HEPPS (buffer)
Appearance
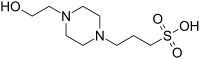
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]propane-1-sulfonic acid
| |
| Other names
HEPPS, EPPS
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.528 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H20N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 252.33 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | (decomposes) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
HEPPS (EPPS) is a buffering agent used in biology and biochemistry. The pKa of HEPPS is 8.00. It is ones of Good's buffers.[1]
Research on mice with Alzheimers disease-like amyloid beta plaques has shown that HEPPS can cause the plaques to break up, reversing some of the symptoms in the mice.[2][3][4]
References
- ^ Good, N. E; Winget, G. D; Winter, W; Connolly, T. N; Izawa, S; Singh, R. M (1966). "Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research". Biochemistry. 5 (2): 467–77. PMID 5942950.
- ^ "Small Molecule Breaks Up Amyloid Aggregates In Mice". Chemical & Engineering News. Retrieved 14 December 2015.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Kim, Hye Yun; Kim, Hyunjin Vincent; Jo, Seonmi; Lee, C. Justin; Choi, Seon Young; Kim, Dong Jin; Kim, YoungSoo (8 December 2015). "EPPS rescues hippocampus-dependent cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice by disaggregation of amyloid-β oligomers and plaques". Nature Communications. 6: 8997. doi:10.1038/ncomms9997. PMC 4686862. PMID 26646366.
- ^ "Chemical clears Alzheimer's protein and restores memory in mice". MedicalXpress. Retrieved December 10, 2015.
See also
