Acupuncture
| This article is part of a series on |
| Alternative medicine |
|---|
 |

Acupuncture is the procedure of inserting and manipulating filiform needles into various points on the body to relieve pain or for therapeutic purposes.[1] The word acupuncture comes from the Latin acus, "needle", and pungere, "to prick". In Standard Chinese, acupuncture is called 针砭 (zhēnbiān), or a related word, 针灸 (zhēnjiǔ), which refers to acupuncture together with moxibustion.[2] According to traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture points are situated on meridians along which qi (a "life energy") flows. Modern acupuncture texts present them as ideas that are useful in clinical practice and continue to inform the practice of acupuncture,[3][4] but there is no evidence to support their existence and they have not been reconciled with contemporary knowledge about biology, physics or chemistry.[5][6]
The earliest written record of acupuncture is the Chinese text Shiji (史記, English: Records of the Grand Historian) with elaboration of its history in the second century BCE medical text Huangdi Neijing (黃帝內經, English: Yellow Emperor's Inner Canon).[7] Different variations of acupuncture are practiced and taught throughout the world. Acupuncture has been the subject of active scientific research since the late 20th century[8] but it remains controversial among conventional medical researchers and clinicians.[8] Due to the invasive nature of acupuncture treatments, it is difficult to create studies that use proper scientific controls.[8][9][10][11][12] Some scholarly reviews have concluded that the effectiveness of acupuncture as a treatment can be explained largely through the placebo effect,[13][14] while others have suggested some efficacy in the treatment of specific conditions.[8][15][16] The World Health Organization published a review of controlled trials using acupuncture and concluded it was effective for the treatment of 28 conditions and there was evidence to suggest it may be effective for several dozen more,[17] though this review has been criticized by several scientists for bias and a focus on studies with a poor methodology.[18][19] Reports from the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM), the American Medical Association (AMA) and various government reports have studied and commented on the efficacy (or lack thereof) of acupuncture. There is general agreement that acupuncture is safe when administered by well-trained practitioners using sterile needles, and that further research is appropriate.[9][20][21][22]
History
Antiquity
Acupuncture's origins in China are uncertain. One explanation is that some soldiers wounded in battle by arrows were cured of chronic afflictions that were otherwise untreated,[23] and there are variations on this idea.[24] In China, the practice of acupuncture can perhaps be traced as far back as the Stone Age, with the Bian shi, or sharpened stones.[25] In 1963 a bian stone was found in Duolon County, Mongolia, pushing the origins of acupuncture into the Neolithic age.[26] Hieroglyphs and pictographs have been found dating from the Shang Dynasty (1600-1100 BCE) which suggest that acupuncture was practiced along with moxibustion.[27] Despite improvements in metallurgy over centuries, it was not until the 2nd century BCE during the Han Dynasty that stone and bone needles were replaced with metal.[26] The earliest records of acupuncture is in the Shiji (史記, in English, Records of the Grand Historian) with references in later medical texts that are equivocal, but could be interpreted as discussing acupuncture. The earliest Chinese medical text to describe acupuncture is the Huangdi Neijing, the legendary Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine (History of Acupuncture) which was compiled around 305–204 B.C. The Huangdi Neijing does not distinguish between acupuncture and moxibustion and gives the same indication for both treatments. The Mawangdui texts, which also date from the second century BC though antedating both the Shiji and Huangdi Neijing, mentions the use of pointed stones to open abscesses and moxibustion but not acupuncture, but by the second century BCE, acupuncture replaced moxibustion as the primary treatment of systemic conditions.[7]
In Europe, examinations of the 5,000-year-old mummified body of Ötzi the Iceman have identified 15 groups of tattoos on his body, some of which are located on what are now seen as contemporary acupuncture points. This has been cited as evidence that practices similar to acupuncture may have been practiced elsewhere in Eurasia during the early Bronze Age.[28]
Middle history
Acupuncture spread from China to Korea, Japan and Vietnam and elsewhere in East Asia.
Around ninety works on acupuncture were written in China between the Han Dynasty and the Song Dynasty, and the Emperor Renzong of Song, in 1023, ordered the production of a bronze statuette depicting the meridians and acupuncture points then in use. However, after the end of the Song Dynasty, acupuncture and its practitioners began to be seen as a technical rather than scholarly profession. It became more rare in the succeeding centuries, supplanted by medications and became associated with the less prestigious practices of shamanism, midwifery and moxibustion.[29] Portuguese missionaries in the 16th century were among the first to bring reports of acupuncture to the West.[30] Jacob de Bondt, a Danish surgeon travelling in Asia, described the practice in both Japan and Java. However, in China itself the practice was increasingly associated with the lower-classes and illiterate practitioners.[31] The first European text on acupuncture was written by Willem ten Rhijne, a Dutch physician who studied the practice for two years in Japan. It consisted of an essay in a 1683 medical text on arthritis; Europeans were also at the time becoming more interested in moxibustion, which ten Rhijne also wrote about.[32] In 1757 the physician Xu Daqun described the further decline of acupuncture, saying it was a lost art, with few experts to instruct; its decline was attributed in part to the popularity of prescriptions and medications, as well as its association with the lower classes.[33]
In 1822, an edict from the Chinese Emperor banned the practice and teaching of acupuncture within the Imperial Academy of Medicine outright, as unfit for practice by gentlemen-scholars. At this point, acupuncture was still cited in Europe with both skepticism and praise, with little study and only a small amount of experimentation.[34]
Modern era
In the 1970s, acupuncture became better known in the United States after an article appeared in The New York Times by James Reston, who underwent an emergency appendectomy while visiting China. While standard anesthesia was used for the actual surgery, Mr. Reston was treated with acupuncture for post-operative discomfort.[35] The National Acupuncture Association (NAA), the first national association of acupuncture in the US, introduced acupuncture to the West through seminars and research presentations. The NAA created and staffed the UCLA Acupuncture Pain clinic in 1972. This was the first legal clinic in a medical school setting in the US.[citation needed] The first acupuncture clinic in the United States is claimed to have been opened by Dr. Yao Wu Lee in Washington, D.C. on July 9, 1972.[36][unreliable source?] The Internal Revenue Service allowed acupuncture to be deducted as a medical expense beginning in 1973.[37]
In 2006, a BBC documentary Alternative Medicine filmed a patient undergoing open heart surgery allegedly under acupuncture-induced anaesthesia. It was later revealed that the patient had been given a cocktail of weak anaesthetics that in combination could have a much more powerful effect. The program was also criticised for its fanciful interpretation of the results of a brain scanning experiment.[38][39][40]
Cosmetic acupuncture is also being increasingly used in attempts to reduce wrinkles and age-lines.[41][42]
Traditional theory
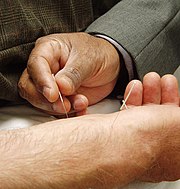
Traditional Chinese medicine
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (December 2008) |
TCM is based on a pre-scientific paradigm of medicine that developed over several thousand years and involves concepts that have no counterpart within contemporary medicine.[9] In TCM, the body is treated as a whole that is composed of several "systems of function" known as the zang-fu (脏腑). These systems are named after specific organs, though the systems and organs are not directly associated. The zang systems are associated with the solid, yin organs such as the liver while the fu systems are associated with the hollow yang organs such as the intestines. Health is explained as a state of balance between the yin and yang, with disease ascribed to either of these forces being unbalanced, blocked or stagnant. The yang force is the immaterial qi, a concept that is roughly translated as "vital energy". The yin counterpart is Blood, which is linked to but not identical with physical blood, and capitalized to distinguish the two. TCM uses a variety of interventions, including pressure, heat and acupuncture applied to the body's acupuncture points (in Chinese 穴 or xue meaning "cavities") to modify the activity of the zang-fu.
Acupuncture points and meridians
Classical texts describe most[dubious – discuss] of the main acupuncture points as existing on the twelve main and two of eight extra meridians (also referred to as mai) for a total of fourteen "channels" through which qi and Blood flow. Other points not on the fourteen channels are also needled. Local pain is treated by needling the tender "ashi" points where qi or Blood is believed to have stagnated. The zang-fu of the twelve main channels are Lung, Large Intestine, Stomach, Spleen, Heart, Small Intestine, Bladder, Kidney, Pericardium, Gall Bladder, Liver and the intangible San Jiao. The eight other pathways, referred to collectively as the qi jing ba mai, include the Luo Vessels, Divergents, Sinew Channels, ren mai and du mai though only the latter two (corresponding to the anterior and posterior sagittal plane of the torso respectively) are needled. The remaining six qi jing ba mai are manipulated by needling points on the twelve main meridians.
Normally qi is described as flowing through each channel in a continuous circuit. In addition, each channel has a specific aspect and occupies two hours of the "Chinese clock".
| Flow of qi through the meridians | ||
| Zang-fu | Aspect | Hours |
| Lung | taiyin | 0300-0500 |
| Large Intestine | yangming | 0500-0700 |
| Stomach | yangming | 0700-0900 |
| Spleen | taiyin | 0900-1100 |
| Heart | shaoyin | 1100-1300 |
| Small Intestine | taiyang | 1300-1500 |
| Bladder | taiyang | 1500-1700 |
| Kidney | shaoyin | 1700-1900 |
| Pericardium | jueyin | 1900-2100 |
| San Jiao | shaoyang | 2100-2300 |
| Gallbladder | shaoyang | 2300-0100 |
| Liver | jueyin | 0100-0300 |
| Lung (repeats cycle) | ||
The zang-fu are divided into yin and yang channels, with three of each type located on each limb. Qi is believed to move in a circuit through the body, travelling both superficially and deeply. The external pathways correspond to the acupuncture points shown on an acupuncture chart while the deep pathways correspond to where a channel enters the bodily cavity related to each organ. The three yin channels of the hand (Lung, Pericardium, and Heart) begin on the chest and travel along the inner surface of the arm to the hand. The three yang channels of the hand (Large Intestine, San Jiao, and Small Intestine) begin on the hand and travel along the outer surface of the arm to the head. The three yin channels of the foot (Spleen, Liver, and Kidney) begin on the foot and travel along the inner surface of the leg to the chest or flank. The three yang channels of the foot (Stomach, Gallbladder, and Urinary Bladder) begin on the face, in the region of the eye, and travel down the body and along the outer surface of the leg to the foot. Each channel is also associated with a yin or yang aspect, either "absolute" (jue-), "lesser" (shao-), "greater" (tai-) or "brightness" (-ming).
A standard teaching text comments on the nature and relationship of meridians (or channels) and the Zang Fu organs:
The theory of the channels is interrelated with the theory of the Organs. Traditionally, the internal Organs have never been regarded as independent anatomical entities. Rather, attention has centered upon the functional and pathological interrelationships between the channel network and the Organs. So close is this identification that each of the twelve traditional Primary channels bears the name of one or another of the vital Organs. In the clinic, the entire framework of diagnostics, therapeutics and point selection is based upon the theoretical framework of the channels. "It is because of the twelve Primary channels that people live, that disease is formed, that people are treated and disease arises." [(Spiritual Axis, chapter 12)]. From the beginning, however, we should recognize that, like other aspects of traditional medicine, channel theory reflects the limitations in the level of scientific development at the time of its formation, and is therefore tainted with the philosophical idealism and metaphysics of its day. That which has continuing clinical value needs to be reexamined through practice and research to determine its true nature.[3]
The meridians are part of the controversy in the efforts to reconcile acupuncture with conventional medicine. The National Institutes of Health 1997 consensus development statement on acupuncture stated that acupuncture points, Qi, the meridian system and related theories play an important role in the use of acupuncture, but are difficult to relate to a contemporary understanding of the body.[9] Chinese medicine forbade dissection, and as a result the understanding of how the body functioned was based on a system that related to the world around the body rather than its internal structures. The 365 "divisions" of the body were based on the number of days in a year, and the twelve meridians proposed in the TCM system are thought to be based on the twelve major rivers that run through China. However, these ancient traditions of Qi and meridians have no counterpart in modern studies of chemistry, biology and physics and to date scientists have been unable to find evidence that supports their existence.[5] A 2008 review of electrical impedance studies concluded that although results were suggestive, the studies available were of poor quality with significant limitations, and because of this there was no clear evidence to demonstrate the existence of acupuncture points or meridians.[43]
Traditional diagnosis
The acupuncturist decides which points to treat by observing and questioning the patient in order to make a diagnosis according to the tradition which he or she utilizes. In TCM, there are four diagnostic methods: inspection, auscultation and olfaction, inquiring, and palpation.[44]
- Inspection focuses on the face and particularly on the tongue, including analysis of the tongue size, shape, tension, color and coating, and the absence or presence of teeth marks around the edge.
- Auscultation and olfaction refer, respectively, to listening for particular sounds (such as wheezing) and attending to body odor.
- Inquiring focuses on the "seven inquiries", which are: chills and fever; perspiration; appetite, thirst and taste; defecation and urination; pain; sleep; and menses and leukorrhea.
- Palpation includes feeling the body for tender "ashi" points, and palpation of the left and right radial pulses at two levels of pressure (superficial and deep) and three positions Cun, Guan, Chi (immediately proximal to the wrist crease, and one and two fingers' breadth proximally, usually palpated with the index, middle and ring fingers).
Other forms of acupuncture employ additional diagnostic techniques. In many forms of classical Chinese acupuncture, as well as Japanese acupuncture, palpation of the muscles and the hara (abdomen) are central to diagnosis.
Traditional Chinese medicine perspective
Although TCM is based on the treatment of "patterns of disharmony" rather than biomedical diagnoses, practitioners familiar with both systems have commented on relationships between the two. A given TCM pattern of disharmony may be reflected in a certain range of biomedical diagnoses: thus, the pattern called Deficiency of Spleen Qi could manifest as chronic fatigue, diarrhea or uterine prolapse. Likewise, a population of patients with a given biomedical diagnosis may have varying TCM patterns. These observations are encapsulated in the TCM aphorism "One disease, many patterns; one pattern, many diseases". (Kaptchuk, 1982)
Classically, in clinical practice, acupuncture treatment is typically highly individualized and based on philosophical constructs as well as subjective and intuitive impressions, and not on controlled scientific research.[45]
Criticism of traditional Chinese medicine theory
Felix Mann, founder and past-president of the Medical Acupuncture Society (1959–1980), the first president of the British Medical Acupuncture Society[46] (1980), and the author of the first comprehensive English language acupuncture textbook Acupuncture: The Ancient Chinese Art of Healing first published in 1962, has stated in his book Reinventing Acupuncture: A New Concept of Ancient Medicine:
- "The traditional acupuncture points are no more real than the black spots a drunkard sees in front of his eyes." (p. 14)
and...
- "The meridians of acupuncture are no more real than the meridians of geography. If someone were to get a spade and tried to dig up the Greenwich meridian, he might end up in a lunatic asylum. Perhaps the same fate should await those doctors who believe in [acupuncture] meridians." (p. 31)[6]
Felix Mann tried to join up his medical knowledge with that of Chinese theory. In spite of his protestations about the theory, he was fascinated by it and trained many people in the west with the parts of it he borrowed. He also wrote many books on this subject. His legacy is that there is now a college in London and a system of needling that is known as "Medical Acupuncture". Today this college trains Doctors and western medical professionals only.
Medical acupuncture has caused much controversy amongst traditional practitioners; the British Acupuncture Council wished for it to be called 'treatment using needles', and removing from it the title 'Acupuncture', as it is so different to traditional methods but have had to retract this after pressure from the medical profession. Mann proposed that the acupuncture points related to the nerve endings and he reassigned the points different uses. He altered the theory so that the treatments given are no longer individual to each client, a central premise of traditional theory. Traditionally the needle combinations differ according to the age of the client, the length of time they had the condition, the type of pain they experience and their health history. In medical acupuncture none of this is addressed and the presenting symptom is treated using a set group of points.
A report for CSICOP on pseudoscience in China written by Wallace Sampson and Barry Beyerstein said:
- "A few Chinese scientists we met maintained that although Qi is merely a metaphor, it is still a useful physiological abstraction (e.g., that the related concepts of Yin and Yang parallel modern scientific notions of endocrinologic [sic] and metabolic feedback mechanisms). They see this as a useful way to unite Eastern and Western medicine. Their more hard-nosed colleagues quietly dismissed Qi as only a philosophy, bearing no tangible relationship to modern physiology and medicine."[47]
George A. Ulett, MD, PhD, Clinical Professor of Psychiatry, University of Missouri School of Medicine states:
- "Devoid of metaphysical thinking, acupuncture becomes a rather simple technique that can be useful as a nondrug method of pain control." He believes that the traditional Chinese variety is primarily a placebo treatment, but electrical stimulation of about 80 acupuncture points has been proven useful for pain control."[48]
Ted J. Kaptchuk,[49] author of The Web That Has No Weaver, refers to acupuncture as "prescientific." Regarding TCM theory, Kaptchuk states:
- "These ideas are cultural and speculative constructs that provide orientation and direction for the practical patient situation. There are few secrets of Oriental wisdom buried here. When presented outside the context of Chinese civilization, or of practical diagnosis and therapeutics, these ideas are fragmented and without great significance. The "truth" of these ideas lies in the way the physician can use them to treat real people with real complaints." (1983, pp. 34-35)[50]
According to the 1997 NIH consensus statement on acupuncture:
- "Despite considerable efforts to understand the anatomy and physiology of the "acupuncture points", the definition and characterization of these points remains controversial. Even more elusive is the basis of some of the key traditional Eastern medical concepts such as the circulation of Qi, the meridian system, and the five phases theory, which are difficult to reconcile with contemporary biomedical information but continue to play an important role in the evaluation of patients and the formulation of treatment in acupuncture."[9]
At least one study found that acupuncture "seems to alleviate pain just barely better than sticking needles into nonspecified parts of the body"[51] and concluded that some of acupuncture's effects may be due to the placebo effect.
According to The Straight Dope, a popular question-and-answer newspaper column published in the Chicago Reader:
- "Traditional acupuncture theory is a quaint patchwork of folklore with about as much relevance to current medical practice as medieval European notions about the four bodily humors. While it may be useful as a guide to future research, no scientist would regard it as satisfactory as it stands.".[52]
Clinical practice
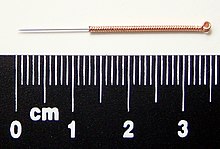
Most modern acupuncturists use disposable stainless steel needles of fine diameter (0.007 to 0.020 in (0.18 to 0.51 mm)), sterilized with ethylene oxide or by autoclave. These needles are far smaller in diameter (and therefore less painful) than hypodermic injection needles since they do not have to be hollow for purposes of injection. The upper third of these needles is wound with a thicker wire (typically bronze), or covered in plastic, to stiffen the needle and provide a handle for the acupuncturist to grasp while inserting. The size and type of needle used, and the depth of insertion, depend on the acupuncture style being practiced.
Warming an acupuncture point, typically by moxibustion (the burning of a combination of herbs, primarily mugwort), is a different treatment than acupuncture itself and is often, but not exclusively, used as a supplemental treatment. The Chinese term zhēn jǐu (針灸), commonly used to refer to acupuncture, comes from zhen meaning "needle", and jiu meaning "moxibustion". Moxibustion is used to varying degrees among current schools of oriental medicine. For example, one well-known technique is to insert the needle at the desired acupuncture point, attach dried moxa to the external end of an acupuncture needle, and then ignite it. The moxa will then smolder for several minutes (depending on the amount adhered to the needle) and conduct heat through the needle to the tissue surrounding the needle in the patient's body. Another common technique is to hold a large glowing stick of moxa over the needles. Moxa is also sometimes burned at the skin surface, usually by applying an ointment to the skin to protect from burns, though burning of the skin is general practice in China.
An example of acupuncture treatment
In Western medicine, vascular headaches (the kind that are accompanied by throbbing veins in the temples) are typically treated with analgesics such as aspirin and/or by the use of agents such as niacin that dilate the affected blood vessels in the scalp, but in acupuncture a common treatment for such headaches is to stimulate the sensitive points that are located roughly in the centers of the webs between the thumbs and the palms of the patient's hands, the hé gǔ points. These points are described by acupuncture theory as "targeting the face and head" and are considered to be the most important points when treating disorders affecting the face and head. The patient reclines, and the points on each hand are first sterilized with alcohol, and then thin, disposable needles are inserted to a depth of approximately 3–5 mm until a characteristic "twinge" is felt by the patient, often accompanied by a slight twitching of the area between the thumb and hand..
In the clinical practice of acupuncturists, patients frequently report one or more of certain kinds of sensation that are associated with this treatment:
- Extreme sensitivity to pain at the points in the webs of the thumbs.
- In bad headaches, a feeling of nausea that persists for roughly the same period as the stimulation being administered to the webs of the thumbs.
- Simultaneous relief of the headache.[53]
Indications according to acupuncturists in the West
The American Academy of Medical Acupuncture (2004) states: "In the United States, acupuncture has its greatest success and acceptance in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain.".[54] They say that acupuncture may be considered as a complementary therapy for the conditions in the list below, noting: "Most of these indications are supported by textbooks or at least 1 journal article. However, definitive conclusions based on research findings are rare because the state of acupuncture research is poor but improving."[54]
- Abdominal distention/flatulence
- Acute and chronic pain control
- Allergic sinusitis
- Anesthesia for high-risk patients or patients with previous adverse responses to anesthetics
- Anorexia
- Anxiety, fright, panic
- Arthritis/arthrosis
- Atypical chest pain (negative workup)
- Bursitis, tendinitis, carpal tunnel syndrome
- Certain functional gastrointestinal disorders (nausea and vomiting, esophageal spasm, hyperacidity, irritable bowel) *
- Cervical and lumbar spine syndromes
- Constipation, diarrhea
| class="col-break " |
- Cough with contraindications for narcotics
- Drug detoxification is suggested[55] but evidence is poor[56][57][58]
- Dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain
- Frozen shoulder
- Headache (migraine and tension-type), vertigo (Meniere disease), tinnitus
- Idiopathic palpitations, sinus tachycardia
- In fractures, assisting in pain control, edema, and enhancing healing process
- Muscle spasms, tremors, tics, contractures
- Neuralgias (trigeminal, herpes zoster, postherpetic pain, other)
- Paresthesias
- Persistent hiccups
- Phantom pain
| class="col-break " |
- Plantar fasciitis
- Post-traumatic and post-operative ileus
- Selected dermatoses (urticaria, pruritus, eczema, psoriasis)
- Sequelae of stroke syndrome (aphasia, hemiplegia)
- Seventh nerve palsy
- Severe hyperthermia
- Sprains and contusions
- Temporo-mandibular joint derangement, bruxism
- Urinary incontinence, retention (neurogenic, spastic, adverse drug effect)
- Weight Loss
Scientific theories and mechanisms of action
Many hypotheses have been proposed to address the physiological mechanisms of action of acupuncture.[59]
Gate-control theory of pain
The gate control theory of pain (developed by Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall in 1962[60] and in 1965)[61] proposed that pain perception is not simply a direct result of activating pain fibers, but modulated by interplay between excitation and inhibition of these pain pathways. According to the theory, the gating of pain is controlled by the inhibitory action on the pain pathways. That is, the perception of pain can be altered (gated on or off) by a number of means, via psychology, pharmacology, or physiology. The gate-control theory was developed in neuroscience independent of acupuncture, which later was proposed as a mechanism to account for the hypothesized analgesic action of acupuncture in the brain stem reticular formation by a German neuroscientist in 1976.[62]
This leads to the theory of central control of pain gating, i.e., pain blockade at the brain (i.e., central to the brain rather than at the spinal cord or periphery) via the release of endogenous opioid neurohormones, such as the endogenous opioid-binding polypeptides, classified as either endorphins or enkephalins.
Neurohormonal theory

Pain transmission can also be modulated at many other levels in the brain along the pain pathways, including the periaqueductal gray, thalamus, and the feedback pathways from the cerebral cortex back to the thalamus. Pain blockade at these brain locations is often mediated by neurohormones, especially those that bind to the opioid receptors (pain-blockade site).
Some studies suggest that the analgesic action of acupuncture is associated with the release of natural endorphins in the brain. This effect can be inferred by blocking the action of endorphins (or morphine) using a drug called naloxone. When naloxone is administered to the patient, the analgesic effects of morphine can be reduced, causing the patient to feel a more appropriate level of pain. When naloxone is administered to an acupunctured patient, the analgesic effect of acupuncture can also be reversed, causing the patient to report an increased level of pain.[63][64][65][66] It should be noted, however, that studies using similar procedures, including the administration of naloxone, have suggested a role of endogenous opioids in the placebo response, demonstrating that this response is not unique to acupuncture.[67]
One study performed on monkeys by recording the neural activity directly in the thalamus of the brain indicated that acupuncture's analgesic effect lasted more than an hour.[68] Furthermore, there is a large overlap between the nervous system and acupuncture trigger points (points of maximum tenderness) in myofascial pain syndrome.[69]
Evidence suggests that the sites of action of analgesia associated with acupuncture include the thalamus using fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)[70] and PET (positron emission tomography)[71] brain imaging techniques,[72] and via the feedback pathway from the cerebral cortex using electrophysiological recording of the nerve impulses of neurons directly in the cortex, which shows inhibitory action when acupuncture stimulus is applied.[73] Similar effects have been observed in association with the placebo response. One study using fMRI found that placebo analgesia was associated with decreased activity in the thalamus, insula and anterior cingulate cortex.[74]
Recently, acupuncture has been shown to increase the nitric oxide levels in treated regions, resulting in increased local blood circulation.[75][76] Effects on local inflammation and ischemia have also been reported.[77]
Scientific research into efficacy
Issues in study design
One of the major challenges in acupuncture research is in the design of an appropriate placebo control group.[10] In trials of new drugs, double blinding is the accepted standard, but since acupuncture is a procedure rather than a pill, it is difficult to design studies in which both the acupuncturist and patient are blinded as to the treatment being given. The same problem arises in double-blinding procedures used in biomedicine, including virtually all surgical procedures, dentistry, physical therapy, etc. As the Institute of Medicine states:
Controlled trials of surgical procedures have been done less frequently than studies of medications because it is much more difficult to standardize the process of surgery. Surgery depends to some degree on the skills and training of the surgeon and the specific environment and support team available to the surgeon. A surgical procedure in the hands of a highly skilled, experienced surgeon is different from the same procedure in the hands of an inexperienced and unskilled surgeon... For many CAM modalities, it is similarly difficult to separate the effectiveness of the treatment from the effectiveness of the person providing the treatment.[12]: 126
Blinding of the practitioner in acupuncture remains challenging. One proposed solution to blinding patients has been the development of "sham acupuncture", i.e., needling performed superficially or at non-acupuncture sites. Controversy remains over whether, and under what conditions, sham acupuncture may function as a true placebo, particularly in studies on pain, in which insertion of needles anywhere near painful regions may elicit a beneficial response.[9][11] A review in 2007 noted several issues confounding sham acupuncture:
Weak physiologic activity of superficial or sham needle penetration is suggested by several lines of research, including RCTs showing larger effects of a superficial needle penetrating acupuncture than those of a nonpenetrating sham control, positron emission tomography research indicating that sham acupuncture can stimulate regions of the brain associated with natural opiate production, and animal studies showing that sham needle insertion can have nonspecific analgesic effects through a postulated mechanism of “diffuse noxious inhibitory control”. Indeed, superficial needle penetration is a common technique in many authentic traditional Japanese acupuncture styles.[78]
An analysis of 13 studies of pain treatment with acupuncture, published in January 2009 in the journal BMJ, concluded there was little difference in the effect of real, sham and no acupuncture.[79]
Evidence-based medicine
There is scientific agreement that an evidence-based medicine (EBM) framework should be used to assess health outcomes and that systematic reviews with strict protocols are essential. Organizations such as the Cochrane Collaboration and Bandolier publish such reviews. In practice, EBM is "about integrating individual clinical expertise and the best external evidence" and thus does not demand that doctors ignore research outside its "top-tier" criteria.[80]
The development of the evidence base for acupuncture was summarized in a review by researcher Edzard Ernst and colleagues in 2007. They compared systematic reviews conducted (with similar methodology) in 2000 and 2005:
The effectiveness of acupuncture remains a controversial issue. ... The results indicate that the evidence base has increased for 13 of the 26 conditions included in this comparison. For 7 indications it has become more positive (i.e. favoring acupuncture) and for 6 it had changed in the opposite direction. It is concluded, that acupuncture research is active. The emerging clinical evidence seems to imply that acupuncture is effective for some but not all conditions.[8]
For acute low back pain there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against either acupuncture or dry needling, though for chronic low back pain acupuncture is more effective than sham treatment but no more effective than conventional and alternative treatments for short-term pain relief and improving function. However, when combined with other conventional therapies, the combination is slightly better than conventional therapy alone.[15][81] A review for the American Pain Society/American College of Physicians found fair evidence that acupuncture is effective for chronic low back pain.[82]
There are both positive[83] and negative[84] reviews regarding the effectiveness of acupuncture when combined with in vitro fertilisation.
A Cochrane Review concluded that acupuncture was effective in reducing the risk of post-operative nausea and vomiting with minimal side effects, though it was less than or equal to the effectiveness of preventive antiemetic medications.[16] A 2006 review initially concluded that acupuncture appeared to be more effective than antiemetic drugs, but the authors subsequently retracted this conclusion due to a publication bias in Asian countries that had skewed their results; their ultimate conclusion was in line with the Cochrane Review - acupuncture was approximately equal to, but not better than preventive antiemetic drugs in treating nausea.[85] Another Cochrane Review concluded that electroacupuncture can be helpful in the treatment of vomiting after the start of chemotherapy, but more trials were needed to test their effectiveness versus modern antivomiting medication.[86]
There is moderate evidence that for neck pain, acupuncture is more likely to be effective than sham treatment and offers short-term improvement compared to those on a waiting list.[87]
There is evidence to support the use of acupuncture to treat headaches that are idiopathic, though the evidence is not conclusive and more studies need to be conducted.[88] Several trials have indicated that migraine patients benefit from acupuncture, although the correct placement of needles seems to be less relevant than is usually thought by acupuncturists. Overall in these trials acupuncture was associated with slightly better outcomes and fewer adverse effects than prophylactic drug treatment.[89]
There is conflicting evidence that acupuncture may be useful for osteoarthritis of the knee, with both positive,[90][91] and negative[92] results. The Osteoarthritis Research Society International released a set of consensus recommendations in 2008 that concluded acupuncture may be useful for treating the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee.[93]
A systematic review of the best five randomized controlled trials available concluded there was insufficient evidence to support the use of acupuncture in the treatment of the symptoms of fibromyalgia.[94]
For the following conditions, the Cochrane Collaboration has concluded there is insufficient evidence to determine whether acupuncture is beneficial, often because of the paucity and poor quality of the research, and that further research is needed:
- Chronic asthma[95]
- Bell's palsy[96]
- Cocaine dependence[97]
- Depression[98]
- Primary dysmenorrhoea (incorporating TENS [99]
- Epilepsy[100]
| class="col-break " |
- Glaucoma[101]
- Insomnia[102]
- Irritable bowel syndrome[103]
- Induction of childbirth[104]
- Rheumatoid arthritis[105]
- Shoulder pain[106]
| class="col-break " |
- Schizophrenia[107]
- Smoking cessation[108]
- Acute stroke[109]
- Stroke rehabilitation[110]
- Tennis elbow[111]
- Vascular dementia[112]
Positive results from some studies on the efficacy of acupuncture may be as a result of poorly designed studies or publication bias.[113][114] Edzard Ernst and Simon Singh state that as the quality of experimental tests of acupuncture have increased over the course of several decades (through better blinding, the use of sham needling as a form of placebo control, etc.) the results have demonstrated less and less evidence that acupuncture is better than placebo at treating most conditions.[115]
Neuroimaging studies
A 2005 literature review examining the use of magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography to document the brainwave activity caused by acupuncture[116] concluded that neuroimaging data to date show some promise for being able to distinguish the cortical effects of expectation, placebo, and real acupuncture. The studies reviewed were mostly small and pain-related, and more research is needed to determine the specificity of neural substrate activation in non-painful indications.
NIH consensus statement
In 1997, the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) issued a consensus statement on acupuncture that concluded that despite research on acupuncture being difficult to conduct, there is sufficient evidence to expand its use and encourage further studies of the phenomenon. The statement was not a policy statement of the NIH but is the considered assessment of a panel convened by the NIH. The consensus group also noted the relative safety of acupuncture compared to certain other medical interventions. They stated that deciding when to use it in clinical practice depends on multiple factors, including the experience of the clinician, the information available on the treatment, and the individual patient's characteristics.[9]
The consensus statement, and the conference that made it, have been criticized by Wallace Sampson, writing for an affiliated publication of Quackwatch. Sampson stated that the meeting was chaired by a strong proponent of acupuncture, failed to include speakers who had obtained negative results on studies of acupuncture, and that he believed the report showed evidence of pseudoscientific reasoning.[117]
In 2006 the NIH's National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine continues to abide by the recommendations of the NIH Consensus Statement the effects of acupuncture have been documented, even if research is still unable to explain its mechanism and relationship to Western medicine.[20]
World Health Organization statement
In 2003, the World Health Organization's Department of Essential Drugs and Medicine Policy published a report on acupuncture that listed a series of diseases, symptoms or conditions for which acupuncture has been demonstrated as an effective treatment:[17]
- Acute bacillary dysentery
- Adverse reactions to radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy
- Allergic rhinitis
- Biliary colic
- Depression
- Essential hypertension
- Headache
- Induction of childbirth and correction of the malposition of fetus
- Inflammation of the tissues surrounding the shoulder
- Leukopenia
- Nausea and vomiting including morning sickness
- Pain in the epigastrium, face, neck, tennis elbow, lower back, knee, during dentistry and after operations
- Primary dysmenorrhea
- Primary hypotension
- Renal colic
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sciatica
- Sprains
- Strokes
The report also listed other conditions for which acupuncture may be effective.
The WHO explained the report's purpose:
- "In order to promote the appropriate use of acupuncture in those Member States where acupuncture has not been widely used, this document is annexed with a brief abstract of each relevant reference for the assessment of acupuncture practice. The clinical conditions covered in the existing data are also included. It must be emphasized that the list of diseases, symptoms or conditions covered in this publication is based on collected reports of clinical trials and, so, can serve only as a reference. Only national health authorities can determine the diseases, symptoms and conditions for which acupuncture treatment can be recommended."
The report was controversial; critics say it is cited by supporters as an endorsement of the practice by the WHO.[18] Several scientists also expressed concern that the evidence supporting acupuncture was weak, and that the WHO had been biased by the involvement of practitioners of alternative medicine.[18] The report was criticized in the 2008 book Trick or Treatment for containing two major errors - including too many results from low-quality clinical trials, and including a large number of trials originating in China. The latter issue is considered problematic because trials originating in the West include a mixture of positive, negative and neutral results while all trials in China are positive (the book's authors attribute this to publication bias rather than fraud). The authors also stated that the report was drafted by a panel that included no critics of acupuncture at all, resulting in a conflict of interest.[19]
American Medical Association statement
In 1997, the following statement was adopted as policy of the American Medical Association (AMA), an association of medical doctors and medical students, after a report on a number of alternative therapies including acupuncture:
"There is little evidence to confirm the safety or efficacy of most alternative therapies. Much of the information currently known about these therapies makes it clear that many have not been shown to be efficacious. Well-designed, stringently controlled research should be done to evaluate the efficacy of alternative therapies."
Specifically regarding acupuncture, the AMA cited reviews conducted in 1992 and 1993 that stated there was not enough evidence to support acupuncture's effectiveness in treating disease, and called for further research.[118]
Safety and risks
Because acupuncture needles penetrate the skin, many forms of acupuncture are invasive procedures, and therefore not without risk. Injuries are rare among patients treated by trained practitioners.[119][120] In most jurisdictions, needles are required by law to be sterile, disposable and used only once; in some places, needles may be reused if they are first resterilized, e.g. in an autoclave. When needles are contaminated, risk of bacterial or other blood-borne infection increases, as with re-use of any type of needle.[121]
Several styles of Japanese acupuncture use non-inserted needling, making for an entirely non-invasive procedure. In non-inserted needling the needle is brought to the skin, but never penetrates it, and various other acupuncture tools are used to tap or stroke along the meridians. Notable examples of these styles are Tōyōhari and the pediatric acupuncture style Shōnishin.
Adverse events
A survey of adverse events related to acupuncture gave rates of 671 minor adverse events per 10,000 treatments, and no major ones.[122] Another survey found that out of 3535 treatments, 402 resulted in minor adverse events including bleeding, bruising, dizziness, fainting, nausea, paresthesia, increased pain and in one case aphasia.[21] That survey concluded: "Acupuncture has adverse effects, like any therapeutic approach. If it is used according to established safety rules and carefully at appropriate anatomic regions, it is a safe treatment method."[21]
Other injury
Other risks of injury from the improper insertion of acupuncture needles include:
- Nerve injury, resulting from the accidental puncture of any nerve.
- Brain damage or stroke, which is possible with very deep needling at the base of the skull.
- Pneumothorax from deep needling into the lung.[123]
- Kidney damage from deep needling in the low back.
- Haemopericardium, or puncture of the protective membrane surrounding the heart, which may occur with needling over a sternal foramen (a hole in the breastbone that occurs as the result of a congenital defect.)[124]
- Risk of terminating pregnancy with the use of certain acupuncture points that have been shown to stimulate the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and oxytocin.
- With unsterilized needles: transmission of infectious diseases
The risk can be reduced through proper training of acupuncturists. Graduates of medical schools and (in the US) accredited acupuncture schools receive thorough instruction in proper technique so as to avoid these events.[125]
Risks from omitting orthodox medical care
Receiving alternative medicine as a replacement for orthodox Western medicine could result in inadequate diagnosis or treatment of conditions for which orthodox medicine has a better treatment record. For this reason many acupuncturists and doctors prefer to consider acupuncture a complementary therapy rather than an alternative therapy.
Researchers also express concern that unethical or naive practitioners may induce patients to exhaust financial resources by pursuing ineffective treatment.[126][127] Some public health departments regulate acupuncture.[128][129][130]
Safety compared with other treatments
Commenting on the relative safety of acupuncture compared with other treatments, the NIH consensus panel stated that "(a)dverse side effects of acupuncture are extremely low and often lower than conventional treatments." They also stated:
- "the incidence of adverse effects is substantially lower than that of many drugs or other accepted medical procedures used for the same condition. For example, musculoskeletal conditions, such as fibromyalgia, myofascial pain, and tennis elbow... are conditions for which acupuncture may be beneficial. These painful conditions are often treated with, among other things, anti-inflammatory medications (aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.) or with steroid injections. Both medical interventions have a potential for deleterious side effects but are still widely used and are considered acceptable treatments."
Legal and political status
Acupuncturists may practice herbal medicine and manipulative therapy (tuina), or be a licensed physician or naturopath who incorporates acupuncture in a simplified form. In many states, medical doctors are not required to have any formal training to perform acupuncture. Over 20 states allow chiropractors to perform acupuncture with less than 200 hours training. The typical amount of hours of medical training by licensed acupuncturists is over 3,000 hours. License is regulated by the state or province in many countries, and often requires passage of a board exam.
In the US, acupuncture is practiced by a variety of healthcare providers. Those who specialize in Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine are usually referred to as "licensed acupuncturists", or L.Ac.'s. The abbreviation "Dipl. Ac." stands for "Diplomate of Acupuncture" and signifies that the holder is board-certified by the NCCAOM.[131] Professional degrees are usually at the level of a Master's degree.
A poll of American doctors in 2005 showed that 59% believe acupuncture was at least somewhat effective.[132] In 1996, the United States Food and Drug Administration changed the status of acupuncture needles from Class III to Class II medical devices, meaning that needles are regarded as safe and effective when used appropriately by licensed practitioners.[133][134] As of 2004, nearly 50% of Americans who were enrolled in employer health insurance plans were covered for acupuncture treatments.[135][136]
Canadian acupuncturists have been licensed in British Columbia since 2003. In Ontario, the practice of acupuncture is now regulated by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Act, 2006, S.O. 2006, chapter 27.[137] The government is in the process of establishing a college[138] whose mandate will be to oversee the implementation of policies and regulations relating to the profession.
In the United Kingdom, acupuncturists are not yet regulated by the government.
In Australia, the legalities of practicing acupuncture also vary by state. Victoria is the only state of Australia with an operational registration board.[139] Currently acupuncturists in New South Wales are bound by the guidelines in the Public Health (Skin Penetration) Regulation 2000,[140] which is enforced at local council level. Other states of Australia have their own skin penetration acts.
Many other countries do not license acupuncturists or require them to be trained.
See also
- Acupoint therapy
- Acupressure
- Acutouch
- Auriculotherapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Medical acupuncture
- Pressure point
- Susuk
- Trigger point
- Veterinary acupuncture
Footnotes
- ^ Acupuncture: the Chinese practice of piercing specific areas of the body along peripheral nerves with fine needles to relieve pain, induce surgical anesthesia, and for therapeutic purposes. Dorland's Pocket Medical Dictionary, 25th ed. W. B. Saunders Co., 1995. ISBN 0-7216-5738-9
- ^ ABC Chinese-English Comprehensive Dictionary edited by John DeFrancis, as used in Wenlin version 3.4.1
- ^ a b O'Connor J & Bensky D (trans. & eds.) (1981). Acupuncture: A Comprehensive Text. Seattle, Washington: Eastland Press. p. 35. ISBN 0-939616-00-9.
- ^ Cheng, 1987, p. 53.
- ^ a b Singh & Ernst, 2008, p. 52-3.
- ^ a b Felix Mann, quoted by Matthew Bauer in Chinese Medicine Times, vol 1 issue 4, August 2006, "The Final Days of Traditional Beliefs? - Part One"
- ^ a b Prioreschi, P (2004). A history of Medicine, Volume 2. Horatius Press. pp. 147–8. ISBN 1888456019.
- ^ a b c d e Ernst E, Pittler MH, Wider B, Boddy K. (2007). "Acupuncture: its evidence-base is changing". Am J Chin Med. 35 (1): 21–5. doi:10.1142/S0192415X07004588. PMID 17265547.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g NIH Consensus Development Program (November 3–5, 1997). "Acupuncture --Consensus Development Conference Statement". National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 2007-07-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ a b White AR, Filshie J, Cummings TM (2001). "Clinical trials of acupuncture: consensus recommendations for optimal treatment, sham controls and blinding". Complement Ther Med. 9 (4): 237–245. doi:10.1054/ctim.2001.0489. PMID 12184353.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Johnson MI (2006). "The clinical effectiveness of acupuncture for pain relief—you can be certain of uncertainty". Acupunct Med. 24 (2): 71–9. doi:10.1136/aim.24.2.71. PMID 16783282.
- ^ a b Committee on the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine by the American Public. (2005). Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States. National Academies Press.
- ^ Madsen MV, Gøtzsche PC, Hróbjartsson A (2009). "Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups". BMJ. 338: a3115. doi:10.1136/bmj.a3115. PMID 19174438.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ernst, Edzard (2006-02). "Acupuncture - a critical analysis". Journal of Internal Medicine. 259 (2): 125–137. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2005.01584.x. PMID 16420542.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Furlan AD, van Tulder MW, Cherkin DC (2005). "Acupuncture and dry-needling for low back pain". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) (1): CD001351. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001351.pub2. PMID 15674876.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Lee A, Done ML (2004). "Stimulation of the wrist acupuncture point P6 for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) (3): CD003281. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003281.pub2. PMID 15266478.
- ^ a b Zhang, X (2003). "Acupuncture: Review and Analysis of Reports on Controlled Clinical Trials". World Health Organization.
- ^ a b c McCarthy, M (2005). "Critics slam draft WHO report on homoeopathy". The Lancet. 366 (9487): 705–6. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67159-0.
- ^ a b Singh & Ernst, 2008, p. 70-73.
- ^ a b "Get the Facts, Acupuncture". National Institute of Health. 2006. Retrieved 2006-03-02.
- ^ a b c Ernst G, Strzyz H, Hagmeister H (2003). "Incidence of adverse effects during acupuncture therapy-a multicentre survey". Complementary therapies in medicine. 11 (2): 93–7. doi:10.1016/S0965-2299(03)00004-9. PMID 12801494.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lao L, Hamilton GR, Fu J, Berman BM (2003). "Is acupuncture safe? A systematic review of case reports". Altern Ther Health Med. 9 (1): 72–83. PMID 12564354.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tiran, D (2000). Complementary therapies for pregnancy and childbirth. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 79. ISBN 0702023280.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ e.g. White, A (1999). Acupuncture: a scientific appraisal. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 1. ISBN 0750641630.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Ma, K (1992). "The roots and development of Chinese acupuncture: from prehistory to early 20th century". Acupuncture in Medicine. 10 ((Suppl)): 92–9. doi:10.1136/aim.10.Suppl.92.
- ^ a b Chiu, M (1993). Chinese acupuncture and moxibustion. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2. ISBN 0443042233.
- ^ Robson, T (2004). An Introduction to Complementary Medicine. Allen & Unwin. pp. 90. ISBN 1741140544.
- ^ Dofer, L; Moser, M; Bahr, F; Spindler, K; Egarter-Vigl, E; Giullén, S; Dohr, G; Kenner, T (1999). "A medical report from the stone age?" (pdf). The Lancet. 354 (9183): 1023–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)12242-0. PMID 10501382.
- ^ Barnes, 2005, p. 25.
- ^ Unschuld, Paul. Chinese Medicine, p. 94. 1998, Paradigm Publications
- ^ Barnes, 2005, p. 58-9.
- ^ Barnes, 2005, p. 75.
- ^ Barnes, 2005, p. 188.
- ^ Barnes, 2005, p. 308-9.
- ^ "Patient Testimonials - First Time". Acupuncture.Com. 1971-07-26. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ "Washington Acupuncture Center õ Dr. Yao Wu Lee". Acupunctureflorida.com. 1972-07-13. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. p. 133. ISBN 0465041957.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Singh, S and Ernzt, E (2008). Trick or Treatment: Alternative medicine on trial. Corgi.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Simon Singh (25 March 2006). "A groundbreaking experiment ... or a sensationalised TV stunt?". The Guardian.
- ^ Simon Singh (14 Feb 2006). Daily Telegraph http://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/science-news/3344833/Did-we-really-witness-the-amazing-power-of-acupuncture.html.
{{cite news}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Text "Did we really witness the 'amazing power' of acupuncture?" ignored (help) - ^ Isaacs, Nora (13 December 2007). "Hold the Chemicals, Bring on the Needles". New York Times. Retrieved 23 November 2009.
- ^ "A few pointers for a new face". Daily Telegraph. 13 Aug 2004. Retrieved 23 November 2009.
- ^ Ahn, AC; Colbert, AP; Anderson, BJ; Martinsen, OG; Hammerschlag, R; Cina, S; Wayne, PM; Langevin, HM (2008). "Electrical properties of acupuncture points and meridians: a systematic review". Bioelectromagnetics. 29 (4): 245–56. doi:10.1002/bem.20403. PMID 18240287.
- ^ Cheng, 1987, chapter 12.
- ^ Medical Acupuncture - Spring / Summer 2000- Volume 12 / Number 1
- ^ British Medical Acupuncture Society
- ^ Sampson, Wallace Sampson (1996). = 2009-09-26 "Traditional Medicine and Pseudoscience in China: A Report of the Second CSICOP Delegation (Part 2)". Skeptical Inquirer. 20 (5).
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Ulett GA, Acupuncture update 1984, Southern Medical Journal 78:233–234, 1985. Comment found at NCBI - Traditional and evidence-based acupuncture: history, mechanisms, and present status. Ulett GA, Han J, Han S.
- ^ Ted J. Kaptchuk, member of NCCAM's National Advisory Council.
- ^ Kaptchuk, Ted J., The Web That Has No Weaver: Understanding Chinese Medicine, McGraw-Hill Professional, 2000 ISBN 0-8092-2840-8, 9780809228409 500 pages
- ^ "Needles Can Stick It To Pain / Science News". Sciencenews.org. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ "Do "auto-acupressure" and acupunture work?". The Straight Dope. 12 October 1984.
- ^ Zhen Jiu Xue, p. 177f et passim.
- ^ a b Braverman S (2004). "Medical Acupuncture Review: Safety, Efficacy, And Treatment Practices". Medical Acupuncture. 15 (3).
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 12623739, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=12623739instead. - ^ Jordan JB (2006). "Acupuncture treatment for opiate addiction: a systematic review". J Subst Abuse Treat. 30 (4): 309–14. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2006.02.005. PMID 16716845.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Gates S, Smith LA, Foxcroft DR (2006). "Auricular acupuncture for cocaine dependence". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1): CD005192. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005192.pub2. PMID 16437523.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bearn J, Swami A, Stewart D, Atnas C, Giotto L, Gossop M (2009). "Auricular acupuncture as an adjunct to opiate detoxification treatment: effects on withdrawal symptoms". J Subst Abuse Treat. 36 (3): 345–9. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2008.08.002. PMID 19004596.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ MedlinePlus: Acupuncture
- ^ P.D. Wall, R. Melzack, On nature of cutaneous sensory mechanisms, Brain, 85:331, 1962.
- ^ R. Melzack, P.D. Wall, Pain mechanisms: A new theory, Science, 150:171-9, 1965.
- ^ Melzack R. Acupuncture and pain mechanisms Anaesthesist. 1976;25:204-7.
- ^ Pomeranz B, Chiu D (1976). "Naloxone blockade of acupuncture analgesia: endorphin implicated". Life Sci. 19 (11): 1757–62. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(76)90084-9. PMID 187888.
- ^
Mayer DJ, Price DD, Rafii A (1977). "Antagonism of acupuncture analgesia in man by the narcotic antagonist naloxone". Brain Res. 121 (2): 368–72. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(77)90161-5. PMID 832169.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Eriksson SV, Lundeberg T, Lundeberg S (1991). "Interaction of diazepam and naloxone on acupuncture induced pain relief". Am. J. Chin. Med. 19 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1142/S0192415X91000028. PMID 1654741.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bishop B. - Pain: its physiology and rationale for management. Part III. Consequences of current concepts of pain mechanisms related to pain management. Phys Ther. 1980, 60:24-37.
- ^ Amanzio, M., Pollo, A., Maggi, G., Benedetti, F. (2001). "Response Variability to Analgesics: a Role for Non-specific Activation of Endogenous Opioids". Pain. 90 (3): 205–215. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00486-3. PMID 11207392.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sandrew BB, Yang RC, Wang SC (1978). "Electro-acupuncture analgesia in monkeys: a behavioral and neurophysiological assessment". Archives internationales de pharmacodynamie et de thérapie. 231 (2): 274–84. PMID 417686.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Melzack R, Stillwell DM, Fox EJ (1977). "Trigger points and acupuncture points for pain: correlations and implications". Pain. 3 (1): 3–23. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(77)90032-X. PMID 69288.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Li K, Shan B, Xu J (2006). "Changes in FMRI in the human brain related to different durations of manual acupuncture needling". Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.). 12 (7): 615–23. doi:10.1089/acm.2006.12.615. PMID 16970531.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pariente J, White P, Frackowiak RS, Lewith G (2005). "Expectancy and belief modulate the neuronal substrates of pain treated by acupuncture". Neuroimage. 25 (4): 1161–7. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.01.016. PMID 15850733.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Shen J (2001). "Research on the neurophysiological mechanisms of acupuncture: review of selected studies and methodological issues". Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.). 7 Suppl 1: S121–7. doi:10.1089/107555301753393896. PMID 11822627.
- ^ Liu JL, Han XW, Su SN (1990). "The role of frontal neurons in pain and acupuncture analgesia". Sci. China, Ser. B, Chem. Life Sci. Earth Sci. 33 (8): 938–45. PMID 2242217.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wager, TD; Rilling, JK; Smith, EE; Sokolik, A; Casey, KL; Davidson, RJ; Kosslyn, SM; Rose, RM; Cohen, JD (2007). "Placebo-Induced Changes in fMRI in the Anticipation and Experience of Pain". Science. 303 (5661): 1162–1167. doi:10.1126/science.1093065. PMID 14976306.
- ^ Tsuchiya M, Sato EF, Inoue M, Asada A (2007). "Acupuncture enhances generation of nitric oxide and increases local circulation". Anesth. Analg. 104 (2): 301–7. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000230622.16367.fb. PMID 17242084.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Blom M, Lundeberg T, Dawidson I, Angmar-Månsson B (1993). "Effects on local blood flux of acupuncture stimulation used to treat xerostomia in patients suffering from Sjögren's syndrome". Journal of oral rehabilitation. 20 (5): 541–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2842.1993.tb01641.x. PMID 10412476.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lundeberg T (1993). "Peripheral effects of sensory nerve stimulation (acupuncture) in inflammation and ischemia". Scandinavian journal of rehabilitation medicine. Supplement. 29: 61–86. PMID 8122077.
- ^ Meta-analysis: acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee. Eric Manheimer, Klaus Linde, Lixing Lao, Lex M Bouter, Brian M Berman. Ann Intern Med. June 19, 2007;146 (12):868-77. Full text (PDF)
- ^ Madsen, MV; Gøtzsche, PC; Hróbjartsson, A (2009). "Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups". BMJ. 338: a3115. doi:10.1136/bmj.a3115. PMID 19174438.
- ^ Vickers, AJ (2001). "Message to complementary and alternative medicine: evidence is a better friend than power" (pdf). BMC Complement Altern Med. 1 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-1-1. PMC 32159. PMID 11346455.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Manheimer E, White A, Berman B, Forys K, Ernst E (2005). "Meta-analysis: acupuncture for low back pain" (PDF). Ann. Intern. Med. 142 (8): 651–63. PMID 15838072.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Chou R, Huffman LH (2007). "Nonpharmacologic therapies for acute and chronic low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society/American College of Physicians clinical practice guideline". Ann Intern Med. 147 (7): 492–504. doi:10.1001/archinte.147.3.492. PMID 17909210.
- ^ Manheimer E, Zhang G, Udoff L, Haramati A, Langenberg P, Berman BM, Bouter LM (2008). "Effects of acupuncture on rates of pregnancy and live birth among women undergoing in vitro fertilisation: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ. 336 (7643): 545–9. doi:10.1136/bmj.39471.430451.BE. PMC 2265327. PMID 18258932.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ El-Toukhy, T; Sunkara, SK; Khairy, M; Dyer, R; Khalaf, Y; Coomarasamy, A (2008). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture in in vitro fertilisation". BMJ. 115 (10): 1203–13. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01838.x. PMID 18652588.
- ^ Lee A, Copas JB, Henmi M, Gin T, Chung RC (2006). "Publication bias affected the estimate of postoperative nausea in an acupoint stimulation systematic review". J Clin Epidemiol. 59 (9): 980–3. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.02.003. PMID 16895822.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ezzo, JM; Richardson, MA; Vickers, A; Allen, C; Dibble, SL; Issell, BF; Lao, L; Pearl, M; Ramirez, G (2006). "Acupuncture-point stimulation for chemotherapy-induced nausea or vomiting". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) (2): CD002285. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002285.pub2. PMID 16625560.
- ^ Trinh K, Graham N, Gross A, Goldsmith C, Wang E, Cameron I, Kay T (2007). "Acupuncture for neck disorders". Spine. 32 (2): 236–43. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000252100.61002.d4. PMID 17224820.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Trinh K, Graham N, Gross A, Goldsmith C, Wang E, Cameron I, Kay T (2006). "Acupuncture for neck disorders". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004870.pub3.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 11279710, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=11279710instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 19160193, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=19160193instead. - ^ White A, Foster NE, Cummings M, Barlas P (2007). "Acupuncture treatment for chronic knee pain: a systematic review". Rheumatology. 46 (3): 384–90. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kel413. PMID 17215263.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Selfe TK, Taylor AG (2008 Jul-Sep). "Acupuncture and osteoarthritis of the knee: a review of randomized, controlled trials". Fam Community Health. 31 (3): 247–54. doi:10.1097/01.FCH.0000324482.78577.0f. PMID 18552606.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Unknown parameter|doi_brokendate=ignored (|doi-broken-date=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ Manheimer E, Linde K, Lao L, Bouter LM, Berman BM (2007). "Meta-analysis: acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee". Ann. Intern. Med. 146 (12): 868–77. doi:10.1001/archinte.146.5.868. PMID 17577006.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|doi_brokendate=ignored (|doi-broken-date=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zhang, W; Moskowitz, RW; Nuki, G; Abramson, S; Altman, RD; Arden, N; Bierma-Zeinstra, S; Brandt, KD; Croft, P (2008). "OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence-based, expert consensus guidelines" (pdf). Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 16 (2): 137–162. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2007.12.013. PMID 18279766.
- ^ Mayhew E; Ernst E (2007). "Acupuncture for fibromyalgia—a systematic review of randomized clinical trials". Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 46 (5): 801–4. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kel406. PMID 17189243.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^
McCarney, RW; Brinkhaus, B; Lasserson, TJ; Linde, K; McCarney, Robert W (2003). "Acupuncture for chronic asthma". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003 (3): CD000008. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000008.pub2. PMID 14973944. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite journal}}: More than one of|first1=and|first=specified (help); More than one of|last1=and|last=specified (help) - ^ He, L; Zhou, MK; Zhou, D; Wu, B; Li, N; Kong, SY; Zhang, DP; Li, QF; Yang, J (2004). "Acupuncture for Bell's palsy". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2007 (4): CD002914. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002914.pub3. PMID 17943775. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ Gates, S; Smith, LA; Foxcroft, DR; Gates, Simon (2006). "Auricular acupuncture for cocaine dependence". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2006 (1): CD005192. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005192.pub2. PMID 16437523. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ Smith, CA; Hay, PP; Smith, Caroline A (2004-03-17). "Acupuncture for depression". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2004 (3): CD004046. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004046.pub2. PMID 15846693. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^
Proctor, ML; Smith, CA; Farquhar, CM; Stones, RW; Zhu, Xiaoshu; Brown, Julie; Zhu, Xiaoshu (2002
volume=2002). "Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and acupuncture for primary dysmenorrhoea". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD002123. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002123. PMID 11869624. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Missing pipe in:|year=(help); line feed character in|year=at position 5 (help)CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ Cheuk, DK; Wong, V; Cheuk, Daniel (2006). "Acupuncture for epilepsy". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2006 (2): CD005062. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005062.pub2. PMID 16625622. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ Law, SK; Li, T; Law, Simon K (2007). "Acupuncture for glaucoma". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2007 (4): CD006030. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006030.pub2. PMID 17943876. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ Cheuk, DK; Yeung, WF; Chung, KF; Wong, V; Cheuk, Daniel KL (2007). "Acupuncture for insomnia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2007 (3): CD005472. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005472.pub2. PMID 17636800. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ Lim, B; Manheimer, E; Lao, L; Ziea, E; Wisniewski, J; Liu, J; Berman, B; Manheimer, Eric (2006). "Acupuncture for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2006 (4): CD005111. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005111.pub2. PMID 17054239. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Smith, CA; Crowther, CA; Smith, Caroline A (2004). "Acupuncture for induction of labour". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2004 (1): CD002962. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002962.pub2. PMID 14973999. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Casimiro, L; Barnsley, L; Brosseau, L; Milne, S; Robinson, VA; Tugwell, P; Wells, G; Casimiro, Lynn (2005). "Acupuncture and electroacupuncture for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005 (4): CD003788. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003788.pub2. PMID 16235342. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Green, S; Buchbinder, R; Hetrick, S; Green, Sally (2005). "Acupuncture for shoulder pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005 (2): CD005319. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005319. PMID 15846753. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Rathbone, J; Xia, J; Rathbone, John (2005). "Acupuncture for schizophrenia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005 (4): CD005475. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005475. PMID 16235404. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ White, AR; Rampes, H; Campbell, JL; White, Adrian R (2006). "Acupuncture and related interventions for smoking cessation". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2006 (1): CD000009. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000009.pub2. PMID 16437420. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Zhang, SH; Liu, M; Asplund, K; Li, L; Liu, Ming (2005). "Acupuncture for acute stroke". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005 (2): CD003317. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003317.pub2. PMID 15846657. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Wu, HM; Tang, JL; Lin, XP; Lau, J; Leung, PC; Woo, J; Li, YP; Wu, Hong Mei (2006). "Acupuncture for stroke rehabilitation". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2006 (3): CD004131. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004131.pub2. PMID 16856031. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Green, S; Buchbinder, R; Barnsley, L; Hall, S; White, M; Smidt, N; Assendelft, W; Green, Sally (2002). "Acupuncture for lateral elbow pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2002 (1): CD003527. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003527. PMID 11869671. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Peng, WN; Zhao, H; Liu, ZS; Wang, S; Weina, Peng (2008). "Acupuncture for vascular dementia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2007 (2): CD004987. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004987.pub2. PMID 17443563. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Tang JL, Zhan SY, Ernst E (1999). "Review of randomised controlled trials of traditional Chinese medicine". BMJ. 319 (7203): 160–1. PMC 28166. PMID 10406751.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vickers A, Goyal N, Harland R, Rees R (1998). "Do certain countries produce only positive results? A systematic review of controlled trials". Control Clin Trials. 19 (2): 159–66. doi:10.1016/S0197-2456(97)00150-5. PMID 9551280.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Singh & Ernst, 2008, p. 79-82.
- ^ Lewith GT, White PJ, Pariente J (2005). "Investigating acupuncture using brain imaging techniques: the current state of play". Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine: eCAM. 2 (3): 315–9. doi:10.1093/ecam/neh110. PMC 1193550. PMID 16136210. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sampson, W (2005-03-23). "Critique of the NIH Consensus Conference on Acupuncture". Quackwatch. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- ^ "Report 12 of the Council on Scientific Affairs (A-97) – Alternative Medicine". American Medical Association. 1997. Retrieved 2009-10-07.
- ^ Lao L, Hamilton GR, Fu J, Berman BM (2003). "Is acupuncture safe? A systematic review of case reports". Alternative therapies in health and medicine. 9 (1): 72–83. PMID 12564354.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Norheim AJ (1996). "Adverse effects of acupuncture: a study of the literature for the years 1981–1994". Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.). 2 (2): 291–7. doi:10.1089/acm.1996.2.291. PMID 9395661.
- ^ http://www.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/340/mar18_1/c1268
- ^ White, A; Hayhoe, S; Hart, A; Ernst, E (2001). "Adverse events following acupuncture: prospective survey of 32 000 consultations with doctors and physiotherapists". British Medical Journal. 323 (7311): 485–6. doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7311.485. PMC 48133. PMID 11532840.
- ^ Leow TK (2001). "Pneumothorax Using Bladder 14". Medical Acupuncture. 16 (2).
- ^ Yekeler, Ensar; Tunaci, M; Tunaci, A; Dursun, M; Acunas, G. "Frequency of Sternal Variations and Anomalies Evaluated by MDCT". American Journal of Roentgenology. 186 (4): 956–60. doi:10.2214/AJR.04.1779. PMID 16554563. Retrieved 2007-11-24.
- ^ Cheng, 1987.
- ^ Be Wary of Acupuncture, Qigong, and "Chinese Medicine"
- ^ Final Report, Report into Traditional Chinese Medicine - NSW Parliament
- ^ Government of Ontario, Canada - News
- ^ Traditional Chinese Medicine Act, 2006, S.O. 2006, c. 27
- ^ CTCMA
- ^ NCCAOM
- ^ "More than half of the physicians (59%) believed that acupuncture can be effective to some extent." Physicians Divided on Impact of CAM on U.S. Health Care; Aromatherapy Fares Poorly; Acupuncture Touted. HCD Research, 9 September 2005. convenience links: Business Wire, 2005; AAMA, 2005. Link to internet archive version: Cumulative Report
- ^ Updates-June 1996 FDA Consumer
- ^ US FDA/CDRH: Premarket Approvals
- ^ Report: Insurance Coverage for Acupuncture on the Rise. Michael Devitt, Acupuncture Today, January, 2005, Vol. 06, Issue 01
- ^ Claxton, Gary (2004). The Kaiser Family Foundation and Health Research and Educational Trust Employer Health Benefits 2004 Annual Survey (PDF). pp. 106–107. ISBN 0-87258-812-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Traditional Chinese Medicine Act, 2006, S.O. 2006, c. 27
- ^ "Welcome to the TC-CTCMPAO". Ctcmpao.on.ca. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ Welcome to the Chinese Medicine Registration Board of Victoria
- ^ "Health NSW" (PDF).
References
- Barnes, LL (2005). Needles, herbs, gods, and ghosts: China, healing, and the West to 1848. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674018729.
- Cheng, X (1987). Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion (1st ed.). Foreign Languages Press. ISBN 7-119-00378-X.
- Singh, S (2008). Trick or treatment: The undeniable facts about alternative medicine. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0393066616.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: checksum (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Free preview at Google Books
Further reading
{{cite book | first = Li | last = Zheng | title = Acupuncture and Hormone Balance (4th ed.) | publisher = Lulu | year = 2008 | isbn = 978-0-557-01917-5 |
- Deadman, P (2007). A Manual of Acupuncture. Journal of Chinese Medicine Publications. ISBN 0951054651.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Jin, G (2006). Contemporary Medical Acupuncture - A Systems Approach (English). Springer. ISBN 7040192578.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Maciocia, G (1989). The Foundations of Chinese Medicine: A Comprehensive Text for Acupuncturists and Herbalists (2nd ed.). Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0443039801.
External links
