Blue: Difference between revisions
←Replaced content with 'ur a faggott' |
m Reverted 1 edit by 72.195.158.153 identified as vandalism to last revision by Alansohn. (TW) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{otheruses1|the colour}} |
|||
ur a faggott |
|||
{{pp-move-indef}} |
|||
{{Infobox colour|title=Blue |
|||
|pic=Image:Color icon blue.svg |
|||
|wavelength=440–490 |
|||
|symbolism=[[ice]], [[water]], [[sky]], [[sadness]], [[winter]], [[Royal family|royalty]], [[boys]], [[cold]], [[calm]], [[conservatism|conservatism (universally)]], [[Liberalism|liberalism (US)]], and [[capitalism]] |
|||
|hex=0000FF|textcolor=white| |
|||
spelling=Colour| |
|||
r=0|g=0|b=255|rgbspace=[[sRGB color space|sRGB]]| |
|||
h=240|s=100|v=100|;ohsv=[[HSV]]| |
|||
source=[[Web colors#HTML color names|HTML/CSS]]<ref name="css3-color">[http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-color/#html4 W3C TR CSS3 Color Module, HTML4 color keywords]</ref> |
|||
<!--c=100|m=100|y=0|k=0| |
|||
h=240|s=100|v=100|--> |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Blue''' is a [[colour]]<!-- NOTE: Not "color": this article is in British English, and should stay that way, per [[WP:ENGVAR]] -->, the [[perception]] of which is evoked by [[light]] having a spectrum dominated by energy with a [[wavelength]] of roughly 440–490 [[Nanometre|nm]]. It is considered one of the [[additive color|additive]] [[primary color|primary colours]]. On the [[HSL and HSV|HSV Colour Wheel]], the [[Complementary color|complement]] of blue is [[yellow]]; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal mixture of [[red]] and [[green]] light. On a colour wheel based on traditional colour theory ([[RYB color model|RYB]]), the complementary colour to blue is considered to be [[orange (colour)|orange]] (based on the [[Munsell color system|Munsell colour wheel]]).<ref>[http://www.sanford-artedventures.com/study/g_color_wheel.html Glossary Term: Color wheel]</ref> |
|||
The [[English language]] commonly uses "blue" to refer to any colour from [[navy blue]] to [[cyan]]. The word itself is derived from the [[Old French]] word ''bleu''. |
|||
==Etymology and definitions== |
|||
[[Image:Bunch of blueberries, one unripe.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Blueberries]] |
|||
The [[modern English]] word ''blue'' comes from the [[Middle English]], ''bleu'' or ''blwe'', which came from an [[Old French]] word ''bleu'' of [[Germanic language|Germanic]] origin (Frankish or possibly [[Old High German]] ''blao'', "shining"). ''Bleu'' replaced Old English ''blaw''. The root of these variations was the Proto-Germanic ''blæwaz'', which was also the root of the Old Norse word ''bla'' and the modern [[Icelandic language|Icelandic]] ''blár'', and the [[North Germanic languages|Scandinavian]] word ''blå'', but it can refer to other non blue colours. <!-- It can also be green or orange occasionally (blue). --> A [[Scots language|Scots]] and [[Scottish English]] word for "blue-grey" is ''blae'', from the Middle English ''bla'' ("dark blue," from the [[Old English language|Old English]] ''blæd''). Ancient Greek lacked a word for blue and [[Homer]] called the colour of the sea "wine dark", except that the word ''kyanos'' (cyan) was used for dark blue enamel. |
|||
As a curiosity, ''blue'' is thought to be cognate with ''[[blond]]'', ''[[blank]]'' and ''[[black]]'' through the Germanic word. Through a [[Proto-Indo-European language|Proto-Indo-European]] root, it is also linked with Latin ''flavus'' ("yellow"; see ''[[flavescent]]'' and ''[[flavine]]''), with Greek ''phalos'' (white), French ''blanc'' (white, blank) (borrowed from [[Old Frankish language|Old Frankish]]), and with Russian белый, ''belyi'' ("white," see ''[[Beluga (whale)|beluga]]''), and Welsh ''blawr'' (grey) all of which derive (according to the ''[[The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language|American Heritage Dictionary]]'') from the [[Proto-Indo-European language|Proto-Indo-European]] [[Root (linguistics)|root]] ''*bhel-'' meaning "to shine, flash or burn", (more specifically the word bhle-was, which meant light coloured, blue, blond, or yellow), whence came the names of various bright colours, and that of colour black from a derivation meaning "burnt" (other words derived from the root ''*bhel-'' include ''[[bleach]]'', ''[[bleak]]'', ''[[blind]]'', ''[[blink]]'', ''[[blank]]'', ''[[blush]]'', ''[[blaze]]'', ''[[flame]]'', ''[[fulminate]]'', ''flagrant'' and ''[[phlegm]]''). |
|||
In the English language, blue may refer to the feeling of sadness. "He was feeling blue". This is because blue was related to rain, or storms, and in Greek mythology, the god [[Zeus]] would make rain when he was sad (crying), and a storm when he was angry. ''Kyanos'' was a name used in [[Ancient Greek]] to refer to ''dark blue tile'' (in [[English (language)|English]] it means blue-green or [[cyan]]).<ref>''Merriam-Webster's Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary'' Springfield, Mass.:1984--Merriam-Webster Page 319 </ref> The phrase "feeling blue" is linked also to a custom among many old deepwater sailing ships. If the ship lost the captain or any of the officers during its voyage, she would fly blue flags and have a blue band painted along her entire hull when returning to home port.<ref> "US Navy - origins of Navy Terminology" [http://www.navy.mil/navydata/traditions/html/navyterm.html#feelblue]</ref> |
|||
Many languages do not have [[Distinguishing blue from green in language|separate terms for blue and or green]], instead using a cover term for both (when the issue is discussed in linguistics, this cover term is sometimes called ''[[grue (color)#Grue as used to translate a color name in natural languages|grue]]'' in English). |
|||
==In science== |
|||
[[Image:Chiemsee010.jpg|200px|thumb|The sky and water often appear blue.]] |
|||
===Pigments=== |
|||
Traditionally, blue has been considered a primary colour in painting, with the secondary colour [[orange (colour)|orange]] as its complement. |
|||
Blue pigments include [[azurite]] (Cu<sub>3</sub>(CO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>(OH)<sub>2</sub>), [[ultramarine]] (Na<sub>8-10</sub>Al<sub>6</sub>Si<sub>6</sub>O<sub>24</sub>S<sub>2-4</sub>), [[cerulean blue]] (primarily cobalt (II) stanate: Co<sub>2</sub>SnO<sub>4</sub>), [[cobalt blue]] (cobalt(II) aluminate: CoAl<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>), and [[Prussian blue]] (milori blue: primarily Fe<sub>7</sub>(CN)<sub>18</sub>). |
|||
===Scientific natural standards for blue=== |
|||
* Emission spectrum of [[Copper|Cu]]<sup>2+</sup> |
|||
* Electronic spectrum of aqua-ions Cu(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> |
|||
===Animals=== |
|||
[[Image:Cyanocitta cristata blue jay.jpg|thumb|200px|right|a [[Blue Jay]]]] |
|||
*When an [[animal]]'s coat is described as "blue", it usually refers to a shade of grey that takes on a bluish tint, a diluted variant of a pure black coat.{{Fact|date=October 2007}} This designation is used for a variety of animals, including [[coat (dog)|dog coats]], some [[rat]] coats, [[cat coat genetics|cat coats]], some [[list of chicken breeds|chicken breed]]s, and some [[equine coat color|horse coat colours]]. |
|||
==Blue in human culture== |
|||
===Symbolic language=== |
|||
* In the English language, blue often represents the human emotion of sadness, e.g. "He was feeling blue". In German, on the other hand, to be "blue" (''blau sein'') is to be drunk. This derives from the ancient use of urine (which is produced copiously by the human body after drinking alcohol) in dyeing cloth blue with [[woad]] or [[indigo]].<ref>Heller, Eva. ''Wie Farben wirken: Farbpsychologie, Farbsymbolik, kreative Farbgestaltung''. Berlin: Rowohlt, 2004.</ref> |
|||
===Music=== |
|||
* The [[blues]] is a style of music originated by [[African Americans]]. |
|||
* In 1999 [[Eiffel 65]] released the song "[[Blue (Da Ba Dee)]]," a hugely popular [[Eurodance]] song which peaked at #2 on the [[Billboard Hot 100]] in the United States, and reached #1 in 17 countries.{{Fact|date=June 2008}} |
|||
* [[Blue (1970s band)|Blue]] is the name of the original Scottish rock group |
|||
* [[Blue (boy band)|Blue]] is also the name of an English pop boy band. |
|||
===National colours=== |
|||
[[Image:Flag of Greece.svg|thumb|200px|right|Flag of Greece]] |
|||
[[Image:Coat of arms of Israel.svg|thumb|200px|right|Coat of Arms symbol of Israel]] |
|||
* ''[[Azure (color)|Azzurro]]'' a light blue, is the national colour of [[Italy]] (from the [[livery]] colour of the former reigning family, the [[House of Savoy]]){{Fact|date=December 2007}}. |
|||
* Blue is the national sports colour for [[India]], as it denotes [[secularism]]. |
|||
* Blue is the national colour used on flags of several countries surrounded by seas or oceans such as [[Australia]] and [[Flag of Europe|Europe]], though not necessarily with this interpretation in mind. |
|||
* Blue and white are the national colours of [[Argentina]], [[El Salvador]], [[Finland]], [[Greece]], [[Guatemala]], [[Honduras]], [[Israel]], [[Federated States of Micronesia|Micronesia]], [[Nicaragua]], and [[Somalia]] as well as of the [[United Nations Organization]] using a light shade of blue symbolizing peace. |
|||
* Blue and yellow are the national colours of [[Barbados]], [[Kazakhstan]], [[Palau]], [[Sweden]], and [[Ukraine]], and along with green, of [[Brazil]], and along with red, of [[Chad]], [[Colombia]], [[Ecuador]], [[Moldova]], [[Romania]], and [[Venezuela]]. |
|||
*Blue, white and yellow are the national colours of [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], [[Kosovo]] and [[Uruguay]]. |
|||
* Blue and red are the national colours of [[Haiti]] and [[Liechtenstein]], and along with white (where it composed the French [[tricolour]] whose simple design or colours were taken by other countries), of [[Australia]], [[Cambodia]], [[Costa Rica]], [[Chile]], [[Croatia]], [[Cuba]], the [[Czech Republic]], the [[Dominican Republic]], [[France]], [[Iceland]], [[North Korea]], [[Laos]], [[Liberia]], [[Luxembourg]], [[Myanmar]], [[Nepal]], the [[Netherlands]], [[New Zealand]], [[Norway]], [[Panama]], [[Paraguay]], [[Russia]], [[Samoa]], [[Serbia]], [[Slovakia]], [[Slovenia]], [[Thailand]], the [[United Kingdom]], and the [[United States]]. |
|||
[[Image:Flag of Somalia.svg|thumb|200px|right|Flag of Somalia]] |
|||
* Blue, white and black are the national colours of [[Estonia]].<ref>"Estonia in brief: National Symbols" at Estonica website (www.estonica.org)[http://www.estonica.org/eng/lugu.html?kateg=73&menyy_id=779&alam=85&leht=1]</ref> |
|||
===Mysticism=== |
|||
* In the [[metaphysics]] of the "[[New Age]] Prophetess", [[Alice Bailey]], in her system called the [[Seven Rays]] which classifies humans into seven different metaphysical [[psychological types]], the "first ray" of "will-power" is represented by the colour blue. People who have this metaphysical psychological type are said to be "on the Blue Ray".<ref>{{cite book | last = Bailey| first= Alice A. | authorlink = Alice Bailey | title = The Seven Rays of Life | location= New York| year= 1995 |publisher = Lucis Publishing Company | isbn = 0853301425}}</ref> |
|||
* In [[Hinduism]], Blue is used to symbolically represent the fifth, throat [[chakra]] ([[Vishuddha]]).<ref>Stevens, Samantha. The Seven Rays: a Universal Guide to the Archangels. City: Insomniac Press, 2004. ISBN 1894663497 pg. 24</ref> |
|||
* [[Psychic]]s who claim to be able to observe the [[Aura (paranormal)|aura]] with their [[third eye]] report that someone with a blue aura is a person who is oriented toward [[spirituality]].<ref> [[Swami Panchadasi]] ''The Human Aura: Astral Colors and Thought Forms'' Des Plaines, Illinois, USA:1912--Yogi Publications Society Page 36</ref> People with blue auras are said to be interested in social service work and to be in occupations such as [[social worker]], [[counsellor]], [[teacher]], [[writer]], and [[psychologist]].<ref> Oslie, Pamalie ''Life Colors: What the Colors in Your Aura Reveal'' Novato, California:2000--New World Library Blue Auras: Pages 117-130 </ref> |
|||
===Politics=== |
|||
{{main|Political colour}} |
|||
{{Unreferenced section|date=October 2007}} |
|||
*Blue has been associated with a variety of political positions, often differentiated from [[communist]] [[red]] or [[anarchism|anarchist]] [[black]]. During the [[revolt in the Vendée]] against the French revolution, blues stood for the revolutionary forces, and white for the counter-revolutionaries. Later movements like the [[Breton blues]] used the colour to signify allegiance to the ideals of the revolution. {{Fact|date=December 2007}} |
|||
*In the [[United Kingdom]] and Canada blue is the colour of the respective [[Conservative Party (UK)|Conservative]] [[Conservative Party of Canada|Parties]]. In the [[United States]], however, it has become fashionable since the 2000 Presidential Election to refer to the [[U.S. Democratic Party|Democratic Party]] as "blue" and the [[U.S. Republican Party|Republican Party]] as "red", particularly as in reference to "[[red states and blue states]]". |
|||
*The [[Blue Dog Coalition|Blue Dog Democrats]] are a group of conservative Democrats in the [[United States House of Representatives]].{{Fact|date=December 2007}} |
|||
[[Image:Blue lion dance.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Blue lion dance]] |
|||
===Religion=== |
|||
*Blue in Hinduism: Many of the gods are depicted as having blue-coloured skin, particularly those associated with [[Vishnu]], who is said to be the Preserver of the world and thus intimately connected to water. [[Krishna]] and [[Ram]], Vishnu's avatars, are usually blue. [[Shiva]], the Destroyer, is also depicted in light blue tones and is called ''neela kantha'', or blue-throated, for having swallowed poison in an attempt to turn the tide of a battle between the gods and demons in the gods' favour. |
|||
*[[Blue in Judaism]]: In the [[Torah]],<ref> [[Book of Numbers|Numbers]] 15:38.</ref> the [[Israelites]] were commanded to put fringes, ''[[tzitzit]]'', on the corners of their garments, and to weave within these fringes a "twisted thread of blue (''tekhelet'')".<ref>http://www.tekhelet.com The Ptil Tekhelet Organization</ref> In ancient days, this blue thread was made from a dye extracted from a Mediterranean snail called the ''hilazon''. [[Maimonides]] claimed that this blue was the colour of "the clear noonday sky"; [[Rashi]], the colour of the evening sky.<ref> ''[[Mishneh Torah]]'', ''Tzitzit'' 2:1; Commentary on Numbers 15:38.</ref> According to several rabbinic sages, blue is the colour of God's Glory.<ref> ''[[Numbers Rabbah]]'' 14:3; ''[[Hullin]]'' 89a.</ref> Staring at this colour aids in mediation, bringing us a glimpse of the "pavement of sapphire, like the very sky for purity", which is a likeness of the Throne of God.<ref> [[Exodus]] 24:10; [[Ezekiel]] 1:26; ''[[Hullin]]'' 89a.</ref> (The [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]] word for glory.) Many items in the ''[[Mishkan]]'', the portable sanctuary in the wilderness, such as the ''[[Menorah (Temple)|menorah]]'', many of the vessels, and the [[Ark of the Covenant]], were covered with blue cloth when transported from place to place.<ref> [[Book of Numbers|Numbers]] 4:6-12.</ref> |
|||
===Symbolism=== |
|||
* In [[Thailand]], blue is associated with Friday on the [[Thai solar calendar]]. Anyone may wear blue on Fridays and anyone born on a Friday may adopt blue as their colour. The [[Thai language]], however, is one that has had trouble [[Distinguishing blue from green in language|distinguishing blue from green]]. The default word for Blue was recently สีน้ำเงิน literally, the colour of silver, a poetical reference to the silvery sheen of the deep blue sea. It now means Navy Blue, and the default word is now สีฟ้า literally, the colour of the sky.<ref>[http://www.thai-language.com/dict/ thai-language.com<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> |
|||
*In the early 1960s, the [[United States Air Force]] ran a television commercial with this jingle: |
|||
::They took the blue from the [[sky|skies]] |
|||
::And the pretty [[girl]]s' [[eyes]] |
|||
::And a touch of [[Old Glory]] too; |
|||
::And gave it to the men who proudly wear the U. S. Air Force Blue! |
|||
==Variations of blue== |
|||
===Dark blue=== |
|||
{{infobox color| |
|||
title=Dark blue|hex=00008B|textcolor=white| |
|||
spelling=colour| |
|||
r=0|g=0|b=139| |
|||
c=1|m=1|y=0|k=0.455| |
|||
h=240|s=100|v= 25 |
|||
|source=[[Web color#X11 color list|X11]]}} |
|||
'''Dark blue''' is a shade of [[blue]]. |
|||
The name comes from the word "[[Dark]]" (which originated from [[Old English]] dark, derk, deork; [[Anglo-Saxon language|Anglo-Saxon]] dearc, and [[Scottish Gaelic language|Gaelic]] and [[Irish language|Irish]] dorch, dorcha) and "Blue" (taken from [[French language|French]] and originated from the [[Proto-Indo-European language|Indo-European]] root bhlewos). |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
===Medium blue=== |
|||
{{infobox color| |
|||
title=Medium blue|hex=0000CD|textcolor=white| |
|||
spelling=colour| |
|||
r=0|g=0|b=205| |
|||
c=1|m=1|y=0|k=0.455| |
|||
h=240|s=100|v=40 |
|||
|source=[[Web color#X11 color list|X11]]}} |
|||
Displayed at right is the colour '''medium blue'''. |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
===Light blue=== |
|||
{{infobox color|title=Light Blue|hex=ADD8E6|textcolor=black| |
|||
r=173|g=216|b=230| |
|||
c= 50|m= 50|y= 0|k= 0| |
|||
h=240|s= 90|v= 80| |
|||
spelling=colour |
|||
|source=[[Web color#X11 color list|X11]]}} |
|||
The web colour '''light blue''' is displayed in the colour box at right. Also could be known as sky blue, baby blue, or angel blue. |
|||
The first recorded use of "light blue" as a colour term in [[English (language)|English]] is in the year 1915.<ref> Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 190 </ref> |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
===Pigment blue=== |
|||
<!-- |
|||
Note: The source says that it is a CMYK color, and this means there is no authoritative RGB value. The hex code is nominal for screen display in this box only, but should not be taken as an RGB standard for the color because the ink colors used in CMYK printing may vary according to different formulations. --> |
|||
{{infobox color|title=Pigment Blue|hex=333399|textcolor=white| |
|||
r=51|g=51|b=153| |
|||
c= 100|m=100|y= 0|k= 0| |
|||
h=240|s= 50|v= 35| |
|||
spelling=colour |
|||
|source=[http://www.tintbook.com/ CMYK]}} |
|||
At right is the colour '''pigment blue'''. This is the colour that is achieved by mixing an equal amount of [[Cyan#Electric cyan vs. process cyan|process cyan]] (printer's cyan) and [[Magenta#Historical development of magenta|process magenta]] (printer's magenta). |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
===Variations of blue in culture=== |
|||
'''[[Fashion]]''' |
|||
* Dark [[clothing]] for [[male]]s such as dark blue [[business suit]]s have become much more popular since about 1995{{Fact|date=June 2008}}, as opposed to the [[pastel]] coloured business suits worn in the 1970s by major [[Leadership|leaders]] in such institutions as the [[United States Congress]] (the vast difference in the clothing worn in the 1970s as opposed to the 2000s can be readily seen by looking at a [[videotape]] of the [[Watergate hearings]]). |
|||
'''[[Law enforcement organization|Law Enforcement]]''' |
|||
* [[Police]] normally wear dark blue or, sometimes, medium blue [[uniform]]s (However, the [[New Age]] [[philosopher]] [[Alan Watts]] suggested in the 1960s that police ought to wear [[baby blue]] uniforms.). |
|||
'''[[Human sexuality|Sexuality]]''' |
|||
* In the [[bandana code]] of the [[Gay (term)|gay]] [[leather subculture]], wearing a medium blue [[Kerchief|bandana]] means one is into the [[sexual fetish|fetish]] of having [[Homosexuality|sex]] with someone who is wearing a [[police]] [[Uniform fetish|uniform]].<ref> Card showing list of bandana colours and their meanings, available at Image Leather, 2199 Market St., San Francisco, CA 94114 </ref> |
|||
*In [[Russian language|Russian]], the word for light blue, голубой, can be used to mean 'homosexual'.<ref>[http://english.gay.ru/life/history/queermoscow/ Gay.ru]</ref> |
|||
'''[[Sociology]]''' |
|||
* Dark blue represents knowledge, power, integrity, and seriousness. In [[Western culture|Western civilization]], those in the [[upper class]]es in high places of [[Politics|political]] or [[Economics|economic]] power often wear dark blue [[Business suit|suits]]. Ordinary members of the [[working class]] (especially those who work in the [[computer industry]]) often refer derisively to these [[management]] functionaries as ''the suits''.<ref>''The Cuckoo's Egg: Tracking a Spy Through the Maze of Computer Espionage'', Clifford Stoll, 1989, ISBN 0-7434-1146-3 </ref> This terminology is also used in the [[Film industry|television industry]]--the [[TV network|network]] executives are often referred to by the creative people ([[actor]]s, [[Television director|director]]s, and [[screenwriter]]s) as ''the suits''.<ref> Shatner, William (with Chris Kreski) ''Star Trek Memories'' New York:1993 Harper Collins </ref> |
|||
*In historical [[atlas (cartography)|atlas]]es published in [[Germany]], light blue is traditionally used as a colour to represent Germany, as opposed to [[pink]] for England, [[purple]] for [[France]], and [[Variations of green|light green]] for [[Russia]].<ref> See the ''Grosshistoricher Weltatlas'', 1965 edition (Other German historical atlases use these same colours.)</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
* [[Blue flag]] |
|||
* [[Blue movie]] |
|||
* [[Turquoise]] |
|||
* [[Distinguishing "blue" from "green" in language]] |
|||
* [[Engineer's blue]] |
|||
* [[Non-photo blue]] |
|||
* [[Lapis lazuli]], a blue stone |
|||
* [[List of colours]] |
|||
* ''[[Three Colors: Blue|Three Colours: Blue]]'', a film |
|||
* [[Blue ribbon]] |
|||
* [[St. Patrick's Blue]] |
|||
* [[Blue Screen of Death]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{wiktionarypar|blue}} |
|||
{{commonscat|blue}} |
|||
{{EMSpectrum}} |
|||
{{web colors|colour}} |
|||
{{Shades of blue|*}} |
|||
[[Category:Optical spectrum]] |
|||
[[Category:Symbols of California]] |
|||
[[af:Blou (kleur)]] |
|||
[[ar:أزرق]] |
|||
[[an:Azul]] |
|||
[[arc:ܙܪܩܐ]] |
|||
[[ast:Azul]] |
|||
[[gn:Hovy]] |
|||
[[ay:Larama]] |
|||
[[az:Mavi]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Nâ-sek]] |
|||
[[map-bms:Biru]] |
|||
[[bs:Plava]] |
|||
[[bg:Син цвят]] |
|||
[[ca:Blau]] |
|||
[[cs:Modrá]] |
|||
[[cy:Glas]] |
|||
[[da:Blå]] |
|||
[[pdc:Bloh]] |
|||
[[de:Blau]] |
|||
[[et:Sinine]] |
|||
[[el:Μπλε]] |
|||
[[myv:Сэнь]] |
|||
[[es:Azul]] |
|||
[[eo:Blua]] |
|||
[[eu:Urdin]] |
|||
[[fa:آبی]] |
|||
[[fr:Bleu]] |
|||
[[ga:Gorm]] |
|||
[[gan:藍]] |
|||
[[gl:Azul]] |
|||
[[hak:Làm-set]] |
|||
[[ko:파랑]] |
|||
[[hi:नीला]] |
|||
[[hr:Plava]] |
|||
[[id:Biru]] |
|||
[[is:Blár]] |
|||
[[it:Blu]] |
|||
[[he:כחול]] |
|||
[[jv:Biru]] |
|||
[[pam:Iro]] |
|||
[[kn:ನೀಲಿ]] |
|||
[[ka:ლურჯი ფერი]] |
|||
[[kg:Bule]] |
|||
[[ht:Ble (koulè)]] |
|||
[[ku:Şîn]] |
|||
[[la:Caeruleus]] |
|||
[[lv:Zilā krāsa]] |
|||
[[lb:Blo]] |
|||
[[lt:Mėlyna]] |
|||
[[ln:Bozinga]] |
|||
[[hu:Kék]] |
|||
[[mk:Сина боја]] |
|||
[[mt:Ikħal]] |
|||
[[mr:निळा]] |
|||
[[ms:Biru]] |
|||
[[nah:Texohtic]] |
|||
[[nl:Blauw]] |
|||
[[ja:青]] |
|||
[[ce:Сийна]] |
|||
[[no:Blå]] |
|||
[[nn:Blå]] |
|||
[[nrm:Bliu]] |
|||
[[nds:Blau]] |
|||
[[pl:Barwa niebieska]] |
|||
[[pt:Azul]] |
|||
[[ro:Albastru]] |
|||
[[qu:Anqas]] |
|||
[[ru:Синий цвет]] |
|||
[[sa:नील]] |
|||
[[sco:Blue]] |
|||
[[sq:Ngjyra vjollcë e kaltër]] |
|||
[[simple:Blue]] |
|||
[[sk:Modrá]] |
|||
[[sl:Modra]] |
|||
[[sr:Плава боја]] |
|||
[[sh:Plavo]] |
|||
[[su:Paul]] |
|||
[[fi:Sininen]] |
|||
[[sv:Blå]] |
|||
[[tl:Asul]] |
|||
[[ta:நீலம்]] |
|||
[[te:నీలము]] |
|||
[[th:สีน้ำเงิน]] |
|||
[[vi:Xanh lam]] |
|||
[[tg:Кабуд]] |
|||
[[tr:Mavi]] |
|||
[[uk:Синій колір]] |
|||
[[ur:نیلا]] |
|||
[[wo:Baxa]] |
|||
[[yi:בלוי]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:藍]] |
|||
[[bat-smg:Mielina]] |
|||
[[zh:藍色]] |
|||
Revision as of 20:09, 13 March 2009
| Blue | |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | 440–490 nm |
| Common connotations | |
| ice, water, sky, sadness, winter, royalty, boys, cold, calm, conservatism (universally), liberalism (US), and capitalism | |
| Hex triplet | #0000FF |
| sRGBB (r, g, b) | (0, 0, 255) |
| HSV (h, s, v) | (240°, 100%, 100%) |
| CIELChuv (L, C, h) | (32, 131, 266°) |
| Source | HTML/CSS[1] |
| B: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) | |
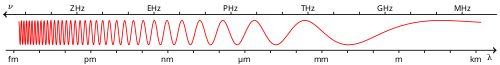
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal mixture of red and green light. On a colour wheel based on traditional colour theory (RYB), the complementary colour to blue is considered to be orange (based on the Munsell colour wheel).[2] The English language commonly uses "blue" to refer to any colour from navy blue to cyan. The word itself is derived from the Old French word bleu.
Etymology and definitions

The modern English word blue comes from the Middle English, bleu or blwe, which came from an Old French word bleu of Germanic origin (Frankish or possibly Old High German blao, "shining"). Bleu replaced Old English blaw. The root of these variations was the Proto-Germanic blæwaz, which was also the root of the Old Norse word bla and the modern Icelandic blár, and the Scandinavian word blå, but it can refer to other non blue colours. A Scots and Scottish English word for "blue-grey" is blae, from the Middle English bla ("dark blue," from the Old English blæd). Ancient Greek lacked a word for blue and Homer called the colour of the sea "wine dark", except that the word kyanos (cyan) was used for dark blue enamel.
As a curiosity, blue is thought to be cognate with blond, blank and black through the Germanic word. Through a Proto-Indo-European root, it is also linked with Latin flavus ("yellow"; see flavescent and flavine), with Greek phalos (white), French blanc (white, blank) (borrowed from Old Frankish), and with Russian белый, belyi ("white," see beluga), and Welsh blawr (grey) all of which derive (according to the American Heritage Dictionary) from the Proto-Indo-European root *bhel- meaning "to shine, flash or burn", (more specifically the word bhle-was, which meant light coloured, blue, blond, or yellow), whence came the names of various bright colours, and that of colour black from a derivation meaning "burnt" (other words derived from the root *bhel- include bleach, bleak, blind, blink, blank, blush, blaze, flame, fulminate, flagrant and phlegm).
In the English language, blue may refer to the feeling of sadness. "He was feeling blue". This is because blue was related to rain, or storms, and in Greek mythology, the god Zeus would make rain when he was sad (crying), and a storm when he was angry. Kyanos was a name used in Ancient Greek to refer to dark blue tile (in English it means blue-green or cyan).[3] The phrase "feeling blue" is linked also to a custom among many old deepwater sailing ships. If the ship lost the captain or any of the officers during its voyage, she would fly blue flags and have a blue band painted along her entire hull when returning to home port.[4]
Many languages do not have separate terms for blue and or green, instead using a cover term for both (when the issue is discussed in linguistics, this cover term is sometimes called grue in English).
In science

Pigments
Traditionally, blue has been considered a primary colour in painting, with the secondary colour orange as its complement.
Blue pigments include azurite (Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2), ultramarine (Na8-10Al6Si6O24S2-4), cerulean blue (primarily cobalt (II) stanate: Co2SnO4), cobalt blue (cobalt(II) aluminate: CoAl2O4), and Prussian blue (milori blue: primarily Fe7(CN)18).
Scientific natural standards for blue
- Emission spectrum of Cu2+
- Electronic spectrum of aqua-ions Cu(H2O)52+
Animals

- When an animal's coat is described as "blue", it usually refers to a shade of grey that takes on a bluish tint, a diluted variant of a pure black coat.[citation needed] This designation is used for a variety of animals, including dog coats, some rat coats, cat coats, some chicken breeds, and some horse coat colours.
Blue in human culture
Symbolic language
- In the English language, blue often represents the human emotion of sadness, e.g. "He was feeling blue". In German, on the other hand, to be "blue" (blau sein) is to be drunk. This derives from the ancient use of urine (which is produced copiously by the human body after drinking alcohol) in dyeing cloth blue with woad or indigo.[5]
Music
- The blues is a style of music originated by African Americans.
- In 1999 Eiffel 65 released the song "Blue (Da Ba Dee)," a hugely popular Eurodance song which peaked at #2 on the Billboard Hot 100 in the United States, and reached #1 in 17 countries.[citation needed]
- Blue is the name of the original Scottish rock group
- Blue is also the name of an English pop boy band.
National colours


- Azzurro a light blue, is the national colour of Italy (from the livery colour of the former reigning family, the House of Savoy)[citation needed].
- Blue is the national sports colour for India, as it denotes secularism.
- Blue is the national colour used on flags of several countries surrounded by seas or oceans such as Australia and Europe, though not necessarily with this interpretation in mind.
- Blue and white are the national colours of Argentina, El Salvador, Finland, Greece, Guatemala, Honduras, Israel, Micronesia, Nicaragua, and Somalia as well as of the United Nations Organization using a light shade of blue symbolizing peace.
- Blue and yellow are the national colours of Barbados, Kazakhstan, Palau, Sweden, and Ukraine, and along with green, of Brazil, and along with red, of Chad, Colombia, Ecuador, Moldova, Romania, and Venezuela.
- Blue, white and yellow are the national colours of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo and Uruguay.
- Blue and red are the national colours of Haiti and Liechtenstein, and along with white (where it composed the French tricolour whose simple design or colours were taken by other countries), of Australia, Cambodia, Costa Rica, Chile, Croatia, Cuba, the Czech Republic, the Dominican Republic, France, Iceland, North Korea, Laos, Liberia, Luxembourg, Myanmar, Nepal, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Russia, Samoa, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.

Mysticism
- In the metaphysics of the "New Age Prophetess", Alice Bailey, in her system called the Seven Rays which classifies humans into seven different metaphysical psychological types, the "first ray" of "will-power" is represented by the colour blue. People who have this metaphysical psychological type are said to be "on the Blue Ray".[7]
- In Hinduism, Blue is used to symbolically represent the fifth, throat chakra (Vishuddha).[8]
- Psychics who claim to be able to observe the aura with their third eye report that someone with a blue aura is a person who is oriented toward spirituality.[9] People with blue auras are said to be interested in social service work and to be in occupations such as social worker, counsellor, teacher, writer, and psychologist.[10]
Politics
- Blue has been associated with a variety of political positions, often differentiated from communist red or anarchist black. During the revolt in the Vendée against the French revolution, blues stood for the revolutionary forces, and white for the counter-revolutionaries. Later movements like the Breton blues used the colour to signify allegiance to the ideals of the revolution. [citation needed]
- In the United Kingdom and Canada blue is the colour of the respective Conservative Parties. In the United States, however, it has become fashionable since the 2000 Presidential Election to refer to the Democratic Party as "blue" and the Republican Party as "red", particularly as in reference to "red states and blue states".
- The Blue Dog Democrats are a group of conservative Democrats in the United States House of Representatives.[citation needed]

Religion
- Blue in Hinduism: Many of the gods are depicted as having blue-coloured skin, particularly those associated with Vishnu, who is said to be the Preserver of the world and thus intimately connected to water. Krishna and Ram, Vishnu's avatars, are usually blue. Shiva, the Destroyer, is also depicted in light blue tones and is called neela kantha, or blue-throated, for having swallowed poison in an attempt to turn the tide of a battle between the gods and demons in the gods' favour.
- Blue in Judaism: In the Torah,[11] the Israelites were commanded to put fringes, tzitzit, on the corners of their garments, and to weave within these fringes a "twisted thread of blue (tekhelet)".[12] In ancient days, this blue thread was made from a dye extracted from a Mediterranean snail called the hilazon. Maimonides claimed that this blue was the colour of "the clear noonday sky"; Rashi, the colour of the evening sky.[13] According to several rabbinic sages, blue is the colour of God's Glory.[14] Staring at this colour aids in mediation, bringing us a glimpse of the "pavement of sapphire, like the very sky for purity", which is a likeness of the Throne of God.[15] (The Hebrew word for glory.) Many items in the Mishkan, the portable sanctuary in the wilderness, such as the menorah, many of the vessels, and the Ark of the Covenant, were covered with blue cloth when transported from place to place.[16]
Symbolism
- In Thailand, blue is associated with Friday on the Thai solar calendar. Anyone may wear blue on Fridays and anyone born on a Friday may adopt blue as their colour. The Thai language, however, is one that has had trouble distinguishing blue from green. The default word for Blue was recently สีน้ำเงิน literally, the colour of silver, a poetical reference to the silvery sheen of the deep blue sea. It now means Navy Blue, and the default word is now สีฟ้า literally, the colour of the sky.[17]
- In the early 1960s, the United States Air Force ran a television commercial with this jingle:
Variations of blue
Dark blue
| Dark blue | |
|---|---|
| Hex triplet | #00008B |
| sRGBB (r, g, b) | (0, 0, 139) |
| HSV (h, s, v) | (240°, 100%, 55%) |
| CIELChuv (L, C, h) | (15, 60, 266°) |
| Source | X11 |
| B: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) | |
Dark blue is a shade of blue. The name comes from the word "Dark" (which originated from Old English dark, derk, deork; Anglo-Saxon dearc, and Gaelic and Irish dorch, dorcha) and "Blue" (taken from French and originated from the Indo-European root bhlewos).
Medium blue
| Medium blue | |
|---|---|
| Hex triplet | #0000CD |
| sRGBB (r, g, b) | (0, 0, 205) |
| HSV (h, s, v) | (240°, 100%, 80%) |
| CIELChuv (L, C, h) | (25, 101, 266°) |
| Source | X11 |
| B: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) | |
Displayed at right is the colour medium blue.
Light blue
| Light Blue | |
|---|---|
| Hex triplet | #ADD8E6 |
| sRGBB (r, g, b) | (173, 216, 230) |
| HSV (h, s, v) | (195°, 25%, 90%) |
| CIELChuv (L, C, h) | (84, 28, 216°) |
| Source | X11 |
| B: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) | |
The web colour light blue is displayed in the colour box at right. Also could be known as sky blue, baby blue, or angel blue. The first recorded use of "light blue" as a colour term in English is in the year 1915.[18]
Pigment blue
| Pigment Blue | |
|---|---|
| Hex triplet | #333399 |
| sRGBB (r, g, b) | (51, 51, 153) |
| HSV (h, s, v) | (240°, 67%, 60%) |
| CIELChuv (L, C, h) | (28, 73, 266°) |
| Source | CMYK |
| B: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) | |
At right is the colour pigment blue. This is the colour that is achieved by mixing an equal amount of process cyan (printer's cyan) and process magenta (printer's magenta).
Variations of blue in culture
- Dark clothing for males such as dark blue business suits have become much more popular since about 1995[citation needed], as opposed to the pastel coloured business suits worn in the 1970s by major leaders in such institutions as the United States Congress (the vast difference in the clothing worn in the 1970s as opposed to the 2000s can be readily seen by looking at a videotape of the Watergate hearings).
- Police normally wear dark blue or, sometimes, medium blue uniforms (However, the New Age philosopher Alan Watts suggested in the 1960s that police ought to wear baby blue uniforms.).
- In the bandana code of the gay leather subculture, wearing a medium blue bandana means one is into the fetish of having sex with someone who is wearing a police uniform.[19]
- In Russian, the word for light blue, голубой, can be used to mean 'homosexual'.[20]
- Dark blue represents knowledge, power, integrity, and seriousness. In Western civilization, those in the upper classes in high places of political or economic power often wear dark blue suits. Ordinary members of the working class (especially those who work in the computer industry) often refer derisively to these management functionaries as the suits.[21] This terminology is also used in the television industry--the network executives are often referred to by the creative people (actors, directors, and screenwriters) as the suits.[22]
- In historical atlases published in Germany, light blue is traditionally used as a colour to represent Germany, as opposed to pink for England, purple for France, and light green for Russia.[23]
See also
- Blue flag
- Blue movie
- Turquoise
- Distinguishing "blue" from "green" in language
- Engineer's blue
- Non-photo blue
- Lapis lazuli, a blue stone
- List of colours
- Three Colours: Blue, a film
- Blue ribbon
- St. Patrick's Blue
- Blue Screen of Death
References
- ^ W3C TR CSS3 Color Module, HTML4 color keywords
- ^ Glossary Term: Color wheel
- ^ Merriam-Webster's Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary Springfield, Mass.:1984--Merriam-Webster Page 319
- ^ "US Navy - origins of Navy Terminology" [1]
- ^ Heller, Eva. Wie Farben wirken: Farbpsychologie, Farbsymbolik, kreative Farbgestaltung. Berlin: Rowohlt, 2004.
- ^ "Estonia in brief: National Symbols" at Estonica website (www.estonica.org)[2]
- ^ Bailey, Alice A. (1995). The Seven Rays of Life. New York: Lucis Publishing Company. ISBN 0853301425.
- ^ Stevens, Samantha. The Seven Rays: a Universal Guide to the Archangels. City: Insomniac Press, 2004. ISBN 1894663497 pg. 24
- ^ Swami Panchadasi The Human Aura: Astral Colors and Thought Forms Des Plaines, Illinois, USA:1912--Yogi Publications Society Page 36
- ^ Oslie, Pamalie Life Colors: What the Colors in Your Aura Reveal Novato, California:2000--New World Library Blue Auras: Pages 117-130
- ^ Numbers 15:38.
- ^ http://www.tekhelet.com The Ptil Tekhelet Organization
- ^ Mishneh Torah, Tzitzit 2:1; Commentary on Numbers 15:38.
- ^ Numbers Rabbah 14:3; Hullin 89a.
- ^ Exodus 24:10; Ezekiel 1:26; Hullin 89a.
- ^ Numbers 4:6-12.
- ^ thai-language.com
- ^ Maerz and Paul A Dictionary of Color New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 190
- ^ Card showing list of bandana colours and their meanings, available at Image Leather, 2199 Market St., San Francisco, CA 94114
- ^ Gay.ru
- ^ The Cuckoo's Egg: Tracking a Spy Through the Maze of Computer Espionage, Clifford Stoll, 1989, ISBN 0-7434-1146-3
- ^ Shatner, William (with Chris Kreski) Star Trek Memories New York:1993 Harper Collins
- ^ See the Grosshistoricher Weltatlas, 1965 edition (Other German historical atlases use these same colours.)