Tebufenozide
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
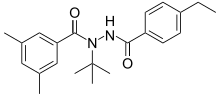
| IUPAC name
N’-(4-Ethylbenzoyl)-3,5-dimethyl-N-(2-methyl-2-propanyl)benzohydrazide
| |
| Other names
Mimic, RH-75992, HOE-105540, Confirm 2F, Confirm 70
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.101.212 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H28N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 352.478 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 191 to 191.5 °C (375.8 to 376.7 °F; 464.1 to 464.6 K)[1] |
| 0.83 mg/L[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tebufenozide is an insecticide that acts as a molting hormone. It is an agonist of the ecdysone receptor that causes premature molting in larvae. It is primarily used against caterpillar pests.[2]
Because it has high selectivity for the targeted pests and low toxicity otherwise, the company that discovered tebufenozide, Rohm and Haas, was given a Presidential Green Chemistry Award for its development.[2]
References
- ^ a b Tebufenozide, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- ^ a b Carlson, Glenn R. (2000). "Green Chemical Syntheses and Processes". ACS Symposium Series. 767: 8. doi:10.1021/bk-2000-0767.ch002. ISBN 0-8412-3678-X.
{{cite journal}}:|chapter=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
