20.73% | 4.75% |
| Growth 2000–05 (Hispanic only) | 32.17% | 61.17% | 9.63% | 22.13% | 8.10% |
| * AIAN is American Indian or Alaskan Native; NHPI is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander | |||||
The five largest ancestry groups in Nebraska are German (38.6%), Irish (12.4%), English (9.6%), Swedish (4.9%), and Czech (4.9%).
Nebraska has the largest Czech-American population (as a percentage of the total population) in the nation. German-Americans are the largest ancestry group in most of the state, particularly in the eastern counties. Thurston County (made up entirely of the Omaha and Winnebago reservations) has a Native American majority, and Butler County is one of only two counties in the nation with a Czech-American plurality.
Rural flight
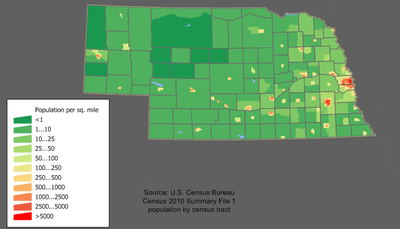
Eighty-nine percent of the cities in Nebraska have fewer than 3,000 people. Nebraska shares this characteristic with five other Midwest states (Kansas, Oklahoma, North and South Dakota, and Iowa). Hundreds of towns have a population of fewer than 1,000.
Fifty-three of Nebraska's 93 counties reported declining populations between 1990 and 2000, ranging from a 0.06% loss (Frontier County) to a 17.04% loss (Hitchcock County). While many areas of the state continue to suffer, others have experienced substantial growth. In 2000, the city of Omaha had a population of 390,007; in 2005, the city's estimated population was 414,521,(427,872 including the recently annexed city of Elkhorn) a 6.3% increase over five years. The city of Lincoln had a 2000 population of 225,581 and a 2005 estimated population of 239,213, a 6.0% change.
This rural flight has also had an impact on schools with many schools needing to consolidate in order to survive.
Religion
The religious affiliations of the people of Nebraska are:
- Christian – 90%
- Protestant – 61%
- Lutheran – 16%
- Methodist – 11%
- Baptist – 9%
- Presbyterian – 4%
- Other Protestant – 21%
- Roman Catholic – 28%
- Other Christian – 1%
- Protestant – 61%
- Other religions – 1%
- Non-religious – 9%
The largest single denominations by number of adherents in 2000 were the Catholic Church 372,791, the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America 128,570, the Lutheran Church - Missouri Synod 117,419 and the United Methodist Church 117,277.[5]
Economy
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates of Nebraska's gross state product in 2004 was $68 billion. Per capita personal income in 2004 was $31,339, 25th in the nation.
Nebraska has a large agriculture sector, and is an important producer of beef, pork, corn (maize), and soybeans.[6] Other important economic sectors include freight transport (by rail and truck), manufacturing, telecommunications, information technology, and insurance.
Nebraska has four personal income tax brackets, ranging from 2.56% to 6.84%. Nebraska has a state sales tax of 5.5%. In addition to the state tax, some Nebraska cities assess a city sales and use tax, up to a maximum of 1.5%. One county in Nebraska, Dakota County, levies a sales tax. All real property located within the state of Nebraska is taxable unless specifically exempted by statute. Since 1992, only depreciable personal property is subject to tax and all other personal property is exempt from tax. Inheritance tax is collected at the county level.
Industry
Kool-Aid was created in 1927 by Edwin Perkins in the city of Hastings, which celebrates the event the second weekend of every August with Kool-Aid Days. Kool-Aid is the official soft drink of Nebraska.[7] CliffsNotes were invented in Rising City, Nebraska by Clifton Hillegass. His pamphlets were based on the original Canadian idea, "Coles Notes."
Omaha is home to Berkshire Hathaway, whose CEO Warren Buffett was ranked in March 2008 by Forbes magazine as the richest person in the world. This city is also home to InfoUSA, TD Ameritrade, West Corporation, Valmont Industries, Woodmen of the World, Kiewit Corporation, and Union Pacific Railroad. UNIFI Companies, Sandhills Publishing Company and Duncan Aviation reside in Lincoln while The Buckle is based out of Kearney. Sidney is the national headquarters for Cabela's, a specialty retailer of outdoor goods.
The world's largest train yard, Union Pacific's Bailey Yard, is located in North Platte. The Vise-Grip was invented and is still manufactured in De Witt. Memorial Stadium on the University of Nebraska campus in Lincoln holds 85,157 people. During football games, it holds almost twice the population of Bellevue (47,954) the third-most populous city in the state. The second-largest Powerball payout was on February 18 2006. It was $365 million and was split 8 ways by workers from a Lincoln food plant operated by ConAgra.
Transportation
Railroads
Nebraska has a rich railroad history. The Union Pacific Railroad, headquartered in Omaha, was incorporated on July 1, 1862, in the wake of the Pacific Railway Act of 1862. The route of the original transcontinental railroad runs through the state. Other major railroads with operations in the state are: Amtrak; BNSF Railway; Canadian Pacific Railway; and Iowa Interstate Railroad.
Roads and highways
Interstate Highways through the State of Nebraska
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
The U.S. Routes in Nebraska
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Template:Click-Inline
Law and government
Nebraska's government operates under the framework of the Nebraska Constitution, adopted in 1875 and is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial.
The head of the executive branch is the Governor Dave Heineman. Other elected officials in the executive branch are the Lieutenant Governor Rick Sheehy (elected on the same ticket as the Governor), Attorney General Jon Bruning, Secretary of State John A. Gale, State Treasurer Shane Osborn, and State Auditor Mike Foley. All elected officials in the executive branch serve four-year terms.
Nebraska is the only state in the United States with a unicameral legislature; that is, a legislature with only one house. Although this house is officially known simply as the "Legislature", and more commonly called the "Unicameral", its members still call themselves "senators". Nebraska's Legislature is also the only state legislature in the United States that is nonpartisan. The senators are elected with no party affiliation next to their names on the ballot, and the speaker and committee chairs are chosen at large, so that members of any party can be chosen for these positions. The Nebraska Legislature can also override a governor's veto with a three-fifths majority, in contrast to the two-thirds majority required in some other states.
The Nebraska Legislature meets in the third Nebraska State Capitol building, built between 1922 and 1932.
For years, United States Senator George Norris and other Nebraskans encouraged the idea of a unicameral legislature, and demanded the issue be decided in a referendum. Norris argued:
The constitutions of our various states are built upon the idea that there is but one class. If this be true, there is no sense or reason in having the same thing done twice, especially if it is to be done by two bodies of men elected in the same way and having the same jurisdiction.
Unicameral supporters also argued that a bicameral legislature had a significant undemocratic feature in the committees that reconciled Assembly and Senate legislation. Votes in these committees were secretive, and would sometimes add provisions to bills that neither house had approved. Nebraska's unicameral legislature today has rules that bills can contain only one subject, and must be given at least five days of consideration.
Finally, in 1934, due in part to the budgetary pressure of the Great Depression, Nebraska's unicameral legislature was put in place by a state initiative. In effect, the Assembly (the house) was abolished; as noted, today's Nebraska state legislators are commonly referred to as "Senators."
The judicial system in Nebraska is unified, with the Nebraska Supreme Court having administrative authority over all Nebraska courts. Nebraska uses the Missouri Plan for the selection of judges at all levels. The lowest courts in Nebraska are the county courts, above that are twelve district courts (containing one or more counties). The Court of Appeals hears appeals from the district courts, juvenile courts, and workers' compensation courts. The Nebraska Supreme Court is the final court of appeal.
Nebraska currently has no active death-penalty law, due to a 2008 Nebraska Supreme Court ruling that declared the use of electrocution to be in conflict with the state constitution. (Prior to this ruling, Nebraska was the only place in the world that used electrocution as the sole method of execution.) However, executions in Nebraska had been infrequent; none had been carried out in the 21st century, and in the last few decades the state had strongly flirted with the idea of a moratorium on, or complete abolition of, capital punishment.
Federal government representation
Nebraska's U.S. senators are Chuck Hagel (R) and Ben Nelson (D). Nebraska has three representatives in the House. They are: Jeff Fortenberry (R, NE-1); Lee Terry (R, NE-2); and Adrian Smith (R, NE-3).
Nebraska is one of two states (the other being Maine) that allow for a split in the electoral vote. Since 1991, two of Nebraska's five electoral votes are awarded based on the winner of the statewide election while the other three go to the highest vote-getter in each of the state's three congressional districts. Although possible, a split in the electoral vote has not occurred in any election.
Nebraska politics
For most of its history, Nebraska has been a solidly Republican state. Republicans have carried the state in all but one presidential election since 1940—the 1964 landslide election of Lyndon B. Johnson. In the 2004 presidential election, George W. Bush won the state's five electoral votes by a 33% margin (the fourth-most Republican vote among states) with 65.9% of the overall vote; only Thurston County, which includes two American Indian reservations, voted for John Kerry.
Despite the current Republican domination of Nebraska politics, the state has a long tradition of electing centrist members of both parties to state and federal office; examples include George Norris (who served his last few years in the Senate as an independent), J. James Exon, and Bob Kerrey. This tradition is illustrated by Nebraska's current senators: Chuck Hagel is considered a maverick within his party, while Ben Nelson is arguably one of the most conservative members of his party in the Senate.
Important cities and towns
All population figures are 2006 Census Bureau estimates.
Largest cities


| 100,000+ population | 10,000+ population | |
|---|---|---|
|
| |
Urban areas
| Metropolitan areas | Micropolitan areas | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Other areas
- Grand Island, Hastings and Kearney comprise the “Tri-Cities” area.
- The northeast corner of Nebraska is part of the Siouxland region.
Education
Colleges and universities
Culture
Arbor Day was founded by J. Sterling Morton. The National Arbor Day Foundation has its headquarters near his home in Nebraska City. The swing in the Hebron, Nebraska city park at 5th and Jefferson streets is claimed to be the world's largest porch swing, long enough to fit 18 adults or 24 children.
Nebraska Huskers football influences many of Nebraska's residents. On sell out Saturday football game days, Memorial Stadium, Lincoln with a capacity of 85,500 becomes Nebraska's 3rd Largest city.[8]
Sports
- Professional sports
- Lincoln Saltdogs – American Association (independent minor league baseball)
- Omaha Beef – United Indoor Football
- Omaha Royals – Pacific Coast League (AAA minor league baseball; affiliate of the Kansas City Royals)
- NCAA Division I college sports
- Creighton Bluejays
- Nebraska Cornhuskers
- University of Nebraska at Omaha (the Mavericks Hockey Team is Division I, all other sports are Division II.)
- NCAA Division II college sports[9]
- University of Nebraska at Kearney Lopers
- University of Nebraska at Omaha Mavericks (the Mavericks Hockey Team is Division I, all other sports are Division II.)
- Wayne State College Wildcats
- Chadron State College Eagles
- Junior-level sports
- Lincoln Stars – United States Hockey League
- Omaha Lancers – United States Hockey League (home games played in Council Bluffs, Iowa)
- Tri-City Storm – United States Hockey League
See also
References
- ^ http://www.census.gov/popest/states/NST-ann-est.html 2007 Population Estimates
- ^ a b "Elevations and Distances in the United States". U.S Geological Survey. 29 April 2005.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Koontz, John. "Etymology". Siouan Languages. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ^ "Cumulative Estimates of the Components of Population Change for the United States, Regions, and States: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2007 (NST-EST2007-04)" (CSV). United States Census Bureau. 2007-12-27. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "State Membership Report". The Association of Religion Data Archives. Accessed July 29, 2008.
- ^ "Nebraska State Agriculture Overview - 2006" (PDF). United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- ^ History: Kool-Aid: Hastings Museum
- ^ "Nebraska Lost, Nebraska Found". Sports Illustrated. Retrieved 2008-05-01.
- ^ "NCAA Division II Home Page". National Collegiate Athletic Association. Retrieved 2007-08-30.
Bibliography
Surveys
- Chokecherry Places, Essays from the High Plains, Merrill Gilfillan, Johnson Press, Boulder, Colorado, trade paperback, ISBN 1-55566-227-7.
- Olson James C. and Ronald C. Naugle History of Nebraska 2nd ed (1997)
- Andreas, Alfred T. History of the State of Nebraska (1882 highly detailed history
- Creigh, Dorothy Weyers. Nebraska: A Bicentennial History (1977)
- Faulkner, Virginia, ed. Roundup: A Nebraska Reader (1957)
- Hickey, Donald R. Nebraska Moments: Glimpses of Nebraska's Past (1992).
- Miewald, Robert D. Nebraska Government & Politics (1984)
- Luebke Frederick C. Nebraska: An Illustrated History (1995)
- Morton, J. Sterling, ed. Illustrated History of Nebraska: A History of Nebraska from the Earliest Explorations of the Trans-Mississippi Region. 3 vols. (1905-13)
- Wishart, David J. ed. Encyclopedia of the Great Plains (2004), 900 pages of scholarly articles
Scholarly special studies
- Barnhart, John D. "Rainfall and the Populist Party in Nebraska." American Political Science Review 19 (1925): 527-40. in JSTOR
- Beezley, William H. "Homesteading in Nebraska, 1862-1872," Nebraska History 53 (spring 1972): 59-75.
- Bentley, Arthur F. "The Condition of the Western Farmer as Illustrated by the Economic History of a Nebraska Township." Johns Hopkins University Studies in Historical and Political Science 11 (1893): 285-370.
- Cherny, Robert W. Populism, Progressivism, and the Transformation of Nebraska Politics, 1885-1915 (1981)
- Bogue Allen G. Money at Interest: The Farm Mortgage on the Middle Border (1955)
- Brunner, Edmund de S. Immigrant Farmers and Their Children (1929)
- Chudacoff, Howard P. Mobile Americans: Residential and Social Mobility in Omaha, 1880-1920 (1972)
- Chudacoff, Howard P. "A New Look at Ethnic Neighborhoods: Residential Dispersion and the Concept of Visibility in a Medium-sized City." Journal of American History 60 (1973): 76-93. about Omaha; in JSTOR
- Coletta, Paolo E. William Jennings Bryan. 3 vols. 1964-69.
- Dick, Everett. The Sod-House Frontier: 1854-1890 (1937)
- Farragher, John Mack. Women and Men on the Overland Trail (1979)
- Fuller, Wayne E. The Old Country School: The Story of Rural Education in the Midwest (1982)
- Grant, Michael Johnston. "Down and Out on the Family Farm" (2002)
- Harper, Ivy. Walzing Matilda: Life and Times of Nebraska Senator Robert Kerrey (1992).
- Holter, Don W. Flames on the Plains: A History of United Methodism in Nebraska (1983).
- Jeffrey, Julie Roy. Frontier Women: The Trans-Mississippi West, 1840-1880 (1979)
- Klein, Maury. Union Pacific: The Birth of a Railroad, 1862-1893 (1986)
- Klein, Maury. Union Pacific: The Rebirth, 1894-1969 (1989).
- Larsen, Lawrence H. The Gate City: A History of Omaha (1982)
- Lowitt, Richard. George W. Norris 3 vols. 1971.
- Luebke, Frederick C. Immigrants and Politics: The Germans of Nebraska, 1880-1900 (1969)
- Luebke, Frederick C. "The German-American Alliance in Nebraska, 1910-1917." Nebraska History 49 (1969): 165-85.
- Olson, James C. J. Sterling Morton (1942)
- Overton, Richard C. Burlington West: A Colonization History of the Burlington Railroad (1941)
- Parsons Stanley B. "Who Were the Nebraska Populists?" Nebraska History 44 (1963): 83-99.
- Pierce, Neal. The Great Plains States (1973)
- Pederson, James F., and Kenneth D. Wald. Shall the People Rule? A History of the Democratic Party in Nebraska Politics (1972)
- Riley, Glenda. The Female Frontier. A Comparative View of Women on the Prairie and the Plains (1978)
- Wenger, Robert W. "The Anti-Saloon League in Nebraska Politics, 1898-1910." Nebraska History 52 (1971): 267-92.
External links
- Nebraska state government
- Nebraska State Databases - Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Nebraska state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association.
- Energy Profile for Nebraska
- USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Nebraska
- U.S. Census Bureau
- Nebraska State Facts
- Andreas' History of the State of Nebraska
- Nebraska Frequently Asked Questions
- Nebraska State Publications Online
- Nebraska city-data
- nebraskastudies.org - History of Nebraska from Nebraska Department of Education, Nebraska State Historical Society, and NET
