Geography of Iowa: Difference between revisions
m Corrected: "resources" |
Rescuing 7 sources and tagging 3 as dead. #IABot (v1.6beta) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Bedrock features== |
==Bedrock features== |
||
Iowa's bedrock geology generally increases in age from west to east. In northwest Iowa [[Cretaceous]] bedrock is ca. 74 million years old, in eastern Iowa [[Cambrian]] bedrock dates to ca. 500 million years ago.<ref>[http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/geoiowa/GEOIOWA.HTM Prior: ''Geology of Iowa: Iowa's Earth History Shaped by Ice, Wind, Rivers, and Ancient Seas'']</ref> |
Iowa's bedrock geology generally increases in age from west to east. In northwest Iowa [[Cretaceous]] bedrock is ca. 74 million years old, in eastern Iowa [[Cambrian]] bedrock dates to ca. 500 million years ago.<ref>[http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/geoiowa/GEOIOWA.HTM Prior: ''Geology of Iowa: Iowa's Earth History Shaped by Ice, Wind, Rivers, and Ancient Seas''] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090416104106/http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/browse/geoiowa/geoiowa.htm |date=2009-04-16 }}</ref> |
||
===Meteor impact structures=== |
===Meteor impact structures=== |
||
====Manson impact structure==== |
====Manson impact structure==== |
||
Seventy-four million years ago, a large asteroid crashed into what is now southeast [[Pocahontas County, Iowa|Pocahontas county]] creating the [[Manson crater]]. Probably a mile in diameter, it would have killed most animals within 650 miles, roughly an area from modern Denver to Detroit. This was originally thought to have been one of the causes of the [[dinosaur]] extinction, but recalculation of the impact's age indicates it occurred some 12 million years before the mass extinction. Although [[glaciation]] has erased all surface evidence of the impact, the bedrock associated with this impact is unique in Iowa.<ref>[http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/manson99/manson.htm Iowa's Manson Impact Structure]</ref> |
Seventy-four million years ago, a large asteroid crashed into what is now southeast [[Pocahontas County, Iowa|Pocahontas county]] creating the [[Manson crater]]. Probably a mile in diameter, it would have killed most animals within 650 miles, roughly an area from modern Denver to Detroit. This was originally thought to have been one of the causes of the [[dinosaur]] extinction, but recalculation of the impact's age indicates it occurred some 12 million years before the mass extinction. Although [[glaciation]] has erased all surface evidence of the impact, the bedrock associated with this impact is unique in Iowa.<ref>[http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/manson99/manson.htm Iowa's Manson Impact Structure] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080616214434/http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/manson99/manson.htm |date=2008-06-16 }}</ref> |
||
====Decorah crater==== |
====Decorah crater==== |
||
[[File:USGS Decorah crater.jpg|thumbnail|[[U.S. Geological Survey]] aerial resistivity map of the [[Decorah, Iowa]] area, showing the [[Decorah crater]].]] |
[[File:USGS Decorah crater.jpg|thumbnail|[[U.S. Geological Survey]] aerial resistivity map of the [[Decorah, Iowa]] area, showing the [[Decorah crater]].]] |
||
A much older meteorite strike created the [[Decorah crater]] during the [[Middle Ordovician]] Period, 470 million years ago. The crater is estimated to be 3.5 miles (5.6 km) in diameter, covered by Winneshiek Shale.<ref name=Post1>{{cite news|last=Vastag|first=Brian|title=Crater found in Iowa points to asteroid break-up 470 million years ago|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/national/health-science/crater-found-in-iowa-points-to-asteroid-break-up-470-million-years-ago/2013/02/18/545131f8-76d5-11e2-aa12-e6cf1d31106b_story.html?wprss=rss_national|accessdate=19 February 2013|newspaper=[[Washington Post]]|date=18 February 2013}}</ref><ref name=gazette1>{{cite news|title=Geological survey: Ancient meteorite crater sits below Decorah|url=http://thegazette.com/2013/03/05/ancient-meteorite-crater-sits-below-decorah-geological-surveys-confirm/|accessdate=6 March 2013|newspaper=[[Cedar Rapids Gazette]]|date=5 March 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=US Geological Survey|title=Iowa Meteorite Crater Confirmed|url=http://www.usgs.gov/newsroom/article.asp?ID=3521|accessdate=7 March 2013}}</ref> There is no surface evidence of the impact, as the Winneshiek Shale is more than 50 feet below the bottom of the [[Upper Iowa River]]. The impact, equivalent to [[TNT equivalent|1,000 megatons of TNT]],<ref name=gazette1 /> did not appear to penetrate the Earth's mantle, but it did push down the underlying Ordovician and Cambrian bedrock several hundred feet.<ref>{{cite web|last=Iowa Department of Natural Resources|title=GEOLOGIC MAPPING FOR WATER QUALITY PROJECTS IN THE UPPER IOWA RIVER WATERSHED|url=ftp://ftp.igsb.uiowa.edu/igspubs/pdf/TIS-54.pdf|work=Technical Information Series No. 54, 2011|accessdate=19 February 2013}}</ref> It may be one of several Middle Ordovician meteors that fell roughly simultaneously 469 million years ago, part of a proposed [[Ordovician meteor event]]. |
A much older meteorite strike created the [[Decorah crater]] during the [[Middle Ordovician]] Period, 470 million years ago. The crater is estimated to be 3.5 miles (5.6 km) in diameter, covered by Winneshiek Shale.<ref name=Post1>{{cite news|last=Vastag|first=Brian|title=Crater found in Iowa points to asteroid break-up 470 million years ago|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/national/health-science/crater-found-in-iowa-points-to-asteroid-break-up-470-million-years-ago/2013/02/18/545131f8-76d5-11e2-aa12-e6cf1d31106b_story.html?wprss=rss_national|accessdate=19 February 2013|newspaper=[[Washington Post]]|date=18 February 2013}}</ref><ref name=gazette1>{{cite news|title=Geological survey: Ancient meteorite crater sits below Decorah|url=http://thegazette.com/2013/03/05/ancient-meteorite-crater-sits-below-decorah-geological-surveys-confirm/|accessdate=6 March 2013|newspaper=[[Cedar Rapids Gazette]]|date=5 March 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=US Geological Survey|title=Iowa Meteorite Crater Confirmed|url=http://www.usgs.gov/newsroom/article.asp?ID=3521|accessdate=7 March 2013}}</ref> There is no surface evidence of the impact, as the Winneshiek Shale is more than 50 feet below the bottom of the [[Upper Iowa River]]. The impact, equivalent to [[TNT equivalent|1,000 megatons of TNT]],<ref name=gazette1 /> did not appear to penetrate the Earth's mantle, but it did push down the underlying Ordovician and Cambrian bedrock several hundred feet.<ref>{{cite web|last=Iowa Department of Natural Resources|title=GEOLOGIC MAPPING FOR WATER QUALITY PROJECTS IN THE UPPER IOWA RIVER WATERSHED|url=ftp://ftp.igsb.uiowa.edu/igspubs/pdf/TIS-54.pdf|work=Technical Information Series No. 54, 2011|accessdate=19 February 2013}}{{dead link|date=October 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> It may be one of several Middle Ordovician meteors that fell roughly simultaneously 469 million years ago, part of a proposed [[Ordovician meteor event]]. |
||
=== Midcontinent rift=== |
=== Midcontinent rift=== |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Image:Iowa topography.jpg|thumb|250px|left|Topography of Iowa, with counties and major streams]] |
[[Image:Iowa topography.jpg|thumb|250px|left|Topography of Iowa, with counties and major streams]] |
||
[[Image:Landforms of Iowa.jpg|thumb|275px|Landforms of Iowa, based on Prior (1991) and [[Samuel Calvin (geologist)|Calvin]] (1904), with major rivers and streams]] |
[[Image:Landforms of Iowa.jpg|thumb|275px|Landforms of Iowa, based on Prior (1991) and [[Samuel Calvin (geologist)|Calvin]] (1904), with major rivers and streams]] |
||
Despite popular perception, Iowa is generally not flat; most of the state consists of rolling hills. Prior<ref>Prior, Jean C. (1991) ''Landforms of Iowa.'' University of Iowa Press, Iowa City. http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/landform.htm. See also Calvin, Samuel (1904) ''Outline Map of the Drift Sheets of Iowa.'' Iowa Publication Co., Davenport.</ref> divides Iowa into eight [[landform]]s based on [[glaciation]], [[soil]]s, [[topography]], and [[river]] drainage: |
Despite popular perception, Iowa is generally not flat; most of the state consists of rolling hills. Prior<ref>Prior, Jean C. (1991) ''Landforms of Iowa.'' University of Iowa Press, Iowa City. {{cite web |url=http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/landform.htm |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2008-06-09 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20090302084724/http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/landform.htm |archivedate=2009-03-02 |df= }}. See also Calvin, Samuel (1904) ''Outline Map of the Drift Sheets of Iowa.'' Iowa Publication Co., Davenport.</ref> divides Iowa into eight [[landform]]s based on [[glaciation]], [[soil]]s, [[topography]], and [[river]] drainage: |
||
===Paleozoic plateau=== |
===Paleozoic plateau=== |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
===Des Moines lobe=== |
===Des Moines lobe=== |
||
[[Image:Barringer-Arial.jpg|thumb|[[Barringer Slough]], a remnant of the extensive prairie wetlands that once covered the Des Moines Lobe.]] |
[[Image:Barringer-Arial.jpg|thumb|[[Barringer Slough]], a remnant of the extensive prairie wetlands that once covered the Des Moines Lobe.]] |
||
Often called the [[Prairie Pothole Region]], the Des Moines Lobe was glaciated up until 12,000 years ago during the [[Wisconsin glaciation]]. The area is marked by rolling terrain and ridges.<ref>http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/landform.htm</ref> Historically, this area was peppered with small interconnected swamps, most of which were drained for farmland. The [[Iowa Great Lakes]] occur along the western edge of the Des Moines lobe. |
Often called the [[Prairie Pothole Region]], the Des Moines Lobe was glaciated up until 12,000 years ago during the [[Wisconsin glaciation]]. The area is marked by rolling terrain and ridges.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/landform.htm |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2008-06-09 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20090302084724/http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/landform.htm |archivedate=2009-03-02 |df= }}</ref> Historically, this area was peppered with small interconnected swamps, most of which were drained for farmland. The [[Iowa Great Lakes]] occur along the western edge of the Des Moines lobe. |
||
===Southern Iowa drift plain=== |
===Southern Iowa drift plain=== |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
[[Image:Iowa rainfall.jpg|thumb|left|Iowa annual rainfall in inches]] |
[[Image:Iowa rainfall.jpg|thumb|left|Iowa annual rainfall in inches]] |
||
[[Image:Mississippi floodplain iowa.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Mississippi River alluvial plain from SIDP bluffs north of Kingston, Iowa]] |
[[Image:Mississippi floodplain iowa.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Mississippi River alluvial plain from SIDP bluffs north of Kingston, Iowa]] |
||
As in most of the U.S., surface water in Iowa is never safe to drink untreated, contamination by agricultural runoff including nitrates, herbicides, pesticides, and animal waste is common. Municipal water supplies are typically heavily chlorinated, this chlorine, combined with high nitrate levels, often give municipal water a strong smell, and the limestone bedrock in much of the state causes hard water.<ref>[http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/service/wateres.htm Iowa City Water Quality] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080517104923/http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/service/wateres.htm |date=May 17, 2008 }}</ref> Some communities, such as [[Iowa City]] resort to additional carbon filtration and [[lime softening]] coagulation-sedimentation to make the water more palatable.<ref>http://www.icgov.org/default/?id=1623</ref> Water treatment can be surprisingly effective; Des Moines' advanced filtration system has led to water quality ranked among the nation's best.<ref>'Drink up - from the city tap.' ''Des Moines Register'' 2 July 2008, http://www.desmoinesregister.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20080702/OPINION03/807020346/1110</ref> |
As in most of the U.S., surface water in Iowa is never safe to drink untreated, contamination by agricultural runoff including nitrates, herbicides, pesticides, and animal waste is common. Municipal water supplies are typically heavily chlorinated, this chlorine, combined with high nitrate levels, often give municipal water a strong smell, and the limestone bedrock in much of the state causes hard water.<ref>[http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/service/wateres.htm Iowa City Water Quality] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080517104923/http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/service/wateres.htm |date=May 17, 2008 }}</ref> Some communities, such as [[Iowa City]] resort to additional carbon filtration and [[lime softening]] coagulation-sedimentation to make the water more palatable.<ref>http://www.icgov.org/default/?id=1623</ref> Water treatment can be surprisingly effective; Des Moines' advanced filtration system has led to water quality ranked among the nation's best.<ref>'Drink up - from the city tap.' ''Des Moines Register'' 2 July 2008, http://www.desmoinesregister.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20080702/OPINION03/807020346/1110{{dead link|date=October 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
||
===Jordan Aquifer=== |
===Jordan Aquifer=== |
||
The Jordan Aquifer is the largest source of groundwater, extending from northeast Iowa to south central Iowa, and is ultimately the source of much of Iowa's agricultural and industrial water. In addition to pollution threats, the aquifer is threatened by overuse in well-source irrigation, [[ethanol]] production, and the diminishment of resupply caused by extensive field tilling. The aquifer has dropped by as much as 300 feet since the 19th century, resulting in dry wells, the disappearance of natural surface springs, and the diminishment of water quality.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://gazetteonline.com/local-news/2009/12/06/heavy-use-draining-aquifer |title=Heavy use draining aquifer |last=Love |first=Orlan |date=Dec 6, 2009 |publisher=Cedar Rapids Gazette |accessdate=20 December 2009 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091209064212/http://gazetteonline.com/local-news/2009/12/06/heavy-use-draining-aquifer |archivedate=December 9, 2009 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://gazetteonline.com/opinion/editorial/2009/12/18/dont-take-aquifer-for-granted|title=Don’t take aquifer for granted|last=Tecklenburg|first=Jeff|date= |
The Jordan Aquifer is the largest source of groundwater, extending from northeast Iowa to south central Iowa, and is ultimately the source of much of Iowa's agricultural and industrial water. In addition to pollution threats, the aquifer is threatened by overuse in well-source irrigation, [[ethanol]] production, and the diminishment of resupply caused by extensive field tilling. The aquifer has dropped by as much as 300 feet since the 19th century, resulting in dry wells, the disappearance of natural surface springs, and the diminishment of water quality.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://gazetteonline.com/local-news/2009/12/06/heavy-use-draining-aquifer |title=Heavy use draining aquifer |last=Love |first=Orlan |date=Dec 6, 2009 |publisher=Cedar Rapids Gazette |accessdate=20 December 2009 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20091209064212/http://gazetteonline.com/local-news/2009/12/06/heavy-use-draining-aquifer |archivedate=December 9, 2009 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://gazetteonline.com/opinion/editorial/2009/12/18/dont-take-aquifer-for-granted|title=Don’t take aquifer for granted|last=Tecklenburg|first=Jeff|date=Dec 18, 2009|publisher=Cedar Rapids Gazette|accessdate=20 December 2009}}{{dead link|date=October 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> |
||
==Soils== |
==Soils== |
||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
*Iowa Geological Survey, http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/ |
*Iowa Geological Survey, http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/ |
||
*Iowa Geographical Map Server, http://cairo.gis.iastate.edu/ |
*Iowa Geographical Map Server, https://web.archive.org/web/20080513085937/http://cairo.gis.iastate.edu/ |
||
*U.S. Geological Survey Iowa Overview, http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=IA |
*U.S. Geological Survey Iowa Overview, http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=IA |
||
*Web Soil Survey, http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/WebSoilSurvey.aspx |
*Web Soil Survey, http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/WebSoilSurvey.aspx |
||
*NRCS Soil Survey, https://web.archive.org/web/20061113181444/http://soils.usda.gov |
*NRCS Soil Survey, https://web.archive.org/web/20061113181444/http://soils.usda.gov/technical/classification/osd/index.html |
||
*Geological Society of Iowa, http://www.iowageology.org/ |
*Geological Society of Iowa, https://web.archive.org/web/20081004055910/http://www.iowageology.org/ |
||
*Loess Hills Geology, http://pubs.usgs.gov/info/loess/ |
*Loess Hills Geology, http://pubs.usgs.gov/info/loess/ |
||
*University of Iowa Geoscience, http://www.uiowa.edu/~geology/ |
*University of Iowa Geoscience, http://www.uiowa.edu/~geology/ |
||
Revision as of 05:49, 13 October 2017
This article is about Iowa geology. For the study of buried human cultural remains in Iowa, see Iowa archaeology.

The geography of Iowa includes the study of bedrock, landforms, geology, and paleontology of the state of Iowa.
Bedrock features
Iowa's bedrock geology generally increases in age from west to east. In northwest Iowa Cretaceous bedrock is ca. 74 million years old, in eastern Iowa Cambrian bedrock dates to ca. 500 million years ago.[1]
Meteor impact structures
Manson impact structure
Seventy-four million years ago, a large asteroid crashed into what is now southeast Pocahontas county creating the Manson crater. Probably a mile in diameter, it would have killed most animals within 650 miles, roughly an area from modern Denver to Detroit. This was originally thought to have been one of the causes of the dinosaur extinction, but recalculation of the impact's age indicates it occurred some 12 million years before the mass extinction. Although glaciation has erased all surface evidence of the impact, the bedrock associated with this impact is unique in Iowa.[2]
Decorah crater
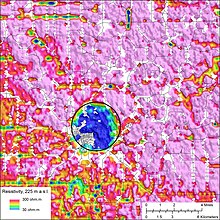
A much older meteorite strike created the Decorah crater during the Middle Ordovician Period, 470 million years ago. The crater is estimated to be 3.5 miles (5.6 km) in diameter, covered by Winneshiek Shale.[3][4][5] There is no surface evidence of the impact, as the Winneshiek Shale is more than 50 feet below the bottom of the Upper Iowa River. The impact, equivalent to 1,000 megatons of TNT,[4] did not appear to penetrate the Earth's mantle, but it did push down the underlying Ordovician and Cambrian bedrock several hundred feet.[6] It may be one of several Middle Ordovician meteors that fell roughly simultaneously 469 million years ago, part of a proposed Ordovician meteor event.
Midcontinent rift

Buried deeply within Iowa's bedrock, the Midcontinent Rift System can be seen clearly in magnetic anomaly maps of Iowa. This is a billion-year-old tectonic plate scar that extends from Kansas through Lake Superior. This rift is not seismically active.[8]
Seismic activity
No major active fault lines exist in Iowa, and Iowa is one of the most seismically stable states in the U.S. With the exception of the 1968 Illinois earthquake which caused the water tower at Lineville to leak,[9] no injuries or significant damage has ever been caused by earthquakes in Iowa. Occasional small earthquakes occur near Fremont County in the far southwest, and the Sioux City area can occasionally be shaken by nearby tremblors. Large earthquakes associated with the New Madrid Fault of far southern Illinois and Missouri can occasionally be felt in eastern Iowa.[10][11] Recent earthquakes centered in Oklahoma have also been felt in Iowa, but have caused no damage.[12]
Fossil fuels

Historically, Iowa was a significant coal producer, particularly the Des Moines River valley from Coalville south. Much of the greater City of Des Moines area was mined. Boone and What Cheer were important in the late 19th century. In the 20th century, the most important mines were farther south around Albia, Centerville, Lucas and Oskaloosa. Iowa coal tends to be too high in sulfur for modern applications, and the last commercial mine closed in 1994.[13]
Iowa has very limited natural gas and oil production.[14]
Sioux quartzite
Although Iowa's bedrock is generally younger in western parts of the state, one exception is a small part of far northwest Iowa where Precambrian Sioux quartzite bedrock is found in northwest Lyon County. Sioux quartzite is a very hard rock of ruddy pink color used extensively in the region for road and railroad beds.[15] Sioux quartzite has been dated to have been laid between 1.64 and 1.76 billion years ago.[16]

Geodes
Geodes are found in southeast Iowa and are the official state rock. They consist of grey to pink cobbles within limestone that when cut or smashed open reveal a hollow crystal-filled interior. Geodes are common around Geode State Park in Henry County.[17]
Landforms and topography
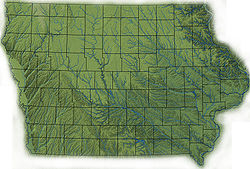

Despite popular perception, Iowa is generally not flat; most of the state consists of rolling hills. Prior[18] divides Iowa into eight landforms based on glaciation, soils, topography, and river drainage:
Paleozoic plateau
Also known as the Driftless Area, this region of scenic, high relief landscapes includes such features as resistant, bluff-forming bedrock outcrops, deep V-shaped valleys, caves, springs, and sinkholes. Glacial deposits and loess are thin or absent over most of the region.
Des Moines lobe

Often called the Prairie Pothole Region, the Des Moines Lobe was glaciated up until 12,000 years ago during the Wisconsin glaciation. The area is marked by rolling terrain and ridges.[19] Historically, this area was peppered with small interconnected swamps, most of which were drained for farmland. The Iowa Great Lakes occur along the western edge of the Des Moines lobe.
Southern Iowa drift plain

The southern Iowa drift plain covers most of the southern half of Iowa. This is probably the most familiar landscape to travelers, since most of Interstate 80 in Iowa runs through the SIDP. The classic Iowa landscape, consisting of rolling hills of Wisconsin-age loess on Illinoian (or earlier) till. The SIDP is some of the most productive agricultural land in the world.
Mississippi alluvial plain

Generally level areas of stream terraces, paleochannels, backwater sloughs, and oxbow lakes are found within the broad Mississippi River valley.
Loess hills
The Loess Hills consist of very thick deposits of loess in far western Iowa deposited during the Wisconsin and Illinoian periods. Highly eroded, leaving stark, beautiful "golden hills".

Iowan surface
Northeast Iowa is covered with eroded Pre-Illinoian till with moderate loess formation, frequently in the form of paha ridges, muted relief except for steep rolling hills near river valleys, and deeper valleys. These picturesque hills are depicted in many of the landscapes of Grant Wood.
Northwest Iowa plains
Like the Iowan Surface, the Northwest Iowa Plains are rolling hills consisting of eroded soils developed since pre-Wisconsinan glaciation, but with significant amounts of loess.
Missouri alluvial plain
Perhaps the only truly flat region of Iowa, the Missouri Alluvial Plain contains areas of terraces, sloughs, and oxbows. Its valley trench is not as deep as the Mississippi River system, and the Missouri River is contained in a much narrower channel. In Iowa, the eastern border of the Missouri Plains is the Loess Hills, forming steep rounded bluffs.
Water


As in most of the U.S., surface water in Iowa is never safe to drink untreated, contamination by agricultural runoff including nitrates, herbicides, pesticides, and animal waste is common. Municipal water supplies are typically heavily chlorinated, this chlorine, combined with high nitrate levels, often give municipal water a strong smell, and the limestone bedrock in much of the state causes hard water.[20] Some communities, such as Iowa City resort to additional carbon filtration and lime softening coagulation-sedimentation to make the water more palatable.[21] Water treatment can be surprisingly effective; Des Moines' advanced filtration system has led to water quality ranked among the nation's best.[22]
Jordan Aquifer
The Jordan Aquifer is the largest source of groundwater, extending from northeast Iowa to south central Iowa, and is ultimately the source of much of Iowa's agricultural and industrial water. In addition to pollution threats, the aquifer is threatened by overuse in well-source irrigation, ethanol production, and the diminishment of resupply caused by extensive field tilling. The aquifer has dropped by as much as 300 feet since the 19th century, resulting in dry wells, the disappearance of natural surface springs, and the diminishment of water quality.[23][24]
Soils
The NRCS divides Iowa into 23 soil regions. In general, soils of southern, eastern, and western Iowa are loess-derived, while soils of northern and central Iowa are till-derived. Most level areas of Iowa have soils highly suitable for agriculture, making Iowa one of the most productive farming regions of the world.[25]
Radon

Like most Upper Midwest and Plains states, radon is a common problem in Iowa, especially in areas with clay-rich soils.[26] In Iowa radon is the highest in the southern and the western parts of Iowa
Paleontology
Devonian Fossil Gorge
Floods in 1993 washed away all the soil and unconsolidated bedrock along the spillway of the Coralville Lake Dam in Johnson County, exposing a rich collection of Devonian-age fossils. This area has been transformed into a visitors' center, where hikers can tour the bedrock. Unfortunately, looters have illegally removed many of the better fossils.[27] The June 2008 floods expanded the fossil bed floor, and removed some of the weathered overburden.[28]
Dinosaurs
Jurassic and Cretaceous bedrock in western Iowa have potential to contain dinosaur remains, and in nearby parts of Nebraska Hadrosaurid (“duck-billed”) ornithopod dinosaur remains have been recovered in Cretaceous bedrock similar to that of Iowa. The deep loess that covers much of western Iowa typically conceals the bedrock, limiting opportunities to finding dinosaurs to mining and quarrying operations.[29]
Paleofauna
Archaeological and paleontological sites in Iowa have produced an extensive collection of Pleistocene and Holocene animals; these have been used to reconstruct past environmental conditions in the Midwest.[30] Some of the earliest paleoclimatic reconstructions of the midcontinent were made from Iowa collections, such as the Cherokee Sewer Site.[31]
A Pleistocene giant sloth is under excavation along West Tarkio Creek near Shenandoah, Iowa. Three individuals of Megalonyx Jeffersoni, or Jefferson's Ground Sloth, have been identified so far, including one adult and two juveniles of different ages.[32][33]
Notable Iowa geologists
Samuel Calvin (1840–1911) was Iowa's first systematic geologist, who helped to make the first bedrock and landform maps of Iowa, as well as lead geological research throughout the state.[34] Calvin Hall at the University of Iowa is named for him. Clair Cameron Patterson (1922–1995) developed the lead-lead dating and calculated an age for the Earth of 4.55 billion years; a figure far more accurate than those that existed at the time and one that has remained unchanged for over 50 years. Charles Rollin Keyes was also an early Iowa geologist who helped map the soils and bedrock of southeast Iowa; he, with Calvin, was a founder of the Iowa Geological Survey.
References
- ^ Prior: Geology of Iowa: Iowa's Earth History Shaped by Ice, Wind, Rivers, and Ancient Seas Archived 2009-04-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Iowa's Manson Impact Structure Archived 2008-06-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vastag, Brian (18 February 2013). "Crater found in Iowa points to asteroid break-up 470 million years ago". Washington Post. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- ^ a b "Geological survey: Ancient meteorite crater sits below Decorah". Cedar Rapids Gazette. 5 March 2013. Retrieved 6 March 2013.
- ^ US Geological Survey. "Iowa Meteorite Crater Confirmed". Retrieved 7 March 2013.
- ^ Iowa Department of Natural Resources. "GEOLOGIC MAPPING FOR WATER QUALITY PROJECTS IN THE UPPER IOWA RIVER WATERSHED" (PDF). Technical Information Series No. 54, 2011. Retrieved 19 February 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Kucks, Robert P.; Hill, Patricia L. (2005). "Iowa magnetic and gravity maps and data". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2009-09-03.
- ^ Midcontinent Rift System In Iowa
- ^ Times-Republican Newspaper, Corydon, Iowa, 19 NOV 1968
- ^ Iowa Earthquake Information
- ^ https://earthquake.usgs.gov/regional/states/iowa/history.php
- ^ Fickau, Ethan (3 September 2016). "What's the likelihood of feeling another earthquake in Iowa?". KCCI Des Moines (CBS). Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ^ Iowa Coal Geology
- ^ Oil, Gas, and Metallic Mineral Regulatory Information
- ^ Sioux Quartzite geology
- ^ Wayne I. Anderson, Iowa's Geological Past: Three Billion Years Of Change, University Of Iowa Press, 1998, p.41 ISBN 978-0877456391
- ^ IA DNR: State Parks, Geode State Park
- ^ Prior, Jean C. (1991) Landforms of Iowa. University of Iowa Press, Iowa City. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-03-02. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). See also Calvin, Samuel (1904) Outline Map of the Drift Sheets of Iowa. Iowa Publication Co., Davenport. - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-03-02. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Iowa City Water Quality Archived May 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ http://www.icgov.org/default/?id=1623
- ^ 'Drink up - from the city tap.' Des Moines Register 2 July 2008, http://www.desmoinesregister.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20080702/OPINION03/807020346/1110[permanent dead link]
- ^ Love, Orlan (Dec 6, 2009). "Heavy use draining aquifer". Cedar Rapids Gazette. Archived from the original on December 9, 2009. Retrieved 20 December 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Tecklenburg, Jeff (Dec 18, 2009). "Don't take aquifer for granted". Cedar Rapids Gazette. Retrieved 20 December 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Information About Soils | Iowa NRCS
- ^ http://www.extension.iastate.edu/Publications/PM1336.pdf
- ^ Flood of 1993 Archived June 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Iowa City Press Citizen, http://www.press-citizen.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20080709/NEWS01/807090324/1079
- ^ Witzke, http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/Browse/dinosaurs/age_of_dinosaurs_in_iowa.htm
- ^ http://www.uiowa.edu/~geology/paleo/
- ^ Anderson and Semken (1980) The Cherokee Excavations: Holocene Ecology and Human Adaptations in Northwestern Iowa. Academic Press, New York.
- ^ http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2006/06/060626123721.htm, http://slothcentral.com/
- ^ Semken and Brenzel (2007) One Sloth Becomes Three. Newsletter of the Iowa Archeological Society 57(1).
- ^ Calvin obituary, The Journal of Geology, July 1911, pp. 385-391.
External links
- Iowa Geological Survey, http://www.igsb.uiowa.edu/
- Iowa Geographical Map Server, https://web.archive.org/web/20080513085937/http://cairo.gis.iastate.edu/
- U.S. Geological Survey Iowa Overview, http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=IA
- Web Soil Survey, http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/WebSoilSurvey.aspx
- NRCS Soil Survey, https://web.archive.org/web/20061113181444/http://soils.usda.gov/technical/classification/osd/index.html
- Geological Society of Iowa, https://web.archive.org/web/20081004055910/http://www.iowageology.org/
- Loess Hills Geology, http://pubs.usgs.gov/info/loess/
- University of Iowa Geoscience, http://www.uiowa.edu/~geology/
- Iowa Geological Society Annual Report, http://ir.uiowa.edu/igsar/
- Iowa Geological Survey Publication on coal, http://ir.uiowa.edu/igs_pubs/
- Samuel Calvin geological photographs, http://digital.lib.uiowa.edu/cdm4/index_calvin.php?CISOROOT=/calvin
