Trøndelag
Trøndelag fylke
Trööndelagen fylhkentjïelte | |
|---|---|
 Seierstad in July 2007 | |
 Trøndelag within Norway | |
| Coordinates: 63°25′37″N 10°23′35″E / 63.42694°N 10.39306°E | |
| Country | Norway |
| County | Trøndelag |
| Region | Central Norway |
| County ID | NO-50 |
| Established | 1 Jan 2018 |
| Administrative centres | Steinkjer (county municipality, county governor) Trondheim (county mayor) |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Frank Jenssen H (2018–present) |
| • County mayor | Tore O. Sandvik Ap (2018–present) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 42,201.59 km2 (16,294.12 sq mi) |
| • Land | 39,493.28 km2 (15,248.44 sq mi) |
| • Water | 2,708.31 km2 (1,045.68 sq mi) 6.4% |
| • Rank | #3 in Norway |
| Population (2020)[2] | |
| • Total | 468,702 |
| • Rank | 5 |
| • Density | 11/km2 (29/sq mi) |
| • Change (10 years) | 10.4% |
| Demonym | Trønder |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Official language form | Neutral |
| Website | www |
Trøndelag (Norwegian pronunciation: [ˈtrœ̂ndəlɑːɡ])[3][4] (Southern Sami: Trööndelage) is a county in the central part of Norway. It was created in 1687, then named Trondhjem County (Norwegian: Trondhjems Amt); in 1804 the county was split into Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag by the King of Denmark-Norway, and the counties were reunited in 2018 after a vote of the two counties in 2016.[5][6]
The largest city in Trøndelag is the city of Trondheim. The administrative centre is Steinkjer, while Trondheim functions as the office of the county mayor.[7] Both cities serve the office of the county governor; however, Steinkjer houses the main functions.[8]
Trøndelag county and the neighbouring Møre og Romsdal county together form what is known as Central Norway. A person from Trøndelag is called a trønder. The dialect spoken in the area, trøndersk, is characterized by dropping out most vowel endings; see apocope.
Trøndelag is one of the most fertile regions of Norway, with large agricultural output. The majority of the production ends up in the Norwegian cooperative system for meat and milk, but farm produce is a steadily growing business.
Name
The Old Norse form of the name was Þrǿndalǫg. The first element is the genitive plural of þrǿndr which means "person from Trøndelag", while the second is lǫg (plural of lag which means "law; district/people with a common law" (compare Danelaw, Gulaþingslǫg and Njarðarlǫg). A parallel name for the same district was Þróndheimr which means "the homeland (heim) of the þrǿndr".[9] Þróndheimr may be older since the first element has a stem form without umlaut.
History
People have lived in this region for thousands of years. In the early iron-age Trøndelag was divided into several petty kingdoms called fylki. The different fylki had a common law, and an early parliament or thing. It was called Frostating and was held at the Frosta-peninsula. By some this is regarded as the first real democracy.
In the time after Håkon Grjotgardsson (838-900), Trøndelag was ruled by the Jarl of Lade. Lade is located in the eastern part of Trondheim, bordering the Trondheimsfjord. The powerful Jarls of Lade continued to play a very significant political role in Norway up to 1030.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1769 | 78,274 | — |
| 1951 | 307,635 | +293.0% |
| 1960 | 327,127 | +6.3% |
| 1970 | 350,297 | +7.1% |
| 1980 | 368,942 | +5.3% |
| 1990 | 377,202 | +2.2% |
| 2000 | 389,960 | +3.4% |
| 2010 | 422,102 | +8.2% |
| 2020 | 468,702 | +11.0% |
| Source: Statistics Norway [1][2][3][4]. 2017 data[2] | ||
Jarls of Lade (Ladejarl) were:
- Håkon Grjotgardsson, the first jarl of Lade.
- Sigurd Håkonsson, son of Håkon. Killed by Harald Greyhide.
- Håkon Sigurdsson, son of Sigurd. Conspired with Harald Bluetooth against Harald Greyhide, and subsequently became vassal of Harald Bluetooth, and in reality independent ruler of Norway. After the arrival of Olaf Trygvason, Håkon quickly lost all support, and was killed by his own slave, Tormod Kark, in 995.
- Eirik Håkonsson, son of Håkon. Together with his brother, Svein, governor of Norway under Sweyn Forkbeard of Denmark from 1000 to 1012.
- Håkon Eiriksson, son of Eirik. Governor of Norway under Sweyn Forkbeard of Denmark from 1012 to 1015.

Trøndelag (together with parts of Møre og Romsdal) was briefly ceded in 1658 to Sweden in the Treaty of Roskilde and was ruled by king Charles X until it was returned to Denmark-Norway after the Treaty of Copenhagen in 1660. During that time, the Swedes conscripted 2,000 men in Trøndelag, forcing young boys down to 15 years of age to join the Swedish armies fighting against Poland and Brandenburg. Charles X feared the Trønders would rise against their Swedish occupiers, and thought it wise to keep a large part of the men away. Only about one third of the men ever returned to their homes; some of them were forced to settle in the then Swedish Duchy of Estonia, as the Swedes thought it would be easier to rule the Trønders there, utilising the ancient maxim of divide and rule.[12]
In the fall of 1718, during the Great Northern War, General Carl Gustaf Armfeldt was ordered by king Charles XII of Sweden to lead a Swedish army of 10,000 men into Trøndelag and take Trondheim. Because of his poor supply lines back to Sweden, Armfeldt's army had to live off the land, causing great suffering to the people of the region. Armfeldt's campaign failed: the defenders of Trondheim succeeded in repelling his siege. After Charles XII was killed in the siege of Fredriksten in Norway's southeast, Armfeldt was ordered back into Sweden. During the ensuing retreat, his 6,000 surviving threadbare and starving Caroleans were caught in a fierce blizzard. Thousands of Caroleans froze to death in the Norwegian mountains, and hundreds more were crippled for life.[13]

Government
The county is governed by the Trøndelag County Municipality. The town of Steinkjer is the seat of the county governor and county administration. Both the county governor and Trøndelag County Municipality, however, also have offices in Trondheim.
The county oversees the 41 upper secondary schools, including nine private schools. Six of the schools have more than 1000 students: four in Trondheim plus the Steinkjer Upper Secondary School and the Ole Vig Upper Secondary School in Stjørdalshalsen. The county has ten Folk high schools, with an eleventh folk high school being possibly being opened in Røros, with a possible start in 2019.[14]
Districts
The county is often sub-divided into several geographical regions:
- Namdal, the greater Namsen river valley
- Fosen, the Fosen peninsula and surrounding areas
- Innherred, the areas surrounding the inner Trondheimsfjorden
- Stjørdalen, the Stjørdalen valley
- Trondheim Region, the areas surrounding the large city of Trondheim
- Gauldalen, the Gaula river valley
- Orkdalen, the Orklaelva river valley
Towns and cities
There are nine towns/cities in Trøndelag, plus the "mining town" of Røros.
- Trondheim (in Trondheim municipality)
- Steinkjer (in Steinkjer municipality)
- Stjørdalshalsen (in Stjørdal municipality)
- Levanger (in Levanger municipality)
- Namsos (in Namsos municipality)
- Verdalsøra (in Verdal municipality)
- Orkanger (in Orkdal municipality)
- Brekstad (in Ørland municipality)
- Kolvereid (in Nærøy municipality)
- Bergstaden Røros (in Røros municipality)
Trøndelag
There are 38 municipalities in Trøndelag.[15]
| Municipal Number |
Name | Adm. Centre | Location in the county |
Established | Old Municipal No. (before 2020) |
Former County |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5001 | Trondheim |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 5001 Trondheim 5030 Klæbu |
Trøndelag | |
| 5006 | Steinkjer |  |
23 Jan 1858 | 5006 Steinkjer 5039 Verran | ||
| 5007 | Namsos | 1 Jan 1846 | 5005 Namsos 5040 Namdalseid 5048 Fosnes | |||
| 5014 | Sistranda |  |
1 Jan 1964 | 1620 Frøya | Sør-Trøndelag | |
| 5020 | Steinsdalen |  |
1 June 1892 | 1633 Osen | ||
| 5021 | Oppdal |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1634 Oppdal | ||
| 5022 | Berkåk |  |
1 Jan 1839 | 1635 Rennebu | ||
| 5025 | Røros |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1640 Røros | ||
| 5026 | Renbygda |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1644 Holtålen | ||
| 5027 | Støren |  |
1 Jan 1964 | 1648 Midtre Gauldal | ||
| 5028 | Melhus |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1653 Melhus | ||
| 5029 | Børsa |  |
1 Jan 1890 | 1657 Skaun | ||
| 5031 | Hommelvik |  |
1 Jan 1891 | 1663 Malvik | ||
| 5032 | Mebonden |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1664 Selbu | ||
| 5033 | Ås |  |
1 Jan 1901 | 1665 Tydal | ||
| 5034 | Midtbygda | 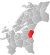 |
1 Jan 1874 | 1711 Meråker | Nord-Trøndelag | |
| 5035 | Stjørdalshalsen | 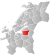 |
1 Jan 1902 | 1714 Stjørdal | ||
| 5036 | Frosta |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1717 Frosta | ||
| 5037 | Levanger | 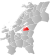 |
1 Jan 1838 | 1719 Levanger | ||
| 5038 | Verdalsøra |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1721 Verdal | ||
| 5041 | Snåsa | 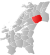 |
1 Jan 1838 | 1736 Snåsa | ||
| 5042 | Sandvika |  |
1 Jan 1964 | 1738 Lierne | ||
| 5043 | Røyrvik |  |
1 July 1923 | 1739 Røyrvik | ||
| 5044 | Namsskogan | 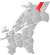 |
1 July 1923 | 1740 Namsskogan | ||
| 5045 | Medjå | 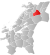 |
1 Jan 1838 | 1742 Grong | ||
| 5046 | Høylandet |  |
1 Jan 1901 | 1743 Høylandet | ||
| 5047 | Ranemsletta | 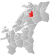 |
1 Jan 1838 | 1744 Overhalla | ||
| 5049 | Lauvsnes |  |
1 Jan 1871 | 1749 Flatanger | ||
| 5052 | Leknes |  |
1 Oct 1860 | 1755 Leka | ||
| 5053 | Straumen |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 1756 Inderøy | ||
| 5054 | Årnset | 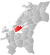 |
1 Jan 2018 | 1624 Rissa | Sør-Trøndelag | |
| 1718 Leksvik | Nord-Trøndelag | |||||
| 5055 | File:Heim komm.png Heim | Kyrksæterøra |  |
1 Jan 2020 | 1571 Halsa | Møre og Romsdal |
| 5011 Hemne 5012 Snillfjord (part) |
Trøndelag | |||||
| 5056 | Fillan |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 5013 Hitra 5012 Snillfjord (part) | ||
| 5057 | Botngård |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 5015 Ørland 5017 Bjugn | ||
| 5058 | Årnes |  |
1 Jan 1838 | 5018 Åfjord 5019 Roan | ||
| 5059 | Orkanger |  |
1 Jan 2020 | 5012 Snillfjord (part) 5016 Agdenes 5023 Meldal 5024 Orkdal | ||
| 5060 | Kolvereid and Rørvik |
 |
1 Jan 2020 | 5050 Vikna 5051 Nærøy | ||
| 5061 | Rindal |  |
1 Jan 1858 | 1567 Rindal | Møre og Romsdal |
Culture
Arts
The region's official theatre is the Trøndelag Teater in Trondheim.[16] At Stiklestad in Verdal, the historical play called The Saint Olav Drama has been played each year since 1954. It depicts the last days of Saint Olaf.
Jazz on a very high level is frequently heard in Trondheim, due to the high-level jazz education in Trondheim. Trondheim is also the national centre of rock music; the popular music museum Rockheim opened there in 2010. Trøndelag is also known for its local variety of rock music, often performed in local dialect, called "trønderrock".
Food and drink
The region is popularly known for its moonshine homebrew, called karsk. Although officially prohibited, the art of producing as pure home-made spirits as possible still has a strong following in parts of Trøndelag. Traditionally served mixed with coffee, local variations apply. In southern regions, people tend to use normal filter coffee, while in the north they choose to serve karsk with as weak coffee as possible.

The "official dish" of the region is sodd which is made from sheep or beef meat and meatballs in boiled stock. The Norwegian Grey Troender sheep is an endangered breed of domesticated sheep that originated from Trøndelag in the late 19th century. There are currently approximately 50 individual animals remaining and efforts are being made to revive the breed.
See also
References
- ^ Statistisk sentralbyrå (2020). "09280: Area of land and fresh water (km²) (M)" (in Norwegian).
- ^ a b Statistisk sentralbyrå (2020). "Table: 06913: Population 1 January and population changes during the calendar year (M)" (in Norwegian).
- ^ Berulfsen, Bjarne (1969). Norsk Uttaleordbok (in Norwegian). Oslo: H. Aschehoug & Co (W Nygaard). p. 336.
- ^ Vanvik, Arne (1985). Norsk Uttaleordbok: A Norwegian pronouncing dictionary (in Norwegian and English). Oslo: Fonetisk institutt, Universitetet i Oslo. p. 311. ISBN 978-8299058414.
- ^ Hofstad, Sigrun (2016-04-27). "Her bankes det for et samlet Trøndelag". NRK (in Norwegian).
- ^ "Trøndelag fylke: English". Trøndelag fylke. Retrieved 2018-01-01.
- ^ "Fakta om Trøndelag". www.trondelagfylke.no (in Norwegian Bokmål). Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- ^ "Om oss". Trøndelag (in Norwegian Bokmål). Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- ^ Sandnes, Jørn; Stemshaug, Ola (1980). Norsk stadnamnleksikon. pp. 322–323.
- ^ Statistics Norway - Church of Norway. Archived 2012-07-16 at archive.today
- ^ Statistics Norway - Members of religious and life stance communities outside the Church of Norway, by religion/life stance. County. 2006-2010
- ^ Gjerset, Knut (1915). History of the Norwegian People, Volumes II. The MacMillan Company. pp. 318–320.
- ^ "Historien" (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2009-04-07.
- ^ Olsen Haugen, Morten, ed. (2018-03-10). "Trøndelag". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 2018-05-05.
- ^ List of Norwegian municipality numbers
- ^ Haugan, Trond E (2008). Byens magiske rom: Historien om Trondheim kino. Tapir Akademisk Forlag. ISBN 9788251922425.)



