Tennessine
| Tennessine | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈtɛnəsiːn/[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | semimetallic (predicted)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mass number | [294] (data not decisive)[a] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Tennessine in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 17 (halogens) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p5 (predicted)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 7 (predicted) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid (predicted)[4][5] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 623–823 K (350–550 °C, 662–1022 °F) (predicted)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 883 K (610 °C, 1130 °F) (predicted)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 7.1–7.3 g/cm3 (extrapolated)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: (none) (−1), (+5) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 138 pm (predicted)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 156–157 pm (extrapolated)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | synthetic | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 54101-14-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after Tennessee region | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Vanderbilt University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (2010) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of tennessine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Tennessine is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Ts and atomic number 117. It is the second-heaviest known element and the penultimate element of the 7th period of the periodic table.
The discovery of tennessine was officially announced in Dubna, Russia, by a Russian–American collaboration in April 2010, which makes it the most recently discovered element as of 2023[update]. One of its daughter isotopes was created directly in 2011, partially confirming the results of the experiment. The experiment itself was repeated successfully by the same collaboration in 2012 and by a joint German–American team in May 2014. In December 2015, the Joint Working Party of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP), which evaluates claims of discovery of new elements, recognized the element and assigned the priority to the Russian–American team. In June 2016, the IUPAC published a declaration stating that the discoverers had suggested the name tennessine after Tennessee, United States, a name which was officially adopted in November 2016.[b]
Tennessine may be located in the "island of stability", a concept that explains why some superheavy elements are more stable compared to an overall trend of decreasing stability for elements beyond bismuth on the periodic table. The synthesized tennessine atoms have lasted tens and hundreds of milliseconds. In the periodic table, tennessine is expected to be a member of group 17, the halogens.[c] Some of its properties may differ significantly from those of the lighter halogens due to relativistic effects. As a result, tennessine is expected to be a volatile metal that neither forms anions nor achieves high oxidation states. A few key properties, such as its melting and boiling points and its first ionization energy, are nevertheless expected to follow the periodic trends of the halogens.
Introduction
Superheavy elements, also known as transactinide elements, transactinides, or super-heavy elements, or superheavies for short, are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 104.[10] The superheavy elements are those beyond the actinides in the periodic table; the last actinide is lawrencium (atomic number 103). By definition, superheavy elements are also transuranium elements, i.e., having atomic numbers greater than that of uranium (92). Depending on the definition of group 3 adopted by authors, lawrencium may also be included to complete the 6d series.[11][12][13][14]
Glenn T. Seaborg first proposed the actinide concept, which led to the acceptance of the actinide series. He also proposed a transactinide series ranging from element 104 to 121 and a superactinide series approximately spanning elements 122 to 153 (though more recent work suggests the end of the superactinide series to occur at element 157 instead). The transactinide seaborgium was named in his honor.[15][16]
Superheavies are radioactive and have only been obtained synthetically in laboratories. No macroscopic sample of any of these elements has ever been produced. Superheavies are all named after physicists and chemists or important locations involved in the synthesis of the elements.
IUPAC defines an element to exist if its lifetime is longer than 10−14 seconds, which is the time it takes for the atom to form an electron cloud.[17]
The known superheavies form part of the 6d and 7p series in the periodic table. Except for rutherfordium and dubnium (and lawrencium if it is included), even the longest-lived known isotopes of superheavies have half-lives of minutes or less. The element naming controversy involved elements 102–109. Some of these elements thus used systematic names for many years after their discovery was confirmed. (Usually the systematic names are replaced with permanent names proposed by the discoverers relatively soon after a discovery has been confirmed.)
Introduction
Synthesis of superheavy nuclei
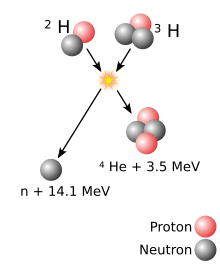
A superheavy[d] atomic nucleus is created in a nuclear reaction that combines two other nuclei of unequal size[e] into one; roughly, the more unequal the two nuclei in terms of mass, the greater the possibility that the two react.[23] The material made of the heavier nuclei is made into a target, which is then bombarded by the beam of lighter nuclei. Two nuclei can only fuse into one if they approach each other closely enough; normally, nuclei (all positively charged) repel each other due to electrostatic repulsion. The strong interaction can overcome this repulsion but only within a very short distance from a nucleus; beam nuclei are thus greatly accelerated in order to make such repulsion insignificant compared to the velocity of the beam nucleus.[24] The energy applied to the beam nuclei to accelerate them can cause them to reach speeds as high as one-tenth of the speed of light. However, if too much energy is applied, the beam nucleus can fall apart.[24]
Coming close enough alone is not enough for two nuclei to fuse: when two nuclei approach each other, they usually remain together for about 10−20 seconds and then part ways (not necessarily in the same composition as before the reaction) rather than form a single nucleus.[24][25] This happens because during the attempted formation of a single nucleus, electrostatic repulsion tears apart the nucleus that is being formed.[24] Each pair of a target and a beam is characterized by its cross section—the probability that fusion will occur if two nuclei approach one another expressed in terms of the transverse area that the incident particle must hit in order for the fusion to occur.[f] This fusion may occur as a result of the quantum effect in which nuclei can tunnel through electrostatic repulsion. If the two nuclei can stay close past that phase, multiple nuclear interactions result in redistribution of energy and an energy equilibrium.[24]
| External videos | |
|---|---|
The resulting merger is an excited state[28]—termed a compound nucleus—and thus it is very unstable.[24] To reach a more stable state, the temporary merger may fission without formation of a more stable nucleus.[29] Alternatively, the compound nucleus may eject a few neutrons, which would carry away the excitation energy; if the latter is not sufficient for a neutron expulsion, the merger would produce a gamma ray. This happens in about 10−16 seconds after the initial nuclear collision and results in creation of a more stable nucleus.[29] The definition by the IUPAC/IUPAP Joint Working Party (JWP) states that a chemical element can only be recognized as discovered if a nucleus of it has not decayed within 10−14 seconds. This value was chosen as an estimate of how long it takes a nucleus to acquire electrons and thus display its chemical properties.[30][g]
Decay and detection
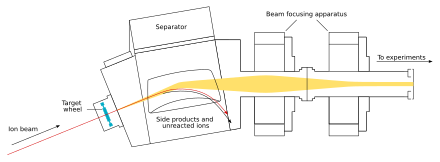
The beam passes through the target and reaches the next chamber, the separator; if a new nucleus is produced, it is carried with this beam.[32] In the separator, the newly produced nucleus is separated from other nuclides (that of the original beam and any other reaction products)[h] and transferred to a surface-barrier detector, which stops the nucleus. The exact location of the upcoming impact on the detector is marked; also marked are its energy and the time of the arrival.[32] The transfer takes about 10−6 seconds; in order to be detected, the nucleus must survive this long.[35] The nucleus is recorded again once its decay is registered, and the location, the energy, and the time of the decay are measured.[32]
Stability of a nucleus is provided by the strong interaction. However, its range is very short; as nuclei become larger, its influence on the outermost nucleons (protons and neutrons) weakens. At the same time, the nucleus is torn apart by electrostatic repulsion between protons, and its range is not limited.[36] Total binding energy provided by the strong interaction increases linearly with the number of nucleons, whereas electrostatic repulsion increases with the square of the atomic number, i.e. the latter grows faster and becomes increasingly important for heavy and superheavy nuclei.[37][38] Superheavy nuclei are thus theoretically predicted[39] and have so far been observed[40] to predominantly decay via decay modes that are caused by such repulsion: alpha decay and spontaneous fission.[i] Almost all alpha emitters have over 210 nucleons,[42] and the lightest nuclide primarily undergoing spontaneous fission has 238.[43] In both decay modes, nuclei are inhibited from decaying by corresponding energy barriers for each mode, but they can be tunneled through.[37][38]
Alpha particles are commonly produced in radioactive decays because the mass of an alpha particle per nucleon is small enough to leave some energy for the alpha particle to be used as kinetic energy to leave the nucleus.[45] Spontaneous fission is caused by electrostatic repulsion tearing the nucleus apart and produces various nuclei in different instances of identical nuclei fissioning.[38] As the atomic number increases, spontaneous fission rapidly becomes more important: spontaneous fission partial half-lives decrease by 23 orders of magnitude from uranium (element 92) to nobelium (element 102),[46] and by 30 orders of magnitude from thorium (element 90) to fermium (element 100).[47] The earlier liquid drop model thus suggested that spontaneous fission would occur nearly instantly due to disappearance of the fission barrier for nuclei with about 280 nucleons.[38][48] The later nuclear shell model suggested that nuclei with about 300 nucleons would form an island of stability in which nuclei will be more resistant to spontaneous fission and will primarily undergo alpha decay with longer half-lives.[38][48] Subsequent discoveries suggested that the predicted island might be further than originally anticipated; they also showed that nuclei intermediate between the long-lived actinides and the predicted island are deformed, and gain additional stability from shell effects.[49] Experiments on lighter superheavy nuclei,[50] as well as those closer to the expected island,[46] have shown greater than previously anticipated stability against spontaneous fission, showing the importance of shell effects on nuclei.[j]
Alpha decays are registered by the emitted alpha particles, and the decay products are easy to determine before the actual decay; if such a decay or a series of consecutive decays produces a known nucleus, the original product of a reaction can be easily determined.[k] (That all decays within a decay chain were indeed related to each other is established by the location of these decays, which must be in the same place.)[32] The known nucleus can be recognized by the specific characteristics of decay it undergoes such as decay energy (or more specifically, the kinetic energy of the emitted particle).[l] Spontaneous fission, however, produces various nuclei as products, so the original nuclide cannot be determined from its daughters.[m]
The information available to physicists aiming to synthesize a superheavy element is thus the information collected at the detectors: location, energy, and time of arrival of a particle to the detector, and those of its decay. The physicists analyze this data and seek to conclude that it was indeed caused by a new element and could not have been caused by a different nuclide than the one claimed. Often, provided data is insufficient for a conclusion that a new element was definitely created and there is no other explanation for the observed effects; errors in interpreting data have been made.[n]
History
Early predictions
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
The heaviest element known at the end of the 19th century was uranium, with an atomic mass of about 240 (now known to be 238) amu. Accordingly, it was placed in the last row of the periodic table; this fueled speculation about the possible existence of elements heavier than uranium and why A = 240 seemed to be the limit. Following the discovery of the noble gases, beginning with argon in 1895, the possibility of heavier members of the group was considered. Danish chemist Julius Thomsen proposed in 1895 the existence of a sixth noble gas with Z = 86, A = 212 and a seventh with Z = 118, A = 292, the last closing a 32-element period containing thorium and uranium.[61] In 1913, Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg extended Thomsen's extrapolation of the periodic table to include even heavier elements with atomic numbers up to 460, but he did not believe that these superheavy elements existed or occurred in nature.[62]
In 1914, German physicist Richard Swinne proposed that elements heavier than uranium, such as those around Z = 108, could be found in cosmic rays. He suggested that these elements may not necessarily have decreasing half-lives with increasing atomic number, leading to speculation about the possibility of some longer-lived elements at Z = 98–102 and Z = 108–110 (though separated by short-lived elements). Swinne published these predictions in 1926, believing that such elements might exist in Earth's core, iron meteorites, or the ice caps of Greenland where they had been locked up from their supposed cosmic origin.[63]
Discoveries
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
Work performed from 1961 to 2013 at four labs – Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in the US, the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in the USSR (later Russia), the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Germany, and Riken in Japan – identified and confirmed the elements lawrencium to oganesson according to the criteria of the IUPAC–IUPAP Transfermium Working Groups and subsequent Joint Working Parties. These discoveries complete the seventh row of the periodic table. The next two elements, ununennium (Z = 119) and unbinilium (Z = 120), have not yet been synthesized. They would begin an eighth period.
List of elements
- 103 Lawrencium, Lr, for Ernest Lawrence; sometimes but not always included[11][12]
- 104 Rutherfordium, Rf, for Ernest Rutherford
- 105 Dubnium, Db, for the town of Dubna, near Moscow
- 106 Seaborgium, Sg, for Glenn T. Seaborg
- 107 Bohrium, Bh, for Niels Bohr
- 108 Hassium, Hs, for Hassia (Hesse), location of Darmstadt
- 109 Meitnerium, Mt, for Lise Meitner
- 110 Darmstadtium, Ds, for Darmstadt)
- 111 Roentgenium, Rg, for Wilhelm Röntgen
- 112 Copernicium, Cn, for Nicolaus Copernicus
- 113 Nihonium, Nh, for Nihon (Japan), location of the Riken institute
- 114 Flerovium, Fl, for Russian physicist Georgy Flyorov
- 115 Moscovium, Mc, for Moscow
- 116 Livermorium, Lv, for Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- 117 Tennessine, Ts, for Tennessee, location of Oak Ridge National Laboratory
- 118 Oganesson, Og, for Russian physicist Yuri Oganessian
Characteristics
Due to their short half-lives (for example, the most stable known isotope of seaborgium has a half-life of 14 minutes, and half-lives decrease with increasing atomic number) and the low yield of the nuclear reactions that produce them, new methods have had to be created to determine their gas-phase and solution chemistry based on very small samples of a few atoms each. Relativistic effects become very important in this region of the periodic table, causing the filled 7s orbitals, empty 7p orbitals, and filling 6d orbitals to all contract inward toward the atomic nucleus. This causes a relativistic stabilization of the 7s electrons and makes the 7p orbitals accessible in low excitation states.[16]
Elements 103 to 112, lawrencium to copernicium, form the 6d series of transition elements. Experimental evidence shows that elements 103–108 behave as expected for their position in the periodic table, as heavier homologs of lutetium through osmium. They are expected to have ionic radii between those of their 5d transition metal homologs and their actinide pseudohomologs: for example, Rf4+ is calculated to have ionic radius 76 pm, between the values for Hf4+ (71 pm) and Th4+ (94 pm). Their ions should also be less polarizable than those of their 5d homologs. Relativistic effects are expected to reach a maximum at the end of this series, at roentgenium (element 111) and copernicium (element 112). Nevertheless, many important properties of the transactinides are still not yet known experimentally, though theoretical calculations have been performed.[16]
Elements 113 to 118, nihonium to oganesson, should form a 7p series, completing the seventh period in the periodic table. Their chemistry will be greatly influenced by the very strong relativistic stabilization of the 7s electrons and a strong spin–orbit coupling effect "tearing" the 7p subshell apart into two sections, one more stabilized (7p1/2, holding two electrons) and one more destabilized (7p3/2, holding four electrons). Lower oxidation states should be stabilized here, continuing group trends, as both the 7s and 7p1/2 electrons exhibit the inert-pair effect. These elements are expected to largely continue to follow group trends, though with relativistic effects playing an increasingly larger role. In particular, the large 7p splitting results in an effective shell closure at flerovium (element 114) and a hence much higher than expected chemical activity for oganesson (element 118).[16]
Element 118 is the last element that has been synthesized. The next two elements, 119 and 120, should form an 8s series and be an alkali and alkaline earth metal respectively. The 8s electrons are expected to be relativistically stabilized, so that the trend toward higher reactivity down these groups will reverse and the elements will behave more like their period 5 homologs, rubidium and strontium. The 7p3/2 orbital is still relativistically destabilized, potentially giving these elements larger ionic radii and perhaps even being able to participate chemically. In this region, the 8p electrons are also relativistically stabilized, resulting in a ground-state 8s28p1 valence electron configuration for element 121. Large changes are expected to occur in the subshell structure in going from element 120 to element 121: for example, the radius of the 5g orbitals should drop drastically, from 25 Bohr units in element 120 in the excited [Og] 5g1 8s1 configuration to 0.8 Bohr units in element 121 in the excited [Og] 5g1 7d1 8s1 configuration, in a phenomenon called "radial collapse". Element 122 should add either a further 7d or a further 8p electron to element 121's electron configuration. Elements 121 and 122 should be similar to actinium and thorium respectively.[16]
At element 121, the superactinide series is expected to begin, when the 8s electrons and the filling 8p1/2, 7d3/2, 6f5/2, and 5g7/2 subshells determine the chemistry of these elements. Complete and accurate calculations are not available for elements beyond 123 because of the extreme complexity of the situation:[64] the 5g, 6f, and 7d orbitals should have about the same energy level, and in the region of element 160 the 9s, 8p3/2, and 9p1/2 orbitals should also be about equal in energy. This will cause the electron shells to mix so that the block concept no longer applies very well, and will also result in novel chemical properties that will make positioning these elements in a periodic table very difficult.[16]
Beyond superheavy elements
It has been suggested that elements beyond Z = 126 be called beyond superheavy elements.[65] Other sources refer to elements around Z = 164 as hyperheavy elements.[66]
See also
- Bose–Einstein condensate (also known as Superatom)
- Island of stability
Notes
- ^ The most stable isotope of tennessine cannot be determined based on existing data due to uncertainty that arises from the low number of measurements. The half-life of 294Ts corresponding to two standard deviations is, based on existing data, 51+76
−32 milliseconds, whereas that of 293Ts is 22+16
−8 milliseconds; these measurements have overlapping confidence intervals.[3] - ^ The declaration by the IUPAC mentioned "the contribution of the Tennessee region (emphasis added), including Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Vanderbilt University, and the University of Tennessee at Knoxville, Tennessee, to superheavy element research, including the production and chemical separation of unique actinide target materials for superheavy element synthesis at ORNL’s High Flux Isotope Reactor (HFIR) and Radiochemical Engineering Development Center (REDC)".
- ^ The term "group 17" refers to a column in the periodic table starting with fluorine. The term "halogen" is sometimes considered as synonymous, but sometimes it instead relates to a common set of chemical and physical properties shared by fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine, all of which precede tennessine in group 17. Unlike the other group 17 members, tennessine might not be a halogen under this stricter definition.[9]
- ^ In nuclear physics, an element is called heavy if its atomic number is high; lead (element 82) is one example of such a heavy element. The term "superheavy elements" typically refers to elements with atomic number greater than 103 (although there are other definitions, such as atomic number greater than 100[18] or 112;[19] sometimes, the term is presented an equivalent to the term "transactinide", which puts an upper limit before the beginning of the hypothetical superactinide series).[20] Terms "heavy isotopes" (of a given element) and "heavy nuclei" mean what could be understood in the common language—isotopes of high mass (for the given element) and nuclei of high mass, respectively.
- ^ In 2009, a team at the JINR led by Oganessian published results of their attempt to create hassium in a symmetric 136Xe + 136Xe reaction. They failed to observe a single atom in such a reaction, putting the upper limit on the cross section, the measure of probability of a nuclear reaction, as 2.5 pb.[21] In comparison, the reaction that resulted in hassium discovery, 208Pb + 58Fe, had a cross section of ~20 pb (more specifically, 19+19
-11 pb), as estimated by the discoverers.[22] - ^ The amount of energy applied to the beam particle to accelerate it can also influence the value of cross section. For example, in the 28
14Si
+ 1
0n
→ 28
13Al
+ 1
1p
reaction, cross section changes smoothly from 370 mb at 12.3 MeV to 160 mb at 18.3 MeV, with a broad peak at 13.5 MeV with the maximum value of 380 mb.[26] - ^ This figure also marks the generally accepted upper limit for lifetime of a compound nucleus.[31]
- ^ This separation is based on that the resulting nuclei move past the target more slowly then the unreacted beam nuclei. The separator contains electric and magnetic fields whose effects on a moving particle cancel out for a specific velocity of a particle.[33] Such separation can also be aided by a time-of-flight measurement and a recoil energy measurement; a combination of the two may allow to estimate the mass of a nucleus.[34]
- ^ Not all decay modes are caused by electrostatic repulsion. For example, beta decay is caused by the weak interaction.[41]
- ^ It was already known by the 1960s that ground states of nuclei differed in energy and shape as well as that certain magic numbers of nucleons corresponded to greater stability of a nucleus. However, it was assumed that there was no nuclear structure in superheavy nuclei as they were too deformed to form one.[46]
- ^ Since mass of a nucleus is not measured directly but is rather calculated from that of another nucleus, such measurement is called indirect. Direct measurements are also possible, but for the most part they have remained unavailable for superheavy nuclei.[51] The first direct measurement of mass of a superheavy nucleus was reported in 2018 at LBNL.[52] Mass was determined from the location of a nucleus after the transfer (the location helps determine its trajectory, which is linked to the mass-to-charge ratio of the nucleus, since the transfer was done in presence of a magnet).[53]
- ^ If the decay occurred in a vacuum, then since total momentum of an isolated system before and after the decay must be preserved, the daughter nucleus would also receive a small velocity. The ratio of the two velocities, and accordingly the ratio of the kinetic energies, would thus be inverse to the ratio of the two masses. The decay energy equals the sum of the known kinetic energy of the alpha particle and that of the daughter nucleus (an exact fraction of the former).[42] The calculations hold for an experiment as well, but the difference is that the nucleus does not move after the decay because it is tied to the detector.
- ^ Spontaneous fission was discovered by Soviet physicist Georgy Flerov,[54] a leading scientist at JINR, and thus it was a "hobbyhorse" for the facility.[55] In contrast, the LBL scientists believed fission information was not sufficient for a claim of synthesis of an element. They believed spontaneous fission had not been studied enough to use it for identification of a new element, since there was a difficulty of establishing that a compound nucleus had only ejected neutrons and not charged particles like protons or alpha particles.[31] They thus preferred to link new isotopes to the already known ones by successive alpha decays.[54]
- ^ For instance, element 102 was mistakenly identified in 1957 at the Nobel Institute of Physics in Stockholm, Stockholm County, Sweden.[56] There were no earlier definitive claims of creation of this element, and the element was assigned a name by its Swedish, American, and British discoverers, nobelium. It was later shown that the identification was incorrect.[57] The following year, RL was unable to reproduce the Swedish results and announced instead their synthesis of the element; that claim was also disproved later.[57] JINR insisted that they were the first to create the element and suggested a name of their own for the new element, joliotium;[58] the Soviet name was also not accepted (JINR later referred to the naming of the element 102 as "hasty").[59] This name was proposed to IUPAC in a written response to their ruling on priority of discovery claims of elements, signed 29 September 1992.[59] The name "nobelium" remained unchanged on account of its widespread usage.[60]
References
- ^ Ritter, Malcolm (9 June 2016). "Periodic table elements named for Moscow, Japan, Tennessee". Associated Press. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- ^ Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Retrieved 4 October 2013.
- ^ a b c Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ a b c d Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". In Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ a b c d Bonchev, D.; Kamenska, V. (1981). "Predicting the Properties of the 113–120 Transactinide Elements". Journal of Physical Chemistry. 85 (9): 1177–1186. doi:10.1021/j150609a021.
- ^ a b c Chang, Zhiwei; Li, Jiguang; Dong, Chenzhong (2010). "Ionization Potentials, Electron Affinities, Resonance Excitation Energies, Oscillator Strengths, And Ionic Radii of Element Uus (Z = 117) and Astatine". J. Phys. Chem. A. 2010 (114): 13388–94. Bibcode:2010JPCA..11413388C. doi:10.1021/jp107411s.
- ^ Khuyagbaatar, J.; Yakushev, A.; Düllmann, Ch. E.; et al. (2014). "48Ca+249Bk Fusion Reaction Leading to Element Z=117: Long-Lived α-Decaying 270Db and Discovery of 266Lr". Physical Review Letters. 112 (17): 172501. Bibcode:2014PhRvL.112q2501K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.172501. PMID 24836239.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (2013). "Experimental studies of the 249Bk + 48Ca reaction including decay properties and excitation function for isotopes of element 117, and discovery of the new isotope 277Mt". Physical Review C. 87 (5): 054621. Bibcode:2013PhRvC..87e4621O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.87.054621.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
notgonnabeahalogenwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Superheavy Element Discovery | Glenn T. Seaborg Institute". seaborg.llnl.gov. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ a b Neve, Francesco (2022). "Chemistry of superheavy transition metals". Journal of Coordination Chemistry. 75 (17–18): 2287–2307. doi:10.1080/00958972.2022.2084394. S2CID 254097024.
- ^ a b Mingos, Michael (1998). Essential Trends in Inorganic Chemistry. Oxford University Press. p. 387. ISBN 978-0-19-850109-1.
- ^ "A New Era of Discovery: the 2023 Long Range Plan for Nuclear Science" (PDF). U.S. Department of Energy. October 2023. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2023 – via OSTI.
Superheavy elements (Z > 102) are teetering at the limits of mass and charge.
- ^ Kragh, Helge (2017). "The search for superheavy elements: Historical and philosophical perspectives". arXiv:1708.04064 [physics.hist-ph].
- ^ IUPAC Provisional Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (2004) (online draft of an updated version of the "Red Book" IR 3-6) Archived October 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c d e f Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean, eds. (2006). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ "Kernchemie". www.kernchemie.de.
- ^ Krämer, K. (2016). "Explainer: superheavy elements". Chemistry World. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ "Discovery of Elements 113 and 115". Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Archived from the original on 11 September 2015. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Eliav, E.; Kaldor, U.; Borschevsky, A. (2018). "Electronic Structure of the Transactinide Atoms". In Scott, R. A. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1–16. doi:10.1002/9781119951438.eibc2632. ISBN 978-1-119-95143-8. S2CID 127060181.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Dmitriev, S. N.; Yeremin, A. V.; et al. (2009). "Attempt to produce the isotopes of element 108 in the fusion reaction 136Xe + 136Xe". Physical Review C. 79 (2): 024608. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.79.024608. ISSN 0556-2813.
- ^ Münzenberg, G.; Armbruster, P.; Folger, H.; et al. (1984). "The identification of element 108" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Physik A. 317 (2): 235–236. Bibcode:1984ZPhyA.317..235M. doi:10.1007/BF01421260. S2CID 123288075. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2015. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
- ^ Subramanian, S. (28 August 2019). "Making New Elements Doesn't Pay. Just Ask This Berkeley Scientist". Bloomberg Businessweek. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Ivanov, D. (2019). "Сверхтяжелые шаги в неизвестное" [Superheavy steps into the unknown]. nplus1.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2 February 2020.
- ^ Hinde, D. (2017). "Something new and superheavy at the periodic table". The Conversation. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ Kern, B. D.; Thompson, W. E.; Ferguson, J. M. (1959). "Cross sections for some (n, p) and (n, α) reactions". Nuclear Physics. 10: 226–234. Bibcode:1959NucPh..10..226K. doi:10.1016/0029-5582(59)90211-1.
- ^ Wakhle, A.; Simenel, C.; Hinde, D. J.; et al. (2015). Simenel, C.; Gomes, P. R. S.; Hinde, D. J.; et al. (eds.). "Comparing Experimental and Theoretical Quasifission Mass Angle Distributions". European Physical Journal Web of Conferences. 86: 00061. Bibcode:2015EPJWC..8600061W. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20158600061. hdl:1885/148847. ISSN 2100-014X.
- ^ "Nuclear Reactions" (PDF). pp. 7–8. Retrieved 27 January 2020. Published as Loveland, W. D.; Morrissey, D. J.; Seaborg, G. T. (2005). "Nuclear Reactions". Modern Nuclear Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 249–297. doi:10.1002/0471768626.ch10. ISBN 978-0-471-76862-3.
- ^ a b Krása, A. (2010). "Neutron Sources for ADS". Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering. Czech Technical University in Prague: 4–8. S2CID 28796927.
- ^ Wapstra, A. H. (1991). "Criteria that must be satisfied for the discovery of a new chemical element to be recognized" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 63 (6): 883. doi:10.1351/pac199163060879. ISSN 1365-3075. S2CID 95737691.
- ^ a b Hyde, E. K.; Hoffman, D. C.; Keller, O. L. (1987). "A History and Analysis of the Discovery of Elements 104 and 105". Radiochimica Acta. 42 (2): 67–68. doi:10.1524/ract.1987.42.2.57. ISSN 2193-3405. S2CID 99193729.
- ^ a b c d Chemistry World (2016). "How to Make Superheavy Elements and Finish the Periodic Table [Video]". Scientific American. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, p. 334.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, p. 335.
- ^ Zagrebaev, Karpov & Greiner 2013, p. 3.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 432.
- ^ a b Pauli, N. (2019). "Alpha decay" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Pauli, N. (2019). "Nuclear fission" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Staszczak, A.; Baran, A.; Nazarewicz, W. (2013). "Spontaneous fission modes and lifetimes of superheavy elements in the nuclear density functional theory". Physical Review C. 87 (2): 024320–1. arXiv:1208.1215. Bibcode:2013PhRvC..87b4320S. doi:10.1103/physrevc.87.024320. ISSN 0556-2813.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, pp. 030001-129–030001-138.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 439.
- ^ a b Beiser 2003, p. 433.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, p. 030001-125.
- ^ Aksenov, N. V.; Steinegger, P.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; et al. (2017). "On the volatility of nihonium (Nh, Z = 113)". The European Physical Journal A. 53 (7): 158. Bibcode:2017EPJA...53..158A. doi:10.1140/epja/i2017-12348-8. ISSN 1434-6001. S2CID 125849923.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 432–433.
- ^ a b c Oganessian, Yu. (2012). "Nuclei in the "Island of Stability" of Superheavy Elements". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 337 (1): 012005-1–012005-6. Bibcode:2012JPhCS.337a2005O. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/337/1/012005. ISSN 1742-6596.
- ^ Moller, P.; Nix, J. R. (1994). Fission properties of the heaviest elements (PDF). Dai 2 Kai Hadoron Tataikei no Simulation Symposium, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki, Japan. University of North Texas. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. Ts. (2004). "Superheavy elements". Physics World. 17 (7): 25–29. doi:10.1088/2058-7058/17/7/31. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ Schädel, M. (2015). "Chemistry of the superheavy elements". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 373 (2037): 20140191. Bibcode:2015RSPTA.37340191S. doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0191. ISSN 1364-503X. PMID 25666065.
- ^ Hulet, E. K. (1989). Biomodal spontaneous fission. 50th Anniversary of Nuclear Fission, Leningrad, USSR. Bibcode:1989nufi.rept...16H.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Rykaczewski, K. P. (2015). "A beachhead on the island of stability". Physics Today. 68 (8): 32–38. Bibcode:2015PhT....68h..32O. doi:10.1063/PT.3.2880. ISSN 0031-9228. OSTI 1337838. S2CID 119531411.
- ^ Grant, A. (2018). "Weighing the heaviest elements". Physics Today. doi:10.1063/PT.6.1.20181113a. S2CID 239775403.
- ^ Howes, L. (2019). "Exploring the superheavy elements at the end of the periodic table". Chemical & Engineering News. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- ^ a b Robinson, A. E. (2019). "The Transfermium Wars: Scientific Brawling and Name-Calling during the Cold War". Distillations. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- ^ "Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Сиборгий (экавольфрам)" [Popular library of chemical elements. Seaborgium (eka-tungsten)]. n-t.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 7 January 2020. Reprinted from "Экавольфрам" [Eka-tungsten]. Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Серебро – Нильсборий и далее [Popular library of chemical elements. Silver through nielsbohrium and beyond] (in Russian). Nauka. 1977.
- ^ "Nobelium - Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table". Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ a b Kragh 2018, pp. 38–39.
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 40.
- ^ a b Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (1993). "Responses on the report 'Discovery of the Transfermium elements' followed by reply to the responses by Transfermium Working Group" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 65 (8): 1815–1824. doi:10.1351/pac199365081815. S2CID 95069384. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 November 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
- ^ Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (1997). "Names and symbols of transfermium elements (IUPAC Recommendations 1997)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 69 (12): 2471–2474. doi:10.1351/pac199769122471.
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 6
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 7
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 10
- ^ van der Schoor, K. (2016). Electronic structure of element 123 (PDF) (Thesis). Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.
- ^ Hofmann, Sigurd (2019). "Synthesis and properties of isotopes of the transactinides". Radiochimica Acta. 107 (9–11): 879–915. doi:10.1515/ract-2019-3104. S2CID 203848120.
- ^ Laforge, Evan; Price, Will; Rafelski, Johann (2023). "Superheavy elements and ultradense matter". The European Physical Journal Plus. 138 (9): 812. arXiv:2306.11989. Bibcode:2023EPJP..138..812L. doi:10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04454-8.
Bibliography
- Audi, G.; Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; et al. (2017). "The NUBASE2016 evaluation of nuclear properties". Chinese Physics C. 41 (3). 030001. Bibcode:2017ChPhC..41c0001A. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/41/3/030001.
pp. 030001-1–030001-17, pp. 030001-18–030001-138, Table I. The NUBASE2016 table of nuclear and decay properties - Beiser, A. (2003). Concepts of modern physics (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-244848-1. OCLC 48965418.
- Hoffman, D. C.; Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T. (2000). The Transuranium People: The Inside Story. World Scientific. ISBN 978-1-78-326244-1.
- Kragh, H. (2018). From Transuranic to Superheavy Elements: A Story of Dispute and Creation. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-75813-8.
- Zagrebaev, V.; Karpov, A.; Greiner, W. (2013). "Future of superheavy element research: Which nuclei could be synthesized within the next few years?". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 420 (1). 012001. arXiv:1207.5700. Bibcode:2013JPhCS.420a2001Z. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/420/1/012001. ISSN 1742-6588.
History
Pre-discovery
In December 2004, the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) team in Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russia, proposed a joint experiment with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, United States, to synthesize element 117 — so called for the 117 protons in its nucleus. Their proposal involved fusing a berkelium (element 97) target and a calcium (element 20) beam, conducted via bombardment of the berkelium target with calcium nuclei:[1] this would complete a set of experiments done at the JINR on the fusion of actinide targets with a calcium-48 beam, which had thus far produced the new elements 113–116 and 118. The ORNL—then the world's only producer of berkelium—could not then provide the element, as they had temporarily ceased production,[1] and re-initiating it would be too costly.[2] Plans to synthesize element 117 were suspended in favor of the confirmation of element 118, which had been produced earlier in 2002 by bombarding a californium target with calcium.[3] The required berkelium-249 is a by-product in californium-252 production, and obtaining the required amount of berkelium was an even more difficult task than obtaining that of californium, as well as costly: It would cost around 3.5 million dollars, and the parties agreed to wait for a commercial order of californium production, from which berkelium could be extracted.[2][4]
The JINR team sought to use berkelium because calcium-48, the isotope of calcium used in the beam, has 20 protons and 28 neutrons, making a neutron–proton ratio of 1.4; and it is the lightest stable or near-stable nucleus with such a large neutron excess. The second-lightest such nucleus, palladium-110 (46 protons, 64 neutrons, neutron–proton ratio of 1.391), is much heavier. Thanks to the neutron excess, the resulting nuclei were expected to be heavier and closer to the sought-after island of stability.[a] Of the aimed for 117 protons, calcium has 20, and thus they needed to use berkelium, which has 97 protons in its nucleus.[5]
In February 2005, the leader of the JINR team — Yuri Oganessian — presented a colloquium at ORNL. Also in attendance were representatives of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, who had previously worked with JINR on the discovery of elements 113–116 and 118, and Joseph Hamilton of Vanderbilt University, a collaborator of Oganessian.[7]
Hamilton checked if the ORNL high-flux reactor produced californium for a commercial order: The required berkelium could be obtained as a by-product. He learned that it did not and there was no expectation for such an order in the immediate future. Hamilton kept monitoring the situation, making the checks once in a while. (Later, Oganessian referred to Hamilton as "the father of 117" for doing this work.)[7]
Discovery
ORNL resumed californium production in spring 2008. Hamilton noted the restart during the summer and made a deal on subsequent extraction of berkelium[8] (the price was about $600,000).[9] During a September 2008 symposium at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tennessee, celebrating his 50th year on the Physics faculty, Hamilton introduced Oganessian to James Roberto (then the deputy director for science and technology at ORNL).[10] They established a collaboration among JINR, ORNL, and Vanderbilt.[4] The eventual collaborating institutions also included The University of Tennessee (Knoxville), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, The Research Institute for Advanced Reactors (Russia), and The University of Nevada (Las Vegas).[11]

In November 2008, the U.S. Department of Energy, which had oversight over the reactor in Oak Ridge, allowed the scientific use of the extracted berkelium.[12]
The production lasted 250 days and ended in late December 2008,[13] resulting in 22 milligrams of berkelium, enough to perform the experiment.[14] In January 2009, the berkelium was removed from ORNL's High Flux Isotope Reactor;[12] it was subsequently cooled for 90 days and then processed at ORNL's Radiochemical Engineering and Development Center to separate and purify the berkelium material, which took another 90 days.[4] Its half-life is only 330 days: after that time, half the berkelium produced would have decayed. Because of this, the berkelium target had to be quickly transported to Russia; for the experiment to be viable, it had to be completed within six months of its departure from the United States.[4] The target was packed into five lead containers to be flown from New York to Moscow.[4] Russian customs officials twice refused to let the target enter the country because of missing or incomplete paperwork. Over the span of a few days, the target traveled over the Atlantic Ocean five times.[4] On its arrival in Russia in June 2009, the berkelium was immediately transferred to Research Institute of Atomic Reactors (RIAR) in Dimitrovgrad, Ulyanovsk Oblast, where it was deposited as a 300-nanometer-thin layer on a titanium film.[13] In July 2009, it was transported to Dubna,[13] where it was installed in the particle accelerator at the JINR.[14] The calcium-48 beam was generated by chemically extracting the small quantities of calcium-48 present in naturally occurring calcium, enriching it 500 times.[citation needed] This work was done in the closed town of Lesnoy, Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia.[12]
The experiment began in late July 2009.[12] In January 2010, scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions announced internally that they had detected the decay of a new element with atomic number 117 via two decay chains: one of an odd–odd isotope undergoing 6 alpha decays before spontaneous fission, and one of an odd–even isotope undergoing 3 alpha decays before fission.[15] The obtained data from the experiment was sent to the LLNL for further analysis.[16] On 9 April 2010, an official report was released in the journal Physical Review Letters identifying the isotopes as 294117 and 293117, which were shown to have half-lives on the order of tens or hundreds of milliseconds. The work was signed by all parties involved in the experiment to some extent: JINR, ORNL, LLNL, RIAR, Vanderbilt, the University of Tennessee (Knoxville, Tennessee, U.S.), and the University of Nevada (Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S.), which provided data analysis support.[17] The isotopes were formed as follows:[18][b]
- 249
97Bk
+ 48
20Ca
→ 297117* → 294117 + 3 1
0
n
(1 event)
- 249
97Bk
+ 48
20Ca
→ 297117* → 293117 + 4 1
0
n
(5 events)
Confirmation

All daughter isotopes (decay products) of element 117 were previously unknown;[18] therefore, their properties could not be used to confirm the claim of discovery. In 2011, when one of the decay products (289115) was synthesized directly, its properties matched those measured in the claimed indirect synthesis from the decay of element 117.[19] The discoverers did not submit a claim for their findings in 2007–2011 when the Joint Working Party was reviewing claims of discoveries of new elements.[20]
The Dubna team repeated the experiment in 2012, creating seven atoms of element 117 and confirming their earlier synthesis of element 118 (produced after some time when a significant quantity of the berkelium-249 target had beta decayed to californium-249). The results of the experiment matched the previous outcome;[21] the scientists then filed an application to register the element.[citation needed] In May 2014, a joint German–American collaboration of scientists from the ORNL and the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt, Hessen, Germany, claimed to have confirmed discovery of the element.[22][23] The team repeated the Dubna experiment using the Darmstadt accelerator, creating two atoms of element 117.[22]
In December 2015, the JWP officially recognized the discovery of 293117 on account of the confirmation of the properties of its daughter 289115,[24] and thus the listed discoverers — JINR, LLNL, and ORNL — were given the right to suggest an official name for the element. (Vanderbilt was left off the initial list of discoverers in an error that was later corrected.)[25]
In May 2016, Lund University (Lund, Scania, Sweden) and GSI cast some doubt on the syntheses of elements 115 and 117. The decay chains assigned to 289115, the isotope instrumental in the confirmation of the syntheses of elements 115 and 117, were found based on a new statistical method to be too different to belong to the same nuclide with a reasonably high probability. The reported 293117 decay chains approved as such by the JWP were found to require splitting into individual data sets assigned to different isotopes of element 117. It was also found that the claimed link between the decay chains reported as from 293117 and 289115 probably did not exist. (On the other hand, the chains from the non-approved isotope 294117 were found to be congruent.) The multiplicity of states found when nuclides that are not even–even undergo alpha decay is not unexpected and contributes to the lack of clarity in the cross-reactions. This study criticized the JWP report for overlooking subtleties associated with this issue, and considered it "problematic" that the only argument for the acceptance of the discoveries of elements 115 and 117 was a link they considered to be doubtful.[26][27]
On 8 June 2017, two members of the Dubna team published a journal article answering these criticisms, analysing their data on the nuclides 293117 and 289115 with widely accepted statistical methods, noted that the 2016 studies indicating non-congruence produced problematic results when applied to radioactive decay: they excluded from the 90% confidence interval both average and extreme decay times, and the decay chains that would be excluded from the 90% confidence interval they chose were more probable to be observed than those that would be included. The 2017 reanalysis concluded that the observed decay chains of 293117 and 289115 were consistent with the assumption that only one nuclide was present at each step of the chain, although it would be desirable to be able to directly measure the mass number of the originating nucleus of each chain as well as the excitation function of the 243Am + 48Ca reaction.[28]
Naming

Using Mendeleev's nomenclature for unnamed and undiscovered elements, element 117 should be known as eka-astatine. Using the 1979 recommendations by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the element was temporarily called ununseptium (symbol Uus) until its discovery was confirmed and a permanent name chosen; the temporary name was formed from Latin roots "one", "one", and "seven", a reference to the element's atomic number 117.[29] Many scientists in the field called it "element 117", with the symbol E117, (117), or 117.[30] According to guidelines of IUPAC valid at the moment of the discovery approval, the permanent names of new elements should have ended in "-ium"; this included element 117, even if the element was a halogen, which traditionally have names ending in "-ine";[31] however, the new recommendations published in 2016 recommended using the "-ine" ending for all new group 17 elements.[32]
After the original synthesis in 2010, Dawn Shaughnessy of LLNL and Oganessian declared that naming was a sensitive question, and it was avoided as far as possible.[33] However, Hamilton declared that year, "I was crucial in getting the group together and in getting the 249Bk target essential for the discovery. As a result of that, I'm going to get to name the element. I can't tell you the name, but it will bring distinction to the region."[17] (Hamilton teaches at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tennessee, U.S.) In a 2015 interview, Oganessian, after telling the story of the experiment, said, "and the Americans named this a tour de force, they had demonstrated they could do [this] with no margin for error. Well, soon they will name the 117th element."[34]
In March 2016, the discovery team agreed on a conference call involving representatives from the parties involved on the name "tennessine" for element 117.[7] In June 2016, IUPAC published a declaration stating the discoverers had submitted their suggestions for naming the new elements 115, 117, and 118 to the IUPAC; the suggestion for the element 117 was tennessine, with a symbol of Ts, after "the region of Tennessee".[c] The suggested names were recommended for acceptance by the IUPAC Inorganic Chemistry Division; formal acceptance was set to occur after a five-month term following publishing of the declaration expires.[35] In November 2016, the names, including tennessine, were formally accepted. Concerns that the proposed symbol Ts may clash with a notation for the tosyl group used in organic chemistry were rejected, following existing symbols bearing such dual meanings: Ac (actinium and acetyl) and Pr (praseodymium and propyl).[36] The naming ceremony for moscovium, tennessine, and oganesson was held on 2 March 2017 at the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow; a separate ceremony for tennessine alone had been held at ORNL in January 2017.[37]
Predicted properties
Other than nuclear properties, no properties of tennessine or its compounds have been measured; this is due to its extremely limited and expensive production[9] and the fact that it decays very quickly. Properties of tennessine remain unknown and only predictions are available.
Nuclear stability and isotopes
The stability of nuclei quickly decreases with the increase in atomic number after curium, element 96, whose half-life is four orders of magnitude longer than that of any subsequent element. All isotopes with an atomic number above 101 undergo radioactive decay with half-lives of less than 30 hours. No elements with atomic numbers above 82 (after lead) have stable isotopes.[38] This is because of the ever-increasing Coulomb repulsion of protons, so that the strong nuclear force cannot hold the nucleus together against spontaneous fission for long. Calculations suggest that in the absence of other stabilizing factors, elements with more than 104 protons should not exist.[39] However, researchers in the 1960s suggested that the closed nuclear shells around 114 protons and 184 neutrons should counteract this instability, creating an "island of stability" where nuclides could have half-lives reaching thousands or millions of years. While scientists have still not reached the island, the mere existence of the superheavy elements (including tennessine) confirms that this stabilizing effect is real, and in general the known superheavy nuclides become exponentially longer-lived as they approach the predicted location of the island.[40][41] Tennessine is the second-heaviest element created so far, and all its known isotopes have half-lives of less than one second. Nevertheless, this is longer than the values predicted prior to their discovery: the predicted lifetimes for 293Ts and 294Ts used in the discovery paper were 10 ms and 45 ms respectively, while the observed lifetimes were 21 ms and 112 ms respectively.[18] The Dubna team believes that the synthesis of the element is direct experimental proof of the existence of the island of stability.[42]

It has been calculated that the isotope 295Ts would have a half-life of about 18 milliseconds, and it may be possible to produce this isotope via the same berkelium–calcium reaction used in the discoveries of the known isotopes, 293Ts and 294Ts. The chance of this reaction producing 295Ts is estimated to be, at most, one-seventh the chance of producing 294Ts.[43][44][45] Calculations using a quantum tunneling model predict the existence of several isotopes of tennessine up to 303Ts. The most stable of these is expected to be 296Ts with an alpha-decay half-life of 40 milliseconds.[46] A liquid drop model study on the element's isotopes shows similar results; it suggests a general trend of increasing stability for isotopes heavier than 301Ts, with partial half-lives exceeding the age of the universe for the heaviest isotopes like 335Ts when beta decay is not considered.[47] Lighter isotopes of tennessine may be produced in the 243Am+50Ti reaction, which was considered as a contingency plan by the Dubna team in 2008 if 249Bk proved unavailable.[48] It was considered again for study in 2017–2018 to investigate the properties of nuclear reactions with a titanium-50 beam, which becomes necessary to synthesize elements beyond oganesson.[49]
Atomic and physical
Tennessine is expected to be a member of group 17 in the periodic table, below the five halogens; fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine, each of which has seven valence electrons with a configuration of ns2np5.[50][d] For tennessine, being in the seventh period (row) of the periodic table, continuing the trend would predict a valence electron configuration of 7s27p5,[30] and it would therefore be expected to behave similarly to the halogens in many respects that relate to this electronic state. However, going down group 17, the metallicity of the elements increases; for example, iodine already exhibits a metallic luster in the solid state, and astatine is expected to be a metal.[51] As such, an extrapolation based on periodic trends would predict tennessine to be a rather volatile metal.[52]

Calculations have confirmed the accuracy of this simple extrapolation, although experimental verification of this is currently impossible as the half-lives of the known tennessine isotopes are too short.[52] Significant differences between tennessine and the previous halogens are likely to arise, largely due to spin–orbit interaction—the mutual interaction between the motion and spin of electrons. The spin–orbit interaction is especially strong for the superheavy elements because their electrons move faster—at velocities comparable to the speed of light—than those in lighter atoms.[53] In tennessine atoms, this lowers the 7s and the 7p electron energy levels, stabilizing the corresponding electrons, although two of the 7p electron energy levels are more stabilized than the other four.[54] The stabilization of the 7s electrons is called the inert pair effect; the effect that separates the 7p subshell into the more-stabilized and the less-stabilized parts is called subshell splitting. Computational chemists understand the split as a change of the second (azimuthal) quantum number l from 1 to 1/2 and 3/2 for the more-stabilized and less-stabilized parts of the 7p subshell, respectively.[55][e] For many theoretical purposes, the valence electron configuration may be represented to reflect the 7p subshell split as 7s2
7p2
1/27p3
3/2.[30]
Differences for other electron levels also exist. For example, the 6d electron levels (also split in two, with four being 6d3/2 and six being 6d5/2) are both raised, so they are close in energy to the 7s ones,[54] although no 6d electron chemistry has been predicted for tennessine.[when?] The difference between the 7p1/2 and 7p3/2 levels is abnormally high; 9.8 eV.[54] Astatine's 6p subshell split is only 3.8 eV,[54] and its 6p1/2 chemistry has already been called "limited".[56] These effects cause tennessine's chemistry to differ from those of its upper neighbors (see below).
Tennessine's first ionization energy—the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom—is predicted to be 7.7 eV, lower than those of the halogens, again following the trend.[30] Like its neighbors in the periodic table, tennessine is expected to have the lowest electron affinity—energy released when an electron is added to the atom—in its group; 2.6 or 1.8 eV.[30] The electron of the hypothetical hydrogen-like tennessine atom—oxidized so it has only one electron, Ts116+—is predicted to move so quickly that its mass is 1.90 times that of a non-moving electron, a feature attributable to relativistic effects. For comparison, the figure for hydrogen-like astatine is 1.27 and the figure for hydrogen-like iodine is 1.08.[57] Simple extrapolations of relativity laws indicate a contraction of atomic radius.[57] Advanced calculations show that the radius of an tennessine atom that has formed one covalent bond would be 165 pm, while that of astatine would be 147 pm.[58] With the seven outermost electrons removed, tennessine is finally smaller; 57 pm[30] for tennessine and 61 pm[59] for astatine.
The melting and boiling points of tennessine are not known; earlier papers predicted about 350–500 °C and 550 °C, respectively,[30] or 350–550 °C and 610 °C, respectively.[60] These values exceed those of astatine and the lighter halogens, following periodic trends. A later paper predicts the boiling point of tennessine to be 345 °C[61] (that of astatine is estimated as 309 °C,[62] 337 °C,[63] or 370 °C,[64] although experimental values of 230 °C[65] and 411 °C[59] have been reported). The density of tennessine is expected to be between 7.1 and 7.3 g/cm3.[66]
Chemical
The known isotopes of tennessine, 293Ts and 294Ts, are too short-lived to allow for chemical experimentation at present. Nevertheless, many chemical properties of tennessine have been calculated.[67] Unlike the lighter group 17 elements, tennessine may not exhibit the chemical behavior common to the halogens.[68] For example, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine routinely accept an electron to achieve the more stable electronic configuration of a noble gas, obtaining eight electrons (octet) in their valence shells instead of seven.[69] This ability weakens as atomic weight increases going down the group; tennessine would be the least willing group 17 element to accept an electron. Of the oxidation states it is predicted to form, −1 is expected to be the least common.[30] The standard reduction potential of the Ts/Ts− couple is predicted to be −0.25 V; this value is negative, unlike for all the lighter halogens.[70]
There is another opportunity for tennessine to complete its octet—by forming a covalent bond. Like the halogens, when two tennessine atoms meet they are expected to form a Ts–Ts bond to give a diatomic molecule. Such molecules are commonly bound via single sigma bonds between the atoms; these are different from pi bonds, which are divided into two parts, each shifted in a direction perpendicular to the line between the atoms, and opposite one another rather than being located directly between the atoms they bind. Sigma bonding has been calculated to show a great antibonding character in the At2 molecule and is not as favorable energetically. Tennessine is predicted to continue the trend; a strong pi character should be seen in the bonding of Ts2.[30][71] The molecule tennessine chloride (TsCl) is predicted to go further, being bonded with a single pi bond.[71]
Aside from the unstable −1 state, three more oxidation states are predicted; +5, +3, and +1. The +1 state should be especially stable because of the destabilization of the three outermost 7p3/2 electrons, forming a stable, half-filled subshell configuration;[30] astatine shows similar effects.[72] The +3 state should be important, again due to the destabilized 7p3/2 electrons.[60] The +5 state is predicted to be uncommon because the 7p1/2 electrons are oppositely stabilized.[30] The +7 state has not been shown—even computationally—to be achievable. Because the 7s electrons are greatly stabilized, it has been hypothesized that tennessine effectively has only five valence electrons.[73]
The simplest possible tennessine compound would be the monohydride, TsH. The bonding is expected to be provided by a 7p3/2 electron of tennessine and the 1s electron of hydrogen. The non-bonding nature of the 7p1/2 spinor is because tennessine is expected not to form purely sigma or pi bonds.[74] Therefore, the destabilized (thus expanded) 7p3/2 spinor is responsible for bonding.[75] This effect lengthens the TsH molecule by 17 picometers compared with the overall length of 195 pm.[74] Since the tennessine p electron bonds are two-thirds sigma, the bond is only two-thirds as strong as it would be if tennessine featured no spin–orbit interactions.[74] The molecule thus follows the trend for halogen hydrides, showing an increase in bond length and a decrease in dissociation energy compared to AtH.[30] The molecules TlTs and NhTs may be viewed analogously, taking into account an opposite effect shown by the fact that the element's p1/2 electrons are stabilized. These two characteristics result in a relatively small dipole moment (product of difference between electric charges of atoms and displacement of the atoms) for TlTs; only 1.67 D,[f] the positive value implying that the negative charge is on the tennessine atom. For NhTs, the strength of the effects are predicted to cause a transfer of the electron from the tennessine atom to the nihonium atom, with the dipole moment value being −1.80 D.[77] The spin–orbit interaction increases the dissociation energy of the TsF molecule because it lowers the electronegativity of tennessine, causing the bond with the extremely electronegative fluorine atom to have a more ionic character.[74] Tennessine monofluoride should feature the strongest bonding of all group 17 monofluorides.[74]
VSEPR theory predicts a bent-T-shaped molecular geometry for the group 17 trifluorides. All known halogen trifluorides have this molecular geometry and have a structure of AX3E2—a central atom, denoted A, surrounded by three ligands, X, and two unshared electron pairs, E. If relativistic effects are ignored, TsF3 should follow its lighter congeners in having a bent-T-shaped molecular geometry. More sophisticated predictions show that this molecular geometry would not be energetically favored for TsF3, predicting instead a trigonal planar molecular geometry (AX3E0). This shows that VSEPR theory may not be consistent for the superheavy elements.[73] The TsF3 molecule is predicted to be significantly stabilized by spin–orbit interactions; a possible rationale may be the large difference in electronegativity between tennessine and fluorine, giving the bond a partially ionic character.[73]
Notes
- ^ Although stable isotopes of the lightest elements usually have a neutron–proton ratio close or equal to one (for example, the only stable isotope of aluminium has 13 protons and 14 neutrons,[5] making a neutron–proton ratio of 1.077), stable isotopes of heavier elements have higher neutron–proton ratios, increasing with the number of protons. For example, iodine's only stable isotope has 53 protons and 74 neutrons, giving neutron–proton ratio of 1.396, gold's only stable isotope has 79 protons and 118 neutrons, yielding a neutron–proton ratio of 1.494, and plutonium's most stable isotope has 94 protons and 150 neutrons, and a neutron–proton ratio of 1.596.[5] This trend[6] is expected to make it difficult to synthesize the most stable isotopes of super-heavy elements as the neutron–proton ratios of the elements they are synthesized from will be too low.
- ^ A nuclide is commonly denoted by the chemical element's symbol immediately preceded by the mass number as a superscript and the atomic number as a subscript. Neutrons are represented as nuclides with atomic mass 1, atomic number 0, and symbol n. Outside the context of nuclear equations, the atomic number is sometimes omitted. An asterisk denotes an extremely short-lived (or even non-existent) intermediate stage of the reaction.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
fn1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The letter n stands for the number of the period (horizontal row in the periodic table) the element belongs to. The letters "s" and "p" denote the s and p atomic orbitals, and the subsequent superscript numbers denote the numbers of electrons in each. Hence the notation ns2np5 means that the valence shells of lighter group 17 elements are composed of two s electrons and five p electrons, all located in the outermost electron energy level.
- ^ The quantum number corresponds to the letter in the electron orbital name: 0 to s, 1 to p, 2 to d, etc. See azimuthal quantum number for more information.
- ^ For comparison, the values for the ClF, HCl, SO, HF, and HI molecules are 0.89 D, 1.11 D, 1.55 D, 1.83 D, and 1.95 D. Values for molecules which do not form at standard conditions, namely GeSe, SnS, TlF, BaO, and NaCl, are 1.65 D, ~3.2 D, 4.23 D, 7.95 D, and 9.00 D.[76]
References
- ^ a b Cabage, B. (2010). "International team discovers element 117" (Press release). Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Vanderbilt physicist plays pivotal role in discovery of new super-heavy element" (Press release). Vanderbilt University. April 2010. Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu.Ts.; Utyonkov, V.K.; Lobanov, Yu.V.; Abdullin, F.Sh.; Polyakov, A.N.; Shirokovsky, I.V.; et al. (2002). "Results from the first 249Cf+48Ca experiment" (PDF). JINR Communication. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f Bardi, J. S. (2010). "An Atom at the End of the Material World". Inside Science. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- ^ a b c Audi, G.; Bersillon, O.; Blachot, J.; Wapstra, A.H. (2003). "The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties" (PDF). Nuclear Physics A. 729 (1): 3–128. Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729....3A. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.692.8504. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2011.
- ^ Karpov, A. V.; Zagrebaev, V. I.; Palenzuela, Y. Martinez; Greiner, Walter (2013). "Superheavy Nuclei: Decay and Stability". Exciting Interdisciplinary Physics. FIAS Interdisciplinary Science Series. p. 69. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-00047-3_6. ISBN 978-3-319-00046-6.
- ^ a b c "What it takes to make a new element". Chemistry World. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ^ Witze, Alexandra (2010). "The backstory behind a new element". Science News. Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Bloombergwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Siner, Emily (2016). "How scientists plan to enshrine Tennessee on the periodic table of elements". National Public Radio. Retrieved 7 March 2017.
- ^ "The Discovery of Tennessine" (PDF). Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ a b c d Roberto, James (2010). "The discovery of element 117" (PDF) (Press release). Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2016. Retrieved 26 June 2017.
- ^ a b c "For the Press" (Press release). Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. 2010. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ^ a b Stark, A.M. (2010). "International team discovers element 117" (Press release). DOE / Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- ^ Greiner, W. (2010). Recommendations (PDF). 31st meeting, PAC for nuclear physics. p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2010.
- ^ "Nations work together to discover new element". DOE Office of Science. U.S. Department of Energy (Press release). U.S. Department of Energy. 2011. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ a b "Heaviest in the world". Arts and Science Magazine. Vanderbilt University. November 2011. Archived from the original on 3 May 2016. Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d Oganessian, Yu.Ts.; Abdullin, F.Sh.; Bailey, P.D.; Benker, D.E.; Bennett, M.E.; Dmitriev, S.N.; et al. (2010). "Synthesis of a new element with atomic number Z = 117". Physical Review Letters. 104 (14): 142502. Bibcode:2010PhRvL.104n2502O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.142502. PMID 20481935. S2CID 3263480.
- ^ Molchanov, E. (2011). В лабораториях ОИЯИ. Возвращение к дубнию [In JINR labs. Returning to dubnium] (in Russian). JINR. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ^ Barber, R.C.; Karol, P.J.; Nakahara, H.; Vardaci, E.; Vogt, E.W. (2011). "Discovery of the elements with atomic numbers greater than or equal to 113". Pure and Applied Chemistry. IUPAC Technical Report. 83 (7): 1485–1498. doi:10.1351/PAC-REP-10-05-01. S2CID 98065999.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
277Mtwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
266Lrwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Chow, D. (1 May 2014). "New super-heavy element 117 confirmed by scientists". Live Science. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ^ "Discovery and assignment of elements with atomic numbers 113, 115, 117 and 118" (Press release). IUPAC. 2015. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- ^ Karol, Paul J.; Barber, Robert C.; Sherrill, Bradley M.; Vardaci, Emanuele; Yamazaki, Toshimitsu (22 December 2015). "Discovery of the elements with atomic numbers Z = 113, 115, and 117" (PDF). Pure Appl. Chem. IUPAC Technical Report. 88 (1–2): 139–153. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-0502. S2CID 101634372. Retrieved 2 April 2016.
- ^ Forsberg, U.; Rudolph, D.; Fahlander, C.; Golubev, P.; Sarmiento, L.G.; Åberg, S.; Block, M.; Düllmann, Ch.E.; Heßberger, F.P.; Kratz, J.V.; Yakushev, A. (9 July 2016). "A new assessment of the alleged link between element 115 and element 117 decay chains" (PDF). Physics Letters B. 760 (2016): 293–296. Bibcode:2016PhLB..760..293F. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2016.07.008. Retrieved 2 April 2016.
- ^ Forsberg, Ulrika; Fahlander, Claes; Rudolph, Dirk (2016). Congruence of decay chains of elements 113, 115, and 117 (PDF). Nobel Symposium NS160 – Chemistry and Physics of Heavy and Superheavy Elements. doi:10.1051/epjconf/201613102003.
- ^ Zlokazov, V.B.; Utyonkov, V.K. (8 June 2017). "Analysis of decay chains of superheavy nuclei produced in the 249Bk + 48Ca and 243Am + 48Ca reactions". Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics. 44 (7): 075107. Bibcode:2017JPhG...44g5107Z. doi:10.1088/1361-6471/aa7293.
- ^ Chatt, J. (1979). "Recommendations for the naming of elements of atomic numbers greater than 100". Pure Appl. Chem. 51 (2): 381–384. doi:10.1351/pac197951020381.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Cite error: The named reference
Hairewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Koppenol, W.H. (2002). "Naming of new elements" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. IUPAC Recommendations 2002. 74 (5): 787–791. doi:10.1351/pac200274050787. S2CID 95859397.
- ^ Koppenol, Willem H.; Corish, John; García-Martínez, Javier; Meija, Juris; Reedijk, Jan (2016). "How to name new chemical elements" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. IUPAC Recommendations 2016. 88 (4): 401–405. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-0802. hdl:10045/55935. S2CID 102245448.
- ^ Glanz, J. (2010). "Scientists discover heavy new element". Department of Chemistry (Press release). Oregon State University. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu.Ts. (10 October 2015). "Гамбургский счет" [Hamburg reckoning] (Interview) (in Russian). Interviewed by Orlova, O. Public Television of Russia. Archived from the original on 11 November 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ "IUPAC Is Naming The Four New Elements Nihonium, Moscovium, Tennessine, and Oganesson" (Press release). IUPAC. 8 June 2016. Retrieved 8 June 2016.
- ^ "IUPAC Announces the Names of the Elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 - IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry". IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. 30 November 2016. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ^ Fedorova, Vera (3 March 2017). "At the inauguration ceremony of the new elements of the periodic table of D.I. Mendeleev". jinr.ru. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ^ de Marcillac, P.; Coron, N.; Dambier, G.; et al. (2003). "Experimental detection of α-particles from the radioactive decay of natural bismuth". Nature. 422 (6934): 876–878. Bibcode:2003Natur.422..876D. doi:10.1038/nature01541. PMID 12712201. S2CID 4415582.
- ^ Möller, P. (2016). "The limits of the nuclear chart set by fission and alpha decay" (PDF). EPJ Web of Conferences. 131: 03002:1–8. Bibcode:2016EPJWC.13103002M. doi:10.1051/epjconf/201613103002.
- ^ Considine, G.D.; Kulik, Peter H. (2002). Van Nostrand's scientific encyclopedia (9th ed.). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-33230-5. OCLC 223349096.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Sobiczewski, A.; Ter-Akopian, G. M. (9 January 2017). "Superheavy nuclei: from predictions to discovery". Physica Scripta. 92 (2): 023003–1–21. Bibcode:2017PhyS...92b3003O. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/aa53c1. S2CID 125713877.
- ^ a b "Element 117 is synthesized". JINR. 2010. Retrieved 28 June 2015.
- ^ Zagrebaev, Karpov & Greiner 2013, p. 3.
- ^ Zhao-Qing, F.; Gen-Ming, Jin; Ming-Hui, Huang; et al. (2007). "Possible Way to Synthesize Superheavy Element Z = 117". Chinese Physics Letters. 24 (9): 2551. arXiv:0708.0159. Bibcode:2007ChPhL..24.2551F. doi:10.1088/0256-307X/24/9/024. S2CID 8778306.
- ^ Zhao-Qing, F.; Jina, Gen-Ming; Li, Jun-Qing; et al. (2009). "Production of heavy and superheavy nuclei in massive fusion reactions". Nuclear Physics A. 816 (1–4): 33. arXiv:0803.1117. Bibcode:2009NuPhA.816...33F. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2008.11.003. S2CID 18647291.
- ^ Chowdhury, R. P.; Samanta, C.; Basu, D. N. (2008). "Search for long lived heaviest nuclei beyond the valley of stability". Physical Review C. 77 (4): 044603. arXiv:0802.3837. Bibcode:2008PhRvC..77d4603C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.77.044603. S2CID 119207807.
- ^ Duarte, S. B.; Tavares, O. A. P.; Gonçalves, M.; et al. (September 2004). "Half-life prediction for decay modes for superheavy nuclei" (PDF). Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics. Notas de Física. 30 (CBPF-NF-022/04). Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas: 1487–1494. Bibcode:2004JPhG...30.1487D. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/30/10/014. ISSN 0029-3865.
- ^ Utyonkov, V. K. (12 February 2008). "Синтез новых элементов 113-118 в реакциях полного слияния 48Ca + 238U-249Cf" [Synthesis of new elements 113–118 in complete fusion reactions 48Ca + 238U–249Cf] (PDF). nuclphys.sinp.msu.ru. Retrieved 28 April 2017.
- ^ Roberto, J. B. (31 March 2015). "Actinide Targets for Super-Heavy Element Research" (PDF). cyclotron.tamu.edu. Texas A & M University. Retrieved 28 April 2017.
- ^ Dhingra, A. (1 December 1999). The Sterling Dictionary Of Chemistry. Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 187. ISBN 978-81-7359-123-5. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ^ Hermann, A.; Hoffmann, R.; Ashcroft, N. W. (2013). "Condensed Astatine: Monatomic and Metallic". Physical Review Letters. 111 (11): 116404-1–116404-5. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.111k6404H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.116404. PMID 24074111.
- ^ a b
GSI (14 December 2015). "Research Program – Highlights". superheavies.de. GSI. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
If this trend were followed, element 117 would likely be a rather volatile metal. Fully relativistic calculations agree with this expectation, however, they are in need of experimental confirmation.
- ^ Thayer 2010, pp. 63–64.
- ^ a b c d Fægri Jr., K.; Saue, T. (2001). "Diatomic molecules between very heavy elements of group 13 and group 17: A study of relativistic effects on bonding". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 115 (6): 2456. Bibcode:2001JChPh.115.2456F. doi:10.1063/1.1385366.
- ^ Thayer 2010, pp. 63–67.
- ^ Thayer 2010, p. 79.
- ^ a b Thayer 2010, p. 64.
- ^ Pyykkö, P.; Atsumi, M. (22 December 2008). "Molecular Single-Bond Covalent Radii for Elements 1-118". Chemistry: A European Journal. 15 (1): 186–197. doi:10.1002/chem.200800987. PMID 19058281.
- ^ a b Sharma, B. K. (2001). Nuclear and radiation chemistry (7th ed.). Krishna Prakashan Media. p. 147. ISBN 978-81-85842-63-9. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ^ a b Seaborg, Glenn T. (1994). Modern alchemy. World Scientific. p. 172. ISBN 978-981-02-1440-1.
- ^ Takahashi, N. (2002). "Boiling points of the superheavy elements 117 and 118". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 251 (2): 299–301. doi:10.1023/A:1014880730282. S2CID 93096903.
- ^ Luig, H.; Keller, C.; Wolf, W.; et al. (2005). "Radionuclides". In Ullmann, F. (ed.). Encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley-VCH. p. 23. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_499. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- ^ Punter, J.; Johnson, R.; Langfield, S. (2006). The essentials of GCSE OCR Additional science for specification B. Letts and Lonsdale. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-905129-73-7.
- ^ Wiberg, E.; Wiberg, N.; Holleman, A. F. (2001). Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press. p. 423. ISBN 978-0-12-352651-9.
- ^ Otozai, K.; Takahashi, N. (1982). "Estimation of the chemical form and the boiling point of elementary astatine by radiogas-chromatography". Radiochimica Acta. 31 (3‒4): 201‒203. doi:10.1524/ract.1982.31.34.201. S2CID 100363889.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
B&Kwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Moody, Ken (30 November 2013). "Synthesis of Superheavy Elements". In Schädel, Matthias; Shaughnessy, Dawn (eds.). The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements (2nd ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 24–8. ISBN 9783642374661.
- ^ "Superheavy Element 117 Confirmed – On the Way to the "Island of Stability"". GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research. Archived from the original on 3 August 2018. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ Bader, R. F. W. "An introduction to the electronic structure of atoms and molecules". McMaster University. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ^ Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Retrieved 4 October 2013.
- ^ a b Pershina 2010, p. 504.
- ^ Thayer 2010, p. 84.
- ^ a b c Bae, Ch.; Han, Y.-K.; Lee, Yo. S. (18 January 2003). "Spin−Orbit and Relativistic Effects on Structures and Stabilities of Group 17 Fluorides EF3 (E = I, At, and Element 117): Relativity Induced Stability for the D3h Structure of (117)F3". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 107 (6): 852–858. Bibcode:2003JPCA..107..852B. doi:10.1021/jp026531m.
- ^ a b c d e Han, Y.-K.; Bae, Cheolbeom; Son, Sang-Kil; et al. (2000). "Spin-orbit effects on the transactinide p-block element monohydrides MH (M=element 113-118)". Journal of Chemical Physics. 112 (6): 2684–2691. Bibcode:2000JChPh.112.2684H. doi:10.1063/1.480842. S2CID 9959620.
- ^ Stysziński 2010, pp. 144–146.
- ^ Lide, D. R. (2003). "Section 9, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopy". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (84th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 9–45, 9–46. ISBN 978-0-8493-0484-2.
- ^ Stysziński 2010, pp. 139–146.
Bibliography
- Audi, G.; Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S. (2017). "The NUBASE2016 evaluation of nuclear properties". Chinese Physics C. 41 (3): 030001. Bibcode:2017ChPhC..41c0001A. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/41/3/030001.
- Barysz, M.; Ishikawa, Y., eds. (2010). Relativistic methods for chemists. Challenges and advances in computational chemistry and physics. Vol. 10. Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- Thayer, J. S. (2010). "Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heavier Main Group Elements". Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 10. p. 63. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- Stysziński, J. (2010). "Why do we need relativistic computational methods?". Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 10. pp. 99–164. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_3. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- Pershina, V. (2010). "Electronic structure and chemistry of the heaviest elements". Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 10. pp. 451–520. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_11. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- Hoffman, D.C.; Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G.T. (2000). The Transuranium People: The Inside Story. World Scientific. ISBN 978-1-78-326244-1.
- Beiser, A. (2003). Concepts of modern physics (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-244848-1. OCLC 48965418.
- Kragh, H. (2018). From Transuranic to Superheavy Elements: A Story of Dispute and Creation. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-75813-8.
- Zagrebaev, V.; Karpov, A.; Greiner, W. (2013). "Future of superheavy element research: Which nuclei could be synthesized within the next few years?". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 420 (1): 1–15. arXiv:1207.5700. Bibcode:2013JPhCS.420a2001Z. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/420/1/012001. ISSN 1742-6588. S2CID 55434734. 012001.


