Psoriasis
| Psoriasis | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Psoriasis is a long-lasting autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin.[1] These skin patches are typically red, itchy, and scaly. They may vary in severity from small and localized to complete body coverage.[2] Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as Koebner phenomenon.[3]
There are five main types of psoriasis: plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic.[1] Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents with red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, around the belly button, and the scalp.[4] Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions.[1] Pustular psoriasis presents with small non-infectious pus-filled blisters.[5] Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds.[1] Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread, and can develop from any of the other types. Fingernails and toenails are affected in most people at some point in time. This may include pits in the nails or changes in nail color.[4]
Psoriasis is generally thought to be a genetic disease which is triggered by environmental factors.[2] In twin studies, identical twins are three times more likely to both be affected compared to non-identical twins; this suggests that shared genetic risk factors predispose to psoriasis. Symptoms often worsen during winter and with certain medications such as beta blockers or NSAIDs.[4] Infections and psychological stress may also play a role.[1][2] Psoriasis is not contagious. The underlying mechanism involves the immune system reacting to skin cells. Diagnosis is typically based on the signs and symptoms.[4]
There is no cure for psoriasis. However, various treatments can help control the symptoms.[4] These treatments may include steroid creams, vitamin D3 cream, ultraviolet light, and immune system suppressing medications such as methotrexate.[1] About 75% of cases can be managed with creams alone.[4] The disease affects 2–4% of the population.[6] Men and women are affected with equal frequency.[1] Psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of psoriatic arthritis, lymphomas, cardiovascular disease, Crohn's disease, and depression.[4] Psoriatic arthritis affects up to 30% of individuals with psoriasis.[5]
Signs and symptoms
Plaque

Psoriasis vulgaris (also known as chronic stationary psoriasis or plaque-like psoriasis) is the most common form and affects 85%–90% of people with psoriasis.[7] Plaque psoriasis typically appears as raised areas of inflamed skin covered with silvery-white scaly skin. These areas are called plaques and are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and back.[7][8] Psoriatic erythroderma (erythrodermic psoriasis) involves widespread inflammation and exfoliation of the skin over most of the body surface. It may be accompanied by severe itching, swelling, and pain. It is often the result of an exacerbation of unstable plaque psoriasis, particularly following the abrupt withdrawal of systemic glucocorticoids.[9] This form of psoriasis can be fatal as the extreme inflammation and exfoliation disrupt the body's ability to regulate temperature and perform barrier functions.[10]
-
Plaques of psoriasis
-
A person's arm covered with plaque psoriasis
-
Psoriasis of the palms
Pustular

Pustular psoriasis appears as raised bumps filled with noninfectious pus (pustules).[11] The skin under and surrounding the pustules is red and tender.[12] Pustular psoriasis can be localized, commonly to the hands and feet (palmoplantar pustulosis), or generalized with widespread patches occurring randomly on any part of the body. Acrodermatitis continua is a form of localized psoriasis limited to the fingers and toes that may spread to the hands and feet.[12] Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris is another form of localized pustular psoriasis similar to acrodermatitis continua with pustules erupting from red, tender, scaly skin found on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet.[12]
Generalized pustular psoriasis (pustular psoriasis of von Zumbusch), also known as impetigo herpetiformis during pregnancy,[13] is a rare and severe form of psoriasis that may require hospitalization. The development of generalized pustular psoriasis is often caused by an infection, abrupt withdrawal of topical corticosteroid treatment, pregnancy, hypocalcemia, medications, or following an irritating topical treatment for plaque psoriasis.[12] This form of psoriasis is characterized by an acute onset of numerous pustules on top of tender red skin. This skin eruption is often accompanied by a fever, muscle aches, nausea, and an elevated white blood cell count.[12] Annular pustular psoriasis (APP), a rare form of generalized pustular psoriasis, is the most common type seen during childhood.[13] APP tends to occur in women more frequently than in men, and is usually less severe than other forms of generalized pustular psoriasis such as impetigo herpetiformis.[13] This form of psoriasis is characterized by ring-shaped plaques with pustules around the edges and yellow crusting.[13] APP most often affects the torso, neck, arms, and legs.[13]
Other skin lesions


Additional types of psoriasis affecting the skin include inverse psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, oral psoriasis, and seborrheic-like psoriasis.[14]
Inverse psoriasis (also known as flexural psoriasis) appears as smooth, inflamed patches of skin. The patches frequently affect skin folds, particularly around the genitals (between the thigh and groin), the armpits, in the skin folds of an overweight abdomen (known as panniculus), between the buttocks in the intergluteal cleft, and under the breasts in the inframammary fold. Heat, trauma, and infection are thought to play a role in the development of this atypical form of psoriasis.[15] Napkin psoriasis is a subtype of psoriasis common in infants characterized by red papules with silver scale in the diaper area that may extend to the torso or limbs.[16] Napkin psoriasis is often misdiagnosed as napkin dermatitis (diaper rash).[17]
Guttate psoriasis is characterized by numerous small, scaly, red or pink, droplet-like lesions (papules). These numerous spots of psoriasis appear over large areas of the body, primarily the trunk, but also the limbs and scalp. Guttate psoriasis is often triggered by a streptococcal infection, typically streptococcal pharyngitis.[15] The reverse is not true.
Oral psoriasis is very rare,[18] in contrast to lichen planus, another common papulosquamous disorder that commonly involves both the skin and mouth. When psoriasis involves the oral mucosa (the lining of the mouth), it may be asymptomatic,[18] but it may appear as white or grey-yellow plaques.[18] Fissured tongue is the most common finding in those with oral psoriasis and has been reported to occur in 6.5–20% of people with psoriasis affecting the skin. The microscopic appearance of oral mucosa affected by geographic tongue (migratory stomatitis) is very similar to the appearance of psoriasis.[19] However, modern studies have failed to demonstrate any link between the two conditions.[20]
Seborrheic-like psoriasis is a common form of psoriasis with clinical aspects of psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis, and may be difficult to distinguish from the latter. This form of psoriasis typically manifests as red plaques with greasy scales in areas of higher sebum production such as the scalp, forehead, skin folds next to the nose, skin surrounding the mouth, skin on the chest above the sternum, and in skin folds.[16]
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of chronic inflammatory arthritis that has a highly variable clinical presentation and frequently occurs in association with skin and nail psoriasis.[21][22] It typically involves painful inflammation of the joints and surrounding connective tissue and can occur in any joint, but most commonly affects the joints of the fingers and toes. This can result in a sausage-shaped swelling of the fingers and toes known as dactylitis.[21] Psoriatic arthritis can also affect the hips, knees, spine (spondylitis), and sacroiliac joint (sacroiliitis).[23] About 30% of individuals with psoriasis will develop psoriatic arthritis.[7] Skin manifestations of psoriasis tend to occur before arthritic manifestations in about 75% of cases.[22]
Nail changes
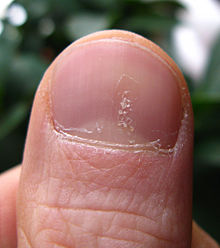

Psoriasis can affect the nails and produces a variety of changes in the appearance of finger and toe nails. Nail psoriasis occurs in 40–45% of people with psoriasis affecting the skin and has a lifetime incidence of 80–90% in those with psoriatic arthritis.[24] These changes include pitting of the nails (pinhead-sized depressions in the nail is seen in 70% with nail psoriasis), whitening of the nail, small areas of bleeding from capillaries under the nail, yellow-reddish discoloration of the nails known as the oil drop or salmon spot, thickening of the skin under the nail (subungual hyperkeratosis), loosening and separation of the nail (onycholysis), and crumbling of the nail.[24]
Medical signs
In addition to the appearance and distribution of the rash, specific medical signs may be used by medical practitioners to assist with diagnosis. These may include Auspitz's sign (pinpoint bleeding when scale is removed), Koebner phenomenon (psoriatic skin lesions induced by trauma to the skin),[16] and itching and pain localized to papules and plaques.[15][16]
Causes
The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but a number of theories exist.
Genetics
Around one-third of people with psoriasis report a family history of the disease, and researchers have identified genetic loci associated with the condition. Identical twin studies suggest a 70% chance of a twin developing psoriasis if the other twin has the disorder. The risk is around 20% for nonidentical twins. These findings suggest both a genetic susceptibility and an environmental response in developing psoriasis.[25]
Psoriasis has a strong hereditary component, and many genes are associated with it, but it is unclear how those genes work together. Most of the identified genes relate to the immune system, particularly the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and T cells. Genetic studies are valuable due to their ability to identify molecular mechanisms and pathways for further study and potential drug targets.[26]
Classic genome-wide linkage analysis has identified nine loci on different chromosomes associated with psoriasis. They are called psoriasis susceptibility 1 through 9 (PSORS1 through PSORS9). Within those loci are genes on pathways that lead to inflammation. Certain variations (mutations) of those genes are commonly found in psoriasis.[26] Genome-wide association scans have identified other genes that are altered to characteristic variants in psoriasis. Some of these genes express inflammatory signal proteins, which affect cells in the immune system that are also involved in psoriasis. Some of these genes are also involved in other autoimmune diseases.[26]
The major determinant is PSORS1, which probably accounts for 35%–50% of psoriasis heritability.[27] It controls genes that affect the immune system or encode skin proteins that are overabundant with psoriasis. PSORS1 is located on chromosome 6 in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), which controls important immune functions. Three genes in the PSORS1 locus have a strong association with psoriasis vulgaris: HLA-C variant HLA-Cw6,[28] which encodes a MHC class I protein; CCHCR1, variant WWC, which encodes a coiled protein that is overexpressed in psoriatic epidermis; and CDSN, variant allele 5, which encodes corneodesmosin, a protein which is expressed in the granular and cornified layers of the epidermis and upregulated in psoriasis.[26]
Two major immune system genes under investigation are interleukin-12 subunit beta (IL12B) on chromosome 5q, which expresses interleukin-12B; and IL23R on chromosome 1p, which expresses the interleukin-23 receptor, and is involved in T cell differentiation. Interleukin-23 receptor and IL12B have both been strongly linked with psoriasis.[28] T cells are involved in the inflammatory process that leads to psoriasis.[26] These genes are on the pathway that up-regulate tumor necrosis factor-α and nuclear factor κB, two genes involved in inflammation.[26] Recently, the first gene directly linked to psoriasis has been identified. A rare mutation in the gene encoding for the CARD14 protein plus an environmental trigger was enough to cause plaque psoriasis (the most common form of psoriasis).[29][30]
Lifestyle
Conditions reported as accompanying a worsening of the disease include chronic infections, stress, and changes in season and climate.[28] Others include hot water, scratching psoriasis skin lesions, skin dryness, excessive alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, and obesity.[28][31][32]
HIV
The rate of psoriasis in HIV-positive individuals is comparable to that of HIV-negative individuals, however, psoriasis tends to be more severe in people infected with HIV.[33] A much higher rate of psoriatic arthritis occurs in HIV-positive individuals with psoriasis than in those without the infection.[33] The immune response in those infected with HIV is typically characterized by cellular signals from Th2 subset of CD4+ helper T cells,[34] whereas the immune response in psoriasis vulgaris is characterized by a pattern of cellular signals typical of Th1 subset of CD4+ helper T cells and Th17 helper T cells.[35][36] It is hypothesized that the diminished CD4+-T cell presence causes an overactivation of CD8+-T cells, which are responsible for the exacerbation of psoriasis in HIV-positive people. Psoriasis in those with HIV/AIDS is often severe and may be untreatable with conventional therapy.[37]
Microbes
Psoriasis has been described as occurring after strep throat, and may be worsened by skin or gut colonization with Staphylococcus aureus, Malassezia, and Candida albicans.[38]
Medications
Drug-induced psoriasis may occur with beta blockers,[5] lithium,[5] antimalarial medications,[5] non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,[5] terbinafine, calcium channel blockers, captopril, glyburide, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor,[5] interleukins, interferons,[5] lipid-lowering drugs,[14]: 197 and paradoxically TNF inhibitors such as infliximab or adalimumab.[39] Withdrawal of corticosteroids (topical steroid cream) can aggravate psoriasis due to the rebound effect.[40]
Mechanism
Psoriasis is characterized by an abnormally excessive and rapid growth of the epidermal layer of the skin.[41] Abnormal production of skin cells (especially during wound repair) and an overabundance of skin cells result from the sequence of pathological events in psoriasis.[12] Skin cells are replaced every 3–5 days in psoriasis rather than the usual 28–30 days.[42] These changes are believed to stem from the premature maturation of keratinocytes induced by an inflammatory cascade in the dermis involving dendritic cells, macrophages, and T cells (three subtypes of white blood cells).[7][33] These immune cells move from the dermis to the epidermis and secrete inflammatory chemical signals (cytokines) such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, interleukin-36 and interleukin-22.[26][43] These secreted inflammatory signals are believed to stimulate keratinocytes to proliferate.[26] One hypothesis is that psoriasis involves a defect in regulatory T cells, and in the regulatory cytokine interleukin-10.[26]
Gene mutations of proteins involved in the skin's ability to function as a barrier have been identified as markers of susceptibility for the development of psoriasis.[44][45]
DNA released from dying cells acts as an inflammatory stimulus in psoriasis[46] and stimulates the receptors on certain dendritic cells, which in turn produce the cytokine interferon-α.[46] In response to these chemical messages from dendritic cells and T cells, keratinocytes also secrete cytokines such as interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α, which signal downstream inflammatory cells to arrive and stimulate additional inflammation.[26]
Dendritic cells bridge the innate immune system and adaptive immune system. They are increased in psoriatic lesions[41] and induce the proliferation of T cells and type 1 helper T cells (Th1). Targeted immunotherapy as well as psoralen and ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy can reduce the number of dendritic cells and favors a Th2 cell cytokine secretion pattern over a Th1/Th17 cell cytokine profile.[26][35] Psoriatic T cells move from the dermis into the epidermis and secrete interferon-γ and interleukin-17.[47] Interleukin-23 is known to induce the production of interleukin-17 and interleukin-22.[41][47] Interleukin-22 works in combination with interleukin-17 to induce keratinocytes to secrete neutrophil-attracting cytokines.[47]
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of psoriasis is usually based on the appearance of the skin. Skin characteristics typical for psoriasis are scaly, erythematous plaques, papules, or patches of skin that may be painful and itch.[15] No special blood tests or diagnostic procedures are needed to make the diagnosis.[12][48]
The differential diagnosis of psoriasis includes dermatological conditions similar in appearance such as discoid eczema, seborrhoeic eczema, pityriasis rosea (may be confused with guttate psoriasis), nail fungus (may be confused with nail psoriasis) or cutaneous T cell lymphoma (50% of individuals with this cancer are initially misdiagnosed with psoriasis).[40] Dermatologic manifestations of systemic illnesses such as the rash of secondary syphilis may also be confused with psoriasis.[40]
If the clinical diagnosis is uncertain, a skin biopsy or scraping may be performed to rule out other disorders and to confirm the diagnosis. Skin from a biopsy will show clubbed epidermal projections that interdigitate with dermis on microscopy. Epidermal thickening is another characteristic histologic finding of psoriasis lesions.[12][49] The stratum granulosum layer of the epidermis is often missing or significantly decreased in psoriatic lesions; the skin cells from the most superficial layer of skin are also abnormal as they never fully mature. Unlike their mature counterparts, these superficial cells keep their nucleus.[12] Inflammatory infiltrates can typically be visualized on microscopy when examining skin tissue or joint tissue affected by psoriasis. Epidermal skin tissue affected by psoriatic inflammation often has many CD8+ T cells while a predominance of CD4+ T cells make up the inflammatory infiltrates of the dermal layer of skin and the joints.[12]
Classification
Morphological
| Psoriasis Type | ICD-10 Code |
|---|---|
| Psoriasis vulgaris | L40.0 |
| Generalized pustular psoriasis | L40.1 |
| Acrodermatitis continua | L40.2 |
| Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris | L40.3 |
| Guttate psoriasis | L40.4 |
| Psoriatic arthritis | L40.50 |
| Psoriatic spondylitis | L40.53 |
| Inverse psoriasis | L40.8 |
Psoriasis is classified as a papulosquamous disorder and is most commonly subdivided into different categories based on histological characteristics.[2][5] Variants include plaque, pustular, guttate, and flexural psoriasis. Each form has a dedicated ICD-10 code.[50] Psoriasis can also be classified into nonpustular and pustular types.[51]
Pathogenetic
Another classification scheme considers genetic and demographic factors. Type 1 has a positive family history, starts before the age of 40, and is associated with the human leukocyte antigen, HLA-Cw6. Conversely, type 2 does not show a family history, presents before age 40, and is not associated with HLA-Cw6.[52] Type 1 accounts for about 75% of persons with psoriasis.[53]
The classification of psoriasis as an autoimmune disease has sparked considerable debate. Researchers have proposed differing descriptions of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis; some authors have classified them as autoimmune diseases[12][28][54] while others have classified them as distinct from autoimmune diseases and referred to them as immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.[26][55][56]
Severity

There is no consensus about how to classify the severity of psoriasis. Mild psoriasis has been defined as a percentage of body surface area (BSA)≤10, a Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) score ≤10, and a dermatology life quality index (DLQI) score ≤10.[57] Moderate to severe psoriasis was defined by the same group as BSA >10 or PASI score >10 and a DLQI score >10.[57] The DLQI is a 10 question tool used to measure the impact of several dermatologic diseases on daily functioning. The DLQI score ranges from 0 (minimal impairment) to 30 (maximal impairment) and is calculated with each answer being assigned 0–3 points with higher scores indicating greater social or occupational impairment.[58]
The psoriasis area severity index (PASI) is the most widely used measurement tool for psoriasis. PASI assesses the severity of lesions and the area affected and combines these two factors into a single score from 0 (no disease) to 72 (maximal disease).[59] Nevertheless, the PASI can be too unwieldy to use outside of research settings, which has led to attempts to simplify the index for clinical use.[60]
Management

While no cure is available for psoriasis,[40] many treatment options exist. Topical agents are typically used for mild disease, phototherapy for moderate disease, and systemic agents for severe disease.[61]
Topical agents
Topical corticosteroid preparations are the most effective agents when used continuously for 8 weeks; retinoids and coal tar were found to be of limited benefit and may be no better than placebo.[62] Greater benefit has been observed with very potent corticosteroids when compared to potent corticosteroids. Vitamin D analogues such as paricalcitol were found to be significantly superior to placebo. Combination therapy with vitamin D and a corticosteroid was superior to either treatment alone and vitamin D was found to be superior to coal tar for chronic plaque psoriasis.[63]
Moisturizers and emollients such as mineral oil, petroleum jelly, calcipotriol, and decubal (an oil-in-water emollient) were found to increase the clearance of psoriatic plaques. Emollients have been shown to be even more effective at clearing psoriatic plaques when combined with phototherapy.[64] However, certain emollients have no impact on psoriasis plaque clearance or may even decrease the clearance achieved with phototherapy. The emollient salicylic acid is structurally similar to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), commonly found in sunscreen, and is known to interfere with phototherapy in psoriasis. Coconut oil, when used as an emollient in psoriasis, has been found to decrease plaque clearance with phototherapy.[64] Medicated creams and ointments applied directly to psoriatic plaques can help reduce inflammation, remove built-up scale, reduce skin turnover, and clear affected skin of plaques. Ointment and creams containing coal tar, dithranol, corticosteroids (i.e. desoximetasone), fluocinonide, vitamin D3 analogs (for example, calcipotriol), and retinoids are routinely used. The use of the finger tip unit may be helpful in guiding how much topical treatment to use.[31][65]
Vitamin D analogues may be useful with steroids; however, alone have a higher rate of side effects.[66] They may allow less steroids to be used.[67]
Another topical therapy used to treat psoriasis is a form of balneotherapy, which involves daily baths in the Dead Sea. This is usually done for four weeks with the benefit attributed to sun exposure. This is cost-effective and it has been propagated as an effective way to treat psoriasis without medication.[68] Decreases of PASI scores greater than 75% and remission for several months have commonly been observed.[68] Side-effects may be mild such as itchiness, folliculitis, sunburn, poikiloderma, and a theoretical risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer or melanoma has been suggested.[68] However, more recent studies have determined that there does not appear to be increased risk of melanoma in the long-term.[69] Data are inconclusive with respect to nonmelanoma skin cancer risk, but support the idea that the therapy is associated with an increased risk of benign forms of sun-induced skin damage such as, but not limited to, actinic elastosis or liver spots.[69] Dead Sea balneotherapy is also effective for psoriatic arthritis.[69]
Phototherapy
Phototherapy in the form of sunlight has long been used for psoriasis.[61] Wavelengths of 311–313 nanometers are most effective, and special lamps have been developed for this application.[61] The exposure time should be controlled to avoid over exposure and burning of the skin. The UVB lamps should have a timer that will turn off the lamp when the time ends. The amount of light used is determined by a person's skin type.[61] Increased rates of cancer from treatment appear to be small.[61] Narrow band UVB light (NBUVB) phototherapy has been demonstrated to have similar efficacy to PUVA.[70]
A major mechanism of NBUVB is the induction of DNA damage in the form of pyrimidine dimers. This type of phototherapy is useful in the treatment of psoriasis because the formation of these dimers interferes with the cell cycle and stops it. The interruption of the cell cycle induced by NBUVB opposes the characteristic rapid division of skin cells seen in psoriasis.[70] The activity of many types of immune cells found in the skin is also effectively suppressed by NBUVB phototherapy treatments. The most common short-term side effect of this form of phototherapy is redness of the skin; less common side effects of NBUVB phototherapy are itching and blistering of the treated skin, irritation of the eyes in the form of conjunctival inflammation or inflammation of the cornea, or cold sores due to reactivation of the herpes simplex virus in the skin surrounding the lips. Eye protection is usually given during phototherapy treatments.[70]
Psoralen and ultraviolet A phototherapy (PUVA) combines the oral or topical administration of psoralen with exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) light. The mechanism of action of PUVA is unknown, but probably involves activation of psoralen by UVA light, which inhibits the abnormally rapid production of the cells in psoriatic skin. There are multiple mechanisms of action associated with PUVA, including effects on the skin's immune system. PUVA is associated with nausea, headache, fatigue, burning, and itching. Long-term treatment is associated with squamous cell carcinoma (but not with melanoma).[32][71] A combination therapy for moderate to severe psoriasis using PUVA plus acitretin resulted in benefit, but acitretin use has been associated with birth defects and liver damage.[72]
Systemic agents

Psoriasis resistant to topical treatment and phototherapy may be treated with systemic therapies including oral medications or injectable treatments.[73] Patients undergoing systemic treatment must have regular blood and liver function tests to check for medication toxicities.[73] Pregnancy must be avoided for most of these treatments. The majority of people experience a recurrence of psoriasis after systemic treatment is discontinued.
Non-biologic systemic treatments frequently used for psoriasis include methotrexate, ciclosporin, hydroxycarbamide, fumarates such as dimethyl fumarate, and retinoids.[74] Methotrexate and ciclosporin are drugs that suppress the immune system; retinoids are synthetic forms of vitamin A. These agents are also regarded as first-line treatments for psoriatic erythroderma.[9]
Biologics are manufactured proteins that interrupt the immune process involved in psoriasis. Unlike generalised immunosuppressive drug therapies such as methotrexate, biologics target specific aspects of the immune system contributing to psoriasis.[74] These medications are generally well-tolerated and limited long-term outcome data have demonstrated biologics to be safe for long-term use in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.[74][75] However, due to their immunosuppressive actions, biologics have been associated with a small increase in the risk for infection.[74] Professional guidelines regard biologics as third-line treatment for plaque psoriasis following inadequate response to topical treatment, phototherapy, and non-biologic systemic treatments.[75] The safety of biologics during pregnancy has not been assessed. European guidelines recommend avoiding biologics if a pregnancy is planned; anti-TNF therapies such as infliximab are not recommended for use in chronic carriers of the hepatitis B virus or individuals infected with HIV.[74]
Several monoclonal antibodies target cytokines, the molecules that cells use to send inflammatory signals to each other. TNF-α is one of the main executor inflammatory cytokines. Four monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) (infliximab, adalimumab, golimumab, and certolizumab pegol) and one recombinant TNF-α decoy receptor, etanercept, have been developed to inhibit TNF-α signaling. Additional monoclonal antibodies have been developed against pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-12, interleukin-23 and interleukin-17[76] and inhibit the inflammatory pathway at a different point than the anti-TNF-α antibodies.[26] IL-12 and IL-23 share a common domain, p40, which is the target of the recently FDA-approved ustekinumab.[28]
Two drugs that target T cells are efalizumab and alefacept. Efalizumab is a monoclonal antibody that specifically targets the CD11a subunit of LFA-1.[74] It also blocks the adhesion molecules on the endothelial cells that line blood vessels, which attract T cells. Efalizumab was voluntarily withdrawn from the European market in February 2009 and from the US market in June 2009 by the manufacturer due to the medication's association with cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.[74] Alefacept also blocks the molecules that dendritic cells use to communicate with T cells and even causes natural killer cells to kill T cells as a way of controlling inflammation.[26]
Individuals with psoriasis may develop neutralizing antibodies against monoclonal antibodies. Neutralization occurs when an antidrug antibody prevents a monoclonal antibody such as infliximab from binding antigen in a laboratory test. Specifically, neutralization occurs when the antidrug antibody binds to infliximab's antigen binding site instead of TNF-α. When infliximab no longer binds tumor necrosis factor alpha, it no longer decreases inflammation, and the psoriasis may worsen. Neutralizing antibodies have not been reported against etanercept, a biologic-drug that is a fusion protein composed of two TNF-α receptors. The lack of neutralizing antibodies against etanercept is probably secondary to the innate presence of the TNF-α receptor, and the development of immune tolerance.[77]
Surgery
Limited evidence suggests removal of the tonsils may benefit people with chronic plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, and palmoplantar pustulosis.[78][79]
Alternative therapy
Uncontrolled studies have suggested that individuals with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis may benefit from a diet supplemented with fish oil rich in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).[80] Conflicting evidence exists indicating that there may be an increased incidence of psoriasis in people with celiac disease. Psoriatic disease severity decreased after 3 months of a gluten free diet in patients with anti-gliadin antibodies.[80]
Prognosis
Most people with psoriasis experience nothing more than mild skin lesions that can be treated effectively with topical therapies.[62]
Psoriasis is known to have a negative impact on the quality of life of both the affected person and the individual's family members.[28] Depending on the severity and location of outbreaks, individuals may experience significant physical discomfort and some disability. Itching and pain can interfere with basic functions, such as self-care and sleep.[42] Participation in sporting activities, certain occupations, and caring for family members can become difficult activities for those with plaques located on their hands and feet.[42] Plaques on the scalp can be particularly embarrassing, as flaky plaque in the hair can be mistaken for dandruff.[81]
Individuals with psoriasis may feel self-conscious about their appearance and have a poor self-image that stems from fear of public rejection and psychosexual concerns. Psoriasis has been associated with low self-esteem and depression is more common among those with the condition.[2] People with psoriasis often feel prejudiced against due to the commonly held incorrect belief that psoriasis is contagious.[42] Psychological distress can lead to significant depression and social isolation; a high rate of thoughts about suicide has been associated with psoriasis.[17] Many tools exist to measure the quality of life of patients with psoriasis and other dermatological disorders. Clinical research has indicated individuals often experience a diminished quality of life.[82] Children with psoriasis may encounter bullying.[83]
Several conditions are associated with psoriasis. These occur more frequently in older people. Nearly half of individuals with psoriasis over the age of 65 have at least three comorbidities, and two-thirds have at least two comorbidities.[84]
Cardiovascular disease
Psoriasis has been associated with obesity[2] and several other cardiovascular and metabolic disturbances. The incidence of diabetes is 27% higher in people affected by psoriasis than in those without the condition.[85] Severe psoriasis may be even more strongly associated with the development of diabetes than mild psoriasis.[85] Younger people with psoriasis may also be at increased risk for developing diabetes.[84][86] Individuals with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis have a slightly higher risk of heart disease and heart attacks when compared to the general population. Cardiovascular disease risk appeared to be correlated with the severity of psoriasis and its duration. There is no strong evidence to suggest that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of death from cardiovascular events. Methotrexate may provide a degree of protection for the heart.[32][84]
The odds of having hypertension are 1.58 times higher in people with psoriasis than those without the condition; these odds are even higher with severe cases of psoriasis. A similar association was noted in people who have psoriatic arthritis—the odds of having hypertension were found to be 2.07 times greater when compared to odds of the general population. The link between psoriasis and hypertension is not currently understood. Mechanisms hypothesized to be involved in this relationship include the following: dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system, elevated levels of endothelin 1 in the blood, and increased oxidative stress.[86][87] The incidence of the heart rhythm abnormality atrial fibrillation is 1.31 times higher in people with mild psoriasis and 1.63 times higher in people with severe psoriasis.[88] There may be a slightly increased risk of stroke associated with psoriasis, especially in severe cases.[32][89] Treating high levels of cholesterol with statins has been associated with decreased psoriasis severity, as measured by PASI score, and has also been associated with improvements in other cardiovascular disease risk factors such as markers of inflammation.[90] These cardioprotective effects are attributed to ability of statins to improve blood lipid profile and because of their anti-inflammatory effects. Statin use in those with psoriasis and hyperlipidemia was associated with decreased levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and TNFα as well as decreased activity of the immune protein LFA-1.[90] Compared to individuals without psoriasis, those affected by psoriasis are more likely to satisfy the criteria for metabolic syndrome.[12][88]
Other diseases
The rates of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are increased when compared with the general population, by a factor of 3.8 and 7.5 respectively.[2] Few studies have evaluated the association of multiple sclerosis with psoriasis, and the relationship has been questioned.[2][91] Psoriasis has been associated with a 16% increase in overall relative risk for non-skin cancer.[32] People with psoriasis have a 52% increased risk cancers of the lung and bronchus, a 205% increase in the risk of developing cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract, a 31% increase in the risk of developing cancers of the urinary tract, a 90% increase in the risk of developing liver cancer, and a 46% increase in the risk of developing pancreatic cancer.[32] The risk for development of non-melanoma skin cancers is also increased. Psoriasis increases the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin by 431% and increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma by 100%.[32] There is no increased risk of melanoma associated with psoriasis.[32]
Epidemiology
Psoriasis is estimated to affect 2–4% of the population of the western world.[6] The rate of psoriasis varies according to age, gender, region and ethnicity; a combination of environmental and genetic factors is thought to be responsible for these differences.[6] It can occur at any age, although it most commonly appears for the first time between the ages of 15 and 25 years. Approximately one third of psoriasis patients report being diagnosed before age 20.[92] Psoriasis affects both sexes equally.[52]
People with inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis are at an increased risk of developing psoriasis.[39] Psoriasis is more common in countries farther from the equator.[39] Persons of white European ancestry are more likely to have psoriasis and the condition is relatively uncommon in African Americans and extremely uncommon in Native Americans.[40]
History
Scholars believe psoriasis to have been included among the various skin conditions called tzaraath (translated as leprosy) in the Hebrew Bible, a condition imposed as a punishment for slander. The patient was deemed "impure" (see tumah and taharah) during their afflicted phase and is ultimately treated by the kohen.[93] However, it is more likely that this confusion arose from the use of the same Greek term for both conditions. The Greeks used the term lepra (λεπρα) for scaly skin conditions. They used the term psora to describe itchy skin conditions.[93] It became known as Willan's lepra in the late 18th century when English dermatologists Robert Willan and Thomas Bateman differentiated it from other skin diseases. Leprosy, they said, is distinguished by the regular, circular form of patches, while psoriasis is always irregular. Willan identified two categories: leprosa graecorum and psora leprosa.[94]
Psoriasis is thought to have first been described in Ancient Rome by Cornelius Celsus. The disease was first classified by English physician Thomas Willan. The British dermatologist Thomas Bateman described a possible link between psoriasis and arthritic symptoms in 1813.[95]
The history of psoriasis is littered with treatments of dubious effectiveness and high toxicity. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Fowler's solution, which contains a poisonous and carcinogenic arsenic compound, was used by dermatologists as a treatment for psoriasis.[93] Mercury was also used for psoriasis treatment during this time period.[93] Sulfur, iodine, phenol were also commonly used treatments for psoriasis during this era when it was incorrectly believed that psoriasis was an infectious disease.[93] Coal tars were widely used with ultraviolet light irradiation as a topical treatment approach in the early 1900s.[93][96] During the same time period, psoriatic arthritis cases were treated with intravenously administered gold preparations in the same manner as rheumatoid arthritis.[96] All of these treatments have been replaced with modern topical and systemic therapies.
Etymology
The word psoriasis is from Greek ψωρίασις, meaning "itching condition" or "being itchy"[97] from psora, "itch" and -iasis, "action, condition".
Society and culture
The International Federation of Psoriasis Associations (IFPA) is the global umbrella organization for national and regional psoriasis patient associations and also gathers the leading experts in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis research for scientific conferences every three years.[98] The Psoriasis International Network, a program of the Fondation René Touraine, gathers dermatologists, rheumatologists and other caregivers involved in the management of psoriasis. Non-profit organizations the National Psoriasis Foundation in the United States, the Psoriasis Association in the United Kingdom, and Psoriasis Australia offer advocacy and education about psoriasis in their respective countries.
Research
The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of psoriasis is currently under investigation. Preliminary research has suggested that antioxidants such as polyphenols may have beneficial effects on the inflammation characteristic of psoriasis.[99]
Many novel drugs being researched target the Th17/IL-23 axis,[99] particularly IL-23p19 inhibitors, as IL-23p19 is present in increased concentrations in psoriasis skin lesions while contributing less to protection against opportunistic infections.[100] Other cytokines such as IL-17 and IL-22 also have been targets for inhibition as they play important roles in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.[100] Another avenue of research has focused on the use of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors to treat psoriasis.[54] Oral agents being investigated as alternatives to medications administered by injection include Janus kinase inhibitors, protein kinase C inhibitors, mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors, and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, all of which have proven effective in various phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.[99][100] However, these agents have potentially severe side-effects due to their immunosuppressive mechanisms.[100]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g "Questions and Answers about Psoriasis". National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. October 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Menter, A.,Gottlieb, A., Feldman, S.R., Van Voorhees, A.S., Leonardi, C.L., Gordon, K.B., Lebwohl, M., Koo, JY., Elmets, C.A., Korman, N.J., Beutner, K.R., Bhushan, R. (May 2008). "Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 1. Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics". J Am Acad Dermatol. 58 (5): 826–50. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.02.039. PMID 18423260.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ely JW, Seabury Stone M (March 2010). "The generalized rash: part II. Diagnostic approach". Am Fam Physician. 81 (6): 735–9. PMID 20229972.
- ^ a b c d e f g Boehncke, WH; Schön, MP (26 May 2015). "Psoriasis". Lancet (London, England). 386: 983–94. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61909-7. PMID 26025581.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Jain, Sima (2012). Dermatology : illustrated study guide and comprehensive board review. New York: Springer. pp. 83–87. ISBN 978-1-4419-0524-6.
- ^ a b c Parisi R, Symmons DP, Griffiths CE, Ashcroft DM; Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team (February 2013). "Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence". J Invest Dermatol. 133 (2): 377–85. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339. PMID 23014338.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d Palfreeman AC, McNamee KE, McCann FE (March 2013). "New developments in the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a focus on apremilast". Drug Des Devel Ther. 7: 201–210. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S32713. PMC 3615921. PMID 23569359.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Colledge, N.R.; Walker, B.R.; Ralston, S.H., ed. (2010). Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (21st ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 1260–1261. ISBN 978-0-7020-3084-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ a b Zattra E, Belloni Fortina A, Peserico A, Alaibac M (May 2012). "Erythroderma in the era of biological therapies". Eur J Dermatol. 22 (2): 167–71. doi:10.1684/ejd.2011.1569. PMID 22321651.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stanway A. "Erythrodermic psoriasis". DermNet NZ. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
- ^ Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, Korman NJ, Lebwohl MG, Bebo BF Jr, Kalb RE (2012). "Treatment of pustular psoriasis: From the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation". J Am Acad Dermatol. 67 (2): 279–88. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.01.032. PMID 22609220.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Raychaudhuri SK, Maverakis E, Raychaudhuri SP (January 2014). "Diagnosis and classification of psoriasis". Autoimmun Rev. S1568-9972 (14): 00020–2. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.008. PMID 24434359.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Naik HB, Cowen EW (July 2013). "Autoinflammatory pustular neutrophilic diseases". Dermatol Clin. 31 (3): 405–25. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.04.001. PMC 3703099. PMID 23827244.
- ^ a b James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. pp. 191–7. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d Weigle N, McBane S (May 2013). "Psoriasis". Am Fam Physician. 87 (9): 626–33. PMID 23668525.
- ^ a b c d Gudjonsson JE, Elder JT, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, Wolff K (2012). "18: Psoriasis". Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine (8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-166904-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Gelmetti C (January 2009). "Therapeutic moisturizers as adjuvant therapy for psoriasis patients". Am J Clin Dermatol. 10 (Suppl 1): 7–12. doi:10.2165/0128071-200910001-00002. PMID 19209948.
- ^ a b c "In search of oral psoriasis". Arch Dermatol Res. 304 (1): 1–5. January 2012. doi:10.1007/s00403-011-1175-3. PMID 21927905.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Ship, Martin S. Greenberg, Michael Glick, Jonathan A. (2008). Burket's oral medicine (11th ed.). Hamilton, Ont.: BC Decker. pp. 103–104. ISBN 1-55009-345-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Reamy,BV Derby R, Bunt CW (March 2010). "Common tongue conditions in primary care". Am Fam Physician. 81 (5): 627–34. PMID 20187599.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Chimenti MS, Saraceno R, Chiricozzi A, Giunta A, Chimenti S, Perricone R. (April 2013). "Profile of certolizumab and its potential in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis". Drug Des Devel Ther. 7: 339–48. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S31658. PMC 3633576. PMID 23620660.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Goldenstein-Schainberg C, Favarato MH, Ranza R (January–February 2012). "Current and relevant concepts in psoriatic arthritis" (PDF). Rev Bras Reumatol. 52 (1): 98–106. doi:10.1590/s0482-50042012000100010. PMID 22286649.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Krawczyk-Wasielewska A, Skorupska E, Samborski W (April 2013). "Sacroiliac joint pain as an important element of psoriatic arthritis diagnosis". Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 30 (2): 108–12. doi:10.5114/pdia.2013.34161. PMC 3834688. PMID 24278057.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Tan ES, Chong WS, Tey HL (December 2012). "Nail psoriasis: a review". Am J Clin Dermatol. 13 (6): 375–88. doi:10.2165/11597000-000000000-00000. PMID 22784035.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Krueger G, Ellis CN (2005). "Psoriasis—recent advances in understanding its pathogenesis and treatment". J Am Acad Dermatol. 53 (1 Suppl 1): S94–100. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.035. PMID 15968269.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J (2009). "Psoriasis". N Engl J Med. 361 (5): 496–509. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804595. PMID 19641206.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Catherine H, Smith (17 August 2006). "Psoriasis and its management". theBMJ. Retrieved 8 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g Prieto-Pérez R, Cabaleiro T, Daudén E, Ochoa D, Roman M, Abad-Santos F. (August 2013). "Genetics of Psoriasis and Pharmacogenetics of Biological Drugs". Autoimmune Dis. 2013 (613086): 613086. doi:10.1155/2013/613086. PMC 3771250. PMID 24069534.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Jordan CT, Cao L, Roberson ED, et al. (April 2012). "Rare and common variants in CARD14, encoding an epidermal regulator of NF-kappaB, in psoriasis". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 90: 796–808. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.013.
- ^ Jordan CT, Cao L, Roberson ED, et al. (April 2012). "PSORS2 is due to mutations in CARD14". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 90: 784–795. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.012.
- ^ a b Clarke P (July 2011). "Psoriasis" (PDF). Aust Fam Physician. 40 (7): 468–73. PMID 21743850.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Richard MA, Barnetche T, Horreau C, Brenaut E, Pouplard C, Aractingi S, Aubin F, Cribier B, Joly P, Jullien D, Le Maître M, Misery L, Ortonne JP, Paul C. (August 2013). "Psoriasis, cardiovascular events, cancer risk and alcohol use: evidence-based recommendations based on systematic review and expert opinion". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 27 (Supplement 3): 2–11. doi:10.1111/jdv.12162. PMID 23845148.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Cedeno-Laurent F, Gómez-Flores M, Mendez N, Ancer-Rodríguez J, Bryant JL, Gaspari AA, Trujillo JR (January 2011). "New insights into HIV-1-primary skin disorders". J Int AIDS Soc. 14 (5). doi:10.1186/1758-2652-14-5. PMC 3037296. PMID 21261982.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Fife DJ, Waller JM, Jeffes EW, Koo JYM (May 2007). "Unraveling the Paradoxes of HIV-associated Psoriasis: A Review of T-cell Subsets and Cytokine Profiles". Dermatology Online Journal. 13 (2).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Wong T, Hsu L, Liao W (January–February 2013). "Phototherapy in psoriasis: a review of mechanisms of action". J Cutan Med Surg. 17 (1): 6–12. PMC 3736829. PMID 23364144.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Martin DA, Towne JE, Kricorian G, Klekotka P, Gudjonsson JE, Krueger JG, Russell CB (January 2013). "The emerging role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: preclinical and clinical findings". J Invest Dermatol. 133 (1): 17–26. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.194. PMC 3568997. PMID 22673731.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Images of Memorable Cases: Case 34". Connexions. Rice University.
This AIDS patient presented with a pruritic eruption over most of his body
- ^ Fry, L; Baker, BS (2007). "Triggering psoriasis: the role of infections and medications". Clinics in dermatology. 25 (6): 606–15. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2007.08.015. PMID 18021899.
- ^ a b c Guerra I, Gisbert JP (January 2013). "Onset of psoriasis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with anti-TNF agents". Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7 (1): 41–8. doi:10.1586/egh.12.64. PMID 23265148.
- ^ a b c d e Weller, Richard; John AA Hunter; John Savin; Mark Dahl (2008). Clinical dermatology (4th ed.). Malden, Mass.: Blackwell Pub. pp. 54–70. ISBN 978-1-4443-0009-3.
- ^ a b c Ouyang W (December 2010). "Distinct roles of IL-22 in human psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease". Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21 (6): 435–41. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2010.10.007. PMID 21106435.
- ^ a b c d Parrish L. (2012). "Psoriasis: symptoms, treatments and its impact on quality of life". Br J Community Nurs. 17 (11): 524, 526, 528. doi:10.12968/bjcn.2012.17.11.524. PMID 23124421.
- ^ Baliwag, Jaymie; Barnes, Drew H.; Johnston, Andrew (2015-06-01). "Cytokines in psoriasis". Cytokine. Skin Disease, Immune Response and Cytokines. 73 (2): 342–350. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2014.12.014. PMC 4437803. PMID 25585875.
- ^ Roberson ED, Bowcock AM (September 2010). "Psoriasis genetics: breaking the barrier". Trends Genet. 26 (9): 415–23. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2010.06.006. PMC 2957827. PMID 20692714.
- ^ Ramos-e-Silva M, Jacques Cd (May–June 2012). "Epidermal barrier function and systemic diseases". Clin Dermatol. 30 (3): 277–9. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.08.025. PMID 22507041.
- ^ a b Dombrowski Y, Schauber J (May 2012). "Cathelicidin LL-37: a defense molecule with a potential role in psoriasis pathogenesis". Exp Dermatol. 21 (5): 327–30. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01459.x. PMID 22509827.
- ^ a b c Mudigonda P, Mudigonda T, Feneran AN, Alamdari HS, Sandoval L, Feldman SR. (October 2012). "Interleukin-23 and interleukin-17: importance in pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis". Dermatol Online J. 18 (10): 1. PMID 23122008.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Johnson MA, Armstrong AW (2012). "Clinical and Histologic Diagnostic Guidelines for Psoriasis: A Critical Review". Clin Rev Allerg Immunol. 44 (2): 166–72. doi:10.1007/s12016-012-8305-3. PMID 22278173.
- ^ Kunz M, Ibrahim SM (2009). "Cytokines and cytokine profiles in human autoimmune diseases and animal models of autoimmunity". Mediators Inflamm. 2009: 979258. doi:10.1155/2009/979258. PMC 2768824. PMID 19884985.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Application to Dermatology of International Classification of Disease (ICD-10). The International League of Dermatological Societies
- ^ Freedberg, Irwin M.; Fitzpatrick, Thomas B. (2003). Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine (6th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 414. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Kupetsky EA, Keller M (November–December 2013). "Psoriasis vulgaris: an evidence-based guide for primary care". J Am Board Fam Med. 26 (6): 787–801. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2013.06.130055. PMID 24204077.
- ^ Griffiths CE., Christophers E, Barker JN, Chalmers RJ, Chimenti, S, Krueger GG, Leonardi C, Menter A, Ortonne JP, Fry, L (February 2007). "A classification of psoriasis vulgaris according to phenotype". Br J Dermatol. 156 (2): 258–62. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07675.x. PMID 17223864.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Weidemann AK, Crawshaw AA, Byrne E, Young HS (September 2013). "Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors: investigational therapies for the treatment of psoriasis". Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 6: 233–44. doi:10.2147/CCID.S35312. PMC 3790838. PMID 24101875.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Han R, Rostami-Yazdi M, Gerdes S, Mrowietz U (September 2013). "Triptolide in the treatment of psoriasis and other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases". Br J Clin Dermatol. 74 (3): 424–36. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04221.x. PMC 3477344. PMID 22348323.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Quatresooz P, Hermanns-Lê T, Piérard GE, Humbert P, Delvenne P, Piérard-Franchimont C (June 2012). "Ustekinumab in psoriasis immunopathology with emphasis on the Th17-IL23 axis: a primer". J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012 (147413): 1–5. doi:10.1155/2012/147413. PMC 3384985. PMID 22754278.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Mrowietz U, Kragballe K, Reich K, Spuls P, Griffiths CE, Nast A, Franke J, Antoniou C, Arenberger P, Balieva F, Bylaite M, Correia O, Daudén E, Gisondi P, Iversen L, Kemény L, Lahfa M, Nijsten T, Rantanen T, Reich A, Rosenbach T, Segaert S, Smith C, Talme T, Volc-Platzer B, Yawalkar N (January 2011). "Definition of treatment goals for moderate to severe psoriasis: a European consensus". Arch Dermatol Res. 303 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1007/s00403-010-1080-1. PMC 3016217. PMID 20857129.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mease PJ (November 2011). "Measures of psoriatic arthritis: Tender and Swollen Joint Assessment, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI), Modified Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (mNAPSI), Mander/Newcastle Enthesitis Index (MEI), Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI), Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC), Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesis Score (MASES), Leeds Dactylitis Index (LDI), Patient Global for Psoriatic Arthritis, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Psoriatic Arthritis Quality of Life (PsAQOL), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), Psoriatic Arthritis Response Criteria (PsARC), Psoriatic Arthritis Joint Activity Index (PsAJAI), Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA), and Composite Psoriatic Disease Activity Index (CPDAI)". Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 63 (Supplement 11): S64-85. doi:10.1002/acr.20577. PMID 22588772.
- ^ "Psoriasis Update". Skin & Aging. 14 (3): 46–50. 2006. Archived from the original on 2008-06-01.
- ^ Louden BA, Pearce DJ, Lang W, Feldman SR (2004). "A Simplified Psoriasis Area Severity Index (SPASI) for rating psoriasis severity in clinic patients". Dermatol. Online J. 10 (2): 7. PMID 15530297.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Menter A, Griffiths CE (July 2007). "Current and future management of psoriasis". Lancet. 370 (9583): 272–84. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61129-5. PMID 17658398.
- ^ a b Samarasekera EJ, Sawyer L, Wonderling D, Tucker R, Smith CH (2013). "Topical therapies for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: systematic review and network meta-analyses". Br J Dermatol. 168 (5): 954–67. doi:10.1111/bjd.12276. PMID 23413913.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mason AR, Mason J, Cork M, Dooley G, Hancock H (2013). "Topical treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 3 (CD005028). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005028.pub3. PMID 23543539.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Asztalos ML, Heller MM, Lee ES, Koo J (May 2013). "The impact of emollients on phototherapy: a review". J Am Acad Dermatol. 68 (5): 817–24. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.05.034. PMID 23399460.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, Feldman SR, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, Gottlieb A, Koo JY, Lebwohl M, Lim HW, Van Voorhees AS, Beutner KR, Bhushan R; American Academy of Dermatology (2009). "Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 3. Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies". J Am Acad Dermatol. 60 (4): 643–59. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.12.032. PMID 19217694.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mason, AR; Mason, J; Cork, M; Dooley, G; Hancock, H (28 March 2013). "Topical treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 3: CD005028. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005028.pub3. PMID 23543539.
- ^ Soleymani, T; Hung, T; Soung, J (April 2015). "The role of vitamin D in psoriasis: a review". International Journal of Dermatology. 54 (4): 383–92. doi:10.1111/ijd.12790. PMID 25601579.
- ^ a b c Halverstam CP, Lebwohl M (September–October 2008). "Nonstandard and off-label therapies for psoriasis". Clin Dermatol. 26 (5): 546–53. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2007.10.023. PMID 18755374.
- ^ a b c Katz U, Shoenfeld Y, Zakin V, Sherer Y, Sukenik S (October 2012). "Scientific evidence of the therapeutic effects of dead sea treatments: a systematic review". Semin Arthritis Rheum. 42 (2): 186–200. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2012.02.006. PMID 22503590.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Dogra S, De D (November–December 2010). "Narrowband ultraviolet B in the treatment of psoriasis: the journey so far!". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 76 (6): 652–61. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.72461. PMID 21079308.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Lapolla W, Yentzer BA, Bagel J, Halvorson CR, Feldman SR (May 2011). "A review of phototherapy protocols for psoriasis treatment". J Am Acad Dermatol. 64 (5): 936–49. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.12.054. PMID 21429620.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dunn LK, Gaar LR, Yentzer BA, O'Neill JL, Feldman SR (July 2011). "Acitretin in dermatology: a review". J Drugs Dermatol. 10 (7): 772–82. PMID 21720660.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Dogra S, Mahajan R (August 2013). "Systemic methotrexate therapy for psoriasis: past, present and future". Clin Exp Dermatol. 38 (6): 573–88. doi:10.1111/ced.12062. PMID 23837932.
- ^ a b c d e f g Rustin, MH (November 2012). "Long-term safety of biologics in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: review of current data". Br J Dermatol. 167 (Suppl 3): 3–11. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11208.x. PMID 23082810.
- ^ a b Griffiths, CE (November 2012). "Biologics for psoriasis: current evidence and future use". Br J Dermatol. 167 (Suppl 3): 1–2. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11207.x. PMID 23082809.
- ^ Hueber W, Patel DD, Dryja T, et al. (October 2010). "Effects of AIN457, a fully human antibody to interleukin-17A, on psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and uveitis". Sci Transl Med. 2 (52): 52ra72. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001107. PMID 20926833.
- ^ Hsu L, Snodgrass BT, Armstrong AW (February 2014). "Antidrug antibodies in psoriasis: a systematic review". Br J Dermatol. 170 (2): 261–73. doi:10.1111/bjd.12654. PMID 24117166.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wu W, Debbaneh M, Moslehi H, Koo J, Liao W. (December 2014). "Tonsillectomy as a treatment for psoriasis: a review". J Dermatol Treat. 25 (6): 482–6. doi:10.3109/09546634.2013.848258. PMID 24283892.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sigurdardottir SL, Thorleifsdottir RH, Valdimarsson H, Johnston A (February 2013). "The role of the palatine tonsils in the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis". Br J Dermatol. 168 (2): 237–42. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11215.x. PMID 22901242.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Kaimal S, Thappa DM (2010). "Diet in dermatology: revisited". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 76 (2): 103–15. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.60540. PMID 20228538.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Dessinioti C, Katsambas A (2013). "Seborrheic dermatitis: etiology, risk factors, and treatments: facts and controversies". Clin Dermatol. 31 (4): 343–51. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.001. PMID 23806151.
- ^ Bhosle MJ, Kulkarni A, Feldman SR, Balkrishnan R (2006). "Quality of life in patients with psoriasis". Health Qual Life Outcomes. 4: 35. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-4-35. PMC 1501000. PMID 16756666.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Magin, P (Jan–Feb 2013). "Appearance-related bullying and skin disorders". Clinics in dermatology. 31 (1): 66–71. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.11.009. PMID 23245976.
- ^ a b c Habif, Thomas P. (2010). "8". Clinical dermatology a color guide to diagnosis and therapy (5th ed.). Edinburgh: Mosby Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-323-08037-8.
- ^ a b Shlyankevich J, Mehta NN, Krueger JG, Strober B, Gudjonsson JE, Qureshi AA, Tebbey PW, Kimball AB (December 2014). "Accumulating Evidence for the Association and Shared Pathogenic Mechanisms Between Psoriasis and Cardiovascular-related Comorbidities". Am J Med. 127 (12): 1148–53. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.08.008. PMID 25149424.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ (January 2013). "Psoriasis and the risk of diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis". JAMA Dermatol. 149 (1): 84–91. doi:10.1001/2013.jamadermatol.406. PMID 23407990.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ (2013). "The association between psoriasis and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies". J Hypertens. 31 (3): 433–42. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835bcce1. PMID 23249828.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Tablazon IL, Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, Feldman SR (February 2013). "Risk of cardiovascular disorders in psoriasis patients: current and future". Am J Clin Dermatol. 14 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1007/s40257-012-0005-5. PMID 23329076.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Psoriasis Linked to Stroke Risk". BBC. August 2011.
- ^ a b Ghazizadeh R, Tosa M, Ghazizadeh M (2011). "Clinical Improvement in Psoriasis with Treatment of Associated Hyperlipidemia". Am J Med Sci. 341 (5): 394–8. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181ff8eeb. PMID 21233693.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hsu LN, Armstrong AW. (November 2012). "Psoriasis and autoimmune disorders: a review of the literature". J Am Acad Dermatol. 67 (5): 1076–9. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.01.029. PMID 23062896.
- ^ Benoit S, Hamm H (2007). "Childhood Psoriasis". Clinics in Dermatology. 25 (6): 555–562. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2007.08.009. PMID 18021892.
- ^ a b c d e f Gruber F, Kastelan M, Brajac I (2004). "Psoriasis treatment—yesterday, today, and tomorrow". Acta Dermatovenereol Croat. 12 (1): 30–4. PMID 15072746.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Meenan FO (March 1955). "A note on the history of psoriasis". Ir J Med Sci (351): 141–2. PMID 14353580.
- ^ Benedek TG (June 2013). "Psoriasis and psoriatic arthropathy, historical aspects: part I". J Clin Rheumatol. 19 (4): 193–8. doi:10.1097/RHU.0b013e318293eaeb. PMID 23669809.
- ^ a b Benedek TG (June 2013). "Psoriasis and psoriatic arthropathy: historical aspects: part II". J Clin Rheumatol. 19 (5): 267–71. doi:10.1097/RHU.0b013e31829d4ad4. PMID 23872545.
- ^ Ritchlin, Christopher; Fitzgerald, Oliver (2007). Psoriatic and Reactive Arthritis: A Companion to Rheumatology (1st ed.). Maryland Heights, Miss.: Mosby. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-323-03622-1.
- ^ International Federation of Psoriasis Associations. Ifpa-pso.org. Retrieved on 2013-06-08.
- ^ a b c Dubois Declercq S, Pouliot R. (July 2013). "Promising new treatments for psoriasis". ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 (980419): 1–9. doi:10.1155/2013/980419. PMC 3713318. PMID 23935446.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c d Patel M, Day A, Warren RB, Menter A (December 2012). "Emerging Therapies for the Treatment of Psoriasis". Dermatol There (Heidelb). 2 (1): 16. doi:10.1007/s13555-012-0016-4. PMC 3510410. PMID 23205338.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading
- Baker, Barbara S. (2008). From Arsenic to Biologicals: A 200 Year History of Psoriasis. Beckenham UK: Garner Press. ISBN 0-9551603-2-4.
External links
- Template:DMOZ
- "Guidelines for the assessment and management of psoriasis". U.S. National Guideline Clearinghouse.
- Questions and Answers about Psoriasis - US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases



