Vitamin B12
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | oral, iv |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | readily absorbed in distal half of the ileum |
| Protein binding | Very high to specific transcobalamins plasma proteins Binding of hydroxocobalamin is slightly higher than cyanocobalamin. |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | Approximately 6 days (400 days in the liver) |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C63H88CoN14O14P |
| Molar mass | 1355.37 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| | |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2010) |
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins. It is normally involved in the metabolism of every cell of the human body, especially affecting DNA synthesis and regulation, but also fatty acid synthesis and energy production. As the largest and most structurally complicated vitamin, it can be produced industrially only through bacterial fermentation-synthesis.
Vitamin B12 consists of a class of chemically-related compounds (vitamers), all of which have vitamin activity. It contains the biochemically rare element cobalt. Biosynthesis of the basic structure of the vitamin in nature is only accomplished by simple organisms such as some bacteria and algae, but conversion between different forms of the vitamin can be accomplished in the human body. A common synthetic form of the vitamin, cyanocobalamin, does not occur in nature, but is used in many pharmaceuticals and supplements, and as a food additive, because of its stability and lower cost. In the body it is converted to the physiological forms, methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin, leaving behind the cyanide, albeit in minimal concentration. More recently, hydroxocobalamin (a form produced by bacteria), methylcobalamin, and adenosylcobalamin can also be found in more expensive pharmacological products and food supplements. The extra utility of these is currently debated.
Vitamin B12 was discovered from its relationship to the disease pernicious anemia, which is an autoimmune disease that destroys parietal cells in the stomach that secrete intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is crucial for the normal absorption of B12, so a lack of intrinsic factor, as seen in pernicious anemia, causes a vitamin B12 deficiency. Many other subtler kinds of vitamin B12 deficiency and their biochemical effects have since been elucidated.
Terminology
The names vitamin B12 or vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, which are sometimes shortened to B12 or B12, and the alternative name cobalamin generally refer to all forms of the vitamin. Some medical practitioners have suggested that its use be split into two different categories, however.
- In a broad sense, B12 refers to a group of cobalt-containing vitamer compounds known as cobalamins: these include cyanocobalamin (an artifact formed from using activated charcoal, which always contains trace cyanide, to purify hydroxycobalamin), hydroxocobalamin (another medicinal form, produced by bacteria), and finally, the two naturally occurring cofactor forms of B12 in the human body: 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin (adenosylcobalamin—AdoB12), the cofactor of Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase (MUT), and methylcobalamin (MeB12), the cofactor of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase (MTR).
- The term B12 may be properly used to refer to cyanocobalamin, the principal B12 form used for foods and in nutritional supplements. This ordinarily creates no problem, except perhaps in rare cases of eye nerve damage, where the body is only marginally able to use this form due to high cyanide levels in the blood due to cigarette smoking, and thus requires cessation of smoking, or else B12 given in another form, for the optic symptoms to abate. However, tobacco amblyopia is a rare enough condition that debate continues about whether or not it represents a peculiar B12 deficiency which is resistant to treatment with cyanocobalamin.
Finally, so-called pseudo-B12 refers to B12-like substances which are found in certain organisms, including Spirulina (a cyanobacterium) and some algae. These substances are active in tests of B12 activity by highly sensitive antibody-binding serum assay tests, which measure levels of B12 and B12-like compounds in blood. However, these substances do not have B12 biological activity for humans, a fact which may pose a danger to vegans and others on diets who may not ingest sufficient quantities of B12 producing bacteria, but who nevertheless may show normal "B12" levels in the standard immunoassay which has become the normal medical method for testing for B12 deficiency.[1]
Medical uses
Vitamin B12, is used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency, cyanide poisoning, and hereditary deficiency of transcobalamin II.[2] It is also given as part of the schilling test for detecting pernicious anemia.[2]
For cyanide poisoning, large amount may be given intravenously, and sometimes in combination with sodium thiosulfate.[3] The mechanism of action is straightforward: the hydroxycobalamin hydroxide ligand is displaced by the toxic cyanide ion, and the resulting harmless B12 complex is excreted in urine. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration approved (in 2006) the use of hydroxocobalamin for acute treatment of cyanide poisoning.[4]
High vitamin B12 level in elderly individuals may protect against brain atrophy or shrinkage, associated with Alzheimer's disease and impaired cognitive function.[5]
Recommended intake
The dietary reference intake for an adult ranges from 2 to 3 µg per day.[citation needed]
Vitamin B12 is believed to be safe when used orally in amounts that do not exceed the recommended dietary allowance (RDA).[citation needed] The RDA for vitamin B12 in pregnant women is 2.6 µg per day and 2.8 µg during lactation periods.[citation needed] There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of consuming greater amounts of vitamin B12 during pregnancy.
The Vegan Society, the Vegetarian Resource Group, and the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, among others, recommend that vegans either consistently eat foods fortified with B12 or take a daily or weekly B12 supplement.[6][7][8] Fortified breakfast cereals are a particularly valuable source of vitamin B12 for vegetarians and vegans. In addition, adults age 51 and older are recommended to consume B12 fortified food or supplements to meet the RDA, because they are a population at an increased risk of deficiency.[9]
Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can potentially cause severe and irreversible damage, especially to the brain and nervous system. At levels only slightly lower than normal, a range of symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and poor memory may be experienced.[10] However, these symptoms by themselves are too nonspecific to diagnose deficiency of the vitamin.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can also cause symptoms of mania and psychosis.[11][12] Vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by the metabolic disorder pernicious anemia.
Adverse effects
- Vitamin B12 has extremely low toxicity and even taking it in enormous doses appears not to be harmful to healthy individuals.[13][14]
- Hematologic: Peripheral vascular thrombosis has been reported. Treatment of vitamin B12deficiency can unmask polycythemia vera, which is characterized by an increase in blood volume and the number of red blood cells. The correction of megaloblastic anemia with vitamin B12 can result in fatal hypokalemia and gout in susceptible individuals, and it can obscure folate deficiency in megaloblastic anemia. Caution is warranted.
- Leber's disease: Vitamin B12 in the form of cyanocobalamin is contraindicated in early Leber's disease, which is hereditary optic nerve atrophy. Cyanocobalamin can cause severe and swift optic atrophy, but other forms of vitamin B12 are available.[citation needed] However, the sources of this statement are not clear, while an opposing view[15] concludes: "The clinical picture of optic neuropathy associated with vitamin B12 deficiency shows similarity to that of Leber's disease optic neuropathy. Both involve the nerve fibres of the papillomacular bundle. The present case reports suggest that optic neuropathy in patients carrying a primary LHON mtDNA mutation may be precipitated by vitamin B12 deficiency. Therefore, known carriers should take care to have an adequate dietary intake of vitamin B12 and malabsorption syndromes like those occurring in familial pernicious anaemia or after gastric surgery should be excluded."
Allergies
Vitamin B12 supplements in theory should be avoided in people sensitive or allergic to cobalamin, cobalt, or any other product ingredients. However, direct allergy to a vitamin or nutrient is extremely rare, and if reported, other causes should be sought.
Interactions
- Alcohol (ethanol): Excessive alcohol intake lasting longer than two weeks can decrease vitamin B12 absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.[citation needed]
- Aminosalicylic acid (para-aminosalicylic acid, PAS, Paser): Aminosalicylic acid can reduce oral vitamin B12 absorption, possibly by as much as 55%, as part of a general malabsorption syndrome. Megaloblastic changes, and occasional cases of symptomatic anemia have occurred, usually after doses of 8 to 12 g/day for several months. Vitamin B12 levels should be monitored in people taking aminosalicylic acid for more than one month.
- Antibiotics: An increased bacterial load can bind significant amounts of vitamin B12 in the gut, preventing its absorption. In people with bacterial overgrowth of the small bowel, antibiotics such asmetronidazole (Flagyl) can actually improve vitamin B12 status. The effects of most antibiotics on gastrointestinal bacteria are unlikely to have clinically significant effects on vitamin B12 levels.
- Hormonal contraception: The data regarding the effects of oral contraceptives on vitamin B12serum levels are conflicting. Some studies have found reduced serum levels in oral contraceptive users, but others have found no effect despite use of oral contraceptives for up to 6 months. When oral contraceptive use is stopped, normalization of vitamin B12 levels usually occurs. Lower vitamin B12serum levels seen with oral contraceptives probably are not clinically significant.
- Chloramphenicol (Chloromycetin): Limited case reports suggest that chloramphenicol can delay or interrupt the reticulocyte response to supplemental vitamin B12 in some patients. Blood counts should be monitored closely if this combination cannot be avoided.
- Cobalt irradiation: Cobalt irradiation of the small bowel can decrease gastrointestinal (GI) absorption of vitamin B12.
- Colchicine: Colchicine in doses of 1.9 to 3.9 mg/day can disrupt normal intestinal mucosal function, leading to malabsorption of several nutrients, including vitamin B12. Lower doses do not seem to have a significant effect on vitamin B12 absorption after 3 years of colchicine therapy. The significance of this interaction is unclear. Vitamin B12 levels should be monitored in people taking large doses of colchicine for prolonged periods.
- Colestipol (Colestid), cholestyramine (Questran): These resins used for sequestering bile acids to decrease cholesterol, can decrease gastrointestinal (GI) absorption of vitamin B12. It is unlikely this interaction will deplete body stores of vitamin B12 unless there are other factors contributing to deficiency. In a group of children treated with cholestyramine for up to 2.5 years, there was not any change in serum vitamin B12 levels. Routine supplements are not necessary.
- H2-receptor antagonists: include cimetidine (Tagamet), famotidine (Pepcid), nizatidine (Axid), and ranitidine (Zantac). Reduced secretion of gastric acid and pepsin produced by H2 blockers can reduce absorption of protein-bound (dietary) vitamin B12, but not of supplemental vitamin B12. Gastric acid is needed to release vitamin B12 from protein for absorption. Clinically significant vitamin B12 deficiency and megaloblastic anemia are unlikely, unless H2 blocker therapy is prolonged (2 years or more), or the person's diet is poor. It is also more likely if the person is rendered achlorhydric(with complete absence of gastric acid secretion), which occurs more frequently with proton pump inhibitors than H2 blockers. Vitamin B12 levels should be monitored in people taking high doses of H2 blockers for prolonged periods.
- Metformin (Glucophage): Metformin may reduce serum folic acid and vitamin B12 levels. These changes can lead to hyperhomocysteinemia, adding to the risk of cardiovascular disease in people withdiabetes.[citation needed] There are also rare reports of megaloblastic anemia in people who have taken metformin for five years or more. Reduced serum levels of vitamin B12 occur in up to 30% of people taking metformin chronically.[16][17] However, clinically significant deficiency is not likely to develop if dietary intake of vitamin B12 is adequate. Deficiency can be corrected with vitamin B12supplements even if metformin is continued. The metformin-induced malabsorption of vitamin B12 is reversible by oral calcium supplementation.[18] The general clinical significance of metformin upon B12 levels is as yet unknown.[19]
- Neomycin: Absorption of vitamin B12 can be reduced by neomycin, but prolonged use of large doses is needed to induce pernicious anemia. Supplements are not usually needed with normal doses.
- Nicotine: Nicotine can reduce serum vitamin B12 levels. The need for vitamin B12supplementation in smokers has not been adequately studied.
- Nitrous oxide: Nitrous oxide inactivates the cobalamin form of vitamin B12 by oxidation. Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency, including sensory neuropathy, myelopathy, and encephalopathy, can occur within days or weeks of exposure to nitrous oxide anesthesia in people with subclinical vitamin B12 deficiency. Symptoms are treated with high doses of vitamin B12, but recovery can be slow and incomplete. People with normal vitamin B12 levels have sufficient vitamin B12 stores to make the effects of nitrous oxide insignificant, unless exposure is repeated and prolonged (such as recreational use). Vitamin B12 levels should be checked in people with risk factors for vitamin B12 deficiency prior to using nitrous oxide anesthesia. Chronic nitrous oxide B12 poisoning (usually from use of nitrous oxide as a recreational drug), however, may result in B12 functional deficiency even with normal measured blood levels of B12.[20]
- Phenytoin (Dilantin), phenobarbital, primidone (Mysoline): These anticonvulsants have been associated with reduced vitamin B12 absorption, and reduced serum and cerebrospinal fluidlevels in some patients. This may contribute to the megaloblastic anemia, primarily caused by folate deficiency, associated with these drugs. It is also suggested that reduced vitamin B12 levels may contribute to the neuropsychiatric side effects of these drugs. Patients should be encouraged to maintain adequate dietary vitamin B12 intake. Folate and vitamin B12 status should be checked if symptoms of anemia develop.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): The PPIs include omeprazole (Prilosec, Losec), lansoprazole(Prevacid), rabeprazole (Aciphex), pantoprazole (Protonix, Pantoloc), and esomeprazole (Nexium). The reduced secretion of gastric acid and pepsin produced by PPIs can reduce absorption of protein-bound (dietary) vitamin B12, but not supplemental vitamin B12. Gastric acid is needed to release vitamin B12 from protein for absorption. Reduced vitamin B12 levels may be more common with PPIs than with H2-blockers, because they are more likely to produce achlorhydria (complete absence of gastric acid secretion). However, clinically significant vitamin B12 deficiency is unlikely, unless PPI therapy is prolonged (2 years or more) or dietary vitamin intake is low. Vitamin B12 levels should be monitored in people taking high doses of PPIs for prolonged periods.
- Zidovudine (AZT, Combivir, Retrovir): Reduced serum vitamin B12 levels may occur when zidovudine therapy is started. This adds to other factors that cause low vitamin B12 levels in people with HIV, and might contribute to the hematological toxicity associated with zidovudine. However, the data suggest vitamin B12 supplements are not helpful for people taking zidovudine.[citation needed]
- Folic acid: Folic acid, particularly in large doses, can mask vitamin B12 deficiency by completely correcting hematological abnormalities. In vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid can produce complete resolution of the characteristic megaloblastic anemia, while allowing potentially irreversible neurological damage (from continued inactivity of methylmalonyl mutase) to progress. Thus, vitamin B12 status should be determined before folic acid is given as monotherapy.
- Potassium: Potassium supplements can reduce absorption of vitamin B12 in some people. This effect has been reported with potassium chloride and, to a lesser extent, with potassium citrate. Potassium might contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency in some people with other risk factors, but routine supplements are not necessary.[21]
Structure
Vitamin B12 is a collection of cobalt and corrin ring molecules which are defined by their particular vitamin function in the body. All of the substrate cobalt-corrin molecules from which B12 is made, must be synthesized by bacteria. However, after this synthesis is complete, the body has a limited power to convert any form of B12 to another, by means of enzymatically removing certain prosthetic chemical groups from the cobalt atom. The various forms (vitamers) of B12 are all deeply red colored, due to the color of the cobalt-corrin complex.
Cyanocobalamin is one such "vitamer" in this B complex, because it can be metabolized in the body to an active co-enzyme form. However, the cyanocobalamin form of B12 does not occur in nature normally, but is a byproduct of the fact that other forms of B12 are avid binders of cyanide (-CN) which they pick up in the process of activated charcoal purification of the vitamin after it is made by bacteria in the commercial process. Since the cyanocobalamin form of B12 is easy to crystallize and is not sensitive to air-oxidation, it is typically used as a form of B12 for food additives and in many common multivitamins. However, this form is not perfectly synonymous with B12, in as much as a number of substances (vitamers) have B12 vitamin activity and can properly be labeled vitamin B12, and cyanocobalamin is but one of them. (Thus, all cyanocobalamin is vitamin B12, but not all vitamin B12 is cyanocobalamin).[22] Pure cyanocoblamin possesses the deep pink colour associated with most octahedral cobalt(II) complexes and the crystals are well formed and easily grown up to milimetre size.
Hydroxocobalamin is another form of B12 commonly encountered in pharmacology, but which is not normally present in the human body. Hydroxocobalamin is sometimes denonoted B12a. This form of B12 is the form produced by bacteria, and is what is converted to cyanocobalmin in the commercial charcoal filtration step of production. Hydroxocobalamin has an avid affinity for cyanide ion and has been used as an antidote to cyanide poisoning. It is supplied typically in water solution for injection. Hydroxocobalamin is thought to be converted to the active enzymic forms of B12 more easily than cyanocobalamin, and since it is little more expensive than cyanocobalamin, and has longer retention times in the body, has been used for vitamin replacement in situations where added reassurance of activity is desired. Intramuscular administration of hydroxocobalamin is also the preferred treatment for pediatric patients with intrinsic cobalamin metabolic diseases, for vitamin B12 deficient patients with tobacco amblyopia (which is thought to perhaps have a component of cyanide poisoning from cyanide in cigarette smoke); and for treatment of patients with pernicious anemia who have optic neuropathy.
B12 is the most chemically complex of all the vitamins. The structure of B12 is based on a corrin ring, which is similar to the porphyrin ring found in heme, chlorophyll, and cytochrome. The central metal ion is cobalt. Four of the six coordination sites are provided by the corrin ring, and a fifth by a dimethylbenzimidazole group. The sixth coordination site, the center of reactivity, is variable, being a cyano group (-CN), a hydroxyl group (-OH), a methyl group (-CH3) or a 5'-deoxyadenosyl group (here the C5' atom of the deoxyribose forms the covalent bond with Co), respectively, to yield the four B12 forms mentioned above. Historically, the covalent C-Co bond is one of first examples of carbon-metal bonds to be discovered in biology. The hydrogenases and, by necessity, enzymes associated with cobalt utilization, involve metal-carbon bonds.[23]
Synthesis and industrial production
Neither plants nor animals are independently capable of constructing vitamin B12.[24] Only bacteria have the enzymes required for its synthesis. The total synthesis of B12 was reported by Robert Burns Woodward[25] and Albert Eschenmoser in 1972,[26][27] and remains one of the classic feats of organic synthesis. Species from the following genera are known to synthesize B12: Acetobacterium, Aerobacter, Agrobacterium, Alcaligenes, Azotobacter, Bacillus, Clostridium, Corynebacterium, Flavobacterium, Micromonospora, Mycobacterium, Nocardia, Propionibacterium, Protaminobacter, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Salmonella, Serratia, Streptomyces, Streptococcus and Xanthomonas.
Industrial production of B12 is through fermentation of selected microorganisms.[28] Streptomyces griseus, a bacterium once thought to be a yeast, was the commercial source of vitamin B12 for many years.[29][30] The species Pseudomonas denitrificans and Propionibacterium shermanii are more commonly used today.[31] These are frequently grown under special conditions to enhance yield, and at least one company, Rhône-Poulenc of France, which has merged into Sanofi-Aventis, used genetically engineered versions of one or both of these species.
The total world production of vitamin B12, by four companies (the French Sanofi-Aventis and three Chinese companies) is said to have been 35 tonnes in 2008.[32] Most of this production is used as an additive to animal feed.[33]
Mechanism of action
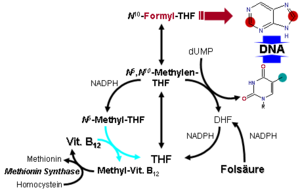
Vitamin B12 is normally involved in the metabolism of every cell of the body, especially affecting the DNA synthesis and regulation but also fatty acid synthesis and energy production. However, many (though not all) of the effects of functions of B12 can be replaced by sufficient quantities of folic acid (vitamin B9), since B12 is used to regenerate folate in the body. Most vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms are actually folate deficiency symptoms, since they include all the effects of pernicious anemia and megaloblastosis, which are due to poor synthesis of DNA when the body does not have a proper supply of folic acid for the production of thymine.[34] When sufficient folic acid is available, all known B12 related deficiency syndromes normalize, save those narrowly connected with the vitamin B12-dependent enzymes MUT, and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase (MTR), also known as methionine synthase; and the buildup of their respective substrates (methylmalonic acid, MMA) and homocysteine.
Coenzyme B12's reactive C-Co bond participates in three main types of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.[35][36]
- Isomerases. Rearrangements in which a hydrogen atom is directly transferred between two adjacent atoms with concomitant exchange of the second substituent, X, which may be a carbon atom with substituents, an oxygen atom of an alcohol, or an amine.
- Methyltransferases. Methyl (-CH3) group transfers between two molecules.
- Dehalogenases. Reactions in which a halogen atom is removed from an organic molecule. Enzymes in this class have not been identified in humans.
In humans, two major coenzyme B12-dependent enzyme families corresponding to the first two reaction types, are known. These are typified by the following two enzymes:
- MUT is an isomerase which uses the AdoB12 form and reaction type 1 to catalyze a carbon skeleton rearrangement (the X group is -COSCoA). MUT's reaction converts MMl-CoA to Su-CoA, an important step in the extraction of energy from proteins and fats (for more see MUT's reaction mechanism). This functionality is lost in vitamin B12 deficiency, and can be measured clinically as an increased methylmalonic acid (MMA) level. Unfortunately, an elevated MMA, though sensitive to B12 deficiency, is probably overly sensitive, and not all who have it actually have B12 deficiency. For example, MMA is elevated in 90–98% of patients with B12 deficiency; however 20–25% of patients over the age of 70 have elevated levels of MMA, yet 25–33% of them do not have B12 deficiency. For this reason, assessment of MMA levels is not routinely recommended in the elderly. There is no "gold standard" test for B12 deficiency because as a B12 deficiency occurs, serum values may be maintained while tissue B12 stores become depleted. Therefore, serum B12 values above the cut-off point of deficiency do not necessarily indicate adequate B12 status[9] The MUT function cannot be affected by folate supplementation, which is necessary for myelin synthesis (see mechanism below) and certain other functions of the central nervous system. Other functions of B12 related to DNA synthesis related to MTR dysfunction (see below) can often be corrected with supplementation with the vitamin folic acid, but not the elevated levels of homocysteine, which is normally converted to methionine by MTR.
- MTR, also known as methionine synthase, is a methyltransferase enzyme, which uses the MeB12 and reaction type 2 to catalyze the conversion of the amino acid homocysteine (Hcy) back into methionine (Met) (for more see MTR's reaction mechanism).[37] This functionality is lost in vitamin B12 deficiency, and can be measured clinically as an increased homocysteine level in vitro. Increased homocysteine can also be caused by a folic acid deficiency, since B12 helps to regenerate the tetrahydrofolate (THF) active form of folic acid. Without B12, folate is trapped as 5-methyl-folate, from which THF cannot be recovered unless a MTR process reacts the 5-methyl-folate with homocysteine to produce methionine and THF, thus decreasing the need for fresh sources of THF from the diet. THF may be produced in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, or may be obtained in the diet. It is converted by a non-B12-dependent process to 5,10-methylene-THF, which is involved in the synthesis of thymine. Reduced availability of 5,10-methylene-THF results in problems with DNA synthesis, and ultimately in ineffective production cells with rapid turnover, in particular blood cells, and also intestinal wall cells which are responsible for absorption. The failure of blood cell production results in the once-dreaded and fatal disease, pernicious anemia. All of the DNA synthetic effects, including the megaloblastic anemia of pernicious anemia, resolve if sufficient folate is present (since levels of 5,10-methylene-THF still remain adequate with enough dietary folate). Thus the best-known "function" of B12 (that which is involved with DNA synthesis, cell-division, and anemia) is actually a facultative function which is mediated by B12-conservation of an active form of folate which is needed for efficient DNA production.[38] Other cobalamin-requiring methyltransferase enzymes are also known in bacteria, such as Me-H4-MPT, coenzyme M methyl transferase.
Enzyme function
If folate is present in quantity, then of the two absolutely vitamin B12-dependent enzyme-family reactions in humans, the MUT-family reactions show the most direct and characteristic secondary effects, focusing on the nervous system (see below). This is because the MTR (methyltransferase-type) reactions are involved in regenerating folate, and thus are less evident when folate is in good supply.
Since the late 1990s, folic acid has begun to be added to fortify flour in many countries, so folate deficiency is now more rare. At the same time, since DNA synthetic-sensitive tests for anemia and erythrocyte size are routinely done in even simple medical test clinics (so that these folate-mediated biochemical effects are more often directly detected), the MTR-dependent effects of B12 deficiency are becoming apparent not as anemia due to DNA-synthetic problems (as they were classically), but now mainly as a simple and less obvious elevation of homocysteine in the blood and urine (homocysteinuria). This condition may result in long term damage to arteries and in clotting (stroke and heart attack), but this effect is difficult to separate from other common processes associated with atherosclerosis and aging.
The specific myelin damage resulting from B12 deficiency, even in the presence of adequate folate and methionine, is more specifically and clearly a vitamin deficiency problem. It has been connected to B12 most directly by reactions related to MUT, which is absolutely required to convert methylmalonyl coenzyme A into succinyl coenzyme A. Failure of this second reaction to occur results in elevated levels of MMA, a myelin destabilizer. Excessive MMA will prevent normal fatty acid synthesis, or it will be incorporated into fatty acid itself rather than normal malonic acid. If this abnormal fatty acid subsequently is incorporated into myelin, the resulting myelin will be too fragile, and demyelination will occur. Although the precise mechanism(s) are not known with certainty, the result is subacute combined degeneration of central nervous system and spinal cord.[39] Whatever the cause, it is known that B12 deficiency causes neuropathies, even if folic acid is present in good supply, and therefore anemia is not present.
Vitamin B12-dependent MTR reactions may also have neurological effects, through an indirect mechanism. Adequate methionine (which, like folate, must otherwise be obtained in the diet, if it is not regenerated from homocysteine by a B12 dependent reaction) is needed to make S-adenosyl-methionine (SAMe), which is in turn necessary for methylation of myelin sheath phospholipids. Although production of SAMe is not B12 dependent, help in recycling for provision of one adequate substrate for it (the essential amino acid methionine) is assisted by B12. In addition, SAMe is involved in the manufacture of certain neurotransmitters, catecholamines and in brain metabolism. These neurotransmitters are important for maintaining mood, possibly explaining why depression is associated with B12 deficiency. Methylation of the myelin sheath phospholipids may also depend on adequate folate, which in turn is dependent on MTR recycling, unless ingested in relatively high amounts.
Absorption and distribution
The human physiology of vitamin B12 is complex, and therefore is prone to mishaps leading to vitamin B12 deficiency. Unlike most nutrients, absorption of vitamin B12 actually begins in the mouth, where small amounts of unbound crystalline B12 can be absorbed through the mucous membrane.[9] Protein-bound vitamin B12 must be released from the proteins by the action of digestive proteases in both the stomach and small intestine.[40] Gastric acid releases the vitamin from food particles, therefore antacid and acid-blocking medications (especially proton-pump inhibitors) may inhibit absorption of B12. In addition some elderly people produce less stomach acid as they age thereby increasing their probability of B12 deficiencies.[41]
B12 taken in a low-solubility, non-chewable supplement pill form may bypass the mouth and stomach and not mix with gastric acids, but these are not necessary for the absorption of free B12 not bound to protein.
Once the B12 is freed from the proteins in food, R-proteins, such as haptocorrins and cobalaphilins, are secreted, which bind to free vitamin B12 to form a B12-R complex. Also in the stomach, intrinsic factor (IF), a protein synthesized by gastric parietal cells, is secreted in response to histamine, gastrin and pentagastrin, as well as the presence of food. If this step fails due to gastric parietal cell atrophy (the problem in pernicious anemia), sufficient B12 is not absorbed later on, unless administered orally in relatively massive doses (0.5 to 1 mg/day). Due to the complexity of B12 absorption, geriatric patients, many of whom are hypoacidic due to reduced parietal cell function, have an increased risk of B12 deficiency.[42]
In the duodenum, proteases digest R-proteins and release B12, which then binds to IF, to form a complex (IF/B12). B12 must be attached to IF for it to be absorbed, as receptors on the enterocytes in the terminal ileum of the small bowel only recognize the B12-IF complex; in addition, intrinsic factor protects the vitamin from catabolism by intestinal bacteria. Therefore, absorption of food vitamin B12 requires an intact and functioning stomach, exocrine pancreas, intrinsic factor, and small bowel. Problems with any one of these organs makes a vitamin B12 deficiency possible. Individuals who lack intrinsic factor have a decreased ability to absorb B12. This results in 80–100% excretion of oral doses in the feces versus 30–60% excretion in feces as seen in individuals with adequate IF.[42]
Once the IF/B12 complex is recognized by specialized ileal receptors, it is transported into the portal circulation. The vitamin is then transferred to transcobalamin II (TC-II/B12), which serves as the plasma transporter. Hereditary defects in production of the transcobalamins and their receptors may produce functional deficiencies in B12 and infantile megaloblastic anemia, and abnormal B12 related biochemistry, even in some cases with normal blood B12 levels.[43] For the vitamin to serve inside cells, the TC-II/B12 complex must bind to a cell receptor, and be endocytosed. The transcobalamin-II is degraded within a lysosome, and free B12 is finally released into the cytoplasm, where it may be transformed into the proper coenzyme, by certain cellular enzymes (see above).
The total amount of vitamin B12 stored in body is about 2–5 mg in adults. Around 50% of this is stored in the liver.[9] Approximately 0.1% of this is lost per day by secretions into the gut, as not all these secretions are reabsorbed. Bile is the main form of B12 excretion; however, most of the B12 secreted in the bile is recycled via enterohepatic circulation.[9] Due to the extremely efficient enterohepatic circulation of B12, the liver can store several years’ worth of vitamin B12; therefore, nutritional deficiency of this vitamin is rare. How fast B12 levels change depends on the balance between how much B12 is obtained from the diet, how much is secreted and how much is absorbed. B12 deficiency may arise in a year if initial stores are low and genetic factors unfavourable, or may not appear for decades. In infants, B12 deficiency can appear much more quickly.[44]
History
B12 deficiency is the cause of pernicious anemia, an anemic disease that was usually fatal and had unknown etiology when it was first described in medicine. The cure, and B12, were discovered by accident. George Whipple had been doing experiments in which he induced anemia in dogs by bleeding them, and then fed them various foods to observe which diets allowed them fastest recovery from the anemia produced. In the process, he discovered that ingesting large amounts of liver seemed to most-rapidly cure the anemia of blood loss. Thus, he hypothesized that liver ingestion might treat pernicious anemia. He tried this and reported some signs of success in 1920.
After a series of careful clinical studies, George Richards Minot and William Murphy set out to partly isolate the substance in liver which cured anemia in dogs, and found that it was iron. They also found that an entirely different liver substance cured pernicious anemia in humans, that had no effect on dogs under the conditions used. The specific factor treatment for pernicious anemia, found in liver juice, had been found by this coincidence. Minot and Murphy reported these experiments in 1926. This was the first real progress with this disease. Despite this discovery, for several years patients were still required to eat large amounts of raw liver or to drink considerable amounts of liver juice.
In 1928, the chemist Edwin Cohn prepared a liver extract that was 50 to 100 times more potent than the natural liver products. The extract was the first workable treatment for the disease. For their initial work in pointing the way to a working treatment, Whipple, Minot, and Murphy shared the 1934 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
These events in turn eventually led to discovery of the soluble vitamin, called vitamin B12, in the liver juice. The vitamin in liver extracts was not isolated until 1948 by the contributions of chemists Mary Shaw Shorb[45] and Karl A. Folkers of the United States and Alexander R. Todd of Great Britain. In 1947, while working for the Poultry Science Department at the University of Maryland, Mary Shorb (in a collaborative project with Folkers and Merck) was provided with a $400 grant to develop the LLD assay. The LLD assay led to the purification and characterization of Vitamin B12 as it caused rapid isolation of the anti-pernicious anemia factor. For this discovery, in 1949 Mary Shorb and Karl Folkers received the Mead Johnson Award from the American Society of Nutritional Sciences.[45]
The chemical structure of the molecule was determined by Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin and her team in 1956, based on crystallographic data. Eventually, methods of producing the vitamin in large quantities from bacteria cultures were developed in the 1950s, and these led to the modern form of treatment for the disease.
Sources
Foods
| Food[46] | µg vitamin B12/100g |
|---|---|
| Panfried beef liver | 83.1 |
| Simmered turkey giblets | 33.2 |
| Braunschweiger pork liver sausage | 20.1 |
| Raw pacific oysters | 16.0 |
| Cooked Alaska king crab | 11.5 |
| Raw clams | 11.3 |
| Simmered chicken giblets | 9.4 |
| Swiss cheese | 3.34 |
| Beef (uncooked sirloin) | 1.15 |
| Egg (raw, whole chicken's egg) | 0.89 |
| Whole cow's milk | 0.45 |
| Raw chicken breast | 0.20 |
Ultimately, animals must obtain vitamin B12 directly or indirectly from bacteria, and these bacteria may inhabit a section of the gut which is posterior to the section where B12 is absorbed. Thus, herbivorous animals must either obtain B12 from bacteria in their rumens, or (if fermenting plant material in the hindgut) by reingestion of cecotrope fæces.
Vitamin B12 is found in foods that come from animals, including fish and shellfish, meat (especially liver), poultry, eggs, milk, and milk products.[10] Eggs are often mentioned as a good B12 source, but they also contain a factor that blocks absorption.[47] Certain insects such as termites contain B12 produced by their gut bacteria, in a way analogous to ruminant animals.[48] An NIH Fact Sheet lists a variety of food sources of vitamin B12.[10]
While lacto-ovo vegetarians usually get enough B12 through consuming dairy products, vegans will lack B12 unless they consume B12-containing dietary supplements or B12-fortified foods. Examples of fortified foods include fortified breakfast cereals, fortified soy products, fortified energy bars, and fortified nutritional yeast. According to the UK Vegan Society, the present consensus is that any B12 present in plant foods is likely to be unavailable to humans because B12 analogues can compete with B12 and inhibit metabolism.[49][50]
Claimed sources of B12 that have been shown to be inadequate or unreliable through direct studies[51] of vegans include laver (a seaweed), barley grass, and human intestinal bacteria (human colonic bacteria produce B12, but it cannot be absorbed from the colon).[52]
Supplements
Vitamin B12 is provided as a supplement in many processed foods, and is also available in vitamin pill form, including multi-vitamins. Vitamin B12 can be supplemented in healthy subjects also by liquid, transdermal patch, nasal spray, or injection and is available singly or in combination with other supplements.
Cyanocobalamin is converted to its active forms, first hydroxocobalamin and then methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin in the liver.
The sublingual route, in which B12 is presumably or supposedly absorbed more directly under the tongue, has not proven to be necessary or helpful, though there are a number of lozenges, pills, and even a lollipop designed for sublingual absorption. A 2003 study found no significant difference in absorption for serum levels from oral vs. sublingual delivery of 0.5 mg of cobalamin.[53] Sublingual methods of replacement are effective only because of the typically high doses (0.5 mg), which are swallowed, not because of placement of the tablet. As noted below, such very high doses of oral B12 may be effective as treatments, even if gastro-intestinal tract absorption is impaired by gastric atrophy (pernicious anemia).
Injection and patches are sometimes used if digestive absorption is impaired, but there is evidence that this course of action may not be necessary with modern high potency oral supplements (such as 0.5 to 1 mg or more). Even pernicious anemia can be treated entirely by the oral route.[54][55][56] These supplements carry such large doses of the vitamin that 1% to 5% of high oral doses of free crystalline B12 is absorbed along the entire intestine by passive diffusion.
However, if the patient has inborn errors in the methyltransfer pathway (cobalamin C disease, combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria), treatment with intravenous, intramuscular hydroxocobalamin or transdermal B12 is needed.[57][58][59][60][61]
Cyanocobalamin is also sometimes added to beverages including Diet Coke Plus and many energy drinks.
Non-cyano forms as supplements
Recently sublingual methylcobalamin has become available in 1 mg tablets. Such tablets have higher bioavailability than the older cyanocobalamin. No cyanide is released with methylcobolamin, although the amount of cyanide (2% of the weight, or 20 micrograms cyanide in a 1 mg cyanocobalamin tab) is far less than ingested in many natural foods. Although the safety of cyanocobalamin has not been seriously questioned, the safety of the other types is also well-established.[62]
References
- ^ [unreliable source?]Vitamin B-12: Rhetoric and Reality (CONT., 3 OF 5)
- ^ a b "Vitamin B12". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ Hall AH, Rumack BH (1987). "Hydroxycobalamin/sodium thiosulfate as a cyanide antidote". The Journal of Emergency Medicine. 5 (2): 115–21. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(87)90074-6. PMID 3295013.
- ^ Dart RC (2006). "Hydroxocobalamin for acute cyanide poisoning: new data from preclinical and clinical studies; new results from the prehospital emergency setting". Clinical Toxicology. 44 (Suppl 1): 1–3. doi:10.1080/15563650600811607. PMID 16990188.
- ^ Vogiatzoglou A, Refsum H, Johnston C; et al. (2008). "Vitamin B12 status and rate of brain volume loss in community-dwelling elderly". Neurology. 71 (11): 826–32. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000325581.26991.f2. PMID 18779510.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stephen Walsh. "What every vegan should know about vitamin B12". Vegan Society. Archived from the original on 2007-07-17. Retrieved 2007-12-03.
- ^ Reed Mangels, Ph.D., R.D. "Vitamin B12 in the Vegan Diet". Vegetarian Resource Group. Retrieved 2008-01-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Don't Vegetarians Have Trouble Getting Enough Vitamin B12?". Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. Retrieved 2008-01-17.
- ^ a b c d e Vitamin B12, usda.gov
- ^ a b c Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Vitamin B12
- ^ Sethi NK, Robilotti E, Sadan Y (2005). "Neurological Manifestations Of Vitamin B-12 Deficiency". The Internet Journal of Nutrition and Wellness. 2 (1).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Masalha R, Chudakov B, Muhamad M, Rudoy I, Volkov I, Wirguin I (2001). "Cobalamin-responsive psychosis as the sole manifestation of vitamin B12 deficiency". Israeli Medical Association Journal. 3: 701–703.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bønaa KH; et al. (2006). "Homocysteine lowering and cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction". The New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (15): 1578–88. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa055227. PMID 16531614.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Lonn E, Yusuf S, Arnold MJ; et al. (2006). "Homocysteine lowering with folic acid and B vitamins in vascular disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (15): 1567–77. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa060900. PMID 16531613.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pott JW, Wong KH (2006). "Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency". Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology. 244 (10): 1357–9. doi:10.1007/s00417-006-0269-7. PMID 16523300.
- ^ Andrès E, Noel E, Goichot B (2002). "Metformin-associated vitamin B12 deficiency". Arch Intern Med. 162 (19): 2251–2. doi:10.1001/archinte.162.19.2251-a. PMID 12390080.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gilligan M (2002). "Metformin and vitamin B12 deficiency". Arch Intern Med. 162 (4): 484–5. doi:10.1001/archinte.162.4.484. PMID 11863489.
- ^ Bauman, WA; Shaw, S; Jayatilleke, E; Spungen, AM; Herbert, V (2000). "Increased intake of calcium reverses vitamin B12 malabsorption induced by metformin". Diabetes care. 23 (9): 1227–31. doi:10.2337/diacare.23.9.1227. PMID 10977010.
- ^ Samantha Copp (2005-12-01). "What effect does metformin have on vitamin B12 levels?". UK Medicines Information, NHS. – report (.doc)
- ^ Conrad, Marcel (2006-10-04). "Pernicious Anemia". Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- ^ Palva IP; et al. (1972). "Drug induced malabsorption of vitamin B12 – IV – malabsorption and deficiency of B12 during treatment with slow-release potassium chloride". Acta Med Scand. 191 (4): 355–7. PMID 5032681.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Herbert V (1988). "Vitamin B-12: plant sources, requirements, and assay". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 48 (3 Suppl): 852–8. PMID 3046314.
- ^ Jaouen, G., ed. (2006). Bioorganometallics: Biomolecules, Labeling, Medicine. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 3-527-30990-X.[page needed]
- ^ Loeffler, G. (2005). Basiswissen Biochemie. Heidelberg: Springer. p. 606. ISBN 3-540-23885-9.
- ^ Khan, Adil Ghani; Eswaran, S. V. (2003). "Woodward's synthesis of vitamin B12". Resonance. 8: 8. doi:10.1007/BF02837864.
- ^ Eschenmoser A, Wintner CE (1977). "Natural product synthesis and vitamin B12". Science. 196 (4297): 1410–20. doi:10.1126/science.867037. PMID 867037.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Riether, Doris; Mulzer, Johann (2003). "Total Synthesis of Cobyric Acid: Historical Development and Recent Synthetic Innovations". European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2003: 30. doi:10.1002/1099-0690(200301)2003:1<30::AID-EJOC30>3.0.CO;2-I.
- ^ Martens JH, Barg H, Warren MJ, Jahn D (2002). "Microbial production of vitamin B12". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 58 (3): 275–85. doi:10.1007/s00253-001-0902-7. PMID 11935176.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Linnell JC, Matthews DM (1984). "Cobalamin metabolism and its clinical aspects". Clinical Science. 66 (2): 113–21. PMID 6420106.
- ^ Vitamin B12. Code of Federal Regulations. U.S. Government Printing Office. Title 21, Volume 3. Revised. April 1, 2001. CITE: 21CFR184.1945 p. 552
- ^ De Baets S, Vandedrinck S, Vandamme EJ (2000). "Vitamins and Related Biofactors, Microbial Production". In Lederberg J (ed.). Encyclopedia of Microbiology. Vol. 4 (2nd ed.). New York: Academic Press. pp. 837–853. ISBN 0122268008.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead.«New round of price slashing in vitamin B12 sector. (Fine and Specialty)», 1/2009.
- ^ 90% of the global production, following «Where does B12 come from?».
- ^ Argument for providing B12 with food fortification of folate, since otherwise folate will correct hematological symptoms while leaving neurological symptoms to progress
- ^ Voet, Judith G.; Voet, Donald (1995). Biochemistry. New York: J. Wiley & Sons. p. 675. ISBN 0-471-58651-X. OCLC 31819701.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Banerjee, R; Ragsdale, SW (2003). "The many faces of vitamin B12: catalysis by cobalamin-dependent enzymes". Annual review of biochemistry. 72: 209–47. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161828. PMID 14527323.
- ^ Banerjee RV, Matthews RG (1990). "Cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase". The FASEB Journal. 4 (5): 1450–9. PMID 2407589.
- ^ Wickramasinghe SN (1995). "Morphology, biology and biochemistry of cobalamin- and folate-deficient bone marrow cells". Baillière's Clinical Haematology. 8 (3): 441–59. doi:10.1016/S0950-3536(05)80215-X. PMID 8534956.
- ^ Naidich MJ, Ho SU (2005). "Case 87: Subacute combined degeneration". Radiology. 237 (1): 101–5. doi:10.1148/radiol.2371031757. PMID 16183926.
- ^ Marks, Allan D. Basic Medical Biochemistry: A Clinical Approach, 3rd Ed., p 757.
- ^ Melinda Beck (January 18, 2011). "Sluggish? Confused? Vitamin B12 May Be Low". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ a b Combs, Gerald F. (2008). The vitamins: fundamental aspects in nutrition and health (3rd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press. ISBN 0121834921. OCLC 150255807.[page needed]
- ^ Marcel E Conrad Pernicious Anemia Aug 26, 2009
- ^ "B12: An essential part of a healthy plant-based diet".
- ^ a b http://ansc.umd.edu/shorb/
- ^ Adapted from:"Vitamin B-12 content of selected foods" (PDF). USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 23. Retrieved 2010-12-20.
- ^ Doscherholmen A; et al. (1975). "Proc Soc Exp Biol Med". 149: 987–90.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Wakayama EJ, Dillwith JW, Howard RW, Blomquist GJ (1984). "Vitamin B12 levels in selected insects". Insect Biochemistry. 14: 175–179. doi:10.1016/0020-1790(84)90027-1.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Walsh, Stephen, RD. "Vegan Society B12 factsheet". Vegan Society. Retrieved 2008-01-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Donaldson, MS (2000). "Metabolic vitamin B12 status on a mostly raw vegan diet with follow-up using tablets, nutritional yeast, or probiotic supplements". Ann Nutr Metab. 44 (5–6): 229–234. doi:10.1159/000046689. PMID 11146329.
- ^ Norris, Jack, RD. "B12 in Tempeh, Seaweeds, Organic Produce, and Other Plant Foods". VeganHealth.org. Retrieved 2008-01-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Walsh, Stephen. "What Every Vegan Should Know about Vitamin B12". VeganHealth.org. Retrieved 2011-02-18.
- ^ Sharabi, A; Cohen, E; Sulkes, J; Garty, M (2003). "Replacement therapy for vitamin B12 deficiency: comparison between the sublingual and oral route". British journal of clinical pharmacology. 56 (6): 635–8. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01907.x. PMC 1884303. PMID 14616423.
- ^ Bolaman Z, Kadikoylu G, Yukselen V, Yavasoglu I, Barutca S, Senturk T (2003). "Oral versus intramuscular cobalamin treatment in megaloblastic anemia: a single-center, prospective, randomized, open-label study". Clin Ther. 25 (12): 3124–34. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(03)90096-8. PMID 14749150.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lane LA, Rojas-Fernandez C (2002). "Treatment of vitamin b(12)-deficiency anemia: oral versus parenteral therapy". Ann Pharmacother. 36 (7–8): 1268–72. doi:10.1345/aph.1A122. PMID 12086562.
- ^ Butler CC; et al. (2006). "Oral vitamin B12 versus intramuscular vitamin B12 for vitamin B12 deficiency: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials". Fam Pract. 23 (3): 279–85. doi:10.1093/fampra/cml008. PMID 16585128.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Andersson HC, Shapira E (1998). "Biochemical and clinical response to hydroxocobalamin versus cyanocobalamin treatment in patients with methylmalonic acidemia and homocystinuria (cblC)". J. Pediatr. 132 (1): 121–4. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(98)70496-2. PMID 9470012.
- ^ Roze E, Gervais D, Demeret S; et al. (2003). "Neuropsychiatric disturbances in presumed late-onset cobalamin C disease". Arch. Neurol. 60 (10): 1457–62. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.10.1457. PMID 14568819.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Thauvin-Robinet C, Roze E, Couvreur G; et al. (2008). "The adolescent and adult form of cobalamin C disease: clinical and molecular spectrum". J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 79 (6): 725. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.133025. PMID 18245139.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Heil SG, Hogeveen M, Kluijtmans LA; et al. (2007). "Marfanoid features in a child with combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria (CblC type)". J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30 (5): 811. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0546-6. PMID 17768669.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tsai AC; et al. (2007). "Late-onset combined homocystinuria and methylmalonic aciduria (cblC) and neuropsychiatric disturbance". Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 143 (20): 2430–4. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31932. PMID 17853453.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ [1] safety of non-cyanocobalamin forms of B12
External links
- Vitamin B12 Fact Sheet from the U.S. National Institutes of Health
- Jane Higdon, "Vitamin B12", Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University
- Vitamin B12. Medline Plus (National Library of Medicine). Part of it was used for this article (US Government public domain), specially for drug and other interactions.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency article in American Family Physician journal
- Cyanocobalamin at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Calculator for estimating the average daily Vitamin B12 intake
