Syriac Christianity
| Part of a series on |
| Eastern Christianity |
|---|
 |
Syriac Christianity (Syriac: ܡܫܝܚܝܘܬܐ ܣܘܪܝܝܬܐ / Mšiḥāyuṯā Suryāyṯā; Arabic: مسيحية سريانية, masīḥiyyat suryāniyya) represents a distinctive branch of Eastern Christianity, whose formative theological writings and traditional liturgies are expressed in Classical Syriac language, a variation of Aramaic language.[1][2][3] In a wider sense, the term can also refer to Aramaic Christianity in general, thus encompassing all Christian traditions that are based on liturgical uses of Aramaic language and its variations, both historical and modern.[4][5][6]
Along with Greek and Latin, Classical Syriac was one of the three most important languages of Early Christianity.[7] It became a vessel for the development of a distinctive Syriac form of Christianity, that flourished throughout the Near East and other parts of Asia during the Late Antiquity and the Early Medieval period, giving rise to various liturgical and denominational traditions, represented in modern times by several Churches that are continuing to uphold religious and cultural heritage of Syriac Christianity.[8][9]
Syriac Christianity comprises two liturgical traditions.[10] The West Syriac Rite (also called Antiochian Syriac Rite or St. James Rite), which has the Divine Liturgy of Saint James as its anaphora, is that of the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Lebanon-based Maronite Church and Syriac Catholic Church, and the Indian Syro-Malankara Catholic Church, Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church, Jacobite Syrian Christian Church (part of the Syriac Orthodox Church), Malabar Independent Syrian Church. Modified (Protestant-influenced) version of this rite are used by the Reformed Eastern Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church[11][12][13] and the more strongly Reformed St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India.
The East Syriac Rite (also known as the Chaldean, Assyrian, or Persian Rite),[14] whose main anaphora is the Holy Qurbana of Saints Addai and Mari, is that of the Iraq-based Chaldean Catholic Church, Assyrian Church of the East and Ancient Church of the East, and the Indian Syro-Malabar Catholic Church and Chaldean Syrian Church (the latter being part of the Assyrian Church of the East).
In India, indigenous Eastern Christians (Saint Thomas Christians) of both liturgical traditions (eastern and western) are called "Syrian" Christians. The traditional East Syriac community is represented by the Syro-Malabar Church and the Chaldean Syrian Church of India (a part of the Assyrian Church of the East). The West Syriac liturgical tradition was introduced after 1665, and the community associated with it is represented by the Jacobite Syrian Christian Church (a part of the Syriac Orthodox Church), and the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church (both of them belonging to the Oriental Orthodoxy), the Malankara Syrian Catholic Church (an Eastern Catholic Church), the Malankara Marthoma Syrian Church (part of the Anglican Communion)and the Malabar Independent Syrian Church (an independent Oriental Orthodox Church not part of the Oriental Orthodox Communion). [15]
The Syriac language is a variety of Aramaic language, that emerged in Edessa, Upper Mesopotamia during the first centuries CE.[16] It is related to the Aramaic of Jesus, a Galilean dialect.[17] This relationship added to its prestige for Christians.[18] The form of the language in use in Edessa predominated in Christian writings and was accepted as the standard form, "a convenient vehicle for the spread of Christianity wherever there was a substrate of spoken Aramaic".[1] The area where Syriac or Aramaic was spoken, an area of contact and conflict between the Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire, extended from around Antioch in the west to Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Sasanian capital (in Iraq), in the east and comprised the whole or parts of present-day Syria, Lebanon, Israel/Palestine, Iraq, and parts of Turkey and Iran.[2][1]
Name
In modern English language, the term "Syriac Christianity" is preferred over the alternative form "Syrian Christianity", that was also commonly used in older literature, as a synonym, particularly during the 19th and the 20th centuries.[19] Since the latter term proved to be very polysemic, a tendency occurred (firstly among scholars) to reduce the term "Syrian Christianity" to its primary (regional) meaning, that designates the Christianity in Syria, while more specific term (Syriac Christianity) came to be used as preferred designation for the entire Syriac branch of Eastern Christianity.[20] That distinction is not yet universally accepted, even among scholars. It is gradually introduced in most of the English speaking world, with some notable exceptions. Churches of Syriac tradition in India still self-identify, in Indian English, as "Syrian" Churches, both for sociolinguistic and legal reasons.[21][22]
Modern distinctions between "Syrian" and "Syriac" (Christianity) are observed in English language as a partially accepted convention, but such distinctions do not exist in most of the other languages, nor on the endonymic (native) level among adherents of Syriac Christianity.[20] Native terms (ethnonyms, demonyms, linguonyms) that were derived from the name of Syria did not possess a distinctive formal duality that would be equivalent to the conventional English distinction between terms Syrian and Syriac.[23] Since the proposed distinction is not yet universally accepted among scholars, its individual and often inconsistent application has created a complex narrative, that is additionally burdened by older problems, inherited from terminological controversies that originated much earlier, within Syriac studies in particular, and also within Aramaic studies in general.[24]
The use of Syrian/Syriac labels was also challenged by common scholarly reduction of Syriac Christianity to the Eastern Aramaic Christian heritage, and its offsprings. Such reduction was detaching Syriac Christianity" from Western Aramaic Christian traditions, that were enrooted in the very homeland of Christianity, encompassing ancient Aramaic-speaking communities in Judea and Palestine, with Galilea and Samaria, and also those in the regions of Nabatea and Palmyrene to the east,[25] and Phoenicia and Syria proper to the north. Since Western Aramaic Christians did not fit into narrow scholarly definition of Syriac Christianity, focused on Eastern Aramaic traditions,[26] various researchers have opted for an additional use of some wider terms, like: Aramaic Christianity,[4][5] or Aramaic Christendom,[6] thus designating a religious, cultural and linguistic continuum, encompassing the entire branch of Christianity that stemmed from the first Aramaic-speaking Christian communities, formed in apostolic times, and then continued to develop throughout history, mainly in the Near East and also in several other regions of Asia, including India and China.[27][28]
In English language, term Aramaic Christianity should not be confused with term Aramean Christianity, since first designation is linguistically defined and thus refers to Aramaic-speaking Christians in general, while second designation is more specific and refers only to Christian Arameans.[29][30]
History

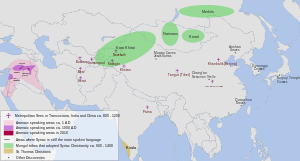
Christianity began in the Near East, in Jerusalem among Aramaic-speaking Jews. It soon spread to other Aramaic-speaking Semitic peoples along the Eastern Mediterranean coast and also to the inland parts of the Roman Empire and beyond that into the Parthian Empire and the later Sasanian Empire,[31] including Mesopotamia, which was dominated at different times and to varying extents by these empires.
The ruins of the Dura-Europos church, dating from the first half of the 3rd century are concrete evidence of the presence of organized Christian communities in the Aramaic-speaking area, far from Jerusalem and the Mediterranean coast, and there are traditions of the preaching of Christianity in the region as early as the time of the Apostles.
However, "virtually every aspect of Syriac Christianity prior to the fourth century remains obscure, and it is only then that one can feel oneself on firmer ground".[32] The fourth century is marked by the many writings in Syriac of Saint Ephrem the Syrian, the Demonstrations of the slightly older Aphrahat and the anonymous ascetical Book of Steps. Ephrem lived in the Roman Empire, close to the border with the Sasanian Empire, to which the other two writers belonged.[32]
Other items of early literature of Syriac Christianity are the Diatessaron of Tatian, the Curetonian Gospels and the Syriac Sinaiticus, the Peshitta Bible and the Doctrine of Addai.
The bishops who took part in the First Council of Nicea (325), the first of the ecumenical councils, included twenty from Syria and one from Persia, outside the Roman Empire.[33] Two councils held in the following century divided Syriac Christianity into two opposing parties.
East-West theological contrast

Syriac Christianity is divided on several theological issues, both Christological and Pneumatological.[34]
In 431, the Council of Ephesus, which is reckoned as the third ecumenical council, condemned Nestorius and Nestorianism. That condemnation was consequently ignored by the East Syriac Church of the East, which had been previously established in the Sasanian Empire as a distinct Church at the Council of Seleucia-Ctesiphon in 410, and which at the Synod of Dadisho in 424 had declared the independence of its head, the Catholicos, in relation to "western" (Roman Empire) Church authorities. Even in its modern form of Assyrian Church of the East and Ancient Church of the East, it honours Nestorius as a teacher and saint.[35]
In 451, the Council of Chalcedon, the fourth ecumenical council, condemned Monophysitism, and also rejected Dyoprosopism.[36] This council was rejected by the Oriental Orthodox Churches, one of which is the Syriac Orthodox Church, that uses the West Syriac Rite. The Patriarchate of Antioch was consequently divided between two communities, pro-Chalcedonian and non-Chalcedonian. The Chalcedonians were often labelled as 'Melkites' (Imperials), while their opponents were labelled Monophysites (those who believe in the one rather than two natures of Christ) and Jacobites (after Jacob Baradaeus).
In 553, the Council of Constantinople, the fifth ecumenical council, anathematized Theodore of Mopsuestia, and also condemned several writings of Theodoret of Cyrus and Ibas of Edessa (see: Three-Chapter Controversy).[36] Since those three theologians were highly regarded among Eastern Syriac Christians, further rifts were created, culminating in 612, when a major council of the Church of the East was held in Seleucia-Ctesiphon. Presided by Babai the Great (d. 628), the council officially adopted specific Christological formulations, using Syriac term qnoma (ܩܢܘܡܐ) as designation for dual (divine and human) properties within one prosopon (person) of Christ.[37]
In the 7th century, further divisions arose, regarding Monoenergism and Monothelitism. The dispute over Monothelitism led to the creation of the ancient Maronite Church,[38] that continued to exist as a distinctive denomination throughout the Middle Ages. Modern Maronite Catholic Church claims that Maronites had always remained in communion with the Catholic Church.
Theological estrangement between East Syriac and West Syriac branches was manifested as a prolonged rivalry, that was particularly intensive between the Church of the East and the Maphrianate of the East (Syriac Orthodox Church).[36] Both sides were claiming that their doctrines were not heretical, also accusing the other side of holding heretical teachings. Their theological estrangement continued to persist throughout medieval and early modern period, up to the present day. In 1999, the Coptic Orthodox Church, a sister-church of the Syriac Orthodox Church, blocked admittance of the Assyrian Church of the East to the Middle East Council of Churches, which has among its members the Chaldean Catholic Church,[39][40][41] and demanded that it remove from its liturgy the mention of Diodorus of Tarsus, Theodore of Mopsuestia and Nestorius, whom it venerates as "the Greek doctors".[42]
East-West liturgical contrast

The liturgies of the East and West Syriacs are quite distinct. The East Syriac Rite is noted especially for its eucharistic Qurbana of Addai and Mari, in which the Words of Institution are absent. West Syriacs use the Syro-Antiochian or West Syriac Rite, which belongs to the family of liturgies known as the Antiochene Rite.
The Syriac Orthodox Church adds to the Trisagion ("Holy God, Holy Mighty, Holy Immortal, have mercy on us") the phrase "who were crucified for us". The Church of the East interpreted this as heretical.[43] Patriarch Timothy I of the Church of the East declared: "And also in all the countries of Babylon, of Persia, and of Assyria, and in all the countries of the sunrise, that is to say, among the Indians, the Chinese, the Tibetans, the Turks, and in all the provinces under the jurisdiction of this Patriarchal See, there is no addition of Crucifixus es pro nobis".[44]
Among the Saint Thomas Christians of India, the East Syriac Rite was the one originally used, but those who in the 17th century accepted union with the Syriac Orthodox Church adopted the rite of that church.
Further divisions

A schism in 1552 in the Church of the East gave rise to a separate patriarchate, which at first entered into union with the Catholic Church but later formed the nucleus of the present-day Assyrian Church of the East and Ancient Church of the East, while at the end of the 18th century most followers of the earlier patriarchate chose union with Rome and, with some others, now form the Chaldean Catholic Church.
In India, all of the Saint Thomas Christians are still collectively called "Syrian Christians". The majority of the Saint Thomas Christians, who initially depended on the Church of the East, maintained union with Rome in spite of discomforts felt at Latinization by their Portuguese rulers and clergy, against which they protested. They now form the Syro-Malabar Catholic Church. A small group, which split from these in the early 19th century, united at the beginning of the 20th century, under the name of Chaldean Syrian Church, with the Assyrian Church of the East.
Those who in 1653 broke with the Catholic Church as dominated by the Portuguese in India and soon chose union with the Syriac Orthodox Church later split into various groups. The first separation was that of the Malabar Independent Syrian Church in 1772.[45] At the end of the 19th century and in the course of the 20th, a division arose among those who remained united with the Syriac Orthodox Church who insisted on full autocephaly and are now called the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church and those, the Jacobite Syrian Christian Church, who remain faithful to the patriarch.
A reunion movement led in 1930 to the establishment of full communion between some of the Malankara Syrian Orthodox and the Catholic Church. They now form the Syro-Malankara Catholic Church.
In the Middle East, the newly enthroned patriarch of the Syriac Orthodox Church, Ignatius Michael III Jarweh, declared himself a Catholic and, having received confirmation from Rome in 1783, became the head of the Syriac Catholic Church.
In the 19th and 20th centuries many Syriac Christians, both East and West, left the Middle East for other lands, creating a substantial diaspora.[46]
In modern times, several Churches of Syriac tradition are actively participating in ecumenical dialogue.[47][48]
Terms for Syriac Christians

Indigenous Aramaic-speaking communities of the Near East (Syriac: ܣܘܪܝܝܐ, Arabic: سُريان)[49] adopted Christianity very early, perhaps already from the first century, and began to abandon their three-millennia-old traditional ancient Mesopotamian religion, although this religion did not fully die out until as late as the tenth century.[citation needed] The kingdom of Osroene, with the capital city of Edessa, was absorbed into the Roman Empire in 114 as a semi-autonomous vassal state and then, after a period under the supremacy of Parthian Empire, was incorporated as a Roman province, first in 214, and finally in 242.[50]
In 431 the Council of Ephesus declared Nestorianism a heresy. Nestorians, persecuted in the Byzantine Empire, sought refuge in the parts of Mesopotamia that were part of the Sasanian Empire. This encouraged acceptance of Nestorian doctrine by the Persian Church of the East, which spread Christianity outside Persia, to India, China, Tibet and Mongolia, expanding the range of this eastern branch of Syriac Christianity. The western branch, the Jacobite Church, appeared after the Council of Chalcedon's condemnation of Monophysitism in 451.[51]
Churches of Syriac traditions
- West Syriac Rite
- Oriental Orthodox
- The Syriac Orthodox Church (Non-Chalcedonian Oriental Orthodox Church of Antioch and all the East)
- The Jacobite Syrian Christian Church (Non-Chalcedonian Oriental Orthodox Church of India within the Syriac Orthodox Patriarchate)
- The Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church (Syrian Church based in Kerala) (Autocephalous; Non-Chalcedonian Oriental Orthodox Church of India) with her part the Brahmavar (Goan) Orthodox Church
- The Malabar Independent Syrian Church (Thozhiyur church), an independent oriental orthodox church based in Kerala, India
- Eastern Catholic Churches with the West Syriac Rite
- The Syriac Catholic Church
- The Maronite Catholic Church
- The Syro-Malankara Catholic Church (Syrian Catholic Church based in Kerala, India)
- The Mar Thoma Syrian Church of Malabar, linked in full communion with the Anglican Communion
- The St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India, of Evangelical-style theology
- Oriental Orthodox
- East Syriac Rite and non-Ephesian tradition
- Church of the East, founded in the Sasanian Empire, became known as the Nestorian Church, once widespread throughout Asia
- The Assyrian Church of the East, traditionalist continuation of the Church of the East that took this name in 1976
- The Chaldean Syrian Church an archbishopric in India of the Assyrian Church of the East
- The Ancient Church of the East, split from the Assyrian Church of the East in the 1960s
- The Assyrian Church of the East, traditionalist continuation of the Church of the East that took this name in 1976
- The East Syriac Rite Churches within the Catholic Church
- The Chaldean Catholic Church, an Eastern Catholic Church that emerged from the Church of the East following splits in 1552, 1667/1668 and 1779
- The Syro(Syrian) Malabar Catholic Church (Syrian Catholic Church based in Kerala)
- Church of the East, founded in the Sasanian Empire, became known as the Nestorian Church, once widespread throughout Asia
East Syriac Christians were involved in the mission to India, and many of the present Churches in India are in communion with either East or West Syriac Churches. These Indian Christians are known as Saint Thomas Christians.
In modern times, even apart from the Reformed Eastern denominations like Mar Thoma Syrian Church of Malabar and St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India, which originated from Churches of the West Syriac Rite,[11] various Evangelical denominations continue to send representatives among Syriac Christians. As a result, several Evangelical groups have been established, particularly the Assyrian Pentecostal Church (mostly in America, Iran, and Iraq) from East Syriac Christians, and the Aramean Free Church (mostly in Germany, Sweden, America and Syria) from West Syriac Christians. Because of their new (Protestant) theology these are sometimes not classified as traditional Churches of Syriac Christianity.
See also
References
- ^ a b c Rompay 2008, pp. 365–386.
- ^ a b Murre van den Berg 2007, p. 249.
- ^ Kitchen 2012, pp. 66–77.
- ^ a b Simmons 1959, p. 13.
- ^ a b Aufrecht 2001, p. 149.
- ^ a b Quispel 2008, p. 80.
- ^ Brock 2005, pp. 5–20.
- ^ Winkler 2019, pp. 119–133.
- ^ Hunter 2019, pp. 783–796.
- ^ Varghese 2019, pp. 391–404.
- ^ a b Pallikunnil, Jameson K. (2017). The Eucharistic Liturgy: A Liturgical Foundation for Mission in the Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church. ISBN 978-1-5246-7652-0.
Metropolitan Juhanon Mar Thoma called it "a Protestant Church in an oriental garb". As a reformed Oriental Church, it agrees with the reformed doctrines of the Western churches. Therefore, there is much in common in faith and doctrine between the MTC and the reformed Churches of the West. As the Church now sees it, just as the Anglican church is a Western Reformed Church, the MTC is an Eastern Reformed Church..
- ^ World Council of Churches, "Mar Thoma Syrian Church of Malabar"
- ^ Ed Hindson, Dan Mitchell (editors), The Popular Encyclopedia of Church History (Harvest House Publishers, 2013), p. 225
- ^ John Hardon (25 June 2013). Catholic Dictionary: An Abridged and Updated Edition of Modern Catholic Dictionary. Crown Publishing Group. p. 493. ISBN 978-0-307-88635-4.
- ^ Perczel 2019, pp. 653–697.
- ^ Brock 1998, p. 708-719.
- ^ Allen C. Myers, ed. (1987), "Aramaic". The Eerdmans Bible Dictionary. Grand Rapids, MI: William B. Eerdmans. p. 72. ISBN 0-8028-2402-1. "It is generally agreed that Aramaic was the common language of Palestine in the first century A.D. Jesus and his disciples spoke the Galilean dialect, which was distinguished from that of Jerusalem (Matt. 26:73)."
- ^ Montgomery 2002, p. 27.
- ^ Robinson & Coakley 2013, p. 1, note 1.
- ^ a b Millar 2006, pp. 107–109.
- ^ O’Mahony 2006, p. 511.
- ^ Winkler 2019, pp. 130–132.
- ^ Andrade 2019, pp. 157–174.
- ^ Burnett 2005, pp. 421–436.
- ^ Jobling 1996, pp. 62–73.
- ^ Rompay 2008, p. 366.
- ^ Dickens 2019, pp. 583–624.
- ^ Takahashi 2019, pp. 625–652.
- ^ Healey 2014, p. 391.
- ^ Healey 2019a, p. 433–446.
- ^ Daryaee 2019, pp. 33–43.
- ^ a b Brock 2004a, p. 362.
- ^ Montgomery 2002, p. 27, 57.
- ^ Hainthaler 2019, p. 377–390.
- ^ Baum & Winkler 2003, pp. 5, 30.
- ^ a b c Meyendorff 1989.
- ^ Brock 1999d, p. 281–298.
- ^ Abouzayd 2019, pp. 731–750.
- ^ Baum & Winkler 2003, pp. 151–152.
- ^ Brock 2004b, p. 58.
- ^ Nichols 2010, p. 137.
- ^ Metropolitan Bishoy, "The Assyrian Churches"
- ^ Marijke Metselaar-Jongens, Defining Christ: The Church of the East and Nascent Islam (Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam 2016), p. 79
- ^ Mingana 1926, p. 466.
- ^ Fenwick, John R.K. "Malabar Independent Syrian Church The Thozhiyur Church".
- ^ Chaillot 1998.
- ^ Brock 1999e, p. 189-197.
- ^ Brock 2004b, p. 44-65.
- ^ Donabed 2015, p. 18.
- ^ Ross 2001, p. 49.
- ^ T.V. Philip, East of the Euphrates: Early Christianity in Asia
Sources
- Abouzayd, Shafiq (2019). "The Maronite Church". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 731–750.
- Andrade, Nathanael J. (2019). "Syriac and Syrians in the Later Roman Empire: Questions of Identity". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 157–174. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Aufrecht, Walter E. (2001). "A Legacy of Syria: The Aramaic Language". Bulletin of the Canadian Society for Mesopotamian Studies. 36: 145–155.
- Bar-Asher Siegal, Michal (2019). "Judaism and Syriac Christianity". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 146–156.
- Baum, Wilhelm; Winkler, Dietmar W. (2003). The Church of the East: A Concise History. London-New York: Routledge-Curzon. ISBN 9781134430192.
- Baumer, Christoph (2006). The Church of the East: An Illustrated History of Assyrian Christianity. London-New York: Tauris. ISBN 9781845111151.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1982). "Christians in the Sasanian Empire: A Case of Divided Loyalties". Studies in Church History. 18: 1–19.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1992). Studies in Syriac Christianity: History, Literature, and Theology. Aldershot: Variorum. ISBN 9780860783053.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1992). "Eusebius and Syriac Christianity". Eusebius, Christianity, and Judaism. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. pp. 212–234.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1997). A Brief Outline of Syriac Literature. Kottayam: St. Ephrem Ecumenical Research Institute.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1998). "Syriac Culture, 337-425". The Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 13. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 708–719.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1999a). From Ephrem to Romanos: Interactions Between Syriac and Greek in Late Antiquity. Aldershot: Ashgate. ISBN 9780860788003.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1999b). "St. Ephrem in the Eyes of Later Syriac Liturgical Tradition" (PDF). Hugoye: Journal of Syriac Studies. 2 (1): 5–25.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1999c). "Eusebius and Syriac Christianity". Doctrinal Diversity: Varieties of Early Christianity. New York and London: Garland Publishing. pp. 258–280. ISBN 9780815330714.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1999d). "The Christology of the Church of the East in the Synods of the Fifth to Early Seventh Centuries: Preliminary Considerations and Materials". Doctrinal Diversity: Varieties of Early Christianity. New York and London: Garland Publishing. pp. 281–298.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1999e). "The Importance of the Syriac Traditions in Ecumenical Dialogue on Christology". Christian Orient. 20: 189–197.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (2004a). "Ephrem and the Syriac Tradition". The Cambridge History of Early Christian Literature. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 362–372.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (2004b). "The Syriac Churches in Ecumenical Dialogue on Christology". Eastern Christianity: Studies in Modern History, Religion and Politics. London: Melisende. pp. 44–65.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (2005). "The Syriac Orient: A Third 'Lung' for the Church?". Orientalia Christiana Periodica. 71: 5–20.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (2006). Fire from Heaven: Studies in Syriac Theology and Liturgy. Aldershot: Ashgate. ISBN 9780754659082.
- Brown, Leslie W. (1956). The Indian Christians of St Thomas: An Account of the Ancient Syrian Church of Malabar. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Burnett, Stephen G. (2005). "Christian Aramaism: The Birth and Growth of Aramaic Scholarship in the Sixteenth Century" (PDF). Seeking Out the Wisdom of the Ancients. Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns. pp. 421–436.
- Chabot, Jean-Baptiste (1902). Synodicon orientale ou recueil de synodes nestoriens (PDF). Paris: Imprimerie Nationale.
- Chaillot, Christine (1998). The Syrian Orthodox Church of Antioch and All the East: A Brief Introduction to Its Life and Spirituality. Geneva: Inter-Orthodox dialogue.
- Daryaee, Touraj (2019). "The Sasanian Empire". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 33–43.
- Debié, Muriel (2009). "Syriac Historiography and Identity Formation". Church History and Religious Culture. 89 (1–3): 93–114. doi:10.1163/187124109X408014.
- Dickens, Mark (2019). "Syriac Christianity in Central Asia". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 583–624.
- Donabed, Sargon G.; Mako, Shamiran (2009). "Ethno-cultural and Religious Identity of Syrian Orthodox Christians" (PDF). Chronos: Revue d'Histoire de l'Université de Balamand. 19: 69–111.
- Donabed, Sargon G. (2015). Reforging a Forgotten History: Iraq and the Assyrians in the Twentieth Century. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 9780748686056.
- Fiey, Jean Maurice (1979) [1963]. Communautés syriaques en Iran et Irak des origines à 1552. London: Variorum Reprints. ISBN 9780860780519.
- Griffith, Sidney H. (1986). "Ephraem, the Deacon of Edessa, and the Church of the Empire". Diakonia: Studies in Honor of Robert T. Meyer. Washington: CUA Press. pp. 25–52.
- Griffith, Sidney H. (2002). "Christianity in Edessa and the Syriac-Speaking World: Mani, Bar Daysan, and Ephraem, the Struggle for Allegiance on the Aramean Frontier". Journal of the Canadian Society for Syriac Studies. 2: 5–20.
- Grillmeier, Aloys; Hainthaler, Theresia (2013). Christ in Christian Tradition: The Churches of Jerusalem and Antioch from 451 to 600. Vol. 2/3. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199212880.
- Haar Romeny, Bas ter (2012). "Ethnicity, Ethnogenesis and the Identity of Syriac Orthodox Christians". Visions of Community in the Post-Roman World: The West, Byzantium and the Islamic World, 300-1100. Farnham: Ashgate Publishing. pp. 183–204.
- Hainthaler, Theresia (2019). "Theological Doctrines and Debates within Syriac Christianity". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 377–390.
- Harvey, Susan A. (2019). "Women and Children in Syriac Christianity: Sounding Voices". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 554–566.
- Healey, John F. (2014). "Aramaean Heritage". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 391–402.
- Healey, John F. (2019a). "Arameans and Aramaic in Transition – Western Influences and the Roots of Aramean Christianity". Research on Israel and Aram: Autonomy, Independence and Related Issues. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. pp. 433–446.
- Healey, John F. (2019b). "The Pre-Christian Religions of the Syriac-Speaking Regions". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 47–67. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Herman, Geoffrey (2019). "The Syriac World in the Persian Empire". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 134–145.
- Hovorun, Cyril (2008). Will, Action and Freedom: Christological Controversies in the Seventh Century. Leiden-Boston: Brill.
- Hunter, Erica C. D. (2019). "Changing Demography: Christians in Iraq since 1991". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 783–796.
- Jakob, Joachim (2014). Ostsyrische Christen und Kurden im Osmanischen Reich des 19. und frühen 20. Jahrhunderts. Münster: LIT Verlag. ISBN 9783643506160.
- Jobling, William J. (1996). "New Evidence for the History of Indigenous Aramaic Christianity in Southern Jordan". Sydney Studies in Society and Culture. 12: 62–73.
- Jullien, Florence (2019). "Forms of the Religious Life and Syriac Monasticism". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 88–104. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Karim, Cyril Aphrem (2004). Symbols of the Cross in the Writings of the Early Syriac Fathers. Piscataway: Gorgias Press. ISBN 9781593332303.
- Kitchen, Robert A. (2012). "The Syriac Tradition". The Orthodox Christian World. London-New York: Routledge. pp. 66–77. ISBN 9781136314841.
- Khoury, Widad (2019). "Churches in Syriac Space: Architectural and Liturgical Context and Development". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 476–553.
- Loopstra, Jonathan A. (2019). "The Syriac Bible and its Interpretation". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 293–308.
- Loosley, Emma (2010). "Peter, Paul and James of Jerusalem: The Doctrinal and Political Evolution of the Eastern and Oriental Churches". Eastern Christianity in the Modern Middle East. London-New York: Routledge. pp. 1–12.
- Loosley, Emma (2019). "The Material Culture of the Syrian Peoples in Late Antiquity and the Evidence for Syrian Wall Paintings". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 460–475.
- Menze, Volker L. (2019). "The Establishment of the Syriac Churches". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 105–118. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Meyendorff, John (1989). Imperial unity and Christian divisions: The Church 450–680 A.D. Crestwood, NY: St. Vladimir's Seminary Press. ISBN 9780881410563.
- Millar, Fergus (2006). A Greek Roman Empire: Power and Belief under Theodosius II (408–450). Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520253919.
- Millar, Fergus (2013). "The Evolution of the Syrian Orthodox Church in the Pre-Islamic Period: From Greek to Syriac?" (PDF). Journal of Early Christian Studies. 21 (1): 43–92.
- Mingana, Alphonse (1926). "The Early Spread of Christianity in India" (PDF). Bulletin of the John Rylands Library. 10 (2): 435–514.
- Montgomery, Robert L. (2002). The Lopsided Spread of Christianity: Toward an Understanding of the Diffusion of Religions. Westport: Praeger Publishers.
- Murre van den Berg, Heleen (2007). "Syriac Christianity". The Blackwell Companion to Eastern Christianity. Malden: Blackwell. pp. 249–268. ISBN 9780470766392.
- Murre van den Berg, Heleen (2008). "Classical Syriac, Neo-Aramaic, and Arabic in the Church of the East and the Chaldean Church between 1500 and 1800". Aramaic in Its Historical and Linguistic Setting. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 335–352.
- Murre van den Berg, Heleen (2015). "Classical Syriac and the Syriac Churches: A Twentieth-Century History". Syriac Encounters: Papers from the Sixth North American Syriac Symposium. Louvain: Peeters Publishers. pp. 119–148.
- Murre-van den Berg, Heleen (2019). "Syriac Identity in the Modern Era". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 770–782.
- Nichols, Aidan (2010) [1992]. Rome and the Eastern Churches: A Study in Schism (2nd revised ed.). San Francisco: Ignatius Press.
- O’Mahony, Anthony (2006). "Syriac Christianity in the modern Middle East". The Cambridge History of Christianity: Eastern Christianity. Vol. 5. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 511–536. ISBN 9780521811132.
- Penn, Michael Philip (2019). "Early Syriac Reactions to the Rise of Islam". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 175–188. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Perczel, István (2019). "Syriac Christianity in India". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 653–697.
- Possekel, Ute (2019). "The Emergence of Syriac Literature to AD 400". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 309–326.
- Quispel, Gilles (2008). Gnostica, Judaica, Catholica: Collected Essays of Gilles Quispel. Leiden-Boston: Brill. ISBN 9789047441823.
- Robinson, Theodore H.; Coakley, James F. (2013) [1915]. Robinson's Paradigms and Exercises in Syriac Grammar (6th revised ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199687176.
- Rompay, Lucas van (2008). "The East: Syria and Mesopotamia". The Oxford Handbook of Early Christian Studies. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 365–386. ISBN 9780199271566.
- Ross, Steven K. (2001). Roman Edessa: Politics and Culture on the Eastern Fringes of the Roman Empire, 114-242 CE. London-New York: Routledge.
- Saint-Laurent, Jeanne-Nicole (2019). "Syriac Hagiographic Literature". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 339–354.
- Seleznyov, Nikolai N. (2008). "The Church of the East & Its Theology: History of Studies". Orientalia Christiana Periodica. 74 (1): 115-131.
- Seleznyov, Nikolai N. (2010). "Nestorius of Constantinople: Condemnation, Suppression, Veneration: With special reference to the role of his name in East-Syriac Christianity". Journal of Eastern Christian Studies. 62 (3–4): 165–190.
- Seleznyov, Nikolai N. (2013). "Jacobs and Jacobites: The Syrian Origins of the Name and its Egyptian Arabic Interpretations". Scrinium: Journal of Patrology, Critical Hagiographyand Ecclesiastical History. 9: 382-398.
- Simmons, Ernest (1959). The Fathers and Doctors of the Church. Milwaukee: Bruce Publishing Company.
- Takahashi, Hidemi (2019). "Syriac Christianity in China". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 625–652.
- Taylor, David G. K. (2019). "The Coming of Christianity to Mesopotamia". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 68–87. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Teule, Herman (2007). "Current Trends in Syriac Studies". Eastern Crossroads: Essays on Medieval Christian Legacy. Piscataway, NJ: Gorgias Press. pp. 387–400. doi:10.31826/9781463212827-024. ISBN 9781463212827.
- Varghese, Baby (2019). "The Liturgies of the Syriac Churches". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 391–404.
- Weltecke, Dorothea; Younansardaroud, Helen (2019). "The Renaissance of Syriac Literature in the Twelfth–Thirteenth Centuries". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 698–717.
- Watt, John W. (2019). "Syriac Philosophy". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 422–437.
- Wilmshurst, David (2019). "The Church of the East in the 'Abbasid Era". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 189–201.
- Winkler, Dietmar W. (2019). "The Syriac Church Denominations: An Overview". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 119–133. ISBN 9781138899018.
- Wood, Philip (2019). "Historiography in the Syriac-Speaking World, 300–1000". The Syriac World. London: Routledge. pp. 405–421.
External links
- Jacobite Syrian Church
- (in French) – Translation into English Syriac Christianity on WikiSyr
- (in French) – Translation into English Syriac Catholic Circle
- Qambel Maran- Syriac chants from South India- a review and liturgical music tradition of Syriac Christians revisited
- Traditions and rituals among the Syrian Christians of Kerala
- Audio Aramaic-Bible
- The Center for the Study of Christianity: A Comprehensive Bibliography on Syriac Christianity




