Gum arabic: Difference between revisions
m →Ceramics: l.c., dash |
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 1 sources, flagging 0 as dead, and archiving 7 sources. (Peachy 2.0 (alpha 8)) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
==Production== |
==Production== |
||
[[Image:Acacia senegal Taub68.png|thumb|left|''[[Acacia senegal|Senegalia senegal]]'' from Paul Hermann Wilhelm Taubert's Leguminosae, in Engelmann (ed.): Natürliche Pflanzenfamilien. Vol. III, 3., 1891]] |
[[Image:Acacia senegal Taub68.png|thumb|left|''[[Acacia senegal|Senegalia senegal]]'' from Paul Hermann Wilhelm Taubert's Leguminosae, in Engelmann (ed.): Natürliche Pflanzenfamilien. Vol. III, 3., 1891]] |
||
[[Image:Acacia seyal Taub66.png|thumb|left|''[[Acacia seyal|Vachellia seyal]]'' from Paul Hermann Wilhelm Taubert's Leguminosae, in Engelmann (ed.): Natürliche Pflanzenfamilien. Vol. III, 3., 1891]] While acacia gum has been harvested in [[Arabia]], [[Sudan]], and [[West Asia]] since antiquity, sub-Saharan acacia gum has a long history as a prized export. The gum exported came from the band of [[acacia]] trees that once covered much of the [[Sahel]] region: the southern littoral of the [[Sahara Desert]] that runs from [[Atlantic Ocean|the Atlantic]] to the [[Red Sea]]. Today, the main populations of gum-producing ''Acacia'' species are harvested in [[Mauritania]], [[Senegal]], [[Mali]], [[Burkina Faso]], [[Niger]], [[Nigeria]], [[Chad]], [[Cameroon]], [[Sudan]], [[Eritrea]], [[Somalia]], [[Ethiopia]], [[Kenya]] and [[Tanzania]]. ''[[Acacia senegal]]'' is tapped for gum by cutting holes in the bark, from which a product called ''kordofan'' or Senegal gum is exuded. ''Seyal'' gum, from ''[[Acacia seyal]]'', the species more prevalent in [[East Africa]], is collected from naturally occurring exudations on the bark. Traditionally harvested by seminomadic desert pastoralists in the course of their [[transhumance]] cycle, acacia gum remains a main export of several African nations, including [[Agriculture in Mauritania|Mauritania]], [[Economy of Niger|Niger]], [[Economy of Chad|Chad]], and [[Economy of Sudan|Sudan]]. The hardened exudations are collected in the middle of the rainy season (harvesting usually begins in July), and exported at the start of the dry season (November). <!-- Retrieved 2008-07-10.</ref>--> Total world gum arabic exports are today (2008) estimated at 60,000 tonnes, having recovered from 1987–1989 and [[2004 locust outbreak|2003–2005 crises]] caused by the destruction of trees by the [[desert locust]]. Sudan, Chad, and Nigeria, which in 2007 together produced 95% of world exports, have been in discussions to create a producers' cartel.<ref>Navarro, Alain (10 July 2008) [http://afp.google.com/article/ALeqM5jfgNmGYOlaBdb6OKP3JEyrw4AHTA Sudan's manna from heaven and strategic weapon], AFP.{{ |
[[Image:Acacia seyal Taub66.png|thumb|left|''[[Acacia seyal|Vachellia seyal]]'' from Paul Hermann Wilhelm Taubert's Leguminosae, in Engelmann (ed.): Natürliche Pflanzenfamilien. Vol. III, 3., 1891]] While acacia gum has been harvested in [[Arabia]], [[Sudan]], and [[West Asia]] since antiquity, sub-Saharan acacia gum has a long history as a prized export. The gum exported came from the band of [[acacia]] trees that once covered much of the [[Sahel]] region: the southern littoral of the [[Sahara Desert]] that runs from [[Atlantic Ocean|the Atlantic]] to the [[Red Sea]]. Today, the main populations of gum-producing ''Acacia'' species are harvested in [[Mauritania]], [[Senegal]], [[Mali]], [[Burkina Faso]], [[Niger]], [[Nigeria]], [[Chad]], [[Cameroon]], [[Sudan]], [[Eritrea]], [[Somalia]], [[Ethiopia]], [[Kenya]] and [[Tanzania]]. ''[[Acacia senegal]]'' is tapped for gum by cutting holes in the bark, from which a product called ''kordofan'' or Senegal gum is exuded. ''Seyal'' gum, from ''[[Acacia seyal]]'', the species more prevalent in [[East Africa]], is collected from naturally occurring exudations on the bark. Traditionally harvested by seminomadic desert pastoralists in the course of their [[transhumance]] cycle, acacia gum remains a main export of several African nations, including [[Agriculture in Mauritania|Mauritania]], [[Economy of Niger|Niger]], [[Economy of Chad|Chad]], and [[Economy of Sudan|Sudan]]. The hardened exudations are collected in the middle of the rainy season (harvesting usually begins in July), and exported at the start of the dry season (November). <!-- Retrieved 2008-07-10.</ref>--> Total world gum arabic exports are today (2008) estimated at 60,000 tonnes, having recovered from 1987–1989 and [[2004 locust outbreak|2003–2005 crises]] caused by the destruction of trees by the [[desert locust]]. Sudan, Chad, and Nigeria, which in 2007 together produced 95% of world exports, have been in discussions to create a producers' cartel.<ref>Navarro, Alain (10 July 2008) [http://afp.google.com/article/ALeqM5jfgNmGYOlaBdb6OKP3JEyrw4AHTA Sudan's manna from heaven and strategic weapon], AFP. {{wayback|url=http://afp.google.com/article/ALeqM5jfgNmGYOlaBdb6OKP3JEyrw4AHTA |date=20130528163750 |df=y }}</ref> |
||
===Political aspects=== |
===Political aspects=== |
||
Revision as of 23:36, 17 October 2015
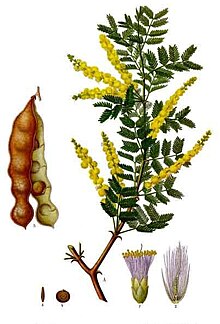

Gum arabic, also known as acacia gum, chaar gund, char goond, or meska, is a natural gum made of the hardened sap of two species of the acacia tree; Senegalia (Acacia) senegal and Vachellia (Acacia) seyal. Producers harvest the gum commercially from wild trees, mostly in Sudan (80%) and throughout the Sahel, from Senegal to Somalia—though it is historically cultivated in Arabia and West Asia.
Gum arabic is a complex mixture of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. It is the original source of the sugars arabinose and ribose, both of which were first discovered and isolated from it, and are named after it.
Gum arabic is used primarily in the food industry as a stabilizer. It is edible and has E number E414. Gum arabic is a key ingredient in traditional lithography and is used in printing, paint production, glue, cosmetics and various industrial applications, including viscosity control in inks and in textile industries, though less expensive materials compete with it for many of these roles.
While gum arabic is now produced mostly throughout the African Sahel, it is still harvested and used in the Middle East. For example, Arab populations use the natural gum to make a chilled, sweetened, and flavored gelato-like dessert.
Usage
Gum arabic's mixture of polysaccharides and glycoproteins gives it the properties of a glue and binder that is edible by humans. Other substances have replaced it where toxicity is not an issue, as the proportions of the various chemicals in gum arabic vary widely and make it unpredictable. Still, it remains an important ingredient in soft drink syrups, "hard" gummy candies such as gumdrops, marshmallows, M&M's chocolate candies—and edible glitter, a popular modern cake-decorating staple. For artists, it is the traditional binder in watercolor paint, in photography for gum printing, and it is used as a binder in pyrotechnic compositions. Pharmaceutical drugs and cosmetics also use the gum as a binder, emulsifying agent, and a suspending or viscosity increasing agent.[1] Wine makers have used gum arabic as a wine fining agent.[2]
It is an important ingredient in shoe polish, and can be used in making homemade incense cones. It is also used as a lickable adhesive, for example on postage stamps, envelopes, and cigarette papers. Lithographic printers employ it to keep the non-image areas of the plate receptive to water.[3] This treatment also helps to stop oxidation of aluminium printing plates in the interval between processing of the plate and its use on a printing press.
Food
Also called acacia after the original source, gum arabic is used as an emulsifier and a thickening agent in icing, fillings, chewing gum and other confectionery treats.[4]
Painting and art


Gum arabic is used as a binder for watercolor painting because it dissolves easily in water. Pigment of any color is suspended within the acacia gum in varying amounts, resulting in watercolor paint. Water acts as a vehicle or a diluent to thin the watercolor paint and helps to transfer the paint to a surface such as paper. When all moisture evaporates, the acacia gum binds the pigment to the paper surface. After the water evaporates, the acacia gum in the paint film increases luminosity and helps prevent the colors from lightening. Gum arabic allows more precise control over washes, because it prevents them from flowing or bleeding beyond the brush stroke. In addition, acacia gum slows evaporation of water, giving slightly longer working time. The addition of a little gum arabic to watercolor pigment and water allows for easier lifting of pigment from paper and thus can be a useful tool when lifting out color when painting in watercolor.
Ceramics
Gum arabic has a long history as additives to ceramic glazes. It acts as a binder, helping the glaze adhere to the clay before it is fired, thereby minimising damage by handling during the manufacture of the piece. As a secondary effect, it also acts as a deflocculant, increasing the fluidity of the glaze mixture but also making it more likely to sediment out into a hard cake if not used for a while. The gum is normally made up into a solution in hot water (typically 10–25 g/litre), and then added to the glaze solution after any ball milling in concentrations from 0.02% to 3% of gum arabic to the dry weight of the glaze.[5] On firing, the gum burns out at a low temperature, leaving no residues in the glaze. More recently, particularly in commercial manufacturing, gum arabic is often replaced by more refined and consistent alternatives, such as CMC.
Photography
The historical photography process of gum bichromate photography uses gum arabic mixed with ammonium or potassium dichromate and pigment to create a coloured photographic emulsion that becomes relatively insoluble in water upon exposure to ultraviolet light. In the final print, the acacia gum permanently binds the pigments onto the paper.
Printmaking
Gum arabic is also used to protect and etch an image in lithographic processes, both from traditional stones and aluminum plates. In lithography, gum by itself may be used to etch very light tones, such as those made with a number five crayon. Phosphoric, nitric or tannic acid is added in varying concentrations to the acacia gum to etch the darker tones up to dark blacks. The etching process creates a gum adsorb layer within the matrix that attracts water, ensuring that the oil based ink does not stick to those areas. Gum is also essential to what is sometimes called paper lithography, printing from an image created by a laser printer or photocopier.
Pyrotechnics
Gum arabic is also used as a water-soluble binder in fireworks composition.
Composition
Arabinogalactan is a biopolymer consisting of arabinose and galactose monosaccharides. It is a major component of many plant gums, including gum arabic. 8-5' Non cyclic diferulic acid has been identified as covalently linked to carbohydrate moieties of the arabinogalactan-protein fraction.[6]
Physical properties
Effect on surface tension in liquids
Acacia gum reduces the surface tension of liquids, which leads to increased foaming in carbonated beverages. This can be exploited in what is known as a Diet Coke and Mentos eruption.
Production


While acacia gum has been harvested in Arabia, Sudan, and West Asia since antiquity, sub-Saharan acacia gum has a long history as a prized export. The gum exported came from the band of acacia trees that once covered much of the Sahel region: the southern littoral of the Sahara Desert that runs from the Atlantic to the Red Sea. Today, the main populations of gum-producing Acacia species are harvested in Mauritania, Senegal, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Cameroon, Sudan, Eritrea, Somalia, Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania. Acacia senegal is tapped for gum by cutting holes in the bark, from which a product called kordofan or Senegal gum is exuded. Seyal gum, from Acacia seyal, the species more prevalent in East Africa, is collected from naturally occurring exudations on the bark. Traditionally harvested by seminomadic desert pastoralists in the course of their transhumance cycle, acacia gum remains a main export of several African nations, including Mauritania, Niger, Chad, and Sudan. The hardened exudations are collected in the middle of the rainy season (harvesting usually begins in July), and exported at the start of the dry season (November). Total world gum arabic exports are today (2008) estimated at 60,000 tonnes, having recovered from 1987–1989 and 2003–2005 crises caused by the destruction of trees by the desert locust. Sudan, Chad, and Nigeria, which in 2007 together produced 95% of world exports, have been in discussions to create a producers' cartel.[7]
Political aspects
West Africa
In 1445, Prince Henry the Navigator set up a trading post on Arguin Island (off the coast of modern Mauritania), which acquired acacia gum and slaves for Portugal. With the merger of the Portuguese and Spanish crowns in 1580, the Spaniards became the dominant influence along the coast. In 1638, however, they were replaced by the Dutch, who were the first to begin exploiting the acacia gum trade. Produced by the acacia trees of Trarza and Brakna, and used in textile pattern printing, this acacia gum was considered superior to that previously obtained in Arabia. By 1678, the French had driven out the Dutch and established a permanent settlement at Saint Louis at the mouth of the Senegal River, where the French Company of the Senegal River (Compagnie Française du Sénégal) had been trading for more than fifty years.[8]

For much of the 19th century, gum arabic was the major export from French and British trading colonies in modern Senegal and Mauritania. France in particular first came into conflict with inland African states over the supply of the commodity, providing an early spur for the conquest of French West Africa. As the Atlantic slave trade weakened in the early 19th century, The Emirate of Trarza and its neighbors, in what is today southern Mauritania, collected taxes on trade, especially gum arabic, which the French were purchasing in ever-increasing quantities for its use in industrial fabric production. West Africa had become the sole supplier of world acacia gum by the 18th century, and its export at the French colony of Saint-Louis doubled in the decade of 1830 alone. Taxes, and a threat to bypass Saint-Louis by sending gum to the British traders at Portendick, eventually brought the Emirate of Trarza into direct conflict with the French. In the 1820s, the French launched the Franco-Trarzan War of 1825. The new emir, Muhammad al Habib, had signed an agreement with the Waalo Kingdom, directly to the south of the river. In return for an end to raids in Waalo territory, the Emir took the heiress of Waalo as a bride. The prospect that Trarza might inherit control of both banks of the Senegal struck at the security of French traders, and the French responded by sending a large expeditionary force that crushed Muhammad's army. The war incited the French to expand to the north of the Senegal River for the first time, heralding French direct involvement in the interior of West Africa.[9] Africa continued to export gum arabic in large quantities—from the Sahel areas of French West Africa (modern Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger) and French Equatorial Africa (modern Chad) until these nations gained their independence in 1959–61.
Sudan
Although from the 1950s to the early 1990s, Sudan accounted for roughly 80% of gum arabic production, today, that figure is under 50%.[10] Hundreds of thousands of Sudanese are dependent on gum arabic for their livelihoods. It is, however, still the world's largest single producer, and the production of gum arabic is heavily controlled by the Sudanese government.[11]
The connection between Sudan and Osama bin Laden brought the otherwise innocuous gum to public consciousness in 2001, as an urban legend arose that bin Laden owned a significant fraction of the gum arabic production in Sudan, and therefore one should boycott products using it.[12]
This story took on somewhat significant proportions, mostly due to an article in The Daily Telegraph a few days after the 11 September attacks, which echoed this claim. Eventually, the State Department issued a release stating that while Osama bin Laden had once had considerable holdings in Sudanese gum arabic production, he divested himself of these when he was expelled from Sudan in 1996.[13]
In a press conference held at the Washington Press Club on 30 May 2007, John Ukec Lueth Ukec, Sudan's ambassador to the United States, threatened to stop exportation of gum arabic from his country if sanctions were imposed. The sanctions proposed by the United States were a political response from the United States to the alleged connection between the government of Sudan and the Janjaweed militia group. Ukec made his speech surrounded by Coca-Cola products, although other sodas use acacia gum as an emulsifier, as well.[14]
Ukec was quoted at the Washington press conference, "I want you to know that the gum arabic which runs all the soft drinks all over the world, including the United States, mainly 80 percent is imported from my country," which he said after raising a bottle of Coca-Cola. According to the Washington Post, a reporter then asked if Sudan was threatening to "stop the export of gum arabic and bring down the Western world." To which Ukec replied, "I can stop that gum arabic and all of us will have lost this," and gestured to the Coke bottle.[14]
Grades
There are two main types of gum arabic used as hydrocolloids: Acacia Senegal and Acacia Seyal. Senegal grade is an emulsifier, much used in beverage emulsions. Seyal grade is used in confectionary, coatings and as a soluble dietary fiber.
References
- ^ Smolinske, Susan C. (1992). Handbook of Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Excipients. p. 7. ISBN 0-8493-3585-X.
- ^ Vivas N, Vivas de Gaulejac N, Nonier M.F and Nedjma M (2001). "Effect of gum arabic on wine astringency and colloidal stability". Progres Agricole et Viticole (in French). 118 (8): 175–176.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Printing Process Explained". dynodan.com. Retrieved 29 August 2012.
- ^ Laura Halpin Rinsky; Glenn Rinsky (2009). The Pastry Chef's Companion: A Comprehensive Resource Guide for the Baking and Pastry Professional. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1, 134. ISBN 0-470-00955-1. OCLC 173182689.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Parmalee, Cullen W.; Harman, Cameron G. (1973). Ceramic Glazes (3rd ed.). Cahners Bookj. pp. 131–133, 145, 589. ISBN 0-8436-0609-6.
- ^ Renard, D; Lavenant-Gourgeon, L; Ralet, MC; Sanchez, C (2006). "Acacia senegal gum: Continuum of molecular species differing by their protein to sugar ratio, molecular weight, and charges". Biomacromolecules. 7 (9): 2637–49. doi:10.1021/bm060145j. PMID 16961328.
- ^ Navarro, Alain (10 July 2008) Sudan's manna from heaven and strategic weapon, AFP. Archived 2013-05-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ ARGUIN, Encyclopædia Britannica (1911).
- ^ Webb, James L. A. (2009). "The Trade in Gum Arabic: Prelude to French Conquest in Senegal". The Journal of African History. 26 (2–3): 149. doi:10.1017/S0021853700036914. JSTOR 181721.
- ^ Policy Note, Export Marketing of acacia gum from Sudan. World Bank (March 2007), p. 4.
- ^ Gerstenzang, James and Sanders, Edmund (30 May 2007). "Impact of Bush's Sudan sanctions doubted". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Urban Legends Reference Pages: Rumors of War (Buy Gum!)". Snopes. 19 September 2001. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
- ^ Bowman, Tom and LoLordo, Ann (15 September 1998). "Sanctions on Sudan bend for gum supply…". The Sun – Baltimore, Md. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Milbank, Dana (31 May 2007). "Denying Genocide in Darfur – and Americans Their Coca-Cola". The Washington Post. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
