Tajiks
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c. 16–20 million (estimates vary) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 9,450,000–11,550,000[citation needed] (2014) 27–33%[citation needed][1][2] | |
| 6,787,000 (2014)[3] | |
| 1,420,000 (2012, official) other, non-official, scholarly estimates are 8 - 11 million[4][5][6] | |
| 220,000[7] | |
| 201,000[8] | |
| 52,000[9] | |
| 47,500[10] | |
| 15,870[11] | |
| 4,255[12] | |
| Languages | |
| Persian varieties of Dari and Tajiki | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Islam Historically Zoroastrianism and Buddhism | |
Tajik (Dari: تاجيک: Tājīk , Template:Lang-tg) is a general designation for a wide range of Persian-speaking people of Iranian origin,[13] with traditional homelands in present-day Tajikistan, Afghanistan and Uzbekistan.
As a self-designation, the term Tajik, which earlier on had been more or less pejorative, has become acceptable only during the last several decades, particularly as a result of Soviet administration in Central Asia.[13] Alternative names for the Tajiks are Fārsī (Persian), Fārsīwān (Persian-speaker), and Dīhgān (cf. Template:Lang-tg, literally "farmer or settled villager", in a wider sense "settled" in contrast to "nomadic" and also described as a class of land-owning magnates during the Sassanid and early Islamic period).[14]
Not all Tajiks speak a variety of modern Persian. They may speak any one of the extant Iranian languages. For example, the Tajiks of China are actually Pamiris and speak the Eastern Iranic Pamiri languages and are distinct from more western Tajiks.[15][16]
History
The Tajiks are an Iranian people, speaking a variety of Persian, concentrated in the Oxus Basin, the Farḡāna valley (Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan) and on both banks of the upper Oxus, i.e., the Pamir Mountains (Mountain Badaḵšān, in Tajikistan) and northeastern Afghanistan (Badaḵšān).[17] Historically the Tajiks were agriculturalists.[18]
According to Richard Nelson Frye, a leading historian of Iranian and Central Asian history, the Persian migration to Central Asia may be considered the beginning of the modern Tajik nation, and ethnic Persians, along with some elements of East-Iranian Bactrians and Sogdians, as the main ancestors of modern Tajiks.[19] In later works, Frye expands on the complexity of the historical origins of the Tajiks. In a 1996 publication, Frye explains that many "factors must be taken into account in explaining the evolution of the peoples whose remnants are the Tajiks in Central Asia" and that "the peoples of Central Asia, whether Iranian or Turkic speaking, have one culture, one religion, one set of social values and traditions with only language separating them."[20]
The geographical division between the eastern and western Iranians is often considered historically and currently to be the desert Dasht-e Kavir, situated in the center of the Iranian plateau.[citation needed]
Name

According to Encyclopaedia Iranica:[17]
The most plausible and generally accepted origin of the word is Middle Persian tāzīk ‘Arab’ (cf. New Persian tāzi), or an Iranian (Sogdian or Parthian) cognate word. The Muslim armies that invaded Transoxiana early in the eighth century, conquering the Sogdian principalities and clashing with the Qarluq Turks (see Bregel, Atlas, Maps 8–10) consisted not only of Arabs, but also of Persian converts from Fārs and the central Zagros region (Bartol’d [Barthold], “Tadžiki,” pp. 455–57). Hence the Turks of Central Asia adopted a variant of the Iranian word, täžik, to designate their Muslim adversaries in general. For example, the rulers of the south Indian Chalukya dynasty and Rashtrakuta dynasty also referred to the Arabs as "Tajika" in the 8th and 9th century.[22][23] By the eleventh century (Yusof Ḵāṣṣ-ḥājeb, Qutadḡu bilig, lines 280, 282, 3265), the Qarakhanid Turks applied this term more specifically to the Persian Muslims in the Oxus basin and Khorasan, who were variously the Turks’ rivals, models, overlords (under the Samanid Dynasty), and subjects (from Ghaznavid times on). Persian writers of the Ghaznavid, Seljuq and Atābak periods (ca. 1000–1260) adopted the term and extended its use to cover Persians in the rest of Greater Iran, now under Turkish rule, as early as the poet ʿOnṣori, ca. 1025 (Dabirsiāqi, pp. 3377, 3408). Iranians soon accepted it as an ethnonym, as is shown by a Persian court official’s referring to mā tāzikān “we Tajiks” (Bayhaqi, ed. Fayyāz, p. 594). The distinction between Turk and Tajik became stereotyped to express the symbiosis and rivalry of the (ideally) nomadic military executive and the urban civil bureaucracy (Niẓām al-Molk: tāzik, pp. 146, 178–79; Fragner, “Tādjīk. 2” in EI2 10, p. 63).
According to the Encyclopaedia of Islam, however, the oldest known usage of the word Tajik as a reference to Persians in Persian literature can be found in the writings of the Persian poet Jalal ad-Din Rumi.[24] The 15th century Turkic-speaking poet Mīr Alī Šer Navā'ī also used Tajik as a reference to Persians.[25]
An example for the usage of the word Tajik in Persian literature is, for example, the writing of Sa'adi:
شایَد کِه بَه پادشاه بگویند
ترک تو بریخت خون تاجیک
Šāyad ki ba pādšāh bigōyand
Turk-i tu birēxt xūn-i Tāǰīk
It's appropriate to tell the King,
Your Turk shed the blood of Tajik
Location


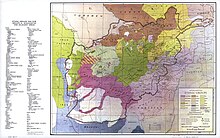
The Tajiks are the principal ethnic group in most of Tajikistan, as well as in northern and western Afghanistan, though there are more Tajiks in Afghanistan than in Tajikistan. Tajiks are a substantial minority in Uzbekistan, as well as in overseas communities. Historically, the ancestors of the Tajiks lived in a larger territory in Central Asia than now.
Afghanistan
According to the World Factbook, Tajiks make up about 27% of the population in Afghanistan,[2] but the Encyclopædia Britannica claims that they constitute about one-fifth of the population.[26] They are predominant in four of the largest cities in Afghanistan (Kabul, Mazar-e Sharif, Herat, and Ghazni) and make up the largest ethnic group in the northern and western provinces of Balkh, Takhar, Badakhshan, Samangan, Parwan, Panjshir, Kapisa, Baghlan, Ghor, Badghis and Herat.
In Afghanistan, the Tajiks do not organize themselves by tribes and refer to themselves by the region, province, city, town, or village that they are from; such as Badakhshi, Baghlani, Mazari, Panjsheri, Kabuli, Herati, Kohistani etc.[27] Although in the past, some non-Pashto speaking tribes were identified as Tajik, for example the Furmuli.[28][29]
Tajikistan
Tajiks comprise around 79.9% of the population of Tajikistan.[3] This number includes speakers of the Pamiri languages, including Wakhi and Shughni, and the Yaghnobi people who in the past were considered by the government of the Soviet Union nationalities separate from the Tajiks. In the 1926 and 1937 Soviet censuses, the Yaghnobis and Pamiri language speakers were counted as separate nationalities. After 1937, these groups were required to register as Tajiks.[30]
Uzbekistan

In Uzbekistan, the Tajiks are the largest part of the population of the ancient cities of Bukhara and Samarkand, and are found in large numbers in the Surxondaryo Province in the south and along Uzbekistan's eastern border with Tajikistan. According to official statistics (2000), Surxondaryo Province accounts for 24.4% of all Tajiks in Uzbekistan, with another 34.3% in Samarqand and Bukhara provinces.[31]
Official statistics in Uzbekistan state that the Tajik community comprises 5% of the nation's total population.[32] However, these numbers do not include ethnic Tajiks who, for a variety of reasons, choose to identify themselves as Uzbeks in population census forms.[33] During the Soviet "Uzbekization" supervised by Sharof Rashidov, the head of the Uzbek Communist Party, Tajiks had to choose either stay in Uzbekistan and get registered as Uzbek in their passports or leave the republic for Tajikistan, which is mountainous and less agricultural.[34] It is only in the last population census (1989) that the nationality could be reported not according to the passport, but freely declared on the basis of the respondent's ethnic self-identification.[35] This had the effect of increasing the Tajik population in Uzbekistan from 3.9% in 1979 to 4.7% in 1989. Expert estimates suggest that Tajiks may make up 35% of Uzbekistan's population.[4][36]
Kazakhstan
According to the 1999 population census, there were 26,000 Tajiks in Kazakhstan (0.17% of the total population), about the same number as in the 1989 census.
Kyrgyzstan
According to official statistics, there were about 47,500 Tajiks in Kyrgyzstan in 2007 (0.9% of the total population), up from 42,600 in the 1999 census and 33,500 in the 1989 census.
Turkmenistan
According to the last Soviet census in 1989,[37] there were 3,149 Tajiks in Turkmenistan, or less than 0.1% of the total population of 3.5 million at that time. The first population census of independent Turkmenistan conducted in 1995 showed 3,103 Tajiks in a population of 4.4 million (0.07%), most of them (1,922) concentrated in the eastern provinces of Lebap and Mary adjoining the borders with Afghanistan and Uzbekistan.[38]
Russia
The population of Tajiks in Russia is about 200,303 according to the 2010 census, up from 38,000 in the last Soviet census of 1989.[39] Most Tajiks came to Russia after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, often as guest workers.
Pakistan
There are an estimated 220,000 Tajiks in Pakistan, mainly refugees from Afghanistan and Tajikistan.[40] Their number was higher in the 1990s, but in the last decade many have left Pakistan and returned to their native countries.[7] Some Tajiks are also living in Hunza, Ishkoman and along the border of Afghanistan and Pakistan called "Broghil".
China
Chinese Tajiks or Mountain Tajiks in China (Sarikoli: [tudʒik], Tujik; Chinese: 塔吉克族; pinyin: Tǎjíkè Zú), including Sarikolis (majority) and Wakhis (minority) in China, are an extension of the Pamiri ethnic group that lives in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China. They are Mountain Tajiks, unlike Plain Tajiks in Tajikistan and Afghanistan. They are one of the 56 nationalities officially recognized by the government of China.
Physical characteristics and genetics

On the whole, Tajiks are a genetically diverse population, displaying a wide range of phenotypes.[citation needed] Around 10% of Tajiks are said to have blond hair, more prevalent in the Zarafshan and Pamir region, where they are known as Pamiri people.[41] Some ethnic Tajiks, particularly those from Tajikistan, show clear Mongoloid admixture possibly originating from their Kyrgyz and Uzbek neighbors. The dominant haplogroup among modern Tajiks is the Haplogroup R1a Y-DNA. ~45% of Tajik men share R1a (M17), ~18% J (M172), and ~8% R2 (M124). Tajiks of Panjikent score 68% R1a, Tajiks of Khojant score 64% R1a.[42] The high frequency of haplogroup R1a in the Tajiks probably reflects a strong founder effect.[43]
Culture
| Part of a series on |
| Tajiks |
|---|
| History and culture |
| Population |
Language

The language of the Tajiks is an eastern dialect of Persian, called Dari (derived from Darbārī, "[of/from the] royal courts", in the sense of "courtly language"), or also Parsi-e Darbari. In Tajikistan, where Cyrillic script is used, it is called the Tajiki language. Historically, it was considered the local dialect of Persian spoken by the Tajik/Persian ethnic group in Central Asia, from where it spread westward only to drive the Arabic language out as the mother tongue of ethnic Persians.[citation needed] In Afghanistan, unlike in Tajikistan, Tajiks continue to use the Perso-Arabic script, as well as in Iran. However, when the Soviet Union introduced the Latin script in 1928, and later the Cyrillic script, the Persian dialect of Tajikistan came to be considered a separate (Persian) language.[dubious – discuss][citation needed] Since the 19th century, Tajiki has been strongly influenced by the Russian language and has incorporated many Russian language loan words.[44] It has also adopted fewer Arabic loan words than Iranian Persian, while retaining vocabulary that has fallen out of use in the latter language. In Tajikistan, in ordinary speech, also known as “zaboni kucha” (lit. "street language", as opposed to “zaboni adabi”, lit. "literary language", which is used in schools, media etc.), many urban Tajiks prefer to use Russian loanwords instead of their literary Persian analogs.
The dialects of the Persians of Iran and of the Tajiks of central Asia have a common origin.[dubious – discuss][citation needed] This is underscored by the Tajiks' claim to such famous writers as Rudaki, Ferdowsi, Anwari, Rumi, Avicenna, Hafez and other famous Persian poets.[citation needed] Russian is widely used in government and business in Tajikistan as well. Since Tajikistan gained independence, there has been a public debate about whether Tajiki should revert to the Perso-Arabic script.[citation needed]
Religion

Various scholars have recorded the Zoroastrian, Buddhist, and Aryan pre-Islamic heritage of the Tajik people. Early temples for fire worship have been found in Balkh and Bactria and excavations in present-day Tajikistan and Uzbekistan show remnants of Zoroastrian fire temples.[45]
Today, however, the great majority of Tajiks follow Sunni Islam, although small Twelver and Ismaili Shia minorities also exist in scattered pockets. Areas with large numbers of Shias include Herat, Bamyan, Badakhshan provinces in Afghanistan, the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Province in Tajikistan, and Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Some of the famous Islamic scholars were from East-Iranian regions lying in Afghanistan and Tajikistan today and therefore can arguably be viewed as Tajiks. They include Abu Hanifa, Imam Bukhari, Tirmidhi, Abu Dawood, Abu Mansur Maturidi, and many others. Since the Tajiks generally follow Islamic belief patterns. Belief in the supernatural, outside of formal Islam, falls into several categories: curative customs, fortune-telling, and ascription of bad fortune to the power of fate or of evil beings called jinn.
According to a 2009 U.S. State Department release, the population of Tajikistan is 98% Muslim, (approximately 85% Sunni and 5% Shia).[46] In Afghanistan, the great number of Tajiks adhere to Sunni Islam. The smaller number of Tajiks who may follow Twelver Shia Islam are locally called Farsiwan[citation needed]. The community of Bukharian Jews in Central Asia speak a dialect of Persian. The Bukharian Jewish community in Uzbekistan is the largest remaining community of Central Asian Jews and resides primarily in Bukhara and Samarkand, while the Bukharaian Jews of Tajikistan live in Dushanbe and number only a few hundred.[47] From the 1970s to the 1990s the majority of these Tajik-speaking Jews emigrated to the United States and to Israel in accordance with Aliyah. Recently, the Protestant community of Tajiks descent has experienced significant growth, a 2015 study estimates some 2,600 Muslim Tajik converted to Christianity.[48]
Tajikistan marked 2009 as the year to commemorate the Tajik Sunni Muslim jurist Abu Hanifa, whose ancestry hailed from Parwan Province of Afghanistan, as the nation hosted an international symposium that drew scientific and religious leaders.[49] The construction of one of the largest mosques in the world, funded by Qatar, was announced in October 2009. The mosque is planned to be built in Dushanbe and construction is said to be completed by 2014.[50]
Recent developments
Cultural revival

The collapse of the Soviet Union and the civil war in Afghanistan both gave rise to a resurgence in Tajik nationalism across the region.[citation needed] Tajikistan in particular has been a focal point for this movement, and the government there has made a conscious effort to revive the legacy of the Samanid empire, the first Tajik-dominated state in the region after the Arab advance. For instance, the President of Tajikistan, Emomalii Rahmon, dropped the Russian suffix "-ov" from his surname and directed others to adopt Tajik names when registering births.[51] According to a government announcement in October 2009, approximately 4,000 Tajik nationals have dropped "ov" and "ev" from their surnames since the start of the year.[52]
In an interview to Iranian news media in May 2008, Tajikistan's deputy culture minister said that Tajikistan would study the issue of switching its Tajik alphabet from Cyrillic to the Persian script used in Iran and Afghanistan when the government feels that "the Tajik people became familiar with the Persian alphabet".[53] More recently, the Islamic Renaissance Party of Tajikistan seeks to have the nation's language referred to as "Tajiki-Farsi" rather than "Tajik." The proposal has drawn criticism from Russian media since the bill seeks to remove the Russian language as the mode of interethnic communication.[54] In 1989, the original name of the language (Farsi) was added to its official name in brackets. However, Rahmon's government renamed the language to simply 'Tajiki' in 1994. On October 2009, Tajikistan adopted the law that removes Russian as the "language for interethnic communication."[55]
See also
Notes and references
- ^ Country Factfiles. — Afghanistan, page 153. // Atlas. Fourth Edition. Editors: Ben Hoare, Margaret Parrish. Publisher: Jonathan Metcalf. First published in Great Britain in 2001 by Dorling Kindersley Limited. London: Dorling Kindersley, 2010, 432 pages. ISBN 9781405350396 "Population: 28.1 million
Religions: Sunni Muslim 84%, Shi'a Muslim 15%, other 1%
Ethnic Mix: Pashtun 38%, Tajik 25%, Hazara 19%, Uzbek, Turkmen, other 18%" - ^ a b "Population of Afghanistan". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). Retrieved 2012-08-09.
- ^ a b "Tajikistan". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. May 5, 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-26.
- ^ a b Richard Foltz (1996). "The Tajiks of Uzbekistan". Central Asian Survey. 15 (2): 213–216. doi:10.1080/02634939608400946.
- ^ Karl Cordell, "Ethnicity and Democratisation in the New Europe", Routledge, 1998. p. 201: "Consequently, the number of citizens who regard themselves as Tajiks is difficult to determine. Tajikis within and outside of the republic, Samarkand State University (SamGU) academic and international commentators suggest that there may be between six and seven million Tajiks in Uzbekistan, constituting 30% of the republic's 22 million population, rather than the official figure of 4.7%(Foltz 1996;213; Carlisle 1995:88).
- ^ Lena Jonson (1976) "Tajikistan in the New Central Asia", I.B.Tauris, p. 108: "According to official Uzbek statistics there are slightly over 1 million Tajiks in Uzbekistan or about 3% of the population. The unofficial figure is over 6 million Tajiks. They are concentrated in the Sukhandarya, Samarqand and Bukhara regions."
- ^ a b United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (2002-10-01). "Long-time Tajik refugees return home from Pakistan". UNHCR. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ Russian 2010 Census results; see also Ethnic groups in Russia
- ^ This figure only includes Tajiks from Afghanistan. The population of people from Afghanistan the United States is estimated as 80,414 (2005). United States Census Bureau. "US demographic census". Retrieved 2008-01-23. Of this number, approximately 65% are Tajiks according to a group of American researchers (Barbara Robson, Juliene Lipson, Farid Younos, Mariam Mehdi). Robson, Barbara and Lipson, Juliene (2002) "Chapter 5(B)- The People: The Tajiks and Other Dari-Speaking Groups" The Afghans – their history and culture Cultural Orientation Resource Center, Center for Applied Linguistics, Washington, D.C., OCLC 56081073.
- ^ "Ethnic composition of the population in Kyrgyzstan 1999–2007" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ This figure only includes Tajiks from Afghanistan. The population of people with descent from Afghanistan in Canada is 48,090 according to Canada's 2006 Census. Tajiks make up an estimated 27% of the population of Afghanistan. The Tajik population in Canada is estimated from these two figures. Ethnic origins, 2006 counts, for Canada.
- ^ State statistics committee of Ukraine – National composition of population, 2001 census (Ukrainian)
- ^ a b C.E. Bosworth, B.G. Fragner (1999). "TĀDJĪK". Encyclopaedia of Islam (CD-ROM Edition v. 1.0 ed.). Leiden, The Netherlands: Koninklijke Brill NV.
- ^ M. Longworth Dames, G. Morgenstierne, and R. Ghirshman (1999). "AFGHĀNISTĀN". Encyclopaedia of Islam (CD-ROM Edition v. 1.0 ed.). Leiden, The Netherlands: Koninklijke Brill NV.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Arlund, Pamela S. (2006). An Acoustic, Historical, And Developmental Analysis Of Sarikol Tajik Diphthongs. PhD Dissertation. The University of Texas at Arlington. p. 191.
- ^ Felmy, Sabine (1996). The voice of the nightingale: a personal account of the Wakhi culture in Hunza. Karachi: Oxford University Press. p. 4. ISBN 0-19-577599-6.
- ^ a b "TAJIK i. THE ETHNONYM: ORIGINS AND APPLICATION".
- ^ Zerjal, Tatiana; Wells, R. Spencer; Yuldasheva, Nadira; Ruzibakiev, Ruslan; Tyler-Smith, Chris (2002). "A Genetic Landscape Reshaped by Recent Events: Y-Chromosomal Insights into Central Asia". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 71 (3): 466–482. doi:10.1086/342096. PMC 419996. PMID 12145751.
- ^ Richard Nelson Frye, "Persien: bis zum Einbruch des Islam" (original English title: "The Heritage Of Persia"), German version, tr. by Paul Baudisch, Kindler Verlag AG, Zürich 1964, pp. 485–498
- ^ Frye, Richard Nelson (1996). The heritage of Central Asia from antiquity to the Turkish expansion. Princeton: Markus Wiener Publishers. p. 4. ISBN 1-55876-110-1.
- ^ Lena Jonson, Tajikistan in the new Central Asia, (I.B.Tauris, 2006), 18.
- ^ Political History of the Chālukyas of Badami by Durga Prasad Dikshit p.192
- ^ The First Spring: The Golden Age of India by Abraham Eraly p.91
- ^ C.E. Bosworth/B.G. Fragner, "Tādjīk", in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition: "... In Islamic usage, [Tādjīk] eventually came to designate the Persians, as opposed to Turks [...] the oldest citation for it which Schraeder could find was in verses of Djalāl al-Dīn Rūmī ..."
- ^ Ali Shir Nava'i Muhakamat al-lughatain tr. & ed. Robert Devereaux (Leiden: Brill) 1966 p6
- ^ "Tajik". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved November 6, 2011.
There were about 5,000,000 in Afghanistan, where they constituted about one-fifth of the population.
- ^ Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress (1997). "Afghanistan: Tajik". Country Studies Series. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ^ Bellew, Henry Walter (1891) An inquiry into the ethnography of Afghanistan The Oriental Institute, Woking, Butler & Tanner, Frome, United Kingdom, page 126, OCLC 182913077
- ^ Markham, C. R. (January 1879) "The Mountain Passes on the Afghan Frontier of British India" Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society and Monthly Record of Geography (New Monthly Series) 1(1): pp. 38–62, p.48
- ^ Suny, Ronald Grigor (2006). "History and Foreign Policy: From Constructed Identities to "Ancient Hatreds" East of the Caspian". In Shaffer, Brenda (ed.). The Limits of Culture: Islam and Foreign Policy. MIT Press. pp. 100–110. ISBN 0-262-69321-6.
- ^ Ethnic Atlas of Uzbekistan, Part 1: Ethnic minorities, Open Society Institute, table with number of Tajiks by province Template:Ru icon.
- ^ "Uzbekistan". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. May 6, 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-26.
- ^ Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor (February 23, 2000). "Uzbekistan". Country Reports on Human Rights Practices – 1999. U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rahim Masov, The History of the Clumsy Delimitation, Irfon Publ. House, Dushanbe, 1991 Template:Ru icon. English translation: The History of a National Catastrophe, transl. Iraj Bashiri, 1996.
- ^ Ethnic Atlas of Uzbekistan, Part 1: Ethnic minorities, Open Society Institute, p. 195 Template:Ru icon.
- ^ Svante E. Cornell, "Uzbekistan: A Regional Player in Eurasian Geopolitics?", European Security, vol. 20, no. 2, Summer 2000.
- ^ http://demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_89.php?reg=14
- ^ Population census of Turkmenistan 1995, Vol. 1, State Statistical Committee of Turkmenistan, Ashgabat, 1996, pp. 75–100.
- ^ "2002 Russian census". Perepis2002.ru. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ The ethnic composition of the 1.7 million registered Afghan refugees living in Pakistan are believed to be 85% Pashtun and 15% Tajik, Uzbek and others. "2012 UNHCR country operations profile – Pakistan". Retrieved 2012-08-08.
- ^ Around the Roof of the World. Nicholas Shoumatoff, Nina Shoumatoff (2000). University of Michigan Press. p.9. ISBN 0-472-08669-3
- ^ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC56946/pdf/pq010244.pdf
- ^ "A Genetic Landscape Reshaped by Recent Events: Y-Chromosomal Insights into Central Asia". PubMed Central (PMC).
- ^ Michael Knüppel. Turkic Loanwords in Persian. Encyclopædia Iranica.
- ^ Lena Jonson, Tajikistan in the New Central Asia: Geopolitics, Great Power Rivalry and Radical Islam (International Library of Central Asia Studies), page 21
- ^ "Background Note: Tajikistan". State.gov. 2012-01-24. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ J. Sloame, "Bukharan Jews", Jewish Virtual Library, (LINK)
- ^ Johnstone, Patrick; Miller, Duane Alexander (2015). "Believers in Christ from a Muslim Background: A Global Census". IJRR. 11 (10): 1–19. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- ^ "Today marks 18th year of Tajik independence and success". Todayszaman.com. 2009-09-09. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ Daniel Bardsley (2010-05-25). "Qatar paying for giant mosque in Tajikistan". Thenational.ae. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ McDermott, Roger (2007-04-25). "Tajikistan restates its strategic partnership with Russia, while sending mixed signals". The Jamestown Foundation. Archived from the original on 2007-10-14. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ^ "Some 4,000 Tajiks opt to use the traditional version of their names this year". Asiaplus.tj. 1962-10-17. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ "Tajikistan may consider using Persian script when the conditions are met", interview of Tajikistan's Deputy Culture Minister with Iranian News Agency, 2 May 2008.
- ^ Tajik Islamic Party Seeks Tajiki-Farsi Designation.
- ^ "Tajikistan Drops Russian As Official Language". Rferl.org. 2009-10-07. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
Further reading
- Dupree, Louis (1980). Afghanistan. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
- Jawad, Nassim (1992). Afghanistan: A Nation of Minorities. London: Minority Rights Group International. ISBN 0-946690-76-6.
- Rahmonov, Emomali (2001). The Tajiks in the Mirror of History: From the Aryans to the Samanids. Guernsey, United Kingdom: London River Editions. p. 272. ISBN 0-9540425-0-6.
- World Almanac and Book of Facts (2003 ed.). World Almanac Books. ISBN 0-88687-882-9.
External links
- Khorasan: selected topics relating to Tajiks
- Uzbekistan: Ethnic Composition And Discrimination
- Ethnologue statistics on Eastern Farsi speakers & statistics regarding Tajiki speakers.
- Male Genetics of Central Asia, South Asia, and West Asia (the origin of R1a1 is under question see) (see Genetics and Archaeogenetics of South Asia)
- Tajik Jewelry
- Free Online Tajik Dictionary
