Gender inequality in the United States: Difference between revisions
Brookepujols (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
==== Gender Differences in Degree Choices ==== |
==== Gender Differences in Degree Choices ==== |
||
Specific to university and college campuses, gender inequalities can be seen when looking into the demographics of particular majors. This initial entrance into a particular field of study is shaped by an individual’s desires to take a certain set of classes, leading to somewhat specific career opportunities and subsequently, salaries. When exploring the depths of college majors, there is a tendency for each gender to cluster into certain majors. These stereotypical “masculine” and “feminine” degrees are key indicators to the inequalities women face in certain fields, specifically within the sciences and mathematics. Based on the Department of Education’s collections of data from the College Class of 2015, “women earn the large majority of degrees in health professions, psychology, education, english and communication, while men earn the large majority of degrees in engineering, computer science, and theology.” These exact percentages can be seen in the table distributed by the Department of Education, exemplifying the overall majority men have in the STEM field. |
Specific to university and college campuses, gender inequalities can be seen when looking into the demographics of particular majors. This initial entrance into a particular field of study is shaped by an individual’s desires to take a certain set of classes, leading to somewhat specific career opportunities and subsequently, salaries. When exploring the depths of college majors, there is a tendency for each gender to cluster into certain majors. These stereotypical “masculine” and “feminine” degrees are key indicators to the inequalities women face in certain fields, specifically within the sciences and mathematics. Based on the Department of Education’s collections of data from the College Class of 2015, “women earn the large majority of degrees in health professions, psychology, education, english and communication, while men earn the large majority of degrees in engineering, computer science, and theology.”<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=http://www.aei.org/publication/table-of-the-day-bachelors-degrees-by-field-and-gender-for-the-class-of-2015/|title=Table of the day: Bachelor's degrees by field and gender for the Class of 2015|date=2017-08-07|website=AEI|language=en-US|access-date=2019-04-07}}</ref> These exact percentages can be seen in the table distributed by the Department of Education, exemplifying the overall majority men have in the STEM field.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
Although not designated for specific genders, majors and minors at universities and colleges carry different stigmas for who should/shouldn’t be part of the program. The results of Sylvia Beyer’s 1995 study surveying 154 female and 111 male students from the University of Wisconsin-Parkside, to test the accuracy of gender stereotypes, conclude that students believe men and women are concentrated in different fields and that specific majors are deemed “masculine” and “feminine.” The participants categorized the masculine majors with computer science, chemistry, business, history, and mathematics, while they placed the feminine majors as psychology, communication, music, and art. These perceptions may not accurately describe the gender percentages in each field, but prove that men are more likely to be seen in STEM concentrations than women. Additionally, Yale researchers have published studies which prove that young male scientists are more likely to be favored than female scientists with the same candidacy. As of 2013, only ⅕ of Physics PHDs were awarded to women and only 14% of physics professors were female. A large factor in the major and minor inequalities seen at the college level come from the encouragement of peers and educators to go forth in certain subjects. Ultimately, women are not receiving the same support and backing as their male counterparts, and thus, do not pursue STEM fields. Since a large sum of money lies in these occupations, women are not receiving an equal share, further perpetuating gendered salary inequalities. |
Although not designated for specific genders, majors and minors at universities and colleges carry different stigmas for who should/shouldn’t be part of the program. The results of Sylvia Beyer’s 1995 study surveying 154 female and 111 male students from the University of Wisconsin-Parkside, to test the accuracy of gender stereotypes, conclude that students believe men and women are concentrated in different fields and that specific majors are deemed “masculine” and “feminine.”<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Beyer|first=Sylvia|date=1999|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/a:1018864803330|journal=Sex Roles|volume=40|issue=9/10|pages=787–813|doi=10.1023/a:1018864803330|issn=0360-0025}}</ref> The participants categorized the masculine majors with computer science, chemistry, business, history, and mathematics, while they placed the feminine majors as psychology, communication, music, and art. These perceptions may not accurately describe the gender percentages in each field, but prove that men are more likely to be seen in STEM concentrations than women. Additionally, Yale researchers have published studies which prove that young male scientists are more likely to be favored than female scientists with the same candidacy. As of 2013, only ⅕ of Physics PHDs were awarded to women and only 14% of physics professors were female.<ref name=":1">{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2013/10/06/magazine/why-are-there-still-so-few-women-in-science.html|title=Why Are There Still So Few Women in Science?|last=Pollack|first=Eileen|date=2013-10-03|work=The New York Times|access-date=2019-04-07|language=en-US|issn=0362-4331}}</ref> A large factor in the major and minor inequalities seen at the college level come from the encouragement of peers and educators to go forth in certain subjects. Ultimately, women are not receiving the same support and backing as their male counterparts, and thus, do not pursue STEM fields. Since a large sum of money lies in these occupations, women are not receiving an equal share, further perpetuating gendered salary inequalities.<ref name=":1" /> |
||
==== Gender Inequality in Representation at Elite Institutions ==== |
==== Gender Inequality in Representation at Elite Institutions ==== |
||
Revision as of 21:21, 7 April 2019
| Part of a series on |
| Feminism |
|---|
 |
|
|
Gender inequality in the United States has been diminishing throughout its history and significant advancements towards equality have been made beginning mostly in the early 1900s. However, despite this progress, gender inequality in the United States continues to persist in many forms, including the disparity in women's political representation and participation, occupational segregation, and the unequal distribution of household labor. In the past 20 years there have been emerging issues for boys/men, an achievement and attainment gap in education is a discussed subject. The alleviation of gender inequality has been the goal of several major pieces of legislation since 1920 and continuing to the present day. As of 2017, the World Economic Forum ranks the United States 22nd best in terms of gender equality out of 144 countries.[1]
In addition to the inequality faced by transgender women, inequality, prejudice, and violence against transgender men and women, as well as gender nonconforming individuals and individuals who identify with genders outside the gender binary, are also prevalent in the United States. Transgender individuals suffer from prejudices in the workforce and employment, higher levels of domestic violence, higher rates of hate crimes, especially murder, and higher levels of police brutality when compared to the cisgender population.[2][3][4]
Current issues for women
Political participation
The Center for American Women and Politics reports that, as of 2013, 18.3% of congressional seats are held by women and 23% of statewide elective offices are held by women; while the percentage of Congress made up of women has steadily increased, statewide elective positions held by women have decreased from their peak of 27.6% in 2001. Women also make up, as of 2013, 24.2% of state legislators in the United States. Among the one hundred largest cities in the United States, ten had female mayors as of 2013.[5]
In 1977, political science professor Susan Welch presented three possible explanations for this underrepresentation of women in politics: one, that women are socialized to avoid careers in politics; two, that women's responsibilities in the home keep them away out of both the work force and the political arena; and three, women are more often than men members of other demographic groups with low political participation rates.[6] In 2001, M. Margaret Conway, political science professor at the University of Florida, also presented three possible explanations for the continuation of this disparity: one, similar to Welch's first explanation, sociological and societal norm discourages women from running; two, women less frequently acquire the necessary skills to hold a political leadership position from nonpolitical activities; and three, gatekeeping in party politics prevents women from running.[7]
Work life and economics
The United States is falling behind other Western countries in the percentage of women engaged in the workforce.[8] Researchers from the Institute for Women's Policy Research at the University of California Hastings College of Law argue that this growing gap is due to a lack of governmental, business and societal support for working women. They ranked the United States last out of 20 industrialized countries in an index that measured such programs as family leave, alternative work arrangements, part-time employment, and other means to make workplaces more flexible and family-friendly.[8] The United States is also the only industrialized nation that does not have a paid parental leave policy mandated by law, and is one of only four countries worldwide that does not; in addition, fully paid maternity leave is only offered by around 16 percent of employers in the United States.[9]
Sex discrimination in employment
Women continuously are being mistreated and sexually discriminated against explicitly in the workplace today. This has been an ongoing issue and will continue until something changes in the occupational sphere. According to a study conducted by researchers at California State University, Northridge, when an individual with a PhD applies for a position at a university, that individual is significantly more likely to be offered a higher level of appointment, receive an offer of an academic position leading to tenure, and be offered a full professorship if they are a man when compared to a woman of comparable qualifications.[10] However, these findings have been disputed, with one study finding universities pushed to hire more women, resulting in females being given a 2:1 advantage over males in science, technology engineering and mathematics fields.[11] Another study found that women were significantly less likely to receive a job offer or an interview for a high-paying waiter position when compared to equally qualified men; this study also found that such hiring discrimination may be caused in part by customer's discrimination of preference for male wait staff.[12] Similarly, research conducted at the University of California, Davis focusing on academic dermatology revealed a significant downward trend in the number of women receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health, which the authors concluded was due to a lack of support for women scientists at their home institutions.[13]
Research from Lawrence University has found that men were more likely to be hired in traditionally masculine jobs, such as sales management, and women were more likely to be hired in traditionally feminine jobs, such as receptionist or secretary. However, individuals of either gender with masculine personality traits were advantaged when applying for either masculine or feminine jobs, indicating a possibly valuing of stereotypically male traits above stereotypically female traits.[14]
Occupational segregation by gender
Occupational gender segregation takes the form of both horizontal segregation (the unequal gender distribution across occupations) and vertical segregation (the overrepresentation of men in higher positions in both traditionally male and traditionally female fields).[15]
According to William A. Darity, Jr. and Patrick L. Mason, there is a strong horizontal occupational division in the United States on the basis of gender; in 1990, the index of occupational dissimilarity was 53%, meaning 53% of women or 47% of men would have to move to a different career field in order for all occupations to have equal gender composition.[16] While women have begun to more frequently enter traditionally male-dominated professions, there have been much fewer men entering female-dominated professions; professor of sociology Paula England cites this horizontal segregation of careers as a contributing factor to the gender pay gap.[17]
Pay gap
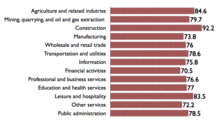
With regards to the gender pay gap in the United States, International Labour Organization notes as of 2010 women in the United States earned about 81% of what their male counterparts did.[19] While the gender pay gap has been narrowing since the passage of the Equal Pay Act, the convergence began to slow down in the 1990s.[20] In addition, overall wage inequality has been increasing since the 1980s as middle-wage jobs are decreasing replaced by larger percentages of both high-paying and low-paying jobs, creating a highly polarized environment.[21]
However numerous studies dispute the claim that discrimination accounts for the majority of the pay gap. When adjusting for industries commonly chosen, hours worked, and benefits received, the pay gap returns to 5%, which has been attributed to less aggressive pay negotiating in women.[22][23][24][25] One study actually found that before 30, females made more than males, and hypothesized that choosing a family over a career resulted in the drop of the female wage advantage during the thirties.[26][27]
According to researchers at the University of California, Berkeley and the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, the primary cause of this gap is discrimination manifested in the tendency of women to be hired more frequently in lower paying occupations, in addition to the fact that male dominated occupations are higher paying than female dominated occupations, and that, even within comparable occupations, women are often paid less than men.[28]
In medicine, female physicians are compensated less,[29] despite the fact that evidence suggest that the quality of care female physicians provide may be higher than that of male physicians.[30][31]
In addition to the gender pay gap, a "family gap" also exists, wherein women with children receive about 10-15% less pay when compared to women without children.[16][32] According to Jane Waldfogel, professor of social work and public affairs at Columbia University, this family gap is a contributing factor to the United States' large gender pay gap.[32] She also noted that men did not seem to be affected by this gap, as married men (who are more likely to have children) generally earned higher than unmarried men.[16][32]
Racial Pay Gap
The gender pay gap has continued to grow throughout the years due to a plethora of reasons. The gender pay gap refers to the median annual pay of all woman who work full time and year-round, thus compared to the pay of a similar background of men. [33] There is not one reason behind this gender pay gap, rather the pay gap is a result of many factors. Another topic of discussion regarding the gender pay gap is the racial pay gap that exists in our country today. Not only are women discriminated against for their gender, but also women are discriminated against for their race. The racial pay gap in the workplace is just another aspect of the pay gap issue that our society needs to overcome as soon as possible. Overall, different groups of women experience distinct gaps in pay in the workplace due to solely their race. [34]
Generally, among women of all ethnicities and races, the hourly earnings of Asian and white women tend to be higher than African American and Hispanic women [35] A recent study actually found that Asian women, on average, receive about 18 dollars an hour, while white women earn 17 dollars, African American women get 13 dollars, and Hispanic women receive 12 dollars. [36] In recent years, Asian women have actually come closer and narrowed the wage gap with white men. For example, in 2015 Asian women have earned about 87 cents per dollar earned by white men in median hourly earnings. [37] Even though Asian women are discriminated against in the workplace due to both their gender and race, Asian women are actually earning more than other women of different races in the workplace. This rise in pay for Asian women compared to other races can be attributed to the high percentage of Asian women that earn a bachelor's degree or even experience more education. [38] Education continues to play a huge role in the racial pay gap between women of different races, and Asian women tend to go to college and obtain a prestigious education. The racial pay gap persists among Asian American women and have caused these women to experience difficulties when trying to provide for themselves and their families. If the racial pay gap was eliminated for Asian American women specifically, the extra income would help Asian American families in many ways. For example, about 45 percent of Asian American mothers provide nearly 40 percent of their families' income, so their households rely on their incomes in order to afford everything necessary.[39] It is time for our government to enact laws and policies in order for this gender and racial pay gap to decline. Asian women are experiencing discrimination and harassment in the workplace purely due to their gender and race.
Female Hispanic women earn wages far less than there women and male counterparts. According to the Institute for Women's Policy Research, in 2017, the median salary for a white male was $60,388, $46,513 for white women and 32,002 for Latino women. They earn the lowest among all ethnicities including Asian and Black women workers. for every 1 dollar, a white male worker a Hispanic women earns 53 cents in 2017. Whereas, the white female employee makes 80.5 cents for each dollar a man makes. That is 47 percent less than white males and 31 percent less than white females. [40] The Institute for Women's Policy Research stated that in 2016, 31.2 percent of Latino women were unmarried and the primary provider for the family. 21.3 percent were married and still the families' primary source of income. This struggle for them to provide, while earning low salaries, interferes with affording childcare services, and taking off days from work to take care of themselves and their children. [41]
The pay gap between women and men is clearly evident. However, the several subgroups that pertain to women show how race, alongside gender, cause innate disadvantages in the workplace for certain individuals. In general, a woman would have to work nearly four extra months per year in order to earn the same annual salary an average man receives. For Native American women specifically, equal pay would not be received for an extra nine months per year. [42]
The pay gap between Caucasian women and Caucasian men is substantial. In 2018, the median weekly pay for all Caucasian women with full time job was $789 while the median weekly pay for men was $973. These numbers depict that on average, white women make around 81% of what white men do. While these numbers clearly describe the inequality between white men and white women, the pay gap between them is much closer than other races including Hispanic, Native American, American Indian and Native Hawaiian.[43] New awareness of gender inequality in the workplace has caused the annual earnings for women to increase by 1.6% from 2016-2017. While women’s median annual earnings may not increase significantly every year, it is generally on an upward trend.[44] One of the biggest factors that leads to this gap between white men and women is parenting. While many white women are staying home to take care of their family, men are continuing to work and earn money. When white women eventually go back to work, their average earnings decrease around 39% compared to women who were not parenting a child.[45] If the government were to implement free child care services, women would have a greater opportunity to work. Despite the gradual decrease in pay gap between men and women, the government needs to implement more laws so that this pay gap eventually disappears. A big difference in the salary earnings between Caucasian men and women is due to job titles and experience. Despite these differences, studies have shown that women will make $.98 to every man’s $1 even if they have the same exact job title and experience.[46] This is a prime example of the inequalities Caucasian women face in the workforce. Despite all of these inequalities for Caucasian women in the workplace, there are many ways to reduce the pay gap. One way the government can help women even the playing field would be to add mentoring programs. These programs could help women negotiate their salaries and working conditions.[47]
Social life
Researchers from the University of Michigan have found that from 1970 to 1985, the percentage of men and women who supported traditional social roles for wives and believed that maternal employment damages mother-child relationships or children's development decreased.[48] Similarly, Jane Wilke from the University of Connecticut found that men's support the idea that men should be the sole source of income in a married couple decreased from 32 to 21 percent from 1972 to 1989; in practice only 15 percent of households were supported by a male spouse's income alone at the time of the study.[49]
However, more recent research in 2011 has found that attitudes towards gender and societal roles have changed very little since the mid-1990s, with attitudes hovering at about sixty to seventy percent egalitarian. This study theorized that a "egalitarian but traditional" gender frame emerged in popular culture during this period, which supports each gender assuming their traditional roles without appearing sexist or discriminatory, and is responsible for this backlash.[50]
Stephanie Coontz, a professor of family history at Evergreen State College, noted that one of the factors contributing to the gender inequality in the United States is that most men still expect women and men to assume traditional gender roles in the households and for women to carry out a larger share of the housework.[51] This has been confirmed by a number of other studies; for example Makiko Fuwa from University of California, Irvine noted that while there has been movement towards greater equality, "in 1995 American women still spent nearly twice as much time on housework than men" and there is also a segregation of household tasks.[52] This gendered division of household labor creates what is known as the second shift or double burden, where working women in a heterosexual couple with a working partner spend significally more time on childcare and household chores.[53]
Researchers from the University of Maryland have found that while men have steadily begun to perform more household labor since 1965, most of the essential and traditionally feminine tasks are still carried out by women; men generally carry out more nonessential or infrequent tasks, such as taking out the trash or mowing the lawn.[54] While both genders tend to have roughly equal amounts of leisure time, men have more uninterrupted leisure time when compared to women.[55] Working mothers also tend to get less sleep when compared to their working husbands.[56]
Education
Literacy and enrollment in primary and secondary education are at parity in the United States, and women are overrepresented in tertiary education.[1] There is, however, a notably gender segregation in degree choice, correlated with lower incomes for graduates with "feminine" degrees, such as education or nursing, and higher incomes for those with "masculine" degrees, such as engineering.[57][58] Females started outnumbering males in higher education in 1992.
Gender Inequality in Elementary and Middle Schools
To study gender inequality in elementary and middle schools, researchers from NYU and Indiana University used data from the nationally-representative Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, specifically the 1998 to 1999 and 2010 to 2011 cohorts. When looking at the average math test scores of boys and girls in kindergarten, they did not come across an average gender gap. However, when looking at the data on these students when they were in second or third grade, the researchers saw the boys perform better on the math tests (by a standard deviation of 0.25 in terms of the average gender gap). The researchers also found that when teachers were asked to compare a boy and a girl of the same socio-economic status and race who received the same scores on math tests and had similar behavioral records in school, teachers overwhelmingly stated that the boy had superior mathematical abilities, a finding replicated in a study over a decade later. It is possible that the gender gap in mathematical abilities among kindergarteners could be much less in the United States today, if teachers more equally evaluated students on their abilities. Replicated studies demonstrate a systematic undervaluing of girls’ mathematical abilities by teachers, which has likely contributed to a false perception of girls’ abilities as being lower than test scores would indicate.
From kindergarten until college, girls are more focused and attentive about their homework than boys. Overall, they spend more time studying and receive better grades. However, 95% of the executive directors and CEOs in the largest public companies remain men. Where does this stark gender disparity come from? Researchers believe that it is not due to a lack of competence, but instead, a lack of confidence. Most men, even those who may be underprepared or less qualified, never hesitate to pursue leadership roles or advancement in their careers. However, most women, even those who are overly qualified and overly prepared hold back from pursuing leadership roles or advancement. This lack of confidence in girls stems from their early years of education.
Starting in elementary school, boys will often do the minimum amount of work needed to pass. When boys succeed in school by putting in a very small amount of effort, they become extremely confident in their abilities. During elementary, middle, and high school, boys continue to become more confident in their abilities and rely on their intelligence to succeed. However, girls slave over their homework, notes, and study materials until they are absolutely perfect. For example, girls will complete extra credit even when they have an A+ in the class. Especially as they enter middle and high school, girls become extremely anxious about their schoolwork and devote hours and hours to perfecting their assignments and acing their tests. Some stress is normal and healthy, however, being overly-stressed at all points of the day (as many young girls are) is not healthy. As adolescent girls work vigorously on their homework assignments they develop competence but not confidence. Girls will attribute their success to external factors while boys will attribute their success to their own intelligence. In the workforce, confidence often goes farther than competence. When girls enter the workforce, they are competent in their field, but lack confidence to seek promotions or advancement. Thus, the lack of female leadership roles is partially due to the socialization of girls and boys beginning in elementary school.
When favoritism occurs in the classroom, the majority of teachers declare they do not purposefully favor one gender over another. Research demonstrates that teachers end up silencing girls in their classes. Oftentimes, girls are rewarded in school for good behavior. Usually, this means sitting silently and attentively in class. However, these types of rewards can have very negative societal consequences. When girls are taught to be silent in class, they will often remain silent in the greater years of their life. The fact that young girls are commended to be silent may be the reason that they do not speak up when they are older, especially in serious cases such as seuxal assault.
Research also shows teachers divide time unequally between boys and girls. They ask boys more questions, provide them with more feedback, and allow them to speak out of turn more often. Conversely, teachers do not call on girls as much, which causes them to raise their hands less frequently. Research shows that teachers will spend 65% more of their time speaking with male students than female students. Additionally, they will allow boys to interrupt girls more often than they allow girls to interrupt boys. At the same time, girls are praised for being orderly and quiet in class. Research has also found that teachers give boys more chances to exhibit their knowledge to the class and they will often look at boys (insteads of girls) after posing a question to the class. For female students of color (specifically African American female students), the problem is even worse. African American female students are 6 times more likely to be disciplined in school than white female students. They are often told that they are “defiant” and “disobedient”. These biases that girls face from such a young age engrain an understanding in their mind that gender inequality is normal.
During a study of almost 20,000 young students, only 8% of females and 4% of males favored female leaders in politics. The results of this study demonstrate that from such a young age, girls are trained to believe that men are better leaders than they are. This knowledge never leaves them and hurts them as they enter the workforce. Additionally, dress code is a school policy that has very serious emotional consequences for young girls. They feel as though they are constantly being judged, especially by male faculty members. In this case, when boys watch girls receive praise for being silent, they begin to always expect silence from their female classmates. When boys speak up the most in class, they start to internalize the idea that their opinions are more important than their female classmates’ opinions, and they begin to internalize the idea that it is okay to interrupt girls in class.
So often in our society, girls receive signals from an early age that they are not good at math, or that boys are simply better. This can occur at home, when wives ask their husbands for help when it comes to math. In 2013, women received 57% of all Bachelor’s degrees, however they only received 43% of math degrees, 19% of engineering degrees, and 18% of computer science degrees. At school and at home, many young girls receive the message that they either “have the math gene or they do not.” When a mother tells her daughter that she wasn’t good at math in school, oftentimes, the daughter’s mathematical achievement will decrease. Oftentimes, women do not realize they are sending these messages to their daughters.
Gender Differences in Degree Choices
Specific to university and college campuses, gender inequalities can be seen when looking into the demographics of particular majors. This initial entrance into a particular field of study is shaped by an individual’s desires to take a certain set of classes, leading to somewhat specific career opportunities and subsequently, salaries. When exploring the depths of college majors, there is a tendency for each gender to cluster into certain majors. These stereotypical “masculine” and “feminine” degrees are key indicators to the inequalities women face in certain fields, specifically within the sciences and mathematics. Based on the Department of Education’s collections of data from the College Class of 2015, “women earn the large majority of degrees in health professions, psychology, education, english and communication, while men earn the large majority of degrees in engineering, computer science, and theology.”[59] These exact percentages can be seen in the table distributed by the Department of Education, exemplifying the overall majority men have in the STEM field.[59]
Although not designated for specific genders, majors and minors at universities and colleges carry different stigmas for who should/shouldn’t be part of the program. The results of Sylvia Beyer’s 1995 study surveying 154 female and 111 male students from the University of Wisconsin-Parkside, to test the accuracy of gender stereotypes, conclude that students believe men and women are concentrated in different fields and that specific majors are deemed “masculine” and “feminine.”[60] The participants categorized the masculine majors with computer science, chemistry, business, history, and mathematics, while they placed the feminine majors as psychology, communication, music, and art. These perceptions may not accurately describe the gender percentages in each field, but prove that men are more likely to be seen in STEM concentrations than women. Additionally, Yale researchers have published studies which prove that young male scientists are more likely to be favored than female scientists with the same candidacy. As of 2013, only ⅕ of Physics PHDs were awarded to women and only 14% of physics professors were female.[61] A large factor in the major and minor inequalities seen at the college level come from the encouragement of peers and educators to go forth in certain subjects. Ultimately, women are not receiving the same support and backing as their male counterparts, and thus, do not pursue STEM fields. Since a large sum of money lies in these occupations, women are not receiving an equal share, further perpetuating gendered salary inequalities.[61]
Gender Inequality in Representation at Elite Institutions
Women have recently surpassed men in the ratio of students enrolled in colleges around the nation. In 2017, women were awarded a majority of doctoral degrees, at 53%, for the ninth year in a row. With striking progress from the late 1900’s, gender inequality in higher education persists with the consideration of female representation at elite universities.
The higher representation of women is largely attributed to schools with "higher acceptance rates, lower faculty/student ratios, lower standardized test scores, and lower fees" ; thus, underrepresentation still persists amongst the top schools in the nation. The effects of a less-notable degree play out in the workplace and job recruiting processes. Scholars have reasoned this inequality to be the effect of part-time enrollment and the advanced engineering characteristic of elite universities. With fewer females enrolling in STEM programs, they are less likely to attend universities notable for these programs. Other scholars argue that gender inequality at elite institutions is not an issue of access, accrediting the issue to decentralized school systems , such as the existence of female-only universities (which individually draw a large segment of women attending college).
Gender Inequality in Faculty
Women in academia face many challenges in terms of pay, rank, and composition in faculty. Although female faculty members’ salaries are gradually increasing, the pay gap continues to widen or remain unchanged. The reason for this lies in the fact that male faculty members already earn significantly more than their female counterparts. The wage gap is greatest in private independent colleges. The explanations that have been brought forward for this persistent disparity relate to women’s positions in institutions and disciplines. Within doctoral-granting institutions, containing the highest salary scales, women are outnumbered two to one. Women are extremely underrepresented in high-paying academic disciplines, like science, business, and law, yet overrepresented in low-paying fields, such as English, romance languages, and education. Not only is there a gap in salary, but rank as well. Research has shown that top universities average only 34 percent female in full-time faculty. The disparity only worsens as faculty rank increases. Within top universities, the only category in which female faculty hold the higher proportion is “Non-Eligible for Tenure.” In universities overall, men continue to make up a disproportionate ratio of full professors, while women make up a majority of assistant professors, instructors, and lecturers. Though major strides have been made in increasing female faculty salaries and drawing attention to the issue, action must still be taken to further the progress.
Other issues
Research conducted at Lycoming College has found the enjoyment of sexist humor to be strongly correlated with sexual aggression towards women among male college students.[62] In addition, studies have shown that exposure to sexist humor, particularly humor related to sexual assault, can increase male aggression and their tendency to discriminate against women.[63][64] One study also asserted that the attitudes behind such humor creates an environment where such discriminatory and possibly violent behavior is acceptable.[63] Men's tendency to self-report the likelihood that they would commit sexually violent acts has also been found to increase after exposure to sexist humor, as reported by researchers from the University of Kent.[64]
Benevolent sexism, sometimes referred to as chivalry, which holds women as something to be protected, also has psychological effects. Women who hold these views are more likely to have less ambitious career goals and men who hold these views tend to have a polarized and stereotyped view of women, made up of both very favorable and very unfavorable traits.[65][66] In such cases, the stereotyped view of women is "favorable in content and yet prejudicial in [its] consequences," and attempts to provide justification for discriminatory behaviors presented as helpful or paternal.[66]
Current issues for men
Achievement gap in school
For the past fifty years, there has been a gap in the educational achievement of males and females in the United States, but which gender has been disadvantaged has fluctuated over the years. In the 1970s and 1980s, data showed girls trailing behind boys in a variety of academic performance measures, specifically in test scores in math and science.[67]
Data in the last twenty years shows the general trend of girls outperforming boys in academic achievement in terms of class grades across all subjects and college graduation rates, but boys scoring higher on standardized tests and being better represented in the higher-paying and more prestigious STEM fields (science, technology, engineering, and math).[67]
Graduation rates
According to recent data (from 2007), 55 percent of college students are females and 45 percent are males. From 1995 until 2005, the number of males enrolled in college increased by 18 percent, while the number of female students rose by 27 percent.[68] Males are enrolling in college in greater numbers than ever before, yet fewer than two-thirds of them are graduating with a bachelor's degree. The numbers of both men and women receiving a bachelor's degree have increased significantly, but the increasing rate of female college graduates exceeds the increasing rate for males.[69]
A higher proportion of men (29.4%) hold bachelor's degrees than women (26.1%). In 2007, the United States Census Bureau estimated that 18,423,000 males ages over the age of 18 held a bachelor's degree, while 20,501,000 females over the age 18 held one. In addition, fewer males held master's degrees: 6,472,000 males compared to 7,283,000 females. However, more men held professional and doctoral degrees than women. 2,033,000 males held professional degrees compared to 1,079,000, and 1,678,000 males had received a doctoral degree compared to 817,000 females.[70]
Selective service

In the United States, most male US citizens and residents must register with the Selective Service System within 30 days of their 18th birthday.[71] Those who fail to register may be punished by up to five years in prison and a fine of up to $250,000, although no non-registrants have been prosecuted since January 1986.[72] They may also be ineligible for federal student financial aid, federal job training and federal employment, and for certain states, state employment and even driver's licenses .[73]
Suicide
In the United States, the male-to-female teenage suicide death ratio is estimated at 3:1.[74] Typically males are three to five times more likely to commit suicide than females.[75]
Homelessness
At least 70% to 85% of all homeless are men.[76]
Occupational segregation into dangerous jobs
Men are over-represented in dangerous jobs. The industries with the highest death rates are mining, agriculture, forestry, fishing, and construction, all of which employ more men than women.[77] In one U.S. study, 93% of deaths on the job involved men,[78] with a death rate approximately 11 times higher than women.
Prison
Men receive 65% longer prison sentences for the same crime as women.[79]
Benatar
Benatar identified multiple areas in which men are currently disadvantaged today. He identified military conscription and cited the fact that men are more likely to be the victim of spousal abuse, while being taken less seriously.[80] Benatar also identified the inequality experienced by men in the justice system, such as the increased prison sentences received by males, as well as the increased likelihood of a male being arrested if the accuser is female. Furthermore, the disparity in legal custody cases and alimony payment was cited, with females more frequently getting custody of children.
Current issues for transgender people
Visibility, awareness, and public attitudes
One of the largest factors that causes and perpetuates transgender inequality is a lack of understanding and awareness among cisgender people.[81] A 2002 survey found that, of the American respondents polled, only 70% had heard of the term transgender, while 67% agreed that it is possible for a person to be born as one gender, but inside feel like another gender.[82] In addition, the survey found that 61% of Americans believe that the country needs anti-discrimination laws to protect transgender individuals, 57% incorrectly believed that it was not legal to fire someone on the basis of their gender identity if they are trans, 53% believed being transgender was acceptable while 37% did not, 77% believed that transgender students should be allowed to attend public school, and 8% said they would refuse to work with a transgender co worker.[82] A 2012 study found that the heterosexual cisgender individuals who believe there are natural binary genders and there are natural differences between men and women are more likely to have negative attitudes toward transgender individuals.[83]
Events in the LGBT+ community such as Transgender Awareness Week and the International Transgender Day of Visibility are focused on educating and informing the public about transgender individuals and the challenges they face.[84][85]
Legal rights
According to the Transformative Justice Law Project of Illinois, transgender people are "over-represented in the criminal legal system due to institutionalized oppression and increased poverty and criminalization."[86]
Many transgender individuals have difficulties correcting their name and gender on their ID and personal documents. According to the National Center for Transgender Equality, "only one-fifth (21%) of transgender people who have transitioned in the National Transgender Discrimination Survey have been able to update all of their IDs and records with their new gender and one-third (33%) had updated none of their IDs or records. At the time of the survey, only 59% had been able to update their gender on their driver’s license or state ID; 49% had updated their Social Security Record; 26% their passport; and just 24% their birth certificate."[87] In addition, those transgender people who are successful in correcting their ID and records often must undergo heavy invasions of privacy, including presenting proof of gender reassignment surgery, and those who cannot correct their identification documents often face higher levels of discrimination, since it effectively "outs" them as transgender.[87]
Some state appellate courts- including Kansas, Ohio, Texas, Florida, and Illinois- have upheld that the gender an individual is assigned at birth is their legal gender for life, even if the individual has undergone gender reassignment surgery or similar treatments, and therefore refuse to acknowledge the gender that transgender people identify as.[88]
There have been several legal cases in which transgender parents have lost custody and other parental rights on the basis of their gender.[88] There have also been cases of the validity and legality of married heterosexual couples in which one partner is transgender being contested and, in some cases, the marriage has been voided.[88]
Work life and economics
A 2007 study reported that between fifteen and fifty-seven percent of transgender individuals report some kind of employment discrimination; of these thirteen to fifty-six percent reported being fired due to their gender identity, thirteen to forty-seven percent reported that they were denied employment due to their gender identity, twenty-two to thirty-one percent reported harassment due to their gender identity, and nineteen percent reported being denied promotion due to their gender identity.[2] Another study found that transgender respondents reported twice the national rate of unemployment, while transgender people of color reported four times the national rate of unemployment.[89] This study also found that 90% of respondents reported some kind of workplace harassment, mistreatment or discrimination.[89]
Transgender pay gap
According to the American Psychology Association, around 64% of transgender people have annual incomes of less than $25,000.[90] Another study found that transgender individuals are nearly four times more likely to make less than $10,000 annually when compared to the general population; on the other end of the spectrum, only 14% of transgender respondents reported making more than $100,000 annually compared to 25% of the general population.[89] In addition, transgender women reported their wages decreasing by nearly one-third following their gender transitions but transgender men reported their wages increasing slightly (about 1.5%), according to one study.[91][92]
Social life
Since many public spaces, including schools, are highly gendered with features such as gendered bathrooms and locker rooms, transgender people often face violence in these gendered areas.[86] Transgender people are often asked to present their ID or other invasive question when using a public restroom designated for the gender they identify as and can often face discrimination and violence if their ID has not been correct or if they do not "pass" as the gender they identify as.[93]
One study found that 71% of transgender respondents made efforts to hide their gender or gender transition to avoid discrimination, while 57% reported delaying their gender transition to avoid discrimination.[89]
Transgender individuals also face discrimination within the LGBT+ community, especially from cisgender gay men and lesbians.[94] As a result, they often do not receive the same social support from the community that other queer individuals do.[94]
Education
One study found that 78% of transgender individuals interviewed reported harassment in primary or secondary school, 35% reported physical assault, 12% reported sexual violence, and 6% reported being expelled.[89] According to the study, the effect of this harassment was so severe that 15% of the respondents were forced to leave school at either the primary, secondary, or tertiary level.[89]
Transgender individuals also face barriers when applying to higher education, as was the case with a transgender woman rejected from the all-girls Smith College because she was not legally recognized as female in her home state.[95]
Health and violence
Transgender individuals, especially transgender women, are at a high risk of suffering from domestic abuse due to invisibility, lack of access to support facilities such as shelters, and a lack of legal and social protection.[3] Transgender individuals are also more likely to be sexually and physically assaulted, both by strangers and acquaintances, than cisgender individuals are.[96] In addition, there are several factors that limit transgender people's access to health care facilities and proper medical care, including transphobia and the tendency of gender-segregated homeless and domestic violence shelters to refuse service to transgender and gender nonconforming individuals.[97] One study reported that 19% of transgender individuals interviewed reported being refused medical care due to their gender identity, while 28% reported being harassed in a medical setting and 2% reported violence toward them in a medical setting due to their gender identity.[98] In the same study, 50% percent of transgender respondents reported the need to educate their medical providers about the health care needs of transgender individuals.[98]
Transgender individuals also reported four times the national average of HIV infections when compared to cisgender individuals in one study conducted by the National Center for Transgender Equality and the National Gay and Lesbian Task Force.[98]
The NCAVP's 2012 Report on Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer, and HIV-affected Hate Violence reported that over fifty percent of anti-LGBTQ homicide victims in 2012 were transgender women, a considerable increase from the percentage of transgender women victims in 2011 at 40%.[4] In addition, the report also found that, compared to cisgender people, transgender people were more than three times more likely to experience police violence.[4]
In terms of mental health, transgender individuals have much higher rates of suicide attempts than cisgender individuals and it has been reported that between nineteen and twenty-five of the trans population have attempted suicide.[99]
Government policy
In 1920, the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which insured women's suffrage (although some individual states allowed women the right to vote as early as 1869), was ratified. In addition, the Women's Bureau of the Department of Labor was created to monitor working conditions for women in the workforce.[100]
In 1961, the President's Commission on the Status of Women was started, initially chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt. This commission found that women were suffering considerable workplace discrimination. In 1963, the Equal Pay Act was passed, which made it illegal for a woman to be paid less than a man working in the same position. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 also made discriminatory hiring on the basis of gender illegal. The affirmative action policy of 1965 was expanded in 1967 to cover women as well as racial minorities. In 1973, women's right to safe and legal abortion was established by the Supreme Court's ruling in Roe v. Wade. In 1968, sex-segregated job advertisements were declared illegal by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, this decision was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1973; this allowed women to apply for higher-paying jobs formally restricted only to male applicants. In 1972, Title IX of the Education Amendments, which reads "No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any educational program or activity receiving federal financial assistance," was passed.[101]
In 1986, in the decision of Meritor Savings Bank v. Vinson, sexual harassment was established as illegal and discriminatory.[102] The Family Medical Leave Act of 1993 guarantees that new parents can retain their jobs for 12 weeks after the birth of the child; this unpaid leave is the only form of paternal leave protected by law in the United States.[9] In 1994, the Violence Against Women Act provided legal protection, as well as funds and services, for rape victims and victims of domestic violence. United States v. Virginia established in 1996 that gender-based admission practices violated the Fourteenth Amendment, and establishing a separate all-female school would not suffice as an alternative to integrating an all-male school. Most recently, in 2009 the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009 provides employees (usually female) who suffer from pay discrimination to file a complaint with the government.[102]
The Equal Rights Amendment, which reads, "Equality of rights under the law shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of sex", was first introduced to Congress in 1923 and successfully passed both houses of Congress in 1972. However, it failed to be ratified by an adequate number of states and died in 1982.[101] The United States is one of only a few countries which have not ratified the UN Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (US has only signed the treaty).[103]
Rankings
The World Economic Forum's Gender Gap Index for 2012 ranked United States 22nd best out of 135 countries for gender equality.[1][104] The primary indicators for inequality were related to political empowerment, where the US was ranked 55th (32nd for women in ministerial position and 78th for women in parliament).[1] USA was ranked 33rd for health and survival, 8th for economic participation and opportunity, and tied for 1st (no inequality) in education.[1] Since the Gender Gap report was first published in 2006, the US position remains relatively stable in that index.[1] However, the United States' score decreased between 2011 and 2012.[1][105]
United Nation's Gender Inequality Index (part of the Human Development Report) for 2011 had US ranked 47th out of 173 countries.[106] In addition, the OECD's Better Life Index discusses a number of differences, but does not stress any in particular when it comes to gender.[107][108]
See also
- 21st-century globalization impacts on gender inequality in the United States
- Affirmative action
- Civil Rights Act
- Double burden
- Education Amendments of 1972, Title IX
- Employment discrimination law in the United States
- Equal Pay Act of 1963
- Equal Rights Amendment
- Gender inequality
- Gender role
- Lilly Ledbetter
- Work-family balance in the United States
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Hausmann, Ricardo; Tyson, Laura D.; Zahidi, Saadia (Editors) (2012). "The global gender gap report 2012" (PDF). World Economic Forum, Geneva, Switzerland. Retrieved 26 October 2012.
{{cite web}}:|first3=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Badgett, M. V. Lee; Lau, Holning; Sears, Brad; Ho, Deborah (2007). "Bias in the workplace: Consistent evidence of sexual orientation and gender identity discrimination". The Williams Institute, UCLA School of Law. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ^ a b Greenberg, Kae (2012). "Still hidden in the closet: trans women and domestic violence". Berkeley Journal of Gender, Law and Justice. 27 (2): 198. Retrieved 13 March 2014. Pdf.
- ^ a b c "2012 report on lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and HIV-affected hate violence" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Women in elective office 2013" (PDF). Center for American Women in Politics. Center for American Women in Politics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2013. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Welch, Susan (November 1977). "Women as political animals? A test of some explanations for male-female political participation sifferences". American Journal of Political Science. 21 (4): 711–730. doi:10.2307/2110733. JSTOR 2110733.
- ^ Conway, M. Margaret (2001). "Women and political participation". Political Science and Politics. 34 (2): 231–233. doi:10.1017/s1049096501000385.
- ^ a b Ariane, Hegewisch; Janet C., Gormish (2008). "Statutory routes to workplace flexibility in cross-national perspective" (PDF). Institute for Women's Policy Research.
- ^ a b Hall, Katy; Spurlock, Chris (4 February 2013). "Paid parental leave: U.S. vs. The World (INFOGRAPHIC)". Huffington Post. TheHuffingtonPost.com, Inc. Retrieved 2 November 2013.
- ^ Fidell, L. S. (1 January 1970). "Empirical verification of sex discrimination in hiring practices in psychology". American Psychologist. 25 (12): 1094–1098. doi:10.1037/h0030294.
- ^ Williams, Wendy M.; Ceci, Stephen J. (28 April 2015). "National hiring experiments reveal 2:1 faculty preference for women on STEM tenure track". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (17): 5360–5365. doi:10.1073/pnas.1418878112. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4418903. PMID 25870272.
- ^ Neumark, David; Bank, Roy J.; Van Nort, Kyle D. (1 August 1996). "Sex discrimination in restaurant hiring: an audit study". The Quarterly Journal of Economics. 111 (3): 915–941. doi:10.2307/2946676. JSTOR 2946676.
- ^ Cheng, Michelle A.; Annie Sukhov; Hawa Sultani; Koungmi Kim; Emanual Maverakis (May 2016). "Trends in National Institutes of Health Funding of Principal Investigators in Dermatology Research by Academic Degree and Sex". JAMA Dermatology. 152 (8): 883–888. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.0271. PMID 27191545.
- ^ Glick, Peter; Zion, Cari; Nelson, Cynthia (1 January 1988). "What mediates sex discrimination in hiring decisions?" (PDF). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 55 (2): 178–186. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.55.2.178. Retrieved 2 November 2013.
- ^ Charles, Maria (December 2003). "Deciphering sex segregation: vertical and horizontal inequalities in ten national labor markets". Acta Sociologica. No. 4. 46 (4): 267–287. doi:10.1177/0001699303464001. Pdf.
- ^ a b c Darity, William A.; Patrick L. Mason (Spring 1998). "Evidence on discrimination in employment: codes of color, codes of gender". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 12 (2): 63–90. doi:10.1257/jep.12.2.63.
- ^ England, Paula (Summer 2005). "Gender inequality in labor markets: the rold of motherhood and segregation". Social Politics. 2 (2): 264–288. doi:10.1093/sp/jxi014. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ Bureau of Labor Statistics. Women's earnings and employment by industry, 2009. Chart data, February 16, 2011.
- ^ "Gender inequality and women in the US labor force". Ilo.org. 23 November 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
- ^ Blau, Francine D.; Lawrence M. Kahn (Autumn 2000). "Gender differences in pay" (PDF). The Journal of Economic Perspectives. 14 (4): 75–99. doi:10.1257/jep.14.4.75. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ Mouw, Ted; Kalleberg, Arne L.. (3 June 2010). "Occupations and the structure of wage inequality in the United States, 1980s to 2000s". American Sociological Review. 75 (3): 402–431. doi:10.1177/0003122410363564. Retrieved 2 November 2013.
- ^ "An Analysis of Reasons for the Disparity in Wages Between Men and Women" (PDF). US Department of Labor; CONSAD Research Corp. Retrieved February 16, 2016.
- ^ Jackson, Brooks (June 22, 2012). "Obama's 77-Cent Exaggeration". FactCheck.org.
- ^ Graduating to a Pay Gap – The Earnings of Women and Men One Year after College Graduation (PDF)
- ^ Sommers, Christina H (January 23, 2014). "Wage Gap Myth Exposed – By Feminists". Huffington Post. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ Association, Press (28 August 2015). "Women in their 20s earn more than men of same age, study finds". The Guardian.
- ^ Sahadi, Jeanne (12 April 2016). "Gender pay gap: Young women are asking for (and getting) more pay than men". CNNMoney.
- ^ Petersen, Trond; Laurie A. Morgan (September 1995). "Separate and Unequal: Occupation-Establishment Sex Segregation and the Gender Wage Gap". American Journal of Sociology. No. 2. 101 (2): 329–330. doi:10.1086/230727. JSTOR 2782431.
- ^ Jena, Anupam B.; Olenski, Andrew R.; Blumenthal, Daniel M. (2016-09-01). "Sex Differences in Physician Salary in US Public Medical Schools". JAMA Internal Medicine. 176 (9): 1294–304. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.3284. ISSN 2168-6106. PMC 5558151. PMID 27400435.
- ^ Tsugawa, Yusuke; Jena, Anupam B.; Figueroa, Jose F.; Orav, E. John; Blumenthal, Daniel M.; Jha, Ashish K. (2017-02-01). "Comparison of Hospital Mortality and Readmission Rates for Medicare Patients Treated by Male vs Female Physicians". JAMA Internal Medicine. 177 (2): 206–213. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.7875. ISSN 2168-6106. PMC 5558155. PMID 27992617.
- ^ Wallis, Christopher JD; Ravi, Bheeshma; Coburn, Natalie; Nam, Robert K.; Detsky, Allan S.; Satkunasivam, Raj (2017-10-10). "Comparison of postoperative outcomes among patients treated by male and female surgeons: a population based matched cohort study". BMJ. 359: j4366. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4366. ISSN 0959-8138. PMC 6284261. PMID 29018008.
- ^ a b c Waldfogel, Jane (Winter 1998). "Understanding the "family gap" in pay for women with children". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 12 (1): 137–156. doi:10.1257/jep.12.1.137. JSTOR 2646943.
- ^ Vagins, Deborah. "The Simple Truth about Gender Pay Gap". AAUW. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Vagins, Deborah. "The Simple Truth about Gender Pay Gap". AAUW. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Patten, Eileen. "Racial, gender wage gaps persist in U.S. despite some progress". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Patten, Eileen. "Racial, gender wage gaps persist in U.S. despite some progress". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Patten, Eileen. "Racial, gender wage gaps persist in U.S. despite some progress". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Patten, Eileen. "Racial, gender wage gaps persist in U.S. despite some progress". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ "Asian American and Pacific Island Women and the Wage Gap" (PDF). National Partnership for Women and Families. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Hegewisch, Ariane. "The Gender Wage Gap: 2017; Earnings Differences by Gender, Race, and Ethnicity". Institute for Women's Policy Research. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ^ Anderson, Julie. "Breadwinner Mothers by Race/Ethnicity and State". Institute for Women's Policy Research. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ^ Connley, Courtney. "Reminder: Today isn't Equal Pay Day for all women". CNBC. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ Vagins, Deborah. "The Simple Truth about the Gender Pay Gap". AAUW.
- ^ Hegewisch, Ariane. "The Gender Wage Gap: 2017 Earnings Differences by Race and Ethnicity". Institute for Women's Policy Research.
- ^ Hayes, Abby. "OPINION: Gender Pay Gap – Statistics, Trends, Reasons and Solutions". DoughRoller.
- ^ "THE STATE OF THE GENDER PAY GAP 2019". PayScale.
- ^ "How to Decrease Gender Pay Gap in 7 Steps". Market Inspector.
- ^ Mason, K. O.; Lu, Y. H. (1 March 1988). "Attitudes toward women's familial roles: Changes in the United States, 1977-1985". Gender & Society. 2 (1): 39–57. doi:10.1177/089124388002001004. JSTOR 190468.
- ^ Wilkie, J. R. (1 June 1993). "Changes in U.S. men's attitudes toward the family provider role, 1972-1989". Gender & Society. 7 (2): 261–279. doi:10.1177/089124393007002007. Retrieved 2 November 2013.
- ^ Cotter, David; Hermsen, Joan M.; Vanneman, Reeve (1 July 2011). "The end of the gender revolution? Gender role attitudes from 1977 to 2008". American Journal of Sociology. 117 (1): 259–289. doi:10.1086/658853. JSTOR 658853.
- ^ Coontz, Stephanie (February 16, 2013). "Why gender equality stalled". The New York Times. New York: NYTC. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Fuwa, Makiko (1 December 2004). "Macro-level gender inequality and the division of household labor in 22 countries". American Sociological Review. 69 (6): 751–767. doi:10.1177/000312240406900601. JSTOR 3593041.
- ^ Ferree, Myra M. (1 June 1991). "The gender division of labor in two-earner marriages: dimensions of variability and change". Journal of Family Issues. 12 (2): 158–180. doi:10.1177/019251391012002002. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
- ^ Bianchi, Suzanne M.; Milkie, Melissa A.; Sayer, Liana C.; Robinson, John P. (1 September 2000). "Is anyone doing the housework? Trends in the gender division of household labor". Social Forces. 79 (1): 191–228. doi:10.1093/sf/79.1.191. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
- ^ Bittman, Michael; Wajcman, Judy (1 September 2000). "The rush hour: the character of leisure time and gender equity". Social Forces. 79 (1): 165–189. doi:10.1093/sf/79.1.165. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ^ Maume, David J.; Sebastian, Rachel A.; Bardo, Anthony R. (1 December 2010). "Gender, work-family responsibilities, and sleep". Gender & Society. 24 (6): 746–768. doi:10.1177/0891243210386949.
- ^ Jacobs, Jerry A. (1996). "Gender inequality and higher education". Annual Review of Sociology. 22: 153–185. doi:10.1146/annurev.soc.22.1.153. JSTOR 2083428.
- ^ Davies, Scott; Guppy, Neil (1 June 1997). "Fields of study, college selectivity, and student inequalities in higher education". Social Forces. 75 (4): 1417–1438. doi:10.1093/sf/75.4.1417. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ^ a b "Table of the day: Bachelor's degrees by field and gender for the Class of 2015". AEI. 2017-08-07. Retrieved 2019-04-07.
- ^ Beyer, Sylvia (1999). Sex Roles. 40 (9/10): 787–813. doi:10.1023/a:1018864803330. ISSN 0360-0025 http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/a:1018864803330.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b Pollack, Eileen (2013-10-03). "Why Are There Still So Few Women in Science?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2019-04-07.
- ^ Ryan, Kathryn M.; Kanjorski, Jeanne (1 May 1998). "The enjoyment of sexist humor, rape attitudes, and relationship aggression in college students". Sex Roles. 38 (9–10): 743–756. doi:10.1023/A:1018868913615.
- ^ a b Ford, Thomas E.; Boxer, Christie F.; Armstrong, Jacob; Edel, Jessica R. (February 2008). "More than "just a joke": the prejudice-releasing function of sexist humor". Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. no. 2. 34 (2): 159–170. doi:10.1177/0146167207310022. PMID 18056796. Pdf.
- ^ a b Viki, G. Tendayi; Thomae, Manuela; Cullen, Amy; Fernandez, Hannah (16 December 2007). "The effect of sexist humor and type of rape on men's self-reported rape proclivity and victim blame". Current Research in Social Psychology. 13 (10): 122–132. Retrieved 16 October 2013. Pdf.
- ^ Glick, Peter; Susan T. Fiske (2001). "An ambivalent alliance: hostile and benevolent sexism as complementary justifications for gender inequality" (PDF). American Psychologist. 56 (2): 109–118. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.56.2.109. PMID 11279804. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- ^ a b Jost, John T.; Kay, Aaron C. (1 January 2005). "Exposure to benevolent sexism and complementary gender stereotypes: consequences for specific and diffuse forms of system justification" (PDF). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 88 (3): 498–509. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.333.6801. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.88.3.498. PMID 15740442. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ^ a b Kafir, Krista (April 2007). "Taking the boy crisis in education seriously: how school choice can boost achievement among boys and girls" (PDF). Independent Women's Forum.
- ^ Digest of Education Statistics 2007
- ^ Mead, Sara. (2006). The Evidence Suggests Otherwise: The Truth About Boys and Girls. Washington: Education Sector.
- ^ U.S. Census Bureau, Current Population Survey, Annual Social and Economic Supplement 2007.
- ^ "Selective Service System: Welcome". Selective Service System. Office of Public and Intergovernmental Affairs. February 12, 2015. Archived from the original on April 28, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Hasbrouck, Edward. "Prosecutions of Draft Registration Resisters". Resisters.info. National Resistance Committee. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ^ "Benefits and Programs Linked to Registration". Selective Service System. Office of Public and Intergovernmental Affairs. December 21, 2010. Archived from the original on April 15, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Teen Suicide Statistics". Adolescent Teenage Suicide Prevention. FamilyFirstAid.org. 2001. Retrieved 2006-04-11.
- ^ Murphy, George E. (July 1998). "Why Women are Less Likely Than Men to Commit Suicide". Comprehensive Psychiatry. 39 (4): 165–175. doi:10.1016/S0010-440X(98)90057-8.
- ^ The 2015 Annual Homeless Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress
- ^ Fatal Occupational Injuries - United States, 1980-1997 MMWR Weekly, April 27, 2001
- ^ "Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries Summary, 2013". Bureau of Labor Statistics. United States Department of Labor. 11 September 2014. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ Starr, Sonja B. (14 July 2012). "Estimating Gender Disparities in Federal Criminal Cases". 17 (1). doi:10.2139/ssrn.2110321. ISSN 1556-5068.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Benatar, David (2012). The second sexism : discrimination against men and boys. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 37. ISBN 978-0470674512.
- ^ McInroy, Lauren; Craig, Shelley L.; Ashley, Ashley (2014-01-18). ""There's just a lack of awareness": transgender content in North American social work programs". Society for Social Work and Research 18th Annual Conference: Research for Social Change: Addressing Local and Global Challenges. Conference paper.
- ^ a b The Gender Centre Inc. "U.S. public attitudes to transgender according to a September 2002 survey". The Gender Centre Inc. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ Norton, Aaron T.; Herek, Gregory M. (10 January 2012). "Heterosexuals' attitudes toward transgender people: findings from a national probability sample of U.S. adults". Sex Roles. 68 (11–12): 738–753. doi:10.1007/s11199-011-0110-6. Pdf.
- ^ "Transgender Awareness Week #TransWk and Transgender Day of Remembrance #TDOR". GLAAD. 2012-11-09. Retrieved December 9, 2013.
- ^ Carreras, Jessica. "Transgender Day of Visibility plans erupt locally, nationwide". PrideSource. Retrieved April 3, 2013.
- ^ a b Transformative Justice Law Project of Illinois. "Quick guide to the criminalization of transgender and gender non-conforming people". Transformative Justice Law Project of Illinois. Retrieved 22 March 2014. Pdf.
- ^ a b National Center for Transgender Equality. "ID documents and privacy". National Center for Transgender Equality. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- ^ a b c Cooper, Leslie. "Protecting the rights of transgender parents And their children" (PDF). ACLU and The National Center for Transgender Equality. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f Grant, Jaime; et al. "Injustice at every turn: a report of the national transgender discrimination survey" (PDF). e National Center for Transgender Equality. Retrieved 22 March 2014.
- ^ American Psychology Association. "Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons & socioeconomic Status" (PDF). American Psychology Association. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- ^ Rampell, Catherine (September 25, 2008). "Before that sex change, think about your next paycheck". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- ^ Schilt, Kristen; Matthew Wiswall. "Before and after: gender transitions, human capital, and workplace experiences" (PDF). Retrieved 21 March 2014.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Equal access to public restrooms" (PDF). Lambda Legal. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2011. Retrieved 22 March 2014.
- ^ a b Weiss, Jillian Todd (12 April 2003). "GL vs. BT". Journal of Bisexuality. 3 (3–4): 25–55. doi:10.1300/J159v03n03_02. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ Garcia, Michelle (20 March 2013). "Women's college returns transgender student's application". The Advocate. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ Stotzer, Rebecca L. (2009). "Violence against transgender people: A review of United States data". Aggression and Violent Behavior. 14 (3): 170–179. doi:10.1016/j.avb.2009.01.006.
- ^ Lombardi, Emilia (2007). Public health and trans-people: Barriers to care and strategies to improve treatment (PDF). pp. 638–652. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-31334-4_26. ISBN 978-0-387-28871-0. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Grant, Jaime; et al. "National transgender discrimination survey report on health and health care" (PDF). National Center for Transgender Equality and the National Gay and Lesbian Task Force. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Haas, Ann P.; et al. (2010). "Suicide and suicide risk in lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender populations: review and recommendations". Journal of Homosexuality, Special Issue: Suicide, Mental Health, and Youth Development. 58 (1): 10–51. doi:10.1080/00918369.2011.534038. PMC 3662085. PMID 21213174.
- ^ Imbornoni, Ann-Marie. "Timeline of key events in the American women's rights movement 1848–1920". Information Please Database. Pearson Education, Inc. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ a b Imbornoni, Ann-Marie. "Timeline of key events in the American women's rights movement 1921–1979". Information Please Database. Pearson Education, Inc. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ a b Imbornoni, Ann-Marie. "Timeline of key events in the American women's rights movement 1980-present". Information Please Database. Pearson Education, Inc. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ "UNTC". Treaties.un.org. Archived from the original on 23 August 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Gray, Emma (24 October 2012). "Global gender gap report 2012: the best and worst countries for women". Huffingtonpost.com. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
- ^ Megan Willett (October 24, 2012). "US ranks #22 in global gender gap report". Business Insider. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
- ^ United Nations Development Programme (2011). "Human development report 2011; sustainability and equity" (PDF).
- ^ Pereira, Eva (18 April 2012). "Gender and inequality: how the U.S. stacks up against other OECD countries". Forbes. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
- ^ OECD (2012). "United States – OECD Better Life Index". OECD Trade Policy Papers. Oecdbetterlifeindex.org. doi:10.1787/5k9ffbqlvk0r-en. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
Social Politics, Oxford University Press, Marie Evertsson, 2009, pp. 210–241
