Hassium
| Hassium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈhæsiəm/ [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mass number | [271] (data not decisive)[a] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hassium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | d-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d6 7s2[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 14, 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid (predicted)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 27–29 g/cm3 (predicted)[6][7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: (none) (+3), (+4), (+6), (+8)[8] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 126 pm (estimated)[10] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 134 pm (estimated)[11] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | synthetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | hexagonal close-packed (hcp) (predicted)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 54037-57-9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after Hassia, Latin for Hesse, Germany, where it was discovered[12] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (1984) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of hassium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hassium is a chemical element with the symbol Hs and the atomic number 108. Hassium is highly radioactive; the most stable known isotope, 269Hs, has a half-life of approximately 16 seconds. One of its isotopes, 270Hs, has magic numbers of both protons and neutrons for deformed nuclei, which gives it greater stability against spontaneous fission. Hassium has only been produced in a laboratory, in very small quantities. Natural occurrences of the element have been hypothesised, but none has ever been found.
The first attempts to synthesize element 108 were made in two different experiments at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union, in 1978. More attempts were made at the same venue in 1983 and then in 1984; the latter resulted in a claim that element 108 had been produced. Later in 1984, a synthesis claim followed from the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI) in Darmstadt, Hesse, West Germany. The 1993 report by the Transfermium Working Group, formed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry and the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics, concluded the report from Darmstadt was more conclusive on its own and the major credit was assigned to the German scientists. Following the recognition, GSI formally announced they wished to name the element hassium after the German state of Hesse home to the facility. Two rulings from the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) followed in 1994 and 1995 to establish permanent names of a series of elements that included element 108; both were met with rejection by competing scientists and scrapped. A third ruling, published in 1997, named the element hassium per the original suggestion by GSI; it was accepted by the scientific community and the name was established as final.
In the periodic table of elements, hassium is a transactinide element, a member of the 7th period and group 8; it is thus the sixth member of the 6d series of transition metals. Chemistry experiments have confirmed that hassium behaves as the heavier homologue to osmium, reacting readily with oxygen to form a volatile tetroxide. The chemical properties of hassium have only been partly characterized, but they compare well with the chemistry of the other group 8 elements.
Introduction to the heaviest elements
Superheavy elements, also known as transactinide elements, transactinides, or super-heavy elements, or superheavies for short, are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 104.[14] The superheavy elements are those beyond the actinides in the periodic table; the last actinide is lawrencium (atomic number 103). By definition, superheavy elements are also transuranium elements, i.e., having atomic numbers greater than that of uranium (92). Depending on the definition of group 3 adopted by authors, lawrencium may also be included to complete the 6d series.[15][16][17][18]
Glenn T. Seaborg first proposed the actinide concept, which led to the acceptance of the actinide series. He also proposed a transactinide series ranging from element 104 to 121 and a superactinide series approximately spanning elements 122 to 153 (though more recent work suggests the end of the superactinide series to occur at element 157 instead). The transactinide seaborgium was named in his honor.[19][20]
Superheavies are radioactive and have only been obtained synthetically in laboratories. No macroscopic sample of any of these elements has ever been produced. Superheavies are all named after physicists and chemists or important locations involved in the synthesis of the elements.
IUPAC defines an element to exist if its lifetime is longer than 10−14 seconds, which is the time it takes for the atom to form an electron cloud.[21]
The known superheavies form part of the 6d and 7p series in the periodic table. Except for rutherfordium and dubnium (and lawrencium if it is included), even the longest-lived known isotopes of superheavies have half-lives of minutes or less. The element naming controversy involved elements 102–109. Some of these elements thus used systematic names for many years after their discovery was confirmed. (Usually the systematic names are replaced with permanent names proposed by the discoverers relatively soon after a discovery has been confirmed.)
Introduction
Synthesis of superheavy nuclei
A superheavy[b] atomic nucleus is created in a nuclear reaction that combines two other nuclei of unequal size[c] into one; roughly, the more unequal the two nuclei in terms of mass, the greater the possibility that the two react.[27] The material made of the heavier nuclei is made into a target, which is then bombarded by the beam of lighter nuclei. Two nuclei can only fuse into one if they approach each other closely enough; normally, nuclei (all positively charged) repel each other due to electrostatic repulsion. The strong interaction can overcome this repulsion but only within a very short distance from a nucleus; beam nuclei are thus greatly accelerated in order to make such repulsion insignificant compared to the velocity of the beam nucleus.[28] The energy applied to the beam nuclei to accelerate them can cause them to reach speeds as high as one-tenth of the speed of light. However, if too much energy is applied, the beam nucleus can fall apart.[28]
Coming close enough alone is not enough for two nuclei to fuse: when two nuclei approach each other, they usually remain together for about 10−20 seconds and then part ways (not necessarily in the same composition as before the reaction) rather than form a single nucleus.[28][29] This happens because during the attempted formation of a single nucleus, electrostatic repulsion tears apart the nucleus that is being formed.[28] Each pair of a target and a beam is characterized by its cross section—the probability that fusion will occur if two nuclei approach one another expressed in terms of the transverse area that the incident particle must hit in order for the fusion to occur.[d] This fusion may occur as a result of the quantum effect in which nuclei can tunnel through electrostatic repulsion. If the two nuclei can stay close past that phase, multiple nuclear interactions result in redistribution of energy and an energy equilibrium.[28]
| External videos | |
|---|---|
The resulting merger is an excited state[32]—termed a compound nucleus—and thus it is very unstable.[28] To reach a more stable state, the temporary merger may fission without formation of a more stable nucleus.[33] Alternatively, the compound nucleus may eject a few neutrons, which would carry away the excitation energy; if the latter is not sufficient for a neutron expulsion, the merger would produce a gamma ray. This happens in about 10−16 seconds after the initial nuclear collision and results in creation of a more stable nucleus.[33] The definition by the IUPAC/IUPAP Joint Working Party (JWP) states that a chemical element can only be recognized as discovered if a nucleus of it has not decayed within 10−14 seconds. This value was chosen as an estimate of how long it takes a nucleus to acquire electrons and thus display its chemical properties.[34][e]
Decay and detection
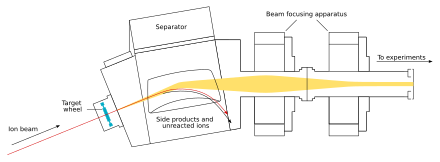
The beam passes through the target and reaches the next chamber, the separator; if a new nucleus is produced, it is carried with this beam.[36] In the separator, the newly produced nucleus is separated from other nuclides (that of the original beam and any other reaction products)[f] and transferred to a surface-barrier detector, which stops the nucleus. The exact location of the upcoming impact on the detector is marked; also marked are its energy and the time of the arrival.[36] The transfer takes about 10−6 seconds; in order to be detected, the nucleus must survive this long.[39] The nucleus is recorded again once its decay is registered, and the location, the energy, and the time of the decay are measured.[36]
Stability of a nucleus is provided by the strong interaction. However, its range is very short; as nuclei become larger, its influence on the outermost nucleons (protons and neutrons) weakens. At the same time, the nucleus is torn apart by electrostatic repulsion between protons, and its range is not limited.[40] Total binding energy provided by the strong interaction increases linearly with the number of nucleons, whereas electrostatic repulsion increases with the square of the atomic number, i.e. the latter grows faster and becomes increasingly important for heavy and superheavy nuclei.[41][42] Superheavy nuclei are thus theoretically predicted[43] and have so far been observed[44] to predominantly decay via decay modes that are caused by such repulsion: alpha decay and spontaneous fission.[g] Almost all alpha emitters have over 210 nucleons,[46] and the lightest nuclide primarily undergoing spontaneous fission has 238.[47] In both decay modes, nuclei are inhibited from decaying by corresponding energy barriers for each mode, but they can be tunneled through.[41][42]
Alpha particles are commonly produced in radioactive decays because the mass of an alpha particle per nucleon is small enough to leave some energy for the alpha particle to be used as kinetic energy to leave the nucleus.[49] Spontaneous fission is caused by electrostatic repulsion tearing the nucleus apart and produces various nuclei in different instances of identical nuclei fissioning.[42] As the atomic number increases, spontaneous fission rapidly becomes more important: spontaneous fission partial half-lives decrease by 23 orders of magnitude from uranium (element 92) to nobelium (element 102),[50] and by 30 orders of magnitude from thorium (element 90) to fermium (element 100).[51] The earlier liquid drop model thus suggested that spontaneous fission would occur nearly instantly due to disappearance of the fission barrier for nuclei with about 280 nucleons.[42][52] The later nuclear shell model suggested that nuclei with about 300 nucleons would form an island of stability in which nuclei will be more resistant to spontaneous fission and will primarily undergo alpha decay with longer half-lives.[42][52] Subsequent discoveries suggested that the predicted island might be further than originally anticipated; they also showed that nuclei intermediate between the long-lived actinides and the predicted island are deformed, and gain additional stability from shell effects.[53] Experiments on lighter superheavy nuclei,[54] as well as those closer to the expected island,[50] have shown greater than previously anticipated stability against spontaneous fission, showing the importance of shell effects on nuclei.[h]
Alpha decays are registered by the emitted alpha particles, and the decay products are easy to determine before the actual decay; if such a decay or a series of consecutive decays produces a known nucleus, the original product of a reaction can be easily determined.[i] (That all decays within a decay chain were indeed related to each other is established by the location of these decays, which must be in the same place.)[36] The known nucleus can be recognized by the specific characteristics of decay it undergoes such as decay energy (or more specifically, the kinetic energy of the emitted particle).[j] Spontaneous fission, however, produces various nuclei as products, so the original nuclide cannot be determined from its daughters.[k]
The information available to physicists aiming to synthesize a superheavy element is thus the information collected at the detectors: location, energy, and time of arrival of a particle to the detector, and those of its decay. The physicists analyze this data and seek to conclude that it was indeed caused by a new element and could not have been caused by a different nuclide than the one claimed. Often, provided data is insufficient for a conclusion that a new element was definitely created and there is no other explanation for the observed effects; errors in interpreting data have been made.[l]
History
Early predictions
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
The heaviest element known at the end of the 19th century was uranium, with an atomic mass of about 240 (now known to be 238) amu. Accordingly, it was placed in the last row of the periodic table; this fueled speculation about the possible existence of elements heavier than uranium and why A = 240 seemed to be the limit. Following the discovery of the noble gases, beginning with argon in 1895, the possibility of heavier members of the group was considered. Danish chemist Julius Thomsen proposed in 1895 the existence of a sixth noble gas with Z = 86, A = 212 and a seventh with Z = 118, A = 292, the last closing a 32-element period containing thorium and uranium.[65] In 1913, Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg extended Thomsen's extrapolation of the periodic table to include even heavier elements with atomic numbers up to 460, but he did not believe that these superheavy elements existed or occurred in nature.[66]
In 1914, German physicist Richard Swinne proposed that elements heavier than uranium, such as those around Z = 108, could be found in cosmic rays. He suggested that these elements may not necessarily have decreasing half-lives with increasing atomic number, leading to speculation about the possibility of some longer-lived elements at Z = 98–102 and Z = 108–110 (though separated by short-lived elements). Swinne published these predictions in 1926, believing that such elements might exist in Earth's core, iron meteorites, or the ice caps of Greenland where they had been locked up from their supposed cosmic origin.[67]
Discoveries
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
Work performed from 1961 to 2013 at four labs – Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in the US, the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in the USSR (later Russia), the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Germany, and Riken in Japan – identified and confirmed the elements lawrencium to oganesson according to the criteria of the IUPAC–IUPAP Transfermium Working Groups and subsequent Joint Working Parties. These discoveries complete the seventh row of the periodic table. The next two elements, ununennium (Z = 119) and unbinilium (Z = 120), have not yet been synthesized. They would begin an eighth period.
List of elements
- 103 Lawrencium, Lr, for Ernest Lawrence; sometimes but not always included[15][16]
- 104 Rutherfordium, Rf, for Ernest Rutherford
- 105 Dubnium, Db, for the town of Dubna, near Moscow
- 106 Seaborgium, Sg, for Glenn T. Seaborg
- 107 Bohrium, Bh, for Niels Bohr
- 108 Hassium, Hs, for Hassia (Hesse), location of Darmstadt
- 109 Meitnerium, Mt, for Lise Meitner
- 110 Darmstadtium, Ds, for Darmstadt)
- 111 Roentgenium, Rg, for Wilhelm Röntgen
- 112 Copernicium, Cn, for Nicolaus Copernicus
- 113 Nihonium, Nh, for Nihon (Japan), location of the Riken institute
- 114 Flerovium, Fl, for Russian physicist Georgy Flyorov
- 115 Moscovium, Mc, for Moscow
- 116 Livermorium, Lv, for Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- 117 Tennessine, Ts, for Tennessee, location of Oak Ridge National Laboratory
- 118 Oganesson, Og, for Russian physicist Yuri Oganessian
Characteristics
Due to their short half-lives (for example, the most stable known isotope of seaborgium has a half-life of 14 minutes, and half-lives decrease with increasing atomic number) and the low yield of the nuclear reactions that produce them, new methods have had to be created to determine their gas-phase and solution chemistry based on very small samples of a few atoms each. Relativistic effects become very important in this region of the periodic table, causing the filled 7s orbitals, empty 7p orbitals, and filling 6d orbitals to all contract inward toward the atomic nucleus. This causes a relativistic stabilization of the 7s electrons and makes the 7p orbitals accessible in low excitation states.[20]
Elements 103 to 112, lawrencium to copernicium, form the 6d series of transition elements. Experimental evidence shows that elements 103–108 behave as expected for their position in the periodic table, as heavier homologs of lutetium through osmium. They are expected to have ionic radii between those of their 5d transition metal homologs and their actinide pseudohomologs: for example, Rf4+ is calculated to have ionic radius 76 pm, between the values for Hf4+ (71 pm) and Th4+ (94 pm). Their ions should also be less polarizable than those of their 5d homologs. Relativistic effects are expected to reach a maximum at the end of this series, at roentgenium (element 111) and copernicium (element 112). Nevertheless, many important properties of the transactinides are still not yet known experimentally, though theoretical calculations have been performed.[20]
Elements 113 to 118, nihonium to oganesson, should form a 7p series, completing the seventh period in the periodic table. Their chemistry will be greatly influenced by the very strong relativistic stabilization of the 7s electrons and a strong spin–orbit coupling effect "tearing" the 7p subshell apart into two sections, one more stabilized (7p1/2, holding two electrons) and one more destabilized (7p3/2, holding four electrons). Lower oxidation states should be stabilized here, continuing group trends, as both the 7s and 7p1/2 electrons exhibit the inert-pair effect. These elements are expected to largely continue to follow group trends, though with relativistic effects playing an increasingly larger role. In particular, the large 7p splitting results in an effective shell closure at flerovium (element 114) and a hence much higher than expected chemical activity for oganesson (element 118).[20]
Element 118 is the last element that has been synthesized. The next two elements, 119 and 120, should form an 8s series and be an alkali and alkaline earth metal respectively. The 8s electrons are expected to be relativistically stabilized, so that the trend toward higher reactivity down these groups will reverse and the elements will behave more like their period 5 homologs, rubidium and strontium. The 7p3/2 orbital is still relativistically destabilized, potentially giving these elements larger ionic radii and perhaps even being able to participate chemically. In this region, the 8p electrons are also relativistically stabilized, resulting in a ground-state 8s28p1 valence electron configuration for element 121. Large changes are expected to occur in the subshell structure in going from element 120 to element 121: for example, the radius of the 5g orbitals should drop drastically, from 25 Bohr units in element 120 in the excited [Og] 5g1 8s1 configuration to 0.8 Bohr units in element 121 in the excited [Og] 5g1 7d1 8s1 configuration, in a phenomenon called "radial collapse". Element 122 should add either a further 7d or a further 8p electron to element 121's electron configuration. Elements 121 and 122 should be similar to actinium and thorium respectively.[20]
At element 121, the superactinide series is expected to begin, when the 8s electrons and the filling 8p1/2, 7d3/2, 6f5/2, and 5g7/2 subshells determine the chemistry of these elements. Complete and accurate calculations are not available for elements beyond 123 because of the extreme complexity of the situation:[68] the 5g, 6f, and 7d orbitals should have about the same energy level, and in the region of element 160 the 9s, 8p3/2, and 9p1/2 orbitals should also be about equal in energy. This will cause the electron shells to mix so that the block concept no longer applies very well, and will also result in novel chemical properties that will make positioning these elements in a periodic table very difficult.[20]
Beyond superheavy elements
It has been suggested that elements beyond Z = 126 be called beyond superheavy elements.[69] Other sources refer to elements around Z = 164 as hyperheavy elements.[70]
See also
- Bose–Einstein condensate (also known as Superatom)
- Island of stability
Notes
- ^ The most stable isotope of hassium cannot be determined based on existing data due to uncertainty that arises from the low number of measurements. The half-life of 271Hs corresponding to one standard deviation is, based on existing data, 46+56
−16 seconds, whereas that of 269Hs is 13+10
−4 seconds; these measurements have overlapping confidence intervals. It is also possible that 277mHs is more stable than both of these, with its half-life likely being 110±70 seconds, but only one event of decay of this isotope has been registered as of 2016[update].[2][3] - ^ In nuclear physics, an element is called heavy if its atomic number is high; lead (element 82) is one example of such a heavy element. The term "superheavy elements" typically refers to elements with atomic number greater than 103 (although there are other definitions, such as atomic number greater than 100[22] or 112;[23] sometimes, the term is presented an equivalent to the term "transactinide", which puts an upper limit before the beginning of the hypothetical superactinide series).[24] Terms "heavy isotopes" (of a given element) and "heavy nuclei" mean what could be understood in the common language—isotopes of high mass (for the given element) and nuclei of high mass, respectively.
- ^ In 2009, a team at the JINR led by Oganessian published results of their attempt to create hassium in a symmetric 136Xe + 136Xe reaction. They failed to observe a single atom in such a reaction, putting the upper limit on the cross section, the measure of probability of a nuclear reaction, as 2.5 pb.[25] In comparison, the reaction that resulted in hassium discovery, 208Pb + 58Fe, had a cross section of ~20 pb (more specifically, 19+19
-11 pb), as estimated by the discoverers.[26] - ^ The amount of energy applied to the beam particle to accelerate it can also influence the value of cross section. For example, in the 28
14Si
+ 1
0n
→ 28
13Al
+ 1
1p
reaction, cross section changes smoothly from 370 mb at 12.3 MeV to 160 mb at 18.3 MeV, with a broad peak at 13.5 MeV with the maximum value of 380 mb.[30] - ^ This figure also marks the generally accepted upper limit for lifetime of a compound nucleus.[35]
- ^ This separation is based on that the resulting nuclei move past the target more slowly then the unreacted beam nuclei. The separator contains electric and magnetic fields whose effects on a moving particle cancel out for a specific velocity of a particle.[37] Such separation can also be aided by a time-of-flight measurement and a recoil energy measurement; a combination of the two may allow to estimate the mass of a nucleus.[38]
- ^ Not all decay modes are caused by electrostatic repulsion. For example, beta decay is caused by the weak interaction.[45]
- ^ It was already known by the 1960s that ground states of nuclei differed in energy and shape as well as that certain magic numbers of nucleons corresponded to greater stability of a nucleus. However, it was assumed that there was no nuclear structure in superheavy nuclei as they were too deformed to form one.[50]
- ^ Since mass of a nucleus is not measured directly but is rather calculated from that of another nucleus, such measurement is called indirect. Direct measurements are also possible, but for the most part they have remained unavailable for superheavy nuclei.[55] The first direct measurement of mass of a superheavy nucleus was reported in 2018 at LBNL.[56] Mass was determined from the location of a nucleus after the transfer (the location helps determine its trajectory, which is linked to the mass-to-charge ratio of the nucleus, since the transfer was done in presence of a magnet).[57]
- ^ If the decay occurred in a vacuum, then since total momentum of an isolated system before and after the decay must be preserved, the daughter nucleus would also receive a small velocity. The ratio of the two velocities, and accordingly the ratio of the kinetic energies, would thus be inverse to the ratio of the two masses. The decay energy equals the sum of the known kinetic energy of the alpha particle and that of the daughter nucleus (an exact fraction of the former).[46] The calculations hold for an experiment as well, but the difference is that the nucleus does not move after the decay because it is tied to the detector.
- ^ Spontaneous fission was discovered by Soviet physicist Georgy Flerov,[58] a leading scientist at JINR, and thus it was a "hobbyhorse" for the facility.[59] In contrast, the LBL scientists believed fission information was not sufficient for a claim of synthesis of an element. They believed spontaneous fission had not been studied enough to use it for identification of a new element, since there was a difficulty of establishing that a compound nucleus had only ejected neutrons and not charged particles like protons or alpha particles.[35] They thus preferred to link new isotopes to the already known ones by successive alpha decays.[58]
- ^ For instance, element 102 was mistakenly identified in 1957 at the Nobel Institute of Physics in Stockholm, Stockholm County, Sweden.[60] There were no earlier definitive claims of creation of this element, and the element was assigned a name by its Swedish, American, and British discoverers, nobelium. It was later shown that the identification was incorrect.[61] The following year, RL was unable to reproduce the Swedish results and announced instead their synthesis of the element; that claim was also disproved later.[61] JINR insisted that they were the first to create the element and suggested a name of their own for the new element, joliotium;[62] the Soviet name was also not accepted (JINR later referred to the naming of the element 102 as "hasty").[63] This name was proposed to IUPAC in a written response to their ruling on priority of discovery claims of elements, signed 29 September 1992.[63] The name "nobelium" remained unchanged on account of its widespread usage.[64]
References
- ^ Hassium. The Periodic Table of Videos. University of Nottingham. 28 January 2011. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- ^ "Radioactive Elements". Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights. 2018. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, p. 030001-136.
- ^ Hoffman, Lee & Pershina 2006, p. 1672.
- ^ a b Östlin, A. (2013). "Transition metals". Electronic Structure Studies and Method Development for Complex Materials (PDF) (Licentiate). pp. 15–16. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Gyanchandani, Jyoti; Sikka, S. K. (10 May 2011). "Physical properties of the 6 d -series elements from density functional theory: Close similarity to lighter transition metals". Physical Review B. 83 (17): 172101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.83.172101.
- ^ Kratz; Lieser (2013). Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications (3rd ed.). p. 631.
- ^ Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". In Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ Hoffman, Lee & Pershina 2006, p. 1673.
- ^ Hoffman, Lee & Pershina 2006, p. 1691.
- ^ Robertson, M. (2011). "Chemical Data: Hassium". Visual Elements Periodic Table. Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 28 November 2012.
- ^ Emsley, J. (2011). Nature's Building Blocks: An A–Z Guide to the Elements (New ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 215–217. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ "Superheavy Element Discovery | Glenn T. Seaborg Institute". seaborg.llnl.gov. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ a b Neve, Francesco (2022). "Chemistry of superheavy transition metals". Journal of Coordination Chemistry. 75 (17–18): 2287–2307. doi:10.1080/00958972.2022.2084394. S2CID 254097024.
- ^ a b Mingos, Michael (1998). Essential Trends in Inorganic Chemistry. Oxford University Press. p. 387. ISBN 978-0-19-850109-1.
- ^ "A New Era of Discovery: the 2023 Long Range Plan for Nuclear Science" (PDF). U.S. Department of Energy. October 2023. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2023 – via OSTI.
Superheavy elements (Z > 102) are teetering at the limits of mass and charge.
- ^ Kragh, Helge (2017). "The search for superheavy elements: Historical and philosophical perspectives". arXiv:1708.04064 [physics.hist-ph].
- ^ IUPAC Provisional Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (2004) (online draft of an updated version of the "Red Book" IR 3-6) Archived October 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c d e f Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean, eds. (2006). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ "Kernchemie". www.kernchemie.de.
- ^ Krämer, K. (2016). "Explainer: superheavy elements". Chemistry World. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ "Discovery of Elements 113 and 115". Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Archived from the original on 11 September 2015. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Eliav, E.; Kaldor, U.; Borschevsky, A. (2018). "Electronic Structure of the Transactinide Atoms". In Scott, R. A. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1–16. doi:10.1002/9781119951438.eibc2632. ISBN 978-1-119-95143-8. S2CID 127060181.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Dmitriev, S. N.; Yeremin, A. V.; et al. (2009). "Attempt to produce the isotopes of element 108 in the fusion reaction 136Xe + 136Xe". Physical Review C. 79 (2): 024608. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.79.024608. ISSN 0556-2813.
- ^ Münzenberg, G.; Armbruster, P.; Folger, H.; et al. (1984). "The identification of element 108" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Physik A. 317 (2): 235–236. Bibcode:1984ZPhyA.317..235M. doi:10.1007/BF01421260. S2CID 123288075. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2015. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
- ^ Subramanian, S. (28 August 2019). "Making New Elements Doesn't Pay. Just Ask This Berkeley Scientist". Bloomberg Businessweek. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Ivanov, D. (2019). "Сверхтяжелые шаги в неизвестное" [Superheavy steps into the unknown]. nplus1.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2 February 2020.
- ^ Hinde, D. (2017). "Something new and superheavy at the periodic table". The Conversation. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ Kern, B. D.; Thompson, W. E.; Ferguson, J. M. (1959). "Cross sections for some (n, p) and (n, α) reactions". Nuclear Physics. 10: 226–234. Bibcode:1959NucPh..10..226K. doi:10.1016/0029-5582(59)90211-1.
- ^ Wakhle, A.; Simenel, C.; Hinde, D. J.; et al. (2015). Simenel, C.; Gomes, P. R. S.; Hinde, D. J.; et al. (eds.). "Comparing Experimental and Theoretical Quasifission Mass Angle Distributions". European Physical Journal Web of Conferences. 86: 00061. Bibcode:2015EPJWC..8600061W. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20158600061. hdl:1885/148847. ISSN 2100-014X.
- ^ "Nuclear Reactions" (PDF). pp. 7–8. Retrieved 27 January 2020. Published as Loveland, W. D.; Morrissey, D. J.; Seaborg, G. T. (2005). "Nuclear Reactions". Modern Nuclear Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 249–297. doi:10.1002/0471768626.ch10. ISBN 978-0-471-76862-3.
- ^ a b Krása, A. (2010). "Neutron Sources for ADS". Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering. Czech Technical University in Prague: 4–8. S2CID 28796927.
- ^ Wapstra, A. H. (1991). "Criteria that must be satisfied for the discovery of a new chemical element to be recognized" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 63 (6): 883. doi:10.1351/pac199163060879. ISSN 1365-3075. S2CID 95737691.
- ^ a b Hyde, E. K.; Hoffman, D. C.; Keller, O. L. (1987). "A History and Analysis of the Discovery of Elements 104 and 105". Radiochimica Acta. 42 (2): 67–68. doi:10.1524/ract.1987.42.2.57. ISSN 2193-3405. S2CID 99193729.
- ^ a b c d Chemistry World (2016). "How to Make Superheavy Elements and Finish the Periodic Table [Video]". Scientific American. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, p. 334.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, p. 335.
- ^ Zagrebaev, Karpov & Greiner 2013, p. 3.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 432.
- ^ a b Pauli, N. (2019). "Alpha decay" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Pauli, N. (2019). "Nuclear fission" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Staszczak, A.; Baran, A.; Nazarewicz, W. (2013). "Spontaneous fission modes and lifetimes of superheavy elements in the nuclear density functional theory". Physical Review C. 87 (2): 024320–1. arXiv:1208.1215. Bibcode:2013PhRvC..87b4320S. doi:10.1103/physrevc.87.024320. ISSN 0556-2813.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, pp. 030001-129–030001-138.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 439.
- ^ a b Beiser 2003, p. 433.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, p. 030001-125.
- ^ Aksenov, N. V.; Steinegger, P.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; et al. (2017). "On the volatility of nihonium (Nh, Z = 113)". The European Physical Journal A. 53 (7): 158. Bibcode:2017EPJA...53..158A. doi:10.1140/epja/i2017-12348-8. ISSN 1434-6001. S2CID 125849923.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 432–433.
- ^ a b c Oganessian, Yu. (2012). "Nuclei in the "Island of Stability" of Superheavy Elements". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 337 (1): 012005-1–012005-6. Bibcode:2012JPhCS.337a2005O. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/337/1/012005. ISSN 1742-6596.
- ^ Moller, P.; Nix, J. R. (1994). Fission properties of the heaviest elements (PDF). Dai 2 Kai Hadoron Tataikei no Simulation Symposium, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki, Japan. University of North Texas. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. Ts. (2004). "Superheavy elements". Physics World. 17 (7): 25–29. doi:10.1088/2058-7058/17/7/31. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Schädel, M. (2015). "Chemistry of the superheavy elements". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 373 (2037): 20140191. Bibcode:2015RSPTA.37340191S. doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0191. ISSN 1364-503X. PMID 25666065.
- ^ Hulet, E. K. (1989). Biomodal spontaneous fission. 50th Anniversary of Nuclear Fission, Leningrad, USSR. Bibcode:1989nufi.rept...16H.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Rykaczewski, K. P. (2015). "A beachhead on the island of stability". Physics Today. 68 (8): 32–38. Bibcode:2015PhT....68h..32O. doi:10.1063/PT.3.2880. ISSN 0031-9228. OSTI 1337838. S2CID 119531411.
- ^ Grant, A. (2018). "Weighing the heaviest elements". Physics Today. doi:10.1063/PT.6.1.20181113a. S2CID 239775403.
- ^ Howes, L. (2019). "Exploring the superheavy elements at the end of the periodic table". Chemical & Engineering News. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- ^ a b Robinson, A. E. (2019). "The Transfermium Wars: Scientific Brawling and Name-Calling during the Cold War". Distillations. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- ^ "Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Сиборгий (экавольфрам)" [Popular library of chemical elements. Seaborgium (eka-tungsten)]. n-t.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 7 January 2020. Reprinted from "Экавольфрам" [Eka-tungsten]. Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Серебро – Нильсборий и далее [Popular library of chemical elements. Silver through nielsbohrium and beyond] (in Russian). Nauka. 1977.
- ^ "Nobelium - Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table". Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ a b Kragh 2018, pp. 38–39.
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 40.
- ^ a b Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (1993). "Responses on the report 'Discovery of the Transfermium elements' followed by reply to the responses by Transfermium Working Group" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 65 (8): 1815–1824. doi:10.1351/pac199365081815. S2CID 95069384. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 November 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
- ^ Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (1997). "Names and symbols of transfermium elements (IUPAC Recommendations 1997)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 69 (12): 2471–2474. doi:10.1351/pac199769122471.
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 6
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 7
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 10
- ^ van der Schoor, K. (2016). Electronic structure of element 123 (PDF) (Thesis). Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.
- ^ Hofmann, Sigurd (2019). "Synthesis and properties of isotopes of the transactinides". Radiochimica Acta. 107 (9–11): 879–915. doi:10.1515/ract-2019-3104. S2CID 203848120.
- ^ Laforge, Evan; Price, Will; Rafelski, Johann (2023). "Superheavy elements and ultradense matter". The European Physical Journal Plus. 138 (9): 812. arXiv:2306.11989. Bibcode:2023EPJP..138..812L. doi:10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04454-8.
Bibliography
- Audi, G.; Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; et al. (2017). "The NUBASE2016 evaluation of nuclear properties". Chinese Physics C. 41 (3). 030001. Bibcode:2017ChPhC..41c0001A. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/41/3/030001.
pp. 030001-1–030001-17, pp. 030001-18–030001-138, Table I. The NUBASE2016 table of nuclear and decay properties - Beiser, A. (2003). Concepts of modern physics (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-244848-1. OCLC 48965418.
- Hoffman, D. C.; Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T. (2000). The Transuranium People: The Inside Story. World Scientific. ISBN 978-1-78-326244-1.
- Kragh, H. (2018). From Transuranic to Superheavy Elements: A Story of Dispute and Creation. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-75813-8.
- Zagrebaev, V.; Karpov, A.; Greiner, W. (2013). "Future of superheavy element research: Which nuclei could be synthesized within the next few years?". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 420 (1). 012001. arXiv:1207.5700. Bibcode:2013JPhCS.420a2001Z. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/420/1/012001. ISSN 1742-6588.
Discovery

Cold fusion
Nuclear reactions used in the 1960s resulted in high excitation energies that required expulsion of four or five neutrons; these reactions used targets made of elements with high atomic numbers to maximize the size difference between the two nuclei in a reaction. While this increased the chance of fusion due to the lower electrostatic repulsion between the target and the projectile, the formed compound nuclei often broke apart and did not survive to form a new element. Moreover, fusion processes inevitably produce neutron-poor nuclei, as heavier elements require more neutrons per proton to maximize stability;[a] therefore, the necessary ejection of neutrons results in final products with typically have shorter lifetimes. As such, light beams (6 to 10 protons) only allowed synthesis of elements up to 106.[3]
To advance to heavier elements, Soviet physicist Yuri Oganessian at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union, proposed a different mechanism, in which the bombarded nucleus would be lead-208, which has magic numbers of protons and neutrons, or one close to it.[4] The magic number of protons and/or neutrons gives the nuclide additional stability, which requires more energy for an external nucleus to penetrate it.[5] More equal atomic numbers of the reacting nuclei result in greater electrostatic repulsion between them, but the greater mass excess of the target nucleus balances it.[4] This leaves less excitation energy for the newly created compound nucleus, which necessitates fewer neutron ejections to reach a stable state.[5] Because of this energy difference, the former mechanism became known as "hot fusion" and the latter as "cold fusion".
Cold fusion was first declared successful in 1974 at JINR, when it was tested for synthesis of the yet-undiscovered element 106.[5] These new nuclei were projected to decay via spontaneous fission. The physicists at JINR concluded those were not seen before because no fissioning nucleus known at the time showed similar parameters of fission and because changing either of the two nuclei in the reactions negated the seen effects. Physicists at LBL also expressed great interest in the new technique.[5] When asked about how far this new method could go and if lead targets were a physics' Klondike, Oganessian responded, "Klondike may be an exaggeration [...] But soon, we will try to get elements 107...108 in these reactions."[5]
Reports
The synthesis of element 108 was first attempted in 1978 by a research team led by Oganessian at the JINR. The team used a reaction that would generate element 108, specifically, the isotope 270108,[b] from fusion of radium (specifically, the isotope 226
88Ra
) and calcium (48
20Ca
). The researchers were uncertain in interpreting their data, and their paper did not unambiguously claim to have discovered the element.[6] The same year, another team at JINR investigated the possibility of synthesis of element 108 in reactions between lead (208
82Pb
) and iron (58
26Fe
); they were uncertain in interpreting the data, suggesting the possibility that element 108 had not been created.[7]

In 1983, new experiments were performed at JINR.[10] The experiments probably resulted in the synthesis of element 108; bismuth (209
83Bi
) was bombarded with manganese (55
25Mn
) to obtain 263108, lead (207
82Pb
, 208
82Pb
) was bombarded with iron (58
26Fe
) to obtain 264108, and californium (249
98Cf
) was bombarded with neon (22
10Ne
) to obtain 270108.[11] These experiments were not claimed as a discovery and Oganessian announced them in a conference rather than in a written report.[10]
In 1984, JINR researchers in Dubna performed experiments set up identically to the previous ones; they bombarded bismuth and lead targets with ions of lighter elements manganese and iron, respectively. Twenty-one spontaneous fission events were recorded; these were assigned to 264108.[12]
Later in 1984, a research team led by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg at Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI; Institute for Heavy Ion Research) in Darmstadt, Hesse, West Germany, attempted to create element 108. The team bombarded a lead (208
82Pb
) target with accelerated iron (58
26Fe
) nuclei.[13] GSI's experiment to create element 108 was delayed until after their creation of element 109 in 1982, as prior calculations had suggested that even–even isotopes of element 108 would have spontaneous fission half-lives of less than one microsecond, making them difficult to detect and identify.[14] The element 108 experiment finally went ahead after 266109 had been synthesized and was found to decay by alpha emission, suggesting that isotopes of element 108 would do likewise, and this was corroborated by an experiment aimed at synthesizing isotopes of element 106. GSI reported synthesis of three atoms of 265108. Two years later, they reported synthesis of one atom of the even–even 264108.[14]
Arbitration
In 1985, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) formed the Transfermium Working Group (TWG) to assess discoveries and establish final names for elements with atomic numbers greater than 100. The party held meetings with delegates from the three competing institutes; in 1990, they established criteria for recognition of an element and in 1991, they finished the work of assessing discoveries and disbanded. These results were published in 1993.[15]
According to the report, the 1984 works from JINR and GSI simultaneously and independently established synthesis of element 108. Of the two 1984 works, the one from GSI was said to be sufficient as a discovery on its own. The JINR work, which preceded the GSI one, "very probably" displayed synthesis of element 108. However, that was determined in retrospect given the work from Darmstadt; the JINR work focused on chemically identifying remote granddaughters of element 108 isotopes (which could not exclude the possibility that these daughter isotopes had other progenitors), while the GSI work clearly identified the decay path of those element 108 isotopes. The report concluded that the major credit should be awarded to GSI.[12] In written responses to this ruling, both JINR and GSI agreed with its conclusions. In the same response, GSI confirmed that they and JINR were able to resolve all conflicts between them; GSI also proposed a name for element 108 that had been officially presented at the facility three weeks earlier.[16]
Naming
Historically, a newly discovered element was named by its discoverer. The first regulation came in 1947, when IUPAC decided that naming required regulation in case there are conflicting names.[17][c] These matters were to be resolved by the Commission of Inorganic Nomenclature and the Commission of Atomic Weights. They would review the names in case of a conflict and select one; the decision would be based on a number of factors, such as usage, and would not be an indicator of priority of a claim. The two commissions would recommend a name to the IUPAC Council, which would be the final authority.[17] The discoverers held the right to name an element, but their name would be subject to approval by IUPAC.[17] The Commission of Atomic Weights distanced itself from element naming in most cases.[17]
Under Mendeleev's nomenclature for unnamed and undiscovered elements, hassium would be known as "eka-osmium". In 1979, IUPAC published recommendations according to which the element was to be called "unniloctium" and assigned the corresponding symbol of "Uno",[18] a systematic element name as a placeholder until the element was discovered and the discovery then confirmed, and a permanent name was decided. Although these recommendations were widely followed in the chemical community, the competing physicists in the field ignored them.[19][20] They either called it "element 108", with the symbols E108, (108) or 108, or used the proposed name "hassium".[21]

In 1990, in an attempt to break a deadlock in establishing priority of discovery and naming of several elements, IUPAC reaffirmed in its nomenclature of inorganic chemistry that after existence of an element was established, the discoverers could propose a name. (In addition, the Commission of Atomic Weights was excluded from the naming process.) The first publication on criteria for an element discovery, released in 1991, specified the need for recognition by TWG.[17]
Armbruster and his colleagues, the officially recognized German discoverers, held a naming ceremony for the elements 107 through 109, which had all been recognized as discovered by GSI, on 7 September 1992. For element 108, the scientists proposed the name "hassium".[22] It is derived from the Latin name Hassia for the German state of Hesse where the institute is located.[11][16] This name was proposed to IUPAC in a written response to their ruling on priority of discovery claims of elements, signed 29 September 1992.[16]
The process of naming of element 108 was a part of a larger process of naming a number of elements starting with element 101; three teams—JINR, GSI, and the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory (LBL; originally Radiation Laboratory, RL, and later Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, LBNL) of the University of California in Berkeley, California, United States—claimed discoveries of several elements and the right to name those elements. Sometimes, these claims clashed; since a discoverer was considered entitled to naming of an element, conflicts over priority of discovery often resulted in conflicts over names of these new elements. These conflicts became known as the Transfermium Wars.[23] Different suggestions to name the whole set of elements from 101 onward and they occasionally assigned names suggested by one team to be used for elements discovered by another.[d] However, not all suggestions were met with equal approval; the teams openly protested naming proposals on several occasions.[25]
In 1994, IUPAC Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry recommended that element 108 be named "hahnium" (Hn) after the German physicist Otto Hahn so elements named after Hahn and Lise Meitner (it was recommended element 109 should be named meitnerium, following GSI's suggestion) would be next to each other, honouring their joint discovery of nuclear fission;[26] IUPAC commented that they felt the German suggestion was obscure.[27] GSI protested, saying this proposal contradicted the long-standing convention of giving the discoverer the right to suggest a name;[28] the American Chemical Society supported GSI.[11] The name "hahnium", albeit with the different symbol Ha, had already been proposed and used by the American scientists for element 105, for which they had a discovery dispute with JINR; they thus protested the confusing scrambling of names.[29] Following the uproar, IUPAC formed an ad hoc committee of representatives from the national adhering organizations of the three countries home to the competing institutions; they produced a new set of names in 1995. Element 108 was again named hahnium; this proposal was also retracted.[30] The final compromise was reached in 1996 and published in 1997; element 108 was named hassium (Hs).[31] Simultaneously, the name dubnium (Db; from Dubna, the JINR location) was assigned to element 105, and the name hahnium was not used for any element.[32][e]
The official justification for this naming, alongside that of darmstadtium for element 110, was that it completed a set of geographic names for the location of the GSI; this set had been initiated by 19th-century names europium and germanium. This set would serve as a response to earlier naming of americium, californium, and berkelium for elements discovered in Berkeley. Armbruster commented on this, "this bad tradition[f] was established by Berkeley. We wanted to do it for Europe."[34] Later, when commenting on the naming of element 112, Armbruster said, "I did everything to ensure that we do not continue with German scientists and German towns."[34]
Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life[g] | Decay mode |
Discovery year[35] |
Discovery reaction[36] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Ref | ||||
| 263Hs | 760 µs | [35] | α, SF | 2009 | 208Pb(56Fe,n) |
| 264Hs | 540 µs | [35] | α, SF | 1986 | 207Pb(58Fe,n) |
| 265Hs | 1.96 ms | [35] | α, SF | 1984 | 208Pb(58Fe,n) |
| 265mHs | 360 µs | [35] | α | 1995 | 208Pb(56Fe,n) |
| 266Hs | 3.02 ms | [35] | α, SF | 2001 | 270Ds(—,α) |
| 266mHs | 280 ms | [35] | α | 2011 | 270mDs(—,α) |
| 267Hs | 55 ms | [37] | α | 1995 | 238U(34S,5n) |
| 267mHs | 990 µs | [37] | α | 2004 | 238U(34S,5n) |
| 268Hs | 1.42 s | [37] | α | 2010 | 238U(34S,4n) |
| 269Hs | 16 s | [37] | α | 1996 | 277Cn(—,2α) |
| 270Hs | 9 s | [37] | α | 2003 | 248Cm(26Mg,4n) |
| 271Hs | 10 s[h] | [38] | α | 2008 | 248Cm(26Mg,3n) |
| 273Hs | 510 ms | [39] | α | 2010 | 285Fl(—,3α) |
| 275Hs | 200 ms | [40] | α | 2004 | 287Fl(—,3α) |
| 277Hs | 11 ms | [41] | α | 2010 | 289Fl(—,3α) |
| 277mHs | 1.8 min[i] | [41] | SF | 2012 | 293mLv(—,4α) |
Hassium has no stable or naturally occurring isotopes. Several radioactive isotopes have been synthesized in the laboratory, either by fusing two atoms or by observing the decay of heavier elements. As of 2019, the quantity of all hassium ever produced was on the order of hundreds of atoms.[42][43] Twelve isotopes with mass numbers ranging from 263 to 277 (with the exceptions of 272, 274, and 276) have been reported, four of which—hassium-265, -267, -269, and -277—have known metastable states,[44] although that of hassium-277 is unconfirmed.[45] Most of these isotopes decay predominantly through alpha decay; this is the most common for all isotopes for which comprehensive decay characteristics are available, the only exception being hassium-277, which undergoes spontaneous fission.[44] The lightest isotopes, which usually have shorter half-lives, were synthesized by direct fusion between two lighter nuclei and as decay products. The heaviest isotope produced by direct fusion is 271Hs; heavier isotopes have only been observed as decay products of elements with larger atomic numbers.[36]
Atomic nuclei have well-established nuclear shells, and the existence of these shells provides nuclei with additional stability. If a nucleus has certain numbers of protons or neutrons, called magic numbers, that complete certain nuclear shells, then the nucleus is even more stable against decay. The highest known magic numbers are 82 for protons and 126 for neutrons. This notion is sometimes expanded to include additional numbers between those magic numbers, which also provide some additional stability and indicate closure of "sub-shells". In contrast to the better-known lighter nuclei, superheavy nuclei are deformed. Until the 1960s, it was thought that deformation made superheavy nuclei incapable of forming a nuclear structure because these nuclei would decay before they could form one;[3] it thus appeared that nuclei with Z ≈ 103[j] were too heavy to exist for a considerable length of time.[46] Subsequent theories proposed greater stability of heavier nuclei.
The earlier liquid drop model thus suggested that spontaneous fission would occur nearly instantly due to disappearance of the fission barrier for nuclei with about 280 nucleons.[47][48] The later nuclear shell model suggested that nuclei with about 300 nucleons would form an island of stability in which nuclei will be more resistant to spontaneous fission and will primarily undergo alpha decay with longer half-lives,[47][48] and the next doubly magic nucleus (having magic numbers of both protons and neutrons) is expected to lie in the center of the island of stability in the vicinity of Z = 110–114 and the predicted magic neutron number N = 184. Subsequent discoveries suggested that the predicted island might be further than originally anticipated; they also showed that nuclei intermediate between the long-lived actinides and the predicted island are deformed, and gain additional stability from shell effects.[48] The addition to the stability against the spontaneous fission should be particularly great against spontaneous fission, although increase in stability against the alpha decay would also be pronounced.[48] The center of the region on a chart of nuclides that would correspond to this stability for deformed nuclei was determined as 270Hs, with 108 expected to be a magic number for protons for deformed nuclei—nuclei that are far from spherical—and 162 a magic number for neutrons for such nuclei.[49] Experiments on lighter superheavy nuclei,[50] as well as those closer to the expected island,[3] have shown greater than previously anticipated stability against spontaneous fission, showing the importance of shell effects on nuclei.
Theoretical models predict a region of instability for some hassium isotopes to lie around A = 275[51] and N = 168–170, which is between the predicted neutron shell closures at N = 162 for deformed nuclei and N = 184 for spherical nuclei.[52] Nuclides within this region are predicted to have low fission barrier heights, resulting in short partial half-lives toward spontaneous fission. This prediction is supported by the observed 11 millisecond half-life of 277Hs and that of the neighbouring isobar 277Mt because the expected hindrance factors from the odd nucleon were shown to be much lower than expected. The measured half-lives are even lower than those predicted for the even–even 276Hs and 278Ds, which suggests a gap in stability away from the shell closures and perhaps a weakening of the shell closures in this region.[52]
In 1991, Polish physicists Zygmunt Patyk and Adam Sobiczewski predicted[53] that 108 is a proton magic number for deformed nuclei and 162 is a neutron magic number for such nuclei. This means such nuclei are permanently deformed in their ground state but have high, narrow fission barriers to further deformation and hence relatively long life-times toward spontaneous fission.[54][55] Computational prospects for shell stabilization for 270Hs made it a promising candidate for a deformed doubly magic nucleus.[56] Experimental data is scarce, but the existing data is interpreted by the researchers to support the assignment of N = 162 as a magic number. In particular, this conclusion was drawn from the decay data of 269Hs, 270Hs, and 271Hs.[k] In 1997, Polish physicist Robert Smolańczuk calculated that the isotope 292Hs may be the most stable superheavy nucleus against alpha decay and spontaneous fission as a consequence of the predicted N = 184 shell closure.[59][60]
Natural occurrence

Hassium is not known to occur naturally on Earth; the half-lives of all of its known isotopes are short enough that no primordial hassium would have survived to the present day. This does not rule out the possibility of the existence of unknown, longer-lived isotopes or nuclear isomers, some of which could still exist in trace quantities if they are long-lived enough. As early as 1914, German physicist Richard Swinne proposed element 108 as a source of X-rays in the Greenland ice sheet. Although Swinne was unable to verify this observation and thus did not claim discovery, he proposed in 1931 the existence of regions of long-lived transuranic elements, including one around Z = 108.[61]
In 1963, Soviet geologist and physicist Viktor Cherdyntsev, who had previously claimed the existence of primordial curium-247,[62] claimed to have discovered element 108—specifically the 267108 isotope, which supposedly had a half-life of 400 to 500 million years—in natural molybdenite and suggested the provisional name sergenium (symbol Sg);[63][l] this name takes its origin from the name for the Silk Road and was explained as "coming from Kazakhstan" for it.[63] His rationale for claiming that sergenium was the heavier homologue to osmium was that minerals supposedly containing sergenium formed volatile oxides when boiled in nitric acid, similarly to osmium.[64]
Cherdyntsev's findings were criticized by Soviet physicist Vladimir Kulakov on the grounds that some of the properties Cherdyntsev claimed sergenium had were inconsistent with the then-current nuclear physics. The chief questions raised by Kulakov were that the claimed alpha decay energy of sergenium was many orders of magnitude lower than expected and the half-life given was eight orders of magnitude shorter than what would be predicted for a nuclide alpha-decaying with the claimed decay energy. At the same time, a corrected half-life in the region of 1016 years would be impossible because it would imply the samples contained about 100 milligrams of sergenium.[64] In 2003, it was suggested that the observed alpha decay with energy 4.5 MeV could be due to a low-energy and strongly enhanced transition between different hyperdeformed states of a hassium isotope around 271Hs, thus suggesting that the existence of superheavy elements in nature was at least possible, although unlikely.[65]
In 2006, Russian geologist Alexei Ivanov hypothesized that an isomer of 271Hs might have a half-life of around (2.5±0.5)×108 years, which would explain the observation of alpha particles with energies of around 4.4 MeV in some samples of molybdenite and osmiridium.[66] This isomer of 271Hs could be produced from the beta decay of 271Bh and 271Sg, which, being homologous to rhenium and molybdenum respectively, should occur in molybdenite along with rhenium and molybdenum if they occurred in nature. Because hassium is homologous to osmium, it should occur along with osmium in osmiridium if it occurs in nature. The decay chains of 271Bh and 271Sg are hypothetical and the predicted half-life of this hypothetical hassium isomer is not long enough for any sufficient quantity to remain on Earth.[66] It is possible that more 271Hs may be deposited on the Earth as the Solar System travels through the spiral arms of the Milky Way; this would explain excesses of plutonium-239 found on the ocean floors of the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Finland. However, minerals enriched with 271Hs are predicted to have excesses of its daughters uranium-235 and lead-207; they would also have different proportions of elements that are formed during spontaneous fission, such as krypton, zirconium, and xenon. The natural occurrence of hassium in minerals such as molybdenite and osmiride is theoretically possible, but very unlikely.[66]
In 2004, the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research started a search for natural hassium in the Modane Underground Laboratory in Modane, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France; this was done underground to avoid interference and false positives from cosmic rays.[11] In 2008–09, an experiment run in the laboratory resulted in detection of several registered events of neutron multiplicity (number of emitted free neutrons after a nucleus hit has been hit by a neutron and fissioned) above three in natural osmium, and in 2012–13, these findings were reaffirmed in another experiment run in the laboratory. These results hinted natural hassium could potentially exist in nature in amounts that allow its detection by the means of analytical chemistry, but this conclusion is based on an explicit assumption that there is a long-lived hassium isotope to which the registered events could be attributed.[67]
Since 292Hs may be particularly stable against alpha decay and spontaneous fission, it was considered as a candidate to exist in nature. This nuclide, however, is predicted to be very unstable toward beta decay and any beta-stable isotopes of hassium such as 286Hs would be too unstable in the other decay channels to be observed in nature.[60] A 2012 search for 292Hs in nature along with its homologue osmium at the Maier-Leibnitz Laboratory in Garching, Bavaria, Germany, was unsuccessful, setting an upper limit to its abundance at 3×10−15 grams of hassium per gram of osmium.[68]
Predicted properties
Various calculations suggest that hassium should be the heaviest group 8 element so far, consistently with the periodic law. Its properties should generally match those expected for a heavier homologue of osmium; as is the case for all 6d metals, a few deviations are expected to arise from relativistic effects.[69]
Very few properties of hassium or its compounds have been measured; this is due to its extremely limited and expensive production[70] and the fact that hassium (and its parents) decays very quickly. A few singular chemistry-related properties have been measured, such as enthalpy of adsorption of hassium tetroxide, but properties of hassium metal remain unknown and only predictions are available.
Relativistic effects

Relativistic effects on hassium should arise due to the high charge of its nuclei, which causes the electrons around the nucleus to move faster—so fast their velocity becomes comparable to the speed of light.[71] There are three main effects: the direct relativistic effect, the indirect relativistic effect, and the spin–orbit splitting. (The existing calculations do not account for Breit interactions, but those are negligible, and their omission can only result in an uncertainty of the current calculations of no more than 2%.)[72]
As atomic number increases, so does the electrostatic attraction between an electron and the nucleus. This causes the velocity of the electron to increase, which leads to an increase its mass. This in turn leads to contraction of the atomic orbitals, most specifically the s and p1/2 orbitals. Their electrons become more closely attached to the atom and harder to pull from the nucleus. This is the direct relativistic effect. It was originally thought to be strong only for the innermost electrons, but was later established to significantly influence valence electrons as well.[73]
Since the s and p1/2 orbitals are closer to the nucleus, they take a bigger portion of the electric charge of the nucleus on themselves ("shield" it). This leaves less charge for attraction of the remaining electrons, whose orbitals therefore expand, making them easier to pull from the nucleus. This is the indirect relativistic effect.[74] The combination of the two leads to that the Hs+ ion, compared to the neutral atom, lacks a 6d electron, rather than a 7s electron. In comparison, Os+ lacks a 6s electron compared to the neutral atom.[75] The ionic radius (in oxidation state +8) of hassium is greater than that of osmium because of the relativistic expansion of the 6p3/2 orbitals, which are the outermost orbitals for an Hs8+ ion (although in practice such highly charged ions would be too polarised in chemical environments to have much reality).[76]
There are several kinds of electronic orbitals, denoted by the letters s, p, d, and f (g orbitals are expected to start being chemically active among elements after element 120). Each of these corresponds to an azimuthal quantum number l: s to 0, p to 1, d to 2, and f to 3. Every electron also corresponds to a spin quantum number s, which may equal either +1/2 or −1/2.[77] Thus, the total angular momentum quantum number j = l + s is equal to j = l ± 1/2 (except for l = 0, for which for both electrons in each orbital j = 0 + 1/2 = 1/2).[77] Spin of an electron interacts with its orbit, which leads to a split of a subshell into two with different energies (the one with j = l − 1/2 is lower in energy and thus these electrons more difficult to extract):[78] for instance, of the six 6p electrons, two become 6p1/2 and four become 6p3/2. This is the spin–orbit splitting (sometimes also referred to as subshell splitting or jj coupling).[79] It is most visible with p electrons,[72] which do not play an important role in the chemistry of hassium,[80] but those for d and f electrons are within the same order of magnitude[72] (quantitatively, spin–orbit splitting in expressed in energy units, such as electronvolts).[77]

These relativistic effects are responsible for the expected increase of the ionization energy, decrease of the electron affinity, and increase of stability of the +8 oxidation state compared to osmium; without them, the trends would be reversed.[81] Relativistic effects decrease the atomization energies of the compounds of hassium because the spin–orbit splitting of the d orbital lowers binding energy between electrons and the nucleus and because relativistic effects decrease ionic character in bonding.[81]
Physical and atomic
The previous members of group 8 have relatively high melting points: Fe, 1538 °C; Ru, 2334 °C; Os, 3033 °C. Much like them, hassium is predicted to be a solid at room temperature[82] although its melting point has not been precisely calculated. Hassium should crystallize in the hexagonal close-packed structure (c/a = 1.59),[82] similarly to its lighter congener osmium.[82] Pure metallic hassium is calculated[82][83] to have a bulk modulus (resistance to uniform compression) of 450 GPa, comparable with that of diamond, 442 GPa.[84] Hassium is expected to have a bulk density of 41 g/cm3[85] at standard pressure and temperature, the highest of any of the 118 known elements and nearly twice the highest density of an element observed to this day (22.6 g/cm3).[m]
The atomic radius of hassium is expected to be around 126 pm.[89] Due to the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital and destabilization of the 6d orbital, the Hs+ ion is predicted to have an electron configuration of [Rn] 5f14 6d5 7s2, giving up a 6d electron instead of a 7s electron, which is the opposite of the behaviour of its lighter homologues. The Hs2+ ion is expected to have an electron configuration of [Rn] 5f14 6d5 7s1, analogous to that calculated for the Os2+ ion.[75] In chemical compounds, hassium is calculated to display bonding characteristic for a d-block element, whose bonding will be primarily executed by 6d3/2 and 6d5/2 orbitals; compared to the elements from the previous periods, 7s, 6p1/2, 6p3/2, and 7p1/2 orbitals should be more important.[90]
Chemical
| Element | Stable oxidation states | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iron | +6 | +3 | +2 | |||||
| ruthenium | +8 | +6 | +5 | +4 | +3 | +2 | ||
| osmium | +8 | +6 | +5 | +4 | +3 | +2 | ||
Hassium is the sixth member of the 6d series of transition metals and is expected to be much like the platinum group metals.[92] Some of these properties were confirmed by gas-phase chemistry experiments.[93][94][95] The group 8 elements portray a wide variety of oxidation states but ruthenium and osmium readily portray their group oxidation state of +8; this state becomes more stable down the group.[91][96][97] This oxidation state is extremely rare: among stable elements, only ruthenium, osmium, and xenon are able to attain it in reasonably stable compounds.[n] Hassium is expected to follow its congeners and have a stable +8 state,[94] but like them it should show lower stable oxidation states such as +6, +4, +3, and +2.[89][100] Hassium(IV) is expected to be more stable than hassium(VIII) in aqueous solution.[101] Hassium should be a rather noble metal.[102] The standard reduction potential for the Hs4+/Hs couple is expected to be 0.4 V.[89]
The group 8 elements show a distinctive oxide chemistry. All of the lighter members have known or hypothetical tetroxides, MO4.[103] Their oxidizing power decreases as one descends the group. FeO4 is not known due to its extraordinarily large electron affinity—the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion[104]—which results in the formation of the well-known oxyanion ferrate(VI), FeO2−
4.[105] Ruthenium tetroxide, RuO4, which is formed by oxidation of ruthenium(VI) in acid, readily undergoes reduction to ruthenate(VI), RuO2−
4.[106][107] Oxidation of ruthenium metal in air forms the dioxide, RuO2.[108] In contrast, osmium burns to form the stable tetroxide, OsO4,[109][110] which complexes with the hydroxide ion to form an osmium(VIII) -ate complex, [OsO4(OH)2]2−.[111] Therefore, eka-osmium properties for hassium should be demonstrated by the formation of a stable, very volatile tetroxide HsO4,[11][93][95][96][112] which undergoes complexation with hydroxide to form a hassate(VIII), [HsO4(OH)2]2−.[113] Ruthenium tetroxide and osmium tetroxide are both volatile due to their symmetrical tetrahedral molecular geometry and because they are charge-neutral; hassium tetroxide should similarly be a very volatile solid. The trend of the volatilities of the group 8 tetroxides is known to be RuO4 < OsO4 > HsO4, which confirms the calculated results. In particular, the calculated enthalpies of adsorption—the energy required for the adhesion of atoms, molecules, or ions from a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid to a surface—of HsO4, −(45.4 ± 1) kJ/mol on quartz, agrees very well with the experimental value of −(46 ± 2) kJ/mol.[114]
Experimental chemistry
The first goal for chemical investigation was the formation of the tetroxide; it was chosen because ruthenium and osmium form volatile tetroxides, being the only transition metals to display a stable compound in the +8 oxidation state.[115] Despite this selection for gas-phase chemical studies being clear from the beginning,[96] chemical characterization of hassium was considered a difficult task for a long time.[96] Although hassium isotopes were first synthesized in 1984, it was not until 1996 that a hassium isotope long-lived enough to allow chemical studies was synthesized. Unfortunately, this hassium isotope, 269Hs, was synthesized indirectly from the decay of 277Cn;[96] not only are indirect synthesis methods not favourable for chemical studies,[116] but the reaction that produced the isotope 277Cn had a low yield—its cross section was only 1 pb[96]—and thus did not provide enough hassium atoms for a chemical investigation.[92] Direct synthesis of 269Hs and 270Hs in the reaction 248Cm(26Mg,xn)274−xHs (x = 4 or 5) appeared more promising because the cross section for this reaction was somewhat larger at 7 pb.[96] This yield was still around ten times lower than that for the reaction used for the chemical characterization of bohrium.[96] New techniques for irradiation, separation, and detection had to be introduced before hassium could be successfully characterized chemically.[96]
Ruthenium and osmium have very similar chemistry due to the lanthanide contraction but iron shows some differences from them; for example, although ruthenium and osmium form stable tetroxides in which the metal is in the +8 oxidation state, iron does not.[96][103] In preparation for the chemical characterization of hassium, research focused on ruthenium and osmium rather than iron[96] because hassium was expected to be similar to ruthenium and osmium, as the predicted data on hassium closely matched that of those two.[117][118]
The first chemistry experiments were performed using gas thermochromatography in 2001, using the synthetic osmium radioisotopes 172Os and 173Os as a reference. During the experiment, seven hassium atoms were synthesized using the reactions 248Cm(26Mg,5n)269Hs and 248Cm(26Mg,4n)270Hs. They were then thermalized and oxidized in a mixture of helium and oxygen gases to form hassium tetroxide molecules.[93][95][119]
- Hs + 2 O2 → HsO4
The measured deposition temperature of hassium tetroxide was higher than that of osmium tetroxide, which indicated the former was the less volatile one, and this placed hassium firmly in group 8.[93][95][120] The enthalpy of adsorption for HsO4 measured, −46±2 kJ/mol, was significantly lower than the predicted value, −36.7±1.5 kJ/mol, indicating OsO4 is more volatile than HsO4, contradicting earlier calculations that implied they should have very similar volatilities. For comparison, the value for OsO4 is −39±1 kJ/mol.[121] (The calculations that yielded a closer match to the experimental data came after the experiment, in 2008.)[114] It is possible hassium tetroxide interacts differently with silicon nitride than with silicon dioxide, the chemicals used for the detector; further research is required to establish whether there is a difference between such interactions and whether it has influenced the measurements. Such research would include more accurate measurements of the nuclear properties of 269Hs and comparisons with RuO4 in addition to OsO4.[120]
In 2004, scientists reacted hassium tetroxide and sodium hydroxide to form sodium hassate(VIII), a reaction that is well known with osmium. This was the first acid-base reaction with a hassium compound, forming sodium hassate(VIII):[113]
- HsO
4 + 2 NaOH → Na
2[HsO
4(OH)
2]
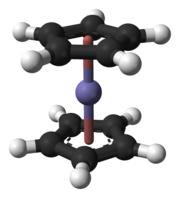
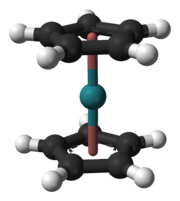
The team from the University of Mainz planned in 2008 to study the electrodeposition of hassium atoms using the new TASCA facility at GSI. Their aim was to use the reaction 226Ra(48Ca,4n)270Hs.[122] Scientists at GSI were hoping to use TASCA to study the synthesis and properties of the hassium(II) compound hassocene, Hs(C5H5)2, using the reaction 226Ra(48Ca,xn). This compound is analogous to the lighter compounds ferrocene, ruthenocene, and osmocene, and is expected to have the two cyclopentadienyl rings in an eclipsed conformation like ruthenocene and osmocene and not in a staggered conformation like ferrocene.[100] Hassocene, which is expected to be a stable and highly volatile compound, was chosen because it has hassium in the low formal oxidation state of +2—although the bonding between the metal and the rings is mostly covalent in metallocenes—rather than the high +8 state that had previously been investigated, and relativistic effects were expected to be stronger in the lower oxidation state. The highly symmetrical structure of hassocene and its low number of atoms make relativistic calculations easier.[100] As of 2019[update], there are no experimental reports of hassocene.[123]
Notes
- ^ Generally, heavier nuclei require more neutrons because as the number of protons increases, so does electrostatic repulsion between them. This repulsion is balanced by the binding energy generated by the strong interaction between quarks within nucleons; it is enough to hold the quarks together in a nucleon together and some of it is left for binding of different nucleons. The more nucleons there are in a nucleus, the more energy there is for binding the nucleons (note that greater total binding energy does not necessarily correspond to greater binding energy per nucleon).[2] However, having too many neutrons per proton, while decreasing electrostatic repulsion per nucleon that negates the binding energy, results in beta decay.
- ^ The superscript number to the left of a chemical symbol refers to the mass of a given nuclide; for instance, 48Ca is the notation for calcium-48. In superheavy element research, elements that have not been assigned a name and a symbol, are often referred to by their atomic numbers in lieu of symbols; if a symbol has been assigned and the number is to be displayed, it is written in subscript to the left of the symbol. 270108 would be 270Hs or 270
108Hs
in modern nomenclature (or hassium-270 if spelled out). - ^ This was intended not only to resolve any future conflicts, but also a number of ones that existed back then: beryllium/glucinium, niobium/columbium, lutecium/cassiopeium, hafnium/celtium, tungsten/wolfram, and protoactinium/brevium.
- ^ For example, Armbruster suggested element 107 be named nielsbohrium; JINR used this name for element 105 which they claimed to have discovered. This was meant to honor Oganessian's technique of cold fusion; GSI had asked JINR for permission.[24]
- ^ American physicist Glenn T. Seaborg suggested that name for element 110 on behalf of LBNL in November 1997 after IUPAC surveyed the three main collaborations (GSI, JINR/LLNL, and LBNL) on how they think the element should be named.[33]
- ^ Similarly, there are names of ruthenium, moscovium, and dubnium for JINR. The only element discovered by RIKEN in Wakō, Saitama Prefecture, Japan, is named nihonium after a Japanese name of Japan.
- ^ Different sources give different values for half-lives; the most recently published values are listed.
- ^ Half-life not precisely measured
- ^ Isotope unconfirmed
- ^ The symbol Z refers to the atomic number—number of protons in an atomic nucleus. The symbol N refers to the neutron number—number of neutrons in a nucleus. The symbol A refers to the mass number—number of neutrons and protons in a nucleus combined.
- ^ In particular, the low decay energy for 270Hs matches calculations.[55] The conclusion for 269Hs was made after its decay data was compared to that of 273Ds; the decay of the latter into the former has an energy sufficiently greater than the decay of the former (11.2 MeV and 9.2 MeV, respectively). The great value of the former energy was explained as a right-to-left crossing of N Template:Eq 162 (273Ds has 163 neutrons and 269Hs has 161).[57] A similar observation and conclusion were made after measurement of decay energy of 271Hs and 267Sg.[58]
- ^ At the time, this symbol had not yet been taken by seaborgium.
- ^ The two densest elements whose densities have been measured so far are osmium and iridium, both from the sixth period. There have been different records on which is denser; different texts published different results.[86][87] More precise measurements from the 1990s onward established that osmium was slightly denser at 22.589 ± 0.005 g/cm3 at the standard conditions (iridium may be the denser one at high pressures).[88]
- ^ While iridium is known to show a +8 state in iridium tetroxide, as well as a unique +9 state in the iridium tetroxide cation IrO+
4, the former is only known in matrix isolation and the latter in the gas phase, and no iridium compounds in such high oxidation states have been synthesized in macroscopic amounts.[98][99]
References
- ^ Aksenov, N. V.; Steinegger, P.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Albin, Yury V.; Bozhikov, Gospodin A.; Chepigin, Viktor I.; Eichler, Robert; Lebedev, Vyacheslav Ya.; Madumarov, Alexander Sh.; Malyshev, Oleg N.; Petrushkin, Oleg V. (2017). "On the volatility of nihonium (Nh, Z = 113)". The European Physical Journal A. 53 (7): 158. Bibcode:2017EPJA...53..158A. doi:10.1140/epja/i2017-12348-8. ISSN 1434-6001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ "Modern Alchemy: Creating Superheavy Elements". inChemistry. American Chemical Society. 2019. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- ^ a b c Oganessian, Yu. (2012). "Nuclei in the "Island of Stability" of Superheavy Elements". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 337 (1): 012005-1–012005-6. Bibcode:2012JPhCS.337a2005O. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/337/1/012005. ISSN 1742-6596.
- ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. Ts. (2004). "Superheavy elements". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 76 (9): 1717–1718. doi:10.1351/pac200476091715. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
coldfusion77was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Ter-Akopian, G. M.; Pleve, A. A. (1978). Опыты по синтезу 108 элемента в реакции 226Ra + 48Ca [Experiments on the synthesis of element 108 in the 226Ra+48Ca reaction] (PDF) (Report) (in Russian). Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ Orlova, O. A.; Pleve, A. A.; Ter-Akop'yan, G. M.; Tret'yakova, S. P.; Chepigin, V. I.; Cherepanov, E. A. (1979). Опыты по синтезу 108 элемента в реакции 208Pb + 58Fe [Experiments on the synthesis of element 108 in the 208Pb + 58Fe reaction] (PDF) (Report) (in Russian). Joint Institute for Nuclear Research.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ "Timeline - GSI". GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Preuss, P. (2001). "Hassium becomes heaviest element to have its chemistry studied". Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ a b Barber 1993, p. 1790.
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
Emsley2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Barber 1993, p. 1791.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
84Mu01was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Hofmann, S. (2016). "The discovery of elements 107 to 112" (PDF). EPJ Web Conf. 131: 4–5. Bibcode:2016EPJWC.13106001H. doi:10.1051/epjconf/201613106001. Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- ^ Barber 1993, p. 1757.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
1993 responseswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e Koppenol, W. H. (2002). "Naming of new elements (IUPAC Recommendations 2002)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 74 (5): 788. doi:10.1351/pac200274050787. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ Chatt, J. (1979). "Recommendations for the naming of elements of atomic numbers greater than 100". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 51 (2): 381–384. doi:10.1351/pac197951020381.
- ^ Öhrström, L.; Holden, N. E. (2016). "The Three-Letter Element Symbols". Chemistry International. 38 (2): 4–8. doi:10.1515/ci-2016-0204.
- ^ Greenwood 1997, p. 30.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1653.
- ^ "GSI - Element 107-109". GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research. 2012. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- ^ Karol, P. (1994). "The Transfermium Wars". Chemical & Engineering News. 74 (22): 2–3. doi:10.1021/cen-v072n044.p002.
- ^ Hoffman 2000, pp. 337–338, 384.
- ^ Hoffman 2000, pp. 385–394.
- ^ Inorganic Chemistry Division: Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (1994). "Names and symbols of transfermium elements (IUPAC Recommendations 1994)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 66 (12): 2419–2421. doi:10.1351/pac199466122419.
- ^ Cotton, S. A. (1996). "After the actinides, then what?". Chemical Society Reviews. 25 (3): 219–227. doi:10.1039/CS9962500219.
- ^ "IUPAC verabschiedet Namen für schwere Elemente: GSI-Vorschläge für die Elemente 107 bis 109 akzeptiert" [IUPAC adopts names for heavy elements: GSI's suggestions for elements 107 to 109 accepted] (PDF). GSI-Nachrichten (in German). Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung. 1997. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 December 2015. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ Yarris, L. (1994). "Naming of element 106 disputed by international committee". Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Hoffman 2000, pp. 392–394.
- ^ Hoffman 2000, pp. 394–395.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
IUPAC97was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hoffman 2000, pp. 396–398.
- ^ a b Aldersey-Williams, H. (2011). Periodic Tales. HarperCollins Publishers. pp. 396–397. ISBN 978-0-06-182473-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g Audi 2017, p. 030001-133.
- ^ a b Thoennessen, M. (2016). The Discovery of Isotopes: A Complete Compilation. Springer. pp. 229, 234, 238. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-31763-2. ISBN 978-3-319-31761-8. LCCN 2016935977.
- ^ a b c d e Audi 2017, p. 030001-134.
- ^ Audi 2017, p. 030001-135.
- ^ Utyonkov, V. K.; Brewer, N. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Dimitriev, S. N.; Grzywacz, R. K.; Itkis, M. G.; Miernik, K.; Polyakov, A. N.; Roberto, J. B.; Sagaidak, R. N.; Shirokovsky, I. V.; Shumeiko, M. V.; Tsyganov, Yu. S.; Voinov, A. A.; Subbotin, V. G.; Sukhov, A. M.; Karpov, A. V.; Popeko, A. G.; Sabel'nikov, A. V.; Svirikhin, A. I.; Vostokin, G. K.; Hamilton, J. H.; Kovrinzhykh, N. D.; Schlattauer, L.; Stoyer, M. A.; Gan, Z.; Huang, W. X.; Ma, L. (30 January 2018). "Neutron-deficient superheavy nuclei obtained in the 240Pu+48Ca reaction". Physical Review C. 97 (14320): 014320. Bibcode:2018PhRvC..97a4320U. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.014320.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts. (2015). "Super-heavy element research". Reports on Progress in Physics. 78 (3): 036301. Bibcode:2015RPPh...78c6301O. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/78/3/036301. PMID 25746203.
- ^ a b Audi 2017, p. 030001-136.
- ^ Scerri, E. (2019). The Periodic Table: Its Story and Its Significance. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-091438-7.
- ^ Helmenstine, A. M. (2019). "Hassium Facts - Hs or Element 108". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 9 July 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Audi 2017, pp. 030001-133–030001-136.
- ^ Hofmann, S.; Heinz, S.; Mann, R.; et al. (2012). "The reaction 48Ca + 248Cm → 296116* studied at the GSI-SHIP". The European Physical Journal A. 48 (5): 62. Bibcode:2012EPJA...48...62H. doi:10.1140/epja/i2012-12062-1.
- ^ Dean, T. (2014). "How to make a superheavy element". Cosmos Magazine. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Pauli, N. (2019). "Nuclear fission" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b c d Oganessian, Yu. Ts. (2004). "Superheavy elements". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 76 (9): 1716–1718. doi:10.1351/pac200476091715. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ Schädel, M. (2015). "Chemistry of the superheavy elements". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 373 (2037): 20140191. Bibcode:2015RSPTA.37340191S. doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0191. ISSN 1364-503X. PMID 25666065.
- ^ Hulet, E. K. (1989). Biomodal spontaneous fission. 50th Anniversary of Nuclear Fission, Leningrad, USSR. Bibcode:1989nufi.rept...16H.
- ^ Zagrebaev 2013, pp. 11–12.
- ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Alexander, C.; et al. (2013). "Experimental studies of the 249Bk + 48Ca reaction including decay properties and excitation function for isotopes of element 117, and discovery of the new isotope 277Mt". Physical Review C. 87 (54621). American Physical Society: 8–9. Bibcode:2013PhRvC..87e4621O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.87.054621.
- ^ Patyk, Z.; Sobiczewski, A. (1991). "Ground-state properties of the heaviest nuclei analyzed in a multidimensional deformation space". Nuclear Physics A. 533 (1): 150. Bibcode:1991NuPhA.533..132P. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(91)90823-O.
- ^ Inman, M. (2006). "A Nuclear Magic Trick". Physical Review Focus. 18. doi:10.1103/physrevfocus.18.19. Archived from the original on 2 June 2018. Retrieved 25 December 2006.
- ^ a b Dvorak, J.; Brüchle, W.; Chelnokov, M.; et al. (2006). "Doubly Magic Nucleus 108270Hs162". Physical Review Letters. 97 (24): 242501. Bibcode:2006PhRvL..97x2501D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.242501. PMID 17280272.
- ^ Smolańczuk, R. (1997). "Properties of the hypothetical spherical superheavy nuclei" (PDF). Physical Review C. 56 (2): 812–824. Bibcode:1997PhRvC..56..812S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.56.812.
- ^ Hofmann, S.; Heßberger, F.P.; Ackermann, D.; Münzenberg, G.; Antalic, S.; Cagarda, P.; Kindler, B.; Kojouharova, J.; Leino, M.; Lommel, B.; Mann, R. (2002). "New results on elements 111 and 112". The European Physical Journal A. 14 (2): 155. Bibcode:2002EPJA...14..147H. doi:10.1140/epja/i2001-10119-x. ISSN 1434-6001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ Schädel, M.; Shaughnessy, D. (2013). The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 458. ISBN 978-3-642-37466-1.
- ^ Karpov, A. V.; Zagrebaev, V. I.; Palenzuela, Y. M.; Ruiz, L. F.; Greiner, W. (2012). "Decay properties and stability of the heaviest elements" (PDF). International Journal of Modern Physics E. 21 (2): 1250013-1–1250013-20. Bibcode:2012IJMPE..2150013K. doi:10.1142/S0218301312500139. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 December 2016. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. (2007). "Heaviest nuclei from 48Ca-induced reactions" (PDF). Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics. 34 (4): R235. Bibcode:2007JPhG...34R.165O. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/34/4/R01. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
- ^ Kragh 2018, pp. 9–10.
- ^ Cherdyntsev, V. V.; Mikhailov, V. F. (1963). "Первозданный заурановый изотоп в природе" [The Primordial Transuranium Isotope in Nature]. Geokhimiya (in Russian). 1: 3–14. OSTI 4748393.
- ^ a b Nikitin, A. (1970). "Новый трансуран найден в природе" [New transuranium found in nature]. Nauka i Zhizn (in Russian). 2: 102–106.
- ^ a b Kulakov, V. M. (1970). "Has element 108 been discovered?". Soviet Atomic Energy. 29 (5): 1166–1168. doi:10.1007/BF01666716.
- ^ Marinov, A.; Gelberg, S.; Kolb, D.; Brandt, R.; Pape, A. (2003). "New outlook on the possible existence of superheavy elements in nature". Physics of Atomic Nuclei. 66 (6): 1137–1145. arXiv:nucl-ex/0210039. Bibcode:2003PAN....66.1137M. doi:10.1134/1.1586428.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Ivanov, A. V. (2006). "The possible existence of Hs in nature from a geochemical point of view". Physics of Particles and Nuclei Letters. 3 (3): 165–168. arXiv:nucl-th/0604052. Bibcode:2006PPNL....3..165I. doi:10.1134/S1547477106030046.
- ^ Sokol, E. (2013). Yakushev, E. (ed.). Report on JINR activities and tasks accomplished in 2013 in Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane (Report). Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ Ludwig, P.; Faestermann, T.; Korschinek, G.; Rugel, G.; Dillmann, I.; Fimiani, L.; Bishop, S.; Kumar, P. (2012). "Search for superheavy elements with 292 ≤ A ≤ 310 in nature with accelerator mass spectrometry" (PDF). Physical Review C. 85 (2): 024315-1–024315-8. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.85.024315. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 December 2018. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ Hoffman 2006, pp. 1666–1669.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Bloombergwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1666.
- ^ a b c Hoffman 2006, p. 1669.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, pp. 1666–1667.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1667–1668.
- ^ a b Hoffman 2006, p. 1672.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1676.
- ^ a b c "Spin Orbit Splitting". X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Reference Pages. University of Western Ontario. 2012. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Thayer, J. S. (2010). "Relativistic effects and the chemistry of the heavier main group elements". In Barysz, M.; Ishikawa, Ya. (eds.). Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 10. Springer Netherlands. p. 65. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, pp. 1668–1669.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1673.
- ^ a b Hoffman 2006, p. 1679.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Oestlinwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Grossman, J. C.; Mizel, A.; Côté, M.; Cohen, M. L.; Louie, S. G. (1999). "Transition metals and their carbides and nitrides: Trends in electronic and structural properties". Phys. Rev. B. 60 (9): 6344. Bibcode:1999PhRvB..60.6343G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.60.6343.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ Cohen, M. (1985). "Calculation of bulk moduli of diamond and zinc-blende solids". Physical Review B. 32 (12): 7988–7991. Bibcode:1985PhRvB..32.7988C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.32.7988. PMID 9936971.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, pp. 1690, 1724.
- ^ Lide 2004, pp. 4-37–4-96.
- ^ Dean, J. A., ed. (1999). Lange's Handbook of Chemistry (15th ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 3.13–3.60. ISBN 978-0-07-016384-3.
- ^ Arblaster, J. W. (2014). "Is Osmium Always the Densest Metal?". Johnson Matthey Technology Review. 58 (3): 137. doi:10.1595/147106714X682337.
- ^ a b c Hoffman 2006, p. 1691.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1677.
- ^ a b Greenwood 1997, pp. 27–28.
- ^ a b Griffith, W. P. (2008). "The Periodic Table and the Platinum Group Metals". Platinum Metals Review. 52 (2): 114–119. doi:10.1595/147106708X297486.
- ^ a b c d Düllmann, C. E. (2011). Superheavy Element Research Superheavy Element - News from GSI and Mainz (Report). University Mainz. Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ a b Düllmann, C. E.; Dressler, R.; Eichler, B.; Gäggeler, H. W.; Glaus, F.; Jost, D. T.; Piguet, D.; Soverna, S.; Türler, A.; Brüchle, W.; Eichler, R.; Jäger, E.; Pershina, V.; Schädel, M.; Schausten, B.; Schimpf, E.; Schött, H.-J.; Wirth, G.; Eberhardt, K.; Thörle, P.; Trautmann, N.; Ginter, T. N.; Gregorich, K. E.; Hoffman, D. C.; Kirbach, U. W.; Lee, D. M.; Nitsche, H.; Patin, J. B.; Sudowe, R.; Zielinski, P. M.; Timokhin, S. N.; Yakushev, A. B.; Vahle, A.; Qin, Z. (2003). "First chemical investigation of hassium (Hs, Z=108)". Czechoslovak Journal of Physics. 53 (1 Supplement): A291–A298. Bibcode:2003CzJPS..53A.291D. doi:10.1007/s10582-003-0037-4.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d "Chemistry of Hassium" (PDF). Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbH. 2002. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 March 2012. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Schädel, M. (2003). The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements. Springer. p. 269. ISBN 978-1402012501. Retrieved 17 November 2012.
- ^ Barnard, C. F. J.; Bennett (2004). "Oxidation States of Ruthenium and Osmium". Platinum Metals Review. 48 (4): 157–158. doi:10.1595/147106704X10801.
- ^ Gong, Yu; Zhou, M.; Kaupp, M.; Riedel, S. (2009). "Formation and Characterization of the Iridium Tetroxide Molecule with Iridium in the Oxidation State +VIII". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (42): 7879–7883. doi:10.1002/anie.200902733. PMID 19593837.
- ^ Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Goettel, J. T.; Schrobilgen, G. G.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Schlöder, T.; Riedel, S. (2014). "Identification of an iridium-containing compound with a formal oxidation state of IX". Nature. 514 (7523): 475–477. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..475W. doi:10.1038/nature13795. PMID 25341786.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
hassocenewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1720.
- ^ Nagame, Yu.; Kratz, J. V.; Schädel, M. (2015). "Chemical studies of elements with Z ≥ 104 in liquid phase". Nuclear Physics A. 944: 632. Bibcode:2015NuPhA.944..614N. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2015.07.013.
- ^ a b Perfiliev, Yu. D.; Sharma, V. K. (2008). "Higher Oxidation States of Iron in Solid State: Synthesis and Their Mössbauer Characterization – Ferrates – ACS Symposium Series (ACS Publications)". Platinum Metals Review. 48 (4): 157–158. doi:10.1595/147106704X10801.
- ^ Nič, M.; Jirát, J.; Košata, B.; Jenkins, A., eds. (2009). "electron affinity, Eea". IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (2.1.0 ed.). International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1351/goldbook.e01977. ISBN 978-0-9678550-9-7. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ Gutsev, G. L.; Khanna, S.; Rao, B.; Jena, P. (1999). "FeO4: A unique example of a closed-shell cluster mimicking a superhalogen". Physical Review A. 59 (5): 3681–3684. Bibcode:1999PhRvA..59.3681G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.59.3681.
- ^ Cotton, S. A. (1997). Chemistry of Precious Metals. London: Chapman and Hall. ISBN 978-0-7514-0413-5.
- ^ Martín, V. S.; Palazón, J. M.; Rodríguez, C. M.; Nevill, C. R. (2006). "Ruthenium(VIII) Oxide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rr009.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ^ Brown, G. M.; Butler, J. H. (1997). "New method for the characterization of domain morphology of polymer blends using ruthenium tetroxide staining and low voltage scanning electron microscopy (LVSEM)". Polymer. 38 (15): 3937–3945. doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(96)00962-7.
- ^ Stellman, J. M. (1998). "Osmium". Encyclopaedia of Occupational Health and Safety. International Labour Organization. p. 63.34. ISBN 978-92-2-109816-4. OCLC 35279504.
- ^ Housecroft, C. E.; Sharpe, A. G. (2004). Inorganic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. pp. 671–673, 710. ISBN 978-0-13-039913-7.
- ^ Thompson, M. "Osmium tetroxide (OsO4)". Bristol University. Archived from the original on 12 July 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1685.
- ^ a b von Zweidorf, A.; Angert, R.; Brüchle, W. (2003). "Final result of the CALLISTO-experiment: Formation of sodium hassate(VIII)" (PDF). Retrieved 13 June 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Pershina, V.; Anton, J.; Jacob, T. (2008). "Fully relativistic density-functional-theory calculations of the electronic structures of MO4 (M = Ru, Os, and element 108, Hs) and prediction of physisorption". Physical Review A. 78 (3): 032518. Bibcode:2008PhRvA..78c2518P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.78.032518.
- ^ Schädel, M. (2006). "Chemistry of Superheavy Elements". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (3): 391. doi:10.1002/anie.200461072. ISSN 1433-7851. PMID 16365916.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1719.
- ^ Düllmann, C. E.; Brüchle, W.; Dressler, R.; et al. (2002). "Chemical investigation of hassium (element 108)". Nature. 418 (6900): 859–862. Bibcode:2002Natur.418..859D. doi:10.1038/nature00980. PMID 12192405.
- ^ Düllmann, C. E.; Eichler, B.; Eichler, R.; et al. (2002). "On the Stability and Volatility of Group 8 Tetroxides, MO4 (M = Ruthenium, Osmium, and Hassium (Z = 108))". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 106 (26): 6679–6680. doi:10.1021/jp0257146. ISSN 1520-6106.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, pp. 1712–1714.
- ^ a b Hoffman 2006, pp. 1714–1715.
- ^ Hoffman 2006, p. 1714.
- ^ Even, J.; Kratz, J. V.; Mendel, M.; Wiehl, N. (2011). "Electrodeposition experiments with hassium" (PDF). Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ Maria, L.; Marçalo, J.; Gibson, J. K. (2019). Evans, W. J.; Hanusa, T. P. (eds.). The Heaviest Metals: Science and Technology of the Actinides and Beyond. John Wiley & Sons. p. 260. ISBN 978-1-119-30408-1.
Bibliography
- Audi, G.; Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S. (2017). "The NUBASE2016 evaluation of nuclear properties". Chinese Physics C. 41 (3): 030001. Bibcode:2017ChPhC..41c0001A. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/41/3/030001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - Barber, R. C.; Greenwood, N. N.; Hrynkiewicz, A. Z.; Jeannin, Y. P; Lefort, M; Sakai, M; Ulehla, I; Wapstra, A. H.; Wilkinson, D. H. (1993). "Discovery of the Transfermium elements" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 65 (8): 1757–1814. doi:10.1351/pac199365081757. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - Beiser, A. (2003). Concepts of modern physics (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-244848-1. OCLC 48965418.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Hoffman, D. C.; Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T. (2000). The Transuranium People: The Inside Story. World Scientific. ISBN 978-1-78-326244-1.
- Kragh, H. (2018). From Transuranic to Superheavy Elements: A Story of Dispute and Creation. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-75813-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Hoffman, D. C.; Lee, D. M.; Pershina, V. (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". In Morss, L. R.; Edelstein, N. M.; Fuger, J. (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 1652–1752. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- Lide, D. R. (2004). Handbook of chemistry and physics (84th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-0566-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Zagrebaev, V.; Karpov, A.; Greiner, W. (2013). "Future of superheavy element research: Which nuclei could be synthesized within the next few years?". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 420 (1): 012001. arXiv:1207.5700. Bibcode:2013JPhCS.420a2001Z. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/420/1/012001. ISSN 1742-6588.