Ahmad Shah Durrani
| Ahmad Shah Durrani احمد شاه دراني احمد شاه درانی | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Padishah Ghazi Shāh Durr-i-Durrān ("King, Pearl of Pearls") | |||||||||
 Portrait of Ahmad Shah Durrani, c. 1757 | |||||||||
| 1st Emir of the Durrani Empire | |||||||||
| Reign | 1747–1772 | ||||||||
| Coronation | July 1747[1] | ||||||||
| Predecessor | Position established | ||||||||
| Successor | Timur Shah Durrani | ||||||||
| Born | Ahmad Khan Abdali 1720–1722[2]: 287 Herat, Sadozai Sultanate of Herat (present-day Afghanistan)[3] or Multan, Mughal Empire (present-day Pakistan)[4][5] | ||||||||
| Died | (aged 49–52)[2]: 409 Maruf, Kandahar Province, Durrani Empire (present-day Afghanistan) | ||||||||
| Burial | June 1772 | ||||||||
| Spouse | Hazrat Begum Iffat-un-Nissa Begum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Dynasty | House of Durrani | ||||||||
| Father | Mohammad Zaman Khan Abdali | ||||||||
| Mother | Zarghona Anaa[6] | ||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī (Template:Lang-ps; Template:Lang-prs), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (احمد شاه ابدالي), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan.[7][8][9] In July 1747, Ahmad Shah was appointed as King of the Afghans by a loya jirga in Kandahar, where he set up his capital.[1] Primarily with the support of the Pashtun tribes,[10] Ahmad Shah pushed east towards the Mughal and Maratha Empires of India, west towards the disintegrating Afsharid Empire of Iran, and north towards the Khanate of Bukhara of Turkestan. Within a few years, he extended his control from Khorasan in the west to North India in the east, and from the Amu Darya in the north to the Arabian Sea in the south.[11][8][12]
Soon after accession, Ahmad Shah adopted the epithet Shāh Durr-i-Durrān, "King, Pearl of Pearls", and changed the name of his Abdali tribe to "Durrani" after himself. The Tomb of Ahmad Shah Durrani is located in the center of Kandahar, adjacent to Kirka Sharif (Shrine of the Cloak), which contains a cloak believed to have been worn by the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Afghans often refer to Ahmad Shah as Ahmad Shāh Bābā, "Ahmad Shah the Father."[7][13][14][15]
Early years

Ahmad's father, Mohammad Zaman Khan, was the Governor of Herat and chief of the Pashtun Abdali tribe, while his mother, Zarghona Anaa, was daughter of Khalu Khan Alakozai and belonged to the Alakozai tribe. Ahmad was born in Herat (then Sadozai Sultanate of Herat, present-day Afghanistan),[3] or Multan (then Mughal Empire, present-day Pakistan)[4][5] in 1720–1722 around the time of his father's death, when the Abdali leadership still controlled the Herat region.
In June 1729, the Abdali forces under Zulfiqar had surrendered to Nader Shah Afshar, the rising new ruler of Persia. However, they soon began a rebellion and took over Herat as well as Mashad. In July 1730, he defeated Ibrahim Khan, a military commander and brother of Nader Shah. This prompted Nader Shah to retake Mashad and also intervene in the power struggle of Harat. By July 1731, Zulfiqar returned to his capital Farah where he had been serving as the governor since 1726. A year later Nadir's brother Ibrahim Khan took control of Farah. During this time Zulfiqar and the young Durrani fled to Kandahar where they took refuge with the Ghiljis. They were later made political prisoners by Hussain Hotak, the Ghilji ruler of the Kandahar region.[16]
Nader Shah had been enlisting the Abdalis in his army since around 1729. After conquering Kandahar in 1738, Durrani and his brother Zulfiqar were freed and provided with leading careers in Nader Shah's administration. Zulfiqar was made Governor of Mazandaran while Durrani remained working as Nader Shah's personal attendant. The Ghiljis, who are originally from the territories east of the Kandahar region, were expelled from Kandahar in order to resettle the Abdalis along with some Qizilbash and other Persians.[17]
Durrani proved himself in Nader Shah's service and was promoted from a personal attendant (yasāwal) to command the Abdali Regiment, a cavalry of four thousand soldiers and officers. The Abdali Regiment was part of Nader Shah's military during his invasion of the Mughal Empire in 1738.[18]
Popular history has it that the Shah could see the talent in his young commander. Later on, according to Pashtun legend, it is said that in Delhi Nader Shah summoned Durrani, and said, "Come forward Ahmad Abdali. Remember Ahmad Khan Abdali, that after me the Kingship will pass on to you.[19] Nader Shah recruited him because of his "impressive personality and valour" also because of his "loyalty to the Persian monarch".[20]
Rise to power

Nader Shah's rule abruptly ended in June 1747 when he was assassinated by his own guards. The guards involved in the assassination did so secretly so as to prevent the Abdalis from coming to their King's rescue. However, Durrani was told that the Shah had been killed by one of his wives. Despite the danger of being attacked, the Abdali contingent led by Durrani rushed either to save the Shah or to confirm what happened. Upon reaching the Shah's tent, they were only to see his body and severed head. Having served him so loyally, the Abdalis wept at having failed their leader,[21] and headed back to Kandahar. Before the retreat to Kandahar, he had "removed" the royal seal from Nader Shah's finger and the Koh-i-Noor diamond tied "around the arm of his deceased master". On their way back to Kandahar, the Abdalis had "unanimously accepted" Durrani as their new leader. Hence he "assumed the insignia of royalty" as the "sovereign ruler of Afghanistan".[22]
At the time of Nadir's death, he commanded a contingent of Abdali Pashtuns. Realizing that his life was in jeopardy if he stayed among the Persians who had murdered Nader Shah, he decided to leave the Persian camp, and with his 4,000 troops he proceeded to Qandahar. Along the way and by sheer luck, they managed to capture a caravan with booty from India. He and his troops were rich; moreover, they were experienced fighters. In short, they formed a formidable force of young Pashtun soldiers who were loyal to their high-ranking leader.[23]
One of Durrani's first acts as chief was to adopt the epithet Shāh Durr-i-Durrān, "King, Pearl of Pearls."[7]
Forming the last Afghan empire
Although Ahmad Shah appointed his fellow Durrani (Abdali) clansmen for most senior military posts, his army was otherwise ethnically diverse with soldiers also from various other ethnic and tribal groups, including non-Durrani Pashtun tribes like the Ghilji, and non-Pashtun groups such as Qizilbash, Hazaras, Tajiks, Uzbeks, and Baloch.[17] He began his military conquest by capturing Qalati Ghilji from its governor Ashraf Tokhi and installed his own governor in Ghazni. He then wrestled Kabul and Peshawar from Mughal-appointed governor Nasir Khan, and conquered the area up to the Indus River. On 15 July 1747, Ahmad Shah appointed Muhammad Hashim Afridi as chief of the Afridi of Peshawar.[1][22] Ahmad Shah conquered Herat in 1750, Balkh and Badakhshan in 1751, and Kashmir in 1752.[24]
He also made two campaigns into Khorasan (1750–51 and 1754–55).[25] During the first campaign he besieged Mashhad in July 1750 but retreated after four months and on November 10 moved onto Nishapur. His forces suffered heavy casualties and were forced to retreat in early 1751. In 1754 he invaded again. In June 1754 he took Tun and on July 23 had besieged Mashhad.[25] Mashhad fell on December 2 and although Shahrokh Shah was re-appointed as leader of Khorasan in May 1755 he was forced to cede Torshiz, Bakharz, Jam, Khaf, and Turbat-e Haidari to the Afghans.[25][13] He invaded Nishapur again and after a 7-day siege the city fell on June 24, 1755, and was utterly destroyed.[25]
Indian invasions

Early invasions

Peshawar served as a convenient point for Ahmad Shah for his military conquests in Hindustan. From 1748 to 1767, he invaded Hindustan eight times. He first crossed the Indus River in 1748, the year after his ascension – his forces sacked and absorbed Lahore. In 1749, Ahmad Shah captured the area of Punjab around Lahore. In the same year, the Mughal ruler was induced to cede Sindh and all of the Punjab including the vital trans-Indus River to him, in order to save his capital from being attacked by the forces of the Durrani Empire[citation needed] Having thus gained substantial territories to the east without a fight, Ahmad Shah and his forces turned westward to take possession of Herat, which was ruled by Nader Shah's grandson, Shah Rukh. The city fell to the Afghans in 1750, after almost a year of siege and bloody conflict; the Afghan forces then pushed on into present-day Iran, capturing Nishapur and Mashhad in 1751.[26] Following the recapture of Mashhad in 1754, Ahmad Shah visited the eighth Imam's sepulchre and ordered repairs to be made.[26] Ahmad Shah then pardoned Shah Rukh and reconstituted Khorasan, but a tributary of the Durrani Empire. This marked the westernmost border of the Afghan Empire as set by the Pul-i-Abrisham, on the Mashhad-Tehran road.[27]
Third battle of Panipat

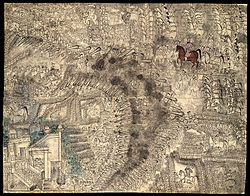
The Mughal power in northern India had been declining since the reign of Aurangzeb, who died in 1707. In 1751–52, the Ahamdiya treaty was signed between the Marathas and Mughals, when Balaji Bajirao was the Peshwa of the Maratha Empire.[28] Through this treaty, the Marathas controlled large parts of India from their capital at Pune and Mughal rule was restricted only to Delhi (Mughals remained the nominal heads of Delhi). Marathas were now straining to expand their area of control towards the Northwest of India. Durrani sacked the Mughal capital and withdrew with the booty he coveted. To counter the Afghans, Peshwa Balaji Bajirao sent Raghunathrao. He succeeded in ousting Timur Shah and his court from India and brought northwest of India up to Peshawar under Maratha rule.[29] Thus, upon his return to Kandahar in 1757, Durrani chose to return to India and confront the Maratha forces to regain northwestern part of the subcontinent.
In 1761, Durrani set out on his campaign to win back lost territories. The early skirmishes ended in victory for the Afghans against the Maratha garrisons in northwest India. By 1759, Durrani and his army had reached Lahore and were poised to confront the Marathas. By 1760, the Maratha groups had coalesced into a big enough army under the command of Sadashivrao Bhau. Once again, Panipat was the scene of a battle for control of northern India. The Third battle of Panipat was fought between Durrani's Afghan forces and the Maratha forces in January 1761, and resulted in a decisive Durrani victory.[30]
Central Asia
The historical area of what is modern day Xinjiang consisted of the distinct areas of the Tarim Basin and Dzungaria, and was originally populated by Indo-European Tocharian and Eastern Iranian Saka peoples who practiced the Buddhist religion. The area was subjected to Turkification and Islamification at the hands of invading Turkic Muslims. Both the Buddhist Turkic Uyghurs and Muslim Turkic Karluks participated in the Turkification and conquest of the native Buddhist Indo-European inhabitants of the Tarim Basin. The Turkic Muslims then proceeded to conquer the Turkic Buddhists in Islamic holy wars and converted them to Islam. The mixture between the invading Turkic peoples and the native Caucasian Indo-European inhabitants resulted in the modern day Turkic speaking hybrid Europoid-East Asian inhabitants of Xinjiang. The Turkification was carried out in the 9th and 10th centuries by two different Turkic Kingdoms, the Buddhist Uyghur Kingdom of Qocho and the Muslim Karluk Kara-Khanid Khanate. Halfway in the 10th century the Saka Iranic Buddhist Kingdom of Khotan came under attack by the Turkic Muslim Karakhanid ruler Musa, and in what proved to be a pivotal moment in the Turkification and Islamification of the Tarim Basin, the Karakhanid leader Yusuf Qadir Khan conquered Khotan around 1006.[31]
The Turkic Muslim sedentary people of the Tarim Basin of Altishahr were originally ruled by the Chagatai Khanate while the nomadic Buddhist Dzungar Oirats in Dzungaria ruled over the Dzungar Khanate. The Naqshbandi Sufi Khojas, descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, had replaced the Chagatayid Khans as the ruling authority of the Tarim Basin in the early 17th century. There was a struggle between two factions of Khojas, the Afaqi (White Mountain) faction and the Ishaqi (Black Mountain) faction. The Ishaqi defeated the Afaqi, which resulted in the Afaqi Khoja inviting the 5th Dalai Lama, the leader of the Tibetan Buddhists, to intervene on his behalf in 1677. The 5th Dalai Lama then called upon his Dzungar Buddhist followers in the Zunghar Khanate to act on this invitation. The Dzungar Khanate then conquered the Tarim Basin in 1680, setting up the Afaqi Khoja as their puppet ruler.
Khoja Afaq asked the 5th Dalai Lama when he fled to Lhasa to help his Afaqi faction take control of the Tarim Basin (Kashgaria).[32] The Dzungar leader Galdan was then asked by the Dalai Lama to restore Khoja Afaq as ruler of Kashgararia.[33] Khoja Afaq collaborated with Galdan's Dzungars when the Dzungars conquered the Tarim Basin from 1678 to 1680 and set up the Afaqi Khojas as puppet client rulers.[34][35][36][37] The Dalai Lama blessed Galdan's conquest of the Tarim Basin and Turfan Basin.[38]
Since 1680 the Dzungars had ruled as suzerain masters over the Tarim, for 16 more years using the Chagatai as their puppet rulers. The Dzungars used a hostage arrangement to rule over the Tarim Basin, keeping as hostages in Ili either the sons of the leaders like the Khojas and Khans or the leaders themselves. Although the Uighur's culture and religion was left alone, the Dzungars substantially exploited them economically .[39] The Uighurs were forced with multiple taxes by the Dzungars which were burdensome and set by a determined amount, and which they did not even have the ability to pay. They included water conservancy tax, draught animal tax, fruit tax, poll tax, land tax, tress and grass tax, gold and silver tax, and trade tax. Annually the Dzungars extracted a tax of 67,000 tangas of silver from the Kashgar people in Galdan Tseren's reign, a five percent tax was imposed on foreign traders and a ten percent tax imposed on Muslim merchants, people had to pay a fruit tax if they owned orchards and merchants had to pay a copper and silver tax. Annually the Dzungars extracted 100,000 silver tangas in tax from Yarkand and slapped livestock, stain, commerce, and a gold tax on them. The Dzungars extracted 700 taels of gold, and also extracted cotton, copper, and cloth, from the six regions of Keriya, Kashgar, Khotan, Kucha, Yarkand, and Aksu as stated by Russian topographer Yakoff Filisoff. The Dzungars extracted over 50% of the wheat harvests of Muslims according to Qi-yi-shi (Chun Yuan), 30–40% of the wheat harvests of Muslims according to the Xiyu tuzhi, which labelled the tax as "plunder" of the Muslims. The Dzungars also extorted extra taxes on cotton, silver, gold, and traded goods from the Muslims besides making them pay the official tax. "Wine, meat, and women" and "a parting gift" were forcibly extracted from the Uighurs daily by the Dzungars who went to physically gather the taxes from the Uighur Muslims, and if they dissatisfied with what they received, they would rape women, and loot and steal property and livestock. Gold necklaces, diamonds, pearls, and precious stones from India were extracted from the Uighurs under Dāniyāl Khoja by Tsewang Rabtan when his daughter was getting married.[40]
67,000 patman (each patman is 4 piculs and 5 pecks) of grain 48,000 silver ounces were forced to be paid yearly by Kashgar to the Dzungars and cash was also paid by the rest of the cities to the Dzungars. Trade, milling, and distilling taxes, corvée labor, saffron, cotton, and grain were also extracted by the Dzungars from the Tarim Basin. Every harvest season, women and food had to be provided to Dzungars when they came to extract the taxes from them.[41]
When the Dzungars levied the traditional nomadic Alban poll tax upon the Muslims of Altishahr, the Muslims viewed it as the payment of jizyah (a tax traditionally taken from non-Muslims by Muslim conquerors).[42]
The Qing defeat of the Dzungars went hand in hand with the anti-Dzungar resistance of the ordinary Uighurs, "many of them, unable to bear their misery, which was like living in a sea of fire, fled but were not able to find a place to settle peacefully." The Uighurs carried out "acts of resistance" like hiding the goods which were collected as taxes or violently resisting the Dzungar Oirat tax collectors, but these incidents were infrequent and widespread anti-Dzungar opposition failed to materialize. Many opponents of Dzungar rule like Uighurs and some dissident Dzungars escaped and defected to Qing China during 1737–1754 and provided the Qing with intelligence on the Dzungars and voiced their grievances. Abdullāh Tarkhān Beg and his Hami Uighurs defected and submitted to Qing China after the Qing inflicted a devastating defeat at Chao-mo-do on the Dzungar leader Galdan in September 1696.[43] The Uighur leader Emin Khoja (Amīn Khoja) of Turfan revolted against the Dzungars in 1720 while the Dzungars under Tsewang Rabtan were being attacked by the Qing, and then he also defected and submitted to the Qing. The Uighurs in Kashgar under Yūsuf and his older brother Jahān Khoja of Yarkand revolted in 1754 against the Dzungars, but Jahān was taken prisoner by the Dzungars after he was betrayed by the Uch-Turfan Uighur Xi-bo-ke Khoja and Aksu Uighur Ayyūb Khoja. Kashgar and Yarkand were assaulted by 7,000 Khotan Uighurs under Sādiq, the son of Jahān Khoja. The Uighurs supported the 1755 Qing assault against the Dzungars in Ili, which occurred at the same time as the Uighur revolts against the Dzungars. Uighurs like Emin Khoja, 'Abdu'l Mu'min and Yūsuf Beg supported the Qing attack against Dawachi, the Dzungar Khan.[44] The Uch-Turfan UighurnBeg Khojis (Huojisi) supported the Qing General Ban-di against in tricking Davachi and taking him prisoner. The Qing and Amin Khoja and his sons worked together to defeat the Dzungars under Amursana.[45]


From the 17th century to the middle of the 18th century, between China proper and Transoxania, all the land was under the sway of the Dzungars. In Semirechye the Kyrgyz and Kazakahs were forcibly driven out by the Dzungars and the Kashgar Khanate was conquered. However, the Dzungar Empire was annihilated by Qing China from 1755 to 1758 in a formidable assault, ending the Central Asian states danger from the Dzungar menace.[46] Uighur Muslims like Emin Khoja from Turfan revolted against their Dzungar Buddhist rulers and pledged allegiance to Qing China to deliver them from Dzungar Buddhist rule. The Qing crushed and annihilated the Dzungars in the Dzungar genocide.
The Dzungar Buddhists brought back the Aqtaghliq Afaqi Khoja Burhan-ud-din and his brother Khan Khoja and installed them as puppet rulers in Kashgar. During the Qing's war against the Dzungars, Burhan-ud-din and his brother Khan Khoja then pledged allegiance to Qing China in exchange for delivering them from Dzungar rule. However, after the Qing defeated the Dzungars, the Afaqi Khoja brothers Burhan-ud-din and Khan Khoja reneged on the deal with the Qing, declared independence and revolted against the Qing. The Qing and loyal Uighurs like Emin Khoja crushed the revolt and drove Burhan-ud-din and Khan Khoja to Badakhshan. The Qing armies reached far in Central Asia and came to the outskirts of Tashkent while the Kazakh rulers made their submissions as vassals to the Qing.[47] The Afaqi brothers died in Badakhshan and the ruler Sultan Shah delivered their bodies to the Qing. Ahmad Shah Durrani accused Sultan Shah of having caused the Afaqi brothers to die.[48]
Durrani dispatched troops to Kokand after rumours that the Qing dynasty planned to launch an expedition to Samarkand, but the alleged expedition never happened and Ahmad Shah subsequently withdrew his forces when his attempt at an anti-Qing alliance among Central Asian states failed.[49] Durrani then sent envoys to Beijing to discuss the situation regarding the Afaqi Khojas.[50]
Death and legacy


Ahmad Shah suffered a wound on his nose during a horse-riding accident in Kabul in 1768, which gradually worsened and spread to other parts of his face, including his left eye. Following the advise of his physicians, he would spend part of the summer in the cooler climate of the Margha plain in the Toba Achakzai range during the last few years of his life. He died of his illness on 4 June 1772 (2 Rabi' al-Awwal 1186) in Maruf, Toba Achakzai, east of Kandahar.[2]: 409 [51][52]
He was buried in the city of Kandahar adjacent to the Shrine of the Cloak, where a large mausoleum was built. It has been described in the following way:
Under the shimmering turquoise dome that dominates the sand-blown city of Kandahar lies the body of Ahmad Shah Abdali, the young Kandahari warrior who in 1747 became the region's first Durrani king. The mausoleum is covered in deep blue and white tiles behind a small grove of trees, one of which is said to cure toothache, and is a place of pilgrimage. In front of it is a small mosque with a marble vault containing one of the holiest relics in the Islamic World, a kherqa, the Sacred Cloak of Mohammed that was given to Ahmad Shah by Mured Beg, the Emir of Bokhara. The Sacred Cloak is kept locked away, taken out only at times of great crisis but the mausoleum is open and there is a constant line of men leaving their sandals at the door and shuffling through to marvel at the surprisingly long marble tomb and touch the glass case containing Ahmad Shah's brass helmet. Before leaving they bend to kiss a length of pink velvet said to be from his robe. It bears the unmistakable scent of jasmine.[53]
In his tomb his epitaph is written:
The King of high rank, Ahmad Shah Durrani,
Was equal to Kisra in managing the affairs of his government.
In his time, from the awe of his glory and greatness,
The lioness nourished the stag with her milk.
From all sides in the ear of his enemies there arrived
A thousand reproofs from the tongue of his dagger.
The date of his departure for the house of mortality
Was the year of the Hijra 1186 (1772 A.D.)[54]
Durrani's victory over the Marathas influenced the history of the subcontinent and, in particular, the policies of the East India Company in the region.[citation needed] His refusal to continue his campaigns deeper into India prevented a clash with the company and allowed them to continue to acquire power and influence after they established complete control over the former Mughal province of Bengal in 1793. However, fear of another Afghan invasion would influence Company policy-makers for almost half a century after the Battle of Panipat.[citation needed] The acknowledgment of Durrani's military accomplishments is reflected in an intelligence report made by Company officials on the Battle of Panipat, which referred to Ahmad Shah as the 'King of Kings'.[55] This fear led in 1798 to a Company envoy being sent to the Persian court in part to instigate the Persians in their claims on Herat to forestall a possible Afghan invasion of India that might have halted Company expansion.[55] Mountstuart Elphinstone wrote of Ahmad Shah:
His military courage and activity are spoken of with admiration, both by his own subjects and the nations with whom he was engaged, either in wars or alliances. He seems to have been naturally disposed to mildness and clemency and though it is impossible to acquire sovereign power and perhaps, in Asia, to maintain it, without crimes; yet the memory of no eastern prince is stained with fewer acts of cruelty and injustice.
His successors, beginning with his son Timur Shah and ending with Shuja Shah Durrani, proved largely incapable of governing the last Afghan empire and faced with advancing enemies on all sides. Much of the territory conquered by Ahmad Shah fell to others by the end of the 19th century. Timur Shah would consolidate the holdings of the Durrani Empire, and fight off civil war and rebellion throughout his reign, he would also lead multiple campaigns into Punjab to try and repeat his fathers success. After the death of Timur Shah, his son, Zaman Shah Durrani ascended to the throne, throughout his reign he would lose the outlying territories but also alienated some Pashtun tribes and those of other Durrani lineages. Zaman Shah would lead campaigns into Punjab, capturing Lahore, however due to internal strife, he was forced to withdraw on all attempts. Zaman Shah would later be deposed by Mahmud Shah Durrani, his brother, and the Durrani Realm would continue to disintegrate in the following years from progressive succession crises, usually between Timur Shah's sons, with Mahmud Shah Durrani, Zaman Shah Durrani, and Shah Shuja Durrani. Afghanistan would remain disunited Until Dost Mohammad Khan's ascendancy in 1826, chaos reigned in Afghanistan, which effectively ceased to exist as a single entity, disintegrating into a fragmented collection of small countries or units. Dost Mohammad throughout his reign had focused on re-uniting Afghanistan and had succeeded in doing so, with the Herat Campaign of 1862-63 in the recapture of Herat, and the eventual conquest of the Principality of Qandahar.
In Pakistan, a short-range ballistic missile Abdali-I, is named in the honour of Ahmad Shah Abdali.[56]
Durrani's poetry
Durrani wrote a collection of odes in his native Pashto. He was also the author of several poems in Persian. One of his most famous Pashto poems was Love of a Nation:[57][58][59]
ستا د عشق له وينو ډک سول ځيګرونه
By blood, we are immersed in love of you
ستا په لاره کښې بايلي زلمي سرونه
The youth lose their heads for your sake
تا ته راسمه زړګی زما فارغ سي
I come to you and my heart finds rest
بې له تا مې اندېښنې د زړه مارونه
Away from you, grief clings to my heart like a snake
که هر څو مې د دنيا ملکونه ډېر سي
Whatever countries I conquer in the world,
زما به هېر نه سي دا ستا ښکلي باغونه
I will never forget your beautiful gardens
د ډیلي تخت هېرومه چې را ياد کړم
I forget the throne of Delhi when I remember,
زما د ښکلي پښتونخوا د غرو سرونه
The mountain tops of my beautiful Pashtunkhwa
د فريد او د حميد دور به بيا سي
The eras of Farid [Sher Shah Suri] and Hamid [Lodi] will return,
چې زه وکاندم پر هر لوري تاختونه
When I launch attacks on all sides
که تمامه دنيا يو خوا ته بل خوا يې
If I must choose between the world and you,
زما خوښ دي ستا خالي تش ډګرونه
I shall not hesitate to claim your barren deserts as my own
Personal life
During Nader Shah's invasion of India in 1739, Ahmad Shah also accompanied him and stayed some days in the Red Fort of Delhi. When he was standing "outside the Jali gate near Diwan-i-Am", Asaf Jah I saw him. He was "an expert in physiognomy" and predicted that Ahmad Shah was "destined to become a king". When Nader Shah learned of it, he "purportedly clipped" his ears with his dagger and made the remark "When you become a king, this will remind you of me". According to other sources, Nader Shah did not believe in it and asked him to be kind to his descendants "on the attaintment of royalty".[20]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In popular culture
- In the 1994 television series The Great Maratha, the character of Ahmad Shah Durrani is portrayed by Bob Christo.[60]
- In the 2019 Bollywood war drama Panipat, Ahmad Shah Abdali appears as the primary antagonist, and is portrayed by Sanjay Dutt.
See also
References
- ^ a b c Nejatie, Sajjad (2017). The Pearl of Pearls: The Abdālī-Durrānī Confederacy and Its Transformation under Aḥmad Shāh, Durr-i Durrān (PhD). University of Toronto. p. 293.
According to the Taẕkira of Anand Ram "Mukhliṣ," Aḥmad Shāh issued a royal edict on 15 July 1747, appointing Muḥammad Hāshim Afrīdī as chief of the Afrīdī of the Peshawar region. This appears to affirm that Aḥmad Shāh's accession took place no later than mid-July.
- ^ a b c Nejatie, Sajjad (2017). The Pearl of Pearls: The Abdālī-Durrānī Confederacy and Its Transformation under Aḥmad Shāh, Durr-i Durrān (PhD). University of Toronto.
- ^ a b Nejatie, Sajjad (2017). The Pearl of Pearls: The Abdālī-Durrānī Confederacy and Its Transformation under Aḥmad Shāh, Durr-i Durrān (PhD). University of Toronto. p. 293.
The fact that numerous sources composed in the ruler's lifetime consistently connect him in his youth to Herat justifies the stance of Ghubār and others that Aḥmad Shāh was, in fact, born in the Herat region, around the time his father passed away and when the Abdālī leadership still exercised authority over the province.
- ^ a b Nichols, Robert (2015). "Aḥmad Shāh Durrānī". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam, THREE. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_ei3_COM_24801. ISSN 1873-9830.
- ^ a b Dalrymple, William (2013). Return of a King: The battle for Afghanistan. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1408818305.
- ^ "Afghan first lady in shadow of 1920s queen?". 1 October 2014 – via www.aljazeera.com.
- ^ a b c "Ahmad Shah and the Durrani Empire". Library of Congress Country Studies on Afghanistan. 1997. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ a b Friedrich Engels (1857). "Afghanistan". Andy Blunden. The New American Cyclopaedia, Vol. I. Archived from the original on 18 October 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ Clements, Frank (2003). Conflict in Afghanistan: a historical encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-85109-402-8. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ D. Balland. "Afghanistan: x. Political History". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Online Edition, 1982.
- ^ "Aḥmad Shah Durrānī". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ Chayes, Sarah (2006). The Punishment of Virtue: Inside Afghanistan After the Taliban. Univ. of Queensland Press. p. 99. ISBN 978-1-932705-54-6. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ a b Singh, Ganḍā (1959). Ahmad Shah Durrani: Father of Modern Afghanistan. Asia Publishing House. p. 457. ISBN 978-1-4021-7278-6. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ "Ahmad Shah Abdali". Abdullah Qazi. Afghanistan Online. Archived from the original on 12 August 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
Afghans refer to him as Ahmad Shah Baba (Ahmad Shah, the father).
- ^ Runion, Meredith L. (2007). The history of Afghanistan. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-313-33798-7. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ Sarkar, p. 124
- ^ a b C. Collin-Davies (1999). "Ahmad Shah Durrani". Encyclopaedia of Islam (CD-ROM Edition v. 1.0).
- ^ Griffiths, John. C (2001) Afghanistan: A History of Conflict p. 12
- ^ Singer, Andre (1983). Lords of the Khyber: The story of the North West Frontier.
- ^ a b Mehta, p. 247
- ^ Olaf Caroe, The Pathans (1981 reprint)
- ^ a b Mehta, p. 248
- ^ Vogelsang, Willem (2002). The Afghans. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 228. ISBN 978-0-631-19841-3. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ Snedden, Christopher (2015). Understanding Kashmir and Kashmiris. ISBN 9781849043427.
- ^ a b c d Noelle-Karimi, Christine (2014). The Pearl in Its Midst: Herat and the Mapping of Khurasan (15th-19th Centuries). Austrian Academy of Sciences Press. ISBN 978-3-7001-7202-4.
- ^ a b Gommans 1995, p. 53.
- ^ Sykes, Percy (2008)A History of Persia READ books. ISBN 978-1-4437-2408-1 p. 76
- ^ Patil, Vishwas. Panipat.
- ^ Roy, Kaushik (2004). India's Historic Battles: From Alexander the Great to Kargil. Permanent Black, India. pp. 80–81. ISBN 978-81-7824-109-8.
- ^ for a detailed account of the battle fought see Chapter VI of The Fall of the Moghul Empire of Hindustan by H. G. Keene. Available online Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ James A. Millward (2007). Eurasian Crossroads: A History of Xinjiang. Columbia University Press. pp. 55–. ISBN 978-0-231-13924-3.
- ^ Millward 2007, p. 86.
- ^ Millward 2007, p. 87.
- ^ Millward 2007, p. 88.
- ^ ed. Starr 2004, p. 50.
- ^ Kim 2008, p. 117
- ^ Newby 1998, p. 279.
- ^ Millward 2007, p. 90.
- ^ eds. Dani & Masson & Unesco 2003, p. 193.
- ^ eds. Dani & Masson & Unesco 2003, pp. 196–97.
- ^ Millward 2007, p. 92.
- ^ Saintly Brokers: Uyghur Muslims, Trade, and the Making of Qing Central Asia, 1696–1814. 2008. pp. 175–. ISBN 978-1-109-10126-3.
- ^ eds. Dani & Masson & Unesco 2003, p. 199.
- ^ eds. Dani & Masson & Unesco 2003, p. 200.
- ^ eds. Dani & Masson & Unesco 2003, p. 201.
- ^ eds. Dani & Masson & Unesco 2003, p. 334.
- ^ Newby 2005, p. 22.
- ^ Newby 2005, p. 33.
- ^ Newby 2005, p. 34.
- ^ Newby 2005, p. 35.
- ^ Bruce Malleson, George (1878). History of Afghanistan From the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878. British India: W.H Allen Company. p. 291. ISBN 9780341781523. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- ^ "The Accession to the Throne of His Highness Timur Shah — Brill". 6 November 2013.
- ^ Lamb, Christina (2002). The Sewing Circles of Herat. HarperCollins. First Perennial edition (2004), p. 38. ISBN 0-06-050527-3.
- ^ Nancy Hatch Dupree – An Historical Guide To Afghanistan – The South (Chapter 16)
- ^ a b "Afghanistan 1747–1809: Sources in the India Office Records"[dead link]
- ^ "Asia Times Online :: South Asia news, business and economy from India and Pakistan". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "Ahmad Shah Durrani (Pashto Poet)". Abdullah Qazi. Afghanistan Online. Archived from the original on 8 September 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ "A Profile of Afghanistan – Ahmad Shah Durrani (Pashto Poet)". Kimberly Kim. Mine Action Information Center. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ Said Hyder Akbar/Susan Burton: Come Back to Afghanistan, Trying to Rebuild a Country with My Father, My [...] [1], US, 2005
- ^ "Mr Christos Mojo - Indian Express". archive.indianexpress.com. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
Notes
- Jaswant Lal Mehta (1 January 2005). Advanced Study in the History of Modern India 1707–1813. ISBN 9781932705546.
- L. J. Newby (2005). The Empire And the Khanate. ISBN 9789004145504.
- Sir Jadunath Sarkar (1988). Fall of the Mughal Empire: 1789–1803. ISBN 9780861317493.
Bibliography
- Caroe, Olaf (1958). The Pathans: 500 B.C.–A.D. 1957. Oxford in Asia Historical Reprints. Oxford University Press, 1983. ISBN 0-19-577221-0.
- Clements, Frank. Conflict in Afghanistan: a historical encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO, 2003. ISBN 1-85109-402-4.
- Dupree, Nancy Hatch. An Historical Guide to Afghanistan. 2nd Edition. Revised and Enlarged. Afghan Air Authority, Afghan Tourist Organization, 1977.
- Elphinstone, Mountstuart. 1819. An account of the kingdom of Caubul, and its dependencies in Persia, Tartary, and India: Comprising a view of the Afghaun nation, and a history of the Dooraunee monarchy. Printed for Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown, and J. Murry, 1819.
- Griffiths, John C. (1981). Afghanistan: a history of conflict. Carlton Books, 2001. ISBN 1-84222-597-9.
- Gommans, Jos J. L. (1995). The Rise of the Indo-Afghan Empire: C. 1710-1780. Brill.
- Habibi, Abdul Hai. 2003. "Afghanistan: An Abridged History." Fenestra Books. ISBN 1-58736-169-8.
- Hopkins, B. D. 2008. The Making of Modern Afghanistan. Palgrave Macmillan, 2008. ISBN 0-230-55421-0.
- Malleson, George Bruce (1878). History of Afghanistan, from the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878. Elibron Classic Replica Edition. Adamant Media Corporation, 2005. ISBN 1-4021-7278-8.
- Romano, Amy. A Historical Atlas of Afghanistan. The Rosen Publishing Group, 2003. ISBN 0-8239-3863-8.
- Singh, Ganda (1959). Ahmad Shah Durrani, father of modern Afghanistan. Asia Publishing House, Bombay. (PDF version archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130207183925/https://web.archive.org/web/20130207183925/http://www.khyber.org/books/pdf/ahmad-shah-baba.pdf 66 MB)
- Vogelsang, Willem. The Afghans. Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. Oxford, UK & Massachusette, US. ISBN 0-631-19841-5.
- Alikuzai, Hamid Wahed: A Concise History of Afghanistan [2] in 25 Volumes, US. 2013, Vol. 14, p. 62, ISBN 978-1-4907-1441-7, 978-1-4907-1442-4
Further reading
- Nejatie, Sajjad (2017). "Iranian Migrations in the Durrani Empire". Comparative Studies of South Asia, Africa and the Middle East. 37. Project Muse: 494–509. doi:10.1215/1089201x-4279212.
