Fin whale
| Fin whale[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| A fin whale surfacing in Greenland | |

| |
| Size compared to an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Balaenopteridae |
| Genus: | Balaenoptera |
| Species: | B. physalus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Balaenoptera physalus | |
| Subspecies | |
| |

| |
| Fin whale range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
| |
The fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus), also known as finback whale or common rorqual and formerly known as herring whale or razorback whale, is a cetacean belonging to the parvorder of baleen whales. It is the second-longest species of cetacean on Earth after the blue whale.[8] The largest reportedly grow to 27.3 m (89.6 ft) long[9] with a maximum confirmed length of 25.9 m (85 ft),[10] a maximum recorded weight of nearly 74 tonnes (73 long tons; 82 short tons),[11] and a maximum estimated weight of around 114 tonnes (112 long tons; 126 short tons). American naturalist Roy Chapman Andrews called the fin whale "the greyhound of the sea ... for its beautiful, slender body is built like a racing yacht and the animal can surpass the speed of the fastest ocean steamship."[12]
The fin whale's body is long and slender, coloured brownish-grey with a paler underside. At least two recognized subspecies exist, in the North Atlantic and the Southern Hemisphere. It is found in all the major oceans, from polar to tropical waters. It is absent only from waters close to the pack ice at the poles and relatively small areas of water away from the open ocean. The highest population density occurs in temperate and cool waters.[13] Its food consists of small schooling fish, squid, and crustaceans including copepods and krill.
Like all other large whales, the fin whale was heavily hunted during the 20th century. As a result, it is an endangered species. Over 725,000 fin whales were reportedly taken from the Southern Hemisphere between 1905 and 1976; as of 1997 only 38,000 survived.[2] Recovery of the overall population size of southern subspecies is predicted to be at less than 50% of its pre-whaling state by 2100 due to heavier impacts of whaling and slower recovery rates.[14]
The International Whaling Commission (IWC) issued a moratorium on commercial hunting of this whale,[15] although Iceland and Japan have resumed hunting. The species is also hunted by Greenlanders under the IWC's Aboriginal Subsistence Whaling provisions. Global population estimates range from less than 100,000 to roughly 119,000.[2][16] The fin whale is estimated to be the most common wild mammal species by total biomass, at about 8 million tons (only surpassed by humans and several domestic mammal species).[17][18]
Taxonomy
The fin whale was first described by Friderich Martens in 1675 and by Paul Dudley in 1725. The former description was used as the primary basis of the species Balaena physalus by Carl Linnaeus in 1758.[19] In 1804, Bernard Germain de Lacépède reclassified the species as Balaenoptera rorqual, based on a specimen that had stranded on Île Sainte-Marguerite (Cannes, France) in 1798. In 1830, Louis Companyo described a specimen that had stranded near Saint-Cyprien, southern France, in 1828 as Balaena musculus. Most later authors followed him in using the specific name musculus, until Frederick W. True (1898) showed that it referred to the blue whale. In 1846, British taxonomist John Edward Gray described a 16.7 m (55 ft) specimen from the Falkland Islands as Balaenoptera australis. In 1865, German naturalist Hermann Burmeister described a roughly 15 m (49 ft) specimen found near Buenos Aires about 30 years earlier as Balaenoptera patachonicus. In 1903, Romanian scientist Emil Racoviță placed all these designations into Balaenoptera physalus.[20][21] The word physalus comes from the Greek word physa, meaning "blows", referring to the prominent blow of the species.[22]
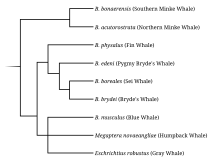
Fin whales are rorquals, members of the family Balaenopteridae, which also includes the humpback whale, the blue whale, Bryde's whale, the sei whale, and the minke whales. The family diverged from the other baleen whales in the suborder Mysticeti as long ago as the middle Miocene.[23]
Recent DNA evidence indicates the fin whale may be more closely related to the humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) and in at least one study the gray whale (Eschrichtius robustus), two whales in different genera, than it is to members of its own genus, such as the minke whales.[24][25][26][27] As of 2023, four subspecies are named, each with distinct physical features and vocalizations. The northern fin whale, B. p. physalus (Linnaeus 1758) inhabits the North Atlantic and the southern fin whale, B. p. quoyi (Fischer 1829) occupies the Southern Hemisphere.[28] Most experts consider the fin whales of the North Pacific to be a third subspecies—this was supported by a 2013 study, which found that the Northern Hemisphere B. p. physalus was not composed of a single subspecies.[29] A 2019 genetic study concluded that the North Pacific fin whales should be considered a subspecies, suggesting the name B. p. velifera (Scammon 1869). The three groups mix at most rarely.[30]
Clarke (2004) proposed a "pygmy" subspecies (B. p. patachonica, Burmeister, 1865) that is purportedly darker in colour and has black baleen. He based this on a single physically mature 19.8 m (65 ft) female caught in the Antarctic in 1947–48, the smaller average size (a few feet) of sexually and physically mature fin whales caught by the Japanese around 50°S, and smaller, darker sexually immature fin whales caught in the Antarctic which he believed were a "migratory phase" of his proposed subspecies.[31] The subspecies has not been genetically established,[30] and is not recognized by the Society for Marine Mammalogy.[32]
Hybrids
The genetic distance between blue and fin whales has been compared to that between a gorilla and human[33] (3.5 million years on the evolutionary tree.[34]) Nevertheless, hybrid individuals between blue and fin whales with characteristics of both are known to occur with relative frequency in both the North Atlantic and North Pacific.[35][36]
The DNA profile of a sampling of whale meat in the Japanese market found evidence of blue/fin hybrids.[37][38]
Anatomy




Size
In the Northern Hemisphere, the average size of adult males and females is about 18.5 and 20 metres (61 and 66 ft), respectively, averaging 38.5 and 50.5 tonnes (42.5 and 55.5 tons),[11] while in the Southern Hemisphere, it is 20.5 and 22 m (67 and 72 ft),[39] weighing 52.5 and 63 tonnes (58 and 69.5 tons).[11]
In the North Atlantic, the longest reported were a 24.4 m (80 ft) male caught off Shetland in 1905 and a 25 m (82 ft) female caught off Scotland sometime between 1908 and 1914,[40][41] while the longest reliably measured were three 20.7 m (68 ft) males caught off Iceland in 1973–74 and a 22.5 m (74 ft) female also caught off Iceland in 1975.[42][43] Mediterranean population are generally smaller, reaching just above 20 m (65.5 ft) at maximum, or possibly up to 21–23 m (68.9–75.5 ft).[44]
In the North Pacific, the longest reported were three 22.9 m (75 ft) males, two caught off California between 1919 and 1926 and the other caught off Alaska in 1925, and a 24.7 m (81 ft) female also caught off California, while the longest reliably measured were a 21 m (69 ft) male caught off British Columbia in 1959 and a 22.9 m (75 ft) female caught off central California between 1959 and 1970.[45][46][47]
In the Southern Hemisphere, the longest reported were a 25 m (82 ft) male and a 27.3 m (89.6 ft) female, while the longest measured by Mackintosh and Wheeler (1929) were a 22.65 m (74.3 ft) male and a 24.53 m (80.5 ft) female.[9] Major F. A. Spencer, while whaling inspector of the factory ship Southern Princess (1936–38), confirmed the length of a 25.9 m (85 ft) female caught in the Antarctic, south of the Indian Ocean;[10] scientist David Edward Gaskin also measured a 25.9 m female as whaling inspector of the British factory ship Southern Venturer in the Southern Ocean in the 1961–62 season.[48] Terence Wise, who worked as a winch operator aboard the British factory ship Balaena, claimed that "the biggest fin [he] ever saw" was a 25.6 m (84 ft) specimen caught near Bouvet Island in January 1958.[49] The largest fin whale ever weighed (piecemeal) was a 22.7 m (74 ft) pregnant female caught by Japanese whalers in the Antarctic in 1948 which weighed 69.5 tonnes (68.4 long tons), not including 6% for loss of fluids during the flensing process.[11] An individual at the maximum confirmed size of 25.9 m is estimated to weigh around 95 tonnes (104.5 tons),[11] varying from about 76 tonnes (84 tons) to 114 tonnes (125.5 tons) depending on fat condition which varies by about 50% during the year.[50]
A newborn fin whale measures about 6.0–6.5 m (19.7–21.3 ft) in length and weighs about 1,800 kilograms (4,000 lb).[51]
Colouration and markings




The fin whale is brownish to dark or light gray dorsally and white ventrally. The left side of the head is dark gray, while the right side exhibits a complex pattern of contrasting light and dark markings. On the right lower jaw is a white or light gray "right mandible patch", which sometimes extends out as a light "blaze" laterally and dorsally unto the upper jaw and back to just behind the blowholes. Two narrow dark stripes originate from the eye and ear, the former widening into a large dark area on the shoulder—these are separated by a light area called the "interstripe wash". These markings are more prominent on individuals in the North Atlantic than in the North Pacific, where they can appear indistinct. The left side exhibits similar but much fainter markings. Dark, oval-shaped areas of pigment called "flipper shadows" extend below and posterior to the pectoral fins. This type of asymmetry is seen in Omura's whale and occasionally in minke whales. It was thought to have evolved because the whale swims on its right side when surface lunging and it sometimes circles to the right while at the surface above a prey patch. However, the whales just as often circle to the left. No accepted hypothesis explains the asymmetry.[52] It has paired blowholes and a broad, flat, V-shaped rostrum. A light V-shaped marking, the chevron, begins behind the blowholes and extends back and then forward again.[8]
The whale has a series of 56–100 pleats or grooves along the bottom of the body that run from the tip of the chin to the navel that allow the throat area to expand greatly during feeding. It has a curved, prominent dorsal fin that ranges in height from 26–75 cm (10–30 in) (usually 45–60 cm [18–24 in]) and averages about 51 cm (20 in), lying about three quarters of the way along the back.[9] Its flippers are small and tapered and its tail is wide, pointed at the tip, and notched in the centre.[16]
When the whale surfaces, the dorsal fin is visible soon after the spout. The spout is vertical and narrow and can reach heights of 6 m (20 ft) or more.[16]
Nervous system
The oral cavity of the fin whale has a very stretchy or extensible nerve system which aids them in feeding.[53]
Life history
Mating occurs in temperate, low-latitude seas during the winter, followed by an 11- to 12-month gestation period. A newborn weans from its mother at 6 or 7 months of age when it is 11 to 12 m (36 to 39 ft) in length, and the calf accompanies the mother to the summer feeding ground. Females reproduce every 2 or 3 years, with as many as six fetuses being reported, but single births are far more common. Females reach sexual maturity between 6 and 12 years of age at lengths of 17.7–19 m (58–62 ft) in the Northern Hemisphere and 20 m (66 ft) in the Southern Hemisphere.[39] Calves remain with their mothers for about one year.[54]
Full physical maturity is attained between 25 and 30 years. Fin whales have a maximum life span of at least 94 years of age,[55] although specimens have been found aged at an estimated 135–140 years.[56]
The fin whale is one of the fastest cetaceans and can sustain speeds between 37 km/h (23 mph)[51] and 41 km/h (25 mph) and bursts up to 46 km/h (29 mph) have been recorded, earning the fin whale the nickname "the greyhound of the sea".[57]
Fin whales are more gregarious than other rorquals, and often live in groups of 6–10, although feeding groups may reach up to 100 animals.[55]
Vocalizations
| Multimedia relating to the fin whale The whale calls have been sped up 10x from their original speed.
|
Like other whales, males make long, loud, low-frequency sounds.[51] The vocalizations of blue and fin whales are the lowest-frequency sounds made by any animal.[58] Most sounds are frequency-modulated (FM) down-swept infrasonic pulses from 16 to 40 hertz frequency (the range of sounds that most humans can hear falls between 20 hertz and 20 kilohertz). Each sound lasts one to two seconds, and various sound combinations occur in patterned sequences lasting 7 to 15 minutes each. The whale then repeats the sequences in bouts lasting up to many days.[59] The vocal sequences have source levels of up to 184–186 decibels relative to 1 micropascal at a reference distance of one metre and can be detected hundreds of miles from their source.[60]
When fin whale sounds were first recorded by US biologists, they did not realize that these unusually loud, long, pure and regular sounds were being made by whales. They first investigated the possibilities that the sounds were due to equipment malfunction, geophysical phenomena, or even part of a Soviet Union scheme for detecting enemy submarines. Eventually, biologists demonstrated that the sounds were the vocalizations of fin whales.[58]
Direct association of these vocalizations with the reproductive season for the species and that only males make the sounds point to these vocalizations as possible reproductive displays.[61][62] Over the past 100 years, the dramatic increase in ocean noise from shipping and naval activity may have slowed the recovery of the fin whale population, by impeding communications between males and receptive females.[63]
Fin whale songs can penetrate over 2,500 m (8,200 ft) below the sea floor and seismologists can use those song waves to assist in underwater surveys.[64]
Breathing

When feeding, they blow five to seven times in quick succession, but while traveling or resting will blow once every minute or two. On their terminal (last) dive they arch their back high out of the water, but rarely raise their flukes out of the water. They then dive to depths of up to 470 m (1,540 ft) when feeding or a few hundred feet when resting or traveling. The average feeding dive off California and Baja lasts 6 minutes, with a maximum of 17 minutes; when traveling or resting they usually dive for only a few minutes at a time.[65]
Ecology
Range and habitat
Like many large rorquals, the fin whale is a cosmopolitan species. It is found in all the world's major oceans and in waters ranging from the polar to the tropical. It is absent only from waters close to the ice pack at both the north and south extremities and relatively small areas of water away from the large oceans, such as the Red Sea, although they can reach into the Baltic Sea, a marginal sea of such conditions.[66][67][68][69] The highest population density occurs in temperate and cool waters. It is less densely populated in the warmest, equatorial regions.[citation needed]
The North Atlantic fin whale has an extensive distribution, occurring from the Gulf of Mexico and Mediterranean Sea, northward to Baffin Bay and Spitsbergen. In general, fin whales are more common north of approximately 30°N latitude, but considerable confusion arises about their occurrence south of 30°N latitude because of the difficulty in distinguishing fin whales from Bryde's whales.[70] Extensive ship surveys have led researchers to conclude that the summer feeding range of fin whales in the western North Atlantic is mainly between 41°20'N and 51°00'N, from shore seaward to the 1,000 fathoms (1,800 m) contour.[71]
Summer distribution of fin whales in the North Pacific is the immediate offshore waters from central Baja California to Japan and as far north as the Chukchi Sea bordering the Arctic Ocean.[72] They occur in high densities in the northern Gulf of Alaska and southeastern Bering Sea between May and October, with some movement through the Aleutian passes into and out of the Bering Sea.[73] Several whales tagged between November and January off southern California were killed in the summer off central California, Oregon, British Columbia, and in the Gulf of Alaska.[72] Fin whales have been observed feeding 250 miles south of Hawaii in mid-May, and several winter sightings have been made there.[74] Some researchers have suggested that the whales migrate into Hawaiian waters primarily in the autumn and winter.[75]
Although fin whales are certainly migratory, moving seasonally in and out of high-latitude feeding areas, the overall migration pattern is not well understood. Acoustic readings from passive-listening hydrophone arrays indicate a southward migration of the North Atlantic fin whale occurs in the autumn from the Labrador-Newfoundland region, south past Bermuda, and into the West Indies.[76] One or more populations of fin whales are thought to remain year-round in high latitudes, moving offshore, but not southward in late autumn.[76] A study based on resightings of identified fin whales in Massachusetts Bay indicates that calves often learn migratory routes from their mothers and return to their mother's feeding area in subsequent years.[54]
In the Pacific, migration patterns are poorly characterized. Although some fin whales are apparently present year-round in the Gulf of California, there is a significant increase in their numbers in the winter and spring.[77] Southern fin whales migrate seasonally from relatively high-latitude Antarctic feeding grounds in the summer to low-latitude breeding and calving areas in the winter. The location of winter breeding areas is still unknown, since these whales tend to migrate in the open ocean.[13]
Population and trends

North Atlantic

North Atlantic fin whales are defined by the International Whaling Commission to exist in one of seven discrete population zones: Nova Scotia-New England, Newfoundland-Labrador, western Greenland, eastern Greenland-Iceland, North Norway, West Norway-Faroe Islands, and Ireland-Spain-United Kingdom-Portugal. Results of mark-and-recapture surveys have indicated that some movement occurs across the boundaries of these zones, suggesting that they are not entirely discrete and that some immigration and emigration does occur.[71] Sigurjónsson estimated in 1995 that total pre-exploitation population size in the entire North Atlantic ranged between 50,000 and 100,000 animals,[78] but his research is criticized for lack of supporting data and an explanation of his reasoning.[13] In 1977, D.E. Sergeant suggested a "primeval" aggregate total of 30,000 to 50,000 throughout the North Atlantic.[79] Of that number, 8,000 to 9,000 would have resided in the Newfoundland and Nova Scotia areas, with whales summering in U.S. waters south of Nova Scotia presumably omitted.[13][80] J. M. Breiwick estimated that the "exploitable" (above the legal size limit of 50 feet) component of the Nova Scotia population was 1,500 to 1,600 animals in 1964, reduced to only about 325 in 1973.[81] Two aerial surveys in Canadian waters since the early 1970s gave numbers of 79 to 926 whales on the eastern Newfoundland-Labrador shelf in August 1980,[82] and a few hundred in the northern and central Gulf of Saint Lawrence in August 1995 – 1996.[83] Summer estimates in the waters off western Greenland range between 500 and 2,000,[84] and in 1974, Jonsgard considered the fin whales off Western Norway and the Faroe Islands to "have been considerably depleted in postwar years, probably by overexploitation".[85] The population around Iceland appears to have fared much better, and in 1981, appeared to have undergone only a minor decline since the early 1960s.[86] Surveys during the summers of 1987 and 1989 estimated of 10,000 to 11,000 between eastern Greenland and Norway.[87] This shows a substantial recovery when compared to a survey in 1976 showing an estimate of 6,900, which was considered to be a "slight" decline since 1948.[88] A Spanish NASS survey in 1989 of the France-Portugal-Spain sub-area estimated a summer population range at 17,355.[89] A formal population assessment has not been conducted since 2016 for the North Atlantic, when the population was estimated to include 70,000 individuals, but population models published by IUCN in 2018 suggest that the number of individuals in the wild is increasing.[90]
A possible resident group was in waters off the Cape Verde Islands in 2000 and 2001.[91]
Mediterranean Sea

Satellite tracking revealed that those found in Pelagos Sanctuary migrate southward to off Tunisia, Malta,[92][93][94] Pantelleria,[95] and Sicily,[96] and also possibly winter off coastal southern Italy, Sardinia,[97] within the Strait of Messina, Aeolian Islands, and off Catalonia,[98][99] Cabrera Archipelago,[100][101] Libya, Kerkennah Islands, Tuscan Archipelago,[102][103] Ischia and adjacent gulfs (e.g. Naples and Pozzuoli[104]), winter feeding ground of Lampedusa,[105][106][107] and whales may recolonize out of the Ligurian Sea to other areas such as in Ionian and in Adriatic Sea. Biology of the species along southern and southeastern parts of the basin such as off Libya, Algeria, and northern Egypt, is unclear due to lacks of scientific approaches although whales have been confirmed off the furthermost of the basin such as along in shore waters of Levantine Sea including Israel,[108] Lebanon,[109] and Cyprus.[110][111] Documented records within Turkish waters have been in very small numbers; one sighting off Antalya in 1994[112] and five documented strandings as of 2016.[113] and a recent sighting on 9 February 2021 by fishermen off the coast of Adana has been documented with images.[114]
It has been shown that populations of Fin whales within the mediterranean have preferred feeding locations that partially overlap with high concentrations of plastic pollution and microplastic debris. High concentrations of microplastics most likely overlap with Fin whales preferred feeding grounds because both microplastic and the whale's food sources are near high trophic upwelling areas.[115]
North Pacific

The total historical North Pacific population was estimated at 42,000 to 45,000 before the start of whaling. Of this, the population in the eastern portion of the North Pacific was estimated to be 25,000 to 27,000.[116] By 1975, the estimate had declined to between 8,000 and 16,000.[72][117] Surveys conducted in 1991, 1993, 1996, and 2001 produced estimates between 1,600 and 3,200 off California and 280 and 380 off Oregon and Washington.[118] The minimum estimate for the California-Oregon-Washington population, as defined in the U.S. Pacific Marine Mammal Stock Assessments: 2005, is about 2,500.[119] Surveys in coastal waters of British Columbia in summers 2004 and 2005 produced abundance estimates of approximately 500 animals.[120] Surveys near the Pribilof Islands in the Bering Sea indicated a substantial increase in the local abundance of fin whales between 1975–1978 and 1987–1989.[121] In 1984, the entire population was estimated to be less than 38% of its historic carrying capacity.[122] Fin whales might have started returning to the coastal waters off British Columbia (a sighting occurred in Johnstone Strait in 2011[123]) and Kodiak Island. Size of the local population migrating to Hawaiian Archipelago is unknown.[124] Historically, several other wintering grounds were scattered in the North Pacific in the past, such as off the Northern Mariana Islands, Bonin Islands, and Ryukyu Islands. There was a sighting of 3 animals nearby Borneo and Palawan in 1999.[125]
For Asian stocks, resident groups may exist in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea, and the Sea of Japan (though these populations are critically endangered and the population off China, Korea, and Japan are either near extinction or in very small numbers). Very small increases in sightings have been confirmed off Shiretoko Peninsula, Abashiri, Kushiro,[126] Tsushima, Sado Island[127] and off Maizuru[128]
Studies of historical catches suggest several resident groups once existed in the North Pacific—the Baja California group and the Yellow Sea–East China Sea (including Ryukyu Islands and western Kyusyu) group.[129] Additionally, respective groups in northern Sea of Japan and the group along Pacific coasts of Japan from Hokkaido to Sanriku might have been resident or less migratory, as well. The only modern record among Ryukyu Islands was of a rotten carcass beached on Ishigaki Island in 2005.[130] Regarding Yellow Sea, a juvenile was accidentally killed along Boryeong in 2014.[131]
There had been congregation areas among Sea of Japan to Yellow Sea such as in East Korea Bay, along eastern coasts of Korean Peninsula, and Ulleungdo.[132]
Modern sightings around the Commander Islands have been annual but not in great numbers, and whales likely to migrate through the areas rather than summering, and possible mixing of western and eastern populations are expected to occur in these waters.[133]
South Pacific
Very little information has been revealed about the ecology of current migration from Antarctic waters are unknown, but small increases in sighting rates are confirmed off New Zealand, such as off Kaikōura, and wintering grounds may exist in further north such as in Papua New Guinea, Fiji,[134] and off East Timor. Confirmations in Rarotonga have been increased recently[135] where interactions with humpback whales occur on occasions.[136] Finbacks are also relatively abundant along the coast of Peru and Chile (in Chile, most notably off Los Lagos region such as Gulf of Corcovado[137] in Chiloé National Park, Punta de Choros [es],[138][139] port of Mejillones,[140][141] and Caleta Zorra. Year-round confirmations indicate possible residents off pelagic north eastern to central Chile such as around coastal Caleta Chañaral and Pingüino de Humboldt National Reserve, east of Juan Fernández Islands, and northeast of Easter Island and possible wintering ground exist for eastern south Pacific population.[142]
Other
Among Northern Indian Ocean and Bay of Bengal, such as along Sri Lanka, India, and Malaysia, sightings and older records of fin whales exist.[143][144][145]
Antarctica
Relatively little is known about the historical and current population levels of the southern fin whale. The IWC officially estimates that the Southern Hemisphere pre-whaling population was 400,000 whales and that the population in 1979 (at the cessation of Antarctic large scale whaling) was 85,200.[146] Both the current and historical estimates should be considered as poor estimates because the methodology and data used in the study are known to be flawed.[13] Other estimates cite current size to be between 15,000 (1983) and 38,000 (1997).[2] As of 2006, there is no scientifically accepted estimate of current population or trends in abundance.[13]
Predation
The only known predator of the fin whale is the killer whale, with at least 20 eyewitness and second-hand accounts of attack or harassment. They usually flee and offer little resistance to attack. Only a few confirmed fatalities have occurred. In October 2005, 16 killer whales attacked and killed a fin whale in the Canal de Ballenas, Gulf of California, after chasing it for about an hour. They fed on its sinking carcass for about 15 minutes before leaving the area. In June 2012, a pod of killer whales was seen in La Paz Bay, in the Gulf of California, chasing a fin whale for over an hour before finally killing it and feeding on its carcass. The whale bore numerous tooth rakes over its back and dorsal fin; several killer whales flanked it on either side, with one individual visible under water biting at its right lower jaw.[147] In July 1908, a whaler reportedly saw two killer whales attack and kill a fin whale off western Greenland. In January 1984, seven were seen from the air circling, holding the flippers, and ramming a fin whale in the Gulf of California, but the observation ended at nightfall.[148][149]
Feeding




The fin whale is a filter-feeder, feeding on small schooling fish, squid and crustaceans including copepods and krill. In the North Pacific, they feed on krill in the genera Euphausia, Thysanoessa, and Nyctiphanes, large copepods in the genus Neocalanus, small schooling fish (e.g. the genera Engraulis, Mallotus, Clupea, and Theragra), and squid. Based on stomach content analysis of over 19,500 fin whales caught by the Japanese whaling fleet in the North Pacific from 1952 to 1971, 64.1% contained only krill, 25.5% copepods, 5.0% fish, 3.4% krill and copepods and 1.7% squid.[150] Nemoto (1959) analyzed the stomach contents of about 7500 fin whales caught in the northern North Pacific and Bering Sea from 1952 to 1958, found that they mainly preyed on euphausiids around the Aleutian Islands and in the Gulf of Alaska and schooling fish in the northern Bering Sea and off Kamchatka. In the northern Bering Sea (north of 58°N), their main prey species were capelin (Mallotus villosus), Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) and Pacific herring (Clupea pallasii); they also consumed saffron cod (Eleginus gracilis). Arctic krill (Thysanoessa raschii) was the only species of euphausiid found in the stomachs of fin whales in the northern Bering Sea. Off Kamchatka, they appeared to primarily feed on herring. They also took large quantities of the copepod Neocalanus cristatus around the Aleutian Islands and in Olyutor Bay off northeast Kamchatka, areas where the species was abundant. Five species of euphausiid (Euphausia pacifica, Thysanoessa spinifera, T. inermis, T. raschii, and T. longipes) were the predominant prey around the Aleutian Islands and in the Gulf of Alaska. Prey varied by region in the Kuril Islands area, with euphausiids (T. longipes, T. inermis, and T. raschii) and copepods (Neocalanus plumchrus and N. cristatus) being the main prey in the northern area and Japanese flying squid (Todarodes pacificus pacificus) and small schooling fish (e.g. Pacific saury, Cololabis saira; and Japanese anchovy, Engraulis japonicus) dominating the diet in the southern area.[151]
Of the fin whale stomachs sampled off British Columbia between 1963 and 1967, euphausiids dominated the diet for four of the five years (82.3 to 100% of the diet), while copepods only formed a major portion of the diet in 1965 (35.7%). Miscellaneous fish, squid, and octopus played only a very minor part of the diet in two of the five years (3.6 to 4.8%).[152] Fin whales caught off California between 1959 and 1970 fed on the pelagic euphausiid Euphausia pacifica (86% of sampled individuals), the more neritic euphausiid Thysanoessa spinifera (9%), and the northern anchovy (Engraulis mordax) (7%); only trace amounts (<0.5% each) were found of Pacific saury (C. saira) and juvenile rockfish (Sebastes jordani).[153] In the Gulf of California, they have been observed feeding on swarms of the euphausiid Nyctiphanes simplex.
In the North Atlantic, they prey on euphausiids in the genera Meganyctiphanes, Thysanoessa and Nyctiphanes and small schooling fish (e.g. the genera Clupea, Mallotus, and Ammodytes). Of the 1,609 fin whale stomachs examined at the Hvalfjörður whaling station in southwestern Iceland from 1967 to 1989 (caught between June and September), 96% contained only krill, 2.5% krill and fish, 0.8% some fish remains, 0.7% capelin (M. villosus), and 0.1% sandeel (family Ammodytidae); a small proportion of (mainly juvenile) blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou) were also found. Of the krill sampled between 1979 and 1989, the vast majority (over 99%) was northern krill (Meganyctiphanes norvegica); only one stomach contained Thysanoessa longicaudata.[154] Off West Greenland, 75% of the fin whales caught between July and October had consumed krill (family Euphausiidae), 17% capelin (Mallotus) and 8% sand lance (Ammodytes sp.). Off eastern Newfoundland, they chiefly feed on capelin, but also take small quantities of euphausiids (mostly T. raschii and T. inermis).[79] In the Ligurian-Corsican-Provençal Basin in the Mediterranean Sea they make dives as deep as 470 m (1,540 ft) to feed on the euphausiid Meganyctiphanes norvegica, while off the island of Lampedusa, between Tunisia and Sicily, they have been observed in mid-winter feeding on surface swarms of the small euphausiid Nyctiphanes couchi.[155]
In the Southern Hemisphere, they feed almost exclusively on euphausiids (mainly the genera Euphausia and Thysanoessa), as well as taking small amounts of amphipods (e.g. Themisto gaudichaudii) and various species of fish. Of the more than 16,000 fin whales caught by the Japanese whaling fleet in the Southern Hemisphere between 1961 and 1965 that contained food in their stomachs, 99.4% fed on euphausiids, 0.5% on fish, and 0.1% on amphipods.[150] In the Southern Ocean they mainly consume E. superba.[156][157][158]
The animal feeds by opening its jaws while swimming at some 11 km/h (6.8 mph) in one study,[159] which causes it to engulf up to 70 cubic metres (18,000 US gal; 15,000 imp gal) of water in one gulp. It then closes its jaws and pushes the water back out of its mouth through its baleen, which allows the water to leave while trapping the prey. An adult has between 262 and 473 baleen plates on each side of the mouth. Each plate is made of keratin that frays out into fine hairs on the ends inside the mouth near the tongue. Each plate can measure up to 76 cm (30 in) in length and 30 cm (12 in) in width.[8]
The whale routinely dives to depths of more than 200 m (660 ft) where it executes an average of four "lunges", to accumulate krill. Each gulp provides the whale with approximately 10 kg (22 lb) of food.[159] One whale can consume up to 1,800 kg (4,000 lb) of food a day,[8] leading scientists to conclude that the whale spends about three hours a day feeding to meet its energy requirements, roughly the same as humans. If prey patches are not sufficiently dense, or are located too deep in the water, the whale has to spend a larger portion of its day searching for food.[159] One hunting technique is to circle schools of fish at high speed, frightening the fish into a tight ball, then turning on its side before engulfing the massed prey.[8]
Parasites, epibiotics, and pathology
Fin whales suffer from a number of pathological conditions. The parasitic copepod Pennella balaenopterae—usually found on the flank of fin whales—burrows into their blubber to feed on their blood,[160] while the pseudo-stalked barnacle Xenobalanus globicipitis is generally found more often on the dorsal fin, pectoral fins, and flukes.[161]
Other barnacles found on fin whales include the acorn barnacle Coronula reginae and the stalked barnacle Conchoderma auritum, which attaches to Coronula or the baleen. The harpacticid copepod Balaenophilus unisetus (heavy infestations of which have been found in fin whales caught off northwestern Spain) and the ciliate Haematophagus also infest the baleen, the former feeding on the baleen itself and the latter on red blood cells.[10]
The remora Remora australis and occasionally the amphipod Cyamus balaenopterae can also be found on fin whales, both feeding on the skin. Infestations of the giant nematode Crassicauda boopis can cause inflammation of the renal arteries and potential kidney failure, while the smaller C. crassicauda infects the lower urinary tract.[122] Out of 87 whales taken and necropsied from the North Atlantic, infection from Crassicauda boopis was found to be very prevalent and invasive, indicating high probability that it was responsible for causing death in these whales.[162] C. boopis was found in 94% of the whales examined. The worms were usually enveloped by "exuberant tissue reactions which in some whales obstructed multiple renal veins". The parasite was most likely by environmental contamination, involving shedding of larvae in urine. Major inflammatory lesions in the mesenteric arteries suggested that the worm larvae were ingested and migrated to the kidney.[162]
These observations suggest that infection from C. boopis can be "lethal by inducing congestive renal failure". Injury to the vascular system is also a result of moderate infections. Therefore, the implication can be made that the feeding migration of fin whales every year in circumpolar waters can be associated with pathologic risk.[162]
An emaciated 13 m (43 ft) female fin whale, which stranded along the Belgian coast in 1997, was found to be infected with lesions of Morbillivirus.[163] In January 2011, a 16.7 m (55 ft) emaciated adult male fin whale stranded dead on the Tyrrhenian coastline of Italy was found to be infected with Morbillivirus and the protozoa Toxoplasma gondii, as well as carrying heavy loads of organochlorine pollutants.[164]
Human interaction
This section needs to be updated. (April 2022) |
Whaling


In the 19th century, the fin whale was occasionally hunted by open-boat whalers, but it was relatively safe, because it could easily outrun ships of the time and often sank when killed, making the pursuit a waste of time for whalers. However, the later introduction of steam-powered boats and harpoons that exploded on impact made it possible to kill and secure them along with blue and sei whales on an industrial scale. As other whale species became overhunted, the whaling industry turned to the still-abundant fin whale as a substitute.[165] It was primarily hunted for its blubber, oil, and baleen. Around 704,000 fin whales were caught in Antarctic whaling operations alone between 1904 and 1975.[166]
The introduction of factory ships with stern slipways in 1925 substantially increased the number of whales taken per year. In 1937–38 alone, over 29,000 fin whales were taken. From 1953–54 to 1961–62, the catch averaged over 30,000 per year. By 1962–63, sei whale catches began to increase as fin whales became scarce. By 1975–76, fewer than 1,000 fin whales were being caught each year. In the North Pacific, over 74,000 fin whales were caught between 1910 and 1975.[167] Between 1910 and 1989, over 55,000 were caught in the North Atlantic.[168] Coastal groups in northeast Asian waters, along with many other baleen species, were likely driven into serious perils or functional extinctions by industrial catches by Japan covering wide ranges of China and Korean EEZ within a very short period in the 20th century.[169] Migrations of the species into Japanese EEZ and in East China Sea were likely to be exterminated relatively earlier, as the last catch records on Amami Ōshima was between the 1910s and 1930s.[170] After the cease of exploiting Asian stocks, Japan kept mass commercial and illegal hunts until 1975. Several thousand individuals were hunted from various stations mainly along coasts of Hokkaido, Sanriku, and the Gotō Islands.[171]
The IWC prohibited hunting in the Southern Hemisphere in 1976.[166] The Soviet Union engaged in the illegal killing of protected whale species in the North Pacific and Southern Hemisphere, over-reporting fin whale catches to cover up illegal takes of other species. In the North Pacific, they reported taking over 10,000 fin whales between 1961 and 1979, while the true catch was less than 9,000. In the Southern Hemisphere, they reported taking nearly 53,000 between 1948 and 1973, when the true total was a little over 41,000.[172][173][174] The fin whale was given full protection from commercial whaling by the IWC in the North Pacific in 1976, and in the North Atlantic in 1987, with small exceptions for aboriginal catches and catches for research purposes.[51] All populations worldwide remain listed as endangered species by the US National Marine Fisheries Service and the International Conservation Union Red List. The fin whale is on Appendix 1 of CITES.[2][175][176]
The IWC has set a quota of 19 fin whales per year for Greenland. Meat and other products from whales killed in these hunts are widely marketed within Greenland, but export is illegal. Iceland and Norway are not bound by the IWC's moratorium on commercial whaling because both countries filed objections to it.[13]
In October 2006, Iceland's fisheries ministry authorized the hunting of 9 fin whales through August 2007.[177] In 2009 and 2010, Iceland caught 125 and 148 fin whales, respectively.[178] An Icelandic company, Hvalur, caught over a hundred fin whales in 2014, and exported a record quantity of 2071 tonnes in a single shipment in 2014. Since 2006, Hvalur has caught more than 500 fin whales and exported more than 5000 tonnes of whale meat to Japan.[179] The International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW) estimates that 991 fin whales have been killed by Icelandic whaling company Hvalur since their return to hunting fin whales in 2009.[180] Icelandic Minister of Fisheries and Agriculture Svandís Svavarsdóttir instituted a ban on Icelandic whaling from mid-June to August 31, 2023; however, whaling has since resumed following the expiration of the temporary ban.[181] The resumption of whaling in Iceland has been met with local and international outcry, including True North, an Icelandic film company. The production company filed an injunction against Hvalur following a statement signed by 67 actors, directors, authors from the international film community, condemning the practice and pledging to boycott Icelandic projects if the whaling continues.[182]
In the Southern Hemisphere, Japan permitted annual takes of 10 fin whales under its Antarctic Special Permit whaling program for the 2005–2006 and 2006–2007 seasons.[183] The proposal for 2007–2008 and the subsequent 12 seasons allowed takes of 50 per year.[13] While 10 fin whales were caught in the 2005–06 season and three in the 2006–07 season, none were caught in the 2007–2008 season. A single fin whale was caught in both the 2008–09 and 2009–10 seasons, two were taken in the 2010–11 season, and one was taken in the 2011–12 season.[184] In 2019, Japan left the International Whaling Commission (IWC) and resumed commercial whaling. Japan reported a catch of 212 total whales in both 2020 and 2021; however, no fin whale catches have yet been reported.[185]
Fin whales have been targets of illegal captures using harpoons for dolphin hunts or intentionally drive whales into nets.[38]
Ship interaction
Collisions with ships are a major cause of mortality. In some areas, they cause a substantial portion of large whale strandings. Most serious injuries are caused by large, fast-moving ships over or near continental shelves.[186]
A 60-foot-long fin whale was found stuck on the bow of a container ship in New York harbour on 12 April 2014.[187]
Two dead fin whales, one 65 feet and one 25 feet, were discovered stuck to the Australian destroyer HMAS Sydney in May 2021 when the ship arrived in Naval Base San Diego.[188]
Ship collisions frequently occur in Tsushima Strait and result in damage done to whales, passengers, and vessels. In response the Japanese Coast Guard has started a surveillance program to monitor large cetacean activity in Tsushima Strait to inform operating vessels in the area.[189]
Museums
Several fin whale skeletons are exhibited in North America. The Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County in Los Angeles, California has an exhibit entitled the "Fin Whale Passage", which displays a 19.2 m (63 ft) fin whale skeleton collected by former museum osteologist Eugene Fischer and field collector Howard Hill in 1926 from the Trinidad whaling station (1920–1926) in Humboldt County, northern California. A steel armature supports the skeleton, which is accompanied by sculpted flukes.[190] Science North, a science museum in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, has a 20 m (66 ft) fin whale skeleton collected from Anticosti Island hanging from the fourth floor of its main building.[191] A 55 ft (17 m) skeleton hangs in the atrium (renovated in 2019–2020) of the science-mathematics building at Knox College (Illinois) in Galesburg, Illinois.[192] Perhaps the largest fin whale skeleton exhibited is at The Grand Rapids Public Museum in Grand Rapids, Michigan, where a 76 ft (23.2 m) skeleton in the Galleria section hangs from the ceiling.[193] Several fin whale skeletons are also exhibited in Europe. The Natural History Museum of Slovenia in Ljubljana, Slovenia, houses a 13 m (43 ft) female fin whale skeleton—the specimen had been found floating in the Gulf of Piran in the spring of 2003.[194] The Hungarian Natural History Museum in Budapest, Hungary, displays a fin whale skeleton hanging near its main entrance which had been caught in the Atlantic Ocean in 1896 and purchased from Vienna in 1900.[195] The Cambridge University Museum of Zoology, in Cambridge, United Kingdom, exhibits a nearly 21 m (69 ft) male fin whale skeleton, which had stranded at Pevensey, East Sussex, in November 1865.[196]
The Otago Museum, in Dunedin, New Zealand, displays a 16.76 m (55.0 ft) fin whale skeleton, which had stranded on the beach at Nelson at the entrance of the Waimea River in 1882.[197]
A 20 m fin whale skeleton is exhibited at Van Thuy Tu Temple in Phan Thiết, Vietnam, where some local fishermen worship whales as near-divine beings who offer protection from storms.[198][199]
-
An 18.8 m (62 ft) fin whale skeleton at the Oceanographic Museum in Monaco
-
Fin whale skeleton, Museum of Zoology Cambridge
-
Fin whale skeleton at the Van Thuy Tu Temple
Whale watching

Fin whales are regularly encountered on whale-watching excursions worldwide. In the Southern California Bight, fin whales are encountered year-round, with the best sightings between November and March. They can even be seen from land (for example, from Point Vicente, Palos Verdes, where they can be seen lunge feeding at the surface only a half mile to a few miles offshore). They are regularly sighted in the summer and fall in the Gulf of St. Lawrence,[200] the Gulf of Maine, the Bay of Fundy, the Bay of Biscay, Strait of Gibraltar, and the Mediterranean. In southern Ireland, they are seen inshore from June to February, with peak sightings in November and December.[201]
Conservation
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2022) |

The fin whale is listed on both Appendix I and Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS).[202]
In addition, the fin whale is covered by the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans in the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area (ACCOBAMS) and the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MOU).[203]
Whaling poses a significant threat to population abundance. Modern whaling technologies have caused a massive decline in fin whale numbers. They are also threatened by vessel collisions, particularly in the Mediterranean Sea where collisions comprise a large part of fin whale mortalities. In the Mediterranean Sea, fin whales and other macro marine fauna are protected and observed under the Fixed Line Transect Mediterranean monitoring Network (FLT Med Net), an international monitoring program that tracks species movements in comparison to maritime traffic and marine litter to manage potential threats.[204] Fin whales occasionally get killed from entanglement and sometimes fishing gear. Military sonar can be problematic for fin whales and the way they communicate during the breeding season, possibly causing a decrease in birth rates.
The International Whaling Commission has set a zero limit for fin whale catches in the North Pacific and southern hemisphere since 1976.[205]
See also
References
- ^ Mead, J. G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 725. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d e Cooke, J.G. (2018). "Balaenoptera physalus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T2478A50349982. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T2478A50349982.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Fischer, Johann Baptist (1829). Synopsis Mammalium. p. 525. Archived from the original on 6 May 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ^ Hist. Nat. Gén. et Partie, des Mamm. et Oiseaux découverts depuis 1788 Archived 23 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Nat. Hist. Cetacea
- ^ Académie Royale Des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts de Belgique (Bruxelles) (1859). Bulletins de l'Académie Royale des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts ... – Académie Royale des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts de Belgique (Bruxelles) – Google ubNX. Hayez. p. 403. ISBN 9781013223624. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Balaenoptera physalus Fin Whale". MarineBio.org. Archived from the original on 29 July 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- ^ a b c Mackintosh, N. A.; Wheeler, J. F. G. (1929). "Southern blue and fin whales". Discovery Reports. I: 259–540.
- ^ a b c Mackintosh, N. A. (1943). "The southern stocks of whalebone whales". Discovery Reports. XXII (3889): 199–300. Bibcode:1944Natur.153..569F. doi:10.1038/153569a0. S2CID 41590649.
- ^ a b c d e Lockyer C (1976). "Body weights of some species of large whales". J. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer. 36 (3): 259–273. doi:10.1093/icesjms/36.3.259.
- ^ Andrews, Roy Chapman. (1916). Whale hunting with gun and camera; a naturalist's account of the modern shore-whaling industry, of whales and their habits, and of hunting experiences in various parts of the world. New York: D. Appleton and Co., p. 158.
- ^ a b c d e f g h National Marine Fisheries Service (2006). Draft recovery plan for the fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus) (PDF). Silver Spring, Maryland: National Marine Fisheries Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 April 2007. Retrieved 25 October 2006.
- ^ CSIRO. 2017. Post-whaling recovery of Southern Hemisphere Archived 21 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Phys.org. Retrieved on 22 August 2017
- ^ "Revised Management Scheme". International Whaling Commission. Archived from the original on 19 December 2008. Retrieved 7 November 2006.
- ^ a b c Shirihai, H.; Jarrett, B. (2006). Whales, Dolphins and Other Marine Mammals of the World. Princeton Field Guides. pp. 43–45. ISBN 978-0-691-12757-6.
- ^ https://www.spektrum.de/news/bestandsaufnahme-was-wiegen-alle-saeugetiere-zusammen/2114073 (in German)
- ^ "Files · master · Milo Lab (Public) / mammal_biomass · GitLab". GitLab. Retrieved 4 April 2023.
- ^ Linnaeus, C (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata (in Latin). Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). p. 824. Archived from the original on 19 March 2015.
- ^ Allen, G. M. (1915). The Whalebone whales of New England. pp. 176–78.
- ^ Cousteau, Jacques (1988). Whales. H.N. Abrams. p. 77. ISBN 9780810910461.
- ^ As described by Martens [1675, p. 132]: "They know the finn-fish by the ... vehement blowing and spouting up of the water....".
- ^ Gingerich, P. (2004). "Whale Evolution". McGraw-Hill Yearbook of Science & Technology. The McGraw Hill Companies. ISBN 978-0-07-142784-5.
- ^ Arnason, U.; Gullberg A. & Widegren, B. (1 September 1993). "Cetacean mitochondrial DNA control region: sequences of all extant baleen whales and two sperm whale species". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 10 (5): 960–970. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040061. PMID 8412655.
- ^ Sasaki, T.; et al. (23 February 2005). "Mitochondrial Phylogenetics and Evolution of Mysticete Whales". Systematic Biology. 54 (1): 77–90. doi:10.1080/10635150590905939. PMID 15805012.
- ^ Hatch, L.T.; Dopman, E.B. & Harrison, R.G. (26 May 2006). "Phylogenetic relationships among the baleen whales based on maternally and paternally inherited characters" (PDF). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 41 (1): 12–27. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.05.023. PMID 16843014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 December 2015. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ^ Seeman, Mette E.; et al. (December 2009). "Radiation of Extant Cetaceans Driven by Restructuring of the Ocean". Systematic Biology. 58 (6): 573–585. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syp060. JSTOR 25677547. PMC 2777972. PMID 20525610.
- ^ "Balaenoptera physalus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- ^ Archer, FI; Morin, PA; Hancock-Hanser, BL; Robertson, KM; Leslie, MS; et al. (2013). "Mitogenomic Phylogenetics of Fin Whales (Balaenoptera physalus spp.): Genetic Evidence for Revision of Subspecies". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e63396. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...863396A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063396. PMC 3656932. PMID 23691042.
- ^ a b Archer, FI; Brownell, Robert; Hancock-Hanser, Brittany; Morin, Phillip; Robertson, Kelly; Sherman, Kathryn; John, Calambokidis; Jorge, Urbán; Rosel, Patricia; Mizroch, Sally; Panigada, Panigoda; Taylor, Barbara (2019). "Revision of fin whale Balaenoptera physalus (Linnaeus, 1758) subspecies using genetics". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1653–1670. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz121.
- ^ Clarke, R. (2004). "Pygmy fin whales". Marine Mammal Science. 20 (2): 329–334. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2004.tb01161.x.
- ^ "List of Marine Mammal Species and Subspecies|April 2022". Society for Marine Mammalogy. 13 November 2016. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ A. Arnason; A. Gullberg (1993). "Comparison between the complete mtDNA sequences of the blue and fin whale, two species that can hybridize in nature". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 37 (4): 312–322. doi:10.1007/BF00178861. PMID 8308901. S2CID 6280748.
- ^ Árnasson, Ú; Spilliaert, R; Pálsdóttir, Á; Árnasson, Ú (January 1998). "A new hybrid between a blue whale, Balaenoptera musculus, and a fin whale, B. physalus: frequency and implications of hybridization". Marine Mammal Science. 14 (1): 82–98. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1998.tb00692.x.
- ^ Bérubé, Martine; Aguilar, Alex (1998). "A new hybrid between a blue whale, Balaenoptera musculus, and a fin whale, B. physalus: frequency and implications of hybridization". Marine Mammal Science. 14 (1): 82–98. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1998.tb00692.x.
- ^ Doroshenko, V.N. (1970). "A whale with features of the fin and blue whale (in Russian)". Izvestia TINRO. 70: 225–257.
- ^ Palumbi, S.R.; Cipriano, F. (1998). "Species Identification Using Genetic Tools: The Value of Nuclear and Mitochondrial Gene Sequences in Whale Conservation". Journal of Heredity. 89 (5): 459–464. doi:10.1093/jhered/89.5.459. PMID 9768497.
- ^ a b Ogino M. (2005)『クジラの死体はかく語る』, Kodansha
- ^ a b Evans, Peter G. H. (1987). The Natural History of Whales and Dolphins. Facts on File.
- ^ Haldane, R.C. (January 1906). "Whaling in Scotland". Ann. Scot. Nat. His. 57: 131.
- ^ Thompson, D'Arcy Wentworth (February 1919). "On whales landed at the Scottish whaling stations, especially during the years 1908–1914. Parts IV. to VI. The bottlenose, humpback, and finner whales". The Scottish Naturalist. 85–86: 6–16.
- ^ Lockyer, C.; Brown, S. G. (1979). "A review of recent biological data for the fin whale population off Iceland". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 29: 185–9.
- ^ Lockyer, C.; Gambell, R.; Brown, S. G. (1977). "Notes on age data of fin whales taken off Iceland, 1967–74". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 27: 427–50.
- ^ Fin whale Archived 23 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine – Ionian Dolphin Project
- ^ Clapham; et al. (1997). "Catches of Humpback and Other Whales from Shore Stations at Moss Landing and Trinidad, California, 1919–1926". Mar Mam. Sci. 13 (3): 368–94. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1997.tb00646.x. Archived from the original on 21 January 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- ^ Reeves, R.R.; Leatherwood, S.; Karl, S.A.; Yohe, E.R. (1985). "Whaling results at Akutan (1912–39) and Port Hobron (1926–37), Alaska". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 35: 441–457.
- ^ Nichol, L. and K. Heise. (1992). The historical occurrence of large whales off the Queen Charlotte Islands. Prep. for South Moresby/Gwaii Haanas National Parks Reserve, Canadian Parks Service, Queen Charlotte City, B.C. 68 pp.
- ^ Gaskin, D. E. (1968). "The New Zealand Cetacea". Fish. Res. Bull., N.Z. (n.s.) 1: 1–92.
- ^ Wise, Terence. 1970. To Catch a Whale. Geoffrey Bles.
- ^ Lockyer, C. (1978). "Growth and Energy Budgets of Large Baleen Whales from the Southern Hemisphere". In Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Working Party on Marine Mammals. Mammals in the Seas: General papers and large cetaceans. Food & Agriculture Org. pp. 503–. ISBN 978-92-5-100513-2.
- ^ a b c d Fox, David (2001). "Balaenoptera physalus (fin whale)". Animal Diversity Web. Archived from the original on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 22 October 2006.
- ^ Tershy, B. R.; D. Wiley (1992). "Asymmetrical pigmentation in the fin whale: a test of two feeding related hypotheses". Marine Mammal Science. 8 (3): 315–318. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1992.tb00416.x.
- ^ Vogl AW, Lillie MA, Piscitelli MA, Goldbogen JA, Pyenson ND, Shadwick RE (2015). "Stretchy nerves are an essential component of the extreme feeding mechanism of rorqual whales". Curr. Biol. 25 (9): R360–1. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.007. PMID 25942546.
- ^ a b Clapham, Phillip J.; Seipt, Irene E. (November 1991). "Resightings of Independent Fin Whales, Balaenoptera physalus, on Maternal Summer Ranges". Journal of Mammalogy. 72 (4): 788–790. doi:10.2307/1381844. JSTOR 1381844.
- ^ a b Martin, Anthony R. (1991). Whales and dolphins. London: Salamander Books. ISBN 978-0-8160-3922-7.
- ^ Ditte Haue (28 October 2010). "Finhvalen var mindst 135 år gammel | Nyheder | DR". Dr.dk. Archived from the original on 10 June 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- ^ "Fin Whale". nature.ca: Canadian Museum of Nature. Archived from the original on 5 February 2007. Retrieved 22 October 2006.
- ^ a b Payne, Roger (1995). Among Whales. New York: Scribner. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-684-80210-7.
- ^ "Finback Whales". Bioacoustics Research Program, Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Archived from the original on 14 July 2007. Retrieved 26 October 2006.
- ^ W. J. Richardson, C. R. Greene, C. I. Malme and D. H. Thomson, Marine Mammals and Noise (Academic Press, San Diego, 1995).
- ^ Croll, D.A.; Clark, C.W.; Acevedo, A.; Flores, S.; Gedamke, J.; Urban, J.; Urban, Jorge (2002). "Only male fin whales sing loud songs" (PDF). Nature. 417 (6891): 809. Bibcode:2002Natur.417..809C. doi:10.1038/417809a. PMID 12075339. S2CID 4432037. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2006.
- ^ Watkins, W.; Tyack, P.; Moore, K.; Bird, J. (1987). "The 20 Hz signals of finback whales (Balaenoptera physalus)". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 82 (6): 1901–1902. Bibcode:1987ASAJ...82.1901W. doi:10.1121/1.395685. PMID 3429729.
- ^ Segelken, R. (19 June 2002). "Humanity's din in the oceans could be blocking whales' courtship songs and population recovery". Cornell University. Archived from the original on 13 February 2007. Retrieved 11 November 2006.
- ^ Andrews, Robin (11 February 2021). "Whale Songs Could Reveal Deep Secrets Beneath the Oceans". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 February 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ Croll, D. A.; Acevedo-Gutiérrez, A.; Tershy, B.R.; Urbán-Ramírez, J. (2001). "The diving behavior of blue and fin whales: is dive duration shorter than expected based on oxygen stores?" (PDF). Comp Biochem Physiol A. 129 (4): 797–809. doi:10.1016/s1095-6433(01)00348-8. PMID 11440866. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 March 2011. Retrieved 22 December 2012.
- ^ "Wieder Finnwal in der Ostsee". Archived from the original on 15 April 2016.
- ^ KG, Ostsee-Zeitung GmbH & Co. "Rostock/Eckernförde – Finnwal in der Ostsee gesichtet – OZ – Ostsee-Zeitung". ostsee-zeitung.de. Archived from the original on 30 October 2016. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ Allgemeine, Augsburger. "Angler filmt Wal in Ostsee-Bucht". Archived from the original on 30 October 2016. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ Jansson N.. 2007. ”Vi såg valen i viken” Archived 7 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Aftonbladet. Retrieved on 7 September 2017
- ^ Mead, J.G. (1977). Records of Sei and Bryde's whales from the Atlantic Coast of the United States, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean. Vol. Spec. Iss. 1. pp. 113–116. ISBN 978-0-906975-03-9.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b Mitchell, E. (1974). "Present status of Northwest Atlantic fin and other whale stocks". In W.E. Schevill (ed.). The Whale Problem: A Status Report. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. pp. 108–169. ISBN 978-0-674-95075-7.
- ^ a b c Rice, D.W. (1974). "Whales and whale research in the eastern North Pacific". In W.E. Schevill (ed.). The Whale Problem: A Status Report. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. pp. 170–195. ISBN 978-0-674-95075-7.
- ^ Reeves, R.R.; M.W. Brown (1985). "Whaling in the Bay of Fundy". Whalewatcher. 19 (4): 14–18.
- ^ Mobley, J.R. Jr.; M. Smultea; T. Norris & D. Weller (1996). "Fin whale sighting north of Kaua'i, Hawai'i". Pacific Science. 50 (2): 230–233.
- ^ Thompson, P.O.; W.A. Friedl (1982). "A long term study of low frequency sound from several species of whales off Oahu, Hawaii". Cetology. 45: 1–19.
- ^ a b Clark, C.W. (1995). "Application of US Navy underwater hydrophone arrays for scientific research on whales". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 45: 210–212.
- ^ Tershy, B.R.; D. Breese & C.S. Strong (1990). Abundance, seasonal distribution and population composition of balaenopterid whales in the Canal de Ballenas, Gulf of California, Mexico. Vol. Spec. Iss. 12. pp. 369–375. ISBN 978-0-906975-23-7.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Sigurjónsson, J. (1995). "On the life history and autecology of North Atlantic rorquals". In A.S. Blix; L. Walløe; Ø. Ulltang (eds.). Whales, Seals, Fish and Man. Elsevier Science. pp. 425–441. ISBN 978-0-444-82070-9.
- ^ a b D.E. Sergeant (1977). "Stocks of fin whales Balaenoptera physalusL. in the North Atlantic Ocean". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 27: 460–473.
- ^ Allen, K. R. (1970). "A note on baleen whale stocks of the north west Atlantic". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 20: 112–113.
- ^ Breiwick, J. M. (1993). Population dynamics and analyses of the fisheries for fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in the northwest Atlantic Ocean (PhD thesis). University of Washington, Seattle.
- ^ Hay, K. (1982). "Aerial line-transect estimates of abundance of humpback, fin, and long-finned pilot whales in the Newfoundland-Labrador area". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 31: 373–387.
- ^ Kingsley, M. C. S.; Reeves, R. R. (1998). "Aerial surveys of cetaceans in the Gulf of St. Lawrence in 1995 and 1996" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Zoology. 76 (8): 1529–1550. doi:10.1139/cjz-76-8-1529. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- ^ Larsen, F. (1995). "Abundance of minke and fin whales off West Greenland". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 45: 365–370.
- ^ Jonsgard, A. (1974). "On whale exploitation in the eastern part of the North Atlantic Ocean". In W.E. Schevill (ed.). The Whale Problem: A Status Report. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. pp. 97–107. ISBN 978-0-674-95075-7.
- ^ Rørvik, C.J.; J. Sigurjónsson (1981). "A note on the catch per unit effort in the Icelandic fin whale fishery". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 31: 379–383.
- ^ Buckland, S.T.; K.L. Cattanach & Th. Gunnlaugsson (1992). "Fin whale abundance in the North Atlantic, estimated from Icelandic and Faroese NASS-87 and NASS-89 data". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 42: 645–651.
- ^ Rørvik, C.J.; J. Jónsson; O.A. Mathisen & Å. Jonsgård (1976). "Fin Whales, Balaenoptera physalus (L.), Off the West Coast of Iceland. Distribution, Segregation by Length and Exploitation". Rit Fiskideildar. 5: 1–30. ISSN 0484-9019.
- ^ Buckland, S.T.; K.L. Cattanach & S. Lens (1992). "Fin whale abundance in the eastern North Atlantic, estimated from Spanish NASS-89 data". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 42: 457–460.
- ^ IUCN (4 February 2018). Balaenoptera physalus: Cooke, J.G.: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T2478A50349982 (Report). International Union for Conservation of Nature. doi:10.2305/iucn.uk.2018-2.rlts.t2478a50349982.en.
- ^ Moore M.; Lisa Steiner L.; Jann B. (2003). "Cetacean surveys in the Cape Verde Islands and the use of cookiecutter shark bite lesions as a population marker for fin whales". Aquatic Mammals. 29 (3): 383–389. doi:10.1578/01675420360736569.
- ^ "Fin Whales in Maltese waters – The Malta Independent". independent.com.mt. Archived from the original on 6 May 2016. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
- ^ Ltd, Allied Newspapers (25 July 2007). "Fin whale spotted close to Malta". Archived from the original on 18 April 2016. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
- ^ Ltd, Allied Newspapers (21 May 2010). "Whales in Maltese waters, and we hardly know about them!". Archived from the original on 18 April 2016. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
- ^ "Pantelleria: la balena del 2008 (video) – Pantelvoice.it". pantelvoice.it. Archived from the original on 25 April 2016.
- ^ Panigada S., Donovan G., Druon N.-J., Lauriano G., Pierantonio N., Pirotta E., Zanardelli M., Zerbini A., 2015, Satellite telemetry on Mediterranean fin whales to identify critical habitats and mitigate ship strikes, SC/66a/HIM/14, International Whaling Commission
- ^ "Sardegna, avvistate 5 balenottere al largo di Cala Gonone /Video". adnkronos.com. Archived from the original on 7 December 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ "EDMAKTUB I Estudio de cetáceos". edmaktub.org. Archived from the original on 25 March 2017. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ^ CASINOS A.. VERICAD R.J.. 2009. THE CETACEANS OF THE SPANISH COASTS : A SURVEY Archived 25 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Mammalia. Volume 40. Issue 2, pp.267–290. ISSN (Online) 1864-1547. ISSN (Print) 0025-1461. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/mamm.1976.40.2.267 Archived 20 October 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Mallorca, Diario de (4 June 2012). "Estudian el paso de ballenas rorcuales por Cabrera – Diario de Mallorca". diariodemallorca.es. Archived from the original on 22 March 2017. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ^ 2011. Avistan tres ballenas en aguas del Parque Nacional de Cabrera Archived 22 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Cori F.. 2016. Wild Tuscany: a guide for animal passionates Archived 29 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 29 March 2017
- ^ 2013. Riproduzione riservata. Capoliveri diserta la cerimonia? Piombino lo sfida a un confronto Archived 29 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 29 March 2017
- ^ Mussi B.. Miragliuolo A.. Monzini E.. Battaglia M.. 1999. Fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus) feeding ground in the coastal waters of Ischia (Archipelago Campano) Archived 23 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine (pdf). The European Cetacean Society. Retrieved on 28 March 2017
- ^ "Satellite telemetry applied to fin whale in the Mediterranean Sea" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "Lampedusa project (5 March 2013)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 April 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Marini L., Germana Villetti G., Consiglio C., WINTERING AREAS OF FIN WHALES (BALAENOPTERA PHYSALUS) IN THE MEDITERRANEAN SEA: A PRELIMINARY SURVEY Archived 22 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine, pp.126-128
- ^ "Literature Review: Update on the Cetacean Fauna of the Mediterranean Levantine Basin". ResearchGate. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ^ firasofski (17 December 2014). "Blue Fin Whale – Lebanon". Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2016 – via YouTube.
- ^ "Action Plan for the Conservation of Cetaceans in Libya" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2016.
- ^ "The Status and Distribution of Cetaceans in Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 September 2016. Retrieved 15 April 2016.
- ^ Notarbartolo-Di-Sciara G.; Zanardelli M.; Jahoda M.; Panigada S.; Airoldi S. (2003). "The fin whale Balaenoptera physalus (L. 1758) in the Mediterranean Sea". Mammal Rev. 33 (2): 105–150. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2907.2003.00005.x.
- ^ "Fifth stranding record of the Fin Whale in Turkey". Archived from the original on 31 March 2016. Retrieved 15 April 2016.
- ^ ADANA, (DHA) - (9 February 2021). "Adana'da oluklu balina heyecanı! İlk kez görüldü". hurriyet.com.tr (in Turkish). Archived from the original on 9 February 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ^ Fossi, Maria Cristina; Romeo, Teresa; Baini, Matteo; Panti, Cristina; Marsili, Letizia; Campani, Tommaso; Canese, Simonepietro; Galgani, François; Druon, Jean-Noël; Airoldi, Sabina; Taddei, Stefano (2017). "Plastic Debris Occurrence, Convergence Areas and Fin Whales Feeding Ground in the Mediterranean Marine Protected Area Pelagos Sanctuary: A Modeling Approach". Frontiers in Marine Science. 4. doi:10.3389/fmars.2017.00167. ISSN 2296-7745.
- ^ Ohsumi, S.; S. Wada (1974). "Status of whale stocks in the North Pacific, 1972". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 24: 114–126.
- ^ Chapman, D.G. (1976). "Estimates of stocks (original, current, MSY level and MSY)(in thousands) as revised at Scientific Committee meeting 1975". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 26: 44–47.
- ^ Barlow, J. (2003). Preliminary estimates of the Abundance of Cetaceans along the U.S. West Coast: 1991–2001 (Report). Administrative report LJ-03-03, available from Southwest Fisheries Science Center, 8604 La Jolla Shores Dr., La Jolla CA 92037.
- ^ Caretta, J.V.; K.A. Forney; M.M. Muto; J. Barlow; J. Baker; B. Hanson & M.S. Lowry (2006). U.S. Pacific Marine Mammal Stock Assessments: 2005 (PDF) (Report). U.S. Department of Commerce Technical Memorandum, NOAA-TM-NMFS-SWFSC-388. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 October 2006. Retrieved 31 October 2006.
- ^ Williams, R.; Thomas, L. (2007). "Distribution and abundance of marine mammals in the coastal waters of BC, Canada" (PDF). Journal of Cetacean Research and Management. 9: 15–28. doi:10.47536/jcrm.v9i1.688. S2CID 18834375. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 February 2011.
- ^ Baretta, L.; G.L. Hunt Jr. (1994). "Changes in the numbers of cetaceans near the Pribilof Islands, Bering Sea, between 1975–78 and 1987–89" (PDF). Arctic. 47 (4): 321–326. doi:10.14430/arctic1304. S2CID 52226419. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 November 2020. Retrieved 31 October 2006.
- ^ a b Mizroch, S.A.; D.W. Rice & J.M. Breiwick (1984). "The fin whale, Balaenoptera physalus". Mar Fish. Review. 46: 20–24.
- ^ "Fin Whale Sighting Off the Coast of Vancouver Island". YouTube. Archived from the original on 11 July 2015. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ "Fin Whale Sighting North of Kaua'i, Hawai'i (PDF Download Available)". ResearchGate. Archived from the original on 23 June 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2017.
- ^ "Literature Review: A note on cetacean observations in the Indian Ocean Sanctuary and the South China Sea, Mauritius to the Philippines, April 1999". ResearchGate. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ^ Kotoe S. (2013). "釧路のすんごい思い出 その1". さかまた組 [kobemap.com/sakamata/]. Archived from the original on 14 May 2014. Retrieved 13 May 2014.
- ^ Yamada T., ed. (2009). "新潟県佐渡郡沢崎鼻沖種不明ナガスクジラ属クジラ目視". National Museum of Nature and Science. p. 海棲哺乳類情報データベース. Archived from the original on 5 January 2013. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ^ "кит в японском море". Archived from the original on 5 May 2021. Retrieved 20 October 2021 – via tomsk.fm.
- ^ Mizroch A.S.; Rice W.D.; Zwiefelhofer D.; Waite J.; Perryman L.W. (2009). "Distribution and movements of fin whales in the North Pacific Ocean". Mammal Review. 39 (3): The Wiley Online Library. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.2009.00147.x.
- ^ Dolphin and Whale Save Project, 八重山周辺海域における鯨類ストライディングデータ(通過目撃等含む) Archived 16 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ {사진추가재업} 오늘 잡힌 서해 괴물고래 (레벨:4) 로또독식 Archived 16 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 17 August 2017
- ^ Chang K.; Zhang C.; Park C.; Kang; Ju S.; Lee; Wimbush M., eds. (2015). Oceanography of the East Sea (Japan Sea). Springer International Publishing. p. 380. ISBN 9783319227207. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2015.
- ^ "Финвал (сельдяной кит) Balaenoptera physalus (Linnaeus, 1758)". komandorsky.ru. Archived from the original on 12 October 2016. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ "Whale watching – whale and dolphin encounters around Levuka, Fiji Islands". owlfiji.com. Archived from the original on 21 April 2016. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
- ^ "Fin Whale visits Rarotonga – Capitola by the Sea". capitolabythesea.com. Archived from the original on 26 October 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2016.
- ^ Travis Horton (12 August 2014). "Humpback Whale Migration – Rarotonga, 2014". Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 7 March 2016.
- ^ Fin whale Archived 13 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine – OceanSounds e.V.
- ^ Toro F.; Vilina A.Y.; Capella J.J.; Gibbons J. (2016). "Novel Coastal Feeding Area for Eastern South Pacific Fin Whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in Mid-Latitude Humboldt Current Waters off Chile" (PDF). Aquatic Mammals. 42 (1): 47–55. doi:10.1578/AM.42.1.2016.47. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- ^ "Bicentinario Chile". tanyadimitrova.blogspot.jp. Archived from the original on 15 April 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- ^ Pacheco S.A.; Villegas K.V.; Riascos M.J.; Waerebeek V.K. (2015). "Presence of fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in Mejillones Bay, a major seaport area in northern Chile". Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía. 50 (2): 383–389. doi:10.4067/S0718-19572015000300017. Archived from the original on 13 April 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- ^ Pacheco S.A.; Villegas K.V.; Riascos M.J.; Waerebeek V.K. (2015). "Presence of fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in Mejillones Bay, a major seaport area in northern Chile". Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía. 50 (2): 383–389. doi:10.4067/S0718-19572015000300017.
- ^ Acevedo J.; O’Grady M.; Wallis B. (2012). "Sighting of the fin whale in the Eastern Subtropical South Pacific: Potential breeding ground?". Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía. 47 (3): 559–563. doi:10.4067/s0718-19572012000300017. Archived from the original on 13 April 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- ^ Sathasivam K.. 2015. A CATALOGUE OF INDIAN MARINE MAMMAL RECORDS Archived 24 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine (pdf)
- ^ "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 25 October 2018.
- ^ Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center – List of Protected Aquatic Species in Myanmar Archived 25 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ IWC (1979). "Report of the sub-committee on protected species. Annex G, Appendix I". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 29: 84–86.
- ^ "Orcas attack, kill large fin whale off La Paz (rare footage)". Pete Thomas Outdoors. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- ^ Jefferson, T. A.; Stacey, P. J.; Baird, R. W. (1991). "A review of killer whale interactions with other marine mammals: predation to co-existence" (PDF). Mammal Review. 21 (4): 151–180. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.1991.tb00291.x. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 September 2011. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ Ford, John K. B.; Reeves, Randall R. (2008). "Fight or flight: Antipredator strategies of baleen whales". Mammal Review. 38 (1): 50–86. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.573.6671. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.2008.00118.x.
- ^ a b Nemoto, T.; A. Kawamura (1977). "Characteristics of food habits and distribution of baleen whales with special reference to the abundance of North Pacific sei and Bryde's whales". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Iss. 1: 80–87.
- ^ Mizroch, S. A., Rice, D. W., Zwiefelhofer, D., Waite, J., and Perryman, W. L. (2009). "Distribution and movements of fin whales in the North Pacific Ocean". Mammal Rev. (39) 193–227.
- ^ Flinn, R.D.; Trites, A.W.; Gregr, E. J.; Perry, R. I. (2002). "Diets of fin, sei, and sperm whales in British Columbia: an analysis of commercial whaling records, 1963–1967". Mar Mam. Sci. 18 (3): 663–679. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2002.tb01065.x.
- ^ Rice, D.W. (1977). "Synopsis of biological data on the sei whale and Bryde's whale in the eastern North Pacific". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Iss. 1: 92–97.
- ^ Sigurjónsson, J.; Víkingsson, G. A. (1997). "Seasonal abundance of and estimated food consumption by cetaceans in Icelandic and adjacent waters". Journal of Northwest Atlantic Fishery Science. 22: 271–287. doi:10.2960/j.v22.a20.
- ^ Canese, S.; Cardinali, A.; Fortuna, C. M.; Giusti, M.; Lauriano, G.; et al. (2006). "The first identified winter feeding ground of fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in the Mediterranean Sea". J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 86 (4): 903–907. doi:10.1017/s0025315406013853. S2CID 86166076.
- ^ Reeves, R.; G. Silber & M. Payne (July 1998). Draft Recovery Plan for the Fin Whale Balaenoptera physalus and Sei Whale Balaenoptera borealis (PDF). Silver Spring, Maryland: National Marine Fisheries Service. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ Reynolds, John Elliott, and Sentiel A. Rommel. (1999). Biology of Marine Mammals. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press.
- ^ S.L. Perry; D.P. DeMaster & G.K. Silber (1999). "Special Issue: The Great Whales: History and Status of Six Species Listed as Endangered Under the U.S. Endangered Species Act of 1973". Marine Fisheries Review. 61 (1): 52–58. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ a b c Lin, Brian (7 June 2007). "Whale Has Super-sized Big Gulp". University of British Columbia. Archived from the original on 15 June 2007. Retrieved 8 June 2007.
- ^ Çíçek, Erdoğan; Öktener, Ahmet; Çapar, Osman Bahadır (2007). "First Report of Pennella balaenopterae Koren and Danielssen, 1877 (Copepoda: Pennelidae) from Turkey" (PDF). Türkiye Parazitoloji Dergisi (Turkish Journal of Parasitology). 31 (3): 239–241. PMID 17918069. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- ^ Rajaguru, Arjuna; Shantha, Gopalsamy (1992). "Association between the sessile barnacle Xenobalanus globiclpitis (Coronulidae) and the bottlenose dolphin Tursiops truncatus (Delphinidae) from the Bay of Bengal, India, with a summary of previous records from cetaceans" (PDF). Fishery Bulletin. 90: 197–202. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 July 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- ^ a b c Lambertsen, Richard H. (15 May 1986). "Disease of the Common Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus): Crassicaudiosis of the Urinary System". Journal of Mammalogy. 67 (2): 353–366. doi:10.2307/1380889. ISSN 0022-2372. JSTOR 1380889.
- ^ Jauniaux, T.; Charlier, G.; Desmecht, M.; Coignoui, F. (1998). "Lesions of morbillivirus infection in a fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus) stranded along the Belgian coast". Veterinary Record. 143 (15): 423–424. doi:10.1136/vr.143.15.423. hdl:2268/77383. PMID 9807793. S2CID 30378912. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- ^ Mazzariol, Sandro; Marcer, Federica; Mignone, Walter; Serracca, Laura; Goria, Mariella; Marsili, Letizia; Giovanni, Giovanni; Guardo, Di; Casalone, Cristina; et al. (2012). "Dolphin Morbillivirus and Toxoplasma gondii coinfection in a Mediterranean fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus)". BMC Veterinary Research. 8 (1): 20. doi:10.1186/1746-6148-8-20. PMC 3319419. PMID 22397492.
- ^ "American Cetacean Society Fact Sheet: Fin Whale, Balaenoptera physalus". American Cetacean Society. Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ a b IWC (1995). "Report of the scientific committee". Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 45: 53–221.
- ^ Barlow, J.; K. A. Forney; P.S. Hill; R.L. Brownell Jr.; J.V. Caretta; D.P. DeMaster; F. Julian; M.S. Lowry; T. Ragen & R.R. Reeves (1997). U.S. Pacific Marine Mammal Stock Assessments: 1996 (PDF) (Report). NOAA Technical Memo NMFD-SWFSC-248. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 October 2006. Retrieved 1 November 2006.
- ^ International Whaling Statistics.
- ^ Ishikawa H.; Watanabe T. (2014). "A catalogue of whales and dolphins recorded in Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan" (PDF). 下関鯨類研究室報告 No.2 (2014). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 January 2015. Retrieved 9 January 2015.
- ^ Miyazaki N.; Nakayama K. (1989). "Records of Cetaceans in the Waters of the Amami Island". 国立科学博物館専報 22, 235–249, 1989. 22: 235–249. Archived from the original on 12 January 2015. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "海域自然環境保全基礎調査 – 海棲動物調査報告書, (2)- 19. シャチ Orcinus orca (Limaeus,1758)マイルカ科" (PDF). 自然環境保全基礎調査: 54. 1998. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 July 2015. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ Clapham, P. J.; Baker, C. Scott (2008). "Reported vs. Actual Catches by the U.S.S.R. in the Southern Hemisphere, 1948–73. Appendix II in Berzin, A. A.; trans. by Y. V. Ivashchenko. "The Truth About Soviet Whaling"". Marine Fisheries Review. 70 (2): 4–59.
- ^ Clapham, P.J.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2008). "Soviet catches of large whales in the North Pacific, 1961–79. Appendix III in Berzin, A. A.; trans. by Y. V. Ivashchenko "The Truth About Soviet Whaling"". Marine Fisheries Review. 70 (2): 4–59.
- ^ Yablokov, A.V. (1994). "Validity of whaling data". Nature. 367 (6459): 108. Bibcode:1994Natur.367..108Y. doi:10.1038/367108a0. S2CID 4358731.
- ^ "UNEP-WCMC Species Database: CITES-Listed Species". UNEP-WCMC. 23 October 2006. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- ^ "Species Profile for Finback whale". U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. Archived from the original on 27 December 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- ^ "Iceland to Resume Whale Hunting, Defying Global Ban". Bloomberg.com. 18 October 2006. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- ^ "Catches under Objection". International Whaling Commission. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010. Retrieved 6 February 2012.
- ^ Revkin, Andrew C. (13 September 2014). "Should Fin Whales Be a Source of Wonder or Meat?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 14 September 2014. Retrieved 14 September 2014.
- ^ "148 fin whales killed in Iceland this season". IFAW. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ "a win for whales: Icelandic minister suspends fin whaling". IFAW. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ Daðason, Kolbeinn Tumi (31 August 2023). "True North krefst lögbanns á hvalveiðar Kristjáns - Vísir". visir.is (in Icelandic). Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ "U.S. Protests Japan's Announced Return to Whaling in Antarctic". Bureau of International Information Programs, U.S. Department of State. 20 November 2006. Archived from the original on 19 May 2009. Retrieved 27 November 2006.
- ^ "Catches under Permit". International Whaling Commission. Archived from the original on 18 June 2012. Retrieved 6 February 2012.
- ^ "Catches taken: Under Objection". iwc.int. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ Laist, D.W.; Knowlton, A.R.; Mead, J.G.; Collet A.S. & Podesta, M. (2001). "Collisions between ships and whales" (PDF). Marine Mammal Science. 17 (1): 35–75. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb00980.x. S2CID 84815248. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- ^ "Whale Found Dead on Bow of Ship Examined in New Jersey". Associated Press. 16 April 2014. Archived from the original on 19 April 2014. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ Lendon, Brad (12 May 2021). "Australian destroyer arrived in San Diego with 2 dead endangered whales stuck to its hull". CNN. Archived from the original on 12 May 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- ^ "Maritime Information and Communication System – 福岡海上保安部 – 海洋生物目撃情報". Japanese Coast Guard. Archived from the original on 11 January 2015. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "The Fin Whale Passage – Natural History Museum of Los Angeles". 3 June 2010. Archived from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ "Science North – Science Education Center – Exhibits". sciencenorth.ca. Archived from the original on 13 March 2012. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ Register-Mail, Matt KoesterThe. "Whale skeleton going up at Knox College". The Register-Mail. Archived from the original on 5 December 2020. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- ^ "VAMC Building Features". Grand Rapids Public Museum. Archived from the original on 21 January 2014. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
- ^ "The mysterious death of young Leonora". Archived from the original on 28 March 2012.
- ^ "Permanent exhibitions – Hungarian Natural History Museum – Fin whale skeleton". Archived from the original on 25 May 2013.
- ^ "The Finback Whale". University Museum of Zoology, Cambridge. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012.
- ^ "Maritime". Otago Museum. Archived from the original on 22 November 2011. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- ^ "The largest whale skeleton in Vietnam". VnExpress International. 8 March 2021. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- ^ Christiansen, Paul (10 April 2018). "Whale Worship: Exploring the Role of Whales in Vietnam's Coastal Lore". Saigoneer. Archived from the original on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- ^ "Whales Online – Fin whale". Archived from the original on 12 July 2012.
- ^ "Irish Whale and Dolphin Group – Fin Whale Species Profile". Archived from the original on 20 February 2012.
- ^ "Appendix I and Appendix II Archived 11 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine" of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). As amended by the Conference of the Parties in 1985, 1988, 1991, 1994, 1997, 1999, 2002, 2005 and 2008. Effective: 5 March 2009.
- ^ "Accobams News". Archived from the original on 16 October 2021. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- ^ "FLT Mediterranean Monitoring Network - marine species and threats". ISPRA Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ Mahalingam, Prashanth; Silberstein, Maya. "Balaenoptera physalus (fin whale)". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
Further reading
- Peter Saundry. 2011. Fin whale. Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for Science and the Environment. Washington DC Archived 10 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine. C. Michael Hogan Ed. Content partner: Encyclopedia of Life
- National Audubon Society Guide to Marine Mammals of the World, Reeves, Stewart, Clapham and Powell, ISBN 0-375-41141-0
- Whales & Dolphins Guide to the Biology and Behaviour of Cetaceans, Maurizio Wurtz and Nadia Repetto. ISBN 1-84037-043-2
- Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, editors Perrin, Wursig and Thewissen, ISBN 0-12-551340-2
External links
- US National Marine Fisheries Service fin whale web page
- ARKive – images and videos of the fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus)
- Finback whale sounds
- Photograph of a fin whale underwater
- Photographs of a fin whale breaching
- World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) – species profile for the fin whale
- Voices in the Sea – Sounds of the Fin Whale Archived 25 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine




