Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario
Sault Ste. Marie | |
|---|---|
| City of Sault Ste. Marie | |
| Nicknames: | |
| Motto: "Naturally Gifted" | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| District | Algoma |
| Incorporated | 1888 (town) |
| Incorporated | 1912 (city) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Corporation |
| • Mayor | Christian Provenzano |
| • Council | Sault Ste. Marie City Council |
| • MP | Terry Sheehan |
| • MPP | David Orazietti |
| Area | |
| • Land | 223.26 km2 (86.20 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 57.46 km2 (22.19 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 805.38 km2 (310.96 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 192.00 m (629.92 ft) |
| Population | |
• City (single-tier) | 75,141 |
| • Density | 336.6/km2 (872/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 67,646 |
| • Urban density | 1,177.2/km2 (3,049/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 79,800 |
| • Metro density | 99.1/km2 (257/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern Standard Time (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)) |
| Postal code FSA | P6A, P6B, P6C |
| Area code(s) | (705) and (249)[5] |
| Highways | |
| Website | www.saultstemarie.ca |
| CA rank: 46th in Canada Municipal rank: 66th in Canada | |
Sault Ste. Marie (/ˈsuː seɪnt məˈriː/ "Soo Saint Marie") is a city on the St. Marys River in Ontario, Canada, close to the US-Canada border. It is the seat of the Algoma District and the third largest city in Northern Ontario, after Sudbury and Thunder Bay.
To the south, across the river, is the United States and the city of Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. These two communities were one city until a new treaty after the War of 1812 established the border between Canada and the United States in this area at the St. Mary's River. In the 21st century, the two cities are joined by the International Bridge, which connects Interstate 75 on the Michigan side, and Huron Street (and former Ontario Secondary Highway 550B) on the Ontario side. Shipping traffic in the Great Lakes system bypasses the Saint Mary's Rapids via the American Soo Locks, the world's busiest canal in terms of tonnage that passes through it, while smaller recreational and tour boats use the Canadian Sault Ste. Marie Canal.
French colonists referred to the rapids on the river as Les Saults de Ste. Marie and the village name was derived from that. The rapids and cascades of the St. Mary's River descend more than 20 feet from the level of Lake Superior to the level of the lower lakes. Hundreds of years ago, this slowed shipping traffic, requiring an overland portage of boats and cargo from one lake to the other. The entire name translates to "Saint Mary's Rapids" or "Saint Mary's Falls". The word sault is pronounced [so] in French, and /ˈsuː/ in the English pronunciation of the city name.[6] Residents of the city are called Saultites.[7]
Sault Ste. Marie is bordered to the east by the Rankin and Garden River First Nation reserves, and to the west by Prince Township. To the north, the city is bordered by an unincorporated portion of Algoma District, which includes the local services boards of Aweres, Batchawana Bay, Goulais and District, Peace Tree and Searchmont. The city's census agglomeration, including the townships of Laird, Prince and Macdonald, Meredith and Aberdeen Additional and the First Nations reserves of Garden River and Rankin, had a total population of 79,800 in 2011.
Native American settlements, mostly of Ojibwe-speaking peoples, existed here for more than 500 years. In the late 17th century, French Jesuit missionaries established a mission at the First Nations village. This was followed by development of a fur trading post and larger settlement, as traders, trappers and Native Americans were attracted to the community. It was considered one community and part of Canada until after the War of 1812 and settlement of the border between Canada and the US at the Ste. Mary's River. The US prohibited British traders from operating in its territory, and the areas separated by the river began to develop as two communities, both named Sault Ste. Marie.[8]
History


The historic Ojibwe, an Anishinaabe language people, originally called this area Baawitigong, meaning "place of the rapids." They used this as a regional meeting place during whitefish season in the St. Mary's Rapids. (The anglicized form of this name, Bawating, is used in institutional and geographic names in the area.)
After the visit of Étienne Brûlé in 1623, the French called it "Sault de Gaston" in honour of Gaston, Duke of Orléans, the brother of King Louis XIII of France. In 1668, French Jesuit missionaries renamed it as Sault Sainte Marie, and established a mission settlement (present-day Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan) on the river's south bank.
Later, a fur trading post was established and the settlement expanded to include both sides of the river. Sault Ste. Marie is one of the oldest French settlements in North America. It was at the crossroads of the 3,000-mile fur trade route, which stretched from Montreal to Sault Ste. Marie and to the North country above Lake Superior. A cosmopolitan, mixed population of Europeans, First Nations peoples, and Métis lived at the village spanning the river.[9]
The city name originates from Saults de Sainte-Marie, archaic French for "Saint Mary's Falls", a reference to the rapids of Saint Marys River. Etymologically, the word sault comes from an archaic spelling of saut (from sauter), which translates most accurately in this usage to the English word cataract. This in turn derives from the French word for "leap" or "jump" (similar to somersault). Citations dating back to 1600 use the sault spelling to mean a cataract, waterfall or rapids. In modern French, however, the words chutes or rapides are more usual. Sault survives almost exclusively in geographic names dating from the 17th century. (See also Long Sault, Ontario, Sault St. Louis, Quebec, and Grand Falls/Grand-Sault, New Brunswick, three other place names where "sault" also carries this meaning.)
Traders regularly interacted with tribes from around the Great Lakes, but the fluid environment changed during and after the War of 1812 between Britain and the United States. Trade dropped during the war and on July 20, 1814 an American force destroyed the North West Company depot on the north shore of the St. Marys River. Since the Americans were unable to capture Fort Mackinac, the British forces retained control of Sault Ste. Marie.[10]

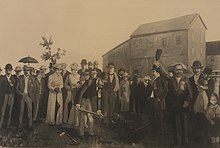
In 1870, the United States refused to give the steamer Chicona, carrying Colonel Garnet Wolseley, permission to pass through the locks at Sault Ste Marie. In order to control their own water passage, the Canadians constructed the Sault Ste. Marie Canal, which was completed in 1895.[11]
Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario was incorporated as a town in 1887 and a city in 1912. The town gained brief international notoriety in 1911 in the trial of Angelina Napolitano, the first person in Canada to use the battered woman defence for murder.[12]
During World War II, and particularly after the US was attacked at Pearl Harbor in 1941, government concern turned to protection of the locks and shipping channel at Sault Ste. Marie. A substantial military presence was established to protect the locks from a possible attack by Nazi German aircraft from the north. The recent development of long-range bombers increased fears of a sudden air raid. Military strategists studied polar projection maps which indicated that the air distance from occupied Norway to the town was about the same as the distance from Norway to New York. That direct route of about 3000 miles is over terrain where there were few observers and long winter nights.
A joint Canadian and US committee called the "Permanent Joint Board on Defence" drove the installation of anti-aircraft defence and associated units of the United States Army Air Forces and Royal Canadian Air Force to defend the locks. An anti-aircraft training facility was established 100 kilometres (62 mi) north of Sault Ste. Marie on the shores of Lake Superior. Barrage balloons were installed, and early warning radar bases were established at five locations in northern Ontario (Kapuskasing, Cochrane, Hearst, Armstrong (Thunder Bay District), and Nakina)[13] to watch for incoming aircraft. Military personnel were established to guard sensitive parts of the transportation infrastructure. A little over one year later, in January 1943, most of these facilities and defences were deemed excessive and removed, save a reduced military base at Sault Ste. Marie.
The first Algerine-class minesweeper in the Royal Canadian Navy was named HMCS Sault Ste. Marie (J334) after the city. It was laid down in 1942 and acted as a convoy in the Battle of the Atlantic.
On January 29, 1990, Sault Ste. Marie became a flashpoint in the Meech Lake Accord constitutional debate when council passed a resolution declaring English as the city's official language[14] and the sole language for provision of municipal services.[15] The city had a sizable French-speaking population and these residents objected strongly to the council's action. The Sault Ste. Marie language resolution was not the first of its kind in Ontario, but the municipality was the largest to have passed such a resolution and the first to do so despite its sizable Franco-Ontarian population.[16] the council's action was very controversial. Many objections were raised by the French-speaking population.
Climate
Sault Ste. Marie has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfb) with cold, snowy winters and warm summers that are moderated to some extent by Lake Superior. Winters are cold but are milder than some inland places.[4] Temperatures drop below −20 °C (−4.0 °F) 24 days per year. Summers are warm with a July high of 24.0 °C (75.2 °F) and temperatures above 30 °C (86.0 °F) occur 4 days per year.[4] The average annual precipitation is 889 millimetres (35.0 in), which is evenly distributed throughout the year though the months September to November are wetter.[4] The record high was 37.2 °C (99.0 °F) on 3 July 1921,[17] while the record low was −41.1 °C (−42.0 °F) on 26 January 1927.[18]
| Climate data for Sault Ste. Marie Airport 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1889–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high humidex | 7.8 | 8.7 | 28.0 | 31.6 | 38.6 | 40.9 | 42.9 | 42.7 | 39.5 | 34.4 | 21.6 | 19.2 | 42.9 |
| Record high °C (°F) | 7.8 (46.0) |
10.8 (51.4) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.8 (82.0) |
32.3 (90.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.2 (99.0) |
36.1 (97.0) |
35.0 (95.0) |
27.8 (82.0) |
21.7 (71.1) |
15.4 (59.7) |
37.2 (99.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −5.0 (23.0) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
1.2 (34.2) |
9.0 (48.2) |
16.4 (61.5) |
21.4 (70.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
23.4 (74.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
11.6 (52.9) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.9 (14.2) |
−9.0 (15.8) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
10.0 (50.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
17.9 (64.2) |
17.5 (63.5) |
13.5 (56.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
4.7 (40.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −14.8 (5.4) |
−14.3 (6.3) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
3.6 (38.5) |
8.4 (47.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
11.6 (52.9) |
8.0 (46.4) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −41.1 (−42.0) |
−39.4 (−38.9) |
−36.7 (−34.1) |
−28.9 (−20.0) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−13.3 (8.1) |
−32.8 (−27.0) |
−36.7 (−34.1) |
−41.1 (−42.0) |
| Record low wind chill | −44.8 | −42.3 | −40.5 | −27.8 | −10.0 | −4.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | −6.0 | −13.9 | −29.2 | −42.8 | −44.8 |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.5 (2.54) |
43.3 (1.70) |
55.6 (2.19) |
65.5 (2.58) |
66.1 (2.60) |
73.7 (2.90) |
71.9 (2.83) |
83.5 (3.29) |
102.1 (4.02) |
102.3 (4.03) |
92.1 (3.63) |
77.4 (3.05) |
897.7 (35.34) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 7.3 (0.29) |
5.2 (0.20) |
23.2 (0.91) |
48.0 (1.89) |
65.5 (2.58) |
73.7 (2.90) |
71.9 (2.83) |
83.5 (3.29) |
101.8 (4.01) |
97.1 (3.82) |
57.3 (2.26) |
16.8 (0.66) |
651.3 (25.64) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 80.2 (31.6) |
52.4 (20.6) |
38.3 (15.1) |
17.4 (6.9) |
0.6 (0.2) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.1) |
5.2 (2.0) |
41.4 (16.3) |
85.0 (33.5) |
320.7 (126.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 20.3 | 14.9 | 13.6 | 11.7 | 11.8 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 11.6 | 14.2 | 16.9 | 17.5 | 20.1 | 175.8 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 2.8 | 2.3 | 5.3 | 8.8 | 11.5 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 11.6 | 14.2 | 15.7 | 10.1 | 4.2 | 109.9 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 19.5 | 14.2 | 10.4 | 4.7 | 0.50 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.20 | 2.6 | 11.1 | 18.0 | 81.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 72.8 | 109.9 | 150.3 | 182.2 | 240.2 | 265.8 | 266.3 | 240.9 | 154.7 | 119.1 | 61.8 | 55.8 | 1,919.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 26.0 | 37.9 | 40.8 | 44.8 | 51.7 | 56.3 | 55.7 | 54.8 | 40.9 | 35.1 | 21.8 | 20.8 | 40.6 |
| Source: Environment Canada[19][20] | |||||||||||||
Economy



The MS Norgoma, a Canadian passenger ship, is a museum ship in the Great Lakes at Sault Ste. Marie.

The city developed considerable industry before and after World War II, especially in steel-making. Essar Steel Algoma (formerly Algoma Steel) is the largest single employer, with 3500 employees at the main plant and approximately 553 (440 unionized and 113 non-unionized) at an adjacent tube mill operated by Tenaris. During the 1940s, the steel and chromium operations were of substantial importance to the war effort in Canada and the United States. Algoma Steel and the Chromium Mining and Smelting Corporation were key producers for transportation and military machines. The Huron Central Railway has been important to the operation of the steel operation, but Genesee and Wyoming, Inc., owner of the railway, has announced its intention to discontinue operations. It continued to operate under an agreement which terminated on August 15, 2010.[24]


Sault Ste. Marie prospered during the 1960s and '70s, but as imported steel began to compete with domestic production, the local industry began to contract. Since the late 1980s, Algoma Steel, has declared bankruptcy twice and laid off large numbers of workers. Algoma was bailed out by the Ontario government with interest-free loans. The company had a swift turnaround in 2004 from its earlier financial troubles of the 1990s. China's increased demand for steel of the past decade has increased the price of steel. Denis Turcotte, CEO, was named "Canadian CEO of the year" in 2006 for his efforts. An offer to purchase ASI by the Essar Group (India) had been recommended by the ASI Board of Directors and was approved. The company was officially sold to the Essar Group in June 2007 for $1.6 billion. Essar Steel Algoma is the most profitable steel company per unit on a global scale.
Forestry is also a major local industry. St. Mary's Paper has been closed and decommissioned, although it was reopened in June 2007 and operated for a time under new ownership. Also related to wood products is Flakeboard Ltd., which employs over 110 people in the community. An adjacent melamine factory manufactures products with Flakeboard's materials. Examples are furniture and cupboards where a finish is added to the product. Together both of Flakeboard's factories employ about 150 people. The Huron Central Railway is important to these local industries as well.
The business process outsourcing industry, with two call centres, Agero and Sutherland Global Services located within city limits, employ about 1500 people. The largest employer of the three call centres is Sutherland Global Services. Nucomm previously had a call centre here as well. The call centre industry has become a large employer in Sault Ste. Marie, which contributed to the economic turn around of the city in the late 1990s.
Another large employer in the community is the Ontario Lottery and Gaming Corporation (OLG). The OLG has a corporate office located on the waterfront. It employs a total of about 900 people in Sault Ste. Marie between the corporate office and OLG Casino Sault Ste. Marie. The prize centre used to be administered in the city but was moved back to Toronto (York Mills) in 2009. The OLG is still the fourth largest employer, after Essar Steel Algoma, Sault Area Hospital, and the call centre industry.
Sault Ste. Marie is one of only a few cities in Ontario where a municipal bylaw prevents stores from opening on December 26, a British holiday known as Boxing Day, and the day after Christmas. As in Sudbury, retail stores in Sault Ste. Marie begin their post-Christmas Boxing Day sales on December 27. A municipal referendum to determine whether voters favour allowing stores to open on Boxing Day was held concurrently with the 2010 municipal election.[25] Voter turnout was not high enough to make the referendum legally binding, but 60.77 per cent of voters opposed allowing stores to open on the holiday.[26]
Alternative energy capital of North America

The city is home to the Sault Ste. Marie Solar Park (68 MW) and, along with the co-generation plant (Brookfield Power), the F. H. Clergue Hydroelectic Generating Station, the nearby Prince Township Wind Farm (189 MW) and several nearby hydroelectric dams, form part of the city's push to be labelled the 'Alternative Energy Capital of North America'.[27] Two other wind farms are proposed for the area: the Goulais wind farm (25 MW)[28] and the Bow Lake wind farm (58 MW), in partnership with the Batchewana First Nation of Ojibways to be built near Montreal River Harbour.[29] Elementa Group has built a pilot waste-to-energy plant in Sault Ste. Marie,[30] and the local Public Utilities Commission collects methane gas from the city's landfill.
Transportation


Sault Ste. Marie is served by Highway 17, which is a segment of the Trans-Canada Highway in the region. The highway connects the city to Thunder Bay to the northwest and Sudbury to the east. The International Bridge connects downtown Sault Ste. Marie to Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, becoming Interstate 75 on the American side. Interstate 75 continues south to Saginaw, Flint, and Detroit before crossing into Ohio, eventually terminating in Hialeah, Florida, near Miami.
The International Bridge also directs traffic from the American side of the border via Sault Ste. Marie's new transport route that runs from the bridge to Second Line. This new limited-access roadway, known as "Carmen's Way" after the late MP Carmen Provenzano, will make it much easier for transport trucks to reach main roads. The route of Carmen's Way has a wide grassy right-of-way on both sides of the roadway, to facilitate future expansion of its lane capacity. Planning is underway to eventually connect Second Line East to the new four-lane section of Highway 17 that recently opened east of the city.
The city plays an inherited role in marine transportation, with the locks in Michigan being an integral component of the St. Lawrence Seaway. The city operates its own small-scale lock which is used by small boats and other pleasure craft in the summer. Also recently opened is a multi-modal terminal designed to take advantage of the Sault as a rail, road, and water transportation hub.
Sault Ste. Marie is also served by Sault Ste. Marie Airport and Sault Transit Services.[31] The city is no longer connected by passenger rail to any other major cities, but is part of the Algoma Central Railway network, which runs north from the city to the small town of Hearst. In 2006 the city's Member of Parliament, Tony Martin, called for passenger rail service to be reinstated between Sault Ste. Marie and Sudbury.[32]
Tourism

Area tourist attractions include the Canadian Bushplane Heritage Centre, the Sault Ste. Marie Canal National Historic Site, boat tours of the Sault locks (which connect Lake Superior with the lower Great Lakes), Whitefish Island, the Ermatinger-Clergue National Historic Site, Casino Sault Ste. Marie, the Art Gallery of Algoma and the Algoma Central Railway's popular Agawa Canyon Tour Train.
Nearby parks include Pancake Bay Provincial Park, Batchawana Bay Provincial Park and Lake Superior Provincial Park. Winter activities are also an asset to Sault Ste Marie's tourism industry with the annual Bon Soo Winter Carnival, Searchmont Resort as a great ski and snowboard destination, Stokely Creek Lodge (cross country ski resort) and Hiawatha a nearby cross country ski trails. The city also hosts a large snowmobile trail system that criss-crosses the province of Ontario.
A new non-motorized HUB trail is being created around the city (20 km) so that walkers, rollerbladers and cyclists (snowshoeing and cross country skiing in winter) can enjoy the beautiful and convenient circle tour around town. The Voyageur Hiking Trail, a long-distance trail that will eventually span from Sudbury to Thunder Bay, originated in Sault Ste. Marie in 1973. The Roberta Bondar Pavilion was created to commemorate the first Canadian female astronaut to go into space.
The city is also home to the Station Mall, one of the largest shopping malls in Northern Ontario.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1871 | 879 | — |
| 1881 | 780 | −11.3% |
| 1891 | 2,414 | +209.5% |
| 1901 | 7,169 | +197.0% |
| 1911 | 10,984 | +53.2% |
| 1921 | 21,092 | +92.0% |
| 1931 | 23,082 | +9.4% |
| 1941 | 25,620 | +11.0% |
| 1951 | 32,452 | +26.7% |
| 1961 | 43,088 | +32.8% |
| 1971 | 80,332 | +86.4% |
| 1981 | 82,697 | +2.9% |
| 1991 | 81,476 | −1.5% |
| 1996 | 80,054 | −1.7% |
| 2001 | 74,566 | −6.9% |
| 2006 | 74,948 | +0.5% |
| 2011 | 75,141 | +0.3% |
| Canada 2011 National Household Survey[33] | Population | % of Total Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visible minority group | South Asian | 270 | 0.37 |
| Chinese | 290 | 0.39 | |
| Black | 260 | 0.35 | |
| Filipino | 35 | 0.05 | |
| Latin American | 110 | 0.15 | |
| Arab | 85 | 0.11 | |
| Southeast Asian | 40 | 0.05 | |
| Korean | 40 | 0.05 | |
| Japanese | 25 | 0.03 | |
| Total visible minority population | 1,215 | 1.65 | |
| Aboriginal group | First Nations | 5,975 | 8.12 |
| Métis | 2,115 | 2.87 | |
| Inuit | 25 | 0.03 | |
| Total Aboriginal population | 7,970 | 10.83 | |
| White | 64,445 | 87.53 | |
| Total population | 73,625 | 100 | |
| 2011 | |
|---|---|
| Population | 75,141 (0.3% from 2006) |
| Land area | 223.26 km2 (86.20 sq mi) |
| Population density | 336.6/km2 (872/sq mi) |
| Median age | |
| Private dwellings | 33,901 (total) |
| Median household income |
Similar to many other Northern Ontario municipalities, Sault Ste. Marie's population has declined in the 1990s and early 2000s, with many individuals migrating to larger cities in southern Ontario. Since the early 1990s, the city had dropped from 84,000 to 74,566 residents, but in the 2006 census the city's population grew very slightly to 74,948. The city's census agglomeration, consisting of the townships of Laird, Prince and Macdonald, Meredith and Aberdeen Additional and the First Nations reserves of Garden River and Rankin, had a total population of 80,098, up from 78,908 in 2001.[37][38]
Ethnicity
Sault Ste. Marie was at one time a haven for Italian immigrants. The city has a large concentration of ethnic Italians for a community its size.[39] The city also has a significant First Nations population, with three reserves nearby.
Those who are of European origin constitute 91.6% of the population, including those who are of Italian, French, English and Nordic descent. Aboriginals or Native Canadians, constitute 7.8%, and those who are of Chinese, Asian, African, and Filipino ancestry make up the last 0.6% of the population.
Religion
| Religion statistics for Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario | ||
| Religion | Population | % |
|---|---|---|
| Christian (all) | 54,745 | 74.36% |
| Catholic 1 | 29,920 | 40.64% |
| United Church | 7,150 | 9.71% |
| Anglican | 4,730 | 6.42% |
| Lutheran | 1,980 | 2.69% |
| Presbyterian | 1,335 | 1.81% |
| Pentecostal | 1,230 | 1.67% |
| Baptist | 1,170 | 1.59% |
| Christian Orthodox | 230 | 0.31% |
| Christian, n.i.e. 2 | 7,000 | 9.51% |
| Jewish | 190 | 0.26% |
| Hindu | 160 | 0.22% |
| Muslim | 135 | 0.18% |
| Traditional (Aboriginal) Spirituality | 60 | 0.08% |
| Buddhist | 25 | 0.03% |
| Other religions 3 | 225 | 0.31% |
| No religious affiliation 4 | 18,080 | 24.56% |
| National Household Survey 2011 [33] | ||
|
1 Includes Roman Catholic, Eastern Catholic, | ||
Christianity is the chief faith in the city, with Roman Catholicism being the largest denomination. This can be attributed to the large number of citizens with a traditional French and Italian Catholic heritage. After Catholicism and Protestantism, those who identify as being non-religious make up almost one-quarter of residents.
-
Precious Blood Cathedral, Roman Catholic Diocese of Sault Sainte Marie
-
St. Luke's Cathedral, Anglican Diocese of Algoma
-
Central United Church
-
St. Andrew's United Church
-
St. Mary's Ukrainian Catholic Church
-
Bishop Fauquier Memorial Chapel
-
St. Mary's Cross, an illuminated 37 m summit cross
-
Beth Jacob Synagogue
Government

The Corporation of the City of Sault Ste. Marie is run by a city council of 12 councillors (representing six wards) and a mayor. The most recent municipal election was held on October 27, 2014, and the mayoralty was won by Christian Provenzano. The outgoing mayor, Debbie Amaroso, was the first woman elected to this office.[40]
The city's crest contains the words "Ojibwa Kitche Gumeeng Odena" (from Ojibwe gichi-gamiing oodena) which means "Town by the large body of water of the Ojibwe" (or simply "Town by Lake Superior") in the Ojibwe language.
The city is served by the Sault Ste. Marie federal electoral district and the Sault Ste. Marie provincial electoral district. The boundaries of these two districts are not identical; the provincial district encompasses the city alone, while the federal district includes the neighbouring Garden River and Rankin reserves, and extends northerly to the Montreal River. The city's current federal Member of Parliament is Terry Sheehan (Liberal), and its Member of Provincial Parliament is David Orazietti (Liberal).
See also Neighbourhoods in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario.
Education


The city is home to Sault College, a college of applied arts and technology, and to Algoma University. While the vast majority of programs at Algoma University and Sault College are delivered on the respective campuses, both institutions also offer joint programs with Lake Superior State University in Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. On June 18, 2008, Algoma University became an independent university, ending their longtime affiliation with Laurentian University in Sudbury. A new school, Shingwauk Kinoomaage Gamig (University), is poised to launch as a federated school of Algoma University. It will offer courses in Anishinaabe culture and language.
Sault Ste. Marie is home to both the Algoma District School Board and the Huron-Superior Catholic District School Board, and is part of the Conseil scolaire de district du Grand Nord de l'Ontario and the Conseil scolaire de district catholique du Nouvel-Ontario. It is also home to the following high schools:
- Korah Collegiate & Vocational School (English, public, offers the International Baccalaureate Programme)
- École Notre-Dame-du-Sault (French, Catholic)
- St. Mary's College (English with French Immersion Program, Catholic, offers Advanced Placement programs)
- Superior Heights Collegiate & Vocational School (English and French Immersion, public, offers Advanced Placement programs)
- White Pines Collegiate & Vocational School (English, public)
Sault Ste. Marie is also home to the Ontario Forest Research Institute and the federal Great Lakes Forestry Centre.
Sault Ste. Marie has over 30 elementary schools between both school boards.
Sports



The Sault Ste. Marie Greyhounds are the city's most recognized sports team having existed since the formation of the Northern Ontario Hockey Association in 1919. The Hounds won national championships twice including the 1993 Memorial Cup and the 1924 Allan Cup. The Greyhounds play in the Essar Centre, a state-of-the-art downtown arena that replaced the Sault Memorial Gardens in 2006. The current Hounds have retired five jerseys since joining the Ontario Hockey League in 1972: #1 John Vanbiesbrouck, #4 Craig Hartsburg, #10 Ron Francis, #5 Adam Foote, and #99 Wayne Gretzky.
Sault Ste. Marie also had a team in hockey's first professional league. The Sault Ste. Marie Marlboros or 'Canadian Soo' team played in the International Professional Hockey League from 1904 to 1907.
Sault Ste. Marie hockey teams have boasted a number of Hockey Hall of Fame members, including Sault natives or residents Phil Esposito, Tony Esposito, Ron Francis, and Didier Pitre, as well as Sault team members Gerry Cheevers, Paul Coffey, Bill Cook, Bun Cook, Wayne Gretzky, Newsy Lalonde, George McNamara, and Marty Walsh.
National Hockey League All-Stars Joe Thornton & Jeff Carter played their entire OHL careers as members of the Greyhounds. Current NHL players from the Sault Ste. Marie area include New Jersey Devils centre Tyler Kennedy, Los Angeles Kings centre Jordan Nolan, and Winnipeg Jets centre Chris Thorburn.
Sault Ste. Marie native Paul Maurice is the current coach of the NHL's Winnipeg Jets, and has been a head coach for parts of 16 seasons with the Hartford/Carolina franchise, Toronto Maple Leafs, and the Jets, becoming the league's youngest ever coach at the age of 28 in 1995, and taking Carolina to the Stanley Cup Finals in 2002. Notably, former Greyhound player and coach Ted Nolan coached parts of 5 seasons in the NHL with the Buffalo Sabres & the New York Islanders, winning the Jack Adams Trophy as the NHL Coach of the Year in 1998 with the Sabres.
Sault Ste. Marie was the host of the 1990 Brier, the Canadian men's curling championship. In 2010, it hosted the Scotties Tournament of Hearts, which serves as Canada's women's curling championship. At the 2013 Tim Hortons Brier held in Edmonton, Alberta, Brad Jacobs and his team from the Soo Curlers Association won the Tim Hortons Brier, and the honour of representing Canada in the 2013 Ford World Men's Curling Championship, where they won silver. The team later won the 2013 Canadian Olympic Curling Trials, earning them the right to represent Canada at the 2014 Winter Olympics, where they won gold. The local curling clubs are the Soo Curlers Association and the Tarentorus Curling Club.
Other notable athletes from Sault Ste. Marie include Canadian Football Hall of Fame inductee Rocky Dipietro, Paralympic swimmer Jessica Tuomela, softball pitcher Darren Zack, and mixed martial artist Antonio Carvalho.
The Sault has been host to many national and international sporting events including the 2003 Eco-Challenge North American Championship, an expedition-length (350–500 km) adventure race through unmarked wilderness by biking, trekking, paddling and using ropes.
The 2007 and 2009 Sault Steelers captured the Canadian Senior Football Championship.
Walk of Fame

The Walk of Fame was created in 2006 as a joint project between the city of Sault Ste. Marie and its Downtown Association, and honours those from the city or the Algoma District who have made outstanding contributions to the community or significant contributions in their chosen field of work. Inductees are added on an annual basis.
Culture
Sault Ste. Marie is home to the Bon Soo winter carnival, held every February. The city also hosts the annual Algoma Fall Festival which draws local and international performing artists. The Kiwanis Community Theatre and the landmark Central United Church are used for the performances. Both venues hold approximately 1,000 people. The Art Gallery of Algoma features an extensive collection of local and international artists' work and presents regular exhibitions. Residents celebrate Community Day on the third weekend of July. The local Rotary International club organizes a three-day event called Rotaryfest.[41]
Sault Ste. Marie was the focus of Kalle Mattson's 'A Love Song to the City', whose music video premiered on USA Today.[42]
Notable residents and groups
- Brigitte Acton, two-time Olympian alpine skier
- David Amber, NHL on Sportsnet reporter and anchor[43]
- Ivan Boldirev, retired NHL centre and 1978 NHL All-Star
- Roberta Bondar, neurologist and the first Canadian female astronaut in space
- Antonio Carvalho, mixed martial artist and UFC veteran
- Phil Esposito, Hockey Hall of Fame inductee, 5th all time NHL goal scorer, and winner of two Stanley Cups
- Tony Esposito, Hockey Hall of Fame inductee and winner of one Stanley Cup
- Aaron Fiacconi, retired CFL offensive lineman
- Ron Francis, 4th All-Time leading scorer in the NHL and winner of two Stanley Cups
- Kevin Hodson, retired NHL goalie and winner of one Stanley Cup & one Memorial Cup
- Lila Kedrova, Academy Award winning actress
- Tyler Kennedy, NHL player currently playing for the New Jersey Devils
- Mac Marcoux, visually-impaired alpine skier and gold medal winner at the 2014 Winter Paralympics[44]
- Kalle Mattson, folk rock musician
- Paul Maurice, current head coach of the NHL's Winnipeg Jets
- Bob McKenzie, TSN hockey broadcaster & analyst[45]
- Jordan Nolan, NHL player currently playing for the Los Angeles Kings
- Ted Nolan, former NHL player and head coach
- John Parco, retired hockey player and member of the Italian men's hockey team at the 2006 Winter Olympics
- Boomer Phillips, actor & comedian
- Didier Pitre, Hockey Hall of Fame inductee and winner of one Stanley Cup
- Crystal Shawanda, Juno Award winning country singer
- Ray Smillie, bronze medal winning boxer at the 1928 Summer Olympics
- Lyndon Slewidge, anthem singer for the Ottawa Senators & retired policeman
- Team Brad Jacobs, 2013 Tim Hortons Brier Champions & 2014 Winter Olympics gold medallists
- Chris Thorburn, NHL player currently playing for the Winnipeg Jets
- Treble Charger, Juno Award nominated alternative rock band
- Jessica Tuomela, visually impaired swimmer and silver medallist at the 2000 Summer Paralympics
- Marty Turco, retired NHL goalie and member of the 2006 Winter Olympics men's hockey team
- Woods of Ypres, Juno Award winning blackened doom metal band
Media
Sister cities
 County Louth, Ireland
County Louth, Ireland Forssa, Finland
Forssa, Finland Maia, Portugal[46]
Maia, Portugal[46] Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, USA [47] (also twin city)
Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, USA [47] (also twin city) Krasnoyarsk, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia (2002)[48]
Krasnoyarsk, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia (2002)[48]
References
- ^ "Factacular : City Nicknames". factacular.com.
- ^ a b "Sault Ste. Marie census profile". 2011 Census of Population. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2012-02-16.
- ^ a b "Sault Ste. Marie (Census agglomeration) census profile". 2011 Census of Population. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2012-02-16.
- ^ a b c d "Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000". Environment Canada. Retrieved 2012-05-06.
- ^ "Time to say goodbye to seven-digit calls", Sootoday
- ^ "History", Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan website
- ^ http://www.saultstar.com/2015/06/15/saultite-receives-honour-from-the-queen
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie – history" , The North View, accessed 20 Dec 2008 Archived 2008-05-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie – history" , The North View, accessed 20 Dec 2008 Archived 2008-05-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Mary Ellen Perkins (ed.) 'Discover your heritage: A Guide to Provincial Plaques in Ontario' Natural Heritage (Jun 30 1989) ISBN 0920474500 – plaque on eastern end of Canadian locks, Huron Street, Saint Ste. Marie
- ^ Mary Ellen Perkins (ed.) 'Discover your heritage: A Guide to Provincial Plaques in Ontario' Natural Heritage (Jun 30 1989) ISBN 0920474500 – plaque near Canadian locks, Huron Street, Saint Ste. Marie
- ^ Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online: Angelina Napolitano. By Franca Iacovetta. University of Toronto/Université Laval, 2004. page accessed June 2008
- ^ Dziuban, Stanley W. (1970). Military Relations Between the United States and Canada 1939–1945. United States Army Center of Military History. p. 196. Retrieved 2010-06-30.
- ^ Canadian Annual Review of Politics and Public Affairs, 1990, David Leyton-Brown (ed.), p.135. "On the language front, a major headache for the government began when the Sault Ste Marie City Council, under pressure from the Alliance for the Preservation of English in Canada, declared English as its official language."
- ^ Crosswords: Language, Education and Ethnicity in French Ontario, Monica Heller, p. 79
- ^ Heller, Crosswords, p. 80
- ^ "July 1921". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ "January 1927". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie A". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie A". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Retrieved September 29, 2013.
- ^ "Sault Ste M Forestry (1889-1933)". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ "Sault Ste Marie (1949-1969)". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ "Sault Ste Marie Insectary". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ "Genesee & Wyoming Reports Results for the Second Quarter of 2010 Aug 3, 2010 (Press release)". GWI Press Release. Genesee & Wyoming, Inc. 2010-08-03. Archived from the original on 2010-08-04. Retrieved 2010-08-04.
GWI has continued to operate HCRY under a temporary operating agreement that terminates in mid-August 2010, unless renewed by the affected parties.
- ^ Wording of Sault Ste. Marie referendum question yet to be decided". Sudbury Star, February 18, 2010.
- ^ "Boxing Day Vote – The People Have Spoken". soonews.ca, October 26, 2010.
- ^ Sault Ste. Marie Economic Development Corporation. "Renewable Energy". Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ Sprott Power. "Goulais". Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ BluEarth Renewables Inc. "Bow Lake Wind Project". Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ Elementa Group. "Commercial Demonstration Plant". Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie Transit". Saulttransitservices.com. Retrieved 2011-03-09.
- ^ "Passenger rail service to Sudbury needed: Sault MP". Retrieved 2011-03-09.
- ^ a b Statistics Canada National Household Survey 2011. "NHS Profile, Sault Ste. Marie, CY, Ontario, 2011". Retrieved 28 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "2011 Community Profiles". 2011 Canadian census. Statistics Canada. March 21, 2019. Retrieved 2012-02-16.
- ^ "2006 Community Profiles". 2006 Canadian census. Statistics Canada. August 20, 2019.
- ^ "2001 Community Profiles". 2001 Canadian census. Statistics Canada. July 18, 2021.
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie (City) community profile". 2006 Census data. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2011-04-15.
- ^ "Sault Ste. Marie (Census agglomeration) community profile". 2006 Census data. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2011-04-15.
- ^ "Ethno-Cultural Portrait of Canada, Table 1". 2.statcan.ca. Retrieved 2011-03-09.
- ^ Debbie Amaroso is our first female mayor! Sootoday.com, October 26, 2010.
- ^ Miramar Design Studio. "Rotaryfest". Rotaryfest. Retrieved 2011-03-09.
- ^ "Premiere: Kalle Mattson's 'A Love Song to the City'".
- ^ "David Amber NHL Network Bio". NHL Network.
- ^ "Sweet 16! Canada's Mac Marcoux wins bronze in Paralympic downhill in Sochi - 2014 Winter Games". 2014 Winter Games. 8 March 2014.
- ^ "404". TSN.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ City of Sault Ste. Marie (Ontario)
- ^ [1] Purvis, Michael (17 August 2012) Saults now sisters, Sault Star
- ^ Контакты с иностранными городами Внешние связи – официальный сайт администрации города Красноярска Template:Ru iconTemplate:En iconTemplate:De icon
External links
- City of Sault Ste. Marie
- Reynolds, Francis J., ed. (1921). . Collier's New Encyclopedia. New York: P. F. Collier & Son Company.
- . . 1914.









