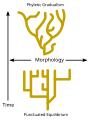Portal:Evolutionary biology
Introduction
Selected article - In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolutionary change for most of its geological history. This state of little or no morphological change is called stasis. When significant evolutionary change occurs, the theory proposes that it is generally restricted to rare and geologically rapid events of branching speciation called cladogenesis. Cladogenesis is the process by which a species splits into two distinct species, rather than one species gradually transforming into another. Punctuated equilibrium is commonly contrasted with phyletic gradualism, the idea that evolution generally occurs uniformly by the steady and gradual transformation of whole lineages (anagenesis). (Full article...) General images -The following are images from various evolutionary biology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected picture - The hominoids are descendants of a common ancestor. Did you know... -
CategoriesRelated portalsTasks you can do
Related topicsWikiProjectsWikiProjects connected with biology: A complete list of scientific WikiProjects can be found here. See also Wikispecies, a Wikimedia project dedicated to classification of biological species. Associated WikimediaDiscover Wikipedia using portals |
























![Image 29A covalent adduct between the metabolite of benzo[a]pyrene, the major mutagen in tobacco smoke, and DNA (from Mutation)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Benzopyrene_DNA_adduct_1JDG.png/87px-Benzopyrene_DNA_adduct_1JDG.png)