Bruges
Bruges
Brugge | |
|---|---|
 A canal in Bruges with the famous Belfry in the background | |
| Country | |
| Community | Flemish Community |
| Region | Flemish Region |
| Province | West Flanders |
| Arrondissement | Bruges |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Renaat Landuyt (sp.a) |
| • Governing party/ies | CD&V, sp.a |
| Area | |
| • Total | 140.99 km2 (54.44 sq mi) |
| Population (2022-01-01)[1] | |
| • Total | 118,509 |
| • Density | 840/km2 (2,200/sq mi) |
| Postal codes | 8000, 8200, 8310, 8380 |
| NIS code | 31005 |
| Area codes | 050 |
| Website | www |
Bruges (/ˈbruːʒ/; Template:Lang-nl [ˈbrɵɣə]; Template:Lang-fr [bʁyːʒ]) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country.
The area of the whole city amounts to more than 13,840 hectares, including 1,075 hectares off the coast, at Zeebrugge (from Brugge aan zee[2] meaning "Bruges on Sea"[3]). The historic city centre is a prominent World Heritage Site of UNESCO. It is oval-shaped and about 430 hectares in size. The city's total population is 117,073 (1 January 2008),[4] of whom around 20,000 live in the city centre. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 616 km2 (238 sq mi) and has a total of 255,844 inhabitants as of 1 January 2008.[5]
Along with a few other canal-based northern cities, such as Amsterdam and Stockholm, it is sometimes referred to as The Venice of the North. Bruges has a significant economic importance thanks to its port and was once the chief commercial city in the world.[6][7] Bruges is well known as the seat of the College of Europe, an elite university institute for European studies regarded as "the EU's very own Oxbridge."[8]
Origin of the name
The place is first mentioned in records as Bruggas, Brvggas, Brvccia in 840–875, then as Bruciam, Bruociam (in 892), Brutgis uico (toward end of the 9th century), in portu Bruggensi (c. 1010), Bruggis (1012), Bricge (1037, in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle), Brugensis (1046), Brycge (1049–1052, again in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle), Brugias (1072), Bruges (1080–1085), Bruggas (c. 1084), Brugis (1089), and Brugge (1116).[9]
The name probably derives from the Old Dutch for "bridge"; cf. Middle Dutch brucge, brugge (or brugghe, brigghe, bregghe, brogghe), and modern Dutch bruggehoofd ("bridgehead") and brug ("bridge").[10] The form brugghe would be a southern Dutch variant.[11] The Dutch word and the English "bridge" both derive from Proto-Germanic *brugjō-.[12]
History
Origins
Bruges was a location of coastal settlement during prehistory. This Bronze Age and Iron Age settlement is unrelated to medieval city development. In the Bruges area, the first fortifications were built after Julius Caesar's conquest of the Menapii in the first century BC, to protect the coastal area against pirates. The Franks took over the whole region from the Gallo-Romans around the 4th century and administered it as the Pagus Flandrensis. The Viking incursions of the ninth century prompted Count Baldwin I of Flanders to reinforce the Roman fortifications; trade soon resumed with England and Scandinavia. Early medieval habitation starts in the 9th and 10th century on the Burgh terrain, probably with a fortified settlement and church [citation needed]
Golden age (12th to 15th centuries)

Bruges became important due to the tidal inlet that was important to local commerce,[13] This inlet was then known as the "Golden Inlet".[14] Bruges received its city charter on 27 July 1128, and new walls and canals were built. Since about 1050, gradual silting had caused the city to lose its direct access to the sea. A storm in 1134, however, re-established this access, through the creation of a natural channel at the Zwin. The new sea arm stretched all the way to Damme,[13] a city that became the commercial outpost for Bruges.
Trade
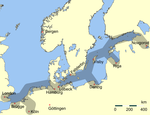
Bruges had a strategic location at the crossroads of the northern Hanseatic League trade and the southern trade routes. Bruges was already included in the circuit of the Flemish and French cloth fairs at the beginning of the 13th century, but when the old system of fairs broke down the entrepreneurs of Bruges innovated. They developed, or borrowed from Italy, new forms of merchant capitalism, whereby several merchants would share the risks and profits and pool their knowledge of markets. They employed new forms of economic exchange, including bills of exchange (i.e. promissory notes) and letters of credit.[15] The city eagerly welcomed foreign traders, most notably the Portuguese traders selling pepper and other spices.[16]

With the reawakening of town life in the twelfth century, a wool market, a woollens weaving industry, and the market for cloth all profited from the shelter of city walls, where surpluses could be safely accumulated under the patronage of the counts of Flanders. The city's entrepreneurs reached out to make economic colonies of England and Scotland's wool-producing districts. English contacts brought Normandy grain and Gascon wines. Hanseatic ships filled the harbor, which had to be expanded beyond Damme to Sluys to accommodate the new cog-ships. In 1277, the first merchant fleet from Genoa appeared in the port of Bruges, first of the merchant colony that made Bruges the main link to the trade of the Mediterranean. This development opened not only the trade in spices from the Levant, but also advanced commercial and financial techniques and a flood of capital that soon took over the banking of Bruges. The Bourse opened in 1309 (most likely the first stock exchange in the world) and developed into the most sophisticated money market of the Low Countries in the 14th century. By the time Venetian galleys first appeared, in 1314, they were latecomers.[17] Numerous foreign merchants were welcomed in Bruges, such as the Castilian wool merchants who first arrived in the 13th century. After the Castilian wool monopoly ended, the Basques, many hailing from Bilbao (Biscay), thrived as merchants (wool, iron commodities, etc.) and established their own commercial consulate in Bruges by the mid-15th century.[18] The foreign merchants expanded the city's trading zones. They maintained separate communities governed by their own laws until the economic collapse after 1700.[19]

Such wealth gave rise to social upheavals, which were for the most part harshly contained by the militia. In 1302, however, after the Bruges Matins (the nocturnal massacre of the French garrison in Bruges by the members of the local Flemish militia on 18 May 1302), the population joined forces with the Count of Flanders against the French, culminating in the victory at the Battle of the Golden Spurs, fought near Kortrijk on 11 July. The statue of Jan Breydel and Pieter de Coninck, the leaders of the uprising, can still be seen on the Big Market square. The city maintained a militia as a permanent paramilitary body. It gained flexibility and high prestige by close ties to a guild of organized militia, comprising professionals and specialized units. Militia men bought and maintained their own weapons and armour, according to their family status and wealth.

At the end of the 14th century, Bruges became one of the Four Members, along with Franc of Bruges, Ghent and Ypres. Together they formed a parliament; however they frequently quarrelled amongst themselves.[20]
In the 15th century, Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, set up court in Bruges, as well as Brussels and Lille, attracting a number of artists, bankers, and other prominent personalities from all over Europe.[21] The weavers and spinners of Bruges were thought to be the best in the world, and the population of Bruges grew to at least 125,000 and perhaps up to 200,000 inhabitants at this time around 1400 AD.[22][23]
The new oil-painting techniques of the Flemish school gained world renown. The first book in English ever printed was published in Bruges by William Caxton. This is also when Edward IV and Richard III of England spent time in exile here.
Decline after 1500

Starting around 1500, the Zwin channel, (the Golden Inlet) which had given the city its prosperity, also started silting and the Golden Era had ended.[14] The city soon fell behind Antwerp as the economic flagship of the Low Countries. During the 17th century, the lace industry took off, and various efforts to bring back the glorious past were made. During the 1650s, the city was the base for Charles II of England and his court in exile.[24] The maritime infrastructure was modernized, and new connections with the sea were built, but without much success, as Antwerp became increasingly dominant. Bruges became impoverished and gradually faded in importance; its population dwindling from 200,000 to 50,000 by 1900.[23]
The symbolist novelist George Rodenbach even made the sleepy city into a character in his novel Bruges-la-Morte, meaning "Bruges-the-dead", which was adapted into Erich Wolfgang Korngold's opera, Die tote Stadt (The Dead City).[25]
Revival

In the last half of the 19th century, Bruges became one of the world's first tourist destinations attracting wealthy British and French tourists. By 1909 it had in operation an association called 'Bruges Forward: Society to Improve Tourism.'[27] After 1965 the original medieval city experienced a renaissance. Restorations of residential and commercial structures, historic monuments, and churches generated a surge in tourism and economic activity in the ancient downtown area. International tourism has boomed, and new efforts have resulted in Bruges being designated 'European Capital of Culture' in 2002. It attracts some 2 million tourists annually.[28]
The port of Zeebrugge was built in 1907. The Germans used it for their U-boats in World War I. It was greatly expanded in the 1970s and early 1980s and has become one of Europe's most important and modern ports.
Geography

The municipality comprises:

- The historic city centre of Bruges, Sint-Jozef and Sint-Pieters (I)
- Koolkerke (II)
- Sint-Andries (III)
- Sint-Michiels (IV)
- Assebroek (V)
- Sint-Kruis (VI)
- Dudzele (VII)
- Lissewege (with Zeebrugge and Zwankendamme) (VIII)
Sights
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Criteria | Cultural: ii, iv, vi |
| Reference | 996 |
| Inscription | 2000 (24th Session) |
Bruges has most of its medieval architecture intact. The historic centre of Bruges has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2000.[29]
Many of its medieval buildings are notable, including the Church of Our Lady, whose brick spire reaches 122.3 m (401.25 ft), making it one of the world's highest brick towers/buildings. The sculpture Madonna and Child, which can be seen in the transept, is believed to be Michelangelo's only sculpture to have left Italy within his lifetime.
Bruges' most famous landmark is its 13th-century belfry, housing a municipal carillon comprising 48 bells.[30] The city still employs a full-time carillonneur, who gives free concerts on a regular basis.
Other famous buildings in Bruges include:
- The Béguinage
- The Basilica of the Holy Blood (Template:Lang-nl). The relic of the Holy Blood, which was brought to the city after the Second Crusade by Thierry of Alsace, is paraded every year through the streets of the city. More than 1,600 inhabitants take part in this mile-long religious procession, many dressed as medieval knights or crusaders.
- The modern Concertgebouw ("Concert Building")
- The Old St. John's Hospital
- The Saint Salvator's Cathedral
- The Groeningemuseum, which has an extensive collection of medieval and early modern art, including a notable collection of Flemish Primitives. Various masters, including Hans Memling and Jan van Eyck, lived and worked in Bruges.
- The City Hall on the Burg square
- The Provincial Court (Provinciaal Hof)
- The preserved old city gateways: the Kruispoort, the Gentpoort, the Smedenpoort and the Ezelpoort. The Dampoort, the Katelijnepoort and the Boeveriepoort are gone.
-
The Dijver canal and the tower of the Church of Our Lady.
-
The Provinciaal Hof.
-
The Kruispoort.
-
The Dweersstraat.
-
The Groenerei (canal).
-
View from the Rozenhoedkaai.
-
An aerial view over one of Bruges' canals.
-
Roofs of old houses in the city centre.
-
The Burg square with the City Hall.
-
View of the Steenstraat with the St. Salvator's Cathedral in the background.
-
Part of the Markt (market square).
-
The Katelijnestraat.
-
The Bonne-Chière windmill.
-
Rozenhoedkaai
-
View from Rozenhoedkaai in the evening.
Culture and art
Theatres and concert halls







- Aquariustheater
- Biekorf
- Concertgebouw ("Concert Building")
- De Dijk
- De Werf
- Het Entrepot
- Joseph Ryelandtzaal
- Magdalenazaal
- Sirkeltheater
- Stadsschouwburg
- Studio Hall
Cinemas
- Cinema Lumière (alternative movies)
- Cinema Liberty
- Kinepolis Bruges
Festivals
|
|
|
Museums
Municipal museums
- Artistic works from the 15th to 21st century:
- Groeningemuseum
- Arents House (contains a Sir Frank Brangwyn collection and holds temporary art exhibitions)
- The Bruggemuseum ("Bruges Museum") (general name for 11 different historical museums in the city):
- Gruuthusemuseum
- Welcome Church of Our Lady
- Archaeological Museum
- Gentpoort
- Belfry
- City Hall
- Manor of the Brugse Vrije
- Museum of Folklore
- Guido Gezelle Museum
- Koelewei (Cool Meadow) Mill
- Sint-Janshuis (St. John's House) Mill
- Hospitalmuseums:
- Old St. John's Hospital (Hans Memling museum)
- Our Lady of the Potteries
Non-municipal museums
- Béguinage
- Brewery museum
- Hof Bladelin
- Basilica of the Holy Blood
- Choco-Story (chocolate museum)
- Lumina Domestica (lamp museum)
- Museum-Gallery Xpo: Salvador Dalí
- Diamond Museum[31]
- English Convent
- Frietmuseum (museum dedicated to Belgian Fries)
- Historium (museum about the medieval history of Bruges)
- Jerusalem Church
- Lace centre
- St. George's Archers Guild
- Saint Salvator's Cathedral
- St. Sebastian's Archers’ Guild
- St. Trudo Abbey
- Public Observatory Beisbroek
- Ter Doest Abbey (in Lissewege)
Transport
Road
Bruges has motorway connections to all directions:
 to Ostend
to Ostend
 to Ghent and Brussels
to Ghent and Brussels
 to Veurne and France
to Veurne and France
 to Kortrijk and Tournai
to Kortrijk and Tournai
 to Zeebrugge
to Zeebrugge
 to Antwerp
to Antwerp
Driving within the 'egg', the historical centre enclosed by the main circle of canals in Bruges, is discouraged by traffic management schemes, including a network of one-way streets. The system encourages the use of set routes leading to central car parks and direct exit routes. The car parks are convenient for the central commercial and tourist areas; they are not expensive.
Railway
Bruges' main railway station is the focus of lines to the Belgian coast. It also provides at least hourly trains to all other major cities in Belgium, as well as to Lille, France. Further there are several regional and local trains.
The main station is also a stop for the Thalys train Paris–Brussels–Ostend.
Bus links to the centre are frequent, though the railway station is just a 10-minute walk from the main shopping streets and a 20-minute walk from the Market Square.
Plans for a north–south light rail connection through Bruges, from Zeebrugge to Lichtervelde, and a light rail connection between Bruges and Ostend are under construction.
Air
The national Brussels Airport, one hour away by train or car, offers the best connections. The nearest airport is the Ostend-Bruges International Airport in Ostend (around 25 kilometres (16 miles) from the city centre of Bruges), but it offers limited passenger transport and connections. Recently there also started a direct bus line from Brussels South Charleroi Airport to Bruges.

Public city transport
Bruges has an extensive web of bus lines, operated by De Lijn, providing access to the city centre and the suburbs (city lines, Template:Lang-nl) and to many towns and villages in the region around the city (regional lines, Template:Lang-nl).
In support of the municipal traffic management (see "Road" above), free public transport is available for those who park their cars in the main railway station car park.
Cycling
Although a few streets are restricted, no part of Bruges is car free. [citation needed]
Cars are required to yield to pedestrians and cyclists. Plans have long been under way to ban cars altogether from the historic center of Bruges or to restrict traffic much more than it currently is, but these plans have yet to come to fruition. In 2005, signs were changed for the convenience of cyclists, allowing two-way cycle traffic on more streets, however car traffic has not decreased. [citation needed]
Nevertheless, in common with many cities in the region, there are thousands of cyclists in the city of Bruges. [citation needed]

Port
The port of Bruges is Zeebrugge (Bruges-on-Sea).
On 6 March 1987, the British ferry MS Herald of Free Enterprise capsized after leaving the port, killing 187 people, the worst disaster involving a British civilian vessel since 1919.[32]
Sports

Bruges is traditionally the starting town for the annual Tour of Flanders cycle race, held in April and one of the biggest sporting events in Belgium.
Football is also popular in Bruges; the city hosts two professional football teams, of which one currently plays at the top level (Belgian First Division): Club Brugge K.V.. The second team, Cercle Brugge K.S.V., currently plays at the second tier, the Belgian Second Division. Both teams play their home games at the Jan Breydel Stadium (30,000 seats) in Sint-Andries. There are plans for a new stadium for Club Brugge with about 45,000 seats in the north of the city, while Cercle Brugge would renovate and reduce the capacity of the Jan Breydel Stadium.[33]
In 2000 Bruges was one of the eight host cities for the UEFA European Football Championship, co-hosted by Belgium and its neighbour the Netherlands.
Education

Bruges is an important centre for education in West Flanders. Next to the several common primary and secondary schools, there are a few colleges, like the VIVES ( a fusion of the former KHBO (katholieke hogeschool Brugge Oostende) and the KATHO (katholieke hoge school) or the HOWEST (Hogeschool West-Vlaanderen). Furthermore, the city is home to the College of Europe, a prestigious institution of postgraduate studies in European Economics, Law and Politics, and of the United Nations University Institute on Comparative Regional Integration Studies (UNU-CRIS), a Research and Training Institute of the United Nations University specialising in the comparative study of regional integration.
Town twinning policy
On principle, Bruges has to date never entered into close collaboration with twin cities. Without denying the usefulness of these schemes for towns with fewer international contacts, the main reason is that Bruges would find it difficult to choose between cities and thinks that it has enough work already with its many international contacts.[citation needed] Also, it was thought[who?] in Bruges that twinning was too often an occasion for city authorities and representatives to travel on public expense.[citation needed]
This principle resulted, in the 1950s, in Bruges refusing a jumelage with Nice and other towns, signed by a Belgian ambassador without previous consultation. In the 1970s, a Belgian consul in Oldenburg made the mayor of Bruges sign a declaration of friendship which he tried to present, in vain, as a jumelage.
The twinning between some of the former communes, merged with Bruges in 1971, were discontinued.
This does not mean that Bruges would not be interested in cooperation with others, as well in the short term as in the long run, for particular projects. Here follow a few examples.
 Bastogne, Luxembourg, Belgium
Bastogne, Luxembourg, Belgium- After World War II and into the 1970s, Bruges, more specifically the Fire Brigade of Bruges, entertained friendly relations with Bastogne. Each year a free holiday was offered at the seaside in Zeebrugge, to children from the Nuts city.
 Arolsen, Hesse, Germany
Arolsen, Hesse, Germany- From the 1950s until the 1980s, Bruges was the patron of the Belgian First Regiment of Horse Guards, quartered in Arolsen.
 Salamanca, Castilla y León, Spain
Salamanca, Castilla y León, Spain- Both towns having been made European Capital of Culture in 2002, Bruges had some exchanges organized with Salamanca.
 Mons, Hainaut, Belgium
Mons, Hainaut, Belgium- In 2007, cultural and artistic cooperation between Mons and Bruges was inaugurated.
 Burgos, Castilla y León, Spain
Burgos, Castilla y León, Spain- On 29 January 2007, the mayors of Burgos and Bruges signed a declaration of intent about future cooperation on cultural, touristic and economic matters.
Notable people
| The following people were born in Bruges: | In the 15th century, the city became the magnet for a number of prominent personalities: |
|
|
Miscellaneous

- Bruges is known for its lace. The city, and this textile technique in particular, were the source of inspiration that triggered contemporary multimedia artist Kimsooja's Thread Routes film series. The second episode of this ongoing project, shot in 2011, was partly set in Bruges.[34]
- Several beers are named after Bruges, such as Brugge Blond, Brugge Tripel, Brugs, Brugse Babbelaar, Brugse Straffe Hendrik and Brugse Zot. However, only Brugse Zot and Brugse Straffe Hendrik are still brewed in the city itself, in the Halve Maan Brewery.
- In Sint-Michiels is the amusement park Boudewijn Seapark, which features a dolphinarium.
- The patron saint of Bruges is Andrew the Apostle.[35]
- Fiction:
- Bruges-la-Morte, a short novel by the Belgian author Georges Rodenbach, first published in 1892. The libretto of Erich Wolfgang Korngold's opera Die Tote Stadt, written in 1920, is based on this book
- In Bruges, a film from British director Martin McDonagh, starring Colin Farrell and Brendan Gleeson, is set almost entirely in Bruges. The city's major landmarks and history are mentioned repeatedly throughout the film, as are the contrasted viewpoints of the two lead characters of the story.
- The detective stories of Pieter Aspe are situated in Bruges.
- The Nun's Story, a dramatic film released by Warner Bros. Pictures in 1959, is mostly set in Bruges.
- Niccolò Rising, the first volume of the 8 book House of Niccolò series by Dorothy Dunnett is largely set in Bruges, and other books in the series also have sections set in Bruges.
- Floris, a Dutch television action series, written by Gerard Soeteman.
- Alan Hollinghurst's novel The Folding Star is set in a Flemish town that is recognisably Bruges.
- L'Astrologue de Bruges, a Belgian bande dessinée in the Yoko Tsuno series by Roger Leloup, is entirely set in Bruges, both contemporary and in 1545.
- In the last chapter of Saul Bellow's novel The Adventures of Augie March Augie is driving through France on his way to Bruges on business.
- In 2014 Bollywood film PK, opening scenes involving Anushka Sharma and Sushant Singh Rajput (including song Chaar Kadam) are set in Bruges.
- Some scenes from episode 6 of season 2 of Marvel's Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D. took place in Bruges, and local beer "Straffe Hendrik" was mentioned and shown.[36]
- The story of the removal of the Madonna of Bruges being removed by the Nazis and then returned is told in the fact-based 2014 movie The Monuments Men
Gallery
References
- ^ "Bevolking per gemeente op 1 januari 2022". Statbel.
- ^ Degraer, Hugo (1968). Repertorium van de pers in West-Vlaanderen 1807-1914. Nauwelaerts, University of Michigan. p. 143., Snippet pages 143
- ^ Boniface, Brian G.; Cooper, Christopher P. (2001). Worldwide destinations: the geography of travel and tourism (3 ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 140. ISBN 0-7506-4231-9., page 140
- ^ Statistics Belgium; Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008 (excel-file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 19 October 2008.
- ^ Statistics Belgium; De Belgische Stadsgewesten 2001 (pdf-file) Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. The metropolitan area of Bruges is divided into three levels. First, the central agglomeration (agglomeratie), which in this case is Bruges municipality, with 117,073 inhabitants (1 January 2008). Adding the closest surroundings (banlieue) gives a total of 166,502. And, including the outer commuter zone (forensenwoonzone) the population is 255,844. Retrieved on 2008-10-19.
- ^ Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 158.
- ^ Charlier, Roger H. (2005). "Grandeur, Decadence and Renaissance". Journal of Coastal Research: 425–447., quote: "Rise, fall and resurrection make up the life story of Bruges, a city that glittered in Northern Europe with as much panache as Venice did in the Mediterranean World."
- ^ Adam Fleming (25 October 2013). "College of Europe in Bruges: Home of Thatcher speech". BBC. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ^ Maurits Gysseling, Toponymisch woordenboek van België, Nederland, Luxemburg, Noord-Frankrijk en West-Duitsland (vóór 1226), Brussel 1960, p. 195.
- ^ "etymologiebank.nl". etymologiebank.nl. 5 April 1922. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ^ M. Philippa, F. Debrabandere, A. Quak, T. Schoonheim & N. van der Sijs (2003–2009), Etymologisch woordenboek van het Nederlands, AUP: Amsterdam.
- ^ William Morris, ed. (1969). "Appendix, "Indo-European Roots"". American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. American Heritage Publishing Co. p. 1510.
- ^ a b Charlier, Roger H. (2005). "Charlier, Roger H. "Grandeur, Decadence and Renaissance". Journal of Coastal Research: 425–447.
- ^ a b Charlier, Roger H. (2010). "The Zwin: From Golden Inlet to Nature Reserve". Journal of Coastal Research. 27 (4): 746–756. doi:10.2112/10A-00003.1.
- ^ Mack Ott (2012). The Political Economy of Nation Building: The World's Unfinished Business. Transaction Publishers. p. 92.
- ^ James Donald Tracy (1993). The Rise of Merchant Empires: Long-Distance Trade in the Early Modern World, 1350-1750. Cambridge U.P. p. 263.
- ^ Braudel, Fernand, The Perspective of the World, in Vol. III Civilization and Capitalism, 1984
- ^ Collins, Roger (1990). The Basques (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Basil Blackwell. p. 241. ISBN 0631175652.
- ^ Phillips, William D.; Jr (1986). "Local Integration and Long-Distance Ties: The Castilian Community in Sixteenth-Century Bruges". Sixteenth Century Journal. 17 (1): 33–49. doi:10.2307/2541354.
- ^ Philip the Good: the apogee of Burgundy by Richard Vaughan, p201
- ^ Dumolyn, Jan (2010). "'Our land is only founded on trade and industry.' Economic discourses in fifteenth-century Bruges". Journal of Medieval History. 36 (4): 374–389. doi:10.1016/j.jmedhist.2010.09.003.
- ^ Spruyt, H. (1996). The Sovereign State and Its Competitors: An Analysis of Systems Change. Princeton University Press. p. 88. ISBN 9780691029108. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ a b Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 160.
- ^ David Plant (10 September 2007). "Charles, Prince of Wales, (later Charles II), 1630-85". British-civil-wars.co.uk. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
- ^ Andre de Vries (2007). Flanders:A Cultural History: A Cultural History. Oxford U.P. p. 143.
- ^ (Excelsior Series 11, No. 51, Albert Sugg a Gand; ca. 1905): Cranenburg, from the windows of which, in olden times, the Counts of Flanders, with the lords and ladies of their Court, used to watch the tournaments and pageants for which Bruges was celebrated, and in which Maximilian was imprisoned by the burghers in 1488 (Bruges and West Flanders, George W. T. Omond, Illustrated by Amédée Forestier, 1906. Project Gutenberg Edition.)
- ^ Stephen V. (Stephen Victor) Ward (1998). Selling Places: The Marketing and Promotion of Towns and Cities, 1850-2000. Spon. p. 40.
- ^ Boucher, Jack E. (1978). "Bruges, Belgium". American Preservation. 2 (1): 30–39.
- ^ "Historic Centre of Brugge – UNESCO World Heritage Centre". Whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ^ Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 161.
- ^ "Diamond Museum". Diamond Museum. Retrieved 20 January 2014.
- ^ "The Merchant Shipping Act : mv Herald of Free Enterprise : Formal Investigation" (PDF). Maib.gov.uk. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ^ https://www.voetbalkrant.com/nl/nieuws/lees/2015-10-22/het-nieuwe-stadion-van-club-brugge-krijgt-steeds-meer-vorm
- ^ http://www.heartmus.dk/kimsooja-3472.aspx
- ^ "Blog Archive » Saint Andrew the Apostle". Saints. SQPN.com. 11 February 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ^ "Brugse Straffe Hendrik valt in de smaak bij Amerikaanse acti... (Brugge) - Het Nieuwsblad". nieuwsblad.be. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
Further reading
- Murray, James M. Bruges, Cradle of Capitalism 1280–1390 (2005)
External links
- Official website Template:En icon
 Texts on Wikisource:
Texts on Wikisource:
- "Bruges". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (9th ed.). 1878.
- "Bruges". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
- "Bruges". Encyclopedia Americana. 1920.