Smart Lander for Investigating Moon: Difference between revisions
→Mission: avoid parentheses |
m →Mission: Removed unnecessary word (starting an sentence with 'The NASA' would sound strange) |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
After the shutdown on 19 January 2024, the mission's operators still hoped that the lander would wake up in a few days when the sun would be correctly oriented to hit to the now askew solar panels.<ref name=":8">{{Cite news |last=Sample |first=Ian |date=2024-01-19 |title=Japan's SLIM spacecraft lands on moon but struggles to generate power |url=https://www.theguardian.com/science/2024/jan/19/japan-slim-spacecraft-lands-on-moon-but-struggles-to-generate-power |access-date=2024-01-20 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077 |archive-date=19 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240119220413/https://www.theguardian.com/science/2024/jan/19/japan-slim-spacecraft-lands-on-moon-but-struggles-to-generate-power |url-status=live }}</ref> The two rovers, LEV-1 and Sora-Q, continued to operate autonomously as planned.<ref name="auto2"/> |
After the shutdown on 19 January 2024, the mission's operators still hoped that the lander would wake up in a few days when the sun would be correctly oriented to hit to the now askew solar panels.<ref name=":8">{{Cite news |last=Sample |first=Ian |date=2024-01-19 |title=Japan's SLIM spacecraft lands on moon but struggles to generate power |url=https://www.theguardian.com/science/2024/jan/19/japan-slim-spacecraft-lands-on-moon-but-struggles-to-generate-power |access-date=2024-01-20 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077 |archive-date=19 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240119220413/https://www.theguardian.com/science/2024/jan/19/japan-slim-spacecraft-lands-on-moon-but-struggles-to-generate-power |url-status=live }}</ref> The two rovers, LEV-1 and Sora-Q, continued to operate autonomously as planned.<ref name="auto2"/> |
||
On 29 January the lander resumed operations after being shut for a week. |
On 29 January the lander resumed operations after being shut for a week. JAXA said it re-established contact with the lander and its solar cells were working again after a shift in lighting conditions allowed it to catch sunlight.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-68125589|title=Japan: Moon lander Slim comes back to life and resumes mission|date=29 January 2024|via=www.bbc.com}}</ref> |
||
{{multiple image |
{{multiple image |
||
Revision as of 19:21, 30 January 2024
This article or section documents a current or recent spaceflight. Details may change as the mission progresses. Initial news reports may be unreliable. The last updates to this article or section may not reflect the most current information. For more information please see WikiProject Spaceflight. |
 Half scale model of SLIM in landing configuration | |
| Names | SLIM |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Lunar lander and lunar rover |
| Operator | JAXA |
| COSPAR ID | 2023-137D |
| SATCAT no. | 57803 |
| Website | Official website |
| Mission duration | 1 year, 2 months, 6 days (elapsed) (since launch) 9 months, 23 days (since landing) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | MELCO |
| Launch mass | 590 kg[1] |
| Dry mass | 120 kg[2] |
| Dimensions | 1.5 × 1.5 × 2 m (4 ft 11 in × 4 ft 11 in × 6 ft 7 in)[1] |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 6 September 2023 23:42:11 UTC[3] |
| Rocket | H-IIA 202 |
| Launch site | Tanegashima Space Center |
| Contractor | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries |
| Lunar orbiter | |
| Orbital insertion | 25 December 2023 07:51 UTC[4] |
| Lunar lander | |
| Landing date | 19 January 2024 15:20:00 UTC[4] |
| Landing site | near Shioli crater 13°18′58″S 25°15′04″E / 13.3160°S 25.2510°E[5] |
Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) is a lunar lander mission of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The lander's initial launch date in 2021[2][6] was postponed until 2023 due to delays in its rideshare, the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM).[7] On 6 September 2023 at 23:42 UTC (7 September 08:42 Japan Standard Time),[3] XRISM successfully launched, and SLIM separated from it later that day.
On 1 October 2023 SLIM executed its trans-lunar orbit injection burns. The lander successfully entered lunar orbit on 25 December 2023 and landed on 19 January 2024 at 15:20 UTC, making Japan the fifth country to soft-land a spacecraft on the Moon.[8]
Background
The main purpose of Japan's first lunar surface mission was to demonstrate precision lunar landing. During its descent the lander recognized lunar craters by applying technology from facial recognition systems, and determined its current location from utilizing observation data collected by the SELENE (Kaguya) lunar orbiter mission. SLIM aimed to soft land with an accuracy range of 100 m (330 ft).[6][9][10] In comparison, the accuracy of the 1969 Apollo 11 Eagle lunar module was an elliptic which was 20 km (12 mi) long in downrange and 5 km (3.1 mi) wide in crossrange.[2]
According to Yoshifumi Inatani, deputy director general of the JAXA Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), succeeding in this extremely precise landing will lead to enhanced quality of space exploration.[11] The expected cost for developing this project is 18 billion yen, or US$121.5 million.[12]
History
The proposal which later came to be known as SLIM existed in 2005, as the Small Lunar Landing Experiment Satellite (小型月着陸実験衛星).[13] On 27 December 2013, ISAS called for proposals for its next "Competitively-Chosen Medium-Sized Focused Mission", and SLIM was among the seven proposals submitted.[2] In June 2014, SLIM passed the semi-final selection along with the DESTINY+ technology demonstration mission, and in February 2015 SLIM was ultimately selected.[14] From April 2016, SLIM gained project status within JAXA.[15] In May 2016, Mitsubishi Electric (MELCO) was awarded the contract for building the spacecraft.[16]
SLIM was not the first Japanese lunar lander built for operation on the Moon's surface; on 27 May 2016 NASA announced that the OMOTENASHI (Outstanding Moon exploration Technologies demonstrated by Nano Semi-Hard Impactor) CubeSat lander jointly developed by JAXA and the University of Tokyo was to be launched as a secondary payload on Space Launch System (SLS) Artemis 1. OMOTENASHI was meant to deploy a mini lunar lander weighing 1 kg; however, on November 21, 2022, JAXA announced that attempts to communicate with the spacecraft had ceased due to the solar cells failing to generate power because they were facing away from the Sun.[17] They would not face the sun again until March 2023.[18]
In 2017, funding difficulties for developing XRISM led to SLIM's launch being switched from its own dedicated Epsilon flight to a rideshare H-IIA flight.[19] The resulting cost savings will be transferred to develop other satellites that are behind schedule due to XRISM.[19]
Rovers
Lunar Excursion Vehicle 1
Lunar Excursion Vehicle 1 (LEV-1) is a lunar rover which moves by hopping. It has its own direct-to-Earth communication equipment, two wide-angle visible light cameras, and electrical components and UHF band antennas courtesy of the MINERVA and OMOTENASHI projects.[20]
Science payloads:
- Thermometer
- Radiation monitor
- Inclinometer
Lunar Excursion Vehicle 2
Lunar Excursion Vehicle 2 (LEV-2) or SORA-Q, is a tiny rover developed by JAXA in joint cooperation with the toy company Tomy, Sony, and Doshisha University.[21] The baseball-sized rover has a mass of 250 g and is equipped with two small cameras. LEV-2 extends its shape to crawl on the lunar surface using two wheels at its sides, a method of locomotion inspired by frogs and sea turtles;[22] it can "run" for approximately two hours.[23] It is the second rover of its kind to attempt operations on the lunar surface; the first was on Hakuto-R Mission 1, which crashed before it could be deployed.[24][25]
Mission
SLIM was successfully launched together with the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) space telescope on 6 September 2023 at 23:42 UTC (7 September 08:42 Japan Standard Time)[3] planning to land near Shioli crater (13.3°S, 25.2°E) via weak stability boundary-like trajectory.[26] SLIM entered lunar orbit 25 December JST.[27]

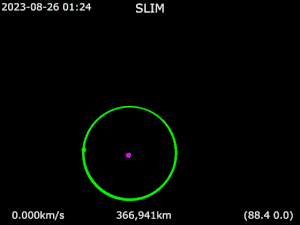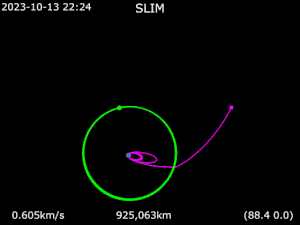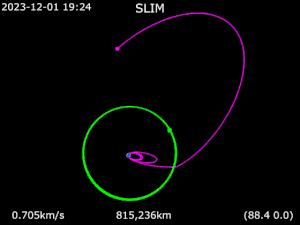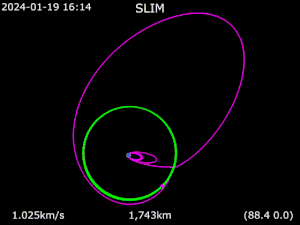
The lunar lander, nicknamed Moon Sniper for its extremely accurate landing precision within the projected 100 meters (330 ft) long landing ellipse, touched down onto the Moon on 19 January 2024 at 15:20 UTC, at the Sea of Nectar (Mare Nectaris), south of the Theophilus crater. Japan thus became the fifth nation to successfully soft land an operational spacecraft on the Moon, after the Soviet Union, United States, China, and India.[28][29][30]
Although SLIM landed successfully, the lander suffered a technical issue with its solar panels, which became oriented westwards facing opposite the Sun at the start of lunar day, thereby failing to generate enough power.[31] The lander was able to operate on internal battery power for a short period of time, but was manually powered down on 19 January 2024 at 17:57 UTC (20 January 02:57 Japan Standard Time) to prevent over-discharge of the battery.[17]
The two lunar rovers, deployed while the lander was hovering just before it touched down, are working as planned, with LEV-1 communicating independently to ground stations.[32] LEV-1 conducted six hops on the lunar surface. Images autonomously taken by Sora-Q (a capability it shares with its sister rover)[33] showed the SLIM had landed at a 90 degree angle, effectively on its nose, and there had been the loss of an engine nozzle during descent and even possible damage to its Earth-oriented antenna.[34] Irrespective of wrong attitude and loss of communication with the lander, the mission is already successful given confirmation of its primary goal: landing within 100 m (330 ft) of its landing spot.[35][36][34] JAXA gave itself 60 out of 100 for the landing.[22]
After the shutdown on 19 January 2024, the mission's operators still hoped that the lander would wake up in a few days when the sun would be correctly oriented to hit to the now askew solar panels.[32] The two rovers, LEV-1 and Sora-Q, continued to operate autonomously as planned.[33]
On 29 January the lander resumed operations after being shut for a week. JAXA said it re-established contact with the lander and its solar cells were working again after a shift in lighting conditions allowed it to catch sunlight.[37]
See also
- List of landing ellipses on extraterrestrial bodies
- Japanese Lunar Exploration Program
- Chandrayaan-3 – Indian lunar lander mission
- List of missions to the Moon
References
- ^ a b "小型月着陸実証機(SLIM)プロジェクト移行審査の結果について" (PDF) (in Japanese). JAXA. 14 July 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 July 2016. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- ^ a b c d "小型探査機による高精度月面着陸の技術実証(SLIM)について" (PDF) (in Japanese). 3 June 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 June 2015. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Davenport, Justin (6 September 2023). "Japanese H-IIA launches X-ray telescope and lunar lander". NASASpaceFlight. Archived from the original on 7 September 2023. Retrieved 7 September 2023.
- ^ a b "JAXA | Moon Landing of the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM)". Archived from the original on 5 December 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ "NASA's LRO Spots Japan's Moon Lander". 26 January 2024. Archived from the original on 26 January 2024. Retrieved 27 January 2024.
- ^ a b Hongo, Jun (12 November 2015). "Japan Plans Unmanned Moon Landing". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 3 March 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ "Missions of Opportunity (MO) in Development – X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM)". GSFC. NASA. Archived from the original on 6 September 2021. Retrieved 6 September 2021.
- ^ "Japans SLIM mission aims for historic lunar landing 2023". 20 January 2024. Archived from the original on 20 January 2024. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ "Small lunar-lander "SLIM" for the pinpoint landing technology demonstration" (PDF). 9 June 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 March 2017. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ^ "[PPS26-10] Introduction of SLIM, a small and pinpoint lunar lander". 30 April 2014. Archived from the original on 11 April 2023. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ "JAXAはどのような構想を描いているのか…スリム計画を関係者に聞く". The Sankei Shimbun (in Japanese). 11 May 2016. Archived from the original on 4 November 2018. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ "日本初の月面着陸機、今年から開発スタート 「世界に先駆け高精度技術目指す」". The Sankei Shimbun (in Japanese). 1 January 2016. Archived from the original on 30 June 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2016.
- ^ Hashimoto, Tatsuaki (30 November 2005). "小型月着陸実験衛星" (PDF) (in Japanese). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ "深宇宙探査技術実証機 DESTINY+" (PDF) (in Japanese). 7 January 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 January 2022. Retrieved 23 June 2016.
- ^ "ISASニュース 2016.5 No.422" (PDF) (in Japanese). Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. 27 May 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 April 2023. Retrieved 23 June 2016.
- ^ "Japanese lunar lander to be built by Mitsubishi Electric". Nikkei Asian Review. 18 May 2016. Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ a b "After landing on 1/20 0:20 JST, power from the solar cells could not be confirmed. At a battery level of 12%, the battery was disconnected (as planned) to avoid being unable to restart for a recovery operation due to over-discharge. SLIM therefore powered down at 01/20 2:57 JST". X (Formerly Twitter). Archived from the original on 22 January 2024. Retrieved 22 January 2024.
- ^ "小型衛星を月へ打ち上げ JAXA・東大、着陸にも挑戦 18年に2基". The Nikkei (in Japanese). 28 May 2016. Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 23 June 2016.
- ^ a b "小型ロケット「イプシロン」、政府が19年度の打ち上げ1機中止". The Nikkei (in Japanese). 27 August 2017. Archived from the original on 11 April 2023. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
- ^ "小型プローブ LEV (Lunar Excursion Vehicle)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2023. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ^ Hirano, Daichi (7 October 2022). "Palm-Sized Lunar Excursion Vehicle 2 (LEV-2)". JAXA. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 22 October 2022.
- ^ a b "JAXA Gives Itself 60 Out of 100 for Lunar Landing | JAPAN Forward". 23 January 2024. Archived from the original on 23 January 2024. Retrieved 27 January 2024.
- ^ "Palm-Sized Lunar Excursion Vehicle 2 (LEV-2)". Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ^ Rabie, Passant (12 December 2022). "SpaceX Launches Moon-Bound Private Japanese Lander Following Delays". Gizmodo. Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- ^ "ispace、2022年末頃の打ち上げに向け、フライトモデル組み立ての最終工程に着手 Hakuto-Rのミッション1と2の進捗報告を実施". ispace. Archived from the original on 27 June 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "SLIM Project 概要説明資料" (PDF) (in Japanese). JAXA Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. 25 August 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 August 2023. Retrieved 25 August 2023.
- ^ "JAXA | Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) lunar orbit insertion". JAXA | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. Archived from the original on 26 December 2023. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ^ "Japans SLIM mission aims for historic lunar landing 2023". 20 January 2024. Archived from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ "15h00-16h00 GMT". Connect the World with Becky Anderson. 19 January 2024. CNN International.
- ^ "Japan counts down to 'Moon Sniper' landing on lunar surface". Al Jazeera. 19 January 2024. Archived from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ "According to the telemetry data, SLIM's solar cells are facing west. So if sunlight begins to shine on the lunar surface from the west, there is a possibility of generating power, and we are preparing for recovery. #SLIM can operate with power only from the solar cells. #JAXA". X (Formerly Twitter).
- ^ a b Sample, Ian (19 January 2024). "Japan's SLIM spacecraft lands on moon but struggles to generate power". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 20 January 2024.
- ^ a b "Moon lander hits target, looks to be upside-down - PressReader". Archived from the original on 27 January 2024. Retrieved 27 January 2024 – via PressReader.
- ^ a b 小型月着陸実証機(SLIM)および小型プローブ(LEV)の月面着陸の結果・成果等 の記者会見, archived from the original on 25 January 2024, retrieved 25 January 2024
- ^ Jones, Andrew (22 January 2024). "Japan's moon lander forced to power down but may yet be revived". SpaceNews. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ "SLIM Project Press Kit" (PDF). JAXA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 September 2023. Retrieved 25 August 2023.
- ^ "Japan: Moon lander Slim comes back to life and resumes mission". 29 January 2024 – via www.bbc.com.
Further reading
- JAXA | 宇宙航空研究開発機構 [JAXA: Uchūkōkūkenkyūkaihatsukikō] (19 January 2024). 小型月着陸実証機SLIM ピンポイント月着陸ライブ・記者会見 [kogata tsuki chakuriku jisshō-ki SLIM pin pointo tsuki chakuriku raibu kisha kaiken] (in Japanese). Udh6kvjZYC8 on YouTube.
- JAXA: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (19 January 2024). SLIM Moon Landing Live & Press Conference. nvXLt3ET9mE on YouTube.
External links
- SLIM Official project site (in Japanese)
- JAXA, SLIM project page
- ISAS/JAXA, SLIM mission page