2009 swine flu pandemic in Europe: Difference between revisions
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
{{2009 flu pandemic in Europe table}} |
{{2009 flu pandemic in Europe table}} |
||
The '''2009 flu pandemic in Europe''', part of a [[pandemic]] in 2009 of a new strain of [[influenza A virus subtype H1N1]] causing what has been commonly called [[swine influenza|swine flu]], has afflicted at least 125,550 [[human|people]] in [[Europe]], with 216 confirmed deaths in the [[United Kingdom]], |
The '''2009 flu pandemic in Europe''', part of a [[pandemic]] in 2009 of a new strain of [[influenza A virus subtype H1N1]] causing what has been commonly called [[swine influenza|swine flu]], has afflicted at least 125,550 [[human|people]] in [[Europe]], with 216 confirmed deaths in the [[United Kingdom]], 161 confirmed deaths in [[Turkey]], and 120 confirmed deaths in [[Spain]]. |
||
{| class="table" align="center" |
{| class="table" align="center" |
||
| Line 472: | Line 472: | ||
=={{flagicon|Romania}} [[Romania]]== |
=={{flagicon|Romania}} [[Romania]]== |
||
[[File:H1N1 Romania Map.svg|thumb|right|200px|Outbreak evolution in Romania |
[[File:H1N1 Romania Map.svg|thumb|right|200px|Outbreak evolution in Romania: {{legend|#000000|Confirmed deaths}}{{legend|#cd3412|Confirmed cases}}{{legend|#ffcc00|Suspected cases}}{{legend|#b9b9b9|No reported cases}}]] |
||
{{Main|2009 flu pandemic in Romania}} |
{{Main|2009 flu pandemic in Romania}} |
||
| Line 525: | Line 525: | ||
|1<ref>http://txt.newsru.com/russia/23nov2009/irkah1n1.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://txt.newsru.com/russia/23nov2009/irkah1n1.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Kamchatka]] |
|align=left|[[Kamchatka Krai|Kamchatka]] |
||
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
| Line 537: | Line 537: | ||
|1<ref>http://www.regions.ru/news/2252388/</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.regions.ru/news/2252388/</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Khabarovsk]] |
|align=left|[[Khabarovsk Krai|Khabarovsk]] |
||
|2<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
|2<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
| Line 546: | Line 546: | ||
|1<ref>http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091109/192697144.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091109/192697144.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Krasnodar]] |
|align=left|[[Krasnodar Krai|Krasnodar]] |
||
|1<ref>http://kuban.kp.ru/daily/24397.4/574118/</ref> |
|1<ref>http://kuban.kp.ru/daily/24397.4/574118/</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
| Line 558: | Line 558: | ||
|2<ref>http://www.tatar-inform.ru/news/2009/11/13/193300/</ref> |
|2<ref>http://www.tatar-inform.ru/news/2009/11/13/193300/</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Magadan]] |
|align=left|[[Magadan Oblast|Magadan]] |
||
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
| Line 570: | Line 570: | ||
|1<ref>http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091110/192849514.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091110/192849514.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Omsk]] |
|align=left|[[Omsk Oblast|Omsk]] |
||
|1<ref>http://www.regions.ru/news/2254399/</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.regions.ru/news/2254399/</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
| Line 576: | Line 576: | ||
|1<ref>http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091120/194655093.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091120/194655093.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Primorsky]] |
|align=left|[[Primorsky Krai|Primorsky]] |
||
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
| Line 585: | Line 585: | ||
|5<ref>http://www.novayagazeta.ru/news/708584.html</ref> |
|5<ref>http://www.novayagazeta.ru/news/708584.html</ref> |
||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Sakha Republic]] |
|align=left|[[Sakha Republic|Sakha]] |
||
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
|1<ref>http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|align=left|[[Smolensk Oblast|Smolensk]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Sverdlovsk Oblast|Sverdlovsk]] |
|align=left|[[Sverdlovsk Oblast|Sverdlovsk]] |
||
| Line 608: | Line 611: | ||
|align=left|[[Udmurtia]] |
|align=left|[[Udmurtia]] |
||
|3<ref>http://www.regions.ru/news/2253141/</ref> |
|3<ref>http://www.regions.ru/news/2253141/</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|align=left|[[Ugra]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|- class="sortbottom" |
||
|align=left|[[Zabaykalsky Krai|Zabaykalsky]] |
|align=left|[[Zabaykalsky Krai|Zabaykalsky]] |
||
| Line 1,170: | Line 1,170: | ||
|style="background:#ffcccc;"| {{flagicon|Romania}} First '''death''' confirmed in Romania. |
|style="background:#ffcccc;"| {{flagicon|Romania}} First '''death''' confirmed in Romania. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="background:#e2bee5;"| {{flagicon|Netherlands}} '''Mass vaccinations''' in |
|style="background:#e2bee5;"| {{flagicon|Netherlands}} '''Mass vaccinations''' in the Netherlands begins. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="background:#e2bee5;"| {{flagicon|Czech Republic}} '''Mass vaccinations''' in Czech Republic begins |
|style="background:#e2bee5;"| {{flagicon|Czech Republic}} '''Mass vaccinations''' in the Czech Republic begins. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|rowspan="2"| 26 November |
|rowspan="2"| 26 November |
||
|style="background:#ffcccc;"| {{flagicon|Albania}} First '''death''' confirmed in Albania. |
|style="background:#ffcccc;"| {{flagicon|Albania}} First '''death''' confirmed in Albania. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="background:#ffcccc;"| {{flagicon|Montenegro}} First '''death''' confirmed in Montenegro |
|style="background:#ffcccc;"| {{flagicon|Montenegro}} First '''death''' confirmed in Montenegro. |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Revision as of 18:16, 26 November 2009
This article needs to be updated. (November 2009) |
Template:2009 flu pandemic in Europe table
The 2009 flu pandemic in Europe, part of a pandemic in 2009 of a new strain of influenza A virus subtype H1N1 causing what has been commonly called swine flu, has afflicted at least 125,550 people in Europe, with 216 confirmed deaths in the United Kingdom, 161 confirmed deaths in Turkey, and 120 confirmed deaths in Spain.
On 27 April, the European Union health commissioner advised Europeans not to travel to the United States or Mexico unless urgent. This followed the discovery of the first confirmed case in Spain.[1]
EU Foreign relations commissioner Benita Ferrero-Waldner said on 27 April the halt of all travel to Mexico and disinfecting all airports due to the global flu outbreak is being considered.[2]
On 20 July, authorities in Albania reported the first positive case of the swine flu. The infected person was a student from Gjirokastra, whose tests resulted positive.[3] However, the student was later reported to have been fully recovered from the flu, and he was healthy again. A few day later, three other cases of the flu were confirmed. The infected people were two sailors from the Philippines and one from Romania. They are now recovering on the Durrës city hospital. As of July 24, there were four cases of the swine flu confirmed in Albania.
Several possible cases in Austria turned out to be negative, whereas one test, that of a 28-year-old woman from Vienna, had a positive result. Therefore Austria is the 9th country affected by a confirmed case of swine flu.[4] There are still two suspected cases being tested.[5] As of 22 July 2009 64 cases of the virus have been confirmed in the country.
On 2 November 2009, an 11-year-old girl from Bozen, died in the hospital of Innsbruck. This is the first time, the Flu caused the death of a human in Austria.
Six suspected cases of swine flu in Belgium ultimately tested negative.[6]
The Belgian interior ministry announced the first case of A/H1N1 flu in Belgium on 13 May 2009. The infected person is a 28-year old man who lives in Ghent and returned from a holiday in the United States.[7]
Also a second person tested positive for Mexican flu in Belgium on 14 May 2009.
Two new persons tested positive for A/H1N1 flu on 15 May 2009.[8]
A sixth[9] and seventh[10] case of swine flu was discovered on 21 May 2009. An eighth[11] infection was reported on 26 May 2009.
By 22 July, a total of 126 have been confirmed.
On 30 July, a woman from Hoogstraten became the first patient in Belgium to die because of swine flu[12].
By 16 August, a total of 2353 cases have been confirmed.
As of 18 october, 5 people have died as consequence of swine flu infection and it has been estimated that at least 20100 have been infected by it in Belgium.
By 29 October, a total of 76964 cases have been confirmed and 7 people have died.[13]
First case was confirmed in Bosnia and Herzegovina on 29 June.[14] On November 16, 2009 the first fatality related to the H1N1 in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The 40-year-old man died in hospital in Mostar.[15]
The first case of swine flu was a person from New York to Sofia on 27 May. The person developed respiratory problems, cough and high fever on 29 May.[16]
On September 30, 2009 the first fatality related to the H1N1 in Sofia. The 30-year-old man died in hospital in the Bulgarian capital.[17]
On 29 April it was announced that a 22-year old traveller from Florida had been held in quarantine in Osijek under suspicion of swine flu.[18] However, later that day director of infectious disease epidemiology agency, Dr. Ira Gjenero Margan, stated results of the testing were negative "with 99% certainty".[19] On 30 April, a child was held in quarantine in Zagreb but the results were negative.[20] On 15 June health minister Darko Milinovic confirmed the first case of swine flu in Croatia; however few hours later he said that laboratory in London had cross-contaminated the samples and thus created a false positive result, meaning that there were no affected in Croatia.[21] The first case was Laboratory confirmed on 3 July. The patient was a 60-year-old woman, who came from Australia.[22] On 31 October, a 61-year-old man from Split became the first patient in Croatia to die because of swine flu.[23]
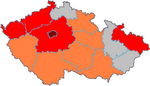
The Czech Republic confirmed its first case of swine flu May 25. The 29-year old man working as a pilot returned from New York. He was held in quarantine in the hospital Bulovka in Prague.
In August 5, 135 Czechs tested positive for swine flu.
Authorities confirmed on 1 May that a Danish citizen had tested positive for swine flu, making it the first reported case in Scandinavia.
By 11 June, a total of 11 cases is confirmed, including a six year old boy.[24][25]
On 29 June, the first case of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance in the world was announced.[26]
On August 28 2009 A truckdriver from Pandrup, Denmark, did die on duty in Norway. This was discovered by the driver of the truck. They both had flu-symptoms, and when the living man from Pandrup arrived at Aalborg Sygehus, he was tested positive on H1N1. Although, it is still not known, if the passenger died caused the flu.
In the moment, 600ish Danes is tested positive for swine flu. Among them, two in isolation in Indionesia and the first known resistant case against tamiflu.


The first case was Laboratory confirmed on 29 May. The patient was a 29-year-old man, who returned from the United States.[27]
On 3 June, two new cases have been Laboratory confirmed.[28]
On 7 June, 4th case was confirmed from the patient, who also returned from the United States on 4 June.
7 new cases were confirmed on June 26. Two of them came from a trip to Mexico. The others are Americans, who were on a trip to Estonia.
On 12th of July, 6 new cases were confirmed.
On 17 July a young Estonian football player infected, he returned from Finland, U-19 European Championships, now there are 22 confirmed cases of H1N1.
On 28th of July, socialminister's vice-chancellor said that the swine flu will infect 500 000 Estonians in 10 weeks. That's about 30% of Estonian population.
As of 9th of November, there are 130 cases confirmed.
As of 11th of November, there are 172 cases of influenza A (H1N1) confirmed, in Harjumaa, Tartumaa, Viljandimaa, Võrumaa, Ida-Virumaa and Lääne-Virumaa.[29]
As of 13th of November, there are 79 new cases confirmed in one week. Total: 217 cases
As of 20 November, there are 269 cases of influenza A (H1N1) confirmed, in 10 counties: Harjumaa, Tartumaa, Viljandimaa, Võrumaa, Ida-Virumaa, Lääne-Virumaa, Jõgevamaa, Põlvamaa, Valgamaa and Pärnumaa.[30]
As of 23 of November. First death of swine influenza. Victim is 13-year old boy, living in Harjumaa region.[31]
On October 16, 2009 the national broadcasting company YLE reported that the first epidemic wave of swine flu was hitting Finland. The National Institute for Health and Welfare (THL) said that the H1N1 outbreaks in northern Finland were reaching epidemic proportions.[32] THL also reported that by 16 October there were 377 confirmed cases in Finland.[33]
The H1N1 strain of influenza was added to the official list of infectious diseases dangerous to public ("yleisvaarallinen tartuntatauti")[34], which guarantees free-of-charge treatment to all residents and allows for involuntary quarantine, effective from May 1, 2009. From the beginning of August it was removed from the list, so free-of-charge treatment is not available to residents any more. [35] Finland's first two H1N1 cases were confirmed on May 12, 2009 in Helsinki metropolitan area. The first confirmed cases were traveling together in Mexico and came to Finland via Amsterdam on May 6, 2009.[36]
According to a Finnish site tracking H1N1 cases there are currently 1,425 confirmed cases (November 9)[37], laboratory testing of every suspected case having stopped by August.[38]. Two serious cases were reported in Finland by September 2.[39] Thousands were infected in Lapland, northern Finland by October 21.[40]
On Saturday October 24 a 25-year old woman from Northern Ostrobothnia also suffering a chronical disease died from H1N1 influenza.[41] On November 2 a 8-year old previously healthy girl died from the disease. The girl and her parents had visited doctor earlier, but were sent back home where the girl later died.[42] According to some estimates, the total number of cases in Finland is probably 10,000-100,000.[43]
A two-year old girl died from the disease (November 13, 2009). [44] After publicity of the death of the two-year old child, Finnish National Institute for Health and Welfare, THL, (November 13, 2009) said they will no longer report deaths caused by H1N1. [45]
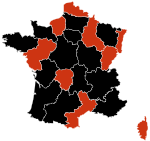
As of 28 April there were twenty suspected cases of swine flu being investigated in France. Since 25 April, over 100 cases of Influenza-like illness have been reported, of which 30 were identified as possible cases. 10 of those cases have since been excluded.[46] On 30 April, the number of suspected cases was revised to 50 (including 4 probable cases).[47]
On 1 May, the French Health Minister has confirmed, during the 8 p.m. TF1 news, that 2 cases of A(H1N1) flu have been detected in France.[48]
On 4 May, two new cases have been confirmed bringing to 4[49] the total number of people infected.
6 May, a fifth case is confirmed in Paris region.[50] Two new cases are also confirmed at the end of the afternoon by the INVS (National Institute for Sanitary Watch),[51] 7 are probable and 32 are suspected.[52]
On 7 May, three new cases were announced by the National Institute for Sanitary Watch. [53]
In November 2009, 351 cases has been detected for each 100.000 inhabitants. Since August, it has been estimated that 1 980 000 persons have been infected by the flu in metropolitan France. 43 of them died (70 including overseas territories) [54]
Two men and a woman from Bielefeld who had been firstly suspected of having the virus tested negative on influenza type A.[55]
On 29 April, the first case of swine flu in Germany was confirmed by the Robert Koch Institute in the area of Regensburg.[56][57][58] A 22-year-old woman from Hamburg is also confirmed to have been infected by swine flu during a trip to Mexico.[58] A 37-year-old woman from Kulmbach is also confirmed to have become infected during a similar trip.[58]
On 1 May, Robert Koch Institute confirmed the first case of human-to-human spreading of swine flu in Munich. Infected was the nurse who had contact with one of the infected people. At approx. 10:00 she was claimed to be already healed.[59] At the time of 13:00 one further infection in Bavaria was confirmed, but the patient is also claimed to be healthy again.[60]
On 2 May, a new human-to-human infection, in the same hospital in Munich, was confirmed. The new patient, who was in the same room with the original infected German that came from Mexico, is currently being reported to show no signs of the new influenza strain anymore.[61]
On 3 May, two further cases of swine flu in Brandenburg were reported. Two people from the same flight as patient in Hamburg were also infected.[62]
On 5 May, one new case in Saxony-Anhalt has been confirmed bringing to 9[63] the total number of people infected.
On 7 May, another new case in Saxony-Anhalt is reported.[64]
On 8 May an adult male living in Bavaria who had recently been to USA.[65]
On 11 May the case of a 27 years old Bavarian woman, who stayed for some weeks in Mexico and medicated patients in a hospital, is reported.[66]
On 15 May two more cases were reported, a female human and her son from Saxony-Anhalt have been infected obviously by her husband / his father, who returned from Mexico.[67]
On 21 May a case was found in a 43 year old woman from Düsseldorf in North Rhine-Westphalia who returned from New York.[68] One day later, Robert Koch Institute confirmed that that her husband has been tested positive with swine influenza too. Furthermore their six years old daughter who did not stay in New York has been infected by her parents, bringing the total to 17.[69]
Until 5 June, 2009, the total number of confirmed cases increased to 49. Most of them have been recent travellers to Mexico, the US or the UK. However, there was also a single-digit number of (isolated) in-country-transmissions.
Gibraltar has reported its first confirmed case of swine flu on 24 July.[70]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled 2009 flu pandemic in Greece. (Discuss) (November 2009) |
On 19 May 2009[citation needed] the authorities confirmed the first case of the new flu in Greece. The infected person is a 19 year old Greek student who studies in New York and who flew to Greece a few days ago. He is hospitalised at Sismanogleion[71] but is not gravely ill. The authorities have contacted many of the passengers who sat near this patient on the plane and are examining them for suspicious symptoms. At this point in time Greece has enough antivirals to cover 12% of the population[72] (at least 10% is the amount proposed by the EU directives). The 19-year-old is now out of the hospital and none of the passengers in his flight are infected.
On 29 May 2009 the fourth case was announced.[73]
On 14 June 2009 the total number of cases have reached 20[74] and on 17 June 2009 reached 25.[75] On 9 July 2009 the total number of cases have reached 216 out of whom 93 have fully recovered.[76]
On 13 July 2009 the total number of cases have reached 290 of which 128 have fully recovered[77]
On July 14, 2009 the total number of cases have reached 323 of which 200 have fully recovered[78]
This article needs to be updated. (November 2009) |
According to the MTI as of 29 April six suspected cases have been reported in Hungary, none of them confirmed to be the swine flu. Samples of the virus from the US health authorities are due to arrive to Hungary in a few days enabling the start of vaccine production.[79]
On 29 May, a case has been confirmed.[80] The infected person, a Brazilian man has since recovered and left the country. On June 18 three new cases of swine flu were confirmed in Hungary, a married couple who returned from New York, and a man who came back from London were new infected.[81]
The first case of A(H1N1) in Iceland was reported on 23 May 2009. The infected person came to the country from New York and got sick shortly after he arrived in Iceland. The second case was announced on 9 June. The infected was a male in the Greater Reykjavík area who also had arrived from the United states. As of 6 August there are 54 cases of H1N1 in Iceland.[82][83][84] [85]
Iceland is currently being briefed by the WHO and is cooperating closely with ECDC, CDC and the EU in terms of monitoring and response. Initially the directorate of health warned people traveling to Mexico and the United States (especially California and Texas) to exercise caution and to contact a doctor immediately if they started showing symptoms of swine flu but on April 28 people travelling to Mexico were advised to cancel their trip unless its very urgent.[86][87]
On 28 April, it was announced that passengers arriving in Iceland from the United States or Mexico would be monitored and will undergo medical examination even if the slightest signs of influenza are detected.[88]
Iceland has stocks of Tamiflu and Relenza for one-third of its population.[88]
In a risk assessment made by the Icelandic government in 2008 in case of a influenza pandemic two scenarios are envisioned:
- A worst-case scenario where 50% of the Icelandic population are infected and 3% of the infected population die.
- A milder scenario where precautionary measures prevent infection, 25% of the Icelandic population are infected and 1% die.[89]
It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled 2009 flu pandemic in Ireland. (Discuss) (November 2009) |
Latest details on cases of A(H1N1) flu in Ireland are to be found on the Health Service Executive website[90]. As of 29 June 2009 there were 39 cases in Ireland.[91].
Ireland has over two million doses of anti-virals and a pandemic plan in place.
On 2 May 2009 the Department of Health's (HSE) announced the first confirmed case in Ireland, an adult male living in Dublin who had recently been to Mexico.
From 25 May to 31 May three more cases were confirmed.[92][93][94]
On 2 June, 3 new cases were confirmed by the HSE on people who returned recently from New York,[95] The total number of cases as of this date was 7.
On 19 June, a case of human swine flu was discovered in a seven-year-old, who was attending a primary school in Co. Mayo and had been abroad. 28 children in the school were treated with Tamiflu. The total number of cases as of this date was 18.[96]
On 21 June a child believed to have recently returned from the United States of America and presenting flu-like symptoms was treated in Kerry General Hospital in Tralee, Co. Kerry, but tests later proved negative.[97]
Saturday 4 July 2009
A free swine flu vaccination is to be offered to the general population in the coming months, as part of a major plan to avoid the worst affects of a global pandemic.
The HSE plans to acquire over 7,500,000 doses of the vaccine, at a cost of almost €90 million.
The jabs would be administered by GPs or through a network of over a hundred swine flu clinics and will be ready by the autumn.
12 new cases of swine flu were confirmed here yesterday, bringing the total number in Ireland to 63.[98]
Friday 10 July 2009
Total number of laboratory confirmed cases in Ireland exceed 100. 9 of these cases are believed to have been in-country transmissions of the virus
Tuesday 21 July
11 new cases of the H1N1 virus have been identified in Ireland bringing the total number of confirmed cases to 164 including 17 cases which are believed to have been in-country transmissions of the virus.
As of July 28, 2009, there are reportedly 276 confirmed cases in Ireland, according to the HSE.[99] A man in his 30s is critically ill in St James's Hospital in Dublin with human swine flu (H1N1). The man, who is originally from Bratislava in Slovakia, was admitted to hospital late last week. He has been working in Ireland for several years.
Around 1,500 people visited GPs last week with suspected swine flu, three times more than the most recent figures released.
Director of the Health Protection Surveillance Centre Dr Darina O'Flanagan said the figure was included in the latest data from the Irish College of General Practitioners.
It represents 37 people per 100,000 and is three times more than figures released yesterday by the Department of Health.
Advertisement The Department said laboratory tests have confirmed 278 cases of the H1N1 virus have been reported but the actual number exceeds that total as family doctors report an increase in the number of cases they have been diagnosing in recent weeks.
Two patients who contracted human swine flu (H1N1) are still being treated in intensive care units.
Chief medical officer at the Department of Health Dr Tony Holohan said yesterday that the HSE expects some deaths from the virus, and further hospitalisations, over the coming weeks and months.
Dr Holohan said 12 people have been hospitalised so far.
A man in his 30s, who was admitted to St James's Hospital last week, remains 'critically ill' with the virus.
It is believed the man, who is originally from Bratislava in Slovakia, contracted the virus abroad. He has been living in Ireland for several years.
The hospital said that all necessary precautions were being taken and that the Health Service Executive and the Department of Health were being fully informed.[100]
Friday, 7 August 2009 18:00 A young Irish woman has died from human swine flu today at Tallaght Hospital in Dublin.
She is the first person to die from the virus here since the first cases emerged in this country in May.
Department of Health officials said this evening that the woman had an underlying medical condition.[101]
Monday, 17 August 2009.
The second death due to the swine flu virus has been reported. The victim is believed to have been living in the east of the country. The death toll currently stands at nine.
On October 1, two further deaths were announced, bringing the total fatalities to four.[102]

Italy's agriculture lobby, Coldiretti, warned against panic reaction, noting that farmers lost hundreds of millions of Euros due to consumer boycotts during the 2001 mad cow scare and the 2005 bird flu outbreak.[103]
A woman who returned from San Diego was hospitalised in Venice for suspected swine flu.[104]
As of 30 April, about 20 suspected cases of swine flu are monitored in Italy.[105]
On 2 May, Reuters confirmed that Italy had a case of the swine flu. It was recorded in a 50 year old man in Massa after he returned from Mexico City. However, he had very mild symptoms (i.e aches, coughing, but no fever) and is recovering well.
As of 26 July the amount of swine flu cases is 618 with community outbreaks contributing to the number.
On 4 September the first death was confirmed in Italy. On 19 September the second death was confirmed in Italy.
On July 24, the authorities in Kosovo announced that the samples of three suspected cases had been sent to the laboratory for analysis.[106] According to the authorities, the three cases had had contact with other people who were infected by the A/H1N1 virus. Two of them had previously been visited Switzerland and Sweden, and one of them was in the United Kingdom.
On July 28, the results of these three suspected cases showed that only the person, who recently was in the United Kingdom was infected with the swine flu.[107] This person was a 9-year-old child, living in the United Kingdom, who along with the family came to spend their vacation in Kosovo. The family arrived to the Pristina Airport from London, and during the flight, health inspectors recommended the child to see a doctor, once they arrived to Pristina.
On November 14, A First Death Was Confirmed In Kosovo.
On June 21, a woman, who had just returned from North America, was hospitalised. Symptoms were observed already when she was still in the plane. It was later confirmed that she has the swine flu. It was the first registered case in Latvia.[108]
In early November, after severe outbreak in Russia and Ukraine, the people suffering from the flu increased. On November 5, there were alone 10 new cases registered, increasing the total amount of cases to 63.[109] Just four days later, on November 9, the number reached 89 cases and the first death of H1N1 in Latvia was confirmed.[110][111] As more people got precautious and the pharmacies weren't supplied enough, already the next day for a moment they ran out of any profilactic drugs against influenza.[112] On November 11 the number of registered cases reached 132.[113] The next day, with another 33 new cases, the total amount reached already 165 people.[114]
It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled 2009 flu pandemic in Lithuania. (Discuss) (November 2009) |
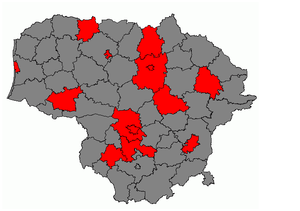
On 26 June Lithuania confirmed country's first influenza A (H1N1) in Tauragė (diagnosed by Lithuanian AIDS Centre).
On 2 July Lithuania confirmed two more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Tauragė and Vilnius.Total number of cases - 3
On 7 July Lithuania confirmed two more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Vilnius region.Total number of cases - 5
As of 11 of July, there was 25 possible cases. All of 25 cases was not confirmed.[115]
On 16 July Lithuania confirmed two more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Vilnius region.Total number of cases - 7
On 23 July Lithuania confirmed three more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Vilnius, Marijampolė and Kaunas region.Total number of cases - 10
On 27 July Lithuania confirmed two more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Vilnius region.Total number of cases - 12
On 29 July Lithuania confirmed three more cases of influenza A (H1N1).Total number of cases - 15
On 31 July Lithuania confirmed seven more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Vilnius, Panevėžys, Klaipėda, Kaunas, Prienai region.Total number of cases - 22.
As of 08 of August, there was 29 cases. Lithuania confirmed eight more cases of influenza, from Kaunas, Vilnius, Ukmergė rajono and Utena region. One of the infected - Israeli citizen, comed to Lithuania.
On 11 of August, Lithuania confirmed six more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Vilnius, Panevėžys, Pasvalys, Prienai region.Total number of cases - 35.
On 13 of August, Lithuania confirmed five more cases of influenza A (H1N1), in Akmenė and Šiauliai. Total number of cases - 40.
On days 14-22 of August, Lithuania confirmed seven more cases of influenza A (H1N1). Total number of cases - 47
As of 30 of August, there was 48 cases. Lithuania confirmed one more case of influenza.
As of 07 of September, there was 51 cases. Lithuania confirmed three more cases of influenza.
As of 03 of November, there was 57 cases. Lithuania confirmed six more cases of influenza.
As of mid-November there was 68 cases. Lithuania comfirmed eleven more cases of influenza.
As of 15 of November. Currently 127 confirmed cases of influenza.
As of 18 of November. First death of swine influenza. Victim is 14-year old boy, living in Kaunas region.
As of 23 of November. Second death of swine influenza. Victim is 40-year old male, living in Visaginas.
On November 24, epidemic is announced in whole Lithuania.
On 2nd of June, the first case of swine flu was detected in Luxembourg.
On 17 of September, the first death relative to swine flu was reported in Luxembourg.
On 18 of October, 785 people were confirmed to have the swine flu.
On 16 of November, a second person died of swine flu.[116]
On 27 April 2009, the government of the Republic of Macedonia prohibited all exports and imports of live pigs. Even though Macedonia is not affected from the Swine Flu, the government ordered a ten days health monitoring period for everybody that comes from an affected country.
On the 4 July, Macedonia confirmed the first two cases of virus A/H1N1.[117][118] As 16th of July Macedonia confirmed 10 cases of A\H1N1 virus
On the 2nd July 2009, two men were diagnosed with swine flu after a holiday in Girona, Spain. Malta had so far been the only country in European Union without swine flu cases. On the 3rd July 2009, 14 more cases were reported, bringing the total to 16. Most cases of swine flu in Malta have been mild, with only two hospital admissions as of 6 July 2009, when there were 24 confirmed cases. Ironically the largest number of cases have occurred in Għarb, Gozo; one of the smallest villages on the islands. On Tuesday 18 August the first death was reported; by then the total cases had increased to 244. On the 3rd of September the 2nd death flu was confirmed. The first death, an 82 year-old-woman, was suffering from a chronic disease whereas the second victim, a 63 year-old-man, had chronic health problems. The third victim, a 32 year-old-woman from Spain, that died at San Pawl il-Baħar area.
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
As of 10 November 2009, there are 132 confirmed cases, and 3 confirmed deaths in Moldova.
Monaco has reported its first confirmed case of swine flu on 17 June. The victim is a young Monegasque who returned from the United States. He was put in the isolation unit of L'archet Hospital.[119]
There are ten confirmed cases of H1N1 in Montenegro.[120]

The Netherlands National Institute for Public Health and the Environment advised any traveller who returned from Mexico since 17 April and developed a fever of 38.5 degrees Celsius (101.3 degrees Fahrenheit) within four days of arriving in the Netherlands to stay at home.[121] On 30 April, 2009 a three year old child tested positive for the swine flu. The child returned from Mexico to the Netherlands on 27 April, 2009. The parents tested negative to the swine flu.[122] The girl was very ill at first according to her parents,[123] but made a full recovery.[124] On 7 May a second case and a day later a third case of swine flu in the Netherlands were announced, concerning a 53 year old woman and a 52 year old man, respectively.[125] Both of them had returned from Mexico recently and are being treated with Tamiflu. The woman made a full recovery,[124] the man is doing well. There are no connections between each of the three cases. People who were seated close to the infected people in the plane were contacted and are being treated with Tamiflu as a precautionary measure. On 3 July, there were 134 confirmed cases in the Netherlands. The number rose to 273 on 24 July[126] and to 517 on 31 July. On 4 August the first person died (after being sick already), and the number of infected people rose to 912 on 7 August.[127] Only 20% of the patients have contracted the flu within the Netherlands. Many of the sick are people who fell ill during or after their holidays in countries like Spain, Greece and the United Kingdom. On November 6 the Netherlands National Institute for Public Health and the Environment says there are 5 more cases of dead (what brings the total on 17) and that there is an epemedic, witch means more then 51 on the 100,000 inhabitants has the flu, more then 2 weeks in a row. On 13 November 2009 the number of fatalities rose to 22.
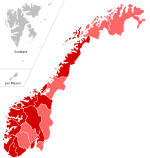
The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (FHI) updates their homepage with information about the swine flu outbreak in Norway every day at 10:00 (UTC).[128]
On 9 May, two Norwegian students from Oslo and Telemark, were confirmed to be infected with swine flu after they came home from studies in Mexico. None of them became seriously ill and they are recovering quickly. A member of one of their families is suspected of being infected as well.[129] One of them (the 20 year-old man from Oslo) have been confirmed completely recovered.[130] These are the first two cases of swine influenza in Norway. By the end of May, there were a total number of 7 infected in Norway.
On 4 June, a Norwegian woman from Vest-Agder who recently had been to the United States was confirmed with the swine influenza. The infected woman is recovering well. This is the ninth confirmed case of swine influenza.[128] By the end of June, the total number of infected by influenza A H1N1 rose to 33.
As of 20 July, The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (FHI) reports a total of 133 infected. 115 were infected abroad and 18 in Norway. Influenza A H1N1 has now reached 16 out of 19 fylker (counties). Most cases are found in Oslo (42), and in Sør-Trøndelag (30). So far, swine flu has not been registered in Finnmark, Nord-Trøndelag and in Hedmark
As of 24 July, 197 cases in 18 out of 19 fylker (counties). Most cases are found in Oslo (60), and in Sør-Trøndelag (36). So far, swine flu has not been registered in Hedmark.
As of 19 November, 23 deaths was reported in Norway.
On 22 October, it was confirmed by authorities that over 100,000 people in Norway had been infected with swine flu. 14 people are reported dead by October 29.

Polish Chief Sanitary Inspectorate (PIS) maintains a webpage[131] on the epidemic situation in Poland which includes daily updates on influenza A/H1N1 outbreak. As of 4 November it confirmed 187 cases, but there are no death cases.
As of 1 July, Poland has 19 confirmed cases, according to the National Institute of Public Health and the news channel TVN 24.[132][133] As of 22 June, at least 200 other patients had been previously investigated but tests turned out negative.[134][135] The Polish Foreign Ministry issued a statement on 25 April recommending that citizens avoid travel to affected areas until the outbreak is totally contained.
On 13 November, 37 years man died in Gdańsk. Epidemical station in Olsztyn confirmed that was A/H1N1[136].
In 16 November, 2009 it confirmed 237 cases, with two death cases.
On 18 November, 24 years woman died in Żywiec.
On 19 November, 47 years man died in Ciechanów.
In 20 November, 2009 it confirmed 400 cases, with five death cases.
In 23 November, 2009 it confirmed 586 cases, with nine death cases.
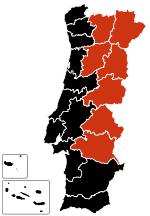
As of 4 May, there has been one confirmed case in Lisbon, Portugal, but it did not represent any concern, because the risk of transmission was no longer present at that time.[137]
On 1 June, Ana Jorge, the Portuguese Health Minister, has confirmed the second case in Portugal, a 33 year old man who travelled from the United States, first landing in Frankfurt, Germany. The case was reported at São João Hospital, Oporto.[138] On 30 June, five new cases were announced in Portugal elevating the total number of cases to 18.[139]
As of 2 July there have been 27 confirmed cases in Portugal.
On 3 July, 6 more cases were reported, making a total of 33 cases. As of 4 July, more 5 cases were confirmed, two of them internal transmitions (one in Azores, and the other one in Lisbon).
On 6 July, there have been confirmed 48 cases in Portugal.
As of 7 July, another 12 people infected were confirmed, making a total of 57 cases in the country. On this day, the first school was closed down for prevention, in Lisbon, as well as a kindergarten in Azores.
On 8 July, 4 more cases were confirmed, including the first in Braga district, making the total cases 61.
As of 14 July, there are a total of 96 confirmed cases in Portugal.[140] On this day, it was also announced that Faro's Hospital will join, on 15 July, the set of hospitals in the country capable of receiving patients infected with the A/H1N1 flu virus[141].
Government officials state the worst case scenario in Portugal is 25% infection with a mortality of 0.1% totaling 8700 casualties in Portugal.[142]
As of August 23 there have been 2244 people infected with the flu in Portugal.[143]
Portugal has the second higher tie of infections in Europe. 20,9 cases per 100,000 persons[144].
On 13 September 2009, Portugal had 9618 cases officially confirmed.
In total, as of September 24, there were 12709 cases confirmed in Portugal[145], and the first death was confirmed in the same day[146].
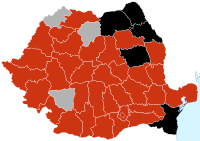
In Sâmbăteni, Arad County, a child of a year and six months and his mother who recently returned from a trip to Portugal and Spain were suspected of having contracted influenza A(H1N1). Tests returned negative.[147][148]
On Wednesday, 27 May a woman returning from America was confirmed with swine flu in Bucharest.[149]
As of August 11, there were 227 confirmed cases in 22 out of 41 counties of Romania.[150]
By mid-September the number of cases in Romania had risen to 296.
As of November, 2nd 2009 the number of cases was 555. No deaths.
As of November, 10th 2009 the number of cases was 1001. No deaths.
As of November, 19th 2009 the number of cases was 1651. No deaths.
The first confirmed case of death came on November, 23rd. [151]
As of November, 25th 2009 the number of cases was 2455 and 2 deaths.
| Federal subjects | Confirmed deaths |
|---|---|
| Total | 119 |
| Altai | 1[152] |
| Amur | 9[153] |
| Bashkortostan | 1[154] |
| Belgorod | 1[155] |
| Chelyabinsk | 9[156] |
| Chita | 3[157] |
| Irkutsk | 1[158] |
| Kamchatka | 1[159] |
| Kalmykia | 3[160] |
| Kaluga | 1[161] |
| Karelia | 1[162] |
| Khabarovsk | 2[163] |
| Khakassia | 1[164] |
| Komi | 1[165] |
| Krasnodar | 1[166] |
| Krasnoyarsk | 4[167] |
| Kursk | 1[168] |
| Lipetsk | 2[169] |
| Magadan | 1[170] |
| Moscow | 14[171] |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 10[172] |
| Novosibirsk | 1[173] |
| Omsk | 1[174] |
| Perm | 1[175] |
| Primorsky | 1[176] |
| Sakhalin | 1[177] |
| Saratov | 5[178] |
| Sakha | 1[179] |
| Smolensk | 3[180] |
| Sverdlovsk | 4[181] |
| Tatarstan | 3[182] |
| Tomsk | 1[183] |
| Tver | 1[184] |
| Vologda | 4[185] |
| Voronezh | 5[186] |
| Udmurtia | 3[187] |
| Zabaykalsky | 16[188] |
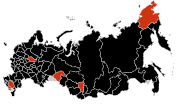
Russia has banned the import of pork meat from Guatemala, Honduras, Dominican Republic, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Nicaragua, Panama, El Salvador, 9 US States (Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Georgia, Kansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Florida) and all types of meat and meat products from Mexico and 5 US States (California, Texas, Kansas, New York and Ohio).[189][190][191]
The President instructed the regional governors to take urgent steps to prevent swine flu from spreading to Russia. Dmitry Medvedev also instructed the presidential plenipotentiary envoys in the federal districts to personally supervise the preventive measures to ensure the disease did not spread [in Russia] and stipulated monthly reports on the situation.[192]
On 1 May officials confirmed that two women who came from USA trip were suspected to have swine flu. Currently both are in hospital for further treatment.[193] As on 2 May, both tourists are reported not to be infected with new strain.[194]

A 71 year old tourist from Texas asked to be tested for swine flu at the Provincial hospital in Novi Sad, on 30 April. The results were negative.[195]
The first confirmed case in Serbia was announced on 24 June. The infected person is a 29-year old male citizen of Montenegro living in Belgrade who came back from a trip to Argentina two days earlier. As he travelled across Croatia and Germany with other people, they were put in semi quarantine.[196] The second case was confirmed on 25 June. The infected person is a 4-year old female citizen of Australia who was visiting Sombor. She had contact with 13 people whose health is being monitored.[197] On 26 June, three more cases were confirmed, out of which two were independent cases while one patient was infected from contact with the previously diagnosed patient.[198] In total 44 people were put under quarantine surveillance.[199] On 28 June, 6 more cases were confirmed - three were citizens of Canada, a mother and her 2- and 5-year old daughters, two were tourists returning from Australia and Egypt and one was infected from contact with the first flu case patient in Serbia.[200][201] Four more cases were confirmed on 1 July, one of the patients is a 73-year old US citizen, while two patients arrived from abroad, from Australia and the USA.[202] On 2 July, an Australian sportsman was diagnosed with flu.[203] On 6 July, the total number of infected patients rose to 26 with two more cases among the Universiade athletes, one from Uganda and one from Argentina.[204][205] On 7 July, four more cases were confirmed with a total number of 30 cases in Serbia.[206] On 8 July four more cases were confirmed with a total number of 34 cases.[207]
International events held in Serbia, 2009 Summer Universiade sport competition and EXIT music festival, led to a sudden increase to over 100 cases of flu in mid-July.[208]
On October 21, 2009 the first fatality related to the H1N1 in Serbia. The 46-year-old woman died in hospital in Kragujevac.
As of November 10, there are 258 people infected , and 7 death cases.[209]
On November 16, there are 295 officialy confirmed cases, with 11 people died as consequence of swine flu infection. [210]
First confirmed infection was confirmed on 19 June; a female who flew from New York to Venice and then drove by car to Slovenia. Institute of Public Health of the Republic of Slovenia has established a web site with information about H1N1 induced influenza. Status of this webpage is updated once a week. As of 5 October 2009, there were 263 people tested positive.[211][212]
On 27 April the Spanish Ministry of Health and Social Policy announced that a man in Castilla-La Mancha who had recently returned from Mexico had contracted the disease. The man, aged 23, had returned from Mexico on 22 April and had been quarantined on the 25th. This was the first confirmed case in Europe.[213]
The Spanish government is also observing other 35 possible swine flu cases in the Basque Country, Catalonia, the Balearic Islands, Andalusia, Murcia, Madrid and the Valencian Community.[214]
AENA, the Spanish state owned company who manages all Spanish airports and Air Traffic Control established a protocol for the flights coming from and to Spain from the affected areas.[215] Three patients who had just returned from Mexico were under observation in multiple regions of Spain.[103]
| County | Confirmed cases (deaths)[216] |
|---|---|
| Total | 1487 |
| Blekinge | 9 |
| Dalarna | 30 |
| Gotland | 4 |
| Gävleborg | 31 |
| Halland | 15 |
| Jämtland | 9 |
| Jönköping | 18 |
| Kalmar | 14 |
| Kronoberg | 32 |
| Norrbotten | 16 |
| Skåne | 220 (1) |
| Stockholm | 630 (3) |
| Södermanland | 34 (1) |
| Uppsala | 59 (2) |
| Värmland | 11 |
| Västerbotten | 54 |
| Västernorrland | 36 (2) |
| Västmanland | 29 (1) |
| Västra Götaland | 198 (1) |
| Örebro | 8 (2) |
| Östergötland | 30 (1) |
On 28 April, at least eighteen Swedish people were tested for swine flu after returning from trips in Mexico and the USA, but the results were negative.[217][218] On 29 April two people, recently returned from Mexico with flu like symptoms were tested.[219]
As of 6 May, the Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control confirms 1 case of influenza A(H1N1). 186 negative test results have been reported. No suspected cases remain to be analysed.[220]
The number of confirmed cases has reached 2 in Sweden, with 435 negative cases reported as of May 15.[221]
A third case was confirmed on Friday, May 15th, and reported on the following Saturday, where the patient, a woman in her sixties, has recovered. In all of the 3 cases the influenza was contracted in the USA.[222]
A fourth case was confirmed 28 May, influenza was contracted in the USA.[223]
As of July 19, 274 cases has been confirmed. On July 20, the number had risen to 322 confirmed cases and to 340 on July 21. 362 cases had been reported on July 22, 390 on July 23 and 408 as of July 24.
Three regions have reported more than 20 cases; Stockholm county with 144, Skåne country with 78 and Västra Götaland with 71.
42 of the 408 cases were contracted domestically.[224]
A 22 year old man in Norrköping is hospitalised with a life threatening condition, requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.[225]
In August, a 37 year old man in Uppsala was the first to die of H1N1 influenza in Sweden. The second case was in September, a 55 year old man in Västerås. On October 31, a three-year old boy died in a hospital after first being turned down treatment even though he suffered several of the obvious symptoms.[226]

The first suspicious case was officially confirmed on 27 April. A young man returning from holiday in Mexico informed his family doctor about fever and flu-like symptoms. He was immediately put under quarantine in a hospital. 8 more people are under observation. A container of inactive swine flu virus samples packed in dry ice exploded on a Swiss train, injuring one person but posing no other risks to humans.[227]
Switzerland has confirmed its first case of swine flu in a 19-year-old student who returned from Mexico on 30 April. The state hospital in Baden said in a statement that the National Influenza Centre in Geneva confirmed the disease shortly after the student was mistakenly released from hospital day before.[228]
Switzerland has confirmed its second case of swine flu in a young woman of 24. She was returning from a trip to Mexico and USA. She is now in the Hospital in Bern.[229]
On 24 May, a third case of swine flu has been announced in a woman who came back from Washington and is resident in Basel.
As of 26 June, there are 49 confirmed cases in ten cantons, with five cases having been community-transmitted.[230]
As of 19 November a total of three persons have been reported to die from swine flu, a baby and two women, all of them with prexisting health problems of other origin.

From the data collected from 43 European countries, on 13th November 2009 the WHO announced that Ukraine had the 8th highest infection rate of A/H1N1 (following Norway, Sweden, Bulgaria, Moldova, Iceland, Ireland and Russia) in Europe. Furthermore, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Poland, various regions of Russia, Northern Ireland, Turkey, Finland, and Ukraine had a high sickness rate of А/Н1N1 flu.[231][232]
On 5 June, 2009 the first case of the virus was officially confirmed in Ukraine. The patient concerned, a 24-year-old Ukrainian citizen, had arrived from New York via Paris at Kiev's Boryspil Airport on May 29, 2009.[233] Before that imports of pork and live pigs from all affected countries had been banned. The ban applied to all shipments after April 21, 2009.[234]
A second swine flu case (in Ukraine) was confirmed on September 29, 2009.[235]
On October 27, 2009, an outbreak of influenza-like illness and deaths of seven people from its complications have been reported in Ternopil region.[236][237] Schools and universities in Ternopil were closed.[236]
On 30 October, 2009, Ukrainian Ministry of Health confirmed 11 new cases of swine flu, and the first death from it. An epidemic was declared and nine out of 25 regions of Ukraine were put under quarantine[238][239], on November 5, 2009 Kirovohrad became the 10th[240]. Due to the outbreak public meetings, including cinema,[241] were forbidden nationwide and all educational institutions were closed for three weeks (subject to extension if necessary).[242][243] Conscription into the Ukrainian army was also suspended,[244] and the Professional Football League of Ukraine postponed football matches in the Ukrainian First League and Second League.[245] Since November 20, 2009 regional commissions can impose or cancel quarantines in higher educational establishments.[246] On November 23 in the regions where the epidemic threshold for flu and respiratory infections wasn't reached educational institutions opened again[247]; for instance on November 25, 2009 all educational institutions and kindergartens in Kiev resumed work.[248]
A large shipment of Tamiflu was delivered from Switzerland to Ukraine on November 1, 2009 for distribution among hospitals for free.[249]
According to the Ukrainian Health Ministry as of November 2, 2009 the number of people who have died of influenza and respiratory diseases has reached 60, the number of people suffering from the flu is 200,000[249] and about 22 patients tested positive for swine flu[250]. On November 5, 2009 the Ministry said the death toll of patients with flu-related and acute respiratory illnesses (ARI) had jumped to 95, a total of 633, 877 cases of flu-related and ARI have been registered from October 29 through November 5 and 15 of 31 patient samples sent to London for laboratory analysis tested positive for the H1N1 virus.[251]
As of November 6, 2009 28 cases of swine flu have been confirmed in Ukraine, of which 13 patients had died.[252] The Ukrainian health ministry estimates that Ukraine requires 12.5 million doses of vaccine against swine flu.[253] As of November 10, 2009 67 cases of swine flu have been confirmed in Ukraine, of which 14 patients had died. 1,031,587 people in Ukraine had contracted flu or a flu-like illness by then and of them 52,742 where in hospital at the time[254] while there where 174 deaths from from acute respiratory viral infections [255]. If at least one person has been diagnosed with swine flu in any of Ukraine's regions everyone diagnosed with the flu in that region receives swine flu treatment.[254]
According to Jukka Pukkila, head of a WHO international mission to Ukraine, "there is no difference concerning the rate of A/H1N1 flu infection in Ukraine compared to other countries".[256] WHO tests of the H1N1 pandemic virus samples taken from Ukrainian patients haven't exposed any signs of mutation.[257]
According to the Ukrainian Health Ministry the average daily number of legalities caused by flu in 2009 was lower than in 2008, when it was 18.[258]
According to Chief State Sanitary Doctor Oleksandr Bilovol, the mass refusal by Ukrainians to be vaccinated (after several persons allegedly died after vaccinations in 2008[259] and 2009[260]) was partly the cause for the epidemic.[243]
A total of 22 countries have assisted Ukraine in fighting its flu epidemic.[261]
 United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies
United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies

Samples from suspected cases have been analysed by the National Institute for Medical Research in London, which is also examining samples of the U.S. strain of the disease.[263]
On 25 April 2009, a member of British Airways cabin crew was taken to Northwick Park Hospital in Harrow and quarantined after falling ill with flu-like symptoms on a flight from Mexico City though he was later found not to have swine flu.[264]
The first cases were confirmed on 27 April in passengers returning from Mexico.
On 1 May the first UK person to person transmission was confirmed. Graeme Pacitti, 24, of Falkirk, picked up the virus after contact with the UK's first cases Iain and Dawn Askham.[265][266]
It was reported on 26 May that a man who has been confirmed with swine flu was critically ill.[267]
On 28 May, people at a Home Office building in Sheffield were quarantined, it was feared someone had caught swine flu on a recent trip to Canada. In fact, not one, but three people had caught it, the person who had been to Canada, one from someone who recently had stayed in Acapulco, Mexico, and one from someone who recently had stayed in London.
On 6 June, the total of swine flu cases hit 508 with 3 people in intensive care in hospital. On 7 June, the total of swine flu cases hit 541 with 3 people in intensive care and one woman with swine flu gave birth in hospital.
As of 11 June, 822 cases of swine flu were clinically confirmed.[268]
On 13 June, the total of swine flu cases hit 1,122 with 4 people in intensive care in hospital. The following day, the first death from swine flu in the United Kingdom is reported from Scotland, making the first death from swine flu in Europe.
By the 9 July there were over 9,718 cases of swine flu and the rate of cases was going up increasingly.[clarification needed]
By the 16 July, over 10000 cases of Swine flu were confirmed, with the British government suggesting a possible 55000 new cases in the week leading up to the 16. There were 29 deaths confirmed, although the majority of these had 'underlying health issues'. (26 in England and 3 in Scotland)
Timeline
References and notes
| a. | ^ Template:Kosovo-note |
- ^ "Europeans urged to avoid Mexico and US as swine flu death toll exceeds 100". Guardian. April 27, 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ EU considers halting all Mexico travel- commissioner[dead link]
- ^ "Albania reports first swine flu case" (in Template:En icon). SETimes.com. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Neue Verdachtsfälle in Vorarlberg und Wien" (in Template:De icon). Orf.at. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Austria confirms first case of swine flu April 29". Alertnet.org. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "www.influenza.be/nl/persberichten/2009-04-27_Communique-touslescassontnegatifs_nl.pdf" (PDF).
- ^ "Griep A/H1N1: een bevestigde geval" (PDF).
- ^ Deux nouveaux cas confirmés de grippe A/H1N1 en Belgique , Deux nouveaux cas confirmés de grippe A/H1N1 en Belgique
- ^ Griep A/H1N1: zesde geval in België , Griep A/H1N1: een zesde geval in België
- ^ Griep A/H1N1: zevende geval in België , Griep A/H1N1: een zevende geval in België
- ^ Achtste geval van A/H1N1-griep in ons land op dinsdag 26 mei
- ^ Eerste dode Mexicaanse griep in België[dead link]
- ^ [1]
- ^ Novi grip stigao u BiH!
- ^ [2]
- ^ http://sofiaecho.com/2009/06/01/728450_swine-flu-case-confirmed-in-bulgaria
- ^ "First swine flu death in Bulgaria : Health". Archived from the original on 2009-10-03. Retrieved 2009-10-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Svinjska gripa i u Hrvatskoj?". Index.hr. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Net.hr". Net.hr. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Potvrđeno: Kod djeteta nije utvrđen virus svinjske gripe". Index.hr. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Nalaz iz Londona je bio lažan: u Hrvatskoj nema svinjske gripe". Jutarnji list (in Croatian). June 15, 2009. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
- ^ "Ovaj put nije lažna uzbuna: Svinjska gripa stigla u Hrvatsku!". dnevnik.hr. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- ^ "Prva smrt od svinjske gripe u Hrvatskoj: "Epidemija će trajati duže od godinu dana!"". index.hr. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
- ^ "Erste bestätigte Fälle in Dänemark und Hongkong". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "Dansker smittet med svineinfluenza". Berlingske Tidende. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ BBC News, "Swine flu 'shows drug resistance'", 16:15 GMT, Monday, 29 June 2009 17:15 UK (accessed 30 June 2009)
- ^ Villak, Hetlin (2009-05-29). "Esimene seagripi juhtum Eestis sai lõpliku kinnituse" (in Estonian). Eesti Päevaleht. Retrieved 2009-11-09.
- ^ Villak, Hetlin (2009-07-03). "Kaks uut seagripi juhtumit said ametliku kinnituse" (in Estonian). Eesti Päevaleht. Retrieved 2009-11-09.
- ^ Villak, Hetlin (2009-11-11). "Seagripp levib juba ilmselt Eesti-siseselt" (in Estonian). Eesti Päevaleht. Retrieved 2009-11-11.
- ^ Kalmus, Kertu (2009-11-20). "Eestis on kinnitatud kokku 269 uue gripi haigusjuhtu" (in Estonian). Eesti Päevaleht. Retrieved 2009-11-22.
- ^ Aug, Tuuli (2009-11-23). "Eestis suri 13-aastane laps seagrippi" (in Estonian). Eesti Päevaleht. Retrieved 2009-11-23.
- ^ http://www.yle.fi/uutiset/news/2009/10/finland_sees_first_signs_of_swine_flu_epidemic_1086910.html
- ^ http://www.ktl.fi/portal/suomi/terveyden_ammattilaisille/tartuntataudit_ja_epidemiat/influenssa_a_h1n1v_raportoidut_tapaukset
- ^ "Sikainfluenssa lisätään tartuntatautiasetukseen - Uutisarkisto - Mediuutiset" (in Template:Fi icon). Mediuutiset.fi. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ http://www.tekniikkatalous.fi/kommentit/uutiskommentti/article311467.ece?s=r&wtm=-28072009
- ^ "Pääkaupunkiseudulla varmistui kaksi sikainfluenssatapausta". Hs.fi.
- ^ http://www.tilannehuone.fi/h1n1/ Map of cases in Finland
- ^ http://www.savonsanomat.fi/uutiset/sikainfluenssa/suomessa-jo-satoja-sikainfluenssatartuntoja/469463 Savon Sanomat, 27.7.2009: Hundreds of H1N1-cases in Finland
- ^ http://www.uusisuomi.fi/kotimaa/70303-h1n1-vyoryy-suomeen-kaksi-taistelee-hengityskoneessa Two serious cases in Finland (2.9). Accessed 2009-09-13. Archived 2009-09-16.
- ^ http://www.savonsanomat.fi/uutiset/sikainfluenssa/sikainfluenssa-levi%C3%A4%C3%A4-yh%C3%A4-pohjois-suomessa/494605
- ^ http://www.yle.fi/uutiset/news/2009/10/finland_faces_first_swine_flu_death_1110950.html
- ^ [3]
- ^ http://yle.fi/uutiset/teksti/kotimaa/2009/11/sikainfluenssa_koko_maassa_-_kaikki_rokotetaan_1154761.html Probably tens of thousands infected in Finland (November 12, 2009, only in Finnish)
- ^ http://yle.fi/uutiset/teksti/kotimaa/2009/11/sikainfluenssa_koko_maassa_-_kaikki_rokotetaan_1154761.html
- ^ http://www.iltalehti.fi/sikainfluenssa/2009111510597320_si.shtml Finnish National Institute for Health and Welfare will no longer report deaths caused by H1N1 (only in Finnish)
- ^ "Vingt cas suspects de grippe porcine en cours d'étude en France". Reuters. 2009-04-28. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ "Cas humains de nouvelle grippe à A(H1N1). Point au 30 avril 2009 - 17h00". InVS. 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Grippe A: deux cas avérés en France". Lexpress.fr. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Two new cases of swine flu confirmed in France". MySinchew.com. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "France confirms a fifth case of swine flu". France24. Retrieved 2009-05-06.
- ^ http://www.invs.sante.fr/display/?doc=presse/2009/communiques/Cas_grippe_h1n1_confirme_060509/index.html
- ^ http://www.lemonde.fr/planete/article/2009/05/06/un-cinquieme-cas-de-grippe-a-en-france_1189414_3244.html#ens_id=1185166
- ^ http://www.invs.sante.fr/display/?doc=surveillance/grippe_dossier/points_h1n1/grippe_A_h1n1_070509/index.html
- ^ http://www.grog.org/cgi-files/db.cgi?action=bulletin_grog
- ^ "Spiegel Online: Bielefeld - Entwarnung bei Schweinegrippe-Verdachtsfällen". Spiegel Online. 2009-04-27. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "Spiegel Online: Erster Schweinegrippe-Fall in Deutschland". Spiegel Online. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ "Bavaria reports first case of swine flu in Germany". Reuters. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ a b c "Virologen stellen drei Schweinegrippe-Fälle in Deutschland fest". Spiegel online. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ "Spiegel Online: Erste Mensch-zu-Mensch-Infektion mit Schweinegrippe in Deutschland". Spiegel Online. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "Spiegel Online: Virologen erwarten weitere Schweinegrippe-Infektionen in Deutschland". Spiegel Online. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "Spiegel Online: Zweite Mensch-zu-Mensch-Infektion in Deutschland". Spiegel Online. 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Schweinegrippe erreicht Brandenburg". Focus Online. 2009-05-03. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ "Spiegel Online: Neunter Schweinegrippe-Fall in Deutschland". Spiegel Online. 2009-05-05. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ^ "Welt Online: Zehnter Fall von Schweinegrippe in Deutschland". Welt Online. 2009-05-07. Retrieved 2009-05-07.
- ^ "Spiegel Online: ZH1N1-Virus erstmals aus den USA eingeschleppt". Spiegel Online. 2009-05-08. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "Welt Online: Zwölfter deutscher Schweinegrippe-Fall bestätigt". Welt Online. 2009-05-11. Retrieved 2009-05-12.
- ^ "Welt Online: Zwei neue Schweinegrippe-Fälle in Deutschland". Welt Online. 2009-05-15. Retrieved 2009-05-17.
- ^ "Welt Online: Düsseldorferin an Schweinegrippe erkrankt". Welt Online. 2009-05-20. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ^ "Situationseinschätzung zur Neuen Influenza (Situation assessment to the new influenza)" (in German). 2009-05-22. Retrieved 2009-05-22.
- ^ [4]
- ^ http://www.kathimerini.gr/4dcgi/_w_articles_kathremote_1_21/05/2009_280697
- ^ http://www.forbes.com/feeds/afx/2009/05/18/afx6435498.html
- ^ "Τέταρτο κρούσμα της νέας γρίπης Α στην Ελλάδα Μία 23χρονη Ελληνίδα είναι το νέο κρούσμα της νέας γρίπης στην χώρα. Το Κέντρο Αναφοράς Γρίπης Νοτίου Ελλάδας (Ινστιτούτο Παστέρ) επιβεβαίωσε το τέταρτο κρούσμα" (in Greek). Kathimerini. 2009-05-29. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
{{cite news}}: line feed character in|title=at position 46 (help) - ^ "ΑΝΑΚΟΙΝΩΣΗ ΤΥΠΟΥ-ΥΠ. ΥΓΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΚΗΣ ΑΛΛΗΛΕΓΓΥΗΣ. Επιβεβαιώνεται ότι ο τελικός αριθμός των ατόμων που έχουν προσβληθεί από τον νέο ιό, ανέρχεται σε 20, εκ των οποίων οι 8 έχουν ιαθεί πλήρως" (in Greek). Retrieved 2009-06-14.
{{cite news}}: line feed character in|title=at position 56 (help) - ^ "Ακόμη δύο κρούσματα της νέας γρίπης εντοπίστηκαν στη χώρα - Στα 25 τα περιστατικά" (in Greek). in.gr. 2009-06-17. Retrieved 2009-060-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ http://www.mohaw.gr/ministry/deltia_tupou/dekapente-epipleon-kroysmata
- ^ "Στα 290 τα κρούσματα της γρίπης Α στην Ελλάδα" (in Greek). Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ^ "Σε 323 ανέρχονται τα κρούσματα της Νέας Γρίπης" (in Greek).
{{cite news}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Text "http://www.mohaw.gr/ministry/deltia_tupou/se-323-anerchontai-ta-kroysmata-tis-neas-gripis" ignored (help) - ^ "Swine flu - Virus strain may arrive in Hungary in a few days, official says". MTI. 2009-04-29. Retrieved on 2009-04-30
- ^ http://www.news24.com/News24/World/SwineFlu/0,,2-10-2501_2524471,00.html
- ^ [5]. 2009-06-18. Retrieved on 2009-06-18
- ^ "Var bara tímaspursmál" (in Template:Is icon). mbl.is. Retrieved 2009-05-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Fyrsta tilfelli inflúensu A(H1N1) greint á Íslandi" (in Template:Is icon). Landlæknisembættið. Retrieved 2009-05-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Nýtt flensutilfelli á Íslandi".
- ^ "Annað tilfelli inflúensu A(H1N1) staðfest á Íslandi".
- ^ мsland. "RзV - TvЖ hugsanleg svМnaflensutilfelli" (in Template:Is icon). Ruv.is. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Landlæknisembættið - Fréttir". Landlaeknir.is. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ a b "Fylgst með farþegum". mbl.is. Retrieved 2009-04-28.
- ^ . 2008 http://www.influensa.is/lisalib/getfile.aspx?itemid=3515. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Health Service Executive of Ireland: A(H1N1) Flu Information
- ^ Northern Ireland Health Services
- ^ RTÉ News: Second Swine Flu case reported in Ireland
- ^ RTE News
- ^ IOL News
- ^ http://www.rte.ie/news/2009/0602/swineflu.html
- ^ RTÉ News: Child treated for swine flu in Mayo
- ^ RTÉ News: Kerry swine flu tests negative
- ^ http://www.herald.ie/breaking-news/national-news/government-to-provide-free-swine-flu-jab-1806257.html
- ^ http://www.rte.ie/news/2009/0728/swineflu.html
- ^ http://www.rte.ie/news/2009/0729/swineflu.html
- ^ http://www.rte.ie/news/2009/0807/swineflu.html
- ^ "RTÉ News: Two further swine flu deaths confirmed". Archived from the original on 2009-10-03. Retrieved 2009-10-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Jordans Frank (April 26, 2009). "Swine flu fears prompt quarantine plans, pork bans". The Associated Press. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ "Possible Swine Flu Case in Venice". Javno.com. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "About 20 suspected cases of swine flu monitored in Italy". News.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Gripi i derrave arrin edhe në vendin tonë?". RTK Live. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
- ^ "Nuk ka arsye për panik pas shfaqjes së virusit A/H1N1 në Kosovë". RTK Live. Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ "Latvijā atklāts pirmais saslimušais ar tā dēvēto 'cūku gripu'"
- ^ Latvijā diennaktī lielākais saslimušo skaits ar cūku gripu
- ^ Latvijā reģistrēti jau 89 ‘cūku gripas’ gadījumi
- ^ No ‘cūku gripas’ mirušajai bijušas arī citas kaites
- ^ Zāļu tirgotājiem beigušies pretgripas medikamenti
- ^ Jaunā gripa konstatēta vēl 22 cilvēkiem; mediķi aicina necelt paniku
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
latviawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lietuvos Rytas. ""Lietuvoje užsikrėtusiųjų kiaulių gripu skaičius gali padidėti iki trisdešimties"" (in Template:Lt icon). lrytas.lt. Retrieved 2009-07-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ http://www.grippe.public.lu/actualite/index.html |title=Confirmed swine flu in Luxembourg(French)
- ^ http://a1.com.mk/vesti/default.aspx?VestID=110965 |title=Confirmed swine flu in Macedonia(on Macedonian)
- ^ Deng Shasha (2009-04-29). "Macedonian senior officials monitored for possible swine flu".
- ^ Monaco swine flu
- ^ Saopštenje Ministarstva zdravlja povodom oboljelih od virusa gripa A(H1N1)
- ^ Frank Jordans (2009-04-25). "WHO declares international concern over swine flu". Associated Press.
- ^ "Mexicaanse griep in Nederland". ANP. 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Meisje is aan de beterende hand". Algemeen Dagblad. 2009-05-04. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ a b "Derde geval Mexicaanse griep in Nederland". NU.nl. 2009-05-08. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "Third H1N1 flu case confirmed". Radio Netherlands. 2009-05-08. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "Forse stijging Mexicaanse griep". ANP. 2009-07-24.
- ^ "Nieuwe Influenza A (H1N1)". RIVM. 2009-08-07. Retrieved 2009-08-07.
- ^ a b http://www.fhi.no/eway/default.aspx?pid=233&trg=MainLeft_5799&MainArea_5661=5799:0:15,5008:1:0:0:::0:0&MainLeft_5799=5544:76458::1:5800:1:::0:0
- ^ "Svineinfluensa påvist i Norge". TV 2 Nyhetene. 2009-05-10. Retrieved 2009-05-11.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ http://www.aftenposten.no/nyheter/iriks/article3068354.ece
- ^ "Główny Inspektorat Sanitarny". 2009-07-08. Retrieved 2009-07-09.
- ^ "Stan na dzień 5 maja 2009 r. z godziny 11:00". 2009-05-05. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ^ "Wirus zaatakował 1003 osoby". 2009-05-04. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "W Polsce nie stwierdzono świńskiej grypy". tvn24.pl. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ "Para wróciła z Meksyku, trafiła na obserwację". interia.pl. Retrieved 2009-04-28.
- ^ "Ostatecznie: 37-latek z Gdańska miał A/H1N1". 2009-11-13. Retrieved 2009-11-13.
- ^ http://ultimahora.publico.clix.pt/noticia.aspx?id=1378416&idCanal=62
- ^ Second case of swine flu in Portugal
- ^ http://diariodigital.sapo.pt/news.asp?section_id=62&id_news=396657
- ^ http://www.jornaldigital.com/noticias.php?noticia=18908
- ^ http://ultimahora.publico.clix.pt/noticia.aspx?id=1391763&idCanal=62
- ^ http://dn.sapo.pt/inicio/portugal/interior.aspx?content_id=1311206
- ^ http://www.portaldasaude.pt/portal/conteudos/a+saude+em+portugal/ministerio/comunicacao/comunicados+de+imprensa/relatorio+xxviviii.htm
- ^ 20,9 cases per 100,000 people in Portugal
- ^ Correio Da Manha. "Correio da Manhã". Archived from the original on 2009-09-26. Retrieved 2009-09-23.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Primeira morte confirmada em Portugal". Archived from the original on 2009-09-26. Retrieved 2009-09-23.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "UPDATE Suspiciunea de gripa porcina in cazul copilului din Arad a fost infirmata (April 30)". Hotnews.ro. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "O mamă şi un copil din Arad, suspecţi de gripă porcină. Streinu Cercel: "E o alarmă falsă" (April 30)". Antena3.ro. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ http://www.hindustantimes.com/StoryPage/StoryPage.aspx?sectionName=HomePage&id=83a8a7bc-fd37-48c8-8902-ff49813cab8a&Headline=Romania+announces+first+confirmed+swine+flu+case
- ^ http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/files/pdf/Health_topics/Situation_Report_090811_1700hrs.pdf
- ^ http://www.realitatea.net/romania-a-anuntat-primul-deces-cauzat-de-gripa-porcina_688063.html
- ^ http://www.regions.ru/news/2253637/
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://translate.googleusercontent.com/translate_c?hl=en&sl=ru&tl=en&u=http://www.pravda.ru/news/accidents/05-11-2009/329370-gripp-0&rurl=translate.google.com&usg=ALkJrhj08pfkFA9nLDm9IJ_A6xUIwZFVRA
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091106/192225376.html
- ^ http://www.nr2.ru/258218.html
- ^ http://english.ruvr.ru/2009/10/28/2125133.html
- ^ http://txt.newsru.com/russia/23nov2009/irkah1n1.html
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://txt.newsru.com/russia/23nov2009/irkah1n1.html
- ^ http://txt.newsru.com/russia/19nov2009/tatargtipp.html
- ^ http://www.regions.ru/news/2252388/
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091106/192239769.html
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091109/192697144.html
- ^ http://kuban.kp.ru/daily/24397.4/574118/
- ^ http://krsk.kp.ru/daily/24397/574562/
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091106/192211041.html
- ^ http://www.tatar-inform.ru/news/2009/11/13/193300/
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091120/194677612.html
- ^ http://www.newsnn.ru/portal/content/view/42284/39/
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091110/192849514.html
- ^ http://www.regions.ru/news/2254399/
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091120/194655093.html
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091110/192771990.html
- ^ http://www.novayagazeta.ru/news/708584.html
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1228536.html
- ^ http://www.tatar-inform.ru/news/2009/11/19/194201/
- ^ http://txt.newsru.com/russia/19nov2009/tatargtipp.html
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091106/192225376.html
- ^ http://www.regions.ru/news/2253141/
- ^ http://www.regnum.ru/news/1226838.html
- ^ http://www.rian.ru/flu/20091118/194348899.html
- ^ http://www.regions.ru/news/2253141/
- ^ http://translate.google.com/translate?u=http://www.rian.ru/flu_news/20091118/194311578.html&sl=ru&tl=en
- ^ "Russia-ban on meat import" (in Russian). Ria Novosti. April 27, 2009.
- ^ "О мерах Россельхознадзора в связи со вспышками гриппа, вызванного вирусом H1N1, в Мексике и США" (in Russian). Rosselkhoznadzor. April 26, 2009.
- ^ "В дополнение к указанию от 26.04.2009 № ФС-2-02/179 о запрете на ввоз поднадзорных грузов в связи с распространением гриппа H1N1" (in Russian). Rosselkhoznadzor. April 26, 2009.
- ^ "Dmitry Medvedev instructed Russia's regional authorities to take urgent measures to prevent the spread of swine flu in Russia" (in Russian). kremlin.ru. April 27, 2009.
- ^ "Две россиянки госпитализированы с подозрением на "калифорнийский грипп"" (in Russian). Channel One. 0May 1 2009.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "У гражданок России, прилетевших накануне из США, не обнаружили опасной инфекции" (in Russian). Channel One. 0May 2 2009.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Nema meksičkog gripa u Novom Sadu" (in Template:Sr icon). Rts.rs. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Novi grip i u Srbiji" (in Template:Sr icon). Politika. Retrieved 2009-06-25.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Potvrđen slučaj novog gripa i u Somboru
- ^ Tri nova slučaja gripa H1N1
- ^ Pod lekarskim nadzorom 44 osobe
- ^ U Srbiji još pet slučajeva gripa
- ^ Za 24 sata novih šest zaraženih
- ^ Četiri nova slučaja gripa
- ^ Igre počele s gripom!
- ^ Obolela još dvojica učesnika Univerzijade
- ^ U Srbiji 26 obolelih od novog gripa
- ^ "Od novog gripa u Srbiji obolelo 30 ljudi". RTS. 2009-07-08. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ Prvi slučaj novog gripa na Egzitu
- ^ U Srbiji preko 100 slučajeva gripa
- ^ Могуће проглашење епидемије
- ^ [6]
- ^ V Sloveniji doslej potrjenih 263 primerov okužbe z novim virusom gripe A (H1N1)
- ^ "Informacije o bolezni, ki jo povzroča novi virus gripe". Institute of Public Health of the Republic of Slovenia, Ljubljana. Retrieved 2009-08-22.
- ^ "Europe's first swine flu case confirmed in Spain". Agence France-Presse. April 27, 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "Sanidad confirma un caso de gripe porcina en Albacete". eitb.com. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "Sanitary protocol to follow, recommended by AENA" (PDF) (in Spanish). aena.es. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ http://smi.se/nyainfluensan/analys-av-nyainfluensan/
- ^ TT. "Ingen konstaterad smitta i Sverige | Inrikes | SvD" (in Template:Sv icon). Svd.se. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ TT. "Nya misstänkta fall i Sverige var negativa | Sverige | DN" (in Template:Sv icon). DN.se. Retrieved 2009-04-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Dalarnas tidningar (2009-04-29). "Två misstänks ha influensan i Dalarna | Sverige | SVT" (in Template:Sv icon). svt.se. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ SMI. "Utförda analyser i Sverige" (in Template:Sv icon). smittskyddsinstitutet.se. Retrieved 2009-05-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ SMI. "Utförda analyser i Sverige" (in Template:Sv icon). smittskyddsinstitutet.se. Retrieved 2009-05-16.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Dagens Nyheter. "Tredje fallet av influensa bekräftat i Sverige" (in Template:Sv icon). dn.se. Retrieved 2009-05-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ SMI. "Utförda analyser i Sverige" (in Template:Sv icon). smittskyddsinstitutet.se. Retrieved 2009-05-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ SMI. "Utförda analyser i Sverige" (in Template:Sv icon). smittskyddsinstitutet.se. Retrieved 2009-07-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ -DI. "Livshotande för influensasjuk 22-åring" (in Template:Sv icon). di.se. Retrieved 2009-07-20.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ SvD - Pojke med svininfluensa avled
- ^ "Verdachtsfall von Schweinegrippe im Aargau (Panorama, NZZ Online)". Nzz.ch. 2009-02-24. Retrieved 2009-04-28.
- ^ "Switzerland confirms 1st case of swine flu". Thejakartapost.com. 2009-03-30. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Grippe A/H1N1: 2e cas confirmé en Suisse" (in French).
- ^ "Bundesamt für Gesundheit - Grippe A(H1N1)" (in German).
- ^ WHO: A/H1N1 infection rate in Ukraine not the highest in Europe, Kyiv Post (November 19, 2009)
- ^ EuroFlu Weekly Electronic Bulletin 13.11.2009
- ^ First case of A (H1N1) virus officially confirmed in Ukraine, says Health Ministry, Interfax-Ukraine (June 5, 2009)
- ^ The world response to flu crisis, BBC News, 2009-04-28. Retrieved on 2009-04-30.
- ^ Second А(H1N1) swine flu case confirmed in Ukraine Kyiv Post (September 29, 2009)
- ^ a b "Seven die of unknown flu virus in Ukraine's Ternopol region". ITAR-TASS. 2009-10-27. Retrieved 2009-10-27.
- ^ "Seven people died of ILI complications in Ternopil region" (in Template:Ru icon). Inter TV-channel. 2009-10-27. Retrieved 2009-10-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ В Украине началась эпидемия "свиного" гриппа. Стране грозит карантин Podrobnosti.ua (September 30, 2009)
- ^ "Quarantine ordered". KyivPost. 2009-10-30. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
- ^ Kirovohrad region became next to impose quarantine, Kyiv Post (November 5, 2009)
- ^ Flu epidemic causes panic in Ukraine, Euranet (October 30, 2009)
- ^ Ukraine shuts schools, halts campaigning over H1N1, Reuters (October 30, 2009)
- ^ a b Chief doctor: mass refusal by citizens to be vaccinated partly to blame for A(H1N1) epidemic, Kyiv Post (November 1, 2009)
- ^ Draft into Ukrainian army suspended due to flu epidemic, Interfax-Ukraine (October 31, 2009)
- ^ %5b%5b:Template:Uk icon%5d%5d "Епідемія переносів [оновлюється] (Epidemic causes postponements (renewed))". PFL. 2009-10-30. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
{{cite news}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ Ukrainians still running high risk of contracting flu, respiratory infections, says first-vice premier, Interfax-Ukraine (November 20, 2009)
- ^ Education institutions in regions with low rate of flu cases to resume working on Nov. 23, Kyiv Post (November 21, 2009)
- ^ Quarantine ends in educational institutions of Kyiv on Nov. 25, Kyiv Post (November 21, 2009)
- ^ a b Ukrainian Hospitals To Distribute Tamiflu For Free, Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (November 2, 2009)
- ^ Ukraine Mystery Outbreak Sparks WHO Concern as Disease Spreads, Bloomberg L.P. (November 2, 2009)
- ^ Update: more death, illness, Kyiv Post (November 5, 2009)
- ^ Twenty-eight swine flu cases confirmed in Ukraine, 13 die of swine flu, says emergencies ministry, Interfax-Ukraine (November 6, 2009)
- ^ Health ministry estimates Ukraine needs 12.5 million doses of vaccine against A (H1N1), Kyiv Post (November 6, 2009)
- ^ a b Government: Ukraine records 67 swine flu cases, 14 of them fatal, Kyiv Post (November 10, 2009)
- ^ Health Ministry confirms 174 deaths, acute respiratory viral infections, Kyiv Post (November 10, 2009)
- ^ Health Ministry sees no need to publish information about confirmed cases of A/H1N1 flu, Kyiv Post (November 16, 2009)
- ^ World Health Organization: Initial tests show no mutation in H1N1 virus samples from Ukraine, Kyiv Post (November 17, 2009)
- ^ Health Ministry: Flu, respiratory infections kill 315 people in Ukraine, Kyiv Post (November 16, 2009)
- ^ Teenager’s death spurs vaccination questions, fears, Kyiv Post (October 29, 2008)
- ^ Vaccinations against flu proving to be hard sell, Kyiv Post (November 12, 2009)
- ^ Twenty-two countries ready to assist Ukraine in fighting flu epidemic, Kyiv Post (November 17, 2009)
- ^ HPA. "HPA Weekly epidemiological updates archive". Retrieved 2009-08-06.
- ^ "NIMR scientists discuss swine-like human influenza A H1N1". National Institute for Medical Research. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ^ "Cabin crew member in hospital after flight from swine flu-struck Mexico". Guardian. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "UK | Tests confirm flu transfer in UK". BBC News. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ HPA. "First case of onward human to human swine flu transmission in England confirmed". Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/glasgow_and_west/8068992.stm
- ^ "Update on confirmed swine flu cases". Health Protection Agency. 2009-06-11. Retrieved 2009-06-12.