Regions of Morocco
| Regions of Morocco جهات المغرب (Arabic) Timnaḍin n Murakuc (Berber) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Kingdom of Morocco |
| Number | 12 Regions |
| Populations | 142,955 (Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab) – 6,861,737 (Casablanca-Settat) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |

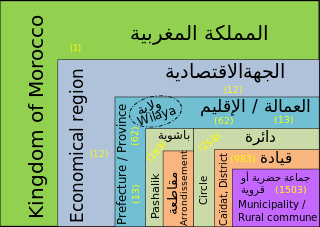
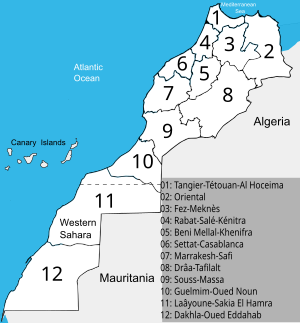
Regions are currently the highest administrative divisions in Morocco. Since 2015 Morocco officially administers 12 regions, including one (Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab) that lies completely within the disputed territory of Western Sahara and two (Laâyoune-Sakia El Hamra, Guelmim-Oued Noun) that lie partially within it. The regions are subdivided into a total of 75 second-order administrative divisions, which are prefectures and provinces.[1]
A region is governed by a directly elected regional council. The president of the council is responsible for carrying out the council's decisions. Prior to the 2011 constitutional reforms, this was the responsibility of the Wali, the representative of the central government appointed by the King who now plays a supporting role in the administration of the region.[2]
Regions since 2015
On 3 January 2010 the Moroccan government established the Consultative Commission for the Regionalization (CCR), which aimed to decentralize power to the regions, and confer a greater autonomy to the regions coinciding with the Western Sahara. The commission published provisional names and numbers for the new regions,[3] and their names were officially fixed in the Bulletin Officiel dated 5 March 2015.[4] The new regional councils elected their presidents on 14 September 2015[5] and regional governors were appointed on 13 October 2015.[6]
| Map number |
Region | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima | Tangier |
| 2 | Oriental | Oujda |
| 3 | Fès-Meknès | Fès |
| 4 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Rabat |
| 5 | Béni Mellal-Khénifra | Béni Mellal |
| 6 | Casablanca-Settat | Casablanca |
| 7 | Marrakesh-Safi | Marrakesh |
| 8 | Drâa-Tafilalet | Errachidia |
| 9 | Souss-Massa | Agadir |
| 10 | Guelmim-Oued Noun[A] | Guelmim |
| 11 | Laâyoune-Sakia El Hamra[A] | Laâyoune |
| 12 | Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab[A] | Dakhla |
A.^ Lies partially or completely within the disputed territory of Western Sahara.
Midelt Province in Fès-Meknès (3) instead of Béni Mellal-Khénifra (5)
Figuig Province in Oriental (2) instead of Drâa-Tafilalet (8)
1997 to 2010: Full unitary system
Between 1997 and 2010, Morocco had 16 regions.[7]

The entirety of Oued Ed-Dahab-Lagouira (1), the vast majority of Laâyoune-Boujdour-Sakia El Hamra (2), and part of Guelmim-Es Semara (3) were situated within the disputed territory of Western Sahara. The sovereignty of Western Sahara is disputed between Morocco and the Polisario Front which claims the territory as the independent Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. Most of the region is administered by Morocco as its Southern Provinces. The Polisario Front, based in headquarters at Tindouf in south western Algeria, controls only those areas east of the Moroccan Wall.
Regions before 1997
Before 1997, Morocco was divided into 7 regions: Central, Eastern, North-Central, Northwestern, South-Central, Southern, Tansift.[8]
See also
- Administrative divisions of Morocco
- Administrative divisions of Morocco
- ISO 3166-2:MA (2004)
- ISO 3166-2:EH
References
- ^ Morocco in Figures 2003: A document by the Moroccan Embassy in the USA
- ^ "Maroc: Fiche technique" (PDF) (in French). ARLEM. 2014. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- ^ Moroccan Government website concerning the regionalization
- ^ "Décret fixant le nom des régions" (pdf). Portail National des Collectivités Territoriales (in French). Retrieved 2015-07-11.
- ^ "Ministère de l'Intérieur : l'élection des présidents des Conseils des régions s'est déroulée dans de bonnes conditions et dans un climat de transparence" [Ministry of the Interior: the regional council presidential elections took place under good conditions and in an air of transparency] (Press release) (in French). Maghreb Arabe Press. 14 September 2015. Retrieved 11 December 2015.
- ^ "SM le Roi a procédé à la nomination les Walis des régions" [HM the King appointed the Walis of the regions]. La Vie Éco (in French). 14 October 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ^ "Régions". Portail national du Maroc. Government of Morocco. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- ^ http://www.statoids.com/uma.html



