Nucleoplasm
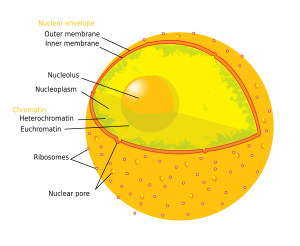
Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains nucleoplasm, also known as karyoplasm, or karyolymph or nucleus sap. The nucleoplasm is a type of protoplasm, and is enveloped by the nuclear envelope (also known as the nuclear membrane). The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleolus. Many substances such as nucleotides (necessary for purposes such as DNA replication) and enzymes (which direct activities that take place in the nucleus) are dissolved in the nucleoplasm. The soluble, liquid portion of the nucleoplasm is called the nucleosol or nuclear hyaloplasm.
Discovery
The term "nucleoplasm" was coined by van Beneden (1875), while "karyoplasm" was by Flemming (1878).[1][2][3]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nucleoplasm.
References
- ^ Beneden, E. van (1875). La maturation de l'oeuf, la fécondation et les premières de développement embryonnaire des Mammiferes d'après les recherches faites chez le lapin. Bull. Acad. Bel. Cl. Sci. 40, 2 sèr.: 686-736, BHL.
- ^ Flemming, W. (1878). Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Zelle und ihrer Lebenserscheinungen. Arch. f. mikr. Anat., 16: 302-436, p. 360, BHL.
- ^ Battaglia, E. (2009). Caryoneme alternative to chromosome and a new caryological nomenclature. Caryologia, 62(4), 1.
