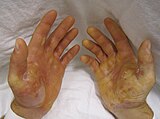
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
Appearance
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS),is a disorder resulting from mutations in the genes encoding keratin 5 or keratin 14.[1]: 598
Blister formation of EBS occurs at the dermoepidermal junction. Sometimes EBS is called epidermolytic.[citation needed]
Cause
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2018) |
Diagnosis
Classification
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex may be divided into multiple types:
| Type | Locus & Gene | OMIM |
|---|---|---|
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with migratory circinate erythema | 12q13 (KRT5) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation. | 12q13 (KRT5) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, autosomal recessive | 17q12-q21 (KRT14) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Generalized epidermolysis bullosa simplex | 17q12-q21 (KRT5), 12q13 (KRT14) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Localized epidermolysis bullosa simplex | 17q12-q21 (KRT5), 17q11-qter, 12q13 (KRT14) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa herpetiformis | 17q12-q21 (KRT5), 12q13 (KRT14) | Template:OMIM2 |
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy
|
8q24 (PLEC1) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with pyloric atresia | 8q24 (PLEC1) | Template:OMIM2 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex of Ogna | 8q24 (PLEC1) | Template:OMIM2 |
Management
- no cure for EB
- treat symptomatic
- protect skin, stop blisters formation, promote healing
- prevents complications
- Necessary treatment: use oral & topical steroid for healing & prevent complication
- maintain cool environment, avoid overheating & decreases friction
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ^ a b c d e f James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Harel, A, et al. "Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex with Mottled Pigmentation Resulting from a Recurrent Mutation in KRT14." Journal of Investigative Dermatology. (2006) 126, 1654–1657. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700296; published online 6 April 2006. [1]
- ^ a b c d Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
Further reading
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Epidermolysis bullosa simplex.
