Capra (genus)
| Capra Temporal range: Early Pleistocene – Present
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Capra, St. Leonhard in Passeier, Italy | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Caprinae |
| Tribe: | Caprini |
| Genus: | Capra Linnaeus, 1758 |
| Type species | |
| Capra hircus | |
| Species | |
|
See text. | |

| |
| Approximate range of the Capra species | |
Capra is a genus of mammals, the goats, comprising ten species, including the markhor and several species known as ibexes. The domestic goat (Capra hircus) is a domesticated species derived from the bezoar ibex (Capra aegagrus aegagrus). It is one of the oldest domesticated species of animal—according to archaeological evidence its earliest domestication occurred in Iran at 10,000 calibrated calendar years ago.[1]
Wild goats are animals of mountain habitats. They are very agile and hardy, able to climb on bare rock and survive on sparse vegetation. They can be distinguished from the genus Ovis, which includes sheep, by the presence of scent glands close to the feet, in the groin, and in front of the eyes, and the absence of other facial glands, and by the presence of a beard in some specimens, and of hairless calluses on the knees of the forelegs.[2]
Taxonomy
[edit]

All members of the genus Capra are bovids (members of the family Bovidae), and more specifically caprines (subfamily Caprinae). As such they are ruminants, meaning they chew the cud, and have four-chambered stomachs which play a vital role in digesting, regurgitating, and redigesting their food.
The genus has sometimes been taken to include Ovis (sheep) and Ammotragus (Barbary sheep),[3] but these are usually regarded as distinct genera, leaving Capra for ibexes. In this smaller genus, some authors have recognized only two species, the markhor on one side and all other forms included in one species on the other side.[4] Today, nine wild species are usually accepted to which is added the domestic goat:[5]
- West Asian ibex also known as the wild goat (Capra aegagrus)
- Bezoar ibex (Capra aegagrus aegagrus)
- Sindh ibex (Capra aegagrus blythi)
- Domestic goat (Capra hircus; includes feral goat; sometimes considered a subspecies of C. aegagrus)
- Asian ibex also known as the Siberian ibex (Capra sibirica)[6]
- Markhor (Capra falconeri)
- West Caucasian tur (Capra caucasica)
- East Caucasian tur (Capra cylindricornis)
- Alpine ibex (Capra ibex)
- Iberian ibex also known as the Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica)[7]
- Nubian ibex (Capra nubiana)[8]
- Walia ibex (Capra walie)
The goats of the genus Capra have complex systematic relationships, which are still not completely resolved. Recent studies based on mitochondrial DNA suggest that the Asian ibex and the Nubian ibex represent distinct species, which are not very closely related to the physically similar Alpine ibex. The Alpine ibex forms a group with the Iberian ibex. The West Caucasian tur appears to be more closely related to the wild goat than to the East Caucasian tur. The markhor is relatively little separated from other forms—previously it had been considered to be a separate branch of the genus.[9]
Almost all wild goat species are allopatric (geographically separated)—the only geographical overlaps are the wild goat (Capra aegagrus) with the East Caucasian tur (Capra cylindricornis), and the markhor (Capra falconeri) with the Asian ibex (Capra sibirica). In both cases, the overlapping species do not usually interbreed in the wild, but in captivity, all Capra species can interbreed, producing fertile offspring.[10]
Species and subspecies
[edit]| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian ibex, Siberian ibex | Capra sibirica Pallas, 1776 Four subspecies
|
Central & North Asia, Afghanistan, West and North China (mainly Xinjiang), NW India, SE Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, North Pakistan, South Russia, Tajikistan, East Uzbekistan.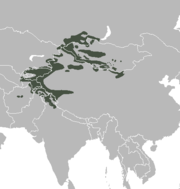
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
NT
|
| Markhor | Capra falconeri (Wagner, 1839) Five subspecies
|
South Asia; the Karakoram and Himalaya ranges.
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
NT
|
| Domestic goat | Capra hircus Linnaeus, 1758 |
Cosmopolitan distribution; domesticated. | Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Wild goat | Capra aegagrus Erxleben, 1777 Four subspecies
|
Turkey, the Caucasus to Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan | Size: Habitat: Diet: |
NT
|
| East Caucasian tur | Capra cylindricornis (Blyth, 1841) |
Greater Caucasus Mountains. | Size: Habitat: Diet: |
NT
|
| West Caucasian tur | Capra caucasica Güldenstädt and Pallas, 1783 |
Caucasus Mountains. | Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EN
|
| Alpine ibex | Capra ibex Linnaeus, 1758 |
Austria, Bavaria, France, Italy, Liechtenstein, Slovenia & Switzerland.
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Iberian ibex | Capra pyrenaica (Schinz, 1838) |
Iberian Peninsula: Andorra, Pyrenees Mountains, Spain to Portugal. | Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Nubian ibex | Capra nubiana F. Cuvier, 1825 |
Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.[11] | Size: Males: 52–74.7 kg (115–165 lb)
Females: 25.3–32.7 kg (56–72 lb) |
VU
|
| Walia ibex | Capra walie Rüppell, 1835 |
Ethiopian Highlands & Simien Mountains.
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
VU
|
Domestication and uses
[edit]Along with sheep, goats were among the first domesticated animals. The domestication process started at least 10,000 years ago in what is now northern Iran.[13] Easy human access to goat hair, meat, and milk were the primary motivations. Goat skins were popularly used until the Middle Ages for water and wine bottles when traveling and camping, and in certain regions as parchment for writing.
-
Goats used for natural weed control
-
Ibex securely climbing rocky slope
References
[edit]- ^ Zeder, Melinda A.; Hesse, Brian (2000). "The Initial Domestication of Goats (Capra hircus) in the Zagros Mountains 10,000 Years Ago". Science. 287 (5461): 2254–7. Bibcode:2000Sci...287.2254Z. doi:10.1126/science.287.5461.2254. PMID 10731145. Archived from the original on July 7, 2022. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- ^ Parrini, F.; et al. (2009). "Capra ibex (Artiodactyla: Bovidae)". Mammalian Species. 830: 1–12. doi:10.1644/830.1.
- ^ Ansell, W. F. H. 1972. Order Artiodactyla. Part 15. Pp. 1–84, in The mammals of Africa: An identification manual (J. Meester and H. W. Setzer, eds.) [issued 2 May 1972]. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C., not continuously paginated. (quoted in Grubb, P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-8221-4. OCLC 62265494.)
- ^ Haltenorth, T. 1963. Klassifikation der Säugetiere: Artiodactyla I. Handbuch der Zoologie, 8(32):1–167 (quoted in Grubb, P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-8221-4. OCLC 62265494.)
- ^ Pidancier, Nathalie; Jordan, Steve; Luikart, Gordon; Taberlet, Pierre (2006). "Evolutionary history of the genus Capra (Mammalia, Artiodactyla): Discordance between mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome phylogenies". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 40 (3): 739–749. Bibcode:2006MolPE..40..739P. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.04.002. PMID 16757184.
- ^ Sarasa, M. (2023). "Common names of the Asiatic ibex superspecies at a turning point in its taxonomy and management". Animal Biodiversity and Conservation: 79–86. doi:10.32800/abc.2023.46.0079. ISSN 2014-928X. S2CID 257346317.
- ^ Sarasa, Mathieu; Alasaad, Samer; Pérez, Jesús M. (2012). "Common names of species, the curious case of Capra pyrenaica and the concomitant steps towards the 'wild-to-domestic' transformation of a flagship species and its vernacular names". Biodiversity and Conservation. 21 (1): 1–12. Bibcode:2012BiCon..21....1S. doi:10.1007/s10531-011-0172-3. ISSN 1572-9710. S2CID 254282784.
- ^ Mendelssohn, Heinrich; Yom-Tov, Yoram (1999). Mammalia of Israel. Fauna Palaestina. Jerusalem: Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities. ISBN 978-965-208-145-2.
- ^ Kazanskaya, E. Y.; Kuznetsova, M. V.; Danilkin, A. A. (2007). "Phylogenetic reconstructions in the genus Capra (Bovidae, Artiodactyla) based on the mitochondrial DNA analysis". Russian Journal of Genetics. 43 (2): 181–189. doi:10.1134/S1022795407020135.
- ^ V. G. Heptner: Mammals of the Sowjetunion Vol. I UNGULATES. Leiden, New York, 1989 ISBN 90-04-08874-1
- ^ Ross, S.; Elalqamy, H.; Al Said, T.; Saltz, D. "Capra nubiana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T3796A22143385. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3796A22143385.en.
- ^ Ross, S.; Elalqamy, H.; Al Said, T.; Saltz, D. "Capra nubiana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T3796A22143385. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T3796A22143385.en.
- ^ Zeder, Melinda A.; Hesse, Brian (2000). "The Initial Domestication of Goats ( Capra hircus ) in the Zagros Mountains 10,000 Years Ago". Science. 287 (5461): 2254–2257. Bibcode:2000Sci...287.2254Z. doi:10.1126/science.287.5461.2254. PMID 10731145.
External links
[edit]- . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.












