Antipodes: Difference between revisions
m →top: Typo fixing, replaced: straight line line → straight line using AWB |
→Air travel between antipodes: updated TNG-WRE flight distances; Great Circle Mapper currently indicates 10,800 nm and 20,001 km; updated corresponding text too |
||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
Among flights with fuel stop and crew-change stop but still same flight number, [[Air New Zealand]] has one of the longest, [[Auckland]]–[[Los Angeles]]–[[London]], {{convert|19240|km|mi}}. |
Among flights with fuel stop and crew-change stop but still same flight number, [[Air New Zealand]] has one of the longest, [[Auckland]]–[[Los Angeles]]–[[London]], {{convert|19240|km|mi}}. |
||
A hypothetically perfect antipode flight would be [[Tangier Ibn Battouta Airport]], [[Morocco]] ([[IATA]]: TNG) to [[Whangarei Aerodrome]], [[New Zealand]] (IATA: WRE), whose designated locators are {{ |
A hypothetically perfect antipode flight would be [[Tangier Ibn Battouta Airport]], [[Morocco]] ([[IATA]]: TNG) to [[Whangarei Aerodrome]], [[New Zealand]] (IATA: WRE), whose designated locators are {{c |
||
10,800 nmi (20,001 km)<!-- EACH TO 5-DIGIT PRECISION --> apart,<ref>[http://www.gcmap.com/mapui?P=tng-wre%0D%0A&R=&PM_q=%2A&PM=%2A&MS=wls&MP=&MC=&PC=red&PW=&PT=&RC=navy&RW=&RS=&DU=nm&DM=&SG=&SU=kts&EV=&EU=kts Great Circle Mapper] Access date: 2017-09-24,</ref> the maximum possible distance, but their actual runways cross in projection. However, with only a length of 3599 ft, Whangarei's runway is too short to accommodate any current ({{as of|2015|lc=y}}) commercial jet airliner, especially one with the required range. Taipei and Asuncion are 19,912 km apart; Santiago and Xian are 19,897 km apart; Madrid and Auckland are 19,590 km apart; Buenos Aires and Beijing are 19,260 km apart; Johannesburg and Honolulu are 19,188 km apart; New York City and Perth are 18,700 km apart.{{citation needed|date=November 2015}} |
|||
==List of antipodes== |
==List of antipodes== |
||
Revision as of 01:47, 24 September 2017
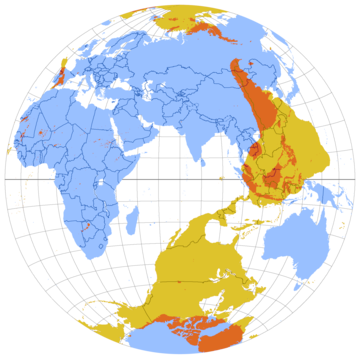

In geography, the antipode (/ænˈtɪpədiː/) of any spot on Earth is the point on Earth's surface diametrically opposite to it; the antipodes of a region similarly represent the area opposite it. A pair of points antipodal (/ænˈtɪpədəl/) to each other are situated such that a straight line connecting the two would pass through Earth's center. Such points are as far away from each other as possible, a great-circle distance of 10,800 nautical miles (20,000 km).
In the Northern Hemisphere, "the Antipodes" may be used to refer to Australia and New Zealand, and "Antipodeans" to their inhabitants.[1] Geographically, the antipodes of Britain and Ireland are in the Pacific Ocean, south of New Zealand. This gave rise to the name of the Antipodes Islands of New Zealand, which are close to the antipode of London at about 50°S 179°E / 50°S 179°E. The antipodes of Australia are in the North Atlantic Ocean, while parts of Spain, Portugal, and Morocco are antipodal to New Zealand.
Approximately 15%[citation needed] of land territory is antipodal to other land, representing approximately 4.4% of the Earth's surface. The largest antipodal land masses are the Malay Archipelago, antipodal to the Amazon Basin and adjoining Andean ranges; east China and Mongolia, antipodal to Chile and Argentina; and Greenland and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, antipodal to East Antarctica. There is a general paucity of antipodal land because the Southern hemisphere has fairly little land, and of that, the antipodes of Australia are in the North Atlantic Ocean, while the antipodes of Africa are in the Pacific Ocean.
Geography
The antipode of any place on the Earth is the place that is diametrically opposite it, so a line drawn from the one to the other passes through the centre of the Earth and forms a true diameter.[2] For example, the antipodes of New Zealand's lower North Island lie in Spain. Most of the Earth's land surfaces have ocean at their antipodes, this being a consequence of most land being in the land hemisphere.
The singular antipode is a back-formation (c. 1540-50 CE) from the plural antipodes,[3] which in Greek is the plural of the singular antipous.
The antipode of any place on Earth is distant from it by 180° of longitude and as many degrees to the north of the equator as the original is to the south (or vice versa); in other words, the latitudes are numerically equal, but one is north and the other south.[2] The maps shown here are based on this relationship; they show a Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection of the Earth, in yellow, overlaid on which is another map, in blue, shifted horizontally by 180° of longitude and inverted about the equator with respect to latitude.
Noon at one place is midnight at the other (ignoring daylight saving time and irregularly shaped time zones) and, with the exception of the tropics, the longest day at one point corresponds to the shortest day at the other, and midwinter at one point coincides with midsummer at the other. Sunrise and sunset do not quite oppose each other at antipodes due to refraction of sunlight.
Mathematical description
If the geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) of a point on the Earth's surface are (φ, θ), then the coordinates of the antipodal point are (−φ, θ ± 180°). This relation holds true whether the Earth is approximated as a perfect sphere or as a reference ellipsoid.
In terms of the usual way these geographic coordinates are given, this transformation can be expressed symbolically as
- x° N/S y° E/W ↦ x° S/N (180 − y)° W/E,
that is, for the latitude (the North/South coordinate) the magnitude of the angle remains the same but N is changed to S and vice versa, and for the longitude (the East/West coordinate) the angle is replaced by its supplementary angle while E is exchanged for W. For example, the antipode of the point in China at 37° N 119° E (a few hundred kilometres from Beijing) is the point in Argentina at 37° S 61° W (a few hundred kilometres from Buenos Aires).
Etymology
The word antipodes comes from the Greek: ἀντίποδες (antípodes),[4] plural of ἀντίπους (antipous), "with feet opposite (ours)",[5] from ἀντί (antí, “opposite”) + πούς (poús, “foot”). The Greek word is attested in Plato's dialogue Timaeus, already referring to a spherical Earth, explaining the relativity of the terms "above" and "below":
For if there were any solid body in equipoise at the centre of the universe, there would be nothing to draw it to this extreme rather than to that, for they are all perfectly similar; and if a person were to go round the world in a circle, he would often, when standing at the antipodes of his former position, speak of the same point as above and below; for, as I was saying just now, to speak of the whole which is in the form of a globe as having one part above and another below is not like a sensible man.
— Plato[6]
The term is taken up by Aristotle (De caelo 308a.20), Strabo, Plutarch and Diogenes Laertius, and was adopted into Latin as antipodes. The Latin word changed its sense from the original "under the feet, opposite side" to "those with the feet opposite", i.e. a bahuvrihi referring to hypothetical people living on the opposite side of the Earth. Medieval illustrations imagine them in some way "inverted", with their feet growing out of their heads, pointing upward.
In this sense, Antipodes first entered English in 1398 in a translation of the 13th century De Proprietatibus Rerum by Bartholomeus Anglicus, translated by John of Trevisa:
Yonde in Ethiopia ben the Antipodes, men that haue theyr fete ayenst our fete.
(In Modern English: Yonder in Ethiopia are the Antipodes, men that have their feet against our feet.)
Historical significance
Pomponius Mela, the first Roman geographer, asserted that the earth had two habitable zones, a North and South one, but that it would be impossible to get into contact with each other because of the unbearable heat at the equator.

From the time of St Augustine, the Christian church was skeptical of the notion. Augustine asserted that "it is too absurd to say that some men might have set sail from this side and, traversing the immense expanse of ocean, have propagated there a race of human beings descended from that one first man."[7]
In the Early Middle Ages, Isidore of Seville's widely read encyclopedia presented the term "antipodes" as referring to antichthones (people who lived on the opposite side of the Earth), as well as to a geographical place; these people came to play a role in medieval discussions about the shape of the Earth.[8] In 748, in reply to a letter from Saint Boniface, Pope Zachary declared the belief "that beneath the earth there was another world and other men, another sun and moon" to be heretical. In his letter, Boniface had apparently maintained that Vergilius of Salzburg held such a belief.[9][10][11][12]
The antipodes being an attribute of a spherical Earth, some ancient authors used their perceived absurdity as an argument for a flat Earth.[13] However, knowledge of the spherical Earth was widespread during the Middle Ages, only occasionally disputed — the medieval dispute surrounding the antipodes mainly concerned the question whether people could live on the opposite side of the earth: since the torrid clime was considered impassable, it would have been impossible to evangelize them. This posed the problem that Christ told the apostles to evangelize all mankind; with regard to the unreachable antipodes, this would have been impossible. Christ would either have appeared a second time, in the antipodes, or left the damned irredeemable. Such an argument was forwarded by the Spanish theologian Alonso Tostado as late as the 15th century and "St. Augustine doubts" was a response to Columbus's proposal to sail westwards to the Indies.[14]
The author of the Norwegian book Konungs Skuggsjá, from around 1250, discusses the existence of antipodes. He notes that (if they exist) they will see the sun in the north in the middle of the day and that they will have seasons opposite those of the Northern Hemisphere.
The earliest surviving account by a European who had visited the Southern Hemisphere is that of Marco Polo (who, on his way home in 1292, sailed south of the Malay Peninsula). He noted that it was impossible to see the star Polaris from there.
The idea of dry land in the southern climes, the Terra Australis, was introduced by Ptolemy and appears on European maps as an imaginary continent from the 15th century. In spite of having been discovered relatively late by European explorers, Australia was inhabited very early in human history; the ancestors of the Indigenous Australians reached it at least 50,000 years ago.
Air travel between antipodes
There are no non-stop scheduled flights between any two antipodal locations by commercial airline service—or anything even close. There is currently no commercial aircraft capable of travelling between antipodes at full load non-stop. (The current record holder Boeing 777-200LR's maximum range is rated at 17,395 km.) There are also regulations regarding pilot's work time, so relief crewmembers would be needed.[citation needed]
The longest non-stop scheduled flight was the Singapore Airlines Flight 21 between Newark, New Jersey and Singapore (discontinued as of November 2013), covering 15,343 km (9,534 miles) in about 18.5 hours flight time, and this was far from a journey between nearly antipodal locations.
Among flights with fuel stop and crew-change stop but still same flight number, Air New Zealand has one of the longest, Auckland–Los Angeles–London, 19,240 kilometres (11,960 mi).
A hypothetically perfect antipode flight would be Tangier Ibn Battouta Airport, Morocco (IATA: TNG) to Whangarei Aerodrome, New Zealand (IATA: WRE), whose designated locators are {{c 10,800 nmi (20,001 km) apart,[15] the maximum possible distance, but their actual runways cross in projection. However, with only a length of 3599 ft, Whangarei's runway is too short to accommodate any current (as of 2015[update]) commercial jet airliner, especially one with the required range. Taipei and Asuncion are 19,912 km apart; Santiago and Xian are 19,897 km apart; Madrid and Auckland are 19,590 km apart; Buenos Aires and Beijing are 19,260 km apart; Johannesburg and Honolulu are 19,188 km apart; New York City and Perth are 18,700 km apart.[citation needed]
List of antipodes
Earth
Around 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by oceans, and seven-eighths of the Earth's land is confined to the land hemisphere, so the majority of locations on land do not have land-based antipodes.
The two largest human inhabited antipodal areas are located in East Asia (mainly eastern China) and South America (mainly northern Argentina and Chile). The Australian mainland is the largest landmass with its antipodes entirely in ocean, although some locations of mainland Australia and Tasmania are close to being antipodes of islands (Bermuda, Azores, Puerto Rico) in the North Atlantic Ocean. The largest landmass with antipodes entirely on land is the island of Borneo, whose antipodes are in the Amazon rainforest.
Cities
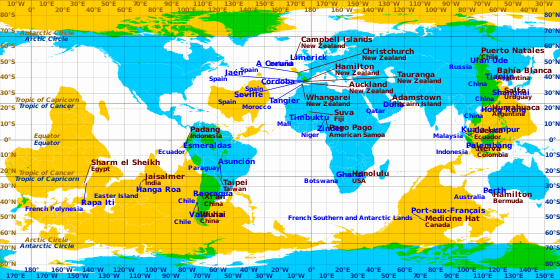
Exact or almost exact antipodes:
- Christchurch (New Zealand) — A Coruña (Spain)
- Hamilton (New Zealand) — Córdoba (Spain)
- Hong Kong — La Quiaca (Argentina)
- Lianyungang (China) — Junín (Argentina)
- Madrid (Spain) — Weber (New Zealand)
- Mangawhai (New Zealand) — Rock of Gibraltar (Overseas British Territory)
- Masterton (New Zealand) — Segovia (Spain)
- Nelson (New Zealand) — Mogadouro (Portugal)
- Padang (Indonesia) — Esmeraldas (Ecuador)
- Palembang (Indonesia) — Neiva (Colombia)
- Pekanbaru (Indonesia) — Machachi (Ecuador)
- Tauranga (New Zealand) — Jaén (Spain)
- Ulan Ude (Russia) — Puerto Natales (Chile)
- Wellington (capital of New Zealand) — Alaejos (Valladolid, Spain)
- Whangarei (New Zealand) — Tangier (Morocco)
- Wuhai (China) — Valdivia (Chile)
- Wuhu (China) — Rafaela (Argentina)
To within 100 km, with at least one major city (population of at least 1 million):
- Auckland (New Zealand) — Seville and Málaga (Andalusia, Spain)
- Beijing (China) — Bahía Blanca (Argentina)
- Nanjing (China) — Rosario (Argentina)
- Shanghai (China) — Salto (Uruguay)
- Taipei (Taiwan) — Asunción (Paraguay)
- Tianjin (China) — Bahía Blanca (Argentina)
- Xi'an (China) — Santiago, or more precisely Rancagua or San Bernardo (Chile)
Taiwan (formerly called Formosa) is partly antipodal to the province of Formosa in Argentina.
Other major cities or capitals close to being antipodes:
- Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) — Tokyo (Japan); the host cities of successive Summer Olympic Games (2016 and 2020), ~1,450 km
- Beijing (China) — Buenos Aires (Argentina); both cities have populations in the millions, and have been twinned since 1983, ~540 km
- Shanghai (China) — Buenos Aires (Argentina); Buenos Aires is actually closer (~380 km) to the antipode of Shanghai (Salto, Uruguay) than to the antipode of Beijing (Bahía Blanca)
- Tongchuan (China) — Licantén (Chile)
- Bogotá (Colombia) — Jakarta (Indonesia), ~200 km
- Guayaquil (Ecuador) — Medan (Indonesia), ~220 km
- Phnom Penh (Cambodia) — Lima (Peru), ~220 km
- Dili (Timor-Leste) — Paramaribo (Suriname), ~310 km
- Irkutsk (Russia) — Punta Arenas (Chile)
- Suva (Fiji) — Timbuktu (Mali)
- Melbourne and Canberra (Australia) - Azores, Atlantic Ocean (Portugal)
- Cherbourg (France) — Antipodes Islands (New Zealand)
- Pago Pago (American Samoa) — Zinder (Niger)
- Barranquilla (Colombia) — Christmas Island (Australia)
- Doha (Qatar) — Pitcairn Island (Overseas British Territory)
- Hué and Da Nang (Vietnam) — Arequipa (Peru)
- Manila (Philippines) — Cuiabá (Brazil)
- Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia) — Cuenca (Ecuador)
- San Juan (Puerto Rico) — Karratha (Australia)
- Limerick (Ireland) — Campbell Islands (New Zealand)
- Arrecife, Lanzarote (Canary Islands) — Norfolk Island
- Sharm el Sheikh (Egypt) — Rapa Iti (French Polynesia)
- Bangkok (Thailand) — Lima (Peru)
- Quito (Ecuador) — Singapore
- Perth (Australia) — Hamilton (Bermuda)
- Montevideo (Uruguay) — Gwangju (South Korea)
Cities and geographic features
Gibraltar is approximately antipodal to Te Arai Beach about 85 km north of Auckland, New Zealand. This illustrates the old yet correct saying that the sun never sets on the British Empire; the sun still does not set on the Commonwealth of Nations.
The northern part of New Caledonia, an overseas territory of France, is antipodal to some thinly populated desert in Mauritania, a part of the former French West Africa. Portions of Suriname, a former Dutch colony, are antipodal to Sulawesi, an Indonesian island spelled Celebes when it was part of the Netherlands East Indies. Luzon, the largest island of the Philippines, is antipodal to eastern Bolivia. As with the British Empire, the sun set neither on the French Empire, the Dutch Empire, nor the Spanish Empire at their peaks.
Santa Vitória do Palmar, the most southerly town of more than 10,000 people in Brazil, is antipodal to Jeju Island, the southernmost territory of South Korea.
The Big Island of Hawaii is antipodal to the Okavango Delta in Botswana, with the island's largest city, Hilo, antipodal to Nxai Pan National Park.
Easter Island is antipodal to Desert National Park, 35 km from Jaisalmer, India.
Desolate Kerguelen Island is antipodal to an area of thinly inhabited plains on the border between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan and the US state of Montana.
The Heard Island and McDonald Islands, an uninhabited Australian territory, is antipodal to an area in central Saskatchewan, including the towns of Leask and Shellbrook.
St. Paul Island and Amsterdam Island are antipodal to thinly populated parts of the eastern part of the US state of Colorado.
South Georgia Island is antipodal to the northernmost part of Sakhalin Island.
Lake Baikal is partially antipodal to the Straits of Magellan.
The Russian Antarctic research base Bellingshausen Station is antipodal to a land location in Russian Siberia.
Rottnest Island, off the coast of Western Australia, is approximately antipodal to Bermuda.
Flores Island, the westernmost island of the Azores, is nearly antipodal to Flinders Island between Tasmania and the Australian mainland.
Point Nemo, the point in the South Pacific Ocean most distant from any other land, is precisely opposite a desolate piece of desert in western Kazakhstan.
By definition, the North Pole and the South Pole are antipodes.
As can be seen on the purple/blue map, the Pacific Ocean is so large that it stretches halfway around the world; parts of the Pacific off the coast of Peru are antipodal to parts of the same ocean off the coast of Southeast Asia.
Countries
The following countries are opposite more than one other country. (Antarctica is considered separately from any territorial claims.)
Countries matching up with just one other country are Morocco, Spain, Chad, Libya, Cameroon (with the Cook Islands of New Zealand); Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia (with French Polynesia); Senegal (Vanuatu); the UAE (Pitcairn); Ghana, Ivory Coast (Tuvalu); Burkina Faso (Rotuma in Fiji); Guinea (Solomon Islands); India (Easter Island); Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Thailand (all with Peru); Singapore (Ecuador); Brunei, Palau, Micronesia (all with Brazil); Venezuela and Suriname (Indonesia).
Of these, the larger countries which are entirely antipodal to land are the Philippines, Malaysia, Taiwan, Fiji, Vanuatu, Brunei, and Samoa. Chile was as well prior to its expansion into the Atacama with the War of the Pacific.
Extraterrestrial examples
In a number of cases on extraterrestrial bodies in the Solar System, unusual geologic features (e.g., jumbled terrain or unique volcanic constructs) are located antipodal to major impact basins. It has been hypothesized that this results from focusing of some of the seismic waves (p-waves and surface waves) produced by an impact at its antipode.[16]
- Caloris Basin - "Weird Terrain" (Mercury)[16]
- Mare Orientale - Mare Marginis (The Moon)[16]
- Mare Imbrium - Mare Ingenii (The Moon)[16]
- Hellas Planitia - Alba Mons (Mars)[17][18][19]
- Isidis Planitia - Noctis Labyrinthus (Mars)[17][18][19]
In popular culture
Literature
- New Zealand writer Mark Price undertook a tour in 2005–06 of the length of New Zealand and its land antipodes in Morocco and Spain, from Kerikeri 35°13′01.4″S 173°57′46.6″E / 35.217056°S 173.962944°E (near Larache and Lixus, Morocco 35°13′01.4″N 6°02′13.4″W / 35.217056°N 6.037056°W) to Cathedral Square, Christchurch 43°31′52.2″S 172°38′08.8″E / 43.531167°S 172.635778°E (near Foz, Spain 43°31′52.2″N 7°21′51.2″W / 43.531167°N 7.364222°W).[20]
Television
- A gag in American animated television series was "digging all the way to China".[citation needed]
- On the popular TV show Angel, the Deeper Well is a hole that goes through the world, with its entrance in the Cotswolds in England and its antipode in New Zealand.
- The May 19, 2008, official Lost audio podcast gave credence to a theory that the Island (where the show is set) is located at Tunisia's antipode, in the south Pacific east of New Zealand.[citation needed]
- "The Gathering", a fourth series episode of Torchwood, refers to Shanghai and Buenos Aires as being antipodes of each other. The tenth and final episode notes more precisely that they are "perfect antipodes" while acknowledging that is only accurate "give or take a hundred miles or so."
- At the closing ceremonies of the Rio 2016 Olympics, they used the antipodes as a tool to invite viewers to the Tokyo 2020 Olympics. There was an image of the video game character Mario using his pipes to travel between Tokyo and Rio, arriving at the closing ceremonies.[citation needed]
Webcasts
- In 2006, Ze Frank challenged viewers of his daily webcast the show with zefrank to create an "Earth sandwich" by simultaneously placing two pieces of bread at antipodal points on the Earth's surface. The challenge was successfully completed by viewers in Spain and New Zealand.[21]
See also
- Antichthones
- Antipodal hotspot
- Antipodal point
- Antipodes Islands
- Clime
- Pole of inaccessibility
- Spherical Earth
References
- ^ Compact Oxford English Dictionary, 2008, "Antipodes" Access date: 2010-02-21.
- ^ a b One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Antipodes". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 2 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 133–134.
- ^ "antipode". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 2016-09-02.
- ^ ἀντίποδες, Liddell and Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ ἀντίπους Liddell and Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ Plato, Timaeus 63a, translated by Benjamin Jowett, (Indianapolis: Bobbs Merrill, 1949).[1]
- ^ De Civitate Dei, Book XVI, Chapter 9 — Whether We are to Believe in the Antipodes, translated by Rev. Marcus Dods, D.D.; from the Christian Classics Ethereal Library at Calvin College
- ^ Stevens, Wesley M. (1980), "The Figure of the Earth in Isidore's "De natura rerum"", Isis, 71 (2): 274, doi:10.1086/352464, JSTOR 230175
- ^ Loughlin, James (1907), Antipodes in The Catholic Encyclopedia
{{citation}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ ¥Hasse, Wolfgang; Reinhold, Meyer, eds. (1993), The Classical Tradition and the Americas, Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, ISBN 3-11-011572-7
{{citation}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Moretti, Gabriella (1993), The Other World and the 'Antipodes'. The Myth of Unknown Countries between Antiquity and the Renaissance, p. 265. In Hasse & Reinhold (1993, pp.241–84).
{{citation}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ MGH, Epistolae Selectae, 1, 80, pp. 178–9; translation in M. L. W. Laistner, Thought and Letters in Western Europe, pp. 184–5.; see also Jaffe, Biblioth. rerum germ., III, 191
- ^ Lactantius (311), "The Divine Institutes, Book III, Chapter XXIV", in Rev. Alexander Roberts, D.D.; James Donaldson, LL.D. (eds.), THE ANTE-NICENE FATHERS, vol. VII, W.B.Eerdmans Publishing Co., Grand Rapids, MI (published 1979), pp. 94–95, retrieved 20 July 2013
- ^ Ferdinand Columbus (1543). The Life of the Admiral Chrispher Columbus (Translation by Benjamin Keen ed.). London, The Folio Society, 1960. p. 62.
- ^ Great Circle Mapper Access date: 2017-09-24,
- ^ a b c d Schultz, P. H.; Gault, D. E. (1975). "Seismic effects from major basin formations on the moon and Mercury". The Moon. 12 (2): 159–177. Bibcode:1975Moon...12..159S. doi:10.1007/BF00577875.
- ^ a b Peterson, J. E. (March 1978). "Antipodal Effects of Major Basin-Forming Impacts on Mars". Lunar and Planetary Science. IX: 885–886. Bibcode:1978LPI.....9..885P. Retrieved 2012-07-04.
- ^ a b Williams, D. A.; Greeley, R. (1991). "The Formation of Antipodal-Impact Terrains on Mars" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Science. XXII: 1505–1506. Retrieved 2012-07-04.
- ^ a b Williams, D. A.; Greeley, R. (1994). "Assessment of antipodal-impact terrains on Mars". Icarus. 110: 196–202. Bibcode:1994Icar..110..196W. doi:10.1006/icar.1994.1116.
- ^ Price, Mark Price (2009). Antipodes: The Ingenious and Exhilarating Expedition of El Lider and La Campana. Dunedin: Longacre Press. ISBN 978 1 877460 36 4.
- ^ "If the earth were a sandwich". the show with zefrank.
External links
- Antipodes Map Interactive map which draws a tunnel to the other side of the world.
- findLatitudeAndLongitude, interactive tool to show antipodes
- 3D dual globe schematic 3D representation of the earth and the anti-earth on the same place.
- Map Tunneling Tool Tunnel to the Other Side of the Earth
- Calculate the other side of the world
- Antipodes An online and photographic project which pairs webcam images from places on opposite sides of the globe.
- Map Tunneller Find out what part of the earth is directly below you using the interactive maps
- Antipodal hotspots and bipolar catastrophes: Were oceanic large-body impacts the cause?
