Windows Mobile
| Windows Mobile Logo | |
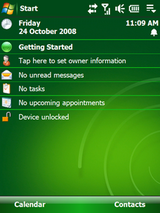
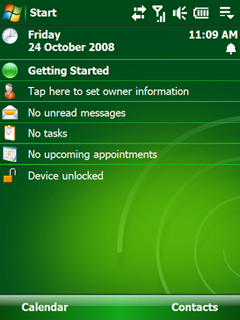 Windows Mobile 6.1 Professional Today Screen | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Windows CE |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Closed source |
| Latest release | 6.1 / April 1, 2008 |
| Marketing target | Mobile devices |
| License | Microsoft EULA |
| Official website | Windows Mobile |
Windows Mobile is a compact operating system combined with a suite of basic applications for mobile devices based on the Microsoft Win32 API. Devices that run Windows Mobile include Pocket PCs, Smartphones, Portable Media Centers, and on-board computers for certain automobiles. It is designed to be somewhat similar to desktop versions of Windows, feature-wise and aesthetically. Additionally, third-party software development is available for Windows Mobile. Originally appearing as the Pocket PC 2000 operating system, Windows Mobile has been updated several times, with the current version being Windows Mobile 6.1, and a new release scheduled for 2010.[1]
Microsoft projected in 2008 that shipments of devices with Windows Mobile will increase from 11 million to 20 million units, but it missed its initial goal in only selling 18 million licenses citing the delayed launch of certain smartphones. Windows Mobile's market share as an operating system for smartphones worldwide has fallen from 23% in 2004 down to 12% in 2008.[2] Windows Mobile has a worldwide smartphone market share of 13% now.[3] Microsoft licenses Windows Mobile to four out of the five world's largest mobile phone manufacturers, with Nokia being the other.[4]
Italic text==Common features==
This article contains a list of miscellaneous information. (August 2008) |
Windows Mobile for Pocket PC carries these standard features in most of its versions:
- Today Screen shows the current date, owner information, upcoming appointments, e-mail messages, and tasks.
- The taskbar shows the current time and the volume.
- Office Mobile a suite of Mobile versions of Microsoft Office applications
- Outlook Mobile comes with Windows Mobile.
- Internet Explorer Mobile is an Internet browser developed by Microsoft for Pocket PC and Handheld PC that comes loaded by default with Windows Mobile and Windows CE for Handheld PC.
- Windows Media Player for Windows Mobile.
- Client for PPTP VPNs.
- Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) which in mobile phones allows attached computers to share internet connections via USB and Bluetooth.
Hardware platforms
Windows Mobile runs on multiple hardware platforms including Pocket PCs, smartphones, Portable Media Center, and automobiles. These hardware platforms did not always exist from the inception of Windows Mobile.



Pocket PC
The Pocket PC was the original intended platform for the Windows Mobile operating system. These devices consisted of both standalone Pocket PC devices without mobile phone capabilities, and those that included mobile phone capabilities. The most current name of Windows Mobile intended for use on Pocket PCs is officially "Windows Mobile 6 Professional" for devices with mobile phone capabilities and "Windows Mobile 6 Classic" for devices without mobile phone capabilities.
Smartphone
The Smartphone became the next hardware platform after the Pocket PC to run Windows Mobile, and debuted with the release of Pocket PC 2002. Although in the broad sense of the term "Smartphone", both Pocket PC phones and Microsoft branded Smartphones each fit into this category, it should be noted that Microsoft's use of the term "Smartphone" includes only more specific hardware devices that differ from Pocket PC phones. Such Smartphones were originally designed without touchscreens, intended to be operated more efficiently with only one hand, and typically had lower resolution displays than Pocket PCs. Microsoft's focus for the Smartphone platform was to create a device that functioned well as a phone and data device in a more integrated manner.[5] The current name of Windows Mobile intended for use on Smartphones is officially "Windows Mobile 6 Standard".
Portable Media Center
The Portable Media Center was a device that focused on integration with Microsoft's Windows Media Center and Windows Media Player to allow users to carry their media libraries with them on the go. The Portable Media Center was officially introduced in 2004, and ran a modified version of Windows Mobile. These devices became the predecessor to Microsoft's Zune, and after 2006 Microsoft discontinued the project in favor of the latter.
Automobiles
"Windows Mobile for Automotive" is the name for Microsoft's operating system that facilitates multiple functions in automobiles including communication, entertainment, information systems.[6] Windows Mobile for use in automobiles is the latest platform for the operating system, and was introduced by Microsoft in February of 2006 at the Geneva International Motor Show.[7] Windows Mobile for Automotive comes in two different versions. The Basic version includes a Bluetooth connectivity and USB interface for music playback. The Standard version includes this also, but additionally it features a built-in GPS, GSM phone, and security features. These systems are more widely known as SYNC. The Windows Mobile for Automotive hardware specification includes a 300 MHz ARM processor, 32 MB of RAM, and a microphone.[6]
Versions
Pocket PC 2000
Pocket PC 2000, originally codenamed "Rapier",[8] was released in April of 2000, and was based on Windows CE 3.0. It was the debut of what was later dubbed the Windows Mobile operating system, and meant to be a successor to the operating system aboard Palm-Size PCs. Backwards compatibility was retained with such Palm-Size PC applications. Pocket PC 2000 was intended mainly for Pocket PC devices, however several Palm-Size PC devices had the ability to be updated as well. In addition, several Pocket PC 2000 phones were released, however the Smartphone hardware platform was not yet created. The only resolution supported by this release was 240 x 320 (QVGA). Removable storage card formats that were supported were CompactFlash and MultiMediaCard. At this time Pocket PC devices had not been standardized with a specific CPU architecture. As a result, Pocket PC 2000 was released on multiple CPU architectures; SH-3, MIPS, and ARM.
Aesthetically, the original Pocket PC operating system was similar to Windows 98, Windows Me, and Windows 2000 operating systems.
Features/built-in applications for Pocket PC 2000 included the following:[9]
- Pocket Office
- Pocket Word
- Pocket Excel
- Pocket Outlook
- Pocket Internet Explorer
- Windows Media Player
- Microsoft Reader
- Microsoft Money
- Notes, a note taking application
- Character recognition support
- Infrared (IR) File beaming capability
Pocket PC 2002

Pocket PC 2002, originally codenamed "Merlin",[8] was released in October 2001. Like Pocket PC 2000, it was powered by Windows CE 3.0. Although targeted mainly for 240 × 320 (QVGA) Pocket PC devices, Pocket PC 2002 was also used for Pocket PC phones, and for the first time, Smartphones.[10] These Pocket PC 2002 Smartphones were mainly GSM devices. With future releases, the Pocket PC and Smartphone lines would increasingly collide as the licensing terms were relaxed allowing OEMs to take advantage of more innovative, individual design ideas. Aesthetically, Pocket PC 2002 was meant to be similar in design to the then newly released Windows XP.
New features/built-in applications included the following:[11][12][13][14]
- Enhanced UI with theme support
- Spell checker and Word count tool in Pocket Word
- Savable downloads and WAP in Pocket Internet Explorer
- Virtual Private Networking support
- Synchronization of folders
- MSN Messenger
- Terminal Services
- Windows Media Player 8 with streaming capability
- Microsoft Reader 2
- Palm OS support for file beaming
- Improved Pocket Outlook
- Digital rights management (DRM) support in Microsoft Reader
Windows Mobile 2003
Windows Mobile 2003, originally codenamed "Ozone",[8] was released on June 23, 2003, and was the first release under the Windows Mobile banner. It came in four editions: "Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Premium Edition", "Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Professional Edition", "Windows Mobile 2003 for Smartphone" and "Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Phone Edition". The last was designed especially for Pocket PCs which include phone functionalities. The Professional Edition was used in Pocket PC budget models such as the iPAQ rz1700 series. It lacked a number of features that were in the Premium Edition, such as a client for L2TP/IPsec VPNs. Windows Mobile 2003 was powered by Windows CE 4.20.
New features/built-in applications included the following:[15]
- Support for add-on keyboards
- Enhanced communications interface with Bluetooth device management
- Bluetooth file beaming support
- Bluetooth headset support
- Pictures application with viewing, cropping, e-mail, and beaming support
- Jawbreaker game
- Enhanced Pocket Outlook with vCard and vCal support
- Improved Pocket Internet Explorer
- Windows Media Player 9.0 with streaming optimization
- SMS reply options for Phone Edition
- MIDI file support as ringtones in Phone Edition
Windows Mobile 2003 SE
Windows Mobile 2003 Second Edition, also known as "Windows Mobile 2003 SE", was released on March 24, 2004 and first offered on the Dell Axim x30.
New features/built-in applications included the following:
- Portrait and Landscape switching for Pocket PCs
- Single-Column layout in Pocket Internet Explorer
- VGA (640×480), 240x240, and 480x480 Screen resolution
- Wi-Fi Protected Access support
Windows Mobile 5

Windows Mobile 5.0, originally codenamed "Magneto",[8] was released at Microsoft's Mobile and Embedded Developers Conference 2005 in Las Vegas, May 9–May 12, 2005, and first offered on the Dell Axim x51. It was powered by Windows CE 5.0 and used the .NET Compact Framework 1.0 SP3 — an environment for programs based on .NET. Windows Mobile 5.0 included Microsoft Exchange Server "push" functionality improvements that worked with Exchange 2003 SP2.[16] The "push" functionality also required vendor/device support[17] With AKU2 software upgrades all WM 5.0 devices supported DirectPush. WM 5.0 featured increased battery life due to Persistent storage capability. Previously up to 50% (enough for 72 hours of storage) of battery power was reserved just to maintain data in volatile RAM. This continued the trend of Windows-based devices moving from using RAM as their primary storage medium to the use of flash memory. With Windows Mobile 5.0, OS updates were released as Adaptation kit upgrades. AKU3.5 is the most current release.
New features/built-in applications included the following:
- A new version of Office called "Office Mobile"
- PowerPoint Mobile
- Graphing capability in Excel Mobile
- Tables and graphics insertion in Word Mobile
- Windows Media Player 10 Mobile
- Photo Caller ID
- DirectShow support
- Picture and Video package, which converged the management of videos and pictures
- Enhanced Bluetooth support
- Global Positioning System (GPS) management interface
- Microsoft Exchange Server "push" functionality improvements
- Default QWERTY keyboard-support
- Error reporting facility similar to that present in desktop and server Windows systems
- ActiveSync 4.2 with 15% increased synchronization speed
- Persistent storage (PS) support in Pocket PCs
- Increased battery life
Windows Mobile 6
Windows Mobile 6, formerly codenamed "Crossbow",[8] was released on February 12, 2007[18] at the 3GSM World Congress 2007. It comes in three different versions: "Windows Mobile 6 Standard" for Smartphones (phones without touchscreens), "Windows Mobile 6 Professional" for Pocket PCs with phone functionality, and "Windows Mobile 6 Classic" for Pocket PCs without cellular radios.[19]
Windows Mobile 6 is powered by Windows CE 5.0 (version 5.2) and is strongly linked to Windows Live and Exchange 2007 products. Windows Mobile 6 Standard was first offered on the Orange's SPV E650,[20] while Windows Mobile 6 Professional was first offered on the O2's Xda Terra.[21] Aesthetically, Windows Mobile 6 was meant to be similar in design to the then newly released Windows Vista.
New features/built-in applications include the following:[22]
- 320x320 and 800x480 (WVGA) screen resolution support
- Office Mobile support for Smartphones
- Operating System Live Update[23]
- Improved Remote Desktop access[24](Available for only certain Pocket PCs)[25]
- VoIP (Internet calling) support with AEC (Acoustic Echo Cancelling) and MSRT Audio Codec
- Windows Live for Windows Mobile[26]
- Customer Feedback option[27]
- Enhanced Microsoft Bluetooth Stack
- Storage Card Encryption (encryption keys are lost if device is cold-booted).
- Smartfilter for searching within programs
- Improved Internet Sharing
- HTML email support in Outlook Mobile
- Search ability for contacts in an Exchange Server Address Book
- AJAX, JavaScript, and XMLDOM support on Internet Explorer Mobile
- Out of Office Replies with Microsoft Exchange 2007
- Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) support for select operators
- Server Search on Microsoft Exchange 2007
- .NET Compact Framework v2 SP2 Preinstalled in ROM
- Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Compact Edition Preinstalled in ROM
- OneNote Mobile as a companion to Microsoft Office OneNote
- Office Mobile 6.1 announced[28] with support for Office 2007 document formats (pptx, docx, xlsx).
Windows Mobile 6.1
Windows Mobile 6.1 was announced April 1, 2008. It is a minor upgrade to the existing Windows Mobile 6 platform which brings with it a redesigned Home screen featuring horizontal tiles that expand on clicking to display more information, although this new home screen is featured only on Windows Mobile Standard edition. This feature was inexplicably left out of the Professional edition.[29] Several other improvements such as threaded SMS, full page zooming in IE and 'Domain Enroll' have also been added. Domain Enroll is functionality to connect the device to System Center Mobile Device Manager 2008, a product to manage mobile devices.[30]
Future versions
Windows Mobile 6.5
Recently confirmed by Steve Ballmer[31], version 6.5 will be a minor upgrade to the existing Windows Mobile platform. It is said to include significant new added features.[32] It will also include the new Internet Explorer Mobile browser dubbed "IE 6 On 6".[33] Windows Mobile device makers have already recieved the final updates to the new browser, and Microsoft expects some of the first phones with it to be available in Asia and Europe by the end of calendar year 2008, with U.S. offerings to follow.[34] Motorola expects to release a phone running Windows Mobile 6.5 in the second half of 2009.[35]
Windows Mobile 7
Codenamed "Photon"[36], Windows Mobile 7 is a major upgrade planned for release in the second half of 2009.[37] Not much else is known about the release, though leaked information suggests a revamped UI, multi-touch and motion-related features.[38] Companies such as MWg and HTC are expected to release Pocket PC phones supporting this version.[39][40] Features include redesigned interface, new Office Mobile version, next Internet Explorer Mobile, accelerometer functionality with interface (gestures), new media player version.[41] Microsoft has somewhat confirmed the leaks, showing the homescreen during a commercial of their Live Mesh software operating on what appears to be an HTC Touch Dual.[42] Microsoft also plans on bringing some form of Zune functionality or software to this version.[43]
Windows Mobile 8
Windows Mobile 8 will be based on Midori rather than Windows CE.[44] Gizmodo writes about Windows Mobile 8. That's the one that will be started completely from scratch, with "new plumbing." This is the version you've been waiting for, implementing a completely redesigned user interface, "revolutionary" features like global search, and new concepts such as automation and connections within the phone, ideas borrowed from other smartphone operating systems. This means that you'll be able to go from viewing a person's address info in his contact card to seeing where he lives in map view in one click. There will be much more of this intuitive flow, and far less digging through menus.[45] Windows Mobile 8 will add support for gestures on auxiliary screens.[46]
Naming conventions
| Pocket PC 2000 | Pocket PC 2002 | Windows Mobile 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE |
Windows Mobile 5.0 |
Windows Mobile 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocket PC (Without Mobile Phone) | Pocket PC 2000 | Pocket PC 2002 | Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC | Windows Mobile 2003 SE for Pocket PC | Windows Mobile 5.0 for Pocket PC | Windows Mobile 6 Classic |
| Pocket PC (With Mobile Phone) | Pocket PC 2000 Phone Edition | Pocket PC 2002 Phone Edition | Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Phone Edition | Windows Mobile 2003 SE for Pocket PC Phone Edition | Windows Mobile 5.0 for Pocket PC Phone Edition | Windows Mobile 6 Professional |
| Smartphone (Without Touch Screen) | N/A | Smartphone 2002 | Windows Mobile 2003 for Smartphone | Windows Mobile 2003 SE for Smartphone | Windows Mobile 5.0 for Smartphone | Windows Mobile 6 Standard |
Other: Windows Mobile for Automotive 1.0, Windows Mobile software for Portable Media Centers
Software development
Third-party software development is available for the Windows Mobile operating system. There are several options for developers to use when deploying a mobile application. This includes writing native code with Visual C++, writing Managed code that works with the .NET Compact Framework, or Server-side code that can be deployed using Internet Explorer Mobile or a mobile client on the user's device. The .NET Compact Framework is actually a subset of the .NET Framework and hence shares many components with software development on desktop clients, application servers, and web servers which have the .NET Framework installed, thus integrating networked computing space (a.k.a. "The Cloud")[47].
Microsoft typically releases Windows Mobile Software development kits (SDKs) that work in conjunction with their Visual Studio development environment. These SDKs include emulator images for developers to test and debug their applications while writing them. Microsoft also distributes Visual Studio 2008 / 2005 Professional Editions, and server / database counterparts to students as downloads free of charge via its DreamSpark program[48].
Prior to the release of Windows Mobile 2003, third-party software was developed using Microsoft's eMbedded Visual Tools.[49]
See also
- ActiveSync
- Adaptation kit upgrade
- Dashtop Mobile
- Handheld PC
- Microsoft Office Mobile
- Mobile learning
- Mobile platform
- Symbian OS
- Windows Mobile Device Center
References
- ^ Smith, Tony (October 10, 2006). "Vista-inspired Windows Mobile 6 spied on web". The Register Hardware.
- ^ "Windows Mobile market share changes"
- ^ http://seattlepi.nwsource.com/business/372906_msftmobile31.html
- ^ "Sony Ericsson makes major move"
- ^ Mobile Phones|Smartphone - Software Features Overview. Microsoft. Retrieved 6 September 2007 from the Internet Archive.
- ^ a b Windows Mobile for Automotive 1.0. Microsoft. Retrieved 6 September 2007.
- ^ "Microsoft Windows Mobile for Automotive Launches with Fiat System". Geekzone (4 March 2006). SohoSolutions. Retrieved 6 September 2007.
- ^ a b c d e De Herrera, Chris. Windows CE/Windows Mobile Versions. pocketpcfaq.com. Retrieved 6 September 2007.
- ^ De Herrera, Chris. More Than a PDA!. Pocket PC Magazine. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ Morris, John; Taylor, Josh, Microsoft jumps in the all-in-one game, zdnet.com, Retrieved from the Internet Archive 6 September 2007.
- ^ Announcing the New Pocket PC 2002, Microsoft, Retrieved from the Internet Archive 6 September 2007.
- ^ Gray, Douglas. HP to unveil Jornada 560 series of handhelds. ITWorld.com. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ Gray, Douglas. Palming new handhelds: Pocket PC 2002. CNN. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ De Herrera, Chris. The Pocket PC 2002 Gets More Features for Work and Play. Pocket PC Magazine. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ De Herrera, Chris. Windows Mobile 2003. Pocket PC Magazine. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ^ "New Mobility Features in Exchange Server 2003 SP2". Microsoft Technet. 2005. Retrieved 2007-06-04.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Boulton, Clint (October 19, 2005). "Microsoft Looks to Mobilize With Exchange SP2". internetnews. Retrieved 2007-06-04.
- ^ "Windows Mobile 6 press release" (Press release). Microsoft. February 7, 2007.
- ^ Langridge, Jason. "Differences between platforms" (png). Microsoft MSDN blogs.
- ^ Langridge, Jason (April 11, 2007). "Windows Mobile 6 offered on Orange, HTC Vox". Microsoft MSDN.
- ^ Hess, Arne (April 24, 2007). "Windows Mobile 6 offered on Xda, HTC Herald". The Unwired. Retrieved 2007-06-04.
- ^ Langridge, Jason (February 8, 2007). "Summary of Windows Mobile 6 Specs". Microsoft MSDN blogs.
- ^ "Image Gallery: Windows Mobile 6 Professional screenshots, Windows Update, screen 1". ZDNet. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- ^ Improved Remote Desktop access
- ^ RDP Client is not included in many WM6 devices
- ^ Windows Live
- ^ Customer Feedback Option
- ^ "Office Mobile 2007 to be offered on Q3 2007". CNET. June 6, 2007.
- ^ Experiencing the goodness that is Windows Mobile 6.1
- ^ Microsoft Press release
- ^ "Ballmer confirms Windows Mobile 6.5".
- ^ "Motorola Delays Cell-Phone Spinoff, Drops Platforms".
- ^ "BROWSER: Microsoft's Internet Explorer Mobile 6 aka 6 on 6 is real and shows its face".
- ^ "Internet Explorer Mobile 6 with Flash, Faster Rendering Debuting Soon".
- ^ "Motorola Delays Cell-Phone Spinoff, Drops Platforms".
- ^ "Windows Mobile 7: A Pocket PC Central Brief". Retrieved 2008-05-31.
- ^ "Windows Mobile 7 release delayed". Retrieved 2008-09-24.
- ^ "HTC: Android Q4, Windows Mobile 7 Q1 09". Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ "MWg releasing Windows Mobile 7 gear before the year's out?".
- ^ "HTC exec claims Q109 for first Windows Mobile 7 phones?".
- ^ "Is this Windows Mobile 7?". Retrieved 2008-09-11.
- ^ "Live Mesh "Synchronizing your life"".
- ^ "Steve Ballmer confirms Zune coming to Windows Mobile".
- ^ http://msmobiles.com/news.php/7531.html
- ^ http://gizmodo.com/gadgets/what.s-wrong-with-windows-mobile/whats-wrong-with-windows-mobile-and-how-wm7-and-wm8-are-going-to-fix-it-333536.php
- ^ http://74.125.77.132/search?q=cache:GD0Jqi2LA4sJ:microsoft.blognewschannel.com/archives/2008/01/06/exclusive-windows-mobile-7-to-focus-on-touch-and-motion-gestures/+%22windows+mobile+8%22&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=3&gl=us
- ^ Differences Between the .NET Compact Framework and the .NET Framework
- ^ Microsoft Gives Students Access to Technical Software at No Charge to Inspire Success and Make a Difference
- ^ Learn Windows Mobile: Overview. Microsoft. Retrieved 5 October 2007.
Italic text==External links==
