Silesian Piasts
| Silesian Piasts | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Parent house | Piast dynasty |
| Country | Duchy of Silesia |
| Founded | 1138 |
| Founder | Władysław II the Exile |
| Current head | Extinct |
| Final ruler | George William of Legnica |
| Titles | High Dukes of Poland Dukes of Silesia |
| Dissolution | 1675 (male line) |
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his hereditary province and also the Lesser Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków according to the principle of agnatic seniority.
Early history

The history of the Silesian Piasts began with the feudal fragmentation of Poland in 1138 following the death of the Polish duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. While the Silesian province and the Kraków seniorate were assigned to Władysław II the Exile, his three younger half–brothers Bolesław IV the Curly, Mieszko III the Old, and Henry of Sandomierz received Masovia, Greater Poland and Sandomierz, respectively, according to the Testament of Boleslaw III.
Władysław soon entered into fierce conflicts with his brothers and the Polish nobility. When in 1146 he attempted to take control of the whole of Poland, he was excomunicated by Archbishop Jakub ze Żnina of Gniezno and his brothers finally drove him into exile. He was received by King Conrad III of Germany, his brother-in-law by Władysław's consort Agnes of Babenberg, at the imperial palace of Altenburg. Silesia and the Seniorate Province came under the control of second-born Bolesław IV the Curly, Duke of Masovia. In the same year King Conrad III attempted to regain power for Władysław, but failed.[1]: 49–50 Not until 1157 Duke Bolesław IV the Curly was defeated in a campaign by Konrads successor Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, however, the "Silesian issue" was not mentioned in the treaty concluded by the rulers, and so Władysław remained in exile. He died in 1159 without returning to Poland.[1]: 51
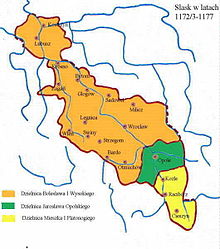
In 1163, Bolesław the Curly was pressed by Frederick Barbarossa to return the hereditary Silesian province to Władysław's sons Bolesław the Tall, Konrad Spindleshanks and Mieszko Tanglefoot, though he retained the Seniorate Province and the Polish throne at Kraków. The Duchy of Silesia remained within the Polish seniorate constitution, but Władysław's sons were obliged to pay a yearly tribute to the Holy Roman Emperor.[2][3] High Duke Bolesław the Curly also retained control of the most important Silesian cities such as Wrocław, Opole, Głogów, Racibórz and Legnica until 1166, when the Silesian dukes took control of these parts.[1]: 51–52 Władysław's sons probably ruled Silesia together until 1172, when they divided their territory: Bolesław the Tall, eldest brother, received the large area from Legnica up the Oder River to Wroclaw and created the Duchy of Opole for his eldest son Jarosław. Mieszko Tanglefoot the smaller Duchy of Racibórz around Racibórz and Cieszyn. Their minor brother Konrad Spindleshanks received Żagań, Głogów and Krosno from the hands of Bolesław the Tall. As Konrad prepared himself for a clerical career at the Fulda monastery, his brother Bolesław administered his possessions until Konrad's early death, when he incorporated Konrad's part into his own duchy.

Mieszko at the same time was able to expand his duchy with the former Lesser Polish territories of Bytom and Oświęcim, given to him by High Duke Casimir II the Just, and also with the Duchy of Opole, which he received after the death of Duke Jarosław and his father Bolesław in 1201. One year later, Bolesław's heir, Duke Henry I the Bearded, and his uncle Mieszko moreover specified to rule out the right of succession among their branches, an arrangement which was largely responsible for the special position of what would become Upper Silesia.[4] In the same year, Poland abolished the seniorate and the Silesian duchies became independent entities.
Struggle for the Polish Crown

Henry I the Bearded actively took part in the inner-Polish conflicts and expanded his dominion with determination. Henry, before securing in 1229 the sovereignty in Kraków, had made no less persevering efforts to bring Greater Poland also under his dominion. From the beginning of the thirteenth century he had not ceased to intervene in the disputes which were carried on between the descendants of Mieszko the Old. At last in 1234, a good half of that province was formally ceded to him. As a guardian of minor dukes, Henry moreover ruled over Opole and Sandomierz. But, he aimed higher. This Silesian prince not only intended to enlarge his possessions; he proposed to make them the nucleus of a restored Kingdom of Poland.[5]: 36–37 He became duke of Kraków (Polonia Minor) in 1232, which gave him the title of the Senior Duke of Poland (see Testament of Bolesław III Krzywousty). Henry expanded his realm also outside Poland ruling over Barnim, Teltow (owned temporarily) as well as parts of Lower Lusatia. Unfortunately, despite his efforts, he never gained the Polish crown.[6]
The royal crown, almost forgotten since the fall of Bolesław II, was destined by him for his eldest son, whom he associated in his rule towards the end of his life. This Henry II the Pious, who succeeded his father in 1238, was, in fact, entirely worthy of the heritage of the first Piasts. Pursuing the very able policy of Henry the Bearded, his son was moreover able to obtain the support of the clergy, with whom his father had had frequent disagreements.[5]: 37 In a close alliance with his brother-in-law, Bohemian king Wenceslaus, he consolidated his position in Greater Poland against Barnim I of Pomerania and repelled an attack on castle Lubusz by the margrave of Brandenburg and the archbishop of Magdeburg.[7] Following an old tradition of his dynasty, he placed himself under the protection of the Holy See, with which he also allied himself against Frederick II. In spite of all his German connections, Henry the Pious would, therefore, assuredly have maintained the independence and prestige of the kingdom if all his plan had not been annihilated by an unforeseen catastrophe. In 1241, he died as a Christian hero in the Battle of Legnica, in which he was attempting to arrest the Mongolian invasion.[5] His death left the Silesian Piast dynasty deeply shaken.
Fragmentation and turn to Bohemia

After Henry's death in 1241 his brother Bolesław II ruled on behalf of his underage brothers. Since all male members of the family were eligible to rule, a principle critical for the coming years, a hereditary division was put into practice in 1248/51.[8][9] Bolesław established the duchy of Legnica, Konrad I Glogow, Henry III kept Wroclaw together with Ladislaus, who would become archbishop of Salzburg. Soon the next generation divided the territory again. Jawor and Lwówek Śląski split off from Legnica, Duchy of Żagań and Ścinawa from Głogów. In the next generation Brzeg was detached from Wrocław, Świdnica and Duchy of Ziębice from Lwówek Śląski-Jawor and Oleśnica from Głogów. The Duchy of Opole, which was established by Mieszko I and called after its residence Opole, wasn't spared from the divisions, they only began one generation later. The four sons of Wladislaw I of Opole, a grandson of Mieszko, split the duchy into Opole, Koźle- Bytom, Racibórz and Teschen. These duchies were also split again in the next generation. Opole was divided into Opole, Niemodlin and Strzelce Opolskie, Koźle-Bytom in Koźle, Bytom and Toszek, Teschen in Teschen and Oświęcim.
These divisions often were the result of fierce and militant conflicts, in which not only the Silesian parties but also their partisans from neighboring Poland and Bohemia were involved. Whereas the connections to Poland diminished the political ties with Bohemia became increasingly stronger, a development mirrored by the inner Silesian changes caused by the Ostsiedlung, which was started by Piasts when they returned from their exile. The reign of duke Henry IV Probus was exemplary for the position of Silesias duchies in the area of tension between Poland and Bohemia. After the death of his father Henry III he was raised in Prague at the court of Bohemian king Ottokar II, who also became his guardian. After Ottokar's death he did not, as expected, became viceregent of Bohemia for underage Wenceslaus II but was compensated with Kłodzko by Rudolf of Habsburg, who also ennobled Henry to a count of the Holy Roman Empire and granted him his duchy as a fief.[10][11] Henry not only obtained the preeminence in Silesia but, with the help of the German party in Polonia Minor,[10][12][13] also the duchy of Kraków and became duke of Poland. He initially wanted Wenceslaus to become his successor, but changed his plan on the deathbed and granted Wrocław to Henry III and Kraków to Przemysł II, whereas Kłodzko returned to Bohemia.
Vassals of Bohemia and decline

As Przemysł II united Poland, the weak and divided Silesian dukes needed a strong partner who could provide cover. They now separated from the Polish state and subjected to the Bohemian crown.
After the death of Wenceslaus III, king of Bohemia and Poland, the right to the Polish crown was disputed, being claimed by various Piast dukes as well as the successors of Wenceslaus III on the Bohemian throne. In 1327, John of Bohemia invaded Poland in order to gain the Polish crown. After the intervention of King Charles I of Hungary he left Polonia Minor, but on his way back he enforced his supremacy over the Upper Silesian Piasts. In February 1327, five principalities were carved out of Polish Upper Silesia and placed under Bohemian suzerenity: Duchy of Niemodlin, Duchy of Cieszyn, Duchy of Racibórz, Duchy of Koźle and Bytom and the Duchy of Oświęcim and Zator. In April the dukes of Opole and Wrocław also became the tributaries of king John.[14][15]
In 1329, Władysław I the Elbow-high started a war with the Teutonic Order. The Order was supported by John of Bohemia who managed to enforce his supremacy over the dukes of Masovia and Lower Silesia. In April–May 1329, following Lower Silesian duchies became subjects of the Bohemian crown: Ścinawa, Oleśnica, Żagań, Legnica-Brzeg and Jawor. In 1331 the Duchy of Głogów separated from Poland as well.[16]
The last independent Silesian Piast – Bolko II of Świdnica – died in 1368. His wife Agnes ruled the Świdnica duchy until her death in 1392. From that time on, all remaining Silesian Piasts were vassals of the Bohemian crown, although they maintained their sovereign rights.

In 1335, John of Bohemia renounced his claim to the title of king of Poland in favour of Casimir the Great, who in return renounced his claims to Silesia.[17] This was formalized in the treaties of Trenčín and Visegrád, ratified in 1339.[18]: 127
The division into small and smallest territories led to a decline of prestige and power. Many Silesian Piasts now merely had the status of squires with greater rights. Some Piasts entered foreign services as mercenary leaders, like Johann II von Glogau and Sagan. Henry IX traveled through Europe as a goliard. The descent of the dynasty was also illustrated by the marriages of the dukes. The Silesian Piasts of the 13th and 14th century married into princely families especially from German families, but also other European royal lines, whereas later Piasts also married non-princely and even bourgeois women.[4]
With the adoption of the Protestant faith in Silesia, the Piasts again gained importance. Against the Catholic Habsburg dynasty, which ruled Silesia since 1526, the dukes sought political support by entering matrimonies with Protestant, imperial rulers like the Hohenzollern dynasty.[19] Their last attempts of independent policies were the candidatures of Frederick II of Liegnitz for the Bohemian crown (1526) and of Henry XI (1573), Frederick IV (1576) and Christian (1668) for the Polish crown.[19]
During the 15th, 16th and 17th centuries, various branches of the Silesian Piasts became extinct. In 1532, the last Duke of Opole, John II the Good, died, leaving most of Upper Silesia under direct Bohemian rule. In 1675, the last legitimate Silesian Piast – George William, Duke of Liegnitz – died. The last male Silesian Piast was baron Ferdinand II Hohenstein, who died in 1706, the last female Piast, Charlotte, died in 1707.[4]
Silesian Piasts and Poland
The Silesian Piasts formed the oldest branch of the first Polish royal dynasty. This was the reason that even after the fragmentation of Poland their interest in the Polish matters was still strong. Norman Davies stated that the dynastic loyalty of all Piast dukes as well as a single ecclesiastic organisation still secured the unity of the divided Kingdom of Poland. In his opinion the alleged "will" to separate from Poland is contradicted by the continuous involvement of the Silesian Piasts in Polish affairs. He remarks that the dukes of Silesia did not break their connections with their relatives in the rest of Poland. The most visible evidence of this is said to be the fact that in the 13th century three Silesian Dukes – Henry I, Henry II and Henry IV – took control of Kraków and therefore of the senior throne of the whole of Poland.[18]: 113
In Davies' opinion, the Germanisation of Silesia did not necessarily mean a desire to move apart from Poland. He suggests that it was more likely a way to satisfy the Silesian Piasts' ambitions inside Poland. The planned introduction of German settlers would strengthen Silesia, and also the Silesian Piast claims to the senioral throne in Kraków. Only when the Silesian Piasts' ambitions to rule in Kraków were thwarted did they decide to set their province on a different course.[18]: 114
Footnotes
- ^ a b c Andrzej Chwalba (2000). Wydawnictwo Literackie (ed.). Kalendarium Historii Polski (in Polish). Kraków. pp. 49–52. ISBN 83-08-03136-6.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Weczerka, p. XXXIV
- ^ Petry, p. 86
- ^ a b c Pagenstecher, p. 405
- ^ a b c Oskar Halecki; Antony Polonsky (1978). A history of Poland. Routledge. pp. 36–37. ISBN 0-7100-8647-4.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) Google Books - ^ Benedykt Zientara (1997). Henryk Brodaty i jego czasy (in Polish). Warsaw: Trio. pp. 317–320. ISBN 83-85660-46-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Appelt, p. 393
- ^ Weczerka, p. XLII
- ^ Petry, p. 112
- ^ a b Appelt, p. 394
- ^ Petry, p. 122
- ^ Weczerka, p. XLIV
- ^ Petry, p. 131
- ^ Rosamond McKitterick, Michael Jones, Paul Fouracre, Timothy Reuter, David Abulafia, Christopher Allmand, David Luscombe, Jonathan Riley-Smith (2005). Cambridge University Press (ed.). The new Cambridge medieval history. Cambridge. p. 747. ISBN 9780521362900.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Template:En icon Template:La icon Balázs Nagy; Frank Schaer; Ferdinand Seibt (2001). Central European University Press (ed.). Autobiography of Emperor Charles IV. pp. 78–83. ISBN 9789639116320.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ "The new Cambridge medieval history", p. 747
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica: Silesia
- ^ a b c Norman Davies, Roger Moorhouse (2002). Znak (ed.). Mikrokosmos (in Polish). Kraków. pp. 113–114, 127. ISBN 83-240-0172-7.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Pagenstecher, p. 404
References
- Weczerka, Hugo (2003). Handbuch der historischen Stätten: Schlesien. Stuttgart: Kröner Stuttgart. ISBN 3-520-31602-1.
- Pagenstecher (2001). Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB) Bd.20. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot.
- Appelt, Heinrich (1969). Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB) Bd.8. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot.
- Petry, Ludwig; Josef Joachim Menzel; Winfried Irgang (2000). Geschichte Schlesiens. Band 1: Von der Urzeit bis zum Jahre 1526. Stuttgart: Jan Thorbecke Verlag Stuttgart. ISBN 3-7995-6341-5.
