From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Sulfinalol
Names
IUPAC name
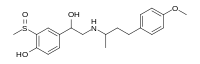
4-[1-Hydroxy-2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-ylamino]ethyl]-2-methylsulfinylphenol
Identifiers
UNII
InChI=1S/C20H27NO4S/c1-14(4-5-15-6-9-17(25-2)10-7-15)21-13-19(23)16-8-11-18(22)20(12-16)26(3)24/h6-12,14,19,21-23H,4-5,13H2,1-3H3
Key: PAQZZCOZHPGCFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
CC(CCC1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)NCC(C2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)S(=O)C)O
Properties
C 20 H 27 N O 4 S
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
Sulfinalol is a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist .[ 1]
Synthesis
The methyl group on a sulfoxide is sufficiently acidic to substitute for phenolic hydroxyl.
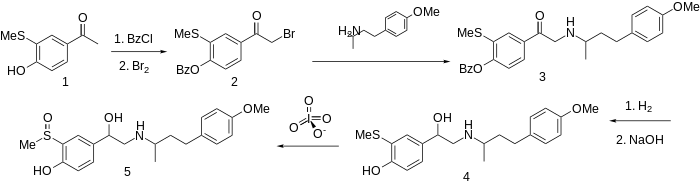
Sulfinalol synthesis: R. E. Philion, DE 2728641 Sterling ), C.A. 90, 137468 (1979). The preparation of this combined α- and β-blocker sulfinalol begins by protection of the phenolic hydroxyl as its benzoate ester. Bromination followed by condensation with 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (not PMA ) gives the aminoketone 3 . Successive catalytic reduction and saponification affords aminoalcohol 4 . Oxidation of the sulfide to the sulfoxide with a reagent such as metaperiodate gives sulfinalol (5 ).
References
^ "Studies on the mechanism of the acute antihypertensive and vasodilator actions of several beta-adrenoceptor antagonists". J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol . 4 (5): 749–58. 1982. PMID 6182405 .
α1
Agonists Antagonists
Abanoquil Ajmalicine Alfuzosin Anisodamine Anisodine Atiprosin Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., brexpiprazole , clozapine , olanzapine , quetiapine , risperidone )Benoxathian Beta blockers (e.g., adimolol , amosulalol , arotinolol , carvedilol , eugenodilol , labetalol )Buflomedil Bunazosin Corynanthine Dapiprazole Domesticine Doxazosin Ergolines (e.g., acetergamine , ergotamine , dihydroergotamine , lisuride , nicergoline , terguride )Etoperidone Fenspiride Hydroxyzine Indoramin Ketanserin L-765,314 mCPP Mepiprazole Metazosin Monatepil Moxisylyte Naftopidil Nantenine Neldazosin Niaprazine Niguldipine Pardoprunox Pelanserin Perlapine Phendioxan Phenoxybenzamine Phentolamine Phenylpiperazine antidepressants (e.g., hydroxynefazodone , nefazodone , trazodone , triazoledione )Piperoxan Prazosin Quinazosin Quinidine Silodosin Spegatrine Spiperone Talipexole Tamsulosin Terazosin Tiodazosin Tolazoline Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine , maprotiline , mianserin )Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline , clomipramine , doxepin , imipramine , trimipramine )Trimazosin Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , fluphenazine , loxapine , thioridazine )Urapidil WB-4101 Zolertine
α2
Agonists Antagonists
1-PP Adimolol Amesergide Aptazapine Atipamezole Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine , brexpiprazole , clozapine , lurasidone , olanzapine , paliperidone , quetiapine , risperidone , zotepine )Azapirones (e.g., buspirone , gepirone , ipsapirone , tandospirone )BRL-44408 Buflomedil Cirazoline Efaroxan Esmirtazapine Fenmetozole Fluparoxan Idazoxan Ketanserin Lisuride mCPP Mianserin Mirtazapine NAN-190 Pardoprunox Phentolamine Phenoxybenzamine Piperoxan Piribedil Rauwolscine Rotigotine Setiptiline Spegatrine Spiroxatrine Sunepitron Terguride Tolazoline Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , fluphenazine , loxapine , thioridazine )Yohimbine
β