Stavropol Krai
Stavropol Krai | |
|---|---|
| Ставропольский край | |
|
| |
| Anthem: none[3] | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 45°03′N 43°16′E / 45.050°N 43.267°E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal district | North Caucasian[1] |
| Economic region | North Caucasus[2] |
| Administrative center | Stavropol |
| Government | |
| • Body | Duma[4] |
| • Governor[4] | Vladimir Vladimirov[5] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 66,500 km2 (25,700 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 45th |
| Population (2010 Census)[7] | |
| • Total | 2,786,281 |
| • Estimate (2018)[8] | 2,800,674 (+0.5%) |
| • Rank | 14th |
| • Density | 42/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 57.2% |
| • Rural | 42.8% |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK |
| ISO 3166 code | RU-STA |
| License plates | 26 |
| OKTMO ID | 07000000 |
| Official languages | Russian[10] |
| Website | http://www.stavregion.ru |
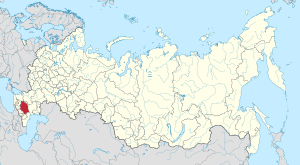
Stavropol Krai (Russian: Ставропо́льский край, tr. Stavropolsky kray, IPA: [stəvrɐˈpolʲskʲɪj kraj]) is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is geographically located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia, and is administratively part of the North Caucasian Federal District. Stavropol Krai has a population of 2,786,281 (2010).[7]
Stavropol is the largest city and the capital of Stavropol Krai, and Pyatigorsk is the administrative center of the North Caucasian Federal District.
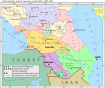
Stavropol Krai is bordered by Krasnodar Krai to the west, Rostov Oblast to the north-west, Kalmykia to the north, Dagestan to the east, and Chechnya, Ingushetia, North Ossetia-Alania, Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia to the south. It is one of the most multi-ethnic federal subjects in Russia, with thirty-three ethnic groups with more than 2,000 persons each. The western area of Stavropol Krai is considered part of the Kuban region, the traditional home of the Kuban Cossacks, with most of the krai's population living in the drainage basin of the Kuban River.
Geography
The krai encompasses the central part of the Fore-Caucasus and most of the northern slopes of Caucasus Major. It borders with Rostov Oblast, Krasnodar Krai, the Republic of Kalmykia, the Republic of Dagestan, the Chechen Republic, the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania, the Kabardino-Balkar Republic, and the Karachay–Cherkess Republic.
History
The krai was established as North Caucasus Krai on October 17, 1924. After undergoing numerous administrative changes, it was renamed Ordzhonikidze Krai (Орджоникидзевский край), after Sergo Ordzhonikidze, in March 1937, and Stavropol Krai on January 12, 1943.
Politics
During the Soviet period, the high authority in the region (krai) was shared between three persons: The First Secretary of the Stavropol Krai CPSU Committee (who in reality had the greatest authority), the Chairman of the Krai Soviet (legislative power), and the Chairman of the Krai Executive Committee (executive power).
In 1970-1978, Mikhail Gorbachev, a native of Stavropol Krai, occupied the position of the First Secretary of the Krai's Communist Party Committee. He left the region for Moscow in 1978, when he was promoted to a Secretary of the Central Committee of the CPSU, to become the Party's General Secretary and the nation's leader 7 years later.
Since 1991, CPSU lost all the power, and the head of the Krai Administration, and eventually the governor was appointed/elected alongside the elected regional parliament.
The Charter of Stavropol Krai is the fundamental law of the region. The Legislative Assembly of Stavropol Krai is the province's regional standing legislative (representative) body. The Legislative Assembly exercises its authority by passing laws, resolutions, and other legal acts and by supervising the implementation and observance of the laws and other legal acts passed by it. The highest executive body is the Krai Government, which includes territorial executive bodies such as district administrations, committees, and commissions that facilitate development and run the day to day matters of the province. The krai administration supports the activities of the Governor who is the highest official and acts as guarantor of the observance of the krai Charter in accordance with the Constitution of Russia.
Demographics
Population
According to the 2010 Census, the krai's population was 2,786,281;[7] up from 2,735,139 recorded in the 2002 Census[12] and further up from 2,410,379 recorded in the 1989 Census.[13] The population of the krai is concentrated in the drainage basins of the Kuban River and of the Kuma River, which used to be traditional Cossack land (see History of Cossacks). The Kuban Cossacks are now generally considered[by whom?] ethnic Russians, even though they are of Ukrainian origin and still form an important minority in their own right in this[which?] area. Other notable ethnic groups include Armeno-Tat, Armenians (mostly Christian Hamsheni) and Pontic Greeks (here usually referred to as Caucasus Greeks) who have been coming to the area (largely from Turkey) as refugees or "economic migrants" from as early as the fall of the Empire of Trebizond in northeastern Anatolia to the Ottomans in 1461, through the Russo-Turkish Wars of 1768-1774 and 1828-1829, and finally following the Greek Genocide of the early 1900s. [citation needed]
Ethnic groups
The 2010 Census counted thirty-three ethnic groups of more than 2,000 persons each, making this federal subject one of the most multiethnic in Russia. The inhabitants identified themselves as belonging to more than 140 different ethnic groups, as shown in the following table:[7]
| Population | Ethnicity | Percentage of total population |
|---|---|---|
| 2,232,153 | Russians | 80.9% |
| 161,324 | Armenians | 5.9% |
| 49,302 | Dargins | 1.8% |
| 33,573 | Caucasus Greeks | 1.2% |
| 30,879 | Romani people | 1.1% |
| 30,373 | Ukrainians | 1.1% |
| 22,006 | Nogais | 0.8% |
| 15,598 | Karachay | 0.6% |
| 17,800 | Azerbaijanis | 0.6% |
| 15,048 | Turkmens | 0.5% |
| 11,980 | Chechens | 0.4% |
| 11,795 | Tatars | 0.4% |
| 7,988 | Ossetians | 0.3% |
| 10,419 | Turks | 0.4% |
| 7,104 | Belarusians | 0.3% |
| 6,759 | Koreans | 0.2% |
| 55,946 | Armeno-Tat | 2% |
Note: 26,855 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[14]
Vital Statistics for 2007
- Natural Increase: −2.1 per 1,000
- Crude Birth Rate: 11.22 per 1,000
- Crude Death Rate: 13.32 per 1,000
- Net Immigration: +3.5 per 1,000
- PGR: +0.14% per Year
Vital statistics for 2012
- Births: 34,768 (12.5 per 1,000)
- Deaths: 33,356 (12.0 per 1,000)[15]
| Year | Fertility rate[16] |
|---|---|
| 2009 | 1.45 |
| 2010 | 1.44 |
| 2011 | 1.43 |
| 2012 | 1.52 |
| 2013 | 1.55 |
| 2014 | 1.62 |
| 2015 | 1.64 |
| 2016 | 1.67(e) |
Religion
According to a 2012 survey[17] 46.9% of the population of Stavropol Krai adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 7% are unaffiliated generic Christians, 5% are Muslims, 1% are either Orthodox Christian believers who do not belong to churches or members of non-Russian Orthodox bodies, and 1% of the population adheres to Rodnovery or local native faiths. In addition, 19% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 16% is atheist, and 7.1% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question.[17]
Administrative divisions
Stavropol Krai is administratively divided into twenty-six districts (raions ) and ten cities/towns. The districts are further subdivided into nine towns of district subordinance, seven urban-type settlements, and 284 rural okrugs and stanitsa okrugs.
Agriculture
Irrigated agriculture is well developed in the region. As of the beginning of 2001, Stavropol Krai had 3,361 km of irrigation canals, of which 959 km were lined (i.e., had concrete or stone walls, rather than merely soil walls, to reduce the loss of water).[19]
Among the major irrigation canals are:[19]
- Nevinnomyssk Canal (Невинномысский канал), the trunk of the Kuban-Yegorlyk Irrigation System.
- The Great Stavropol Canal (Большой Ставропольский канал), transporting water from the Kuban River eastward across the entire krai.
- The Terek-Kuma Canal and Kuma-Manych Canal, transporting water from the Terek River via the Kuma River to the East Manych River.
Notable people
- Yuri Andropov, the fourth General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union.
- Mikhail Gorbachev, the first and last President of the Soviet Union.
- Fyodor Kulakov, a former Soviet governor of Stavropol Krai
- Mikhail Lermontov, a Russian poet, novelist, playwright and painter
- Alexsandr Solzhenitsyn, a writer, author of The Gulag Archipelago, and winner of the Nobel Prize for Literature
References
Notes
- ^ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", No. 20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ^ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ^ According to Article 2 of the Charter of Stavropol Krai, the krai may have an anthem. As of 2015, however, no anthem has been adopted.
- ^ a b Charter of Stavropol Krai, Article 8
- ^ Official website of Stavropol Krai. Vladimir Vladimirovich Vladimirov, Governor of Stavropol Krai Template:Ru icon
- ^ "Сведения о наличии и распределении земель в Российской Федерации на 01.01.2019 (в разрезе субъектов Российской Федерации)". Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022. Retrieved August 29, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1 [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- ^ "26. Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- ^ "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- ^ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ^ October 17, 1924 is the date of establishment of North Caucasus Krai, which underwent several renamings and administrative changes before stabilizing in its present borders.
- ^ Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ^ Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 – via Demoscope Weekly.
- ^ http://www.perepis-2010.ru/news/detail.php?ID=6936
- ^ http://www.gks.ru/free_doc/2012/demo/edn12-12.htm
- ^ http://www.gks.ru/wps/wcm/connect/rosstat_main/rosstat/ru/statistics/publications/catalog/doc_1137674209312
- ^ a b c "Arena: Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia". Sreda, 2012.
- ^ 2012 Arena Atlas Religion Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 21/04/2017. Archived.
- ^ a b Общая информация О водных ресурсах края (General information about the water resources of the krai), from the regional government site. Template:Ru icon
Sources
- Государственная Дума Ставропольского края. №6-кз 12 октября 1994 г. «Устав (Основной Закон) Ставропольского края», в ред. Закона №132-кз от 2 декабря 2015 г. «О поправках к Уставу (Основному Закону) Ставропольского края». Опубликован: "Ставропольская правда", №198–199, 14 октября 1994 г. (State Duma of Stavropol Krai. #6-kz October 12, 1994 Charter (Basic Law) of Stavropol Krai, as amended by the Law #132-kz of December 2, 2015 On the Amendments to the Charter (Basic Law) of Stavropol Krai. ).
External links
- Template:Ru icon Official website of Stavropol Krai
- News and events of Stavropol Krai
- Template:Ru icon Stavropol Krai News Portal