From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Sympathomimetic and mydriatic agent
Berefrine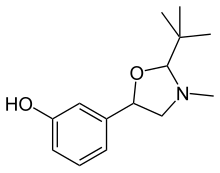 |
|
| ATC code | |
|---|
|
3-[(5R)-3-Methyl-2-(2-methyl-2-propanyl)-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl]phenol
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
|
| Formula | C14H21NO2 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 235.327 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
CC(C)(C)C1N(C[C@H](O1)c2cccc(c2)O)C
|
InChI=1S/C14H21NO2/c1-14(2,3)13-15(4)9-12(17-13)10-6-5-7-11(16)8-10/h5-8,12-13,16H,9H2,1-4H3/t12-,13?/m0/s1 Key:ORIOFGXXYYXLNY-UEWDXFNNSA-N
|
Berefrine (INN, USAN), also known as burefrine, is a sympathomimetic and mydriatic agent that was never marketed.[1][2] It is an oxazolidine prodrug of phenylephrine, and hence, an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist.[1]
References
|
|---|
| α1 | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- Abanoquil
- Ajmalicine
- Alfuzosin
- Anisodamine
- Anisodine
- Atiprosin
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., brexpiprazole, clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone)
- Benoxathian
- Beta blockers (e.g., adimolol, amosulalol, arotinolol, carvedilol, eugenodilol, labetalol)
- Buflomedil
- Bunazosin
- Corynanthine
- Dapiprazole
- Domesticine
- Doxazosin
- Ergolines (e.g., acetergamine, ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, lisuride, nicergoline, terguride)
- Etoperidone
- Fenspiride
- Hydroxyzine
- Indoramin
- Ketanserin
- L-765,314
- mCPP
- Mepiprazole
- Metazosin
- Monatepil
- Moxisylyte
- Naftopidil
- Nantenine
- Neldazosin
- Niaprazine
- Niguldipine
- Pardoprunox
- Pelanserin
- Perlapine
- Phendioxan
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Phentolamine
- Phenylpiperazine antidepressants (e.g., hydroxynefazodone, nefazodone, trazodone, triazoledione)
- Piperoxan
- Prazosin
- Quinazosin
- Quinidine
- Silodosin
- Spegatrine
- Spiperone
- Talipexole
- Tamsulosin
- Terazosin
- Tiodazosin
- Tolazoline
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, maprotiline, mianserin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, clomipramine, doxepin, imipramine, trimipramine)
- Trimazosin
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Urapidil
- WB-4101
- Zolertine
|
|---|
|
|---|
| α2 | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- 1-PP
- Adimolol
- Amesergide
- Aptazapine
- Atipamezole
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine, brexpiprazole, clozapine, lurasidone, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, zotepine)
- Azapirones (e.g., buspirone, gepirone, ipsapirone, tandospirone)
- BRL-44408
- Buflomedil
- Cirazoline
- Efaroxan
- Esmirtazapine
- Fenmetozole
- Fluparoxan
- Idazoxan
- Ketanserin
- Lisuride
- mCPP
- Mianserin
- Mirtazapine
- NAN-190
- Pardoprunox
- Phentolamine
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Piperoxan
- Piribedil
- Rauwolscine
- Rotigotine
- Setiptiline
- Spegatrine
- Spiroxatrine
- Sunepitron
- Terguride
- Tolazoline
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Yohimbine
|
|---|
|
|---|
| β | |
|---|
|

