YUV 4:2:2 and North America: Difference between pages
added SDI-link |
m →Usage of the term: FALSE citation, already checked. And this is about the usage of North America not Central America or South America. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:LocationNorthAmerica.png|thumb|250px|World map showing North America]] |
|||
'''YUV 4:2:2''' is a specific encoding for digital representation of the [[YUV]] color space. |
|||
[[Image:North America satellite orthographic.jpg|thumb|250px|A satellite composite image of North America. [http://www.earth-puzzle.com/NAmerica.html Clickable map]]] |
|||
'''North America''' is a [[continent]] in the [[Earth]]'s [[northern hemisphere]] and almost fully in the [[western hemisphere]]. It is bordered on the north by the [[Arctic Ocean]], on the east by the North [[Atlantic Ocean]], on the southeast by the [[Caribbean Sea]], and on the south and west by the North [[Pacific Ocean]]; [[South America]] lies to the southeast, connected to North America by the [[isthmus of Panama]]. It covers an [[area]] of about 24,490,000 [[Square kilometre|km²]]<!--spelled out per WP:MOSNUM --> (9,450,000 [[square mile|sq mi]]), or about 4.8% of the planet's surface. As of [[October]] [[2006]], its [[population]] was estimated at over 514,600,000. It is the third-largest continent in area, following [[Asia]] and [[Africa]], and is fourth in population after Asia, Africa, and [[Europe]]. |
|||
==Etymology== |
|||
In YUV 4:2:2, the basic unit is composed of two [[pixel]]s, and occupies four [[byte]]s of space. Each pixel has an individual 8 [[bit]] Y channel. Then, the first pixel specifies an 8 bit U channel, and the second pixel an 8 bit V channel. Both pixels use the same U and V channels. |
|||
North and South America are widely accepted as having been named after [[Amerigo Vespucci]] by the German cartographer [[Martin Waldseemüller]]. Vespucci was the first European to suggest that the Americas were not the East Indies, but a new world, previously undiscovered by Europeans. |
|||
The second and less generally accepted theory is that the continents are named after an English merchant named [[Richard Amerike]] from Bristol, who is believed to have financed [[John Cabot]]'s voyage of discovery from England to Newfoundland in 1497. A minutely explored belief that has been advanced is that America was named for a Spanish sailor bearing the ancient [[Visigothic]] name of 'Amairick'. Another is that the name is rooted in an [[Indigenous peoples of the Americas|American Indian]] language. [http://www.uhmc.sunysb.edu/surgery/america.html] |
|||
==Geography and extent== |
|||
{{see|Geography of North America}} |
|||
The sequence of data is the following: |
|||
North America occupies the northern portion of the landmass generally referred to as the [[New World]], the [[Western Hemisphere]], [[Americas|the Americas]], or simply America. North America's only land connection is to [[South America]] at the narrow [[Isthmus of Panama]]. (Geopolitically, all of [[Panama]]—including the segment east of the [[Panama Canal]] in the isthmus—is often considered a part of North America alone.) According to some authorities, North America begins not at the Isthmus of Panama but at the [[Isthmus of Tehuantepec]], [[Mexico]] with the intervening region called [[Central America]] (or [[Middle America]] if the [[Caribbean]] is included) and resting on the [[Caribbean Plate]]. Before the Central American isthmus was raised, the region had been underwater. The islands of the [[West Indies]] delineate a submerged former [[land bridge]], which had connected North America and [[South America]] via [[Florida]] and [[Venezuela]]. |
|||
Y1 U1 Y2 V2 Y3 U3 Y4 V4 .... |
|||
The continental coastline is long and irregular. The [[Gulf of Mexico]] is the largest body of water indenting the continent, followed by [[Hudson Bay]]. Others include the [[Gulf of Saint Lawrence]] and the [[Gulf of California]]. |
|||
Pixels will be actually reconstructed as follows: |
|||
There are numerous [[island]]s off the continent’s coasts: principally, the [[Canadian Arctic Archipelago|Arctic Archipelago]], the [[Greater Antilles|Greater]] and [[Lesser Antilles]], the [[Alexander Archipelago]], and the [[Aleutian Islands]]. [[Greenland]], a [[Denmark|Danish]] self-governing island and the [[list of islands by area|world's largest]], is on the same [[tectonic plate]] (the [[North American Plate]]) and is part of North America geographically. [[Bermuda]] is not part of the Americas, but is an oceanic island which was formed on the fissure of the [[Mid-Atlantic Ridge]] over 100 million years ago. The nearest landmass to it is [[Cape Hatteras]], [[North Carolina]], and it is often thought of as part of North America, especially given its historical political and cultural ties to [[Virginia]] and other parts of the continent. |
|||
Y1 U1 V2 |
|||
Y2 U1 V2 |
|||
Y3 U3 V4 |
|||
Y4 U3 V4 |
|||
===Physical geography=== |
|||
YUV 4:2:2 is commonly used on ''professional-quality video equipment'': e.g. [[Serial Digital Interface]] (SDI) streams are all in YUV 4:2:2. The loss of quality due to the reduced U and V information is usually not noticeable, because the human [[eye]] is much better at seeing differences in brightness than in color. |
|||
[[Image:North america rock types.jpg|thumb|100px|right|[[:Image:North america rock sedimentary.jpg|Sedimentary]], [[:Image:North america rock volcanic.jpg|volcanic]], [[:Image:North america rock plutonic.jpg|plutonic]], [[:Image:North america rock metamorphic.jpg|metamorphic]] rock types of North America. ]] |
|||
The vast majority of North America is on the [[North American Plate]]. Parts of [[California]] and western [[Mexico]] form the partial edge of the [[Pacific Plate]], with the two plates meeting along the [[San Andreas fault]]. The southern portion of the continent and much of the [[Caribbean|West Indies]] lie on the [[Caribbean Plate]], while the [[Juan de Fuca Plate|Juan de Fuca]] and [[Cocos Plate]]s border the North American Plate on its western frontier. |
|||
== External link == |
|||
*http://www.fourcc.org/ |
|||
The continent can be divided into four great regions (each of which contains many sub-regions): the [[Great Plains]] stretching from the [[Gulf of Mexico]] to the [[Northern Canada|Canadian Arctic]]; the geologically young, mountainous west, including the [[Rocky Mountains]], the [[Great Basin]], [[Geography of California|California]] and [[Alaska]]; the raised but relatively flat plateau of the [[Canadian Shield]] in the northeast; and the varied eastern region, which includes the [[Appalachian Mountains]], the coastal plain along the Atlantic seaboard, and the [[Florida]] peninsula. Mexico, with its long [[plateau]]s and [[American cordillera|cordilleras]], falls largely in the western region, although the eastern coastal plain does extend south along the Gulf. |
|||
[[Category:Video and movie technology]] |
|||
The western mountains are split in the middle, into the main range of the Rockies and the [[Pacific Coast Ranges|coast ranges]] in California, [[Oregon]], [[Washington]], and [[British Columbia]] with the Great Basin – a lower area containing smaller ranges and low-lying deserts – in between. The highest peak is [[Denali]] in Alaska. |
|||
The [http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/elvadist/elvadist.html#Geographic%20Centers United States Geographical Survey] states that the geographic center of North America is “6 miles west of Balta, Pierce County, North Dakota” at approximately 48° 10′North, 100° 10′West, approximately 15 miles (25 km) from [[Rugby, North Dakota]]. The USGS further states that “No marked or monumented point has been established by any government agency as the geographic center of either the 50 States, the conterminous United States, or the North American continent.” Nonetheless, there is a 15 foot (4.5 [[metre|m]]) field stone [[obelisk]] in Rugby claiming to mark the center. |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Image:North america terrain 2003 map.jpg|North America bedrock and terrain. |
|||
Image:North america basement rocks.png|North American [[craton]]s and basement rocks. |
|||
Image:North America Tectonic Elements.jpg|Tectonic elements of North America |
|||
Image:North america craton nps.gif|North American [[craton]]. |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
<br style="clear:both;"> |
|||
===Human geography=== |
|||
The most spoken languages in North America are [[English language|English]], [[Spanish language|Spanish]] and [[French language|French]]. The term [[Anglo-America]] is occasionally used to refer to [[Belize]], the [[United States]], [[Canada]], the [[English language|anglophone]] parts of the Caribbean, and [[Guyana]] (the only English-speaking nation of [[South America]]), and are included in the [[Anglosphere]]. The remaining [[Central America|Central American]] nations, [[Mexico]], and the Spanish-speaking Caribbean and the other South American countries where [[Romance language]]s prevail (namely Spanish, [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]] and French), are referred to as [[Latin America]]. This latter term has entered into common parlance, although the term "Anglo-America" is much less commonly used. |
|||
The French language has historically played a significant role in North America and remains a distinctive presence in some regions. Canada has two official languages; French is the official language of the province of [[Quebec]], and, along with English, one of the two official languages of the province of [[New Brunswick]]. Other French-speaking locales include: the [[French West Indies]] and [[Saint-Pierre and Miquelon]]. [[Haiti]] is included with this group based on past historical association but Haitians speak [[Haitian Creole language|Creole]] and French. Although the former language is derived from French, it is not French. |
|||
Socially and culturally, North America presents a well-defined entity. Canada and the United States have a shared culture and similar traditions as a result of both countries being former [[Great Britain|British]] colonies. A common cultural and economic market has developed between the two nations because of the strong economic and historical ties. Spanish-speaking North America shares a common past as former [[Spain|Spanish]] colonies. In Central American countries and Mexico where civilizations like the [[Maya]] developed, indigenous people preserve traditions across modern boundaries. Central American and Spanish-speaking Caribbean nations have historically had more in common due to geographical proximity and the fact that, after winning independence from Spain, Mexico never took part in an effort to build a Central American Union. |
|||
Economically, Canada and the United States are the wealthiest and most [[developed country|developed nations]] in the continent; the countries of Central America and the Caribbean are much [[developing country|less developed]], while [[Mexico]] – a [[newly industrialized countries|newly industrialized country]] – lies between these two extremes. The most important [[trade bloc]]s are the [[Caribbean Community|Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM)]], the [[North American Free Trade Agreement|North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)]], and the recently signed [[Central American Free Trade Agreement|Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA)]] – the last of these being an example of the economic integration sought by the nations of this subregion as a way to improve their financial status. |
|||
Demographically, North America is a racially and ethnically diverse continent. Its three main ethnic groups are [[White people|Whites]], [[Mestizo]]s and [[African-American]]s.{{fact}} There is a significant minority of [[Amerindians]] and [[Chinese people|Chinese]] among other less numerous groups. |
|||
==Countries and territories== |
|||
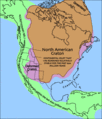
[[Image:North America.png|right|thumb|Political highlights of North America]] |
|||
North America is often divided into subregions but no universally accepted divisions exist. "Central America" comprises the southern portion of the continent, but its northern terminus varies between sources. The [[United Nations]] includes Mexico in Central America, while most other definitions of the region do not (e.g., the [[European Union]] excludes Belize and Mexico from the area). The term [[Middle America (disambiguation)|Middle America]] is sometimes used to refer to Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean collectively. |
|||
[[Northern America]] is used to refer to the northern countries and territories of North America: Canada, the United States, Greenland, Bermuda, and St. Pierre and Miquelon. They are often considered distinct from the southern portion of the Americas, which largely comprise [[Latin America]]. |
|||
The [[Caribbean]] refers to the islands in and around the [[Caribbean Sea]] and the surrounding coasts. |
|||
<!--{{editnote | The countries in this table are not categorised. Please see the talk page for more details, but there's a tenuous consensus that an unsorted table is acceptable, while every other proposed categorisation has been rejected by some editors as POV. For the love of [[WP:CONSENSUS]], please bring proposed categorisations to the talk page.}}--> |
|||
{| border="1" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="border:1px solid #aaa; border-collapse:collapse" |
|||
|- bgcolor="#ECECEC" |
|||
! [[Country]] or <br>[[Territory (country subdivision)|territory]] with [[flag]] |
|||
! [[List of countries by area|Area]]<br>(km²) |
|||
! [[List of countries by population|Population]]<br>(1 July 2005 est.) |
|||
! [[List of countries by population density|Population density]]<br>(per km²) |
|||
! [[Capital]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Anguilla}} [[Anguilla]] ([[United Kingdom|UK]]) |
|||
| align="right" | 102 |
|||
| align="right" | 13,254 |
|||
| align="right" | 129.9 |
|||
| [[The Valley, Anguilla|The Valley]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Antigua and Barbuda}} [[Antigua and Barbuda]] |
|||
| align="right" | 443 |
|||
| align="right" | 68,722 |
|||
| align="right" | 155.1 |
|||
| [[St. John's, Antigua and Barbuda|St. John's]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Aruba}} [[Aruba]] ([[Netherlands]])<ref name="two">Depending on definitions, [[Aruba]], [[Netherlands Antilles]], [[Panama]], and [[Trinidad and Tobago]] have territory in [[Transcontinental nation|one or both of]] North and [[South America]].<br></ref> |
|||
| align="right" | 193 |
|||
| align="right" | 71,566 |
|||
| align="right" | 370.8 |
|||
| [[Oranjestad, Aruba|Oranjestad]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Bahamas}} [[Bahamas]] |
|||
| align="right" | 13,940 |
|||
| align="right" | 301,790 |
|||
| align="right" | 21.6 |
|||
| [[Nassau, Bahamas|Nassau]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Barbados}} [[Barbados]] |
|||
| align="right" | 431 |
|||
| align="right" | 279,254 |
|||
| align="right" | 647.9 |
|||
| [[Bridgetown]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Belize}} [[Belize]] |
|||
| align="right" | 22,966 |
|||
| align="right" | 279,457 |
|||
| align="right" | 12.2 |
|||
| [[Belmopan]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Bermuda}} [[Bermuda]] (UK) |
|||
| align="right" | 53 |
|||
| align="right" | 65,365 |
|||
| align="right" | 1,233.3 |
|||
| [[Hamilton, Bermuda|Hamilton]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|British Virgin Islands}} [[British Virgin Islands]] (UK) |
|||
| align="right" | 153 |
|||
| align="right" | 22,643 |
|||
| align="right" | 148.0 |
|||
| [[Road Town]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Canada}} [[Canada]] |
|||
| align="right" | 9,984,670 |
|||
| align="right" | 32,805,041 |
|||
| align="right" | 3.3 |
|||
| [[Ottawa]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Cayman Islands}} [[Cayman Islands]] (UK) |
|||
| align="right" | 262 |
|||
| align="right" | 44,270 |
|||
| align="right" | 169.0 |
|||
| [[George Town, Cayman Islands|George Town]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Costa Rica}} [[Costa Rica]] |
|||
| align="right" | 51,100 |
|||
| align="right" | 4,016,173 |
|||
| align="right" | 78.6 |
|||
| [[San José, Costa Rica|San José]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Cuba}} [[Cuba]] |
|||
| align="right" | 110,860 |
|||
| align="right" | 11,346,670 |
|||
| align="right" | 102.4 |
|||
| [[Havana]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Dominica}} [[Dominica]] |
|||
| align="right" | 754 |
|||
| align="right" | 69,029 |
|||
| align="right" | 91.6 |
|||
| [[Roseau]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Dominican Republic}} [[Dominican Republic]] |
|||
| align="right" | 48,730 |
|||
| align="right" | 8,950,034 |
|||
| align="right" | 183.7 |
|||
| [[Santo Domingo]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|El Salvador}} [[El Salvador]] |
|||
| align="right" | 21,040 |
|||
| align="right" | 6,704,932 |
|||
| align="right" | 318.7 |
|||
| [[San Salvador]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Greenland}} [[Greenland]] ([[Denmark]]) |
|||
| align="right" | 2,166,086 |
|||
| align="right" | 56,375 |
|||
| align="right" | 0.026 |
|||
| [[Nuuk]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Grenada}} [[Grenada]] |
|||
| align="right" | 344 |
|||
| align="right" | 89,502 |
|||
| align="right" | 260.2 |
|||
| [[St. George's, Grenada|St. George's]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Guadeloupe}} [[Guadeloupe]] ([[France]]) |
|||
| align="right" | 1,780 |
|||
| align="right" | 448,713 |
|||
| align="right" | 252.1 |
|||
| [[Basse-Terre]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Guatemala}} [[Guatemala]] |
|||
| align="right" | 108,890 |
|||
| align="right" | 14,655,189 |
|||
| align="right" | 134.6 |
|||
| [[Guatemala City]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Haiti}} [[Haiti]] |
|||
| align="right" | 27,750 |
|||
| align="right" | 8,121,622 |
|||
| align="right" | 292.7 |
|||
| [[Port-au-Prince]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Honduras}} [[Honduras]] |
|||
| align="right" | 112,090 |
|||
| align="right" | 6,975,204 |
|||
| align="right" | 62.2 |
|||
| [[Tegucigalpa]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Jamaica}} [[Jamaica]] |
|||
| align="right" | 10,991 |
|||
| align="right" | 2,731,832 |
|||
| align="right" | 248.6 |
|||
| [[Kingston, Jamaica|Kingston]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Martinique}} [[Martinique]] (France) |
|||
| align="right" | 1,100 |
|||
| align="right" | 432,900 |
|||
| align="right" | 393.5 |
|||
| [[Fort-de-France]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Mexico}} [[Mexico]] <ref>[[Physical geography|Physiographically]], the southeastern portion of [[Mexico]] (east of the [[Isthmus of Tehuantepec]]) is considered a part of [[Central America]].[http://www.britannica.com/ebc/article-9360160][http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761574502/Central_America.html] [[Geopolitics|Geopolitically]], Mexico is frequently not reckoned in Central America.[http://www.bartleby.com/61/8/C0200800.html][http://columbia.thefreedictionary.com/central+america]</ref> |
|||
| align="right" | 1,972,550 |
|||
| align="right" | 106,202,903 |
|||
| align="right" | 53.8 |
|||
| [[Mexico City]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Montserrat}} [[Montserrat]] (UK) |
|||
| align="right" | 102 |
|||
| align="right" | 9,341 |
|||
| align="right" | 91.6 |
|||
| [[Plymouth, Montserrat|Plymouth]]; [[Brades, Montserrat|Brades]]<ref>Due to ongoing activity of the [[Soufriere Hills volcano]] beginning 1995, much of [[Plymouth, Montserrat|Plymouth]], [[Montserrat]]'s ''[[de jure]]'' capital, was destroyed and government offices relocated to [[Brades, Montserrat|Brades]].</small></ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|United States}} [[Navassa Island]] ([[United States|USA]]) |
|||
| align="right" | 5 |
|||
| align="right" | — |
|||
| align="right" | — |
|||
| — |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Netherlands Antilles}} [[Netherlands Antilles]] (Netherlands)<ref name="two" /> |
|||
| align="right" | 960 |
|||
| align="right" | 219,958 |
|||
| align="right" | 229.1 |
|||
| [[Willemstad, Netherlands Antilles|Willemstad]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Nicaragua}} [[Nicaragua]] |
|||
| align="right" | 129,494 |
|||
| align="right" | 5,465,100 |
|||
| align="right" | 42.2 |
|||
| [[Managua]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Panama}} [[Panama]]<ref>[[Panama]] is generally considered a transcontinental country in Central America (UN region) and South America; population and area figures are for North American portion only, west of the [[Panama Canal]].</small><br></ref> |
|||
| align="right" | 52,853 |
|||
| align="right" | 2,498,717 |
|||
| align="right" | 47.3 |
|||
| [[Panama City]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Puerto Rico}} [[Puerto Rico]] (USA) |
|||
| align="right" | 9,104 |
|||
| align="right" | 3,916,632 |
|||
| align="right" | 430.2 |
|||
| [[San Juan, Puerto Rico|San Juan]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Saint Kitts and Nevis}} [[Saint Kitts and Nevis]] |
|||
| align="right" | 261 |
|||
| align="right" | 38,958 |
|||
| align="right" | 149.3 |
|||
| [[Basseterre]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Saint Lucia}} [[Saint Lucia]] |
|||
| align="right" | 616 |
|||
| align="right" | 166,312 |
|||
| align="right" | 270.0 |
|||
| [[Castries]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Saint-Pierre and Miquelon}} [[Saint-Pierre and Miquelon]] (France) |
|||
| align="right" | 242 |
|||
| align="right" | 7,012 |
|||
| align="right" | 29.0 |
|||
| [[Saint-Pierre, Saint-Pierre and Miquelon|Saint-Pierre]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Saint Vincent and the Grenadines}} [[Saint Vincent and the Grenadines]] |
|||
| align="right" | 389 |
|||
| align="right" | 117,534 |
|||
| align="right" | 302.1 |
|||
| [[Kingstown]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Trinidad and Tobago}} [[Trinidad and Tobago]]<ref name="two" /> |
|||
| align="right" | 5,128 |
|||
| align="right" | 1,088,644 |
|||
| align="right" | 212.3 |
|||
| [[Port of Spain]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|Turks and Caicos Islands}} [[Turks and Caicos Islands]] (UK) |
|||
| align="right" | 430 |
|||
| align="right" | 20,556 |
|||
| align="right" | 47.8 |
|||
| [[Cockburn Town]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|United States}} [[United States|United States of America]]<ref>Includes the [[U.S. state|US state]] of [[Hawaii]], which is distant from the North American landmass in the [[Pacific Ocean]] and is, thus, commonly included with the other territories of [[Oceania]].</small></ref> |
|||
| align="right" | 9,629,091 |
|||
| align="right" | 300,165,500 |
|||
| align="right" | 30.7 |
|||
| [[Washington, D.C.]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{flagicon|U.S. Virgin Islands}} [[U.S. Virgin Islands]] (USA) |
|||
| align="right" | 352 |
|||
| align="right" | 108,708 |
|||
| align="right" | 308.8 |
|||
| [[Charlotte Amalie, U.S. Virgin Islands|Charlotte Amalie]] |
|||
|- style=" font-weight:bold; " |
|||
| Total |
|||
| align="right" | 24,486,305 |
|||
| align="right" | 518,575,412 |
|||
| align="right" | 21.0 |
|||
|} |
|||
''Notes:''<br> |
|||
<div class="references-small"> |
|||
<references /> |
|||
</div> |
|||
==Usage of the term== |
|||
"North America" may mean different things to different people in the world according to the context: |
|||
* In English, the term North America is also used to mean the United States and Canada only. |
|||
<small>Sources: ''[[Fowler's Modern English Usage]]''. (ISBN 0-19-861021-1) New York: Oxford University Press, p. 48; http://geography.about.com/library/faq/blqzamericas.htm |
|||
* In Latin America, Iberia, and some other parts of Europe, the Americas are considered to be a single continent, with North America considered a [[subcontinent]] containing only [[Canada]], [[United States|U.S.]] and [[Mexico]]{{fact}}. |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{portal}} |
|||
{{Commons|North America}} |
|||
* [[Americas (terminology)]] |
|||
* [[History of North America]] |
|||
* [[Discoverer of the Americas]] |
|||
* [[Economy of North America]] |
|||
* [[European colonization of the Americas]] |
|||
==Sources== |
|||
<div class="references-small"> |
|||
* "[http://www.bartleby.com/65/na/NAmer.html North America]"/"[http://www.bartleby.com/65/ce/CentrAm.html Central America]". ''[http://www.bartleby.com/65/ The Columbia Encyclopedia]'', 6th ed. 2001-6. New York: Columbia University Press. |
|||
* "[http://www.britannica.com/eb/article?tocId=9373623 North America]"/"[http://www.britannica.com/ebc/article-9360160 Central America]". ''[[Encyclopædia Britannica]]''. 2006. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. |
|||
* [http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm UN Statistics Division: Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings] |
|||
* [http://www.xist.org/earth/pop_region.aspx GeoHive: The population of continents, regions and countries] |
|||
* "[http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761562468/North_America.html North America]"/ "[http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761574502/Central_America.html Central America]". ''[[Encarta|MSN Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006]].'' |
|||
* [http://www.bartleby.com/61/64/N0156400.html American Heritage Dictionaries, North America] and [http://www.bartleby.com/61/8/C0200800.html Central America] |
|||
* [http://www.answers.com/topic/north-america Houghton Mifflin Company, "North America"] |
|||
* [http://wordnet.princeton.edu/perl/webwn?s=central+america WordNet Princeton University: Central America] |
|||
* [http://www.reference.com/browse/crystal/23124 Crystal Reference Encyclopedia, "North America"] |
|||
</div> |
|||
==External links== |
|||
*http://www.america-norte.com/america-norte-mapa.htm |
|||
*[http://www.earth-puzzle.com/NAmerica.html http://www.earth-puzzle.com] clickable map with links to related Wikipedia articles |
|||
*This [http://www.north-america-map.com/ North America map] site includes a political map and a relief map of North America. |
|||
{{Continents of the world}} |
|||
{{Regions of the world}} |
|||
[[Category:Continents]] |
|||
[[Category:North America| ]] |
|||
<!-- interwiki --> |
|||
[[af:Noord-Amerika]] |
|||
[[ang:Norðamerica]] |
|||
[[ar:أمريكا الشمالية]] |
|||
[[an:America d'o Norte]] |
|||
[[ast:Norteamérica]] |
|||
[[az:Şimali Amerika]] |
|||
[[bn:উত্তর আমেরিকা]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Pak Bí-chiu]] |
|||
[[be:Паўночная Амерыка]] |
|||
[[bs:Sjeverna Amerika]] |
|||
[[br:Norzhamerika]] |
|||
[[bg:Северна Америка]] |
|||
[[ca:Amèrica del Nord]] |
|||
[[cv:Çӳрçěр Америка]] |
|||
[[cs:Severní Amerika]] |
|||
[[cy:Gogledd America]] |
|||
[[da:Nordamerika]] |
|||
[[de:Nordamerika]] |
|||
[[arc:ܐܡܪܝܟܐ ܓܪܒܝܐ]] |
|||
[[et:Põhja-Ameerika manner]] |
|||
[[es:América del Norte]] |
|||
[[eo:Nordameriko]] |
|||
[[eu:Ipar Amerika]] |
|||
[[fa:آمریکای شمالی]] |
|||
[[fo:Norðuramerika]] |
|||
[[fr:Amérique du Nord]] |
|||
[[fy:Noard-Amearika]] |
|||
[[ga:Meiriceá Thuaidh]] |
|||
[[gl:América do Norte]] |
|||
[[gu:ઉત્તર અમેરિકા]] |
|||
[[ko:북아메리카]] |
|||
[[haw:ʻAmelika ʻĀkau]] |
|||
[[hi:उत्तरी अमरीका]] |
|||
[[hsb:Sewjerna Amerika]] |
|||
[[hr:Sjeverna Amerika]] |
|||
[[id:Amerika Utara]] |
|||
[[ia:America del Nord]] |
|||
[[is:Norður-Ameríka]] |
|||
[[it:America settentrionale]] |
|||
[[he:אמריקה הצפונית]] |
|||
[[ka:ჩრდილოეთი ამერიკა]] |
|||
[[ht:Amerik dinò]] |
|||
[[ku:Emerîkaya Bakur]] |
|||
[[la:America Septentrionalis]] |
|||
[[lv:Ziemeļamerika]] |
|||
[[lb:Nord- a Mëttelamerika]] |
|||
[[lt:Šiaurės Amerika]] |
|||
[[li:Noord-Amerika]] |
|||
[[hu:Észak-Amerika]] |
|||
[[mk:Северна Америка]] |
|||
[[mr:उत्तर अमेरिका]] |
|||
[[nl:Noord-Amerika]] |
|||
[[ja:北アメリカ]] |
|||
[[no:Nord-Amerika]] |
|||
[[nn:Nord-Amerika]] |
|||
[[nrm:Améthique du Nord]] |
|||
[[nds:Noordamerika]] |
|||
[[pl:Ameryka Północna]] |
|||
[[pt:América do Norte]] |
|||
[[ro:America de Nord]] |
|||
[[qu:Chinchay Abya Yala]] |
|||
[[ru:Северная Америка]] |
|||
[[se:Davvi-Amerihkká]] |
|||
[[scn:Amèrica dû Nord]] |
|||
[[simple:North America]] |
|||
[[sk:Severná Amerika]] |
|||
[[sl:Severna Amerika]] |
|||
[[sr:Северна Америка]] |
|||
[[sh:Severna Amerika]] |
|||
[[fi:Pohjois-Amerikka]] |
|||
[[sv:Nordamerika]] |
|||
[[tl:Hilagang Amerika]] |
|||
[[ta:வட அமெரிக்கா]] |
|||
[[th:ทวีปอเมริกาเหนือ]] |
|||
[[vi:Bắc Mỹ]] |
|||
[[tr:Kuzey Amerika]] |
|||
[[uk:Північна Америка]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:北美洲]] |
|||
[[zh:北美洲]] |
|||
Revision as of 17:59, 27 January 2007

North America is a continent in the Earth's northern hemisphere and almost fully in the western hemisphere. It is bordered on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the east by the North Atlantic Ocean, on the southeast by the Caribbean Sea, and on the south and west by the North Pacific Ocean; South America lies to the southeast, connected to North America by the isthmus of Panama. It covers an area of about 24,490,000 km² (9,450,000 sq mi), or about 4.8% of the planet's surface. As of October 2006, its population was estimated at over 514,600,000. It is the third-largest continent in area, following Asia and Africa, and is fourth in population after Asia, Africa, and Europe.
Etymology
North and South America are widely accepted as having been named after Amerigo Vespucci by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller. Vespucci was the first European to suggest that the Americas were not the East Indies, but a new world, previously undiscovered by Europeans.
The second and less generally accepted theory is that the continents are named after an English merchant named Richard Amerike from Bristol, who is believed to have financed John Cabot's voyage of discovery from England to Newfoundland in 1497. A minutely explored belief that has been advanced is that America was named for a Spanish sailor bearing the ancient Visigothic name of 'Amairick'. Another is that the name is rooted in an American Indian language. [5]
Geography and extent
North America occupies the northern portion of the landmass generally referred to as the New World, the Western Hemisphere, the Americas, or simply America. North America's only land connection is to South America at the narrow Isthmus of Panama. (Geopolitically, all of Panama—including the segment east of the Panama Canal in the isthmus—is often considered a part of North America alone.) According to some authorities, North America begins not at the Isthmus of Panama but at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico with the intervening region called Central America (or Middle America if the Caribbean is included) and resting on the Caribbean Plate. Before the Central American isthmus was raised, the region had been underwater. The islands of the West Indies delineate a submerged former land bridge, which had connected North America and South America via Florida and Venezuela.
The continental coastline is long and irregular. The Gulf of Mexico is the largest body of water indenting the continent, followed by Hudson Bay. Others include the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the Gulf of California.
There are numerous islands off the continent’s coasts: principally, the Arctic Archipelago, the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the Alexander Archipelago, and the Aleutian Islands. Greenland, a Danish self-governing island and the world's largest, is on the same tectonic plate (the North American Plate) and is part of North America geographically. Bermuda is not part of the Americas, but is an oceanic island which was formed on the fissure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge over 100 million years ago. The nearest landmass to it is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, and it is often thought of as part of North America, especially given its historical political and cultural ties to Virginia and other parts of the continent.
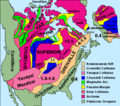
Physical geography

The vast majority of North America is on the North American Plate. Parts of California and western Mexico form the partial edge of the Pacific Plate, with the two plates meeting along the San Andreas fault. The southern portion of the continent and much of the West Indies lie on the Caribbean Plate, while the Juan de Fuca and Cocos Plates border the North American Plate on its western frontier.
The continent can be divided into four great regions (each of which contains many sub-regions): the Great Plains stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to the Canadian Arctic; the geologically young, mountainous west, including the Rocky Mountains, the Great Basin, California and Alaska; the raised but relatively flat plateau of the Canadian Shield in the northeast; and the varied eastern region, which includes the Appalachian Mountains, the coastal plain along the Atlantic seaboard, and the Florida peninsula. Mexico, with its long plateaus and cordilleras, falls largely in the western region, although the eastern coastal plain does extend south along the Gulf.
The western mountains are split in the middle, into the main range of the Rockies and the coast ranges in California, Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia with the Great Basin – a lower area containing smaller ranges and low-lying deserts – in between. The highest peak is Denali in Alaska.
The United States Geographical Survey states that the geographic center of North America is “6 miles west of Balta, Pierce County, North Dakota” at approximately 48° 10′North, 100° 10′West, approximately 15 miles (25 km) from Rugby, North Dakota. The USGS further states that “No marked or monumented point has been established by any government agency as the geographic center of either the 50 States, the conterminous United States, or the North American continent.” Nonetheless, there is a 15 foot (4.5 m) field stone obelisk in Rugby claiming to mark the center.
-
North America bedrock and terrain.
-
North American cratons and basement rocks.
-
Tectonic elements of North America
-
North American craton.
Human geography
The most spoken languages in North America are English, Spanish and French. The term Anglo-America is occasionally used to refer to Belize, the United States, Canada, the anglophone parts of the Caribbean, and Guyana (the only English-speaking nation of South America), and are included in the Anglosphere. The remaining Central American nations, Mexico, and the Spanish-speaking Caribbean and the other South American countries where Romance languages prevail (namely Spanish, Portuguese and French), are referred to as Latin America. This latter term has entered into common parlance, although the term "Anglo-America" is much less commonly used.
The French language has historically played a significant role in North America and remains a distinctive presence in some regions. Canada has two official languages; French is the official language of the province of Quebec, and, along with English, one of the two official languages of the province of New Brunswick. Other French-speaking locales include: the French West Indies and Saint-Pierre and Miquelon. Haiti is included with this group based on past historical association but Haitians speak Creole and French. Although the former language is derived from French, it is not French.
Socially and culturally, North America presents a well-defined entity. Canada and the United States have a shared culture and similar traditions as a result of both countries being former British colonies. A common cultural and economic market has developed between the two nations because of the strong economic and historical ties. Spanish-speaking North America shares a common past as former Spanish colonies. In Central American countries and Mexico where civilizations like the Maya developed, indigenous people preserve traditions across modern boundaries. Central American and Spanish-speaking Caribbean nations have historically had more in common due to geographical proximity and the fact that, after winning independence from Spain, Mexico never took part in an effort to build a Central American Union.
Economically, Canada and the United States are the wealthiest and most developed nations in the continent; the countries of Central America and the Caribbean are much less developed, while Mexico – a newly industrialized country – lies between these two extremes. The most important trade blocs are the Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM), the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and the recently signed Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) – the last of these being an example of the economic integration sought by the nations of this subregion as a way to improve their financial status.
Demographically, North America is a racially and ethnically diverse continent. Its three main ethnic groups are Whites, Mestizos and African-Americans.[citation needed] There is a significant minority of Amerindians and Chinese among other less numerous groups.
Countries and territories

North America is often divided into subregions but no universally accepted divisions exist. "Central America" comprises the southern portion of the continent, but its northern terminus varies between sources. The United Nations includes Mexico in Central America, while most other definitions of the region do not (e.g., the European Union excludes Belize and Mexico from the area). The term Middle America is sometimes used to refer to Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean collectively.
Northern America is used to refer to the northern countries and territories of North America: Canada, the United States, Greenland, Bermuda, and St. Pierre and Miquelon. They are often considered distinct from the southern portion of the Americas, which largely comprise Latin America.
The Caribbean refers to the islands in and around the Caribbean Sea and the surrounding coasts.
| Country or territory with flag |
Area (km²) |
Population (1 July 2005 est.) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102 | 13,254 | 129.9 | The Valley | |
| 443 | 68,722 | 155.1 | St. John's | |
| 193 | 71,566 | 370.8 | Oranjestad | |
| 13,940 | 301,790 | 21.6 | Nassau | |
| 431 | 279,254 | 647.9 | Bridgetown | |
| 22,966 | 279,457 | 12.2 | Belmopan | |
| 53 | 65,365 | 1,233.3 | Hamilton | |
| 153 | 22,643 | 148.0 | Road Town | |
| 9,984,670 | 32,805,041 | 3.3 | Ottawa | |
| 262 | 44,270 | 169.0 | George Town | |
| 51,100 | 4,016,173 | 78.6 | San José | |
| 110,860 | 11,346,670 | 102.4 | Havana | |
| 754 | 69,029 | 91.6 | Roseau | |
| 48,730 | 8,950,034 | 183.7 | Santo Domingo | |
| 21,040 | 6,704,932 | 318.7 | San Salvador | |
| 2,166,086 | 56,375 | 0.026 | Nuuk | |
| 344 | 89,502 | 260.2 | St. George's | |
| 1,780 | 448,713 | 252.1 | Basse-Terre | |
| 108,890 | 14,655,189 | 134.6 | Guatemala City | |
| 27,750 | 8,121,622 | 292.7 | Port-au-Prince | |
| 112,090 | 6,975,204 | 62.2 | Tegucigalpa | |
| 10,991 | 2,731,832 | 248.6 | Kingston | |
| 1,100 | 432,900 | 393.5 | Fort-de-France | |
| 1,972,550 | 106,202,903 | 53.8 | Mexico City | |
| 102 | 9,341 | 91.6 | Plymouth; Brades[3] | |
| 5 | — | — | — | |
| 960 | 219,958 | 229.1 | Willemstad | |
| 129,494 | 5,465,100 | 42.2 | Managua | |
| 52,853 | 2,498,717 | 47.3 | Panama City | |
| 9,104 | 3,916,632 | 430.2 | San Juan | |
| 261 | 38,958 | 149.3 | Basseterre | |
| 616 | 166,312 | 270.0 | Castries | |
| 242 | 7,012 | 29.0 | Saint-Pierre | |
| 389 | 117,534 | 302.1 | Kingstown | |
| 5,128 | 1,088,644 | 212.3 | Port of Spain | |
| 430 | 20,556 | 47.8 | Cockburn Town | |
| 9,629,091 | 300,165,500 | 30.7 | Washington, D.C. | |
| 352 | 108,708 | 308.8 | Charlotte Amalie | |
| Total | 24,486,305 | 518,575,412 | 21.0 |
Notes:
- ^ a b c Depending on definitions, Aruba, Netherlands Antilles, Panama, and Trinidad and Tobago have territory in one or both of North and South America.
- ^ Physiographically, the southeastern portion of Mexico (east of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec) is considered a part of Central America.[1][2] Geopolitically, Mexico is frequently not reckoned in Central America.[3][4]
- ^ Due to ongoing activity of the Soufriere Hills volcano beginning 1995, much of Plymouth, Montserrat's de jure capital, was destroyed and government offices relocated to Brades.
- ^ Panama is generally considered a transcontinental country in Central America (UN region) and South America; population and area figures are for North American portion only, west of the Panama Canal.
- ^ Includes the US state of Hawaii, which is distant from the North American landmass in the Pacific Ocean and is, thus, commonly included with the other territories of Oceania.
Usage of the term
"North America" may mean different things to different people in the world according to the context:
- In English, the term North America is also used to mean the United States and Canada only.
Sources: Fowler's Modern English Usage. (ISBN 0-19-861021-1) New York: Oxford University Press, p. 48; http://geography.about.com/library/faq/blqzamericas.htm
- In Latin America, Iberia, and some other parts of Europe, the Americas are considered to be a single continent, with North America considered a subcontinent containing only Canada, U.S. and Mexico[citation needed].
See also
- Americas (terminology)
- History of North America
- Discoverer of the Americas
- Economy of North America
- European colonization of the Americas
Sources
- "North America"/"Central America". The Columbia Encyclopedia, 6th ed. 2001-6. New York: Columbia University Press.
- "North America"/"Central America". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- UN Statistics Division: Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings
- GeoHive: The population of continents, regions and countries
- "North America"/ "Central America". MSN Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006.
- American Heritage Dictionaries, North America and Central America
- Houghton Mifflin Company, "North America"
- WordNet Princeton University: Central America
- Crystal Reference Encyclopedia, "North America"
External links
- http://www.america-norte.com/america-norte-mapa.htm
- http://www.earth-puzzle.com clickable map with links to related Wikipedia articles
- This North America map site includes a political map and a relief map of North America.