Laptop: Difference between revisions
Bitch, please. |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
A '''laptop''' is a portable [[personal computer]] with a [[Flip (form)|clamshell]] form factor, suitable for [[mobile computing|mobile use]].<ref name="webopedia">[http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/l/laptop_computer.html What is a laptop computer]</ref> They are also sometimes called '''notebook computers''' or '''notebooks'''. Laptops are commonly used in a variety of settings, including work, education, and personal multimedia. They are frequently used as a primary PC platform amongst young people. |
A '''laptop''' is a portable [[personal computer]] with a [[Flip (form)|clamshell]] form factor, suitable for [[mobile computing|mobile use]].<ref name="webopedia">[http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/l/laptop_computer.html What is a laptop computer]</ref> They are also sometimes called '''notebook computers''' or '''notebooks'''. Laptops are commonly used in a variety of settings, including work, education, and personal multimedia. They are frequently used as a primary PC platform amongst young people. |
||
A laptop combines the components and inputs as a desktop computer; including [[Computer display|display]], [[computer speaker|speakers]] [[computer keyboard|keyboard]], and pointing device (such as a [[touchpad]]), into a single device. Most modern day laptop computers also have a webcam and a mic (microphone) pre-installed. {{citation needed|date=December 2013}} A laptop can be powered either from a [[rechargeable battery]], or by [[mains electricity]] via an [[AC adapter]]. Laptops are a diverse category of devices, and other more specific terms, such as [[ultrabooks]] or [[netbooks]], refer to specialist ''types'' of laptop which have been optimised for certain uses. Hardware specifications change vastly between these classifications, forgoing greater and greater degrees of processing power to reduce heat emissions. |
A laptop combines the components nishanth and inputs as a desktop computer; including [[Computer display|display]], [[computer speaker|speakers]] [[computer keyboard|keyboard]], and pointing device (such as a [[touchpad]]), into a single device. Most modern day laptop computers also have a webcam and a mic (microphone) pre-installed. {{citation needed|date=December 2013}} A laptop can be powered either from a [[rechargeable battery]], or by [[mains electricity]] via an [[AC adapter]]. Laptops are a diverse category of devices, and other more specific terms, such as [[ultrabooks]] or [[netbooks]], refer to specialist ''types'' of laptop which have been optimised for certain uses. Hardware specifications change vastly between these classifications, forgoing greater and greater degrees of processing power to reduce heat emissions. |
||
[[Portable computer]]s, originally [[monochrome monitor|monochrome]] CRT-based and developed into the modern laptops, were originally considered to be a small niche market, mostly for specialized field applications such as the military, accountants and sales representatives. As portable computers became smaller, lighter, cheaper, and more powerful and as screens became smaller and of better quality, laptops became very widely used for a variety of purposes. {{citation needed|date=December 2013}} |
[[Portable computer]]s, originally [[monochrome monitor|monochrome]] CRT-based and developed into the modern laptops, were originally considered to be a small niche market, mostly for specialized field applications such as the military, accountants and sales representatives. As portable computers became smaller, lighter, cheaper, and more powerful and as screens became smaller and of better quality, laptops became very widely used for a variety of purposes. {{citation needed|date=December 2013}} |
||
Revision as of 06:29, 22 January 2014

A laptop is a portable personal computer with a clamshell form factor, suitable for mobile use.[1] They are also sometimes called notebook computers or notebooks. Laptops are commonly used in a variety of settings, including work, education, and personal multimedia. They are frequently used as a primary PC platform amongst young people.
A laptop combines the components nishanth and inputs as a desktop computer; including display, speakers keyboard, and pointing device (such as a touchpad), into a single device. Most modern day laptop computers also have a webcam and a mic (microphone) pre-installed. [citation needed] A laptop can be powered either from a rechargeable battery, or by mains electricity via an AC adapter. Laptops are a diverse category of devices, and other more specific terms, such as ultrabooks or netbooks, refer to specialist types of laptop which have been optimised for certain uses. Hardware specifications change vastly between these classifications, forgoing greater and greater degrees of processing power to reduce heat emissions.
Portable computers, originally monochrome CRT-based and developed into the modern laptops, were originally considered to be a small niche market, mostly for specialized field applications such as the military, accountants and sales representatives. As portable computers became smaller, lighter, cheaper, and more powerful and as screens became smaller and of better quality, laptops became very widely used for a variety of purposes. [citation needed]
The functions of the laptops are : A microprocessor for processing data A keyboard for entering data Accepting data –accepts data input from the user through various input devices. (e.g. microphone, memory card and digital camera )
History


As the personal computer (PC) became feasible in the 1970s, the idea of a portable personal computer followed. A "personal, portable information manipulator" was imagined by Alan Kay at Xerox PARC in 1968,[2] and described in his 1972 paper as the "Dynabook".[3]
The IBM Special Computer APL Machine Portable (SCAMP), was demonstrated in 1973. This prototype was based on the IBM PALM processor (Put All Logic in Microcode or 128 bit).[4]
The IBM 5100, the first commercially available portable computer, appeared in September 1975, and was based on the SCAMP prototype.[5]
As 8-bit CPU machines became widely accepted, the number of portables increased rapidly. The Osborne 1, released in 1981, used the Zilog Z80 and weighed 23.6 pounds (10.7 kg). It had no battery, a 5 in (13 cm) CRT screen, and dual 5.25 in (13.3 cm) single-density floppy drives. In the same year the first laptop-sized portable computer, the Epson HX-20, was announced.[6] The Epson had a LCD screen, a rechargeable battery, and a calculator-size printer in a 1.6 kg (3.5 lb) chassis. Both Tandy/RadioShack and HP also produced portable computers of varying designs during this period.[7][8]
The first laptops using the flip form factor appeared in the early 1980s. The Dulmont Magnum was released in Australia in 1981–82, but was not marketed internationally until 1984–85. The US$8,150 (US$25,730 today) GRiD Compass 1100, released in 1982, was used at NASA and by the military among others. The Gavilan SC, released in 1983, was the first computer described as a "laptop" by its manufacturer.[9] From 1983 onward, several new input techniques were developed and included in laptops, including the touchpad (Gavilan SC, 1983), the pointing stick (IBM ThinkPad 700, 1992) and handwriting recognition (Linus Write-Top,[10] 1987). Some CPUs, such as the 1990 Intel i386SL, were designed to use minimum power to increase battery life of portable computers, and were supported by dynamic power management features such as Intel SpeedStep and AMD PowerNow! in some designs.
Displays reached VGA resolution by 1988 (Compaq SLT/286), and colour screens started becoming a common upgrade in 1991 with increases in resolution and screen size occurring frequently until the introduction of 17"-screen laptops in 2003. Hard drives started to be used in portables, encouraged by the introduction of 3.5" drives in the late 1980s, and became common in laptops starting with the introduction of 2.5" and smaller drives around 1990; capacities have typically lagged behind physically larger desktop drives. Optical storage, read-only CD-ROM followed by writeable CD and later read-only or writeable DVD and Blu-ray, became common in laptops early in the 2000s.
Classification

The term "laptop" can refer to a number of classes of small portable computers:[11][12]
- Full-size laptop: A laptop large enough to accommodate a "full-size" keyboard (a keyboard with the minimum QWERTY key layout, which is at least 13.5 keys across that are on ¾ (0.750) inch centers, plus some room on both ends for the case). The measurement of at least 11 inches across has been suggested as the threshold for this class.[13] The first laptops were the size of a standard U.S. "A size" notebook sheet of paper (8.5 × 11 inches)[citation needed], but later "A4-size" laptops were introduced, which were the width of a standard ISO 216 A4 sheet of paper (297 mm, or about 11.7 inches), and added a vertical column of keys to the right and wider screens. It can also be laid sideways when not in use.
- Netbook: A smaller, lighter, and therefore more portable laptop with less computing power than traditional laptops. It is usually cheaper than a full-size laptop, and has fewer features. The smaller keyboards of a netbook can be more difficult to operate. There is no definitive demarcation between netbooks and inexpensive small laptops, some 11.6" models are marketed as netbooks. Since netbook laptops are quite small in size and designed to be light and inexpensive they typically do not come with an internal optical drive. The Asus Eee PC launched this product class, while the term was coined later by Intel. Most netbooks feature cheaper, slower, but more energy efficient CPUs, as compared to traditional laptops, such as the Intel Atom CPU.
- Tablet PC: These have touch screens, for finger or stylus use, or both. There can be either are "convertible" or "hybrid" tablets where the keyboard is removable or moves out of the way; the original "Microsoft Tablet PC" form factor used a rotating mount but more recent alternatives include sliding fully inverting the main screen hinge. Other "slate" form-factor machines are touch-screen only. The distinction between a "Tablet PC" and an Internet Tablet has become increasingly blurred, especially since the release of Windows 8.
- Ultra-mobile PC: An ultra-mobile PC (ultra-mobile personal computer or UMPC) is a small form factor version of a pen computer, a class of laptop whose specifications were launched by Microsoft and Intel in spring 2006. Sony had already made a first attempt in this direction in 2004 with its Vaio U series, which was only sold in Asia. UMPCs are smaller than subnotebooks, have a TFT display measuring (diagonally) about 12.7 to 17.8 cm, and are operated like tablet PCs using a touchscreen or a stylus. This term is commonly (if inaccurately) used for small notebooks and/or netbooks.
- Handheld PC: A Handheld PC, or H/PC for short, is a term for a computer built around a form factor which is smaller than any standard laptop computer. It is sometimes referred to as a Palmtop. The first handheld device compatible with desktop IBM personal computers of the time was the Atari Portfolio of 1989. Other early models were the Poqet PC of 1989 and the Hewlett Packard HP 95LX of 1991. Other DOS compatible hand-held computers also existed.
- Rugged: Engineered to operate in tough conditions (mechanical shocks, extreme temperatures, wet and dusty environments, etc.)
- Ultrabook: A very thin version of a laptop by definition less than 0.8 inches thick. Most versions of Ultrabooks contain SSD, or Solid-State Drives, instead of the common rotational hard disk drives. This term is formally a registered trademark of Intel with a narrow qualification to use the term in advertising,[14] but it is used in common speech for many thin-and-light laptop of a similar form factor—notably including the prominent examples of Apple's Macbook Air.
Desktop replacement
A desktop-replacement computer is a large laptop which is not intended primarily for mobile use; they are bulkier and not as portable as other laptops, and they are intended for use as compact and transportable alternatives to a desktop computer.[12] They were traditionally intended to provide the approximate capabilities of a desktop computer, with a similar level of performance, but since around 2010 the distinction in performance between mainstream desktop and laptops have disappeared. The distinction lives on in size: desktop replacements are larger and (typically) heavier than other classes of laptops. They are capable of containing more powerful components and have a 15" or larger display.[12]
Their operation time on batteries is typically shorter than other laptops; in rare cases they have no battery at all. In the past, some laptops in this class use a limited range of desktop components to provide better performance for the same price at the expense of battery life, although the practice has largely died out.[15]
Up until the early 2000s, desktops were more powerful, easier to upgrade, and much cheaper than laptops, but in later years laptops have become much cheaper and more powerful than before,[16] and most peripherals are available in laptop-compatible USB versions which minimize the need for internal add-on cards.
The names "Media Center Laptops" and "Gaming Laptops" are used to describe specialized notebook computers, often overlapping with the desktop replacement form factor.[11]

Subnotebook
A subnotebook or ultraportable is a laptop designed and marketed with an emphasis on portability (small size, low weight and often longer battery life). Subnotebooks are usually smaller and lighter than standard laptops, weighing between 0.8 and 2 kg (2 to 5 pounds);[11] the battery life can exceed 10 hours.[17] Since the introduction of netbooks and ultrabooks, the line between subnotebooks and either category has been blurry; netbooks are in essence a cheap subcategory of subnotebooks, and while some ultrabooks have a screen size too large to qualify as a subnotebook, most ultrabooks are also subnotebooks..
To achieve the size and weight reductions, ultraportables use 13" and smaller screens (down to 6.4") Most subnotebooks achieve a further portability improvement by omitting an optical/removable media drive. In the past, they often had relatively few ports but with the move to standardize on USB and HDMI this distinction has largely vanished.
Similarly, in the past they often employed expensive components designed for minimal size and best power efficiency, and utilized advanced materials and construction methods, but over the past several years these techniques and parts have become mainstream and there is often little distinction besides screen size.
The term "subnotebook" is generally reserved to laptops that run general-purpose desktop operating systems such as Windows, Linux or Mac OS X, rather than a mobile-device-specific OS such as Windows CE, iOS, Palm OS or Android (although in a few cases devices marketed as laptops have used those operating systems). At present, two cases, Windows RT and the Chrome OS, tend to blur the branding; there is little to distinguish the smaller ChromeBook models from any reasonable general definition of subnotebooks.
At Computex 2011 Intel announced a new class for ultraportables called Ultrabooks. The term is used to describe a highly portable laptop that has strict limits for size, weight, battery life, and have tablet-like features such as instant on functionality. Intel estimates that by the end of 2012, 40 percent of the consumer laptop market segment will be Ultrabooks.[18] Since then, the term has entered general parlance for thin-and-light notebooks, regardless of whether they can legally be sold as "Ultrabooks" under the trademark.
Netbook
Netbooks were a market segment of laptops that are inexpensive, light-weight, economical, energy-efficient and especially suited for wireless communication and Internet access.[19][20] Hence the name netbook (as "the device excels in web-based computing performance").[21] The term came to prominence in the late 2000s, and is largely obsolete as of 2013, although a few of the least powerful lightweight notebooks retain that branding.
With primary focus given to web browsing and e-mailing, netbooks are intended to "rely heavily on the Internet for remote access to web-based applications"[21] and are targeted increasingly at cloud computing users who rely on servers and require a less powerful client computer.[22] A common distinguishing feature is the lack of optical disk (i.e. CD, DVD or Blu-ray) drives. While the devices range in size from below 5 inches to over 12 inches,[23] most are between 9 and 11 inches (280 mm) and weigh between 0.9–1.4 kg (2–3 pounds).[21]
Netbooks were mostly sold with light-weight operating systems such as Linux, Windows XP and Windows 7 Starter edition.
Netbooks had a few disadvantages. In order to limit weight and cost, the first products introduced to the market utilized very small early-generation solid-state drives for internal storage instead of traditional hard disks, lowering storage space tremendously—typical sizes were between 8gb-16gb at a time when typical low end laptop hard drives were 120-160gb—and unlike modern solid state drives, offered little to no performance benefit over rotational disk. Hard disk drive technology and form factors have since been adapted to fit into netbooks providing more hard drive space without much increase cost, a key point of a netbook. Another issue with netbooks is expansion. In order to produce small, inexpensive laptops, netbooks generally lack significant upgrade ability, and the Atom processors used in most netbooks tend to have their own limits.
A majority of netbooks only have a single memory slot and will not recognize any amount beyond 2 GB of RAM. This limits the capabilities of the netbook beyond basic functionality (internet, e-mail, etc.). Finally because of their size and cost compared to typical subnotebooks, netbooks almost always have a slower CPU[24]
In 2009, Google announced an operating system called Google Chrome OS for this market and in 2011 the Google Chromebook was released running on the Google Chrome OS; while Google has never advertised the ChromeBook machines as a netbook they are in many ways a present evolution of the concept.
The big breakthrough for netbook computers did not happen until the weight, diagonal form-factor and price combination of < 1 kg, < 9", < U.S. $400, respectively, became commercially available in around 2008.
Rugged laptop

A rugged/ruggedized laptop is designed to reliably operate in harsh usage conditions such as strong vibrations, extreme temperatures, and wet or dusty environments. Rugged laptops are usually designed from scratch, rather than adapted from regular consumer laptop models. Rugged laptops are bulkier, heavier, and much more expensive than regular laptops,[25] and thus are seldom seen in regular consumer use.
The design features found in rugged laptops include rubber sheeting under the keyboard keys, sealed port and connector covers, passive cooling, superbright displays easily readable in daylight, cases and frames made of magnesium alloys that are much stronger than plastic found in commercial laptops, and solid-state storage devices or hard disc drives that are shock mounted to withstand constant vibrations. Rugged laptops are commonly used by public safety services (police, fire and medical emergency), military, utilities, field service technicians, construction, mining and oil drilling personnel. Rugged laptops are usually sold to organizations, rather than individuals, and are rarely marketed via retail channels.
Convertible laptop

Typical modern convertible laptops have a complex joint between the keyboard housing and the display permitting the display panel to swivel and then lie flat on the keyboard housing. Tablet laptops also contain touchscreen displays alongside the traditional touchpad.
Typically, the base of a tablet laptop attaches to the display at a single joint called a swivel hinge or rotating hinge. The joint allows the screen to rotate through 180° and fold down on top of the keyboard to provide a flat writing surface. This design, although the most common, creates a physical point of weakness on the laptop.
Some manufacturers have attempted to overcome these weak points by adopting innovative methods such as a sliding design in which the screen slides up from the slate-like position and locks into place to provide the laptop mode. Newer iterations of tablet laptops are of hybrid design. Hybrid tablets incorporate a removable keyboard base allowing the user to easily choose between functioning as a laptop with the keyboard attached or as a slate device utilizing the touchscreen alone.
A variant of notebook has 2 screens, inner screen is usual as notebook and the outer screen (back to back with inner screen) can be used as tablet which can be a mirror from inner screen or even both can run different applications together.[26]
Another variant has 2 processors, 2 Operating Systems and 2 storage devices which can run either Windows 8 or Android and can switch between the operating system by press a button.[27]
Components
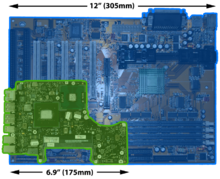

The basic components of laptops function identically to their desktop counterparts; traditionally they were miniaturized and adapted to mobile use, although as of the present decade (2010-) an increasing number of desktop systems use the same smaller, lower-power parts which originally evolved for mobile use. The design bounds on power, size, and cooling of laptops limit the maximum performance of laptop parts compared to that of desktop components, although that difference has increasingly narrowed over recent years.
The following list summarizes the differences and distinguishing features of laptop components in comparison to desktop personal computer parts:[28]
- Central processing unit (CPU): Laptop CPUs have advanced power-saving features and produce less heat than processors intended purely for desktop use; typically these days they will have two processor cores, although 4-core models are available. For low price and mainstream performance, there is no longer a distinction between laptop CPU performance and desktop, but at the high end the fastest 4-to-8-core desktop processors still substantially outperform the fastest 4-core laptop processors, at the expense of massively higher power utilization and heat generation—the fastest laptop processors top out at 56 watts of heat, while the fastest desktop processors top out at 150 watts.
There have been a wide range of CPUs designed for laptops available from both Intel, AMD and other manufacturers. On non-x86 architectures, Motorola and IBM produced the chips for the former PowerPC-based Apple laptops (iBook and PowerBook). Many laptops have removable CPUs, although this has become less common in the past few years as the trend has been to increasingly thin and light models. In other laptops the CPU is soldered on the motherboard and is non-replaceable; this is nearly universal in ultrabooks, for example.
In the past, some laptops have used a desktop processor instead of the laptop version and have high performance gains at the cost of greater weight, heat, and limited battery life. The practice is largely extinct as of 2013.

- Memory (RAM): Most laptops use SO-DIMM memory modules; these are about half the size of desktop DIMMs.[28] They may be accessible from the bottom of the laptop for ease of upgrading, or placed in locations not intended for user replacement. Most laptops have two memory sockets, although some of the lowest-end will have only one, and some high end models (usually mobile engineering workstations, and a few high-end models intended for gaming have 4.) Because of the limitation of DDR3 SO-DIMMs to a maximum of 8gb per module, this means most laptops can only be expanded to a total of 16GB of memory until systems using DDR4 memory start becoming available. Most mid-range laptops are factory equipped with 4-6 GB of RAM. Netbooks are commonly equipped with only 1-2 GB of RAM and generally only expandable to 2 GB, if at all. Increasingly, a small number of models (notably including the 2013 models of MacBook Pro and MacBook Air) have memory soldered to the motherboard so as to save space inside the case; this eliminates the possibility of expansion but allows a thinner and lighter design.
- Expansion cards: in the past, a PC Card (formerly PCMCIA) or ExpressCard slot for expansion cards was often present on laptops to allow adding and removing functionality, even when the laptop is powered on; these are becoming increasingly rare since the introduction of USB 3.0. Some internal subsystems such as: ethernet, Wi-Fi, or a Wireless cellular modem can be implemented as replaceable internal expansion cards, usually accessible under an access cover on the bottom of the laptop. The standards for such cards is PCI Express, which comes in both mini and even smaller M.2 or "Next Generation Form Factor" sizes. In newer laptops it is not uncommon to also see Micro SATA (mSATA) functionality on PCI Express Mini or M.2 card slots allowing the us e of those slots for SATA based solid state drives.[29]
- Power supply: Laptops are typically powered by an internal rechargeable battery that is charged using an external power supply, which outputs a DC voltage typically in the range of 7.2– 24 volts. The power supply is usually external, and connected to the laptop through an DC connector cable. In most cases it can charge the battery and power the laptop simultaneously; when the battery is fully charged, the laptop continues to run on power supplied by the external power supply. The charger typically adds about 400 grams (1 lb) to the overall "transport weight" of the notebook, although some models are substantially heavier or lighter.
- Battery: Current laptops utilize lithium ion batteries, with some thinner models using the flatter lithium polymer technology. These two technologies have largely replaced the older nickel metal-hydride batteries. Battery life is highly variable by model and workload, and can range from 1 hour to nearly a day. A battery's performance gradually decreases with time; substantial reduction in capacity is typically evident after one to three years of regular use, depending on the charging and discharging pattern and the design of the battery. This large-capacity main battery should not be confused with the much smaller battery nearly all computers use to run the real-time clock and to store the BIOS configuration in CMOS when the computer is off. Lithium-ion batteries do not have a memory effect as older batteries may have. Innovations in laptops and batteries have seen situations which the battery can provide up to 24 hours of continued operation, assuming average power consumption levels. An example is the HP EliteBook 6930p when used with its ultra-capacity battery.[30]
- Video display controller: On most laptops the video controller is integrated into the CPU to conserve power and space; this was introduced by Intel with the Core-i series of mobile processors in 2010, and similar "APU" processors by AMD later that year. Prior to that, lower-end machines tended to use graphics processors integrated to the system chipset, while higher end machines had a separate graphics processor. In the past, laptops lacking a separate graphics processor were limited in their utility for gaming and professional applications involving 3D graphics, but the capabilities of CPU-integrated graphics has converged with the low end of dedicated graphics processors in the past few years. Higher-end laptops intended for gaming or professional 3D work still come with dedicated graphics processors on the motherboard or as an internal expansion card; since 2011, these almost always involve switchable graphics so that when there is not demand for the higher performance dedicated graphics processor, the more power-efficient integrated graphics processor will be used. Nvidia Optimus is an example of this sort of system of switchable graphics.
- Display: Most modern laptops feature 13 inches (33 cm) or larger color active matrix displays based on CCFL or LED lighting with resolutions of 1280×800 (16:10) or 1366 × 768 (16:9) pixels and above. Models with LED-based lighting offer lesser power consumption, and often higher brightness. Netbooks with a 10 inches (25 cm) or smaller screen typically use a resolution of 1024×600, while netbooks and subnotebooks with a 11.6 inches (29 cm) or 12 inches (30 cm) screen use standard notebook resolutions. Having a higher resolution display may allow more items to fit onscreen at a time, improving the user's ability to multitask, although at the higher resolutions on smaller screens, the resolution may only serve to display sharper graphics and text rather than increasing the usable area. Since the introduction of the MacBook Pro with Retina display in 2012, there has been an increase in the availability of very-high resolution (FHD 1920x1080 and higher) displays, even in relatively small systems, and in typical 15" screens resolutions as high as 3200x1800 are available.

- Removable media drives: until recently. DVD/CD reader/writer drive was nearly universal on full-sized models, and it remains fairly common for now although the trend towards thinner and lighter machines will probably eliminate it. It is very uncommon on subnotebooks and unknown on netbooks or ultrabooks. Laptop optical drives tend to follow a standard form factor, and usually have a standard mini-SATA connector (not to be confused with Micro-SATA used for SSD cards); it is often possible to replace an optical drive with a newer model, or to replace it with a second hard drive using a caddy that fills the extra space the optical drive would have occupied.
- Internal storage: Laptop hard disks are physically smaller—2.5 inches (64 mm) or 1.8 inches (46 mm) —compared to desktop 3.5 inches (89 mm) drives. Some newer laptops (usually ultraportables) employ more expensive, but faster, lighter and power-efficient flash memory-based SSDs instead. Currently, 250 GB to 1 TB sizes are common for laptop hard disks (64 to 512 GB for SSDs).
- Input: A pointing stick, touchpad or both are used to control the position of the cursor on the screen, and an integrated keyboard is used for typing. An external keyboard and/or mouse may be connected using USB or PS/2 port, or wirelessly via a USB receiver or Bluetooth (if present).
- Ports: several USB ports, an external monitor port (VGA, DVI, mini-DisplayPort or HDMI), audio in/out (sometimes via a single connector), and often an Ethernet network port are found on most laptops. Legacy ports such as a PS/2 keyboard/mouse port, serial port, parallel port or Firewire are increasingly rare. On Apple's systems, and on a handful of non-Apple-produced laptops, there are also Thunderbolt ports.
- Cooling: Waste heat from operation is difficult to remove in the compact internal space of a laptop. Early laptops used heat sinks placed directly on the components to be cooled, but when these hot components are deep inside the device, a large space-wasting air duct is needed to exhaust the heat. Modern laptops instead rely on heat pipes to rapidly move waste heat towards the edges of the device, to allow for a much smaller and compact fan and heat sink cooling system. Waste heat is usually exhausted away from the device operator, towards the rear or sides of the device. Multiple air intake paths are used since some intakes can be blocked, such as when the device is placed on a soft conforming surface like a chair cushion. It is believed that some designs with metal cases, like Apple's aluminum MacBook Pro and MacBook Air, also employ the case of the machine as a "gigantic" heat sink, allowing it to supplement cooling by dissipating heat out of the device core. Secondary device temperature monitoring may reduce performance or trigger an emergency shutdown if it is unable to dissipate heat, such as if the laptop were to be left running and placed inside a carrying case. Such a condition has the potential to melt plastics or ignite a fire.
Docking stations
A docking station (sometimes referred to simply as a "dock") is a laptop accessory that contains multiple ports, and in some cases also expansion slots and/or bays for fixed or removable drives. A laptop connects and disconnects easily to a docking station, typically through a single large proprietary connector; in the past it was distinguished from a port replicator—a simplified docking station that only provides connections from the laptop to input/output ports—although as of 2013 the terms are generally used interchangeably, and the traditional docs with PCI or PCI-E slots are vanishingly rare. Both docking stations and port replicators are intended to be used at a permanent working place (a desk) to offer instant connection to multiple input/output devices and to extend a laptop's capabilities.
Docking stations became a common laptop accessory in the early 1990s. The most common use was in a corporate computing environment where the company had standardized on a common network card and this same card was placed into the docking station. These stations were very large and quite expensive. As the need for additional storage and expansion slots became less critical because of the high integration inside the laptop, port replicators have gained popularity, being a cheaper, often passive device that often simply mates to the connectors on the back of the notebook, or connects via a standardized port such as USB or FireWire.
Charging stations
Laptop charging trolleys, also known as laptop trolleys or laptop carts, are mobile storage containers to charge laptops, netbooks and tablet computers all together. The trolleys are predominantly used in schools that have replaced their traditional static ICT[31] suites of desktop computers with laptops, but do not have enough plug sockets in their buildings to charge all of the devices.
The trolleys can be wheeled between rooms and classrooms so that anyone in a particular building can access fully charged IT[32] equipment. Laptop charging trolleys are also used to deter and protect against opportunistic and organized theft. Schools, especially those with open plan designs, are often prime targets for thieves and laptops, netbooks and tablets can easily be concealed and removed from buildings. Laptop charging trolleys were designed and constructed to protect against theft. They are generally made out of steel, and the laptops remain locked up while not in use. Although the trolleys can be moved between areas in buildings, they can often also be mounted to the floor or walls to prevent thieves walking off with investments, especially overnight.[31]
Solar panels
In some laptops, solar panels are able to generate enough solar power for the laptop to operate.[33] The One Laptop Per Child Initiative released the OLPC XO-1 laptop which was tested and successfully operated by use of solar panels.[34] Presently, they are designing a OLPC XO-3 laptop with these features. The OLPC XO-3 can operate with 2 Watts of electricity because its renewable energy resources generate a total of 4 Watts.[35][36] Samsung has also designed a NC215S Solar powered notebook that will be sold commercially in the US market.[37]
Standards
In general, components other than the categories listed above are not intended to be replaceable; a few, such as processors, follow their own standards but are difficult to replace because of other factors (for example, in the case of processors cooling and access limitations can make upgrades very difficult or impossible.)
In particular, motherboards are almost always make and model-specific: locations of ports, and design and placement of internal components are not standard. Those parts are neither interchangeable with parts from other manufacturers (replaceable) nor upgradeable. If broken or damaged, they must be substituted with an exact replacement part. Those users uneducated in the relevant fields are those the most affected by incompatibilities, especially if they attempt to connect their laptops with incompatible hardware or power adapters.
Intel, Asus, Compal, Quanta and some other laptop manufacturers have created the Common Building Block standard for laptop parts to address some of the inefficiencies caused by the lack of standards.[38]
Advantages



Portability is usually the first feature mentioned in any comparison of laptops versus desktop PCs.[39] Physical portability allows that a laptop can be used in many places— not only at home and at the office, but also during commuting and flights, in coffee shops, in lecture halls and libraries, at clients' location or at a meeting room, etc. The portability feature offers several distinct advantages:
- Productivity: Using a laptop in places where a desktop PC can not be used, and at times that would otherwise be wasted. For example, an office worker managing their e-mails during an hour-long commute by train, or a student doing his/her homework at the university coffee shop during a break between lectures.[40][41]
- Immediacy: Carrying a laptop means having instant access to various information, personal and work files. Immediacy allows better collaboration between coworkers or students, as a laptop can be flipped open to present a problem or a solution anytime, anywhere.
- Up-to-date information: If a person has more than one desktop PC, a problem of synchronization arises: changes made on one computer are not automatically propagated to the others. There are ways to resolve this problem, including physical transfer of updated files (using a USB flash memory stick or CDRs) or using synchronization software over the Internet. However, using a single laptop at both locations avoids the problem entirely, as the files exist in a single location and are always up-to-date.
- Connectivity: A proliferation of Wi-Fi wireless networks and cellular broadband data services (HSDPA, EVDO and others) combined with a near-ubiquitous support by laptops[42] means that a laptop can have easy Internet and local network connectivity while remaining mobile. Wi-Fi networks and laptop programs are especially widespread at university campuses.[43]
Other advantages of laptops:
- Size: Laptops are smaller than desktop PCs. This is beneficial when space is at a premium, for example in small apartments and student dorms. When not in use, a laptop can be closed and put away.
- Low power consumption: Laptops are several times more power-efficient than desktops. A typical laptop uses 20–90 W, compared to 100–800 W for desktops. This could be particularly beneficial for businesses (which run hundreds of personal computers, multiplying the potential savings) and homes where there is a computer running 24/7 (such as a home media server, print server, etc.)
- Quiet: Laptops are often quieter than desktops, due both to the components (quieter, slower 2.5-inch hard drives) and to less heat production leading to use of fewer and slower cooling fans.
- Battery: a charged laptop can continue to be used in case of a power outage and is not affected by short power interruptions and blackouts. A desktop PC needs a UPS to handle short interruptions, blackouts and spikes; achieving on-battery time of more than 20–30 minutes for a desktop PC requires a large and expensive UPS.[44]
- All-in-One: designed to be portable, laptops have everything integrated into the chassis. For desktops (excluding all-in-ones) this is divided into the desktop, keyboard, mouse, display, and optional peripherals such as speakers.
Disadvantages
Compared to desktop PCs, laptops have disadvantages in the following areas:
Performance
While the performance of mainstream desktops and laptop is comparable, and the cost of laptops has fallen less rapidly than desktops, laptops remain more expensive than desktop PCs at the same performance level.[45] The upper limits of performance of laptops remain much lower than the highest-end desktops (especially "workstation class" machines with two processor sockets), and "bleeding-edge" features usually appear first in desktops and only then, as the underlying technology matures, are adapted to laptops.
For Internet browsing and typical office applications, where the computer spends the majority of its time waiting for the next user input, even relatively low-end laptops (such as Netbooks) can be fast enough for some users.[46] As of mid-2010, at the lowest end, the cheapest netbooks—between US$200–300—remain more expensive than the lowest-end desktop computers (around US$200) only when those are priced without a screen/monitor. Once an inexpensive monitor is added, the prices are comparable.
Most higher-end laptops are sufficiently powerful for high-resolution movie playback, some 3D gaming and video editing and encoding. However, laptop processors can be disadvantaged when dealing with higher-end database, maths, engineering, financial software, virtualization, etc. Also, the top-of-the-line mobile graphics processors (GPUs) are significantly behind the top-of-the-line desktop GPUs to a greater degree than the processors, which limits the utility of laptops for high-end 3D gaming and scientific visualization applications.
Some manufacturers work around this performance problem by using desktop CPUs for laptops.[47]
Upgradeability
Upgradeability of laptops is very limited compared to desktops, which are thoroughly standardized. In general, hard drives and memory can be upgraded easily. Optical drives and internal expansion cards may be upgraded if they follow an industry standard, but all other internal components, including the motherboard, CPU and graphics, are not always intended to be upgradeable. Intel, Asus, Compal, Quanta and some other laptop manufacturers have created the Common Building Block standard for laptop parts to address some of the inefficiencies caused by the lack of standards.
The reasons for limited upgradeability are both technical and economic. There is no industry-wide standard form factor for laptops; each major laptop manufacturer pursues its own proprietary design and construction, with the result that laptops are difficult to upgrade and have high repair costs. With few exceptions, laptop components can rarely be swapped between laptops of competing manufacturers, or even between laptops from the different product-lines of the same manufacturer.
Some upgrades can be performed by adding external devices, either USB or in expansion card format such as PC Card. Devices such as sound cards, network adapters, hard and optical drives, and numerous other peripherals are available, but these upgrades usually impair the laptop's portability, because they add cables and boxes to the setup and often have to be disconnected and reconnected when the laptop is on the move.
Ergonomics and health effects
Wrists

Because of their small and flat keyboard and trackpad pointing devices, prolonged use of laptops can cause repetitive strain injury.[48] Usage of separate, external ergonomic keyboards and pointing devices is recommended to prevent injury when working for long periods of time; they can be connected to a laptop easily by USB or via a docking station. Some health standards require ergonomic keyboards at workplaces.
Neck, spinal
The integrated screen often requires users to lean over for a better view, which can cause neck and/or spinal injuries. A larger and higher-quality external screen can be connected to almost any laptop to alleviate that and to provide additional screen space for more productive work. Another solution is to use a computer stand.
For anyone not buying a new screen, a simple method to reduce risk of spinal injury is to position the laptop's screen in a manner that an obtuse angle (more than 90 degrees open) is formed. It is then possible for the neck to remain straight during use of the device.
Possible effect on fertility
A study by State University of New York researchers found that heat generated from laptops can increase the temperature of the lap of male users when balancing the computer on their lap, potentially putting sperm count at risk. The study, which included roughly two dozen men between the ages of 21 and 35, found that the sitting position required to balance a laptop can increase scrotum temperature by as much as 2.1 °C (3.78 °F). However, further research is needed to determine whether this directly affects male sterility.[49]
A 2010 study of 29 males published in Fertility and Sterility found that men who kept their laptops on their laps experienced scrotal hyperthermia (overheating) in which their scrotal temperatures increased by up to 2 °C. The resulting heat increase, which could not be offset by a laptop cushion, may increase male infertility.[50][51][52][53][54]
A common practical solution to this problem is to place the laptop on a table or desk, or to use a book or pillow between the body and the laptop.[citation needed] Another solution is to obtain a cooling unit for the laptop. These are usually USB powered and consist of a hard thin plastic case housing one, two or three cooling fans – with the entire assembly designed to sit under the laptop in question – which results in the laptop remaining cool to the touch, and greatly reduces laptop heat buildup.[citation needed]
Thighs
Heat generated from using a laptop on the lap can also cause skin discoloration on the thighs known as "toasted skin syndrome."[55][56][57][58]
Durability

Equipment wears
Because of their portability, laptops are subject to more wear and physical damage than desktops. Components such as screen hinges, latches, power jacks and power cords deteriorate gradually from ordinary use. A liquid spill onto the keyboard, a rather minor mishap with a desktop system, can damage the internals of a laptop and result in a costly repair. One study found that a laptop is three times more likely to break during the first year of use than a desktop.[59]
Parts replacement
Original external components are expensive, and usually proprietary and non-interchangeable; other parts are inexpensive—a power jack can cost a few dollars—but their replacement may require extensive disassembly and reassembly of the laptop by a technician. Other inexpensive but fragile parts often cannot be purchased separate from larger more expensive components.[60] The repair costs of a failed motherboard or LCD panel often exceed the value of a used laptop.
Heating and cooling
Laptops rely on extremely compact cooling systems involving a fan and heat sink that can fail from blockage caused by accumulated airborne dust and debris. Most laptops do not have any type of removable dust collection filter over the air intake for these cooling systems, resulting in a system that gradually causes it to conduct more heat and noise as the years pass. In some cases the laptop starts to overheat even at idle load levels. This dust is usually stuck inside, where the fan and heat sink meet, where casual cleaning and vacuuming cannot remove it. Compressed air can dislodge the dust and debris but may not always remove it; after the device is turned on, the loose debris builds back up the cooling system by the fans. A complete dis-assembly is usually required to clean the laptop. Many laptops are difficult to disassemble by the normal user and contain components that are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD).

Battery life
Battery life is limited because the capacity drops with time, eventually requiring replacement after as little as a year. A new battery typically stores enough energy to run the laptop for three to five hours, depending on usage, configuration, and power management settings. Yet, as it ages, the battery's energy storage will dissipate progressively until it lasts only a few minutes. The battery is often easily replaceable and a higher capacity model may be obtained for longer life. Some laptops (specifically ultrabooks) do not have the usual removable battery and have to be brought to the service center of its manufacturer to have its battery replaced. Replacement batteries can also be expensive.
Security and privacy

Because they are valuable, common, and portable, laptops are prized targets for theft. Every day, over 1,600 laptops go missing from U.S. airports.[61] The cost of stolen business or personal data, and of the resulting problems (identity theft, credit card fraud, breach of privacy), can be many times the value of the stolen laptop itself. Consequently, physical protection of laptops and the safeguarding of data contained on them are both of great importance.
Most laptops have a Kensington security slot, which can be used to tether them to a desk or other immovable object with a security cable and lock. In addition, modern operating systems and third-party software offer disk encryption functionality, which renders the data on the laptop's hard drive unreadable without a key or a pass phrase. Some laptops also now have additional security elements added by the consumer, including eye recognition software and fingerprint scanning components.[62] Software such as LoJack for Laptops, Laptop Cop, and GadgetTrack have been engineered to help victims locate and recover a laptop in the event of theft.
In Robbins v. Lower Merion School District (Eastern District of Pennsylvania 2010), school-issued laptops loaded with special software afforded two high schools with the capability to take secret webcam shots of their students at home, via their students' laptops.[63][64][65]
Laptop Theft Recovery
Laptop theft is a serious problem, with less than 5% of lost or stolen laptops ever recovered by the companies that own them.[66] However, that number may decrease due to a variety of companies and software solutions specializing in laptop recovery. For example, LoJack for Laptops is security software that includes an Investigations and Theft Recovery Team made up of ex law enforcement officers who locate and recover stolen laptops. The service utilizes persistent technology, which means it can't be removed or disabled by a thief. LoJack can only work to track down a missing laptop when it is turned on and it is connected to the Internet. The owner can also remotely delete files or lock their device, so no one can access their personal data.
Major brands and manufacturers

There are a multitude of laptop brands and manufacturers; several major brands, offering notebooks in various classes, are listed in the box to the right.
The major brands usually offer good service and support, including well-executed documentation and driver downloads that will remain available for many years after a particular laptop model is no longer produced. Capitalizing on service, support and brand image, laptops from major brands are more expensive than laptops by smaller brands and ODMs.
Some brands are specializing in a particular class of laptops, such as gaming laptops (Alienware), high-performance laptops (HP Envy), netbooks (EeePC) and laptops for children (OLPC).
Many brands, including the major ones, do not design and do not manufacture their laptops. Instead, a small number of Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) design new models of laptops, and the brands choose the models to be included in their lineup. In 2006, 7 major ODMs manufactured 7 of every 10 laptops in the world, with the largest one (Quanta Computer) having 30% of world market share.[67] Therefore, there often are identical models available both from a major label and from a low-profile ODM in-house brand.
Sales
Battery-powered portable computers had just 2% worldwide market share in 1986.[68] However, laptops have become increasingly popular, both for business and personal use.[69] Around 109 million notebook PCs shipped worldwide in 2007, a growth of 33% compared to 2006.[70] In 2008 it was estimated that 145.9 million notebooks were sold, and that the number would grow in 2009 to 177.7 million.[71] The third quarter of 2008 was the first time when worldwide notebook PC shipments exceeded desktops, with 38.6 million units versus 38.5 million units.[69][72][73][74]
When looking at operating systems, for Microsoft Windows laptops the average selling price (ASP) showed a decline in 2008/2009, possibly due to low-cost netbooks, drawing US$689 at U.S. retail in August 2008. In 2009, ASP had further fallen to $602 by January and to $560 in February. While Windows machines ASP fell $129 in these seven months, Apple (Mac) OS X laptop ASP declined just $12 from $1,524 to $1,512.[75]
Extreme environments
The ruggedized Grid Compass computer was used since the early days of the Space Shuttle program. The first commercial laptop used in space was a Macintosh portable in 1991 aboard Space Shuttle mission STS-43.[76][77][78] Mac and other laptop computers continue to be flown aboard manned spaceflights though the only long duration flight certified computer for the International Space Station is the ThinkPad.[79] As of 2011 over 100 ThinkPads were aboard the ISS. Laptops used aboard the International Space Station and other spaceflights are generally the same ones that can be purchased by the general public but needed modifications are made to allow them to be used safely and effectively in a weightless environment such as updating the cooling systems to function without relying on hot air rising and accommodation for the lower cabin air pressure.[80]
Laptops operating in harsh usage environments and conditions, such as strong vibrations, extreme temperatures and wet or dusty conditions differ from those used in space in that they are custom designed for the task and do not use commercial off-the-shelf hardware.
Accessories
A common accessory for laptops is a laptop sleeve, laptop skin or laptop case, which provides a degree of protection from drops or impacts. Sleeves, which are distinguished by being relatively thin and flexible, are most commonly made of neoprene, with sturdier ones made of LRPu (low-resilience polyurethane), with some wrapped in ballistic nylon to provide some measure of waterproofing. Bulkier and sturdier cases can be made of metal with polyurethane padding inside, and may have locks, for added security.
Another common accessory is a laptop cooler. This device helps lower the internal temperature of the laptop by using either active or passive methods. A general active method is plugging a laptop cooler into the laptop and using fans to draw heat away from the laptop. A common passive method is just propping the laptop up on some type of pad so it can receive more air flow.[81]
Former features
Features that certain early models of laptops used to have but not available anymore in most recent models of laptops include:
- Reset (Cold restart) button in a hole
- Instant power off button in a hole
- Integrated charger or power adapter inside the laptop
- Floppy disk drive
- Serial port
- Parallel port
- Modem
- Shared PS/2 input device port
- IrDA
- S-video port[82]
See also
References
- ^ What is a laptop computer
- ^ John W. Maxwell (2006). "Tracing the Dynabook: A Study of Technocultural Transformations" (PDF). Retrieved 17 October 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Alan C. Kay (1972). "A Personal Computer for Children of All Ages" (PDF). Retrieved 17 October 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "IBM Personal Computer". IBM Inc.
- ^ "IBM 5100 computer". oldcomputers.net. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ "Epson SX-20 Promotional Brochure" (PDF). Epson America, Inc. 1987. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ "Tandy/Radio Shack model 100 portable computer". oldcomputers.net. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ "Hewlett-Packard model 85". oldcomputers.net. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ "Gavilian SC computer". oldcomputers.net. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
- ^ "Linus Write-Top". Retrieved 18 October 2008.
- ^ a b c "Types of Laptops: How Do You Compute". PC Magazine. Ziff Davis Publishing Holdings Inc. 18 September 2006. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ a b c "Laptop Buying Guide". CBS Interactive Inc. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ 11" Macbook Air See "Keyboard and Trackpad"
- ^ Usage Guidelines for the Ultrabook™ Trademark
- ^ "Desktop notebooks stake their claim". CBS Interactive Inc. 8 January 2003. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Desktop are Dying Slain by Laptops".
- ^ "Breaking the Mold: New Lenovo ThinkPad laptop and Tablet PCs Defy Ultraportable Computing". Lenovo. 23 September 2008. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ Intel's Maloney Talks Mobile Growth, Industry Opportunities at Computex
- ^ The Net Impact of Netbooks? It Depends on Who Uses Them for What
- ^ Bergevin, Paul (3 March 2008). "Thoughts on Netbooks". Intel.com.
- ^ a b c Netbook Trends and Solid-State Technology Forecast (PDF). pricegrabber.com. p. 7. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- ^ Copeland, Michael (16 October 2008). "Disruptor: The 'netbook' revolution". CNNMoney/Fortune. Retrieved 29 December 2009.
- ^ Worlds First review of Inspiron Mini 12: Dell’s super-slim netbook!
- ^ "Cheap PCs Weigh on Microsoft". Business Technologies. 8 December 2008.
- ^ "Rugged Laptop: Choices, Pointers & Specs of Buying Rugged Laptops". Linux-on-laptops.com. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ "Asus Taichi, Laptop 2 Layar yang Bisa Jadi Tablet". Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ^ "Asus Tawarkan Book Trio". 19 December 2013.
- ^ a b Catherine Roseberry. "What Makes Laptops Work – The Laptop Motherboard". About.com. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ Gabriel Torres (25 November 2004). "Innovations in Notebook Expansion". Hardware Secrets, LLC. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ "HP EliteBook 6930p Notebook PC specifications - HP Products and Services Products". H10010.www1.hp.com. 25 May 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^ a b Woods, Dough. "Getting rid of the ICT suite". Blog.
- ^ Wilce, Hilary (1 December 2000). "Welcome to Lapland". TES Magazine.
- ^ Clarke, Gavin. "The SOLAR-POWERED Ubuntu laptop". THE REGISTER. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ "OLPC XO laptop powered by a solar panel". YouTube. 9 January 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ Elizabeth Woyke (18 April 2012). "A Look at OLPC's XO 3.0 Tablet's Solar And Kinetic Chargers". Forbes. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ "One Laptop per Child (OLPC): Frequently Asked Questions". Laptop.org. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ "Samsung's Solar Powered Laptop Will Be First Sun Powered Laptop Sold in US | Inhabitat — Sustainable Design Innovation, Eco Architecture, Green Building". Inhabitat. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ "Common Building Blocks Platform" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved September 2005.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Should I buy a laptop or desktop?". IT Division – University of Wisconsin. 19 March 2008. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ "ECU Advantage: Why have a laptop?". ECU. Archived from the original on 18 July 2008. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ "Student Laptop Buying Guide". Pulsar Online. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ Almost all laptops contain a Wi-Fi interface; broadband cellular devices are available widely as extension cards and USB devices, and also as internal cards in select models.
- ^ Josh Fischman (7 August 2008). "Faster Wi-Fi Predicted for Colleges". The Chronicle of Higher Education. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ A sample line of UPS devices and on-battery power: "Back-UPS RS". APC. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ In a comparison between laptop and desktop of equal cost, the desktop's System Benchmark Score was twice that of the laptop. "What to Buy, a Notebook or Desktop PC?". Tom's Hardware. 11 June 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2008.
- ^ For example, a review of the MSI Wind Netbook says that "The device is rarely sluggish in general use. It renders Web pages quickly, launches most applications without becoming too bogged down and generally doesn't feel like it's a budget laptop." Reid, Rory (7 July 2008). "MSI Wind Review". CNET Australia. Retrieved 28 November 2008.
- ^ Rock delivers BD / Core i7-equipped Xtreme 790 and Xtreme 840 gaming laptops – Engadget
- ^ Martin, James A. (9 June 2000). "The Pain of Portable Computing". PC World. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ Sheynkin, Y. (9 December 2004). "Increase in scrotal temperature in laptop computer users". Human Reproduction. 20 (2). Epub: 452–5. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh616. PMID 15591087.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Sheynkin, Yefim (8 November 2010). "Protection from scrotal hyperthermia in laptop computer users". Fertility and Sterility. 95 (2): 647–651. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.10.013. PMID 21055743.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Yin, Sara (11.08.2010). "Study: Laptop Pads Don't Prevent Male Infertility". PC Magazine. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Men, your laptop may be roasting your testicles". The Independent. 8 November 2010. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
- ^ Caulfield, Philip (7 November 2010). "Study finds men who place laptop computer on lap put testicles at risk of overheating, infertility". Daily News. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
- ^ Joelving, Frederik (8 November 2010). Reuters http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE6A457320101108. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
{{cite news}}:|url=missing title (help) - ^ Levinbook, WS. (2007). "Laptop computer—associated erythema ab igne". Cutis. 80 (4). Quadrant HealthCom: 319–20. PMID 18038695.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Diaz, Jesus (7 October 2010). "What Is Toasted Skin Syndrome?". Gizmodo. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
- ^ Hendrick, Bill (4 October 2010). "Laptop Risk: 'Toasted Skin Syndrome'". WebMD. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
- ^ Tanner, Lindsey (10/4/2010 8:05:40 am ET 2010-10-04T12:05:40). "Laptops lead to 'toasted skin syndrome'". Associated Press. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Gartner: Notebook PCs still prone to hardware failure". IDG News Service / ITWorld. 27 June 2006. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ^ For example, the video display cable and the backlight power cable that pass through the lid hinges to connect the motherboard to the screen will eventually break from repeated opening and closing of the lid. These tiny cables usually cannot be purchased from the original manufacturer separate from the entire LCD panel, with the price of hundreds of dollars, although for popular models an aftermarket in pulled parts generally exists.
- ^ [1], Ponemon Institute, Airport Insecurity: The Case of Lost Laptops, June 2008
- ^ "Biometric Devices".
- ^ Holmes, Kristin E. (31 August 2010). "Lower Merion School District ordered to pay plaintiff's lawyer $260,000". Philadelphia Inquirer. Retrieved 20 September 2010.
- ^ "Main Line Media News". Main Line Media News. 18 September 2010. Retrieved 20 September 2010.
- ^ "A lawyer in the Lower Merion webcam case wants to be paid now", Philly.com
- ^ [2], Ponemon Institute, The Billion Dollar Lost Laptop Problem, September 2010
- ^ "Identical Laptops, Different Prices: Don't Be Fooled by Branding" (Registration required for the full article). Info-Tech Research Group. 10 October 2006. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^
"Lap-top computers gain stature as power grows". Daily News of Los Angeles (CA). 12 April 1987. Retrieved 2001-01-01/2008.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "The Falling Costs of Mobile Computing". Falling Costs of Mobile Computing Drive Corporate Adoption. Computer Economics, Inc. 2005. Retrieved 2001-01-01/2008.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Worldwide notebook shipments grow 33% on year in 2007, says IDC, 31 January 2008, Yen Ting Chen, DigiTimes, retrieved at 12 September 2011
- ^ Analysis: Did Intel underestimate netbook success?, Accessed at 10 January 2009
- ^ Notebook PC Shipments Exceed Desktops for First Time in Q3, isuppli.com, accessed at 13 January 2009
- ^ Randall Stross (18 April 2008). "The PC Doesn't Have to Be an Anchor". New York Times. Retrieved 20 April 2009.
- ^ "Intel: laptop/desktop crossover coming sooner than expected". The Register, UK. Retrieved 10 October 2008.
- ^ Netbooks Are Destroying the Laptop Market and Microsoft Needs to Act Now
- ^ "Macintosh Portable: Used in Space Shuttle". Support.apple.com. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ Linzmayer, Owen W. (2004). Apple confidential 2.0 : the definitive history of the world's most colorful company ([Rev. 2. ed.]. ed.). San Francisco, Calif.: No Starch Press. ISBN 1-59327-010-0.
- ^ "This Week in Apple History — August 22–31: "Welcome, IBM. Seriously," Too Late to License". The Mac Observer. 31 October 2004. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ IBM Archives: IBM ThinkPads in space
- ^ 2001: A Space Laptop | SpaceRef – Your Space Reference
- ^ Assourian, Elya. "Laptop Blog Author". http://www.laptopforcollegestudents.com/. Elya Assourian. Retrieved 17 August 2011.
{{cite web}}: External link in|work= - ^ Unconfirmed if this exists in most recent models of laptops.
