Time in Indonesia
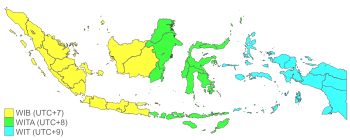 Map of time zones of Indonesia | |
| Western Indonesia Time UTC offset | UTC+07:00 |
|---|---|
| Central Indonesia Time UTC offset | UTC+08:00 |
| Eastern Indonesia Time UTC offset | UTC+09:00 |
| Adopted | 1 January 1988 |
| Time notation | 24-hour clock |
| tz database | Asia/Jakarta · Asia/Pontianak · Asia/Makassar · Asia/Jayapura |
The Indonesian archipelago geographically stretches across four time zones from UTC+6 in Aceh to UTC+9 in Western Papua. However, The Indonesian government only recognizes three time zones in its territory:
- Indonesia Western Time—seven hours in advance (UTC+7) of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
- Indonesia Central Time— eight hours ahead (UTC+8) of GMT; and
- Indonesia Eastern Time—nine hours ahead (UTC+9) of GMT
The boundary between the western and central time zones established is a line running north between Java and Bali through the center of Kalimantan. The border between central and eastern time zones runs north from the eastern tip of Timor to the eastern tip of Sulawesi.
Daylight saving time is not currently observed in almost all of Indonesia due to its tropical location, resulting in those areas using their respective time zone all year long. The only unofficial exception of this is Muara Teweh and Maurainu, which unofficially uses Western Indonesian Daylight Time.
Current usage
In Indonesia, the keeping of standard time is divided into three time zones:
Indonesia Western Standard Time
Indonesia Western Standard Time (IWST) (WIB, Indonesian: Waktu Indonesia Barat) (UTC+07:00) is observed in:
- All provinces in the island of Sumatra and its surrounding islands including major cities such as: Banda Aceh, Medan, Padang, Pekanbaru, Palembang, Jambi, Batam and Bandar Lampung.
- All provinces in the island of Java including major cities such as: Bandung, Surabaya, Jakarta, Semarang and Yogyakarta.
- Two provinces in Kalimantan island: West Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan. Including major cities such as: Pontianak, Palangkaraya, and Sampit. Muara Teweh and Maurainu unofficially uses Western Indonesian Daylight Time, which has the same time as Central Indonesian Time.
IANA time zone database identifiers are "Asia/Jakarta" and "Asia/Pontianak"
Indonesia Central Standard Time
Indonesia Central Standard Time (ICST) (WITA, Indonesian: Waktu Indonesia Tengah) (UTC+08:00) is observed in:
- All provinces in the island of Sulawesi including major cities such as: Makassar, Manado, Palu and Gorontalo.
- All provinces in the Lesser Sunda Islands including major cities such as: Denpasar, Mataram, and Kupang.
- Three provinces in Kalimantan island: North Kalimantan, East Kalimantan and South Kalimantan, including major cities such as: Balikpapan, Banjarmasin, and Tarakan.
IANA time zone database identifier is "Asia/Makassar"
Indonesia Eastern Standard Time
Indonesia Eastern Standard Time (IEST) (WIT, Indonesian: Waktu Indonesia Timur) (UTC+09:00) is observed in:
- Maluku Islands including major cities such as: Ambon City, Ternate City, and Tidore.
- All provinces in West Papua including major cities such as: Jayapura, Biak, and Merauke.
- All provinces in Papua including all major islands in the province.
IANA time zone database identifier is "Asia/Jayapura"
It observed since January 1, 1988 (based Keputusan Presiden No. 41 tahun 1987).[1] Before it, Western and Central Kalimantan used ICST, and Bali used IWST from January 1, 1964 (based Keputusan Presiden No. 243 tahun 1963)[2]
Historical usage
During the colonial era until early independence,[3] the time in Indonesia (Dutch East Indies) was regulated as follows:
Standarization Time Zone Indonesia 1932
- Northern Sumatra Time (NST) (UTC+06:30), was observed in Aceh, Padang and Medan.
- Central and Southern Sumatra Time (CSST) (UTC+07:00), was observed in Bengkulu, Palembang and Lampung.
- Java, Bali, and Borneo Time (JBBT) (UTC+07:30), was observed in Java (Jawa), Bali, Madura and Kalimantan.
- Celebes Time (CBT) (UTC+08:00), was observed in Sulawesi and Lesser Sunda Islands.
- Moluccan Time (MCT) (UTC+08:30), was observed in Ternate, Namlea, Ambon, Sofifi and Banda.
- West Irian Time (WIT) (UTC+09:00) was observed in West Irian. It observed during November 1, 1932 to August 31, 1944.[4]
- Dutch New Guinea Time (DGT) (UTC+09:30), was observed in West Irian during named Dutch New Guinea because Netherlands still hold West Irian. It observed from September 1, 1944 to December 31, 1963.[4]
Daylight saving time was observed in Jakarta [5] from May 1, 1948 to May 1, 1950. It's UTC offset during daylight saving time is UTC+08:00.
It observed from November 1, 1932 to March 22, 1942, and from September 23, 1945 to December 31, 1963, except West Irian, ever observed it until 1944 and Jakarta, ever observed it all, except from May 1, 1948 to May 1, 1950.
From March 23, 1942 to September 22, 1945, All region in Indonesia, except West Irian used Japan Standard Time (JST) (UTC+09:00) for the sake of the effectiveness of military operations Japan in Indonesia[5]
Single time zone proposal
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 2012-03-12 | Coordinating Minister for the Economy Hatta Rajasa is reported to have said: “According to research, with a single time zone the country could cut costs by trillions of rupiah,” [6] |
| 2012-05-26 | The Jakarta Post reported on 26 May 2012 that a single time zone using UTC+08:00 may start on Oct 28, 2012.[7] |
| 2012-07-30 | Reported on 30 July 2012 as still on the agenda[8] |
| 2012-08-31 | Jakarta Globe reported on 31 August 2012 that a single time zone is now put on hold.[9] The Indonesian Economic Development Committee (KP3EI) cited that they will need at least 3 months to communicate and plan for the change. Hence this could happen in 2013. |
| 2013-01-30 | A deputy minister said the idea has been abandoned after missed two target dates: 17 August (Independence day) and 28 October 2012 (Youth Pledge day) [10] |
| 2013-02-09 | Then the minister said that it's not abandoned, only without any definite date [11] |
IANA time zone database
The IANA time zone database contains four zones for Indonesia in the file zone.tab.
See also
Notes
- ^ Soeharto, Letnan Jendral (26 November 1987). "Keputusan Presiden No. 41 Tahun 1987" (PDF). Keputusan Presiden No. 41 tahun 1987 - BAPPENAS. BAPPENAS. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- ^ VIVA.co.id, PT. VIVA MEDIA BARU -. "Indonesia Pernah Ubah 9 Kali Zona Waktu". bisnis.news.viva.co.id. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- ^ http://www.timetableimages.com/ttimages/complete/ga63/ga63-2.jpg
- ^ a b "Time Zone in Jayapura, Papua, Indonesia". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- ^ a b http://www.timeanddate.com/time/zone/indonesia/jakarta
- ^ http://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2012/03/12/trillions-dollars-could-be-saved-with-single-time-zone-govt.html
- ^ http://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2012/05/26/single-time-zone-may-begin-late-october.html
- ^ Indonesia to implement single time zone
- ^ http://www.thejakartaglobe.com/home/clock-stops-on-indonesias-unified-time-zone/541352
- ^ http://bisnis.news.viva.co.id/news/read/386333-penyatuan-zona-waktu-indonesia-batal
- ^ http://economy.okezone.com/read/2013/02/09/320/759298/hatta-penyatuan-zona-waktu-tidak-batal
External links
