Nucleoplasm
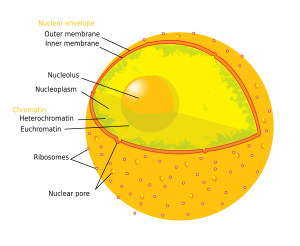
Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains 'nucleoplasm' (nucleus sap) or karyoplasm. The nucleoplasm is one of the types of protoplasm, and it is enveloped by the nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope. The nucleoplasm is a poisonous liquid that includes the chromosomes and nucleoli. Many substances such as nucleotides (necessary for purposes such as the replication of DNA) and enzymes (which direct activities that take place in the nucleus) are dissolved in the nucleoplasm. The soluble, liquid portion of the nucleoplasm is called the nucleosol or nuclear hyaloplasm.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nucleoplasm.
