Tornadoes of 2024
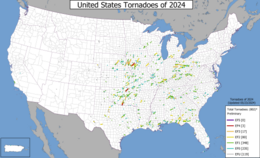 A map of 2024 United States tornado paths from the results of preliminary surveys. | |
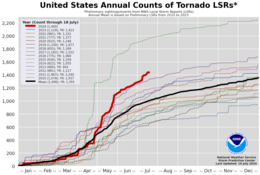 A chart of the 2024 United States tornado local storm report count compared to years 2005 through 2023, and the 2005–2023 mean. | |
| Timespan | January 3 – ongoing |
|---|---|
| Maximum rated tornado | EF3 tornado
|
| Fatalities (worldwide) | 11 |
This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2024. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh and Eastern India but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during summer in the Northern Hemisphere and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including thunderstorms, tropical cyclones, strong winds and hail.
Worldwide, 10000 tornado-related deaths have been confirmed: Five each in India and the United States and one in Indonesia.[1]
North America
Approximate touchdown location of deadly tornadoes in 2024 Summary of tornadoes[2]
|
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 61 | 100 | 33 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 207 |
- Note: One tornado has been officially confirmed but is not yet rated.
There have been 207 confirmed tornadoes in the United States.
United States tornadoes by month
January 8–9 (United States)
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 13 | 15 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
During the evening of January 8 through January 9, a severe weather outbreak brought damaging winds and numerous tornadoes to the Southeastern and Eastern United States. On January 7, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for severe weather in the states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, including a 10% hatched risk for tornadoes.
The outbreak began with several brief EF0 tornadoes touching down in Louisiana and Mississippi on January 8. Later that night, multiple tornadic supercell thunderstorms formed over the Gulf of Mexico and began moving toward the Gulf Coast and Florida Panhandle. In the early morning hours of January 9, a powerful tornadic waterspout formed offshore of Panama City Beach, Florida and moved inland at EF3 intensity, causing major damage in the Lower Grand Lagoon community. Multiple homes, condominiums, apartment buildings, and businesses were severely damaged or destroyed, and large boat storage warehouses sustained damage at the Pirate's Cove Marina. The tornado continued to cause lesser damage in the western part of Panama City before it dissipated. A high-end EF2 tornado also touched down in Lynn Haven, Florida, causing significant damage along the shores of Deer Point Lake to dozens of mobile and frame homes. A brief but strong EF2 tornado significantly damaged houses in Callaway, and an EF1 tornado caused moderate damage in Santa Rosa Beach as well.[3][4]

Another strong EF2 tornado impacted the outskirts of Marianna, where many RVs were thrown and destroyed at an RV park, and dozens of frame homes were badly damaged or destroyed in subdivisions. The longest-tracked and widest tornado of the outbreak touched down southwest of Graceville, Florida before it crossed into Alabama and struck Cottonwood at EF2 strength, unroofing homes, collapsing the walls of a brick business, and completely destroying a Moose Lodge building. One person was killed near Cottonwood when the tornado destroyed a mobile home. Several more EF1 tornadoes also touched down in Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina, including a tornado that struck the eastern edge of Claremont, North Carolina and rolled a manufactured home, resulting in another fatality. The final significant tornado of the day was an EF2 tornado that struck Bamberg, South Carolina, where multiple historic brick buildings were destroyed and a barrel factory suffered major damage. In all, 35 tornadoes were confirmed, resulting in two fatalities. Four additional fatalities unrelated to tornadoes occurred during the event as well.[3] The system responsible for this tornado outbreak also produced heavy snow and blizzard conditions in parts of the Pacific Northwest, the Midwest, and the Northeastern United States.[3][5][4]
February 8 (United States)
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A localized severe weather threat from Illinois to Wisconsin produced multiple supercells, one of which spawned a long-tracked tornado near Evansville, Wisconsin. Numerous farmsteads were struck, with many outbuildings being completely destroyed. One well-constructed metal outbuilding was destroyed, leading to a high-end EF2 rating with estimated wind speeds of at least 130 mph (210 km/h), resulting in an injury. An EF1 tornado that touched down near Juda, Wisconsin and preceded the tornado near Evansville was the first ever tornado to occur in Wisconsin in the month of February.[6] An EF1 tornado that tracked near Henry and McNabb, Illinois was also confirmed.[3]
February 27–28 (United States)
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 11 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A bimodal severe weather outbreak produced multiple tornadoes from northern Illinois to Ohio.[7][8] Multiple tornadoes were confirmed to have occurred overnight on February 27 and in the early morning on February 28. These included an EF2 tornado near Grand Blanc, Michigan, as well as several EF1 and EF0 tornadoes throughout Michigan, Indiana, and Illinois. Additional numerous instances of straight-line wind and hail damage occurred throughout northern Illinois, including within the Chicago metropolitan area.[3][7][9][10]
During the evening of February 27, three weak parallel tornadoes moved through the towns of South Barrington, Hoffman Estates, Inverness, and Palatine, prompting the National Weather Service to issue a tornado warning for most of the northwestern suburbs of Chicago. O'Hare and Midway International Airports issued ground stops as the system moved through the area, and travelers were encouraged to seek shelter, hundreds moving to interior locations and underground tunnels.[11][12] Damage from the EF2 tornado in Grand Blanc was more significant, causing downed power lines, uprooted trees, damaged gas lines[13] and complete demolition of the Waretech Industrial Park.[14][15][16][17][18] As the early morning of February 28 approached, a number of tornadoes touched down in the Dayton and Columbus metro areas in Ohio. Three EF2 tornadoes were confirmed, including one northeast of Dayton, one northeast of Columbus, and another southeast of Miltonsburg in Monroe County. Additional EF1 and EF0 tornadoes touched down near the communities of Hilliard and London. One EF1 tornado notably damaged parts of the Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and the far southwestern portion of Wright State University. [19][20][3] No casualties and few injuries were reported as a result of the tornadoes over the entire outbreak.[21]
March 9 (United States)
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A small severe weather event swept through the states of Alabama, Georgia, and Florida, where a few tornadoes occurred. In the early morning hours, a high-end EF1 tornado touched down east of Ozark, Alabama, causing tree damage and impacting several homes and outbuildings. Later that morning, another EF1 tornado occurred north of Miccosukee, Florida, resulting in tree damage only.[22] Another tornado formed northeast of Argyle, Georgia, damaging two structures and numerous trees and receiving a rating of EF1.[23] During the early afternoon, a significant tornado touched down southeast of Nahunta, Georgia. This tornado caused significant damage, including the roof of a home being severely damaged and the destruction of a travel trailer. Additionally, a double-wide manufactured home was completely destroyed, with its undercarriage thrown into trees and bent. Five people sustained injuries, and the tornado received a high-end EF2 rating, with wind speeds up to 130 mph (210 km/h). In total, four tornadoes were confirmed during this event.[3]
March 13–15 (United States)
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 |

From the evening of March 13 through March 15, a severe weather outbreak caused damaging winds and numerous tornadoes across the Central, Midwestern, and Southern United States.
On March 13, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for severe weather across Kansas and Missouri. Two tornadoes touched down that day in Kansas, both rated EF2. The first tornado snapped trees east of Alta Vista, Kansas, while the second tornado partially tore the roof off one home and damaged several outbuildings near Rossville. The following day, the Storm Prediction Center issued another enhanced risk area for parts of Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Missouri, including a 10% risk area for tornadoes. That morning, a few weak tornadoes occurred in Missouri and Illinois, preceding a larger event during the afternoon and evening. A low-end EF2 tornado touched down in Hanover, Indiana, tearing the roofs off a few homes, before crossing into Kentucky and striking the town of Milton, destroying numerous trailers and causing severe roof damage to many homes. The tornado then re-entered Indiana and destroyed more trailers near Brooksburg before lifting. [3]
On the evening of the 14th, a long-tracked supercell produced numerous tornadoes in Indiana and Ohio. The first tornado spawned by this supercell was a brief EF1 tornado that crossed from Indiana into Ohio near Celina, before another EF1 tornado directly struck Celina and the nearby community of St Marys. The supercell then spawned a multiple-vortex, high-end EF3 tornado that impacted the towns of Wapakoneta, Lakeview, and Indian Lake, destroying manufactured homes, uprooting and partially debarking trees, and obliterating RVs at a trailer park where a site-built structure was also destroyed. Three people were killed and numerous others were injured by this tornado. Shortly thereafter, an EF2 tornado completely destroyed a manufactured home near Plymouth. A high-end EF3 tornado touched down near Selma, Indiana, tearing the roof off numerous homes, continuing east into Winchester where many homes, a church, and a Taco Bell restaurant were destroyed, later dissipating as it moved into Darke and Miami counties in Ohio. The tornado injured 38 people. Further south, a low-end EF2 tornado destroyed a metal structure and snapped many trees in Hot Springs Village, Arkansas. In total, 30 tornadoes were confirmed from this outbreak. [3]
April 1–3 (United States)
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 | 43 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
From April 1 through April 3, a derecho[24] and significant tornado outbreak occurred in the Central Plains, Mississippi Valley, Ohio Valley, Southeastern United States, and Mid-Atlantic. On April 1, several tornadoes occurred in Arkansas, Missouri, and a tornado family of five tornadoes occurred in northeastern Oklahoma.[25] On April 2 northeast of Louisville, Kentucky, an EF2 tornado crossed I-265 near Utica, Indiana, where it overturned several vehicles (including Semi-trailer trucks) before striking Prospect, Kentucky.[26] The tornado also caused "significant damage" in the northern part of Jeffersonville, Indiana, where six injuries were reported.[27] The storm system left roughly 123,000 customers without power in West Virginia.[28] A low-end EF2 tornado southeast of Atlanta, Georgia also caused considerable damage and two injuries near Conyers.[3] One person was directly killed by flooding as a result of these storms,[29] and one more was indirectly killed.[30] On April 3, another fatality occurred in Armonk, New York due to the storms, and 50,000 customers lost power.[31] Fifteen others have also been injured. In total, 74 tornadoes were confirmed.
Europe
According to the European Severe Storms Laboratory, there have been 41 confirmed tornadoes in Europe in 2024, resulting in 12 injuries.[32]
January 3 (Belgium)
A tornado struck the communities of Onze-Lieve-Vrouw-Waver and Putte in Belgium. Approximately 40 homes were damaged, and a mobile home was blown over. One person and several horses were injured. The European Severe Storms Laboratory rated the tornado IF1.5.[32][33][34]
February 14 (Cyprus and Turkey)
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Several tornadoes and waterspouts touched down in Cyprus and Turkey. At 01:00 local time, an IF1.5 rated tornado touched down in Germasogeia, Limassol, Cyprus. One person suffered injuries and around 150 homes were damaged, displacing multiple families. Trees and tree branches were brought down and a crane collapsed. Additionally, an IF0.5 rated tornado touched down in Tece, Mersin Province, Turkey, damaging trees. Two waterspouts were observed in Cyprus and Turkey.[32]
March 5 (Turkey and France)
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Several tornadoes and waterspouts touched down in Europe.[32] One waterspout hit Demre, Turkey, causing IF1 damage to 175 decares of greenhouses and electricity poles.[35] A second IF1 tornado affected Göksu, Hacıveliler, Yenimahalle, Kumluca and Toptaş in Antalya Province, along a 12 km long and 80 meter wide path. Weak greenhouses were damaged, a mobile construction trailer was shifted, roofs were damaged and trees were downed. Six people sustained injuries.[36][37] Another IF1 tornado hit Payallar, causing near complete destruction of a weak greenhouse facility, and tossing a container into the greenhouse facility, causing one injury. A total of three people were injured.[38] Two unrated tornadoes touched down in France.[39][40][41]
March 27 (Italy and France)
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A weak unrated tornado occured just north-east of downtown Verona, Italy within the north-eastern surburb of Borgo Venezia. Another IF2 tornado hit Port-Joinville, France, damaging 60 roofs and downing trees. One person sustained injuries.[32][42][43][44]
Asia
January 9 (Indonesia)
A tornado damaged or destroyed 57 houses in three villages within the Langke Rembong District.[45]
January 18 (Indonesia)
A tornado damaged or destroyed 253 homes in the villages of Walidono and Cangkring, causing 19 injuries.[46][47]
February 4 (Indonesia)
A significant tornado damaged or destroyed numerous buildings in the village of Kedung Wonokerto, Prambon District, Indonesia. One person was killed by flying debris, when the zinc shop he was in was completely destroyed by the tornado.[48]
February 21 (Indonesia)
A strong tornado caused significant damage and was caught on video from multiple angles as it struck district Rancaekek, Bandung Regency and parts of Sumedang Regency, damaging or destroying 497 homes and 18 businesses, and causing 22 injuries.[49] The damaging tornado was given a rating of F2 on the Fujita scale.[50][51]
March 2 (India)
A significant tornado touched down near the city of Moga in India's Punjab state. This tornado was accompanied by a hailstorm.[52][53][54]
March 31 (India)
A tornado, accompanied by a nor'wester, struck the city of Jalpaiguri, West Bengal, killing five people and injuring over 100 others. More than 100 houses were destroyed by the tornado.[55][56]
Elsewhere
February 22 (Brazil)
A rare northern Brazil tornado hit Estrela de Alagoas, Alagoas. According to MetSul Meteorologia, the damage caused by the twister is consistent with an F1 tornado.[57]
See also
- Weather of 2024
- Tornado
- List of tornado outbreaks
- List of tornado outbreaks by Outbreak Intensity Score
- List of F5 and EF5 tornadoes
- List of F4 and EF4 tornadoes
- List of North American tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of 21st-century Canadian tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of European tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks in Asia
- List of Southern Hemisphere tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes striking downtown areas of large cities
- List of tornadoes with confirmed satellite tornadoes
- Tornado intensity
References
- ^ Joyce, Elijah (2024). "The Killer Tornadoes of 2024". Medium. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ "Annual U.S. Killer Tornado Statistics". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Branches of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration; National Weather Service; National Severe Storms Laboratory (2024). "Damage Assessment Toolkit". DAT. United States Department of Commerce.
- ^ a b NWS Damage Survey for 1/9/24 Tornado Event – Update #1 (Public Information Statement). Tallahassee, Florida: National Weather Tallahassee, FL. January 11, 2024. Retrieved January 11, 2024 – via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
- ^ National Weather Service in Columbia, South Carolina (10 January 2024). "Bamberg EF-2 Tornado in Bamberg County, SC" (Public Information Statement). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 11 January 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "NWS Damage Survey for 02/08/2024 Tornado Event" (Public Information Statement). Sullivan, Wisconsin: National Weather Service Sullivan, Wisconsin. February 9, 2024. Retrieved February 9, 2024 – via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
- ^ a b US Department of Commerce, NOAA. "February 27, 2024: Record Warmth Culminates in Evening Severe Storms With Large Hail and Several Tornadoes". www.weather.gov. Retrieved 2024-03-10.
- ^ US Department of Commerce, NOAA. "Severe Storms, High Winds, and Tornadoes - February 27, 2023". www.weather.gov. Retrieved 2024-03-10.
- ^ National Weather Service Chicago Illinois. "NWS Damage Survey for 2/27/2024 Tornado Event Final Update". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ National Weather Service Detroit/Pontiac Michigan. "NWS Damage Survey for 02/28/24 Tornado Event". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ Kleist, Mary Kay; Terry, Jermont; Curran, Ed (February 28, 2024). "Severe storms bring tornadoes, hail to Chicago area and beyond as cold front pounds through - CBS Chicago". www.cbsnews.com.
- ^ US Department of Commerce, NOAA. "February 27, 2024: Record Warmth Culminates in Evening Severe Storms With Large Hail and Several Tornadoes". www.weather.gov.
- ^ Powers, Sara (February 28, 2024). "National Weather Service confirms EF-2 tornado hit Grand Blanc - CBS Detroit". www.cbsnews.com.
- ^ Erwin, Alyssa (March 4, 2024). "Waretech Industrial Park in Grand Blanc 'total loss' after tornado". ABC 12 WJRT-TV.
- ^ Bowling, Erin (February 28, 2024). "Tornado in Marshall shocks residents, causing considerable damage". WILX.
- ^ "'Sounded like a freight train': Cleanup continues after EF-2 tornado hits Grand Blanc, taking down trees and utility lines". www.audacy.com. 2024-02-28. Retrieved 2024-03-10.
- ^ Powers, Sara (2024-02-28). "National Weather Service confirms EF-2 tornado hit Grand Blanc - CBS Detroit". www.cbsnews.com. Retrieved 2024-03-10.
- ^ "National Weather Service confirms 11 tornadoes in Illinois, NW Indiana". ABC7 Chicago. 2024-02-28. Retrieved 2024-03-10.
- ^ "NWS confirms 2 tornadoes in Dayton area following severe weather". 28 February 2024.
- ^ "Tornado damages homes, ruptures gas lines as rare February storm hits Michigan". 28 February 2024.
- ^ "Sixth Ohio tornado now confirmed. See the paths they took during Wednesday's storms". The Columbus Dispatch.
- ^ National Weather Service Tallahassee, Florida. "NWS Damage Survey for 03/09/2024 Tornado Event". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- ^ National Weather Service Jacksonville, Florida. "NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/09/24 TORNADO EVENT IN NORTHWEST CLINCH AND NORTHWEST WARE COUNTIES (GA)". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. Retrieved 20 March 2024.
- ^ Rukavina, Jennifer (6 April 2024). "NWS confirms at least 17 tornadoes touched down during national radar outage" (News article). The Paducah Sun. Paducah, Kentucky: Paxton Media Group & WPSD-TV. Archived from the original on 6 April 2024. Retrieved 6 April 2024.
The Storm Prediction Center said this storm system was significant enough to be classified as a Derecho event: a type of severe weather event defined by a bowing line of damaging winds over a far distance.
- ^ National Weather Service (2024). "2024 Tornado Events in Eastern Oklahoma + Northwest Arkansas" (StoryMap). ArcGIS StoryMaps. Tulsa, Oklahoma, United States: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 6 April 2024. Retrieved 6 April 2024.
- ^ "Tornadoes Confirmed Amid Severe Weather Outbreak | Weather.com". The Weather Channel. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- ^ Stowe, Daja (2024-04-03). "Jeffersonville mayor reports significant damage from tornado". Indianapolis News | Indiana Weather | Indiana Traffic | WISH-TV |. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- ^ Appalachian Power Company (2 April 2024). "Storm and Outage Details: Appalachian Power Storm Response Update #1". Appalachian Power. Archived from the original on 4 April 2024.
- ^ "Deadly storms with flooding rain and tornadoes leave path of destruction in multiple states". NBC News. 2024-04-04. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- ^ "Gov. Beshear confirms one person killed during Kentucky tornadoes". whas11.com. 2024-04-03. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- ^ At least 1 dead, 50K without power as violent thunderstorms thrash NYC area, NBC New York, April 4, 2024
- ^ a b c d e Staff of the European Severe Storms Laboratory (2024). "European Severe Weather Database" (Interactive map and database). ESWD. European Severe Storms Laboratory.
- ^ "LIVE. Windhoos laat spoor van vernieling achter in oosten van regio Mechelen - Steeds meer huizen onder water in Vlaams-Brabant". GVA. Gazet van Antwerpen. 3 January 2024. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ Additional references listed by the European Severe Storms Laboratory:
- "03/01/2024 – Tornade F2 à Putte". 3 January 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- "LIVE. Hevige regenval veroorzaakt wateroverlast in Vlaanderen". 3 January 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ""Oh my god!": waanzinnige beelden tonen hoe bewoners maar nipt kunnen vluchten voor rondvliegend puin door windhoos". 3 January 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- "Muur ingestort, dak verdwenen, tuinhuis in puin: dronebeelden tonen ravage in Putte na doortocht windhoos". 4 January 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ "Antalya'da hortum! Korku dolu anlar kamerada". Ensonhaber (in Turkish). 8 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ "Antalya'da hortum felaketi! Tarım alanları zarar gördü". CNN (in Turkish). 5 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ "Antalya'da hortum her yeri dağıttı! Zarar büyük". Milliyet (in Turkish). 5 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ "Alanya'da hortum dehşeti!". Yeni Alanya (in Turkish). 6 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ "Des vents de 115km/h font de nombreux dégâts à Villeneuve-sur-Lot". La Dépêche (in French). 5 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ "TEMOIGNAGE. "On s'est planqué sous la table, c'était d'une violence inouïe" : le passage d'une tornade à Cahors a fait de nombreux dégâts". La Dépêche (in French). 6 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ "Toitures envolées, tôles sur la voie ferrée, poteau tombé... Une tornade fait des dégâts au sud de Cahors". La Dépêche (in French). 6 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ https://www.keraunos.org/actualites/fil-infos/2024/mars/tornade-possible-rafale-ile-d-yeu-27-mars-2024-orage-vendee
- ^ https://france3-regions.francetvinfo.fr/pays-de-la-loire/vendee/la-roche-sur-yon/tempete-nelson-une-blessee-sur-l-ile-d-yeu-et-des-forts-coups-de-vent-en-vendee-2946738.html
- ^ https://auth.actu.fr/auth/realms/actu-fr/protocol/openid-connect/auth?client_id=actu-fr-editorial&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Factu.fr%2Fpays-de-la-loire%2Fl-ile-d-yeu_85113%2Ftempete-nelson-une-mini-tornade-a-lile-dyeu-a-touche-une-soixantaine-de-maisons_60876962.html&state=d990a6aa-f1a5-438d-8a48-2fd46e621a29&response_mode=fragment&response_type=code&scope=openid&nonce=6d7d6727-9ffe-47d3-9305-6766b6af8f20&prompt=none&code_challenge=HV_IZULBxqYS_HIJ-WY89TbGp_uAd0x_igqidB933bk&code_challenge_method=S256
- ^ "BPBD Manggarai identifikasi puluhan rumah rusak akibat angin puting beliung". 10 January 2024.
- ^ "Amukan Puting Beliung Rusak 60 Rumah di Prajekan Bondowoso". 18 January 2024.
- ^ "Kerusakan Akibat Puting Beliung di Bondowoso Terus Bertambah". 20 January 2024.
- ^ "Satu Warga Tewas Tertimpa Seng Akibat Puting Beliung di Sidoarjo" (News article) (in Indonesian). Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia: Ngopibareng.id. 4 February 2024. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ COSTA, FABIO MARIA LOPES (2024-02-22). "Tornado in Bandung-Sumedang causes 706 buildings to be damaged". kompas.id (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2024-02-22.
- ^ "Bandung Experiences First F2 Tornado in Indonesia, Sign of Climate Change Extremes". Social Expat. 2024-02-22. Retrieved 2024-02-22.
- ^ "BPBD Establishes Refugee Tents In 3 Bandung Districts Affected By Puting Beliung". VOI - Waktunya Merevolusi Pemberitaan. Retrieved 2024-02-22.
- ^ @navdeepdahiya55 (March 2, 2024). "Another visual of #Moga #Tornado from this evening. #Punjab" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ @iamgurparvesh (March 3, 2024). "After Yesterday's #Tornado and #Hailstorm Show Scenes From A Place Where This Tornado Has Caused Heavy Damage Location : Hamirgarh HP Filling Station and Radha Soami Satsang Beas Village Hamirgarh Close to Bhagta Bhaika (Malwa) #BhagtaBhaika #WeatherUpdate #Punjab" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ @VortixWx (March 3, 2024). "Tornado in Moga, #Punjab, #India several hours ago" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Kumari, Sweety (31 March 2024). "IMD warns of more tornadoes in northern Bengal after 5 killed and over 100 injured in Jalpaiguri". The Indian Express. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ https://twitter.com/Centinela_35/status/1774816348494868498
- ^ "RARO TORNADO PROVOCA ESTRAGOS NO INTERIOR DO NORDESTE DO BRASIL". 22 February 2024.