Ocean acidification: Difference between revisions
All of "Earth's oceans" are directly connected, only separated in name traditions ... hence the World Ocean wp article and wp:piped link replacement; far more useful link than generic oceans. |
Arthur Rubin (talk | contribs) m Reverted edits by 99.181.146.24 (talk) to last version by Awickert |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The [[carbon cycle]] describes the fluxes of carbon dioxide ({{chem|CO|2}}) between the oceans, [[Earth|terrestrial]] [[biosphere]], [[lithosphere]],<ref>"carbon cycle." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 11 Feb.2010 <http://www.search.eb.com/eb/article-9020247>.</ref> and the [[atmosphere]]. Human activities such as [[land use]] changes, the [[combustion]] of [[fossil fuel]]s, and the production of [[cement]] have led to a new flux of {{chem|CO|2}} into the atmosphere. Some of this has remained there; some has been taken up by terrestrial [[plant]]s,<ref name=cramer01>{{Cite journal| last=Cramer | first=W. | coauthors=''et al.'' | year=2001 | title=Global response of terrestrial ecosystem structure and function to {{co2}} and climate change: results from six dynamic global vegetation models | journal=Global Change Biology | volume=7 | pages=357–373 | doi=10.1046/j.1365-2486.2001.00383.x}}</ref> and some has been absorbed by the oceans.<ref name=raven99>{{Cite journal| last=Raven | first=J.A. | coauthors=Falkowski, P.G. | year=1999 | title=Oceanic sinks for atmospheric {{co2}} | journal=Plant Cell Environ. | volume=22 | pages=741–755 | doi=10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00419.x}}</ref> |
The [[carbon cycle]] describes the fluxes of carbon dioxide ({{chem|CO|2}}) between the oceans, [[Earth|terrestrial]] [[biosphere]], [[lithosphere]],<ref>"carbon cycle." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 11 Feb.2010 <http://www.search.eb.com/eb/article-9020247>.</ref> and the [[atmosphere]]. Human activities such as [[land use]] changes, the [[combustion]] of [[fossil fuel]]s, and the production of [[cement]] have led to a new flux of {{chem|CO|2}} into the atmosphere. Some of this has remained there; some has been taken up by terrestrial [[plant]]s,<ref name=cramer01>{{Cite journal| last=Cramer | first=W. | coauthors=''et al.'' | year=2001 | title=Global response of terrestrial ecosystem structure and function to {{co2}} and climate change: results from six dynamic global vegetation models | journal=Global Change Biology | volume=7 | pages=357–373 | doi=10.1046/j.1365-2486.2001.00383.x}}</ref> and some has been absorbed by the oceans.<ref name=raven99>{{Cite journal| last=Raven | first=J.A. | coauthors=Falkowski, P.G. | year=1999 | title=Oceanic sinks for atmospheric {{co2}} | journal=Plant Cell Environ. | volume=22 | pages=741–755 | doi=10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00419.x}}</ref> |
||
The carbon cycle comes in two forms: the organic carbon cycle and the inorganic carbon cycle. The inorganic carbon cycle is particularly relevant when discussing ocean acidification for it includes the many forms of dissolved {{chem|CO|2}} present in the |
The carbon cycle comes in two forms: the organic carbon cycle and the inorganic carbon cycle. The inorganic carbon cycle is particularly relevant when discussing ocean acidification for it includes the many forms of dissolved {{chem|CO|2}} present in the Earth's oceans.<ref>Kump, Lee R., James F. Kasting, and Robert G. Crane. “The Earth System.” Second ed. Pages: 162-164. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2003.</ref> |
||
When {{chem|CO|2}} dissolves, it reacts with water to form a balance of [[ion]]ic and non-ionic chemical species: dissolved free carbon dioxide ({{chem|CO|2|(aq)}}), [[carbonic acid]] ({{chem|H|2|CO|3}}), [[bicarbonate]] ({{chem|HCO|3|-}}) and [[carbonate]] ({{chem|CO|3|2-}}). The ratio of these species depends on factors such as [[seawater]] [[temperature]] and [[alkalinity]] (see the article on the ocean's [[solubility pump]] for more detail). |
When {{chem|CO|2}} dissolves, it reacts with water to form a balance of [[ion]]ic and non-ionic chemical species: dissolved free carbon dioxide ({{chem|CO|2|(aq)}}), [[carbonic acid]] ({{chem|H|2|CO|3}}), [[bicarbonate]] ({{chem|HCO|3|-}}) and [[carbonate]] ({{chem|CO|3|2-}}). The ratio of these species depends on factors such as [[seawater]] [[temperature]] and [[alkalinity]] (see the article on the ocean's [[solubility pump]] for more detail). |
||
Revision as of 07:59, 19 May 2011

2 between the 1700s and the 1990s
Ocean acidification is the name given to the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans, caused by their uptake of anthropogenic carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.[1] Between 1751 and 1994 surface ocean pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14,[2] representing an increase of approaching 30% in "acidity" (H+ ion concentration) in the world's oceans.[3][4][5]
Carbon cycle

2 cycle between the atmosphere and the ocean
The carbon cycle describes the fluxes of carbon dioxide (CO
2) between the oceans, terrestrial biosphere, lithosphere,[6] and the atmosphere. Human activities such as land use changes, the combustion of fossil fuels, and the production of cement have led to a new flux of CO
2 into the atmosphere. Some of this has remained there; some has been taken up by terrestrial plants,[7] and some has been absorbed by the oceans.[8]
The carbon cycle comes in two forms: the organic carbon cycle and the inorganic carbon cycle. The inorganic carbon cycle is particularly relevant when discussing ocean acidification for it includes the many forms of dissolved CO
2 present in the Earth's oceans.[9]
When CO
2 dissolves, it reacts with water to form a balance of ionic and non-ionic chemical species: dissolved free carbon dioxide (CO(aq)
2), carbonic acid (H
2CO
3), bicarbonate (HCO−
3) and carbonate (CO2−
3). The ratio of these species depends on factors such as seawater temperature and alkalinity (see the article on the ocean's solubility pump for more detail).
Acidification

Dissolving CO
2 in seawater increases the hydrogen ion (H+
) concentration in the ocean, and thus decreases ocean pH. Caldeira and Wickett (2003)[1] placed the rate and magnitude of modern ocean acidification changes in the context of probable historical changes during the last 300 million years.
| Time | pH | pH change | Source | H+ concentration change relative to pre-industrial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-industrial (18th century) | 8.179 | 0.000 | analysed field[11] | 0% |
| Recent past (1990s) | 8.104 | -0.075 | field[11] | + 18.9% |
| Present levels | ~8.069 | -0.11 | field[3][4][12][13] | + 28.8% |
| 2050 (2×CO 2 = 560 ppm) |
7.949 | -0.230 | model[10] | + 69.8% |
| 2100 (IS92a)[14] | 7.824 | -0.355 | model[10] | + 126.5% |
Since the industrial revolution began, it is estimated that surface ocean pH has dropped by slightly more than 0.1 units on the logarithmic scale of pH, representing an approximately 29% increase in H+
, and it is estimated that it will drop by a further 0.3 to 0.5 pH units (an additional doubling to tripling of today's post-industrial acid concentrations) by 2100 as the oceans absorb more anthropogenic CO
2.[1][10][15] These changes are predicted to continue rapidly as the oceans take up more anthropogenic CO
2 from the atmosphere, the degree of change to ocean chemistry, for example ocean pH, will depend on the mitigation and emissions pathways society takes.[16] Note that, although the ocean is acidifying, its pH is still greater than 7 (that of neutral water), so the ocean could also be described as becoming less basic.
Although the largest changes are expected in the future,[10] a report from NOAA scientists found large quantities of water undersaturated in aragonite are already upwelling close to the Pacific continental shelf area of North America.[17] Continental shelves play an important role in marine ecosystems since most marine organisms live or are spawned there, and though the study only dealt with the area from Vancouver to northern California, the authors suggest that other shelf areas may be experiencing similar effects.[17]
Rate of Acidification
Similarly, one of the first detailed datasets examining temporal variations in pH at a temperate coastal location found that acidification was occurring at a rate much higher than that previously predicted, with consequences for near-shore benthic ecosystems.[18][19]
A December 2009 National Geographic report quoted Thomas Lovejoy, former chief biodiversity advisor to the World Bank on recent research suggesting "the acidity of the oceans will more than double in the next 40 years. This rate is 100 times faster than any changes in ocean acidity in the last 20 million years, making it unlikely that marine life can somehow adapt to the changes."[20]
According to research, from the University of Bristol, published in the journal Nature Geoscience in February 2010, compared current rates of ocean acidification with the greenhouse event at the Paleocene-Eocene boundary, about 55 million years ago when surface ocean temperatures rose by 5-6 degrees Celsius, during which time no catastrophe is seen in surface ecosystems, yet bottom-dwelling organisms in the deep ocean experienced a major extinction. They concluded that the current acidification is on path to reach levels higher than any seen in the last 65 million years.[21] The study also found that the current rate of acidification is "ten times the rate that preceded the mass extinction 55 million years ago," and Ridgwell commented that the present rate "is an almost unprecedented geological event."[22] A National Research Council study released in April 2010 likewise concluded that "the level of acid in the oceans is increasing at an unprecedented rate."[23]
A review by climate scientists at the RealClimate blog, of a 2005 report by the Royal Society of the UK similarly highlighted the centrality of the rates of change in the present anthropogenic acidification process, writing:[24]
"The natural pH of the ocean is determined by a need to balance the deposition and burial of CaCO
3 on the sea floor against the influx of Ca2+
and CO2−
3 into the ocean from dissolving rocks on land, called weathering. These processes stabilize the pH of the ocean, by a mechanism called CaCO
3 compensation...The point of bringing it up again is to note that if the CO
2 concentration of the atmosphere changes more slowly than this, as it always has throughout the Vostok record, the pH of the ocean will be relatively unaffected because CaCO
3 compensation can keep up. The [present] fossil fuel acidification is much faster than natural changes, and so the acid spike will be more intense than the earth has seen in at least 800,000 years."
A July 2010 article in Scientific American quoted marine geologist William Howard of the Antarctic Climate and Ecosystems Cooperative Research Center in Hobart, Tasmania stating that "the current rate of ocean acidification is about a hundred times faster than the most rapid events" in the geologic past.[25] Research at the University of South Florida has shown that in the 15-year period 1995-2010 alone, acidity has increased 6 percent in the upper 100 meters of the Pacific Ocean from Hawaii to Alaska.[26]
Calcification
Changes in ocean chemistry can have extensive direct and indirect effects on organisms and their habitats. One of the most important repercussions of increasing ocean acidity relates to the production of shells and plates out of calcium carbonate (CaCO
3).[15] This process is called calcification and is important to the biology and survival of a wide range of marine organisms. Calcification involves the precipitation of dissolved ions into solid CaCO
3 structures, such as coccoliths. After they are formed, such structures are vulnerable to dissolution unless the surrounding seawater contains saturating concentrations of carbonate ions. The saturation state of seawater for a mineral (known as Ω) is a measure of the thermodynamic potential for the mineral to form or to dissolve, and is described by the following equation:
Here Ω is the product of the concentrations (or activities) of the reacting ions that form the mineral (Ca2+
and CO2−
3), divided by the product of the concentrations of those ions when the mineral is at equilibrium (K
sp), that is, when the mineral is neither forming nor dissolving.[27] In seawater, a natural horizontal boundary is formed as a result of temperature, pressure, and depth, and is known as the saturation horizon, or lysocline.[15] Above this saturation horizon, Ω has a value greater than 1, and CaCO
3 does not readily dissolve. Most calcifying organisms live in such waters.[15] Below this depth, Ω has a value less than 1, and CaCO
3 will dissolve. However, if its production rate is high enough to offset dissolution, CaCO
3 can still occur where Ω is less than 1. The carbonate compensation depth occurs at the depth in the ocean where production is exceeded by dissolution.[28]
Calcium carbonate occurs in 2 common polymorphs: aragonite and calcite. Aragonite is much more soluble than calcite, with the result that the aragonite saturation horizon is always nearer to the surface than the calcite saturation horizon.[15] This also means that those organisms that produce aragonite may possibly be more vulnerable to changes in ocean acidity than those that produce calcite.[10] Increasing CO
2 levels and the resulting lower pH of seawater decreases the saturation state of CaCO
3 and raises the saturation horizons of both forms closer to the surface.[29] This decrease in saturation state is believed to be one of the main factors leading to decreased calcification in marine organisms, as it has been found that the inorganic precipitation of CaCO
3 is directly proportional to its saturation state.[30]
Possible impacts
Although the natural absorption of CO
2 by the world's oceans helps mitigate the climatic effects of anthropogenic emissions of CO
2, it is believed that the resulting decrease in pH will have negative consequences, primarily for oceanic calcifying organisms. These span the food chain from autotrophs to heterotrophs and include organisms such as coccolithophores, corals, foraminifera, echinoderms, crustaceans and molluscs. As described above, under normal conditions, calcite and aragonite are stable in surface waters since the carbonate ion is at supersaturating concentrations. However, as ocean pH falls, so does the concentration of this ion, and when carbonate becomes undersaturated, structures made of calcium carbonate are vulnerable to dissolution. Even if there is no change in the rate of calcification, therefore, the rate of dissolution of calcareous material increases.[31]
Research has already found that corals,[32][33][34] coccolithophore algae,[35][36][37][38] coralline algae,[39] foraminifera,[40] shellfish[41] and pteropods[10][42] experience reduced calcification or enhanced dissolution when exposed to elevated CO
2.
The Royal Society of London published a comprehensive overview of ocean acidification, and its potential consequences, in June 2005.[15] However, some studies have found different response to ocean acidification, with coccolithophore calcification and
photosynthesis both increasing under elevated atmospheric pCO2,[43][44][45] an equal decline in primary production and calcification in response to elevated CO2[46] or the direction of the response varying between species.[47] Recent work examining a sediment core from the North Atlantic found that while the species composition of coccolithophorids has remained unchanged for the industrial period 1780 to 2004, the calcification of coccoliths has increased by up to 40% during the same time.[45] While the full ecological consequences of these changes in calcification are still uncertain, it appears likely that many calcifying species will be adversely affected.
When exposed in experiments to pH reduced by 0.2 to 0.4, larvae of a temperate brittlestar, a relative of the common sea star, fewer than 0.1 percent survived more than eight days.[26] There is also a suggestion that a decline in the coccolithophores may have secondary effects on climate, contributing to global warming by decreasing the Earth's albedo via their effects on oceanic cloud cover.[48]
Aside from calcification, organisms may suffer other adverse effects, either directly as reproductive or physiological effects (e.g. CO
2-induced acidification of body fluids, known as hypercapnia), or indirectly through negative impacts on food resources.[15] Ocean acidification may also force some organisms to reallocate resources away from productive endpoints such as growth in order to maintain calcification.[49] It has even been suggested that ocean acidification will alter the acoustic properties of seawater, allowing sound to propagate further, increasing ocean noise and impacting animals that use sound for echolocation or communication.[50] However, as with calcification, as yet there is not a full understanding of these processes in marine organisms or ecosystems.[51]
Leaving aside direct biological effects, it is expected that ocean acidification in the future will lead to a significant decrease in the burial of carbonate sediments for several centuries, and even the dissolution of existing carbonate sediments.[52] This will cause an elevation of ocean alkalinity, leading to the enhancement of the ocean as a reservoir for CO2 with moderate (and potentially beneficial) implications for climate change as more CO2 leaves the atmosphere for the ocean.[53]
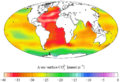
Gallery
-
"Present day" (1990s) sea surface pH
-
"Present day" (1990s) sea surface anthropogenic CO
2 -
Vertical inventory of "present day" (1990s) anthropogenic CO
2 -
Change in surface CO2−
3 ion from the 1700s to the 1990s
See also
- Biological pump
- Carbon dioxide sinks
- Carbonate compensation depth
- Continental shelf pump
- Greenhouse Gas
- Global Ocean Data Analysis Project
- Seawater pH
- Solubility pump
References
- ^ a b c Caldeira, K. (2003). "Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH" (PDF). Nature. 425 (6956): 365–365. doi:10.1038/425365a. PMID 14508477.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Jacobson, M.Z. (2005). "Studying ocean acidification with conservative, stable numerical schemes for nonequilibrium air-ocean exchange and ocean equilibrium chemistry". J. Geophys. Res. Atm. 110: D07302. Bibcode:2005JGRD..11007302J. doi:doi:10.1029/2004JD005220.
{{cite journal}}: Check|doi=value (help) - ^ a b Hall-Spencer JM, Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Martin S; et al. (2008). "Volcanic carbon dioxide vents show ecosystem effects of ocean acidification". Nature. 454 (7200): 96–9. doi:10.1038/nature07051. PMID 18536730.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Ocean acidification and the Southern Ocean" by the Australian Antarctic Division of the Australian Government
- ^ [www.scor-int.org/OBO2009/A&O_Report.pdf Report of the Ocean Acidification and Oxygen Working Group, International Council for Science's Scientific Committee on Ocean Research (SCOR) Biological Observatories Workshop]
- ^ "carbon cycle." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 11 Feb.2010 <http://www.search.eb.com/eb/article-9020247>.
- ^ Cramer, W. (2001). "Global response of terrestrial ecosystem structure and function to CO2 and climate change: results from six dynamic global vegetation models". Global Change Biology. 7: 357–373. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.2001.00383.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Raven, J.A. (1999). "Oceanic sinks for atmospheric CO2". Plant Cell Environ. 22: 741–755. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00419.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Kump, Lee R., James F. Kasting, and Robert G. Crane. “The Earth System.” Second ed. Pages: 162-164. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2003.
- ^ a b c d e f g Orr, James C. (2005). "Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the twenty-first century and its impact on calcifying organisms" (PDF). Nature. 437 (7059): 681–686. doi:10.1038/nature04095. PMID 16193043. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 June 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Key, R.M. (2004). "A global ocean carbon climatology: Results from GLODAP". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 18: GB4031. Bibcode:2004GBioC..18.4031K. doi:10.1029/2004GB002247.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ EPA weighs action on ocean acidification post at official blog of EPOCA, the European Project on Ocean Acidification
- ^ Report of the Ocean Acidification and Oxygen Working Group, International Council for Science's Scientific Committee on Ocean Research (SCOR) Biological Observatories Workshop
- ^ Review of Past IPCC Emissions Scenarios, IPCC Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (ISBN 0521804930).
- ^ a b c d e f g Raven, J. A. et al. (2005). Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Royal Society, London, UK.
- ^ Turley, C. (2008). "Impacts of changing ocean chemistry in a high-CO
2 world". Mineralogical Magazine. 72 (1): 359–362. doi:10.1180/minmag.2008.072.1.359. - ^ a b Feely RA, Sabine CL, Hernandez-Ayon JM, Ianson D, Hales B (2008). "Evidence for upwelling of corrosive "acidified" water onto the continental shelf". Science. 320 (5882): 1490–2. doi:10.1126/science.1155676. PMID 18497259.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wootton, J.T. (2008). "Dynamic patterns and ecological impacts of declining ocean pH in a high-resolution multi-year dataset". PNAS. 105 (48): 18848–18853. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810079105. PMC 2596240. PMID 19033205.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Ocean Growing More Acidic Faster Than Once Thought; Increasing Acidity Threatens Sea Life". Science Daily. 26 November 2008. Retrieved 26 November 2008.
- ^ UN: Oceans are 30 percent more acidic than before fossil fuels
- ^ Rate of ocean acidification the fastest in 65 million years
- ^ An Ominous Warning on the Effects of Ocean Acidification
- ^ Report: Ocean acidification rising at unprecedented rate
- ^ The Acid Ocean – the Other Problem with CO2 Emission
- ^ Ancient Ocean Acidification Intimates Long Recovery from Climate Change
- ^ a b How Acidification Threatens Oceans from the Inside Out
- ^ Atkinson, M.J.; Cuet, P. (2008). "Possible effects of ocean acidification on coral reef biogeochemistry: topics for research". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 373: 249–256. doi:10.3354/meps07867.
- ^ Thurman, H.V.; Trujillo, A.P. (2004). Introductory Oceanography. Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0131438880.
- ^ The Royal Society. Ocean Acidification Due To Increasing Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide, The Clyvedon Press Ltd. (2005): 11.
- ^ Marubini, F.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Furla, P.; Allemand, D. (2008). "Coral calcification responds to seawater acidification: a working hypothesis towards a physiological mechanism". Coral Reefs. 27: 491–499. doi:10.1007/s00338-008-0375-6.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.0206, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1098/rspb.2010.0206instead. - ^ Gattuso, J.-P. (1998). "Effect of calcium carbonate saturation of seawater on coral calcification". Global and Planetary Change. 18 (1–2): 37–46. doi:10.1016/S0921-8181(98)00035-6.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Gattuso, J.-P. (1999). "Photosynthesis and calcification at cellular, organismal and community levels in coral reefs: a review on interactions and control by carbonate chemistry". American Zoologist. 39: 160–183.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Langdon, C (2005). "Effect of elevated pCO2 on photosynthesis and calcification of corals and interactions with seasonal change in temperature/irradiance and nutrient enrichment". J. Geophysical Res. 110 (C09S07): C09S07. Bibcode:2005JGRC..11009S07L. doi:10.1029/2004JC002576.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Riebesell, Ulf (2000). "Reduced calcification of marine plankton in response to increased atmospheric CO
2" (abstract). Nature. 407 (6802): 364–367. doi:10.1038/35030078. PMID 11014189.{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) (Subscription required) - ^ Zondervan, I. (2001). "Decreasing marine biogenic calcification: a negative feedback on rising atmospheric CO2". Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 15: 507–516. Bibcode:2001GBioC..15..507Z. doi:10.1029/2000GB001321.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Zondervan, I. (2002). "Effect of CO2 concentration on the PIC/POC ratio in the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi grown under light limiting conditions and different day lengths". J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 272: 55–70. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00037-0.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Delille, B. (2005). "Response of primary production and calcification to changes of pCO2 during experimental blooms of the coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi". Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 19: GB2023. Bibcode:2005GBioC..19.2023D. doi:10.1029/2004GB002318.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); line feed character in|journal=at position 7 (help) - ^ Kuffner, I.B. (2007). "Decreased abundance of crustose coralline algae due to ocean acidification". Nature Geoscience. 1 (2): 114–117. doi:10.1038/ngeo100.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Phillips, Graham (13 September 2007). "Ocean Acidification – The BIG global warming story". ABC TV Science: Catalyst. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 18 September 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Gazeau, F. (2007). "Impact of elevated CO
2 on shellfish calcification". Geophysical Research Letters. 34: L07603. Bibcode:2007GeoRL..3407603G. doi:10.1029/2006GL028554.{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^
Comeau, C. (2009). "Impact of ocean acidification on a key Arctic pelagic mollusc ("Limacina helicina")". Biogeosciences. 6: 1877–1882. doi:10.5194/bg-6-1877-2009.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^
Buitenhuis, E.T. (1999). "Photosynthesis and calcification by Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae) as a function of inorganic carbon species". J. Phycology. 35: 949–959. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3550949.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Nimer, N.A. (1993). "Calcification rate in Emiliania huxleyi Lohmann in response to light, nitrate and availability of inorganic carbon". New Phytologist. 123: 673–677. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1993.tb03776.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.D. (2008). "Phytoplankton Calcification in a High-CO2 World". Science. 320 (5874): 336–340. doi:10.1126/science.1154122. PMID 18420926.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^
Sciandra, A. (2003). "Response of coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi to elevated partial pressure of CO2 under nitrogen limitation". Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 261: 111–112. doi:10.3354/meps261111.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^
Langer, G. (2006). "Species-specific responses of calcifying algae to changing seawater carbonate chemistry". Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 7: Q09006. Bibcode:2006GGG.....709006L. doi:10.1029/2005GC001227.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Ruttiman, J. (2006). "Sick Seas". Nature. 442 (7106): 978–980. doi:10.1038/442978a. PMID 16943816. (Subscription required)
- ^ [1] Wood et al (2008). Ocean acidification may increase calcification rates, but at a cost
- ^ Acid In The Oceans: A Growing Threat To Sea Life by Richard Harris. All Things Considered, 12 August 2009.
- ^ The Australian (2008). Swiss marine researcher moving in for the krill.
- ^ Ridgwell, A. (2007). "Assessing the potential long-term increase of oceanic fossil fuel CO2 uptake due to CO2-calcification feedback". Biogeosciences. 4: 481–492. doi:10.5194/bg-4-481-2007.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Tyrrell, T. (2008). "Calcium carbonate cycling in future oceans and its influence on future climates". J. Plankton Res. 30: 141–156. doi:10.1093/plankt/fbm105.
Further reading
- Antarctic Climate and Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre (ACE CRC) (2008). Position analysis: CO2 emissions and climate change: OCEAN impacts and adaptation issues. ISSN: 1835–7911. Hobart, Tasmania.
- Cicerone, R. (2004). "The Ocean in a High CO
2 World" (PDF). EOS, Transactions American Geophysical Union. 85 (37): 351–353. Bibcode:2004EOSTr..85R.351C. doi:10.1029/2004EO370007.{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Doney, S. C. (2006). "The Dangers of Ocean Acidification". Scientific American. 294 (3): 58–65. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0306-58. ISSN 0036-8733. PMID 16502612.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help), (Article preview only).
- Feely, R. A. (2004). "Impact of Anthropogenic CO
2 on the CaCO
3 System in the Oceans" (abstract). Science. 305 (5682): 362–366. doi:10.1126/science.1097329. PMID 15256664.{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Harrould-Kolieb, E.; Savitz, J. (2008). "Acid Test: Can We Save Our Oceans From CO2?". Oceana.
- Henderson, Caspar (5 August 2006). "Ocean acidification: the other CO2 problem". NewScientist.com news service.
- Jacobson, M. Z. (2005). "Studying ocean acidification with conservative, stable numerical schemes for nonequilibrium air-ocean exchange and ocean equilibrium chemistry". Journal of Geophysical Research - Atmospheres. 110: D07302. Bibcode:2005JGRD..11007302J. doi:10.1029/2004JD005220.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
- Kleypas, J.A., R.A. Feely, V.J. Fabry, C. Langdon, C.L. Sabine, and L.L. Robbins. (2006). Impacts of Ocean Acidification on Coral Reefs and Other Marine Calcifiers: A Guide for Further Research, report of a workshop held 18–20 April 2005, St. Petersburg, FL, sponsored by National Science Foundation , NOAA and the U.S. Geological Survey, 88pp.
- Kolbert, E. (20 November 2006). "The Darkening Sea: Carbon emissions and the ocean". The New Yorker.
- Kump, Lee R.; Kasting, James F.; Crane., Robert G. (2003). The Earth System (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall. pp. 162–164. ISBN 0613918142.
- Riebesell, U., V. J. Fabry, L. Hansson & J.-P. Gattuso (Eds.). (2010). Guide to best practices for ocean acidification research and data reporting, 260 p. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union.
- Sabine, C. L. (2004). "The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO
2" (abstract). Science. 305 (5682): 367–371. doi:10.1126/science.1097403. PMID 15256665.{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Stone, R. (2007). "A World Without Corals?". Science. 316 (5825): 678–681. doi:10.1126/science.316.5825.678. PMID 17478692.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
External links
Scientific sources:
- How Acidification Threatens Oceans from the Inside Out Scientific American August 9, 2010 by Marah J. Hardt and Carl Safina
- Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide, report by the Royal Society (UK)
- AR4 WG1 Chapter 5: Oceanic Climate Change and Sea Level, IPCC
- State of the Science FACT SHEET: Ocean acidification, NOAA
- Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC), the primary data analysis center of the U.S. Department of Energy (located at Oak Ridge National Laboratory)
- Ocean acidification introduction, USGS
- Climate change threatening the Southern Ocean, report by CSIRO
- The Ocean in a High CO
2 World, an international science symposium series - The Acid Ocean – the Other Problem with CO
2 Emission, David Archer, a RealClimate discussion - Regularly updated "blog" of ocean acidification publications and news, Jean-Pierre Gattuso
- Task Force on Ocean Acidification in the Pacific, including recent presentations on ocean acidification, Pacific Science Association
- Ocean Acidification, a multimedia, interactive site from The World Ocean Observatory
- Acidic Oceans: Why should we care? Perspectives in ocean science, Andrew Dickson, Scripps Institution of Oceanography
- Climate Change: Coral Reefs on the Edge A video presentation by Prof. Ove Hoegh-Guldberg on impact of ocean acidification on coral reefs
Scientific projects:
- Dr. Francisco Chavez on Ocean Acidification - Smithsonian Ocean Portal
- European Project of Ocean Acidification (EPOCA), a 4-year-long EU initiative to investigate ocean acidification (initiated June 2008)
- Biological Impacts of Ocean Acidification (BIOACID), a German initiative funded by BMBF
- Ocean Acidification Research Programme (UKOARP), a 5-year-long UK initiative funded by NERC, Defra and DECC
- Research Program on Ocean Acidification at the Cluster of Excellence "Future Ocean", Kiel
- Ocean Acidification Research Center at University of Alaska at Fairbanks
Popular media sources:
- Threatening Oceans from the Inside Out: How Acidification Affects Marine Life, Scientific American
- "The Darkening Sea, article in The New Yorker magazine, Nov. 20, 2006 (requires registration)
- "Growing Acidity of Oceans May Kill Corals", Washington Post
- "Scientists Grapple with Ocean Acidification", ABC News
- "Ocean Acidification & Climate", by Clayton Sandell ABC News
- A World Without Whales? by Philippe Cousteau, The Huffington Post
- Acid Test: Can we save our oceans from CO
2?, Oceana - The Acid Ocean, Stanford University
Videos on Ocean Acidification:
- The Other CO
2 Problem, an EPOCA-commissioned educational animation created by students from Ridgeway School, Plymouth - Acid Test: The Global Challenge of Ocean Acidification, by Natural Resources Defense Council
- A Sea Change: Imagine a world without fish, an award-winning documentary and related blog about ocean acidification
- Ocean Acidification in a Nutshell, by Greenpeace Aotearoa New Zealand
Carbonate system calculators
The following packages calculate the state of the carbonate system in seawater (including pH):
- CO2SYS, a stand-alone executable (also available in a version for Microsoft Excel/VBA)
- seacarb, a R package for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux (also available here)
- CSYS, a Matlab script

![{\displaystyle {\Omega }={\frac {\left[Ca^{2+}\right]\left[CO_{3}^{2-}\right]}{K_{sp}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5f9baed6b8de226d311fcba713744429d402e506)