Bhutan
Kingdom of Bhutan འབྲུག་ཡུལ Druk Yul | |
|---|---|
| Motto: none | |
| Anthem: Druk tsendhen | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Thimphu |
| Official languages | Dzongkha, English |
| Government | Monarchy |
| Independence | |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• 2005 estimate | 2,232,291 (139th) |
• 2002 census | 2,094,175 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
• Total | $2.913 billion (162nd) |
• Per capita | $3,330 (124th) |
| Currency | Ngultrum (BTN) |
| Time zone | UTC+6:00 (BTT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+6:00 (not observed) |
| Calling code | 975 |
| ISO 3166 code | BT |
| Internet TLD | .bt |
The Kingdom of Bhutan (IPA: [buː'tɑːn] ) is a landlocked nation in the Himalaya Mountains, situated between India and the People's Republic of China in South Asia. The local name for the country is Druk Yul. It is also called Druk Tsendhen (land of the thunder dragon), because the thunder there is said to be the sound of roaring dragons. Historically, Bhutan was known by many names, such as Lho Mon (southern land of darkness), Lho Tsendenjong (southern land of the cypress), and Lhomen Khazhi (southern land of four approaches). The origins of the name Bhutan are unclear; historians have suggested that it may have originated in variations of the Sanskrit words Bhota-ant (the end of Bhot – another word for Tibet), or Bhu-uttan (highlands). The word Bhutan as a name for the country dates from the late 19th century.
Bhutan is one of the most isolated nations in the world; foreign influences and tourism are heavily regulated by the government to preserve its traditional culture. The landscape ranges from subtropical plains to the Himalayan heights, an elevation gain of more than 7000 m. Mahayana Buddhism is the state religion; about 70 percent of the population are Buddhists. Thimphu is the capital and largest town.
History
Stone tools, weapons, and remnants of large stone structures provide evidence that Bhutan was inhabited as early as 2000 BC. Historians have theorised that the state of Lhomon (literally, "southern darkness"), or Monyul ("dark land", a reference to the Monpa – the aboriginal peoples of Bhutan) may have existed between 500 BC and AD 600. The names Lhomon Tsendenjong (sandalwood country), and Lhomon Khashi, or southern Mon (country of four approaches) have been found in ancient Bhutanese and Tibetan chronicles.
The earliest transcribed event in Bhutan was the passage of the Buddhist saint Guru Rinpoche in the 8th century. Bhutan's early history is unclear, because most of the records were destroyed after fire ravaged Punakha, the ancient capital in 1827. By the tenth century, Bhutan's political development was heavily influenced by its religious history. Various sub-sects of Buddhism emerged which were patronised by the various Mongol and Tibetan overlords. After the decline of the Mongols in the 14th century, these sub-sects vied with each other for supremacy in the political and religious landscape, eventually leading to the ascendancy of the Drukpa sub-sect by the sixteenth century.

Until the early 17th century, Bhutan existed as a patchwork of minor warring fiefdoms until unified by the Tibetan lama and military leader Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal. To defend the country against intermittent Tibetan forays, Namgyal built a network of impregnable dzong (fortresses), and promulgated a code of law that helped to bring local lords under centralised control. Many such dzong still exist. After his death in 1652, Bhutan fell under a state of anarchy. Taking advantage of the chaos, the Tibetans attacked Bhutan in 1710, and again in 1730 with the help of the Mongols. Both assaults were successfully thwarted, and an armistice was signed in 1759.

In the 18th century, the Bhutanese invaded and occupied the kingdom of Cooch Behar to the south. In 1772, Cooch Behar appealed to the British East India Company who assisted them in ousting the Bhutanese, and later attacking Bhutan itself in 1774. A peace treaty was signed in which Bhutan agreed to retreat to its pre-1730 borders. However, the peace was tenuous, and border skirmishes with the British were to continue for the next hundred years. The skirmishes eventually led to the Duar War (1864–65), a confrontation over who would control the Bengal Duars. After Bhutan lost the war, the Treaty of Sinchula was signed between British India and Bhutan. As part of the reparations, the Duars were ceded to Britain in exchange for a rent of Rs. 50,000. The treaty ended all hostilities between British India and Bhutan.
During the 1870s, power struggles between the rival valleys of Paro and Trongsa led to civil war in Bhutan, eventually leading to the ascendancy of Ugyen Wangchuck, the ponlop (governor) of Tongsa. From his power base in central Bhutan, Ugyen Wangchuck defeated his political enemies and united the country following several civil wars and rebellions in the period 1882–85.
In 1907, an epochal year for the country, Ugyen Wangchuck was unanimously chosen as the hereditary king of the country by an assembly of leading Buddhist monks, government officials, and heads of important families. The British government promptly recognised the new monarchy, and in 1910 Bhutan became a suzerain of the British government in exchange for political autonomy. After India gained independence from Britain in August 1947, kingdoms such as Bhutan were given the option to remain independent or to join the Indian Union. Bhutan chose to remain independent, and on August 8, 1949, Bhutan's independence was recognised by India.
After the People's Liberation Army entered Tibet in 1951, Bhutan sealed its northern frontier and improved bilateral ties with India. To reduce the risk of Chinese encroachment, Bhutan began a modernisation program that was largely sponsored by India. In 1953, King Jigme Dorji Wangchuk established the country's legislature – a 130-member National Assembly – to promote a more democratic form of governance. In 1965, he set up a Royal Advisory Council, and in 1968 he formed a Cabinet. In 1971, Bhutan was admitted to the United Nations, having held observer status for three years. In July 1972, Jigme Singye Wangchuck ascended to the throne at the age of 16 after the death of his father, Dorji Wangchuk.
Government decrees promulgated in the 1980s sought to preserve Bhutan's cultural identity in a "one nation, one people" policy called driglam namzha (national customs and etiquette). For example, a Bhutia-derived national dress is required of all Bhutanese, even those who are not ethnic Bhutias. Nepali-language education has also been restricted on grounds of national unity.
Such policies continue to be severely criticized by human rights groups as well as Bhutan's Nepalese community, who perceive the policy to be directed against them. From the perspective of Bhutan's dominant Bhutia caste, the issue is one of preserving a Himalayan Buddhist culture and way of life (which is under threat in nearby Sikkim and Tibet). To the Nepalese, the Bhutia are clinging to power at the expense of human rights, pluralism, and democratic principles.
Simmering tensions between ethnic Nepali and Bhutia communities were exacerbated in the late 1980s after the government moved to implement the 1985 Citizenship Act, which provided that only those Nepalese immigrants who could show they had resided in Bhutan for at least 15 to 20 years (depending on occupational status) be deemed the citizens of Bhutan. This led to the setting up of numerous organisations to protest against what was seen as an injustice against resident Nepalis. Matters reached a head in 1991 after protests by the Nepali community led to violence, leaving 300 dead and 2,000 under arrest. After protests by the government of Nepal, the Bhutanese government released most of those arrested. However, the issue of expatriate Nepalis remains unresolved, with at least 100,000 living in UNHCR camps in Nepal and Sikkim.
In 1998, Wangchuck introduced significant political reforms, transferring most of his powers to the Prime Minister and allowing for impeachment of the King by a two-thirds majority of the National Assembly. In late 2003, the Bhutanese army launched a large-scale operation to flush out anti-India insurgents who were operating training camps in southern Bhutan.
A new constitution is likely to be put up for ratification by a referendum at the end of 2005.
Geography
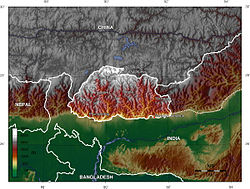
The northern region consists of an arc of glaciated mountain peaks with an extremely cold climate at the highest elevations. Most peaks in the north are over 7,000 m above sea level; the highest point is the Kula Kangri, at 7,553 m, and Gangkhar Puensum, at 7,541 m, has the distinction of being the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. Watered by snow-fed rivers, alpine valleys in this region provide pasturage for livestock, tended by a sparse population of migratory shepherds.
The Black Mountains in central Bhutan form a watershed between two major river systems: the Mo Chhu and the Drangme Chhu. Peaks in the Black Mountains range between 1,500 m and 2,700 m above sea level, and fast-flowing rivers have carved out deep gorges in the lower mountain areas. Woodlands of the central region provide most of Bhutan's forest production. The Torsa, Raidak, Sankosh, and Manas are the main rivers of Bhutan, flowing through this region. Most of the population lives in the central highlands.

In the south, the Shiwalik Hills are covered with dense, deciduous forests, alluvial lowland river valleys, and mountains up to around 1,500 m above sea level. The foothills descend into the subtropical Duars plain. Most of the Duars is located in India, although a 10–15 km wide strip extends into Bhutan. The Bhutan Duars is divided into two parts: the northern and the southern Duars. The northern Duars which abuts the Himalayan foothills has rugged, sloping terrain and dry, porous soil with dense vegetation and abundant wildlife. The southern Duars has moderately fertile soil, heavy savannah grass, dense, mixed jungle, and freshwater springs. Mountain rivers, fed by either the melting snow or the monsoon rains, empty into the Brahmaputra river in India. Over 70% of Bhutan is forested.
The climate in Bhutan varies with altitude, from subtropical in the south to temperate in the highlands and polar-type climate, with year-round snow in the north. Bhutan experiences five distinct seasons: summer, monsoon, autumn, winter and spring. Western Bhutan has the heavier monsoon rains; southern Bhutan has hot humid summers and cool winters; central and eastern Bhutan is temperate and drier than the west with warm summers and cool winters. Template:Inote
Economy
Bhutan's economy is one of the world's smallest and least developed, and is based on agriculture, forestry, and the sale of hydroelectric power to India. Agriculture provides the main livelihood for more than 90% of the population. Agrarian practices consist largely of subsistence farming and animal husbandry. Handicrafts are a small cottage industry and a source of income for many. Sculpting of religious figurines is a popular occupation, and gilded Buddha statues and Buddhist saints are sold to tourists. A landscape that varies from hilly to ruggedly mountainous has made the building of roads, and other infrastructure difficult and expensive. This, and a lack of access to the sea, has meant that Bhutan has never been able to benefit from significant trading of its produce. Bhutan currently does not have a railway system, though the Indian Railways plans to link up southern Bhutan with its vast network under an agreement signed in January 2005.[1] Historically, there have been well patronised trading routes from the Tibetan plateau to the Indian subcontinent through Bhutan, but haulage has been limited to human porters and livestock. The industrial sector is minimal, production being of the cottage-industry type. Most development projects, such as road construction, rely on Indian contract labour. Agricultural produce includes rice, corn, root crops, citrus, food grains, dairy products and eggs. Industries include cement, wood products, processed fruits, alcoholic beverages and calcium carbide.Template:Inote
Bhutan's currency, the ngultrum, is pegged to the Indian Rupee. The rupee is also accepted as legal tender in the country. Incomes of over Nu 100,000 per annum are taxed, but very few wage and salary earners qualify. Bhutan's inflation rate was estimated at about 3% in 2003. Bhutan has a Gross Domestic Product of around USD 2,913 million (adjusted to Purchasing Power Parity), making it the 162nd largest economy in the world. Per capita income is around $1,400 (€1,170), ranked 124th. Government revenues total €122 million ($146 million), though expenditures amount to €127 million ($152 million). 60%Template:Inote of the budget expenditure, however, is financed by India's Ministry of External Affairs.[2] Bhutan's exports of mainly electricity, cardamom, gypsum, timber, handicrafts, cement, fruit, precious stones and spices total €128 million ($154 million) (2000 est.). Imports, however, total €164 million ($196 million), leading to a trade deficit. Main items imported include fuel and lubricants, grain, machinery, vehicles, fabrics and rice. Bhutan's main export partner is India, exporting 87.9% of its goods to that country. Bangladesh (4.6%) and the Philippines (2%) are the other two top exporting partners. As its border with Tibet is closed, trade between Bhutan and China is now almost non-existent. Bhutan's import partners include India (71.3%), Japan (7.8%) and Austria (3%).Template:Inote
In a response to accusations in 1987 by a journalist from UK's Financial Times that the pace of development in Bhutan was slow, the King said that "Gross National Happiness is more important than Gross National Product." [3] This statement appears to have presaged recent findings by western economic psychologists, including 2002 Nobel Laureate Daniel Kahneman, that questions the link between levels of income and happiness. It signalled his commitment to building an economy that is appropriate for Bhutan's unique culture, based on Buddhist spiritual values, and has served as a unifying vision for the economy.
Government and politics

Bhutan's head of state is the Dragon King, or Druk Gyalpo, presently Jigme Singye Wangchuck. Although his title is hereditary, he can be removed by a two-thirds majority vote by the parliament, the unicameral National Assembly, or Tshogdu. The 154-seat National Assembly is composed of locally elected town representatives (105), religious representatives (12), and members nominated by the king (37), all of whom serve a three-year term. Suffrage in Bhutan is unique in that each family-unit, rather than individual, has one vote.
In 1998, the monarch's executive powers were transferred to the council of ministers, or cabinet (Lhengye Shungtsog). Candidates for the council of ministers are elected by the National Assembly for a fixed, five-year term, and must be a part of the legislative assembly. The cabinet is headed by the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. The post of Prime Minister rotates each year between the five candidates who secured the highest number of votes. Recently, a new constitution that includes provision for a two-party democratic system was unveiled after four years of preparation. This constitution is likely to be put to the people in a referendum at the end of 2005; at the behest of the monarch, the referendum proposes a significant reduction in his powers.
In Bhutan's judicial system, the monarch is the final court of appeal (the "Supreme Court of Appeal"). The Royal High Court of Bhutan is the highest court in the country. The Royal High Court has original jurisdiction over the 20 districts of the nation. Bhutan's legal system is based on Indian law and English common law. Judicial appointments are made by the monarch.
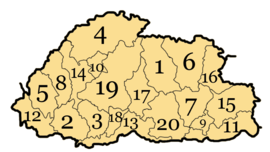
Districts
For administrative purposes, Bhutan is divided into four dzongdey (administrative zones). Each dzongdey is further divided into dzongkhag (districts). There are 20 dzongkhag in Bhutan. Large dzongkhags are further divided into subdistricts known as dungkhag. At the basic level, groups of villages form a constituency called gewog and is administered by gup, who is elected by the people.
|
Military and foreign affairs
- Main articles: Military of Bhutan, Foreign relations of Bhutan
The Royal Bhutan Army is Bhutan's military service. It includes the Royal Bodyguard and the Royal Bhutan Police. Membership is voluntary, and the minimum age for recruitment is 18. The standing army numbers about 6,000 and is trained by the Indian Army.[4] It has an annual budget of about US$13.7 million—1.8% of the GDP.
India handles most of Bhutan's foreign affairs by way of conducting formal communications to and from other countries as Bhutan has a shortage of diplomatic personnel. Template:Inote Bhutan sometimes seeks India's advice on external affairs, but is not obliged to follow it. Bhutan has diplomatic relations with 22 countries, including the European Union, with missions in India, Bangladesh, Thailand and Kuwait. It has two UN missions, one in New York and one in Geneva. Only India and Bangladesh have residential embassies in Bhutan, while Thailand has consulate office in Bhutan. By a longstanding treaty, Indian and Bhutanese citizens may travel to each others' countries without a passport or visa. Bhutanese citizens may also work in India without legal restriction. Bhutan does not have formal diplomatic ties with its northern neighbour, China, although exchanges of visits at various levels between the two have significantly increased in the recent past. Bhutan’s border with China is largely undemarcated and thus disputed in some places. Both countries hope to resolve the dispute amicably and quietly.[5]
Demographics

Citizens of Bhutan are called Bhutanese. Bhutan has a population of 2,232,291[6], with a density of 45 per square kilometer and a growth rate of 2.11 percent per year. The Drukpa Kagyu school of Mahayana Buddhism is the state religion of Bhutan and its adherents comprise 70 percent of the population. In south Bhutan, Hinduism is the predominant religion, with 25 percent of the population. About 5 percent of Bhutanese are Islamic.Template:Inote
The Bhutia are the largest ethnic group in the country, comprising about half of the population. Ethnic Nepalese make up 35 percent, and southwestern tribes such as the Sharchops make up 5 percent. Template:Inote
Dzongkha is the national language and lingua franca. Chhokey, a form of Tibetan script, is used for writing. The government recognizes 19 dialects of Dzongkha. English also has official status. In some southern dzongkhags, Nepali is spoken by a minority. Ngalopkha, a derivative of Tibetan, is spoken in parts of western Bhutan. Sharchopkh, also called Tshangla, is spoken in the eastern parts. Ethnologue lists 24 languages currently spoken in Bhutan, all of them in the Tibeto-Burman family - except Nepali, an Indo-European language.
The literacy rate is only 42.2 percent (56.2 percent of males and 28.1 percent of females). People 14 years old and younger comprise 39.1 percent, while people between 15 and 59 comprise 56.9 percent, and those over 60 are only 4 percent. The country had a median age of 20.4 years. Bhutan has a low life expectancy of 54.4 years (54.7 for males and 54.1 for females). There are 1070 males to every 1000 females in the country.Template:Inote
Over half of the people live in the central highlands of Bhutan, and 40 percent live in the southern plains bordering India. The remaining 10 percent are dispersed in the northern mountains and in the eastern tracts. Ninety-two percent of the population live in rural settlements. The largest town is the capital, Thimpu, has a population of 50,000.
Culture
Bhutan remains one of the most secluded nations in the world, and foreigners are not permitted to travel to many of its areas to minimise the effects of tourism on the local culture.
The traditional dress for men is the gho, a knee-length robe tied at the waist by a cloth belt known as the kera. Women wear an ankle-length dress, the kira, which is clipped at one shoulder and tied at the waist. An accompaniment to the kira is a long-sleeved blouse, which is worn underneath the outer layer. Social status and class is determined by the texture, colours, and decorations that embellish the garments. Scarves and shawls are also indicators of social standings. Earrings are worn by both males and females.
Rice and, increasingly, corn are the staple foods of the country. The diet in the hills is rich in protein because of the consumption of meat—chiefly poultry, yak and mutton. Soups of meat, rice, and corn spiced with chillies are a favourite meal during the cold seasons. Soups, rice or corn, and curries spiced with chillies are major components of the Bhutanese diet. Dairy foods, particularly butter and cheese from yaks and cows, are also popular, despite the scarcity of milk. Popular beverages include butter tea and beer. Bhutan is the only country in the world to have banned tobacco smoking and sale of tobacco.

Bhutan's national sport is archery, and competitions are held regularly in most villages. Another traditional sport is the digor, a type of shot put. Soccer is an increasingly popular sport. Rigsagar is the dominant style of popular music, played on a stringed instrument, and dates back to the late 1960s; it shows the influence of Indian popular music, a hybrid form of traditional and Western popular influences. Traditional genres include the zhungdra and boedra. Characteristic of the region is a type of fortress known as dzong architecture.

Bhutan has numerous public holidays, most of which centre around traditional seasonal, secular and religious festivals. They include winter solstice (around January 1, depending on the lunar calendar), lunar New Year (January or February), the king's birthday and the anniversary of his coronation, the official start of monsoon season (September 22), National Day (December 17), and various Buddhist and Hindu celebrations. Even the secular holidays have religious overtones, including religious dances and prayers for blessing the day.
Masked dances and dance dramas are common traditional features at festivals, usually accompanied by traditional music. Energetic dancers, wearing colourful wooden or composition facemasks and stylised costumes, depict heroes, demons, death heads, animals, gods, and caricatures of common people. The dancers enjoy royal patronage, and preserve ancient folk and religious customs and perpetuate the ancient art of mask making.
The Kuensel is Bhutan's only newspaper, circulated biweekly in Dzongkha, English and Nepali. Bhutan has about 15,000 Internet users, 25,200 landline users, and 23,000 mobile phone subscribers. The Bhutan Broadcasting Service was established in 1973 as a radio service, broadcasting in short wave nationally, and on the FM band in Thimpu. The service started television broadcasts in 1999, and was the last country in the world to introduce television. As part of its modernization program, the ban on television was lifted and cable television was introduced. By 2002, however, the crime rate had increased appreciably, and the introduction of cable television is alleged to be responsible for the spurt in crime.[7]
See also
- List of Bhutan-related topics
- Communications in Bhutan
- Districts of Bhutan
- Foreign relations of Bhutan
- Military of Bhutan
- Music of Bhutan
- Transport in Bhutan
External links
- Government of Bhutan portal
- Department of Tourism — Official tourism bureau site
- The Centre for Bhutan Studies — Research and scholarship on Bhutan
- Template:Wikitravel
Notes
- ^ The Tribune
- ^ India's Ministry of External Affairs provides financial aid to neighbouring countries under "technical and economic cooperation with other countries and advances to foreign governments." The Tribune, Chandigarh
- ^ Yoga Journal
- ^ Asian Times
- ^ Bhutan News Online
- ^ Official Bhutan government figure is much smaller than the figure mentioned here, which is sourced from the CIA factbook. The reason for this discrepancy is that Nepali citizens who do not meet the citizenship critera are not counted in the official national census. All figures on this page are quoted from the CIA factbook.
- ^ Fast forward into trouble, The Guardian
References
- "A Country Study: Bhutan". Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Bhutan". CIA World Factbook. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Bhutan Portal". Government of Bhutan. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Bhutan". MSN Encarta. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Bhutan army sees action at last". Asia Times Online. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Bhutan-China Relations". Bhutan News Online. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "MoUs with Bhutan on rail links, power projects". The Tribune, Chandigarh. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Border tension pushes MEA allocation". The Tribune, Chandigarh. September 8.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Happy Land". Yoga Journal. September 12.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Fast forward into trouble". The Guardian Unlimited. September 16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "A New Measure of Well-Being From a Happy Little Kingdom". The New York Times. October 4.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - . ISBN 8187592079.
{{cite book}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|Author=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|Publisher=ignored (|publisher=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|Title=ignored (|title=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|Year=ignored (|year=suggested) (help)
