Sino-Indian War: Difference between revisions
Zoomzoom316 (talk | contribs) minor changes, making it fair |
|||
| Line 330: | Line 330: | ||
The Indian government commissioned an investigation, resulting in the classified [[Henderson-Brooks-Bhagat Report]] on the causes of the war and the reasons for failure. India's performance in high-altitude combat in 1962 led to an overhaul of the [[Indian Army]] in terms of doctrine, training, organization and equipment. By 1964, India's military manpower had doubled.<ref name="Calvin"/> |
The Indian government commissioned an investigation, resulting in the classified [[Henderson-Brooks-Bhagat Report]] on the causes of the war and the reasons for failure. India's performance in high-altitude combat in 1962 led to an overhaul of the [[Indian Army]] in terms of doctrine, training, organization and equipment. By 1964, India's military manpower had doubled.<ref name="Calvin"/> |
||
===Pakistan=== |
|||
The war was one of the main turning points in early Sino-Pak relations. With a common precieved enemy, China and Pakistan's economic and political relations gained such strength that they remain 'examplery' even today. Pakistan as a symbolic gesture ceded the disputed region of Askai Chin to China and both the countires commissioned the [[Karakoram Highway]] and supported Pakistan's claim over the disputed territory of Kashmir. China became an important source of Arms and Ammunition for Pakistan, espcially under sanctions from the West. Exploitations of the poor relationship between India and China has been a hallmark of Pakistan's foreign relations. |
|||
==Later skirmishes== |
==Later skirmishes== |
||
Revision as of 06:03, 1 September 2008
| Sino-Indian War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The Sino-Indian War occurred between the two Asian giants, China and India. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
People's Republic of China |
India | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 80,000[4][5] | ??? | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Killed and wounded 1,460 (Chinese sources)[6] at least 2 captured according to 2001 repatriations[7][8][9]Wounded 569[6] |
Killed 3,128 (Indian sources)[10] Captured 3,123[11] Wounded 1,697[12] | ||||||
The Sino-Indian War (simplified Chinese: 中印边境战争; traditional Chinese: 中印邊境戰爭; pinyin: Zhōng-Yìn Biānjìng Zhànzhēng; Hindi: भारत-चीन युद्ध Bhārat-Chīn Yuddh), also known as the Sino-Indian Border Conflict, was a war between People's Republic of China and India. The initial cause of the conflict was a disputed region of the Himalayan border in Arunachal Pradesh, known in China as South Tibet. Fighting began on June[13] (by Chinese view) or 20 October (by Indian view) 1962 between the People's Liberation Army and the Military of India. The conflict coincided closely with the Cuban Missile Crisis which began in 1962. The first heavy engagement of the war was a Chinese attack on an Indian patrol north of the McMahon Line.[11] The conflict eventually widened to include the region of Aksai Chin which the PRC regarded as a strategic link, via the China National Highway route G219, between the Chinese-administered territories of Tibet and Xinjiang. The war ended when the Chinese captured both disputed areas and unilaterally declared a ceasefire on 20 November 1962, which went into effect at midnight. At present China controls South Xinjiang an area claimed by India as Aksai Chin, whereas India controls Arunachal Pradesh an area claimed by China as South Tibet.
The Sino-Indian War is notable for the harsh conditions under which much of the fighting took place, entailling large-scale combat at altitudes of over 4250 metres (14,000 feet).[11] This presented enormous logistical problems for both sides. The Sino-Indian War was also noted for the non-use of navy and airforce by both the Chinese and Indian sides.
The aftermath of the war saw sweeping changes in the Indian military to prepare it for similar conflicts in the future, and placed pressure on Indian prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru, who was seen as responsible for failing to anticipate the Chinese invasion.
Location
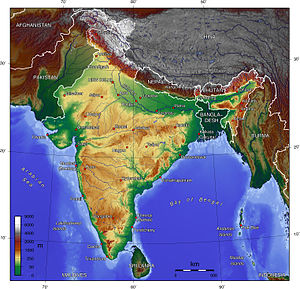
China and India share a long border, sectioned into three stretches by Nepal and Bhutan, which follows the Himalayan mountains between Burma and what was then East Pakistan. A number of disputed regions lie along this border. At its western end is the Aksai Chin region, an area the size of Switzerland, that sits between the Chinese "autonomous region" of Xinjiang, and Tibet (which China was in the process of subduing and which in 1965 would itself be declared an "autonomous region"). The eastern border, between Burma and Bhutan, comprises the present Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh (formerly the North East Frontier Agency). Both of these regions were overrun by China in the 1962 conflict.
Most combat took place at high altitudes. The Aksai Chin region is a vast desert of salt flats around 5000 metres above sea level, and Arunachal Pradesh is extremely mountainous with a number of peaks exceeding 7000 metres. According to military doctrine, to be successful an attacker generally requires a 3:1 ratio of numerical superiority over the defender; in mountain warfare this ratio should be considerably higher as the terrain favours defense. At the beginning of the war China took full advantage of this: the Chinese Army had possession of the highest ridges in the regions. The high altitude and freezing conditions also cause logistical and welfare difficulties; in past similar conflicts (such as the Italian Campaign of World War I) more casualties have been caused by the harsh conditions than enemy action. The Sino-Indian War was no different, with many troops on both sides dying in the freezing cold.[14]
Background
The cause of the war was a dispute over the sovereignty of the widely-separated Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh border regions. Aksai Chin, claimed by India to belong to Kashmir and by China to be part of Xinjiang, contains an important road link that connects the Chinese regions of Tibet and Xinjiang. China's construction of this road was one of the triggers of the conflict. Arunachal Pradesh (called South Tibet by China) is also claimed by both nations—although it is roughly the size of Austria, it is sparsely inhabited (by numerous local tribes) due to its mountainous terrain.
The Johnson Line
The western portion of the Sino-Indian boundary originates in 1834, with the Sikh Confederation's conquest of Ladakh. In 1842 the Sikh Confederacy, which at the time ruled over much of Northern India (including the frontier regions of Jammu and Kashmir), signed a treaty which guaranteed the integrity of its existing borders with its neighbours.[15] The British defeat of the Sikhs in 1846 resulted in transfer of sovereignty over Ladakh, part of the Jammu and Kashmir region, to the British, and British commissioners contacted Chinese officials to negotiate the border. The boundaries at its two extremities, Pangong Lake and Karakoram Pass, were well-defined, but the Aksai Chin area in between lay undefined.[7]
In 1865, British surveyor W H Johnson came to an agreement with the Maharaja of Kashmir, in whose service he was employed,[16] on a proposed "Johnson Line" which placed Aksai Chin in Kashmir.[17] China rejected the arrangement, and the British government also harboured doubts, so decided to take up the issue in an attempt to reach a settlement. However in 1892, before the issue had been resolved, China erected boundary markers at Karakoram Pass on the ancient caravan route between Xinjiang and Ladakh (which were disputed by the British Indian Government).[11][17]
Throughout most of the 19th century Great Britain and the expanding Russian Empire were jockeying for influence in Central Asia, and Britain decided to hand over Aksai Chin to Chinese administration as a buffer against Russian invasion. The newly-created border was known as the MacCartney-MacDonald Line, and both British-controlled India and China now began to show Aksai Chin as Chinese.[17] In 1911 the Xinhai Revolution resulted in power shifts in China, and by 1918 (in the wake of the Russian Bolshevik Revolution) the British no longer saw merit in China's continuing possession of the region. On British maps the border was redrawn as the original Johnson Line,[11] but despite this reversion the new border was left unmanned and undemarcated.[11][17] According to Neville Maxwell, the British had used as many as 11 different boundary lines in the region, as their claims shifted with the political situation[18] By the time of Indian independence in 1947, the Johnson Line had become India's official western boundary.[11] On July 1, 1954, Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru definitively stated the Indian position.[19] He claimed that Aksai Chin had been part of the Indian Ladakh region for centuries, and that the border (as defined by the Johnson Line) was non-negotiable.[7] According to George N. Patterson, when the Indian government finally produced a report detailing the alleged proof of India's claims to the disputed area, "the quality of the Indian evidence was very poor, including some very dubious sources indeed".[20][21]
At the time, Chinese officials issued no condemnation of Nehru's claims or made any opposition to Nehru's open declarations of control over Aksai Chin. In 1956, Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai stated that he had no claims over Indian controlled territory.[8] He later argued that Aksai Chin was already under Chinese jurisdiction, implying that there was therefore no contradiction with his earlier statement since China did not regard the region as "Indian controlled", and that since the British hand-over China had regarded the McCartney MacDonald Line as the relevant border.[7] Zhou later argued that as the boundary was undemarcated and had never been defined by treaty between any Chinese or Indian government, the Indian government could not unilaterally define Aksai Chin's borders.[18]
During the 1950s, China constructed a road through Aksai Chin, connecting Xinjiang and Tibet, which ran south of the Johnson Line in many places.[17][11][22] Aksai Chin was easily accessible to the Chinese, but access from India, which meant negotiating the Karakoram mountains, was more problematic.[7] Consequently India did not even learn of the existence of the road until 1957 — finally confirmed when the road was shown in Chinese maps published the following year.[3]
The McMahon Line
In 1826 India and China gained a common border, including the area of what is now called Myanmar, following British annexations in the Anglo-Burmese Wars. In 1913, representatives of Great Britain, China and Tibet attended a conference in Simla regarding the borders between Tibet, China and India. Whilst all three representatives initialed the agreement, Beijing later objected to the proposed boundary between the regions of Outer Tibet and Inner Tibet and did not ratify it. The details of the Indo-Tibetan boundary was not revealed to China at the time.[11] The foreign secretary of the Indian government, Henry McMahon, who drew up the proposal, decided to bypass the Chinese (although instructed not to by his superiors) and settle the border bilaterally by negotiating directly with Tibet.[23] According to later Indian claims, this border was intended to run through the highest ridges of the Himalayas, as the areas south of the Himalayas were traditionally Indian.[24] However, the McMahon Line lay south of the boundary India claims.[7] India's government held the view that the Himalayas were the ancient boundaries of the Indian subcontinent, and thus should be the modern boundaries of India[24] while it is the position of the Chinese government that the disputed area in the Himalayas have been geographically and culturally part of Tibet since ancient times[25]
Months after the Simla agreement, China set up boundary markers south of the McMahon Line. T O'Callaghan, an official in the Eastern Sector of the North East Frontier, relocated all these markers to a location slightly south of the McMahon Line, and then visited Rima to confirm with Tibetan officials that there was no Chinese influence in the area.[11] The British-run Government of India initially rejected the Simla Agreement as incompatible with the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907, which stipulated that neither party was to negotiate with Tibet "except through the intermediary of the Chinese government".[26] The British and Russians cancelled the 1907 agreement by joint consent in 1921.[27] It was not until the late 1930s that the British started to use the McMahon Line on official maps of the region.
China took the position that the Tibetan government should not have been allowed to make a such a treaty, rejecting Tibet's claims of independent rule.[7] For its part, Tibet did not object to any section of the McMahon Line excepting the demarcation of the trading town of Tawang, which the Line placed under British-Indian jurisdiction.[23] However, up until World War II, Tibetan officials were allowed to administer Tawang with complete authority. Due to the increased threat of Japanese and Chinese expansion during this period, British Indian troops secured the town as part of the defense of India's eastern border.[11]
In the 1950s India began actively patrolling the region. It found that, at multiple locations, the highest ridges actually fell north of the McMahon Line.[7] Given India's historic position that the original intent of the Line was to separate the two nations by the highest mountains in the world, in these locations India extended its forward posts northward to the ridges, regarding this move as compliant with the original border proposal, although the Simla Convention did not explicitly state this intention.[7]
Indian military historian V.K. Singh argues that the basis of these boundaries, accepted by British India and Tibet, were that the historical boundaries of India were the Himalayas and the areas south of the Himalayas were traditionally Indian and associated with India. China also cited "traditional boundaries" as justification for its claims on areas south of the McMahon Line (then part of the North East Frontier Agency). However, according to Singh, these claims were unsupported by anyone other than China.[24] Both sides allege that the other's claims are founded on former imperial demarcations.[24][28] The Chinese government regards Indian territorial claims as a continuation of imperialistic claims made by British India.[28] Singh notes that India does not claim all areas which were previously under Indian Imperial Rule, such as those lands conquered by the Mauryans or Cholas.[24]
Events leading up to war
Tibet controversy
The 1940s saw huge change in South Asia with the creation of India and the separate Islamic Republic of Pakistan in 1947, and the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949. One of the most basic policies for the new Indian government was that of maintaining cordial relations with China, reviving its ancient friendly ties. India was among the first nations to grant diplomatic recognition to the newly-created PRC.[8]
However, within a short time the PRC announced its intention to reclaim Tibet from the British, and later extended its influence by placing border posts within the Indian-claimed territory of Aksai Chin.[17] India protested against these moves and decided to look for a diplomatic solution to ensure a stable Sino-Indian border.[17][8] To resolve any doubts about the Indian position, Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru declared in parliament that India regarded the McMahon Line as its official border.[8] The Chinese expressed no concern at this statement,[17][8] and in 1951 and 52, the government of China asserted that there were no frontier issues to be taken up with India.[8]
In 1954, Prime Minister Nehru wrote a memo calling for India's borders to be clearly defined and demarcated:[19] in line with previous Indian philosophy, Indian maps showed a border that, in some places, lay north of the McMahon Line.[29] Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai, in November 1956, again repeated Chinese assurances that the People's Republic had no claims on Indian territory, although official Chinese maps showed 120,000 square kilometres of territory claimed by India as Chinese.[8] CIA documents created at the time revealed that Nehru had ignored Burmese premier Ba Swe when he warned Nehru to be cautious when dealing with Zhou.[30] They also allege that Zhou purposefully told Nehru that there were no border issues with India.[30]
In 1950 the Chinese People's Liberation Army invaded Tibet and defeated the Tibetan Army, and the following year an agreement was ratified in Lhasa affirming China's sovereignty over Tibet.[23][31] Four years later, in 1954, China and India negotiated the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence by which the two nations agreed to abide in settling their disputes. India presented a frontier map which was accepted by China, and the Indian government under Prime Minister Nehru promoted the slogan Hindi-Chini bhai-bhai (Indians and Chinese are brothers). According to Harvard political analyst John W Garver, Nehru's policy on Tibet was to create a strong Sino-Indian partnership which would be catalyzed through agreement and compromise on Tibet. Garver believes that Nehru's previous actions had given him confidence that China would be ready to form an "Asian Axis" with India.[3]
This apparent progress in relations suffered a major setback when, in 1959, Nehru accommodated the Tibetan religious leader, the Dalai Lama, who was fleeing Lhasa after a failed Tibetan uprising against Chinese rule. This was an act which, in China's eyes, eclipsed any former friendly gestures. Although Nehru's motives were humanitarian, from China's perspective India was interfering in its internal affairs and looking to gain influence in Tibet. The Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, Mao Zedong, was humiliated and asked the Xinhua News Agency to produce reports on Indian expansionists operating in Tibet. He further made it clear that the news should be anti-Nehru. Tensions continued to rise as Mao implied that the Lhasa uprising had been caused by Indians, and on 6 May 1959, Mao published "The Revolution in Tibet and Nehru's Philosophy", where he accused Nehru of openly encouraging Tibetan rebels.
Border incidents continued though this period. In August 1959, the Chinese army took an Indian prisoner at Longju, which had an ambiguous position in the McMahon Line,[29][32][11][17] and two months later in Aksai Chin a clash led to the death of nine Indian frontier policemen.[17]
On October 2, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev defended Nehru in a meeting with Mao. This action reinforced China's impression that the Soviet Union, the United States and India all had expansionist designs over China. The PLA went so far as to prepare a self-defensive counterattack plan.[3] However, Mao decided against further escalation because he feared the intervention of the United States.[33] Negotiations were restarted between the nations, but no progress was made.[19][34]
As a consequence of their non-recognition of the McMahon Line (see above), China's maps showed both the North East Frontier Area (NEFA) and Aksai Chin to be Chinese territory.[24] In 1960, Zhou Enlai unofficially suggested that India drop its claims to Aksai Chin in return for a Chinese withdrawal of claims over NEFA. Adhering to his stated position, Nehru believed that China did not have a legitimate claim over either of these territories, and thus was not ready to concede them. This adamance was perceived in China as Indian opposition to Chinese rule in Tibet.[3] Nehru declined to conduct any negotiations on the boundary until Chinese troops withdrew from Aksai Chin; a position supported by the international community.[23] India produced numerous reports on the negotiations, and translated Chinese reports into English to help inform the international debate. China believed that India was simply securing its claim lines in order to continue its "grand plans in Tibet".[3] India's adamance that China withdraw from Aksai Chin caused continual deterioration of the diplomatic situation to the point at which internal forces were pressurizing Nehru to take a military stance against China.[35]
At the beginning of 1961, Nehru appointed General B M Kaul as army Chief of General Staff,[22] but he refused to increase military spending and prepare for a possible war.[22] That summer China's continuing patrols south of the McMahon Line provoked an Indian response known as the "Forward Policy".[11] The aim of this policy was to create outposts behind advancing Chinese troops to interdict their supplies, forcing their return to China.[11][36][32][8] There were eventually 60 such outposts, including 43 north of the McMahon Line.[19][11] China viewed this as further confirmation of Indian expansionist plans directed towards Tibet. According to the Indian official history, implementation of the Forward Policy was intended to provide evidence of Indian occupation in the previously unoccupied region through which Chinese troops had been patrolling. Kaul was confident, through contact with Indian Intelligence and CIA information, that China would not react with force.[23] Indeed at first the PLA simply withdrew, but eventually Chinese forces began to counter-encircle the Indian positions. This led to a tit-for-tat Indian reaction, with both forces attempting to outmanoeuver each other. However, despite the escalating nature of the dispute, the two forces withheld from engaging each other directly.[3]
By January 1962, Mao had lost much of his influence in China, and Chinese President Liu Shaoqi felt able to lead a public condemnation of Mao's disastrous Great Leap Forward[33] Jung Chang writes that China was prepared for war by May to June after the border clashes, albeit that Chinese attention was also diverted at times by the nationalists in Formosa (Taiwan).[33] Other authors including Roderik McFarquhar also state that the most immediate threat to China was from Taiwan.
Chinese studies as recently as the 1990s still support the position that India was planning aggression in Tibet. Most Chinese scholars agree that the root cause of the conflict was India's plan to seize Tibet and turn it into a protectorate or colony of India, to create a "Great Indian Empire". Zhao Weiwen, of the Chinese Ministry of State and Security, places emphasis on Nehru's "dark mentality".[3] China's assumptions about Indian attitudes towards Tibet, whilst perhaps understandable from the Chinese perspective, are believed by most neutral observers to be fundamentally incorrect and a major contributory factor to the conflict. During the buildup to the war the Indian government largely maintained a policy of non-violent reaction and sought Indo-Chinese friendship, even to the point of failing to prepare for military action when its military leaders were recommending such precautions.[11]
Early incidents
Various border conflicts and "military incidents" between India and China flared up throughout the summer and fall of 1962. In May, the Indian Air Force was told not to ready itself for war, although it was assessed as being a feasible way to repel the unbalanced ratio of Chinese to Indian troops.[37] In June, a skirmish caused the deaths of dozens of Chinese troops. The Indian Intelligence Bureau received information about a Chinese buildup along the border which could be a precursor to war.[37]
During the period of June–July 1962, the Indian military planners began advocating "probing actions" against the Chinese, and accordingly, moved mountain troops forward to cut off Chinese supply lines. According to Patterson, the Indian motives were threefold:
- Test Chinese resolve and intentions regarding India.
- Test whether India would enjoy Soviet backing in the event of a Sino-Indian war.
- Create sympathy for India within the US, with whom relations had deteriorated after the Indian annexation of Goa.[20][38]
On July 10, 1962, 350 Chinese troops surrounded an Indian post in Chushul but withdrew after a heated argument via loudspeaker.[14] On July 22, the Forward Policy was extended to allow Indian troops to push back Chinese troops already established in disputed territory.[8] Whereas Indian troops were previously ordered to fire only in self-defense, all post commanders were now given discretion to open fire upon Chinese forces if threatened.[8] In August, the Chinese military improved its combat readiness along the McMahon Line and begun stockpiling ammunition, weapons and gasoline.[11]
Confrontation at Thag La
In June 1962, Indian forces established an outpost at Dhola, on the southern slopes of the Thag La Ridge.[11] Dhola lay north of the McMahon Line but south of the ridges India maintains the McMahon Line was supposed to represent.[29][23][39] In August, China issued diplomatic protests and began occupying positions at the top of Thag La.[3][11] On September 8, a 60-strong PLA unit descended to the south side of the ridge and occupied positions that dominated one of the Indian posts at Dhola. Fire was not exchanged but Nehru said to the media that the Indian Army had instructions to "free our territory" and the troops had been given discretion to use force.[3] On September 11, it was decided that "all forward posts and patrols were given permission to fire on any armed Chinese who entered Indian territory".[8]
However, the operation to retake Thagla was flawed in that Nehru's directives were unclear and it got underway very slowly because of this.[23][11] In addition to this, each man had to carry 35 kg of luggage over the long trek and this severely slowed down the reaction.[40] By the time the Indian battalion reached the point of conflict, Chinese units controlled both banks of the Namka Chu River.[11] The Indian official history states that the Indian troops were given the discretion to fire if a conflict developed between the two sides.[8] On September 20, Chinese troops threw grenades at Indian troops and a firefight developed, triggering a long series of skirmishes for the rest of September.[11][40]
Some Indian troops, including Brigadier Dalvi who commanded the forces at Thag La, were also concerned that the territory they were fighting for was not strictly territory that "we should have been convinced was ours".[32] According to Neville Maxwell, even members of the Indian defence ministry were categorically concerned with the validity of the fighting in Thag La.[7]
On 3 October, a week before the triggering of the war, Zhou Enlai visited Nehru in New Delhi promising there would be no war. On October 4, Kaul assigned some troops with securing regions south of the Thagla Ridge.[11] Kaul decided to first secure Yumtso La, a strategically important position, before re-entering the lost Dhola post.[8] Kaul had then realised that the attack would be desperate and the Indian government tried to stop escalation into an all-out war. Indian troops travelling to Thagla had suffered in the previously unexperienced conditions, two Gurkha troops died of pulmonary edema.[40]
On October 10, an Indian Punjabi patrol of 50 troops to Yumtso La were met by an emplaced Chinese position of some 1000 soldiers.[11] Indian troops were in no position for battle, as Yumtso La was 16,000 feet (4,900 m) above sea level and Kaul did not plan on having artillery support for the troops.[40] The Chinese troops opened fire on the Indians under their belief that they were north of the McMahon Line. The Indians were surrounded by Chinese positions which used mortar fire. However, they managed to hold off the first Chinese assault, inflicting heavy casualties.[11]
At this point, the Indian troops were in a position to push the Chinese back with mortar and machine gun fire. However, Brigadier Dalvi opted not to fire, as it would mean decimating the Rajput who were still in the area of the Chinese regrouping. They helplessly watched the Chinese ready themselves for a second assault.[40] In the second Chinese assault, the Indians began their retreat, realising the situation was hopeless. The Indian patrol suffered 25 casualties, with the Chinese suffering 33. The Chinese troops held their fire as the Indians retreated, and then buried the Indian dead with military honors, as witnessed by the retreating soldiers. This was the first occurrence of heavy fighting in the war.[11]
This attack had grave implications for India and Nehru tried to solve the issue, but by 18 October it was clear that the Chinese were preparing for an attack on India, with massive troop buildups on the border.[11] A long line of mules and porters had also been observed supporting the buildup and reinforcement of positions south of the Thagla ridge.[40]
Preparations for war
Motives
Two of the major factors leading up to China's eventual conflicts with Indian troops were India's stance on the disputed borders and perceived Indian subversion in Tibet. There was "a perceived need to punish and end perceived Indian efforts to undermine Chinese control of Tibet, Indian efforts which were perceived as having the objective of restoring the pre-1949 status quo ante of Tibet" The other was "a perceived need to punish and end perceived Indian aggression against Chinese territory along the border. John W. Garver argues that the first perception was incorrect based on the state of the Indian military and polity in the 1960s, it was, nevertheless a major reason for China's going to war. However, he argues the Chinese perception of aggression to be "substantially accurate".[3]
The CIA's recently declassified POLO documents reveal contemporary American analysis of Chinese motives during the war. According to this document, "Chinese apparently were motivated to attack by one primary consideration--their determination to retain the ground on which PLA forces stood in 1962 and to punish the Indians for trying to take that ground".[30]
Another factor which affected China's decision for war with India was a perceived need to stop a Soviet-US-India encirclement and isolation of China.[3] India's relations with the Soviet Union and United States were both strong at this time, but the Soviets were preoccupied by the Cuban Missile Crisis and would not interfere with the Sino-Indian War.[11] P.B. Sinha suggests that China timed the war exactly in parallel with American actions so as to avoid any chance of American or Soviet involvement. American buildup of forces around Cuba occurred on the same day as the first major clash at Dhola while China's buildup between the 10th and 20th of October coincided exactly with the United States establishment of a blockade against Cuba which began on the 20th of October.[8]
Garver argues that the Chinese correctly assessed Indian border policies, particularly the Forward Policy, as attempts for incremental seizure of Chinese-controlled territory. On Tibet, Garver argues that one of the major factors leading to China's decision for war with India was a common tendency of humans "to attribute others behavior to interior motivations, while attributing their own behavior to situational factors.". Studies from China published in the 1990s confirmed that the root cause for China going to war with India was the perceived aggression in Tibet, with the forward policy simply catalyzing the aggressive Chinese reaction.[3]
Neville Maxwell and Allen Whiting argue that the Chinese leadership believed they were defending territory they believed to be legitimately Chinese, and which was already under de facto Chinese occupation prior to Indian advances, and regarded the Forward Policy as an Indian attempt at creeping annexation.[3] Mao Zedong himself compared the Forward Policy to a strategic advance in Chinese chess:
Their [India's] continually pushing forward is like crossing the Chu Han boundary. What should we do? We can also set out a few pawns, on our side of the river. If they don't then cross over, that’s great. If they do cross, we'll eat them up [chess metaphor meaning to take the opponent's pieces]. Of course, we cannot blindly eat them. Lack of forbearance in small matters upsets great plans. We must pay attention to the situation.[3]
The motive for the Forward Policy was to cut off the supply routes for Chinese troops posted in NEFA and Aksai Chin.[11] According to the official Indian history, the forward policy was continued because of its initial success, as Chinese troops withdrew when they encountered areas already occupied by Indian troops. The Forward Policy was having success in cutting out supply lines of Chinese troops who had advanced South of the McMahon Line. However, the Forward Policy rested on the assumption that Chinese forces "were not likely to use force against any of our posts, even if they were in a position to do so." No serious reappraisal of this policy took place even when Chinese forces ceased withdrawing.[8]
By early 1962, the Chinese leadership began to fear that India's intentions were to launch a massive attack against Chinese troops, and that the Indian leadership wanted a war.[11][3] In 1961, the Indian army had been sent into Goa, a small region without any other international borders apart from the Indian one, after Portugal refused to surrender the exclave colony to the Indian Union. Although this action met little to no international protest or opposition, China saw it as an example of India's expansionist nature, especially in light of heated rhetoric from Indian politicians. India's Home Minister declared, "If the Chinese will not vacate the areas occupied by it, India will have to repeat what she did in Goa. India will certainly drive out the Chinese forces",[11] while another member of the Indian Congress Party pronounced, "India will take steps to end [Chinese] aggression on Indian soil just as she ended Portuguese aggression in Goa".[20] By mid-1962, it was apparent to the Chinese leadership that negotiations had failed to make any progress, and the Forward Policy was increasingly perceived as a grave threat as Delhi increasingly sent probes deeper into border areas and cut off Chinese supply lines.[20] Foreign Minister Marshal Chen Yi commented at one high-level meeting, "Nehru's forward policy is a knife. He wants to put it in our heart. We cannot close our eyes and await death."[3] The Chinese leadership believed that their restraint on the issue was being perceived by India as weakness, leading to continued provocations, and that a major counterblow was needed to stop perceived Indian aggression[3]
Xu Yan, prominent Chinese military historian and professor at the PLA's National Defense University, gives an account of the Chinese leadership's decision to go to war. By late September 1962, the Chinese leadership had begun to reconsider their policy of "armed coexistence", which had failed to address their concerns with the forward policy and Tibet, and consider a large, decisive strike.[3]
Military planning
The Indian side was confident war would not be triggered and made little preparations. India had only two divisions of troops in the region of the conflict.[41] In August 1962, Brigadier D.K. Palit claimed that a war with China in the near future could be ruled out.[41] Even in September 1962, when Indian troops were ordered to "expel the Chinese" from Thag La, Maj. General J.S. Dhillon expressed the opinion that "“experience in Ladakh had shown that a few rounds fired at the Chinese would cause them to run away."[3][8] Because of this, the Indian army was completely unprepared when the attack at Yumtso La occurred.[41][11]
Recently declassified CIA documents which were compiled at the time reveal that India's estimates of Chinese capabilities made them neglect their military in favour of economic growth.[42] It is claimed that if a more military-minded man had been in place instead of Nehru, India would have been more likely to have been ready for the threat from China.[42]
On October 6, 1962, the Chinese leadership convened. Lin Biao reported that PLA intelligence units had determined that Indian units might assault Chinese positions at Thag La on October 10 (Operation Leghorn). The Chinese leadership and the Central Military Council decided upon war to launch a large-scale attack to punish perceived military aggression from India.[3] In Beijing, a larger meeting of Chinese military was convened in order to plan for the coming conflict[3]
The Mao and the Chinese leadership issued a directive laying out the objectives for the war. A main assault would be launched in the eastern sector, which would be coordinated with a smaller assault in the western sector. All Indian troops within China's claimed territories in the eastern sector would be expelled, and the war would be ended with a unilateral Chinese ceasefire and withdrawal to prewar positions, followed by a return to the negotiating table.[3]
Diplomatically, Mao acknowledged possible diplomatic isolation as the Soviet Union, the United States, the Republic of China and other "misinformed countries" would oppose China's actions. India led the Non-Aligned Movement, Nehru enjoyed international prestige, and China, with a larger military would be portrayed as an aggressor. However, he said that a well-fought war "will guarantee at least thirty years of peace" with India, and determined the benefits to offset the costs[3]
On October 8, additional veteran and high-quality divisions were ordered to prepare to move into Tibet from the Chengdu and Lanzhou military regions.[3]
Marshal Liu Bocheng headed a group to determine the strategy for the war. He concluded that the opposing Indian troops were among India's best, and to achieve victory would require deploying crack troops and relying on force concentration to achieve decisive victory. On October 16th, this war plan was approved, and on the 18th, the final approval was given by the Politburo for a "self defensive counter-attack", scheduled for October 20.[3]
Chinese offensive
On October 20, 1962, the Chinese People's Liberation Army launched two attacks, 1000 kilometers apart. In the western theater, the PLA sought to expel Indian forces from the Chip Chap valley in Aksai Chin while in the eastern theater, the PLA sought to capture both banks of the Namka Chu river. Some skirmishes also took place at the Nathula Pass, which is in Sikkim, a protectorate of India at that time. Gurkha rifles travelling north were targeted by Chinese artillery fire. After four days of fierce fighting, the three regiments of Chinese troops succeeded in securing a substantial portion of the disputed territory.[11]
Eastern theatre

Chinese troops launched an attack on the southern banks of the Namka Chu River on October 20.[40] The Indian forces were undermanned, with only an understrength battalion to support them, while the Chinese troops had three regiments positioned on the north side of the river.[40] The Indians expected Chinese forces to cross via one of five bridges over the river and defended those crossings.[11] However their strategy was wrong. As the Indian troops settled for the night on the banks of the river, the PLA crossed over the shallow October river and made their way to the other side. They gathered themselves up into battalions on the Indian-held south side of the river in the camouflage of the night, with each battalion assigned against a separate group of Rajputs.[40]
At 5:14 am, Chinese mortar fire began attacking the Indian positions. Simultaneously, the Chinese cut the Indian telephone lines so that the Indians could not make contact with CHQ. At about 6:30 am, the Chinese infantry, who had been positioned behind the Indians in the night, made their surprise attack and forced the Indians to leave their trench positions. [40]
The Chinese troops overwhelmed the Indians. Proceeding attacks from flanking positions south of the McMahon Line overwhelmed the Indian troops and caused withdrawal from Namka Chu.[40] Fearful of continued losses, Indian troops escaped into Bhutan. However, Chinese forces respected the border and ignored Tsang Le.[11] Now the Chinese troops had occupied the area which was under dispute in the confrontations at Thag La, but they continued to advance into the rest of NEFA.[40]
On October 22, at 12:15 am, the PLA launched a mortar attack on Walong, on the McMahon line.[43] 400 troops proceeded to launch fire on the Indians posted there. Lights fired by Indian troops on October 23 showed the presence of numerous Chinese milling around the valley.[43] The Indians tried to use their mortars against the Chinese but the PLA then lighted a bushfire to create great confusion amongst the enemy troops.[43]
On October 23, Chinese troops launched a three-pronged attack on Tawang, which the Indians evacuated without any resistance.[11]
Western theatre

On the Aksai Chin front, China already controlled most of the disputed territory. China quickly and efficiently got rid of remnants of Indian troops.[44] On October 20, operations in the Chip Chap Valley, Galwan Valley, and Pangong Lake were successful for the PLA. Many outposts and garrisons comprised were unable to defend against the surrounding Chinese troops. Most Indian troops positioned in these posts fought and were either killed or taken prisoner. India did not support its troops, as the Galwan post had been surrounded by China in August and had received no land support from India since then. After the October 20 attack, this post was not heard from again.[11]
Late on October 19, Chinese troops launched various attacks throughout the western theatre.[14] By October 22, all posts north of Chushul had been cleared .[14]
Later on October 24, there was a battle on the Rezang La Ridge to defend an air strip from impending Chinese takeover.[45]
After realizing the magnitude of the attack, Indian Western Command withdrew many of the isolated outposts to the south-east. Daulet Beg Oldi was also evacuated, but it was south of the Chinese claim line and was not approached by Chinese forces. Indian troops were withdrawn so that they could regroup and be ready if China probed south of their claim line.[11]
Indian forces were hampered by their significant inferiority in numbers and lack of combat readiness. The Indian deployment was sparsely put and needed new commanders in the second phase of the war.
Lull in the fighting
By October 24th, the PLA had entered territory previously administered by India to give the PRC a diplomatically strong position over India. The majority of Chinese forces had advanced sixteen kilometres south of the border. Four days of fighting were followed by a three-week lull. Zhou ordered the troops to stop advancing as he attempted to negotiate with Nehru. The Indian forces had retreated into more heavily fortified positions around Se La and Bombdi La which would be difficult to assault.[11] Zhou sent Nehru a letter, proposing
- A negotiated settlement of the boundary
- That both sides disengage and withdraw twenty kilometers from present lines of actual control
- A Chinese withdrawal north in NEFA
- That China and India not cross lines of present control in Aksai Chin.[11]
Nehru's October 27 reply expressed interest in the restoration of peace and friendly relations and suggested a return to the "boundary prior to 8 September 1962". He was categorically concerned about a mutual twenty kilometer withdrawal after "40 or 60 kilometers of blatant military aggression". He wanted the creation of a larger immediate buffer zone and thus resist the possibility of a repeat offensive. Zhou's November 4th reply repeated his 1959 offer to return to the McMahon Line in NEFA and the Chinese traditionally claimed MacDonald Line in Aksai Chin. Facing Chinese forces maintaining themselves on Indian soil and trying to avoid political pressure, the Indian parliament announced a national emergency and passed a resolution which stated their intent to "drive out the aggressors from the sacred soil of India". The United States and the United Kingdom supported India's response, however the Soviet Union was preoccupied with the Cuban Missile Crisis and did not offer the support it had provided in previous years. With the backing of other great powers, a November 14 letter by Nehru to Zhou once again rejected his proposal.[11]
Neither side declared war, used their air force, or fully broke off diplomatic relations; however, the conflict is commonly referred to as a war. This war coincided with the Cuban Missile Crisis and was viewed by the western nations at the time as another act of aggression by the Communist bloc.[46][11] According to Calvin, the Chinese side evidently wanted a diplomatic resolution and discontinuation of the conflict.[11]
Continuation of war
After Zhou received Nehru's letter, the war restarted. The fighting resumed on the eastern theater on November 14th (Nehru's birthday), with an Indian attack on Walong, claimed by China, launched from the defensive position of Se La. The Indians were stopped 50 meters away from the crest and were comprehensively defeated by the Chinese counteroffensive. The Chinese resumed military activity on Aksai Chin and NEFA hours after the Walong battle.[11]
Eastern theatre
On the eastern theatre, the PLA attacked Indian forces near Se La and Bomdi La on November 17th. These positions were defended by the Indian 4th Division. Instead of attacking by road as expected, PLA forces approached via a mountain trail, and their attack cut off a main road and isolated 10,000 Indian troops. Following a battle, the Indians were ordered to begin a retreat to regroup. However, the orderly Indian retreat was cut down into chaos and none of the Indians were seen until three weeks later.[11]
Se La was very high, and faced with this strategic problem, the Chinese captured Thembang, which was a supply route to Se La. The PLA forces proceeded to ambush the comanderless 4th Division and added another comprehensive victory to their tally.[11]
Western theatre
On the western theatre, PLA forces launched a heavy infantry attack on November 18 near Chushul. Their attack started at 4:35 am, despite a mist surrounding most of the areas in the region. At 5:45 the Chinese troops advanced to attack 2 platoons of Indian troops at Gurung Hill.
The Indians did not know what was happening, as communications were dead. As a patrol was sent, China attacked with greater numbers. Indian artillery, shells and MMGs could not hold off against a large Chinese wave. By 9:00 am, Chinese forces attacked Gurung Hill directly and Indian commanders withdrew from the area.[14]
The Chinese had been simultaneously attacking Rezang La. Rezang La was held by 118 Indian troops. At 5:05 am, Chinese troops launched their attack audaciously. Chinese Medium machine gun fire pierced through the Indian tactical defences.[14]
At 6:55 am the sun rose and the Chinese attack on the 8th platoon began in waves. Fighting continued for the next hour, until the Chinese signalled that they had destroyed the 7th platoon. Indians tried to use light machine guns on the medium machine guns from the Chinese but after 10 minutes the battle was over.[14] Logistical inadequacy once again hurt the Indian troops[47] The Chinese gave the Indian troops a respectful military funeral.[47] The battles also saw the death of Major Shaitan Singh of the Kumaon Regiment, who had been instrumental in victory in the first battle of Rezang La.[47]. Kumaoni stand at the Rezang La showed the unintimidated resilience of India against invading China.
With many casualties inflicted, the Indian troops withdrew to high mountain positions. Indian sources believed that their troops were just coming to grips with the mountain combat and finally let go of their pride and called for more troops. However, the Chinese declared a ceasefire, ending the bloodshed.[14]
Both sides suffered heavy casualties, with dead Indian troops bodies being found in the ice, frozen with weapons in hand. This signalled the end of the war in Aksai Chin as China had reached their claim line - many Indian troops were ordered to withdraw from the area China claimed but the Indian troops wanted to fight on until the bitter end. However, the war ended with their withdrawal, so as to limit the amount of casualties.[11]
United States intervention
The PLA penetrated close to the outskirts of Tezpur, Assam, a major frontier town nearly fifty kilometers from the Assam-North-East Frontier Agency border. [7] The local government ordered the evacuation of the civilians in Tezpur to the south of the Brahmaputra River, all prisons were thrown open, and government officials who stayed behind destroyed Tezpur's currency reserves in anticipation of a Chinese advance.[8]
On the evening of November 20, Nehru, seeing the disintegration of his own armies, made an appeal to the United States, for armed aid, including airstrikes, if Chinese forces continued to advance, and air cover, in case of raids by the Chinese air force. With the Chinese outnumbering every Indian division and faced with the idea of bombing on Indian towns, the United States Navy ordered an aircraft carrier to the Bay of Bengal due to reach there in late November. [11]
Ceasefire
China had reached its claim lines so the PLA did not advance farther, and on November 19 it declared a unilateral cease-fire. Zhou Enlai declared a unilateral ceasefire to start on midnight, November 21. Zhou's ceasefire declaration stated,
Beginning from November 21, 1962, the Chinese frontier guards will cease fire along the entire Sino-Indian border. Beginning from December 1, 1962, the Chinese frontier guards will withdraw to positions 20 kilometers behind the line of actual control which existed between China and India on November 7, 1959. In the eastern sector, although the Chinese frontier guards have so far been fighting on Chinese territory north of the traditional customary line, they are prepared to withdraw from their present positions to the north of the illegal McMahon Line, and to withdraw twenty kilometers back from that line. In the middle and western sectors, the Chinese frontier guards will withdraw twenty kilometers from the line of actual control.
Zhou had first given the ceasefire announcement to Indian chargé d'affaires on November 19, (before India's request for United States air support) but New Delhi did not receive it until 24 hours later. The aircraft carrier was ordered back after the ceasefire and thus American intervention on India's side in the war was avoided. Retreating Indian troops, who hadn't come into contact with anyone knowing of the ceasefire, and Chinese troops in NEFA and Aksai Chin, were involved in some minor battles[11] but for the most part the ceasefire signalled an end to the fighting. The United States Air Force flew in supplies to India in November 1962, but neither side wished to continue hostilities.
Militarily, no organized Indian resistance was left in either disputed sector after the retreat of the 48 Brigade at 3 a.m. on November 20th.[11] The Chinese withdrew to the prewar Line of Actual Control and returned all the territory they had captured during the war, but kept disputed territories they had de facto control of prior to the war and had simply affirmed control of during the war by expelling the Indian forces.[48][23][19][11]. Of the disputed areas, China kept most of the Aksai Chin, which comprised 32% of the disputed territory and withdrew from the North East Frontier Agency, which comprised 68%.[11] According to V.K. Singh, China kept territory past their 1960 claim line.[24] However, both the Chinese government[49] and the Indian government[8] state that Chinese forces never advanced south past their claim line. According to the Institute of Peace and Conflict Studies, China since withdrew its claim from part of NEFA (Assam).[50][51]
Over the following months, vehicles, weapons, and prisoners of war were returned by China unconditionally as a show of goodwill.[11] According to Anna Louise Strong, a Marxist living in China during 1962, the return of heavy weapons were said to be due to logistical constraints of transporting them to China.[52] Returning the weapons to India for goodwill purposes was considered more desirable than destroying them or abandoning them to the natives.[52] China released 731 sick and wounded Indian soldiers in December 1962, and the remainder 3,213 soldiers, including one brigadier (Brig. Dalvi), 26 field officers and 29 officers of company grade, started arriving in India from April 1963 onwards.[52] The Indian forces did not take any Chinese prisoners. 26 died due to wounds in the PoW Camp, while another 15 were repatriated in December when the Chinese used them to return confiscated weapons.[23][52]
Toward the end of the war India increased her support for Tibetan refugees and revolutionaries, some of them having settled in India, as they were fighting the same common enemy in the region. The Nehru administration ordered the raising of an elite Indian-trained "Tibetan Armed Force" composed of Tibetan refugees.[53] The CIA had already begun operations in bringing about change in Tibet.[3]
World opinion
The Chinese military action has been viewed by the United States as part of the PRC's policy making of using aggressive wars to settle its border disputes and to distract from its internal issues.[54] According to James Calvin from the United States Marine Corps, western nations at the time viewed China as an aggressor during the China-India border war, and the war was part of a monolithic communist objective for a world dictatorship of the proletariat. This was further triggered by Mao Zedong's views that: "The way to world conquest lies through Havana, Accra, and Calcutta." Calvin believes that Chinese actions show a "pattern of conservative aims and limited objectives, rather than expansionism" and blames this particular conflict from India's provocations towards China. However, Calvin also expresses that China, in the past, has been adamant to gain control over regions to which it has a "traditional claim", which triggered the dispute over NEFA and Aksai Chin and indeed Tibet. He further suggests that China might ultimately try to regain control of everything that it considers as "traditionally Chinese" which in its view includes entire South East Asia.[11]
The Kennedy administration was disturbed by what they considered blatant Chinese communist aggression against India. In a May 1963 National Security Council meeting, contingency planning on the part of the United States in the event of another Chinese attack on India was discussed. Defense Secretary Robert McNamara and General Maxwell Taylor advised the president to use nuclear weapons should the Americans intervene in such a situation. Kennedy insisted that Washington defend India as it would any ally, saying, "We should defend India, and therefore we will defend India"[55] The Johnson Administration considered and then rejected giving nuclear weapons technology to the Indians.
The non-aligned nations, perhaps unsurprisingly, remained non-aligned, and only the United Arab Republic openly supported India[56] Of the non-aligned Six non-aligned nations, Egypt, Burma, Cambodia, Sri Lanka, Ghana and Indonesia, met in Colombo on 10 December 1962.[57] The proposals stipulated a Chinese withdrawal of 20 km from the customary lines without any reciprocal withdrawal on India's behalf.[57] The failure of these six nations to unequivocally condemn China deeply disappointed India.[56]
In 1972, Chinese Premier Zhou made an attempt to explain the Chinese point of view to President Nixon of the US. As for the causes of the war, Zhou asserted that China did not try and expel Indian troops from south of the McMahon line and that three open warning telegrams were sent to Nehru before the war. However, Indian patrols south of the McMahon line were expelled and suffered casualties in the Chinese attack.[58] Zhou also told Nixon that Chairman Mao ordered the troops to return to show good faith.[59] The Indian government maintains that the Chinese military could not advance further south due to logistical problems and the cut-off of resource supplies.
In 1972, Neville Maxwell an Australian journalist and historian, wrote a controversial book which was highly critical of Indian Government — titled "India's China War" — which was banned in India.[60] After reading the Maxwell book President Richard Nixon later adopted a more friendly attitude to Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai in relation to the war, which also related to China's economic rise.[61]
While Western nations did not view Chinese actions favourably because of this war,[11] Pakistan, which had had a turbulent relationship with India ever since the Indian partition, improved its relations with China after the war.[62] Prior to the war, Pakistan also shared a disputed boundary with China, and had proposed to India that the two countries adopt a common defense against "northern" enemies (ie China), which was rejected by India.[8] However, China and Pakistan took steps to peacefully negotiate their shared boundaries, beginning on October 13, 1962, and concluding in December of that year[7]. Pakistan also expressed fear that the huge amounts of western military aid directed to India would allow it to threaten Pakistan's security in future conflicts. Mohammed Ali, External Affairs Minister of Pakistan, declared that massive Western aid to India in the Sino-Indian dispute would be considered an unfriendly act towards Pakistan. As a result Pakistan made efforts to improve its relations with China. The following year, China and Pakistan peacefully settled disputes on their shared border, and negotiated the China-Pakistan Border Treaty in 1963, as well as trade, commercial, and barter treaties.[62] On 2 March 1963, Pakistan conceded its northern claim line in Pakistani-controlled Kashmir to China in favor of a more southerly boundary along the Karakoram Range.[57][7][62] The border treaty largely set the border along the MacCartney-Macdonald Line[19] Because of India's failure against China, Pakistan triggered the Second Kashmir War with India. However, it effectively ended in a stalemate as Calvin states that the Sino-Indian War had caused the previously passive government to take a stand on actively modernizing India's military.[11] China offered diplomatic support to Pakistan in this war but did not offer military support.[57] In January 1966, China condemned the Tashkent Agreement between India and Pakistan as a Soviet-US plot in the region.[57] In the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Pakistan expected China to provide military support, but it was left alone as India successfully helped the rebels in East Pakistan to found the new nation-state of Bangladesh.[63]
Aftermath
China
According to the PLA's official military history, the war achieved China's policy objectives of defeating the Indian forces and securing peaceful borders in the western sector, as China retained de facto control of the Aksai Chin. After the war, India abandoned the Forward Policy, and the de facto borders stabilized along the Line of Actual Control.
Published scholarship in China is still expected to explain and justify, not to criticize, the decisions of the Chinese Communist Party, at least on such sensitive matters as war.[3] Chinese publications on the war themselves do not mention specific dates or events and use generalized terms. The first book-length analysis of the war from China which was allowed to be sold was published in 1993.[3]
India
After India was swiftly defeated by China memorials were erected for the Indian troops who died in the war. Arguably, the main lesson India learned from the war was the need to strengthen its own defences. The country could no longer follow Nehru's trusting polemics of "Hindi-Chini bhai-bhai" and non-violent peace. Because of India's inability to sense danger, Prime Minister Nehru faced harsh accusations from government officials, as he was the one who had promoted good relations with China.[23] Indians in general became highly skeptical of China and its military. Many Indians view the war as a betrayal of India's attempts at establishing a long-standing peace with China. The war also put an end to Nehru's earlier hopes that India and China would form a strong Asian Axis to counteract the increasing influence of the Cold War superpowers.[3]
The unpreparedness of the army was blamed on Defense Minister Menon, who resigned his government post to allow for someone who might modernize India's military further. India's policy of weaponisation via indigenous sources and self-sufficiency was thus cemented. Sensing a weakened army, Pakistan, a close ally of China, initiated the Second Kashmir War with India in 1965, however this war was still indecisive and led to cease fire.[64] Two years later in 1967, there was a short border skirmish, dubbed "Chola Incident" by India, between PLA troops and Indian troops, which went more favourably for India.[65]
The Indian government commissioned an investigation, resulting in the classified Henderson-Brooks-Bhagat Report on the causes of the war and the reasons for failure. India's performance in high-altitude combat in 1962 led to an overhaul of the Indian Army in terms of doctrine, training, organization and equipment. By 1964, India's military manpower had doubled.[11]
Pakistan
The war was one of the main turning points in early Sino-Pak relations. With a common precieved enemy, China and Pakistan's economic and political relations gained such strength that they remain 'examplery' even today. Pakistan as a symbolic gesture ceded the disputed region of Askai Chin to China and both the countires commissioned the Karakoram Highway and supported Pakistan's claim over the disputed territory of Kashmir. China became an important source of Arms and Ammunition for Pakistan, espcially under sanctions from the West. Exploitations of the poor relationship between India and China has been a hallmark of Pakistan's foreign relations.
Later skirmishes
Indian media also declared a series of skirmishes after the 1962's war,but never been confirmed by Chinese or international media. One report is that: In late 1967, there were two skirmishes between Indian and Chinese forces in Sikkim. The first one was dubbed the "Nathu La incident", and the other the "Chola incident". Prior to these incidents had been the Naxalbari uprising in India by the Communist Naxalites and Maoists.[66]
Also Indian media declared on 11th September 1967, Chinese troops opened fire on Indian troops who were protecting an Engineering Company in Nathula. The conflict escalated over the next five days to an exchange of heavy artillery and mortar fire between the Indians and the Chinese. 62 Indian soldiers were killed as the Indians drove back the Chinese forces.[67][68][69][70][71] The extent of Chinese casualties in this incident is not known.
As Indian side's report,a similar incident occurred in 1984, when squads of Indian soldiers began actively patrolling the Sumdorong Chu Valley in Arunachal Pradesh in a move to industrialize the region.[29][72][73][74][75] The Indian team left the area before the winter.[29] In the winter of 1986, the Chinese deployed their troops to the Sumdorong Chu before the Indian team could arrive in the summer and built a helipad.[76]
However, after being quickly deployed to the valley, the Indian Army was successful in shocking the Chinese in Sumdorong Chu reported by some Indian Media.[77][78] Chinese troops were forced to move sideways along the Thag La ridge, away from the valley. The Army's strong response was regarded as the exorcism of the ghost of 1962.[79] By 1987, Beijing's tone becoming ominously similar to that in 1962 and this prompted many Western diplomats to predict war. For logistical and tactical considerations the Chinese focused on the September 7, 1993 “Peace and Tranquility along the LAC Agreement” with India.[79]
Diplomatic process
In 1993 and 1996, the two sides signed the Sino-Indian Bilateral Peace and Tranquility Accords, an agreement to maintain peace and tranquility along the Line of Actual Control (LoAC). Ten meetings of a Sino-Indian Joint Working Group (SIJWG) and five of an expert group have taken place to determine where the LoAC lies, but little progress has occurred. Recently, during the visit of Chinese Prime Minister to India, China recognised the territory of Sikkim and Assam[50] as belonging to India, while India during the visit of its PM, Atal Behari Vajpayee to China, recognized the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) as an autonomous part of China.[80][50][51]
India still has concerns over China's military modernisation. Additionally, China's military aid to Pakistan as well as its proliferation of nuclear technology is a matter of concern to the Indian public,[41] which fought another war with Pakistan in 1999.
In 2001, there were reports that India had actually taken two prisoners during the war, Yang Chen and Shih Liang. They were not released at the conclusion of the war. Instead, the two were imprisoned as spies for three years before being interned in a mental asylum in Ranchi, where they spent the next 38 years under a special prisoner status. After their case was reported on by local journalists, the Indian government took actions to release them. After the Chinese government investigated the case, it lobbied for the release of the two men. Both men, now well into their 60s, have since been reunited with their families in Sichuan.[81] The Government of India has since issued a clarification that the men were not PoWs.[82]
On July 6, 2006, the historic Silk Road passing through this territory was reopened. On November 20, 2006 Indian politicians from Arunachal Pradesh appealed to parliament to take a harder stance on the PRC following a military buildup on the border similar to that in 1962.[51] Since 2004, Chinese military forces have increased patrolling of the Chumar region, which is not even claimed by China. The process of peace is disconnected on both sides and China remains fairly unilateral in their thinking.[citation needed] Both sides have agreed to resolve the issues by peaceful means.
Notes
- ^ Calvin. War was never declared and thus the beginning of the conflict is a matter of dispute. According to James Barnard Calvin's Timeline, the first heavy fighting occurred on October 10. Calvin's chapter detailing the Border War also begins on October 10.
- ^ 6月,印度军队加快了武装入侵中国的速度,东段已越过“麦克马洪线”,进入西藏山南的扯冬地区。截至8月底,印军在中国境内建立了一百多个据点。
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad China's Decision for War with India in 1962 by John W. Garver
- ^ H.A.S.C. by United States. Congress. House Committee on Armed Services — 1999, p. 62
- ^ War at the Top of the World: The Struggle for Afghanistan, Kashmir, and Tibet by Eric S. Margolis, p. 234.
- ^ a b Though Calvin says that no official figures were released by the Chinese, two Chinese sources viz "The Red Walls Witness" 摘自《红墙见证录》,当代中国出版社尹家民 pub 2004 and 中印边疆自卫反击作战史 History of the Sino-India Border Self Defensive War PDF pub 1993, give estimates. The Red Walls book puts Chinese casualties at 1,460, while the other puts killed and wounded figure at 2,400.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Cite error: The named reference
Neville Maxwellwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t History of the Conflict with China, 1962. P.B. Sinha, A.A. Athale, with S.N. Prasad, chief editor, History Division, Ministry of Defence, Government of India, 1992.
- ^ However, there were reports in the media in 2001-03 that 2 Chinese PoWs were being interned at a Mental Hospital in Ranchi, India. These were subsequently repatriated, though the Indian Govt. denied that they were PoWs. However, Chinese media reports say that these two had been classified as Missing-presumed-Dead and declared martyrs in their home village in Sichuan province. Washington Times, World, 2003-07-27.
- ^ This tallies closely with the 1383+1696 which Calvin said were killed and missing. This determined the original Indian Army site for these details. Of these, 2420 were killed in NEFA.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be Calvin, James Barnard (1984). "The China-India Border War". Marine Corps Command and Staff College. Retrieved 2006-06-14.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Official GoI answer to a question raised in the Indian Parliament. However, the US Army says Indian wounded were 1047 and attributes it to Indian Defence Ministry's 1965 report, but this report also included a lower estimate of killed.
- ^ 6月,印度军队加快了武装入侵中国的速度,东段已越过“麦克马洪线”,进入西藏山南的扯冬地区。截至8月底,印军在中国境内建立了一百多个据点。
- ^ a b c d e f g h Battle of Chushul
- ^ The Sino-Indian Border Disputes, by Alfred P. Rubin, The International and Comparative Law Quarterly, Vol. 9, No. 1. (Jan., 1960), pp. 96–125.
- ^ "Obituary: Mr. W. H. Johnson". Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society and Monthly Record of Geography, New Monthly Series, Vol. 5, No. 5 (May, 1883) , pp. 291-293. Retrieved 2007-05-31.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Mohan Guruswamy, Mohan, "The Great India-China Game", Rediff, June 23, 2003.
- ^ a b China and India: The Un-Negotiated Dispute. Neville Maxwell. The China Quarterly, No. 43. (Jul. – Sep., 1970), pp. 47–80.
- ^ a b c d e f A.G. Noorani, "Fact of History", India's National Magazine, September 30, 2003.
- ^ a b c d George W. Patterson, Peking Versus Delhi, Frederick A. Praeger, Inc., 1963
- ^ Patterson, p. 275.
- ^ a b c Maxwell, Neville (2001). "Henderson Brooks Report: An Introduction". stratmag.com. Retrieved 2006-08-18.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j Maxwell, Neville, India's China War, New York, Pantheon, 1970.
- ^ a b c d e f g VK Singh resolving the boundary dispute
- ^ The Sino-Indian Boundary Dispute, Foreign Language Press of the People's Republic of China, 1961.
- ^ GUPTA, Karunakar, "The McMahon Line 1911–45: The British Legacy", The China Quarterly, No. 47. (Jul. – Sep., 1971), pp. 521–45.
- ^ Free Tibet Campaign, "Tibet Facts No.17: British Relations with Tibet".
- ^ a b "The Place of International Law in Chinese Strategy and Tactics: The Case of the Sino-Indian Boundary Dispute", by Arthur A. Stahnke. The Journal of Asian Studies. Vol. 30, No. 1, November 1970. pp. 95–119
- ^ a b c d e A.G. Noorani, "Perseverance in peace process", India's National Magazine, August 29, 2003.
- ^ a b c Chinese deception and Nehru's naivete led to 62 War Times of India
- ^ Maxwell, Neville (September 9, 2006). "Settlements and Disputes: China's Approach to Territorial Issues" (PDF). Economic and Political Weekly. 41 (36): 3876. Retrieved 2006-09-26.
- ^ a b c India's Forward Policy, Review author[s]: A. G. Noorani, The China Quarterly © 1970 School of Oriental and African Studies
- ^ a b c Chang, Jung and Jon Halliday, Mao: The Unknown Story (2006), pp. 568, 579.
- ^ "The Shade of the Big Banyan" Time, Dec. 14, 1959.
- ^ CIA papers blame India for war with China Yahoo! — India News
- ^ Gregory Clark, "Remembering a War — The 1962 India-China Conflict", Rediff
- ^ a b CIA Journals 1962 India-China War and Kargil 1999: Restrictions on Air Power by R. Sukumaran
- ^ Patterson, p. 279
- ^ JOSHI Manoj, "Line of Defense", Times of India, October 21, 2000
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Battle of Namka Chu
- ^ a b c d Swaminathan South Asia Analysis Group Lessons of 1962: A stock taking after 40 years.
- ^ a b China feared military coup in India during 60s DNA India
- ^ a b c The Battle of Walong
- ^ eg. Chip Chap Valley, Pangong
- ^ Men of Steel on Icy Heights Mohan Guruswamy Deccan Chronicle.
- ^ Goldman, Jerry (1997). "The Cuban Missile Crisis, October 18-29 1962". hpol.org. Retrieved 2006-08-18.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c YADAV, Atul, Injustice to the Ahir Martyrs of the 1962 War. The Tribune. 18 November 1999
- ^ Map of Aksai Chin The Hindu
- ^ "Foreign Relations, 1969–1976, Volume XVII", October 1971 – February 1972 (Declassified)
- ^ a b c Institute of Peace and Conflict Studies
- ^ a b c India soft on Arunachal Pradesh
- ^ a b c d Anna Louise Strong Marxists.org
- ^ Chushi Gangdruk "Chushi Gangdruk: History", ChushiGangdruk.Org
- ^ Abstract of "Fighting to Make a Point: Policy-Making by Aggressive War on the Chinese Borders" by Jr Pettis Roy C. — National War College
- ^ [1] — Taipei Times, [2] Indian American Center for Political Awareness
- ^ a b "India: A Year of Stability and Change". Ralph J. Retzlaff. Asian Survey, Vol. 3, No. 2, A Survey of Asia in 1962: Part II. (Feb., 1963), pp. 96–106.
- ^ a b c d e Rediff Indo-China timeline
- ^ "China", "Foreign Relations, 1969–1976, Volume XVII, p. 722", October 1971 – February 1972 (Declassified)
- ^ "China", "Foreign Relations, 1969–1976, Volume XVII, p. 723", October 1971 – February 1972 (Declassified)
- ^ McCarthyism's Indian rebirth
- ^ "China", “Foreign Relations, 1969–1976, Volume XVII, p. 721”, October 1971–February 1972 (Declassified)
- ^ a b c
Dobell, W. M. (1964). "Ramifications of the China-Pakistan Border Treaty". Pacific Affairs. 37 (3): 283–95.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|laysource=,|quotes=,|laysummary=, and|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ The Men Behind Yahya in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 by Stephen R. Shalom, professor of Political Science
- ^ Remembering a War by Swaran Singh — Rediff, October 28, 2002
- ^ The Chola Incident
- ^ Remembering Naxalbari Day
- ^ September 67 Sikkim action KIAs in India-China LoC
- ^ "Punjab". Tribune of India. 2004-09-08.
- ^ "Mahavir Chakra Brigadier Harbhajan Singh". All About Sikhs.
- ^ "IGNCA".
- ^ "Brigadier RS Yadav". War Heroes. Haryana online.
- ^ The Economist, May 23, 1987. The Sumdorong Chu valley "seemed to lie to the north of the McMahon line; but is south of the highest ridge in the area, and the McMahon line is meant to follow the highest points".
- ^ "Sino-Indian Border Dispute Reconsidered", Neville Maxwell, Economic & Political Weekly, Vol. 34, No. 15, April 10–6, 1999.
- ^ Gopal Ji Malaviya in "Indian and Chinese Foreign Policies in Perspective", edited by Surjit Man Singh, 1998, Radiant Publishers, N.Delhi.
- ^ The Militarization of Mother India, Ravi Rikhye, 1990, Chanakya Pub. N.Delhi.
- ^ India's Land of the Rising Sun Deccan Herald
- ^ India Today, 1999.
- ^ [3]"India Today Sundarji"
- ^ a b A former chief of the Indian Army Wester Command comments on the 1986 incident. BS Mallik, Deccan Herald.
- ^ BBC
- ^ Shaikh Azizur Rahman, "Two Chinese prisoners from '62 war repatriated", The Washington Times.
- ^ NIC, India.
Further reading
- CALVIN, James Barnard, The China-India Border War, 1988[1]
- Alastair Lamb, The China-India Border: The Origins of the Disputed Boundaries, 1964,[2]
- Neville Maxwell's India's China War[3]
- Gunnar Myrdal. Asian Drama; An Inquiry into the Poverty of Nations. New York: Random House, 1968
- History of the Conflict with China, 1962. P.B. Sinha, A.A. Athale, with S.N. Prasad, chief editor, History Division, Ministry of Defence, Government of India, 1992. — Official Indian history of the Sino-Indian War.
- 中印边疆自卫反击作战史/Zhong yin bianjiang ziwei fanji zuozhanshi (also spelt Zhong-Yin Bian Jie Zhi Zhan Li Shi Zhen Xiang (History of the Sino-India Border Self Defensive War), Beijing: Junshi kexue chubanshe, 1993. Also quoted written by Xu Yan and published by Tian Di Publishing Co.[4] — Official People's Liberation Army history of the Sino-Indian war.
- Allen S. Whiting. The Chinese Calculus of Deterrence: India and Indochina.
External links
Template:ChineseText Template:IndicText
- Sino-Indian War (1962)
- Remembering a War: The 1962 India-China Conflict — Rediff.com.
- Neville Maxwell: Henderson Brooks Report
- 1962 Sino-Indian War, Hindustan Times
- War in the Himalayas: 1962 Indo-Sino Conflict (includes official war history) from History Division, Ministry of Defence, Government of India
- Critical Asian Studies Article: Sino Indian War 1962
- India, China to speed up border dispute talks: 2005 Xinhuanet
- The Rediff Special/Claude Arpi
- 1962 War and Its Implications For Sino-India Relations
- History of Sino-India Border War Template:Cn icon
- Historical maps of the Sino-Indian border Template:Cn icon
- Conflict in Kashmir: Selected Internet Resources by the Library, University of California, Berkeley, USA; University of California, Berkeley Library Bibliographies and Web-Bibliographies list
- Frontier India India-China Section
- Why China is playing hardball in Arunachal by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, May 13, 2007
- China, India, and the fruits of Nehru's folly by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, June 6, 2007
- ^ Calvin, James Barnard (1984). "The China-India Border War". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 2006-06-14.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Lamb, Alastair (1964). The China-India Border: The Origins of the Disputed Boundaries. L. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Maxwell, Neville, India's China War, New York, Pantheon, 1970.
