Odense: Difference between revisions
→Transport: ref |
→Transport: ref |
||
| Line 353: | Line 353: | ||
By road, Odense connects to Zealand and Jutland by way of the Funish Motorway (''Fynske Motorvej''), a section of the [[European route E20|E20]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.vejdirektoratet.dk/DA/viden_og_data/statens-veje/vejenes_historie/Sider/Fynske-Motorvej.aspx#.U7kbSrHm4ZY|title=Fynske Motorvej (E20) |publisher=Vejdirektoratet|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=Danish}}</ref> and to [[Svendborg]] on the southern part of Funen by way of the Svendborg Motorway (''Svendborgmotorvejen''), which comprises the Danish Route 9.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.vejdirektoratet.dk/DA/viden_og_data/statens-veje/vejenes_historie/Sider/Svendborgmotorvejen.aspx#.U7kaMbHm4ZY|title=Svendborgmotorvejen (rute 9) |publisher=Vejdirektoratet|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=Danish}}</ref> Other, smaller routes connect Odense to the rest of Funen, with direct links to all coastal towns.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hvorligger.dk/vejkort-fyn-danmark.html|title=Vejkort over Fyn|publisher=Hvorligger.dk|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=}}</ref> |
By road, Odense connects to Zealand and Jutland by way of the Funish Motorway (''Fynske Motorvej''), a section of the [[European route E20|E20]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.vejdirektoratet.dk/DA/viden_og_data/statens-veje/vejenes_historie/Sider/Fynske-Motorvej.aspx#.U7kbSrHm4ZY|title=Fynske Motorvej (E20) |publisher=Vejdirektoratet|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=Danish}}</ref> and to [[Svendborg]] on the southern part of Funen by way of the Svendborg Motorway (''Svendborgmotorvejen''), which comprises the Danish Route 9.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.vejdirektoratet.dk/DA/viden_og_data/statens-veje/vejenes_historie/Sider/Svendborgmotorvejen.aspx#.U7kaMbHm4ZY|title=Svendborgmotorvejen (rute 9) |publisher=Vejdirektoratet|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=Danish}}</ref> Other, smaller routes connect Odense to the rest of Funen, with direct links to all coastal towns.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hvorligger.dk/vejkort-fyn-danmark.html|title=Vejkort over Fyn|publisher=Hvorligger.dk|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=}}</ref> |
||
Odense's main railway station [[Odense station]] lies on the line between [[Copenhagen]] and [[Jutland]], the peninsular mainland. International trains connect the town with Sweden and mainland Europe, i.e. [[Stockholm]]. [[Statens Järnvägar|SJ]] has a direct [[X 2000|X2000]] train to Stockholm daily, taking 7 hours to the capital city of [[Sweden]]. Local and regional trains link Odense to the rest of Denmark. A separate passenger railway (''[[Svendborgbanen]]'') operates between Odense and Svendborg. Formerly, railways connected Odense to most of Funen's coastal cities, but these links were closed down in the 1950s and 1960s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.danskejernbaner.dk/|title=danskejernbaner.dk – Oversigt over danske jernbaner, stationer og deres historie|last=Danske Jernbaner|year=2008|language=Danish|accessdate=2 February 2010}}</ref> Today, these regional routes are served by [[bus]]es operated by the public company [[FynBus]], which also operates the town's municipal bus service, connecting the town's suburbs to the city centre. |
Odense's main railway station [[Odense station]] lies on the line between [[Copenhagen]] and [[Jutland]], the peninsular mainland. International trains connect the town with Sweden and mainland Europe, i.e. [[Stockholm]]. [[Statens Järnvägar|SJ]] has a direct [[X 2000|X2000]] train to Stockholm daily, taking 7 hours to the capital city of [[Sweden]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.raildude.com/en/odense/train-connections-city/l/10236|title=Train connections - Odense - Denmark|publisher=Raildude|accessdate=6 July 2014 |language=}}</ref> Local and regional trains link Odense to the rest of Denmark. A separate passenger railway (''[[Svendborgbanen]]'') operates between Odense and Svendborg. Formerly, railways connected Odense to most of Funen's coastal cities, but these links were closed down in the 1950s and 1960s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.danskejernbaner.dk/|title=danskejernbaner.dk – Oversigt over danske jernbaner, stationer og deres historie|last=Danske Jernbaner|year=2008|language=Danish|accessdate=2 February 2010}}</ref> Today, these regional routes are served by [[bus]]es operated by the public company [[FynBus]], which also operates the town's municipal bus service, connecting the town's suburbs to the city centre. |
||
Odense is served by [[Odense Airport]], which operates regular flights only during the summer months. |
Odense is served by [[Odense Airport]], which operates regular flights only during the summer months. |
||
Revision as of 10:09, 6 July 2014
Odense | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | Denmark |
| Region | Southern Denmark (Syddanmark) |
| Municipality | Odense |
| Established | 988 |
| City charter | 1355 |
| Municipality | 1970 |
| Area | |
| • City | 304.34 km2 (117.51 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 13 m (43 ft) |
| Population (2014) | |
| • City | 172,512 |
| • Density | 570/km2 (1,500/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 195,797 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 5000-5270 |
| Area code | (+45) 6 |
| Website | www.odense.dk |
Odense (Danish pronunciation: [ˈoðˀn̩sə] ) is the third largest city in Denmark. It has a population of 172,512 (as of 1 January 2014[update])[1] and is the main city of the island of Funen. By road, Odense is located 45 kilometres (28 mi) north of Svendborg, 144 kilometres (89 mi) to the south of Aarhus and 167 kilometres (104 mi) to the southwest of Copenhagen. The city is the seat of Odense Municipality, with a population of 195,797 (as of 1 January 2014[update]), and was the seat of Odense County until 1970, and Funen County from 1970 until 1 January 2007, when Funen County became part of the Region of Southern Denmark. Odense has close associations with Hans Christian Andersen who is remembered above all for his fairy tales. He was born in the city in 1805 and spent his childhood years there.
There has been human settlement in the Odense area for over 4,000 years, although the name was not mentioned in writing until 988, and by 1070 it had already grown into a thriving city. Canute IV of Denmark, generally considered to be the last Viking king, was murdered by unruly peasants in Odense's St Alban's Priory on 10 July 1086. Although the city was burned in 1249 following a royal rivalry, it quickly recovered and flourished as a centre of commerce in the Middle Ages. After a period of decline, large-scale plans for development were made during the 18th century, which led to the rebuilding of Odense Palace and the building of a canal to the Port of Odense, facilitating trade. In 1865, one of the largest railway terminals in Denmark was built, further increasing the population and commerce, and by 1900 Odense had reached a population of 35,000. Odense's Odinstårnet was the second tallest tower in Europe when built in 1935 but was destroyed by the Nazis during World War II. The University of Southern Denmark was established in 1966.
Today, Odense remains the commercial hub of Funen, and has a notable shopping district with a diversity of stores. Several major industries are located in the city including the Albani Brewery and GASA, Denmark's major dealer in vegetables, fruits and flowers. The city is home to the Odense Palace, erected by King Frederick IV who died there in 1730, the Odense Theatre, the Odense Symphony Orchestra, and the Hans Christian Andersen Museum, situated in the house that was the birthplace of Hans Christian Andersen. In sports, Odense has a number of football clubs including OB, BM, B1909, and B1913, the Odense Bulldogs professional ice hockey team, and the city also hosts the H.C. Andersen Marathon. Odense is served by Odense Airport and Odense station, which lies on the line between Copenhagen and the Jutland peninsula.
History
- For the Catholic ecclesiastical history, see Roman Catholic bishopric of Odense
Early history
The name Odense is derived from Odins Vé, meaning "Odin's sanctuary" as the area was known as a sanctuary for worshippers of the Nordic god Odin.[2]
Odense is one of Denmark's oldest cities. Archaeological excavations in the vicinity show proof of settlement for over 4,000 years since at least the Stone Age.[3][2] The earliest community was centred on the higher ground between the Odense River to the south and Næsbyhoved Lake (now dry) to the north. Nonnebakken, one of Denmark's former Viking ring fortresses, lay to the south of the river.[4] Today, Odense's Møntergården Museum has many artefacts related to the early Viking history in the Odense area.[5] The Vikings built numerous fortifications along the river banks to defend it against invaders coming in from the coast.[3]

The city celebrated its thousandth anniversary in 1988, commemorating the first mention of the town's name in a letter dated 18 March 988 from the German Emperor Otto III which granted rights to Odense and neighbouring settlements.[6] The first church in Odense appears to have been St Mary's,[7] probably built in the late 12th century.[8] The first bishop of Odense was Reginbert who was consecrated by Æthelnoth, archbishop of Canterbury, in 1022.[9]
Recent excavations have shown that from the early 11th century, the town developed in the area around Albani Torv, Fisketorvet, Overgade and Vestergade.[4] By 1070, Odense had already grown into a city of stature in Denmark.[2] Canute IV of Denmark, generally considered to be the last Viking king, was murdered by unruly peasants, discontent with the high taxes he imposed on the town, in Odense's St Alban's Priory on 10 July 1086.[2] He was canonized in 1100.[10] The priory no longer exists, although a church has been situated on the site since about 900. At the beginning of the 12th century, Benedictine monks from England founded St Canute's Abbey. It was here the English monk Ælnoth wrote Denmark's first literary work, Vita et Passio S. Canuti (The Life and Passion of St Canute).[10] Canute's shrine in Odense Cathedral (which was attached to the priory) attracted pilgrims throughout the Middle Ages.[11]
Middle Ages

In the Middle Ages, a number of churches and monasteries were built in the town. St Canute's Church (Skt. Knuds Kirke), now the cathedral, dates from the end of the 13th century and was closely connected to the Benedictine Order. The town's other old churches are St Mary's (Vor Frue Kirke) and St John's (Skt. Hans Kirke) with its adjacent monastery. Greyfiars Monastery (Gråbrødre Kloster) was founded by the Franciscans in 1279.[6]
In 1247, Odense was burned by Abel of Denmark during conflicts with his brother King Erik IV.[12] The cathedral had to be completely rebuilt.[13] Nevertheless, the town continued to flourish as a commercial centre, and was charted in 1335.[11] The city thrived economically during the Middle Ages, attracting many merchants and craftsman who traded their goods.[3]
In 1482, Bishop Karl Rønnov brought the German printer Johann Snell to Odense to print a short prayer book, Breviarium Ottoniense, considered to be the first work to be printed in Scandinavia. In parallel, Snell printed De obsidione et bello Rhodiano, an account of the Turkish siege of the island of Rhodes.[14][15]
After the Danish Reformation, the city enjoyed a sustained period of prosperity from the 1530s to the mid-17th century, becoming northern Funen's commercial centre. One of the main sources of income was the sale of cattle, providing substantial funds for the construction of fine half-timbered houses for the local merchants. The local nobility also participated in the city's development by building residences where they spent the the winter months. But the city's prosperity came to an abrupt end in the late 1650s heavy taxes were imposed after the end of the Swedish Wars. A period of stagnation ensued until the end of the 18th century.[10]
From the 16th century, the town was the meeting-place of several parliaments. Until 1805 Odense was the seat of the provincial assembly of Funen. By 1700, Odense population was only about 4,000.[3]
Development

Dramatic changes began in Odense in the 18th century to modernise the city and a great plan was drawn up for development. In 1720, Frederick IV ordered the rebuilding of Odense Palace, partly on the foundations of the 13th century St. Hans’s Monastery, and the construction of St Hans’s Church by the Knights Hospitallers.[11][16] A 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) long, 7.5 metre (25 ft) deep canal from Odense Harbour to Odense Fjord was built between 1796 and 1806 to facilitate the growth of Odense as a port city, radically increasing its level of trade and population.[2][17] Founded in 1796, Odense Teater is the first provincial theatre in Denmark and the country's second oldest.[18][19]
From the 1840s, the city enjoyed a period of rapid expansion beyond its traditional boundaries, becoming Denmark's second largest city. The city gates were demolished in 1851 and soon afterwards development extended to the area south of the river. Glove production, which had begun in the 18th century, developed into one of the most important industries while the harbour facilities were further expanded.[20] In 1853, Denmark's first modern water and gas works were opened in Odense.[10] Commerce was further boosted by the building of a railway across Funen in 1865, and Odense became one of Denmark's largest rail junctions.[2][3] All this provided an ideal basis for industrialization, attracting a wide range of industries including iron and metals, textiles, and food and beverages. Separate areas of the city were devoted to increased industrial and residential expansion.[18] The population of the city began to grow markedly, and by 1900 it had 35,000 inhabitants.[3]
Modern history
Odense's most famous landmark was Odinstårnet (The Odin Tower) constructed in 1935, as the second-tallest tower in Europe, only surpassed by the Eiffel Tower with its 177 meters. Odinstårnet was blown up by a Danish Nazi group in 1944 and has never been rebuilt.[21] However, a miniature model now stands in Odinsparken in the area where the original was located. During the German occupation in the Second World War, Odense's general stike in August 1943 contributed to terminating collaboration with the Germans.[18]
Until the beginning of the Danish industrial revolution, Odense was also the second-largest city in modern Denmark, but has in recent times been overtaken by Aarhus. From the 1960s, Odense increasingly became a cultural hub, with the establishment of a university in 1966 and the launching of trade shows, including the large Odense Congress Center.[2] In 1988, a major national television network, TV2, was established in Odense.[18]
In celebration of the thousandth anniversary in 1988, a forest, Tusindårsskoven (meaning "The Thousand Year Forest") was planted.[2] In 2005, the city celebrated the 200th anniversary of the birth of Hans Christian Andersen.[2]
The Odense Steel Shipyard (Staalskibsvæeft), which since 1996 had been Denmark's largest ship-building facility, closed in 2012 as a result of international competition. Opened in 1919 by A.P. Møller, it latterly produced container ships for Mærsk, the parent company. The Lindø site was sold to the Port of Odense (Odense Havn) who are developing the Lindø Industrial Park.[22]
Geography and climate
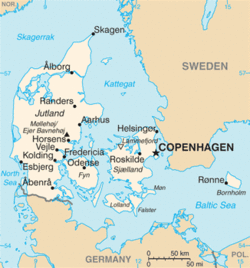
Odense is situated in the northeastern centre of the island of Funen. By road, Odense is located 45 kilometres (28 mi) north of Svendborg, 144 kilometres (89 mi) to the south of Aarhus, 167 kilometres (104 mi) to the southwest of Copenhagen, 136 kilometres (85 mi) east of Esbjerg and 69 kilometres (43 mi) southeast of Kolding.[23] Suburbs of Odense include Stige to the north, Seden, Bullerup and Agedrup to the northeast, Blommenslyst to the west, Bellinge to the southwest, and Neder Holluf and Højby to the south.[23]

The Odense River flows through Odense, to the south of the main shopping quarter.[24] To the northeast of the city is the Odense Fjord, and to the northeast, along the 165 road to Kerteminde is Kerteminde Fjord. The fjord is accessed through the narrow passage of Gabets, between Hals and Skoven, and is connected by canal to the Port of Odense.[25] The small fishing village of Bregnor lies 2.3 miles (3.7 km) to the southeast of the passage. A controlling depth of 11 metres (36 ft) is reported in the northern part of channel between the entrance to the fjord and Lindo Terminal Quay.[25] The bight of Fyns Hoved curves south to form the approach to Odense Fjord. The eastern side of the bight between Fyns Hoved and Skoven, 5.5 metres (18 ft) to the south, is irregular, with a beach and hills behind it, and to the south of the bight is a small, shallow bay, with the Korshavn Light in the vicinity. Skoven is a bare, rugged peninsular, with Dalby Bay (Dalby Bugt) to the east.[25]
In the southwestern part of the Odense Fjord are the islands of Vigelsø and the 21 hectare Tornø, although the latter is connected to the mainland by a 300 metres (980 ft)-long causeway. Vigelsø is the largest island in the fjord at 132 hectares and is an important breeding ground for migratory birds[26] It is part of the Special Area of Conservation No. SPC 94, Odense Fjord under the EU Habitat and Birds Directives and has been subject to close monitoring, with the target to reach at least "good" ecological status by 2015.[27] The island is low-lying, the highest point of Østerhoved only reaching six metres above the sea. There is a 25 hectares forest on the northern part of the island while the southern part consists of coastal meadows.
Climate
Odense has a temperate oceanic climate, classified as Köppen zone Cfb. Mild summers feature average maximum temperatures exceeding 20°C (70°F), while winters are characterized by minimum temperatures dropping just below freezing. Extratropical cyclones frequently affect the region, contributing to abundant precipitation.[28] It is common for Odense Fjord to contain ice between January and March, and the entrance is kept clear by icebreakers. The tidal range in the fjord varies up to 0.6 metres (2 ft 0 in), and winds from the west and northeast may raise the water level by up to 1.8 metres (5 ft 11 in) and winds from the east and southwest may lower it by up to 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in).[25] Climate data for the city are recorded at Hans Christian Andersen Airport (ICAO: EKOD).
| Climate data for Hans Christian Andersen Airport | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2 (36) |
2 (36) |
5 (41) |
11 (52) |
16 (61) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
18 (64) |
12 (54) |
7 (45) |
4 (39) |
12 (54) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0 (32) |
0 (32) |
2 (36) |
7 (45) |
12 (54) |
15 (59) |
17 (63) |
16 (61) |
13 (55) |
9 (48) |
5 (41) |
2 (36) |
8 (46) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2 (28) |
−3 (27) |
−1 (30) |
2 (36) |
6 (43) |
9 (48) |
11 (52) |
12 (54) |
9 (48) |
5 (41) |
3 (37) |
0 (32) |
4.0 (39.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49 (1.9) |
35 (1.4) |
30 (1.2) |
35 (1.4) |
39 (1.5) |
46 (1.8) |
64 (2.5) |
80 (3.1) |
56 (2.2) |
63 (2.5) |
49 (1.9) |
46 (1.8) |
592 (23.3) |
| Source: ClimaTemps[28] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
The land area of Odense is 304 km2, with a population density of 611 per km2 (2005 figures from Helsingin Seudun Aluesarjat). By the end of the 19th century, there were just under 40,000 inhabitants in the city but the population then grew rapidly, reaching some 100,000 in 1950. Thereafter, residents began to move out of the centre into the suburban areas which were included in Odense Municipality after boundaries were redefined in 1970.[18]
The population of Odense city, as of 1 January each year, according to Danmarks Statistik:
| Year | Population | Year | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1976[29] | 138,348 | 1999 | 144,940 |
| 1981 | 136,646 | 2000 | 145,062 |
| 1986 | 137,286 | 2001 | 144,849 |
| 1989 | 138,339 | 2002 | 144,636 |
| 1990 | 138,986 | 2003 | 145,374 |
| 1992 | 140,886 | 2004 | 145,554 |
| 1994 | 143,029 | 2006[30] | 152,060 |
| 1996 | 144,518 | 2007 | 158,453 |
| 1997 | 145,354 | 2008 | 158,163 |
| 1998 | 145,296 | 2009 | 158,678 |
Municipal administration

The mayor of Odense, Anker Boye, is a member of the Social Democratic Party. His first term was from 1993 to 2005 when he was defeated by Jan Boye, a Conservative. He was re-elected in the 2009 election, forming a coalition with the Red–Green Alliance, the Socialist People's Party and the Social Demoncrats.[31][32] The city council's motto is At lege er at leve (Playing is living) summarising a new approach addressing learning, innovation, development and growth with targets for 2017.[33] Anker Boye and his administration have been criticized for mismanaging the celebrations for the 200th anniversary of Hans Christian Andersen in 2005, above all for allegedly signing a contract with Tina Turner for a show which resulted in a deficit of 13 million kroner.[34]
In the 2013 municipal elections, Anker Boye was successful in obtaining sufficient support from the Liberals and the left to ensure his continuation as mayor from the beginning of 2014.[35]
Economy

Odense is Funen's most important industrial and commercial centre, and the city's central location in Denmark makes it one of the national convention and congress centers. Enterprises include the Albani Brewery, ABB (Asea Brown Boveri), Kansas Workwear (clothing), Plus Pack (canning and containers) as well as manufacturers in the electrical sector. In recent years, there has been a general trend from manufacturing into the service sector.[36] By 2002, 51% of the workforce was employed by the service sector while only 13% were working in industry.[20] Lindø Wharf, once Denmark's largest shipbuilding facility, has now been converted into Lindø Industrial Park specializing in the production and storage of components for the offshore industries, creating a variety of new tenants.[37] GASA, a large horticultural centre, supplies fruit, vegetables, flowers and plants to most of the country as well as for export.[19] Established in 1988, Denmark's major commercial television network TV 2 is based in Odense.[38]
In the south-eastern part of Odense the Rosengårdcentret shopping mall is located. The mall dates from 1971 and is the second largest in Denmark with 100,000 m2 (1,100,000 sq ft) of floor space and more than 150 stores as well as restaurants, a cinema and a fitness centre.[39] A wide variety of shops can be found in the city centre, especially on Kongensgade and Vestergade and adjacent pedestrian streets.[40]

Tourism is an important source of income for the city. In 2008, Odense Municipality was listed seventh in Denmark for turnover on tourism, reaching 1.6 million Danish kroner for the year.[41] In 2011, Odense Zoo was Funen's most popular tourist attraction and the eleventh most popular in Denmark with 405,913 visitors.[42] The zoo was founded in 1930 and covers an area of 3.6 hectares (8.9 acres) and has roughly 2,000 animals, covering 147 species.[43] In 2001, Odense Zoo inaugurated a DKK 60 million "Oceanium" featuring South American animal life.
Nightlife in the city culminates in Brandts Passage, which contains numerous restaurants, bars and cafes, such as the Envy-Lounge, Australian Bar, Brandts Kladefabrik and Cafe Biografem.[44] The jazz club, Jazzhus Dexter, is situated on the Vindegade. Other notable nighlife venues include Franck A, Froggys and Club Retro. Restaurants include the Cuckoos Nest bar and restaurant, the Brasserie Klitgaard, the Den Gamle Kro, set in a 17th century half-timbered house, Kvægtorvet, run by leading chef Klavs Styrbæk who serves fresh fish and meat dishes, and the Under Lindetraet in an 18th century cottage opposite the Hans Christian Andersen house which serves Franco-Danish cuisine. [45] Hotels of note include the Radisson SAS HC Anderson Hotel, the First Hotel Grand with its brasserie bar, the 68-room Old English-style Clarion Collection Hotel Plaza, City Hotel, which is in close proximity to the Hans Christian Andersen museum, and the 140-room Danhostel Odense City.[5]
Landmarks
Churches

Odense is the see of the bishop of Funen. Saint Canute's Cathedral (Danish: Sankt Knuds Kirke) was formerly connected with the great Benedictine monastery of the same name, and is one of the largest and finest buildings of its kind in Denmark. It is constructed of brick in a pure Gothic style. Originally dating from 1081–1093, it was rebuilt in the 13th century. Under the altar lies Canute (Danish: Knud), the patron saint of Denmark and his brother on public display. A large fragment of Byzantine cloth is displayed next to the two skeletons. The cathedral also boasts one of Denmark's finest altarpieces, a magnificent triptych by Claus Berg. Kings John (Danish: Hans) and Christian II are buried in the city.[46]
St Mary's Church (Vor Frue Kirke or Our Lady's Church), built in the 13th century and restored in 1851–1852 and again in 1864, contains a carved 16th-century altarpiece by Claus Berg of Lübeck.[47]
St Alban's Church, built in the Neogothic style and consecrated in 1908, is the Roman Catholic church of Odense. Its steeple is 54 m (177 ft) high.[48]
St John's Church (Sankt Hans Kirke), first mentioned in 1295, was built by the Knights Hospitaller, also known as the Order of Saint John. Not much of the original building remains as it was rebuilt in 1636 and subsequently restored. Built of red brick with horizontal decorations on the chancel wall, it has large Gothic windows. The date of 1496 on one of the bells in the step-ribbed tower may well be the year the church was completed. The tower is adjacent to Odense Palace which was originally built as a monastery.[49]
The Peace Church (Fredenskirke) consecrated in 1920 was so named in gratitude for the end of the First World War. The church was the work of Peder Vilhelm Jensen-Klint who went on to design Copenhagen's Grundtvig's Church.[50] Ansgars Church was the first church to be built in Odense since the Middle Ages. Completed in 1902, it was designed by Niels Jacobsen in the late Romanesque style in red brick on granite foundations. The cross-shaped interior is complemented by a spired bell-tower, 45 m (148 ft) high.[51]
City Hall

Odense's City Hall (Odense Rådhus), with its medieval Italian look, was designed by Johan Daniel Herholdt and Carl Lendorf in the Historicist style. Completed in 1883, it combines red masonry with sandstone decorations, stepped gables and a saw-tooth course.[52] It stands on the site of a smaller building from 1480.[53] In 1937, Bent Helveg-Møller won the competition for the building's enlargement. The tower over the main entrance was torn down in 1942 but was not rebuilt. As work was delayed during the war, the extension was not completed until 1955. In conjunction with Hans Christian Andersen's 200th anniversary in 2005, comprehensive renovation work was completed on the building's interiors, including the entrance halls, meeting rooms, banqueting hall and council chamber.[54]
Palaces and theatres


Odense Palace was erected by King Frederick IV, who died there in 1730. Now an administrative building, it stands on the site of a 15th-century monastery. The main white Baroque wing with 13 bays was designed by J.C. Krieger and completed in 1723.[55]
There is the Odense Theatre as well as the Odense Symphony Orchestra. Odense Music School, Nonnebakken and Teater Momentum are also of note.
Odense City Hall has a small scar from a battle between Germans and members of the Danish Resistance on 5 May 1945. The city's coat of arms – located above the main entrance to City Hall – is damaged. On closer inspection, it can be seen that the kneecap of Saint Canute was penetrated by a bullet.
Hans Christian Andersen connections

Remembered above all for his fairy tales, Hans Christian Andersen was born in Odense in 1805. It is thought his birthplace is the small yellow house on the corner of Hans Jensens Stræde and Bangs Boder in the old town.[56] In 1908, the house was opened as the Hans Christian Andersen Museum. It documents his life from his childhood years as the son of a struggling shoemaker, to his schooling, career as an author, and later life, with artefacts providing an insight into his acquaintances and adventures.[57] Andersen's childhood home is on Munkemøllestræde not far from the cathedral. He lived in the little half-timbered house from the age of two until he was 14. Opened as a museum in 1930, the house contains an exhibition of the cobbling tools used by his father and other items based on Andersen's own descriptions.[58]
Throughout the city there are numerous statues and sculptures representing characters from the stories of Hans Christian Andersen. They include the Steadfast Tin Soldier, the Mermaid, the Shepherdess and the Chimney Sweep, the Toad, the Darning Needle, the Emperor's New Clothes, the Sea Horse, the Paper Boat, the Flying Trunk and the Wild Swans.[59] There is also a distinctive statue of Andersen in Eventyrparken (The Fairy Tale Park) beside the cathedral. Sculpted by Louis Hasselriis in 1888, it shows the storyteller with a book in his hand, ready to entertain onlookers with his fairy tales.[60]
Museums

The museums in Odense are mainly governed by the Odense City Museums, a department of the municipal government. Funen's Art Museum (Fyns Kunstmuseum), formerly The Museum of Funen's Abbey, is one of Denmark's oldest art museums, dating to 1885. It contains the principal works by Jens Juel, Dankvart Dreyer, P.S. Krøyer and H. A. Brendekilde, and there are also works by Harald Giersing, Vilhelm Lundstrøm, Olaf Rude and Vilhelm Bjerke Petersen. The museum specializes particularly in concrete and Constructivist art. The open-air The Funen Village museum (Den Fynske Landsby) tries to emulate what country life was like in Denmark at the time of Andersen's life and contains houses of historical Odense.[61]
The Carl Nielsen Museum is dedicated to the life of Carl Nielsen and his wife, the sculptor Anne Marie Carl-Nielsen. It documents his life from his childhood in the town of Nr. Lyndelse, to his career and success on the European music scene, with his violins, his bugle and his grand piano on display, as well as a number of his musical scores, including six symphonies, three concertos, two operas, and chamber music and numerous songs. [62]

The Møntergården cultural history museum of Odense is one of the most notable remaining Renaissance buildings of the city, built in 1646 by the nobleman Falk Gøye. It has many artefacts related to the early Viking history in Odense,[5] and is named after the narrow street Møntestræde adjacent to the building, where a coin workshop once operated in around 1420.[63] Located in a courtyard of half-timbered houses, the museum also has exhibits on Funen's ancient history, as well as Odense in the Middle Ages and the Renaissance.[64]

The Danish Railway Museum is the national railway museum of Denmark, the largest such museum in Scandaniva. It was established in 1975 in a former engine shed adjacent to the city's main railway station and has an area of over 10,000 metres (33,000 ft), with some 50 locomotives and railway carriages on 20 railtracks from all periods of Danish rail history. The oldest steam engine dates back to 1869.[65]
The Brandts Museum of Photographic Art (Museet for Fotokunst) in Odense is the only national Danish art museum dedicated specifically to photographic art. It was founded on 13 September 1985 as part of the Brandts International Center for Art and Culture and opened its own exhibition space in 1987.[66] The museum is an independent institution but as a state-approved art museum it receives partial funding from the Danish Heritage Agency under the Danish Ministry of Culture. It has a special obligation to Danish and international photography from World War II until today. The Media Museum of Odense documents the history of the freedom of speech in Denmark since 1849, and the development of the printing press and the history of Danish broadsheet Berlingske.[67]
Education

Odense University
Odense University, established by law in 1964, was the first of three new provincial universities created to relieve pressure on the universities of Copenhagen and Aarhus. Teaching began in 1966. By the end of the 20th century, there were 11,000 students and some 5,000 employees. Before it became part of the University of Southern Denmark in 1998, it had four faculties covering arts, medicine, natural sciences, and social scienes. The university building which opened in 1971 was designed by KHR Arkitekter.[68]
University of Southern Denmark

The University of Southern Denmark (Syddansk Universitet) was established in 1998 as a merger of Odense University, the Southern Denmark Business School (Handelshøjskole Syd), the Southern Engineering School (Ingeniørhøjskole Syd) and the South Jutland University Centre (Sysjysk Universitetscenter). The main campus is in Odense but there are also departments in Copenhagen, Esbjerg, Kolding, Slagelse and Sønderborg. With some 26,000 students (2012), the establishment is Denmark's third largest university. The Faculty of Engineering (Det Tekniske Fakultet) combines several instutions: Odense Maskinteknikum (a mechanical engineering college which was established in 1905 and in 1962 became the Southern Engineering School), the Mads Clausen Institute and the Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Institute.[69]
Other educational institutions

Odense also includes departments of the University College Lillebaelt headquartered in Vejle. The university is the result of a merger between several further education institutions on Funen and in Jelling, Vejle and Svendborg.[70] UCL is currently undertaking comprehensive renovation of the buildings on Niels Bohrs Allé from the 1960s where it will concentrate its Odense interests. It intends to open University College Lillebælt Campus Odense in August 2014.[71]
Aimed at improving employment opportunities in business, the Lillebaelt Academy of Professional Higher Education (Erhvervsakademiet Lillebælt) was established in 2009 as a result of a merger between Tietgen Business College, SDE college, Kold College and Vejle Business College. In 2014, it had 3,200 students and a staff of 300. Its programmes are offered at various locations in Odense and Vejle.[72] Under the auspices of the municipality, the Odense School of Music (Odense Musikskole) offers educational courses with an emphasis on music to children and young people up to the age of 25.[73]
Kold College is a privately run institution offering vocational courses in food, agriculture and gardening. Founded in 2004, after a merger between Datum Tekniske Skole and Gartnerskolen Søhus, it changed its name to Kold College in 2008. It also offers secondary education courses in the natural sciences.[74] The college is named after Christen Kold who founded vocational schools on Funen in the mid-19th century.[75]
Odense is home to eight gymnasiums (Grammar schools), 21 state grade schools as well as a number of private schools.[76][77]
Sports

Odense's most important football clubs are OB, BM, B1909, and B1913. OB has a history going back to 1887 when it was founded as Odense Kricketklub (Odense Cricket Club). It changed its name to Odense Boldklub in 1893 after football was included in its activities. The club won the Danish Cup in 2002 and 2007 and was runner-up in 2009, 2010 and 2011.[78]
The Odense Bulldogs are a professional ice hockey team based in Odense. They play in the top Danish League AL-Bank Ligaen, as the only team from Funen.[79]
In tennis, Tennis Club Odense is located near Odense River.[80] The country's largest tennis centre is due to open in Marienlyst in 2014.[81]
The H.C. Andersen Marathon is held annually in Odense.[82] On Ascension Sunday, children can participate in Eventyrløbet (the Fairy Tale Run) with circuits from 2.5 to 10 km.[83]
RC Odense represents the city at rugby in combination with Lindø RSC.
There are many smaller sports clubs in Odense covering athletics, badminton, basket ball, boxing, climbing, cycling, fencing, football, golf, gymnastics, handball, jujitsu, karate, riding, roller-skating, shooting, swimming, table tennis, tennis, volley ball, yoga and wrestling as well as several specializing in facilities for handicapped people.[84]
Transport

The Port of Odense consists of three main basins and a number of facilities along the canal with a total quayage of roughly 4,200 metres (13,800 ft). [85]Vessels up to a length of 160 metres (520 ft) and a draft of 6.8 metres (22 ft) are facilitated in the port. The wharf for tankers is situated outside the harbour on the southern side of the canal, with facilities for tankers, general cargo ships, bulk, and LPG ships, and has a depth of 7.5 metres (25 ft).[85] Accessibility to Odense was greatly increased when the ferry service between the two main Danish islands, Zealand and Funen, was replaced by the Great Belt Bridge – opened in 1997 for rail traffic, 1998 for road traffic. When the bridge opened, it was the second longest suspension bridge in the world. Aarhus can be reached by train in 1 hour and 33 minutes while, thanks to the Great Belt Bridge, trains to Copenhagen can take as little as an hour and a quarter.[86]
By road, Odense connects to Zealand and Jutland by way of the Funish Motorway (Fynske Motorvej), a section of the E20,[87] and to Svendborg on the southern part of Funen by way of the Svendborg Motorway (Svendborgmotorvejen), which comprises the Danish Route 9.[88] Other, smaller routes connect Odense to the rest of Funen, with direct links to all coastal towns.[89]
Odense's main railway station Odense station lies on the line between Copenhagen and Jutland, the peninsular mainland. International trains connect the town with Sweden and mainland Europe, i.e. Stockholm. SJ has a direct X2000 train to Stockholm daily, taking 7 hours to the capital city of Sweden.[90] Local and regional trains link Odense to the rest of Denmark. A separate passenger railway (Svendborgbanen) operates between Odense and Svendborg. Formerly, railways connected Odense to most of Funen's coastal cities, but these links were closed down in the 1950s and 1960s.[91] Today, these regional routes are served by buses operated by the public company FynBus, which also operates the town's municipal bus service, connecting the town's suburbs to the city centre.
Odense is served by Odense Airport, which operates regular flights only during the summer months.
Healthcare

The Odense University Hospital (OUH), established in 1912,[92] is of major regional importance, not only for healthcare, but for conducting research in collaboration with the Institute of Clinical Research of the University of Southern Denmark.[93] OUH is the largest hospital unit in Denmark and the largest employer in Odense, and as of 2006 it had 1200 beds and a staff of 7700 people, of which 1300 people were doctors. Today there are about 10,000 employees covering all fields of medicine.[92] The hospital tower block is 57 metres (187 ft) high, has 15 floors and is Odense's tallest building.[94] It is the principal hospital for the northern part of Funen but also takes patients from all over Denmark, as it has highly specialized units within hand replantation surgery and special neuro-radiological intervention. The Hans Christian Andersen Children’s Hospital, part of the hospital, is the only paediatric department on the island of Funen, and also conducts research into nutrition and gastrointestinal diseases, asthma and allergies, hormonal diseases and others. As of 2013, the children's hospital had comprised of seven wards and had 377 employees, with about 10,000 admissions and 25,000 annual outpatient visits annually.[95] A new DKK 6.3 billion hospital is under construction in closer proximity to the University of Southern Denmark, scheduled to be completed in 2018. The hospital will have a floor area of 212,000 square metres (2,280,000 sq ft).[96]
Odense is home to several other private hospitals, including Privathospitalet H. C. Andersen Klinikken,[97] Privathospitalet Hunderup,[98] and Privathospitalet Mariahjemmet.[99]
Media

Odense is the centre for media activity in Funen, and the hub of the regional network. It;s principal newspaper is Fyens Stiftstidende, a daily broadsheet owned by Den Fynske Bladfond and published by Fyens Stiftstidende A/S, which was established on 3 January 1772[100] Until 1841 the newspaper was known as Kongelig Priviligerede Odense Adresse-Contoirs Efterretninger, and on 13 April 1993 the newspaper changed its 221-year-old tradition as a midday newspaper, to a morning paper. It has a circulation of approximately 60,000 on weekdays and 80,000 on weekends.[citation needed] The editor in chief Per Westergård chairs the board of the Centre for Journalism at the University of Southern Denmark, one of the two university journalism departments in Denmark. Denmark's largest university press, the University Press of Southern Denmark, is also based in Odense. It was founded in 1966 as Odense University Press (Odense Universitetsforlag), and its authors are mainly academics from the University of Southern Denmark.[citation needed]
Publicly owned television station TV 2 is based in Odense. The station began broadcasting on 1 October 1988, thereby ending the television monopoly previously exercised by the Danmarks Radio (DR). TV 2 has about 1,000 employees and has a revenue of 1.9 billion DKK (2006). [citation needed] The station has been a full active member of the European Broadcasting Union since 1990. On 23 August 2006 TV 2 acquired at an auction the FM radio license relinquished by Sky Radio (part of Rupert Murdoch's Australia-based News Corporation) when it closed down its Danish operations in November 2005.
Notable residents

- Hans Christian Andersen, novelist, poet and short story writer
- Carl Nielsen, classical composer, born near Odense
- King Canute IV (c. 1043 – July 17, 1086), also known as Canute the Saint and Canute the Holy
- Carl Frederik Tietgen, Industrialist, banker, and philanthropist
- Thomas B. Thrige, Inventor and industrialist
- Anja Andersen, Handball player
- Birgitte, Duchess of Gloucester, born and raised in Odense
- Caroline Wozniacki, tennis player
- Peter Eastgate, winner of the Main Event at the 2008 World Series of Poker
- Abraham Kurland, Olympic medalist in wrestling
- Kim Larsen, musician
- Jens Galschiøt, artist
- Frederik Klokker, cricketer
- Mø, Singer
Twin cities
 Kaunas, Lithuania[101]
Kaunas, Lithuania[101] Klaksvík, Faroe Islands
Klaksvík, Faroe Islands Kiev, Ukraine[102]
Kiev, Ukraine[102] Upernavik, Greenland
Upernavik, Greenland Petah Tikva, Israel
Petah Tikva, Israel Funabashi, Japan
Funabashi, Japan
- For a full list of twin cities, see Odense Municipality
See also
References
- ^ "Population 1st January, by urban areas" database from Statistics Denmark
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Odense, Denmark". Danishnet.com. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f Renouf 2003, p. 58.
- ^ a b "Begyndelsen" (in Danish). Historiens Hus Odense. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- ^ a b c Harding 2009, p. 73.
- ^ a b "Odense Bys Historie" (in Danish). Odense Bys Museer. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ "Ancient See of Odense in Denmark". Catholic Encyclopedia at New Advent. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ "Vor Frue Kirke" (PDF) (in Danish). Danmarks Kirker, Nationalmuseet. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ Larson 2014, p. 136.
- ^ a b c d "Odense - historie" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c "Odense". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- ^ "Abel og hans sønner" (in Danish). Dengang.dk. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ "Snt Knuds Kirke" (in Danish). Odense Bys Museer. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ "John Snell's Printing Works". Kulturarv. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ "Johann Snell". Den Store Danske. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Johanniterordenen" (in Danish). Maritim og historisk information. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ Thestrup, Andersen & Oxenvad 1986, pp. 193–200.
- ^ a b c d e "A History of Odense". Odense Kommune. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ a b "Odense Teater" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b "Danmarks Købstæder: Odense, Byhistorie" (in Danish). Dansk Center for Byhistorie. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ Lauridsen 2007, p. 151.
- ^ "Odense Staalskibsværft" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b "Odense" (Map). Google Maps. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ Harding 2009, p. 72.
- ^ a b c d Griffes, p. 60.
- ^ "Vigelsø" (in Danish). Naturstyrelsen.dk. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ Andersen & Conley 2010, p. 81.
- ^ a b "Climate of Odense, Denmark; Average Weather". ClimaTemps. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ Statistics Denmark tabel BEF4A 1976–2004
- ^ Statistics Denmark tabel BEF44 2006–
- ^ "Anker Boye" (in Danish). Den Store Danke. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Byrådets medlemmer" (in Danish). Odense Kommune. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ "At lege er at leve" (in Danish). Odense Kommune. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ Sinding, Knud; Bøllingtoft, Anne (2012). Cases on Management, Leadership and Organisations. Samfundslitteratur. pp. 136–. ISBN 978-87-593-1698-6.
- ^ "Anker Boye beholder magten i Odense" (in Danish). Fyens.dk. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ "Odense" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "LindøIndustrial Park A/S" (in Danish). Lindø Industripark. Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ "TV2" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Om centret" (in Danish). Rosengårdcentret. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Shopping i Odense" (in Danish). Visit Odense. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Turismen i tal" (PDF) (in Danish). Visit Denmark. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Turist-boom: Fulde huse i fynske attraktioner" (in Danish). Fyens.dk. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Dyr:Savannens Fyrtarne Stortrives" (in Danish). Årsberetning 2011. p. 16. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ Harding 2009, p. 73-4.
- ^ Harding 2009, p. 74.
- ^ "Sankt Knuds kirke" (in Danish). Nordens kirker. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Odense Vor Frue kirke" (in Danish). Nordens kirker. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "History of the Church". Sct. Albani Kirke. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Sct. Hans Kirke" (in Danish). Sct. Hans Kirke. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Om Fredens Kirke" (in Danish). Fredens Kirke. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ "Angars Kirke" (PDF) (in Danish). Danmarks Kirker, National Museet. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ "Odense City Hall". DAC. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ^ "Odense Town Hall". Visit Denmark.
- ^ "Odense Rådhus" (in Danish). Historiens Hus, Odense. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ^ "Odense Palace".
- ^ "Birthplace". Hans Christian Andersen Center. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Hans Christian Andersen Museum". Odense City Museums. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Hans Christian Andersen's Childhood Home". Odense City Museums. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Hans Christian Andersen's statues in Odense". Visit Fyn. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "H.C. Andersen" (in Danish). Historisk Atlas. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "A village from Hans Christian Andersen's time". Museum.odense.dk. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ "The Carl Nielsen Museum". Museum.odense.dk. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ "Møntergården". Museum.odense.dk. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ Bain, Carolyn; Booth, Michael; Parnell, Fran (2008). Denmark. Lonely Planet. pp. 202–. ISBN 978-1-74104-669-4.
- ^ Baedeker & Press 1990, p. 70.
- ^ Booth 2003, p. 254.
- ^ "Media Museum". Museum.odense.dk. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ "Odense Universitet" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 5 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Det Tekniske Fakultet" (in Danish). Den Store Danske. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "UCL's historie" (in Danish). ucl.dk. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ Lars Dalsgaard Adolfsen (13 March 2014). "Stor renovering af ingeniørhøjskolen i Odense" (in Danish). Building Supply. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "About Lillebaelt Academy of Professional Higher Education". eal.dk. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Musik for alvor" (in Danish). Odense Musikskole. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Welcome to Kold College". Kold College. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Skolens historie" (in Danish). Kold College. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Her kan du læse om de uddannelser, der er i Odense" (in Danish). Odense Kommune. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Fri- og Privatskoler i Odense Kommune" (PDF) (in Danish). UUO Ungdommens Uddannelsesvejledning Odense og Omegn. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ Johnny Wøllekær. "Odense Boldklub" (in Danish). Historiens Hus, Odense. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Odense Bulldogs" (in Danish). bulldogs.dk. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Forside" (in Danish). Tennis Club Odense. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Landets største tenniscenter vest for Storebælt: Første spadestik torsdag - åbner senere på året" (in Danish). fyens.dk. Retrieved 6 July.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Hans Christian Andersen Marathon". My Next Run. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Eventyrløbet" (in Danish). Ny Sport. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Sportsklubber i Odense Kommune" (in Danish). Ny Sport. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ a b Griffes, p. 61.
- ^ "Rejser med InterCity og InterCityLyn" (PDF) (in Danish). DSB. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Fynske Motorvej (E20)" (in Danish). Vejdirektoratet. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Svendborgmotorvejen (rute 9)" (in Danish). Vejdirektoratet. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Vejkort over Fyn". Hvorligger.dk. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Train connections - Odense - Denmark". Raildude. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ Danske Jernbaner (2008). "danskejernbaner.dk – Oversigt over danske jernbaner, stationer og deres historie" (in Danish). Retrieved 2 February 2010.
- ^ a b "Odense Universitetshospitals historie - kort fortalt" (in Danish). OUH. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Research". Odense University Hospital. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "Odense's tallest buildings - Top 20". Emporis. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Hans Christian Andersen Children´s Hospital". Odense University Hospital. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "The New OUH". Odense University Hospital. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "Velkommen til Privathospitalet H. C. Andersen Klinikken" (in Danish). Hca-klinikken.dk. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "Privathospitalet Hunderup" (in Danish). Privathospitalethunderup.dk. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "Velkommen til Stiftelsen Mariahjemmets hjemmeside" (in Danish). Mariahjemmet.dk. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "Fyens Stiftstidende Om Fyens Stiftstidende-koncernen" (in Danish). Fyens.dk. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Partnership". Kaunas International Relations. Retrieved 18 November 2011.
- ^ "Twin Cities". Odense Municipality. 22 June 2012. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
Bibliography
- Andersen, Jesper H.; Conley, Daniel J. (30 May 2010). Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems: Towards better understanding and management strategies. Springer. ISBN 978-90-481-3385-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Booth, Michael (1 January 2003). Time Out Copenhagen. Penguin Group USA. ISBN 978-0-14-100839-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Baedeker, Jarrold; Press, Jarrold (1 May 1990). Baedeker's rail guide to Europe. Prentice Hall Pr. ISBN 978-0-13-055971-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Griffes. Baltic Sea (Southern Part). ProStar Publications. ISBN 978-1-57785-762-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Harding, Paul (2009). Scandinavian Europe. Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-74104-928-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Larson, Laurence Marcellus (2014). Canute the Great The Rise of Danish Imperialism during the Viking Age. Bookpubber.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lauridsen, John T. (2007). Over stregen - under besættelsen (in Danish). Gyldendal A/S. ISBN 978-87-02-05199-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Renouf, Norman (2003). Copenhagen and the Best of Denmark Alive!. Hunter Publishing. ISBN 978-1-58843-355-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Thestrup, Poul; Andersen, Dorrit; Oxenvad, Niels (1986). Odense bys historie. Mod bedre tider. Odense 1789–1868 [History of the city of Odense. Towards better times. Odense 1789–1868] (in Danish). Odense Universitetsforlag. ISBN 978-87-7492-610-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- Odense – City of Hans Christian Andersen
- The City of Odense
- FynBus – Municipal and regional bus operator
 Odense travel guide from Wikivoyage
Odense travel guide from Wikivoyage
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)


