Rociletinib: Difference between revisions
m →top: Journal cites:, added 1 PMID |
→Medical uses: +1 ref |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<!-- Clinical data --> |
<!-- Clinical data --> |
||
| pronounce = |
| pronounce = |
||
| tradename = |
| tradename = Xegafri |
||
| Drugs.com = |
| Drugs.com = |
||
| MedlinePlus = |
| MedlinePlus = |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
| ATC_suffix = XE37 |
| ATC_suffix = XE37 |
||
| PubChem = 57335384 |
| PubChem = 57335384 |
||
| DrugBank = |
| DrugBank =DB11907 |
||
| ChemSpiderID = 30646712 |
| ChemSpiderID = 30646712 |
||
| UNII = 72AH61702G |
| UNII = 72AH61702G |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Rociletinib''' |
'''Rociletinib''' is a medication developed to treat [[non-small cell lung carcinoma]]s with a specific mutation. It is a third-generation [[epidermal growth factor receptor]] [[tyrosine kinase inhibitor]].<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.2147/OTT.S97644|pmc=5063481|title=New developments in the management of non-small-cell lung cancer, focus on rociletinib: What went wrong?|journal=OncoTargets and Therapy|pages=6065|year=2016|last1=Van Der Steen|first1=Nele|last2=Caparello|first2=Chiara|last3=Rolfo|first3=Christian|last4=Pauwels|first4=Patrick|last5=Peters|first5=Godefridus|last6=Giovannetti|first6=Elisa|pmid=27785053|volume=9}}</ref> It was being developed by [[Clovis Oncology]].<ref name="OncLive 2015">{{cite web | title=FDA Requests Additional Data for Rociletinib in EGFR T790M-Mutant NSCLC | website=OncLive | date=2015-11-16 | url=http://www.onclive.com/web-exclusives/fda-requests-additional-data-for-rociletinib-in-egfr-t790m-mutant-nsclc | accessdate=2016-01-04}}</ref> In May 2016, development of rociletinib was halted, along with its associated clinical trials, and Clovis Oncology withdrew its [[marketing authorisation application]] from the [[European Medicines Agency]]. Clovis Oncology will continue to supply the drug to people whose physicians had recommended continued treatment.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://clovisoncology.com/about-clovis/ |title=About Clovis |access-date=18 November 2016}}</ref> |
||
==Medical uses== |
|||
Rociletinib was used to treat locally advanced or metastatic [[non-small-cell lung cancer]] (NSCLC), if the cancer cells were positive for the [[T790M]] mutation in the gene coding for [[epidermal growth factor receptor|EGFR]].<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01526928|title=Study to Evaluate Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy of Rociletinib (CO-1686) in Previously Treated Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov|access-date=2018-03-15|language=en}}</ref> The T790M mutation is usually acquired following first-line treatment with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as [[gefitinib]] and [[afatinib]]. |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 15:39, 15 March 2018
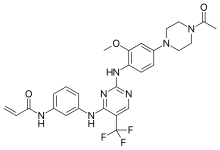 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xegafri |
| Other names | CO-1686, AVL-301 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H28F3N7O3 |
| Molar mass | 555.562 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Rociletinib is a medication developed to treat non-small cell lung carcinomas with a specific mutation. It is a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.[1] It was being developed by Clovis Oncology.[2] In May 2016, development of rociletinib was halted, along with its associated clinical trials, and Clovis Oncology withdrew its marketing authorisation application from the European Medicines Agency. Clovis Oncology will continue to supply the drug to people whose physicians had recommended continued treatment.[3]
Medical uses
Rociletinib was used to treat locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), if the cancer cells were positive for the T790M mutation in the gene coding for EGFR.[4] The T790M mutation is usually acquired following first-line treatment with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as gefitinib and afatinib.
References
- ^ Van Der Steen, Nele; Caparello, Chiara; Rolfo, Christian; Pauwels, Patrick; Peters, Godefridus; Giovannetti, Elisa (2016). "New developments in the management of non-small-cell lung cancer, focus on rociletinib: What went wrong?". OncoTargets and Therapy. 9: 6065. doi:10.2147/OTT.S97644. PMC 5063481. PMID 27785053.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "FDA Requests Additional Data for Rociletinib in EGFR T790M-Mutant NSCLC". OncLive. 2015-11-16. Retrieved 2016-01-04.
- ^ "About Clovis". Retrieved 18 November 2016.
- ^ "Study to Evaluate Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy of Rociletinib (CO-1686) in Previously Treated Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". Retrieved 2018-03-15.
