Runestone


A runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but most of the runestones date from the late Viking Age. Most runestones are located in Scandinavia, but there are also scattered runestones in locations that were visited by Norsemen during the Viking Age. Runestones are often memorials to dead men. Runestones were usually brightly coloured when erected, though this is no longer evident as the colour has worn off. The vast majority of runestones are found in Sweden.
History

The tradition of raising stones that had runic inscriptions first appeared in the 4th and 5th century, in Norway and Sweden, and these early runestones were usually placed next to graves,[2][3] though their precise function as commemorative monuments has been questioned.[4] The earliest Danish runestones appeared in the 8th and 9th centuries, and there are about 50 runestones from the Migration Period in Scandinavia.[5] Most runestones were erected during the period 950–1100 CE, and then they were mostly raised in Sweden, and to a lesser degree in Denmark and Norway.[2]
The tradition is mentioned in both Ynglinga saga and Hávamál:
For men of consequence a mound should be raised to their memory, and for all other warriors who had been distinguished for manhood a standing stone, a custom that remained long after Odin's time.
- —The Ynglinga saga[6]
A son is better,
though late he be born,
And his father to death have fared;
Memory-stones
seldom stand by the road
Save when kinsman honors his kin.— Hávamál[7]
What may have increased the spread of runestones was an event in Denmark in the 960s. King Harald Bluetooth had just been baptised and in order to mark the arrival of a new order and a new age, he commanded the construction of a runestone.[8] The inscription reads
King Haraldr ordered this monument made in memory of Gormr, his father, and in memory of Þyrvé, his mother; that Haraldr who won for himself all of Denmark and Norway and made the Danes Christian.[8][9]
The runestone has three sides of which two are decorated with images. On one side, there is an animal that is the prototype of the runic animals that would be commonly engraved on runestones, and on another side there is Denmark's oldest depiction of Jesus. Shortly after this stone had been made, something happened in Scandinavia's runic tradition[according to whom?]. Scores of chieftains and powerful Norse clans consciously tried to imitate King Harald, and from Denmark a runestone wave spread northwards through Sweden[according to whom?]. In most districts, the fad died out after a generation, but, in the central Swedish provinces of Uppland and Södermanland, the fashion lasted into the 12th century.[8]
Distribution
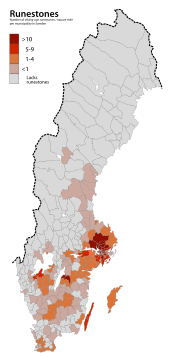
There are about 3,000 runestones among the about 6,000 runic inscriptions in Scandinavia.[3] There are also runestones in other parts of the world as the tradition of raising runestones followed the Norsemen wherever they went, from the Isle of Man (Manx Runestones) in the west to the Black Sea in the east (Berezan' Runestone), and from Jämtland in the north to Schleswig in the south.[2]
The runestones are unevenly distributed in Scandinavia: Denmark has 250 runestones, Norway has 50 while Iceland has none.[5] Sweden has as many as between 1,700[5] and 2,500[3][8] depending on definition. The Swedish district of Uppland has the highest concentration with as many as 1,196 inscriptions in stone, whereas Södermanland is second with 391.[8]
Outside of Scandinavia, the Isle of Man stands out with its 30 runestones from the 9th century and early 11th century.[10] Scattered runestones have also been found in England, Ireland, Scotland and the Faroe Islands.[3] With the exception of the runestone on Berezan', there are no runestones in Eastern Europe, which probably is due to a lack of available stones and the fact that the local population probably did not treat the foreigners' stones with much respect.[11]
Runestones were placed on selected spots in the landscape, such as assembly locations, roads, bridge constructions, and fords. In medieval churches, there are often runestones that have been inserted as construction material, and it is debated whether they were originally part of the church location or had been moved there. In southern Scania, runestones can be tied to large estates that also had churches constructed on their land. In the Mälaren Valley, the runestones appear to be placed so that they mark essential parts of the domains of an estate, such as courtyard, grave field, and borders to neighbouring estates. Runestones usually appear as single monuments and more rarely as pairs. In some cases, such as the Hunnestad Monument, they are part of larger monuments together with other raised stones.[2]
Although scholars know where 95% of all runestones were discovered, only about 40% were discovered in their original location. The remainder have been found in churches, roads, bridges, graves, farms, and water routes.[12] On the other hand, scholars agree that the stones were not moved very far from their original sites.[13]
Effect of religion

In many districts, 50% of the stone inscriptions have traces of Christianity, but, in Uppland, which has the highest concentration of runic inscriptions in the world, about 70% of the 1,196 stone inscriptions are explicitly Christian, which is shown by engraved crosses or added Christian prayers, and only a few runestones are not Christian.[8]
Scholars have suggested that the reason why so many Christian runestones were raised in Uppland is that the district was the focal point in the conflict between Norse paganism and the newly Christianized King of Sweden. It is possible that the chieftains tried to demonstrate their allegiance to the king and to display their Christian faith to the world and to God by adding Christian crosses and prayers on their runestones. What speaks against this theory is the fact that Norway, Denmark, and Götaland did not have any corresponding development in the runestone tradition. Moreover, not a single runestone declares that there was any relationship towards the king.[15] Additionally, the runestones appear to show that the conversion was a rather peaceful process.[16]
According to another theory, it was a social fashion that was popular among certain clans, but not among all of them.[15] Once some clans in southern Uppland had begun to raise runestones, neighbouring clans emulated them. However, in parts where these clans were less influential, the runestone raising did not reach the same popularity.[17] Several scholars have pointed out the long Viking expeditions and the considerable amassment of wealth in the district. At this time, Swedish chieftains near Stockholm had created considerable fortunes through trade and pillaging both in the East and in the West. They had seen the Danish Jelling stones or they had been inspired by Irish high crosses and other monuments.[8]
The runestones show the different ways in which Christianity changed Norse society, and one of the greatest changes involved no longer burying the deceased on the clan's grave field among his ancestors. Instead, he was buried in the cemetery of the church,[18] while the runestone would serve as a memorial at the homestead,[19] but for certain families, there was less change as they had churches built adjoining the family grave field.[20]
Inscriptions

The main purpose of a runestone was to mark territory, to explain inheritance, to boast about constructions, to bring glory to dead kinsmen and to tell of important events. In some parts of Uppland, the runestones also appear to have functioned as social and economical markers.[15]
Virtually all the runestones from the late Viking Age make use of the same formula. The text tells in memory of whom the runestone is raised, who raised it, and often how the deceased and the one who raised the runestone are related to each other. Also, the inscription can tell the social status of the dead person, possible foreign voyage, place of death, and also a prayer, as in the following example,[21] the Lingsberg Runestone U 241:
And Danr and Húskarl and Sveinn had the stone erected in memory of Ulfríkr, their father's father. He had taken two payments in England. May God and God's mother help the souls of the father and son.[21][22]

Stone raisers
Most runestones were raised by men and only one runestone in eight is raised by a single woman, while at least 10% are raised by a woman together with several men. It is common that the runestones were raised by sons and widows of the deceased, but they could also be raised by sisters and brothers. It is almost only in Uppland, Södermanland, and Öland that women raised runestones together with male relatives. It is not known why many people such as sisters, brothers, uncles, parents, housecarls, and business partners can be enumerated on runestones, but it is possible that it is because they are part of the inheritors.[21]
Those commemorated
A vast majority, 94%, are raised in memory of men, but, contrary to common perception, the vast majority of the runestones are raised in memory of people who died at home. The most famous runestones and those that people tend to think of are those that tell of foreign voyages, but they comprise only c. 10% of all runestones,[21] and they were raised in usually memory of those not having returned from Viking expeditions and not as tributes to those having returned.[23] These runestones contain roughly the same message as the majority of the runestones, which is that people wanted to commemorate one or several dead kinsmen.[21]
Expeditions in the East


The first man who scholars know fell on the eastern route was the East Geat Eyvindr whose fate is mentioned on the 9th century Kälvesten Runestone.[21] The epitaph reads:
Styggr/Stigr made this monument in memory of Eyvindr, his son. He fell in the east with Eivísl. Víkingr coloured and Grímulfr.[23][24]
It is unfortunate for historians that the stones rarely reveal where the men died.[23] On the Smula Runestone in Västergötland, we are informed only that they died during a war campaign in the East: "Gulli/Kolli raised this stone in memory of his wife's brothers Ásbjôrn and Juli, very good valiant men. And they died in the east in the retinue".[23][25] Another runemaster in the same province laconically states on the Dalum Runestone: "Tóki and his brothers raised this stone in memory of their brothers. One died in the west, another in the east".[23][26]
The country that is mentioned on the most runestones is the Byzantine Empire, which at the time comprised most of Asia Minor and the Balkans, as well as a part of Southern Italy. If a man died in the Byzantine Empire, no matter how he had died or in which province, the event was noted as "he died in Greece". Sometimes an exception could be made for Southern Italy, which was known as the land of the Lombards, such as Inga's Óleifr who, it is presumed, was a member of the Varangian Guard, and about whom the Djulafors Runestone in Södermanland says: "Inga raised this stone in memory of Óleifr, her ... He ploughed his stern to the east, and met his end in the land of the Lombards."[23][27]
Other Norsemen died in Gardariki (Russia and Ukraine) such as Sigviðr on the Esta Runestone who his son Ingifastr reported had fled in Novgorod (Holmgarðr): "He fell in Holmgarðr, the ship's leader with the seamen."[23][28] There were others who died not as far from home and it appears that there were close contacts with Estonia due to many personal names such as Æistfari ("traveller to Estonia"), Æistulfr ("Wolf of Estonians") and Æistr ("Estonian"). One of the runestones that report of deaths in Estonia is the Ängby Runestone which tells that a Björn had died in Vironia (Virland).[23]
There were many ways to die as reported by the runestones. The Åda Runestone reports that Bergviðr drowned during a voyage to Livonia,[23] and the Sjonhem Runestone tells that the Gotlander Hróðfúss was killed in a treacherous way by what was probably a people in the Balkans.[29] The most famous runestones that tell of eastern voyages are the Ingvar Runestones which tell of Ingvar the Far-Travelled's expedition to Serkland, i.e., the Muslim world. It ended in tragedy as none of the more than 25 runestones that were raised in its memory tells of any survivor.[30]
Expeditions in the West


Other Vikings travelled westwards. The Anglo-Saxon rulers paid large sums, Danegelds, to Vikings, who mostly came from Denmark and who arrived to the English shores during the 990s and the first decades of the 11th century. What may be part of a Danegeld has been found submerged in a creek in Södra Betby in Södermanland, Sweden. At the location, there is also a runestone with the text: "[...] raise the stone in memory of Jôrundr, his son, who was in the west with Ulfr, Hákon's son."[30][31] It is not unlikely that the voyage westwards is connected with the English silver treasure.[30] Other runestones are more explicit with the Danegelds. Ulf of Borresta who lived in Vallentuna travelled westwards several times,[30] as reported on the Yttergärde Runestone:
And Ulfr has taken three payments in England. That was the last that Tosti paid. Then Þorketill paid. Then Knútr paid.[30][32]
Tosti may have been the Swedish chieftain Skoglar Tosti who is otherwise only mentioned by Snorri Sturluson in Heimskringla and who Snorri reports to have been a "great warrior" who "was out for long periods of time on war expeditions". Þorketill was Thorkell the Tall, one of the most famous Viking chieftains, and who often stayed in England. Knútr is no one else but Canute the Great, who became king of England in 1016.[30]
Canute sent home most of the Vikings who had helped him conquer England, but he kept a strong bodyguard, the Þingalið. It was considered to be a great honour to be part of this force, and, on the Häggeby Runestone in Uppland, it is reported that Geiri "sat in the Assembly's retinue in the west",[30][33] and the Landeryd Runestone mentions Þjalfi "who was with Knútr".[30][34] Some Swedish Vikings wanted nothing else but to travel with Danes such as Thorkell and Canute the Great, but they did not make it to their destinations. Sveinn, who came from Husby-Sjuhundra in Uppland, died when he was half-way to England, as explained on the runestone that was raised in his memory: "He died in Jútland. He meant to travel to England".[35][36] Other Vikings, such as Guðvér did not only attack England, but also Saxony, as reported by the Grinda Runestone in Södermanland:[37]
There are in total about 30 runestones that tell of people who went to England,[37] see the England Runestones. Some of them are very laconic and only tell that the Viking was buried in London, or in Bath, Somerset.[37]

Conversion
Swedish men who travelled to Denmark, England, or Saxony and the Byzantine Empire played an important part in the introduction of Christianity in Sweden,[39] and two runestones tell of men baptized in Denmark, such as the runestone in Amnö, which says "He died in christening robes in Denmark."[40][41] A similar message is given on another runestone in Vallentuna near Stockholm that tells that two sons waited until they were on their death beds before they converted: "They died in (their) christening robes."[37][42] Christening robes or baptismal clothes, hvitavaðir, were given to pagan Scandinavians when they were baptized, and in Uppland there are at least seven stones that tell of convertees having died in such robes.[40][43]
The language used by the missionaries appears on several runestones, and they suggest that the missionaries used a rather uniform language when they preached.[39] The expression "light and paradise" is presented on three runestones, of which two are located in Uppland and a third on the Danish island Bornholm. The runestone U 160 in Risbyle says "May God and God's mother help his spirit and soul; grant him light and paradise."[39][44] and the Bornholm runestone also appeals to Saint Michael: "May Christ and Saint Michael help the souls of Auðbjôrn and Gunnhildr into light and paradise."[39][45]
Christian terminology was superimposed on the earlier pagan, and so Paradise substituted Valhalla, invocations to Thor and magic charms were replaced with Saint Michael, Christ, God, and the Mother of God.[39] Saint Michael, who was the leader of the army of Heaven, subsumed Odin's role as the psychopomp, and led the dead Christians to "light and paradise".[46] There are invocations to Saint Michael on one runestone in Uppland, one on Gotland, on three on Bornholm and on one on Lolland.[39]
There is also the Bogesund runestone that testifies to the change that people were no longer buried at the family's grave field: "He died in Eikrey(?). He is buried in the churchyard."[19][47]
Other types of runestones
Another interesting class of runestone is rune-stone-as-self promotion. Bragging was a virtue in Norse society, a habit in which the heroes of sagas often indulged, and is exemplified in runestones of the time. Hundreds of people had stones carved with the purpose of advertising their own achievements or positive traits. A few examples will suffice:
- U 1011: "Vigmund had this stone carved in memory of himself, the cleverest of men. May God help the soul of Vigmund, the ship captain. Vigmund and Åfrid carved this memorial while he lived."
- Frösö Runestone: "Östman Gudfast's son made the bridge, and he Christianized Jämtland"
- Dr 212: "Eskill Skulkason had this stone raised to himself. Ever will stand this memorial that Eskill made;"
- U 164: "Jarlabanki had this stone put up in his own lifetime. And he made this causeway for his soul's sake. And he owned the whole of Täby by himself. May God help his soul."
Other runestones, as evidenced in two of the previous three inscriptions, memorialize the pious acts of relatively new Christians. In these, we can see the kinds of good works people who could afford to commission runestones undertook. Other inscriptions hint at religious beliefs. For example, one reads:
- U 160: "Ulvshattil and Gye and Une ordered this stone erected in memory of Ulv, their good father. He lived in Skolhamra. God and God's Mother save his spirit and soul, endow him with light and paradise."
Although most runestones were set up to perpetuate the memories of men, many speak of women, often represented as conscientious landowners and pious Christians:
- Sö 101: "Sigrid, Alrik's mother, Orm's daughter made this bridge for her husband Holmgers, father of Sigoerd, for his soul"
as important members of extended families:
- Br Olsen;215: "Mael-Lomchon and the daughter of Dubh-Gael, whom Adils had to wife, raised this cross in memory of Mael-Muire, his fostermother. It is better to leave a good fosterson than a bad son"
and as much-missed loved ones:
- N 68: "Gunnor, Thythrik's daughter, made a bridge in memory of her daughter Astrid. She was the most skilful girl in Hadeland."
-
The Jelling stones which triggered the great runestone trend in Scandinavia[according to whom?]
-
The runestone Gs 13 documents an early 11th-century Swedish Viking who died in Finland
-
The Kingittorsuaq Runestone from Greenland
-
Runestone from Tirsted in the National Museum of Denmark
-
Runestone from Tirsted drawing from 1765
As sources
The only existing Scandinavian texts dating to the period before 1050[48] (besides a few finds of inscriptions on coins) are found amongst the runic inscriptions, some of which were scratched onto pieces of wood or metal spearheads, but for the most part they have been found on actual stones.[49] In addition, the runestones usually remain in their original form[48] and at their original locations,[50] and so their importance as historical sources cannot be overstated.[48]
The inscriptions seldom provide solid historical evidence of events and identifiable people but instead offer insight into the development of language and poetry, kinship, and habits of name-giving, settlement, depictions from Norse paganism, place-names and communications, Viking as well as trading expeditions, and, not least, the spread of Christianity.[51] Though the stones offer Scandinavian historians their main resource of information concerning early Scandinavian society, not much can be learned by studying the stones individually. The wealth of information that the stones provide can be found in the different movements and reasons for erecting the stones, in each region respectively. Approximately ten percent of the known runestones announce the travels and deaths of men abroad. These runic inscriptions coincide with certain Latin sources, such as the Annals of St. Bertin and the writings of Liudprand of Cremona, which contain valuable information on Scandinavians/Rus' who visited Byzantium.[52]
Imagery

The inscription is usually arranged inside a band, which often has the shape of a serpent, a dragon or a quadruped beast.[2]
Norse legends
It appears from the imagery of the Swedish runestones that the most popular Norse legend in the area was that of Sigurd the dragon slayer.[53] He is depicted on several runestones, but the most famous of them is the Ramsund inscription. The inscription itself is of a common kind that tells of the building of a bridge, but the ornamentation shows Sigurd sitting in a pit thrusting his sword, forged by Regin, through the body of the dragon, which also forms the runic band in which the runes are engraved. In the left part of the inscription lies Regin, who is beheaded with all his smithying tools around him. To the right of Regin, Sigurd is sitting and he has just burnt his thumb on the dragon's heart that he is roasting. He is putting the thumb in his mouth and begins to understand the language of the marsh-tits that are sitting in the tree. They warn him of Regin's schemes. Sigurd's horse Grani is also shown tethered to the tree.[54]
Another important personage from the legend of the Nibelungs is Gunnarr. On the Västerljung Runestone, there are three sides and one of them shows a man whose arms and legs are encircled by snakes. He is holding his arms stretched out gripping an object that may be a harp, but that part is damaged due to flaking.[54] The image appears to be depicting an older version of the Gunnarr legend in which he played the harp with his fingers, which appears in the archaic eddic poem Atlakviða.[55]
Norse myths

The Norse god who was most popular was Thor,[56] and the Altuna Runestone in Uppland shows Thor's fishing expedition when he tried to capture the Midgard Serpent.[57] Two centuries later, the Icelander Snorri Sturluson would write: "The Midgarth Serpent bit at the ox-head and the hook caught in the roof of its mouth. When it felt that, it started so violently that both Thor's fists went smack against the gunwale. Then Thor got angry, assumed all his godly strength, and dug his heels so sturdily that his feet went right through the bottom of the boat and he braced them on the sea bed." (Jansson's translation).[58] The Altuna Runestone has also included the foot that went through the planks.[59]
It appears that Ragnarök is depicted on the Ledberg stone in Östergötland. On one of its sides it shows a large warrior with a helmet, and who is bitten at his feet by a beast. This beast is, it is presumed, Fenrir, the brother of the Midgard Serpent, and who is attacking Odin. On the bottom of the illustration, there is a prostrate man who is holding out his hands and who has no legs. There is a close parallel from an illustration at Kirk Andreas on the Isle of Man. The Manx illustration shows Odin with a spear and with one of his ravens on his shoulders, and Odin is attacked in the same way as he is on the Ledberg stone. Adding to the stone's spiritual content is a magic formula that was known all across the world of the pagan Norsemen.[59]
On one of the stones from the Hunnestad Monument in Scania, there is an image of a woman riding a wolf using snakes as reins. The stone may be an illustration of the giantess Hyrrokin ("fire-wrinkled"), who was summoned by the gods to help launch Baldr's funeral ship Hringhorni, which was too heavy for them. It was the same kind of wolf that is referred to as the "Valkyrie horse" on the Rök runestone.[59]
Colour

Today, most runestones are painted with falu red, since the colour red makes it easy to discern the ornamentation, and it is appropriate since red paint was also used on runes during the Viking Age.[60] In fact, one of the Old Norse words for "writing in runes" was fá and it originally meant "to paint" in Proto-Norse (faihian).[61] Moreover, in Hávamál, Odin says: "So do I write / and colour the runes"[60][62] and in Guðrúnarkviða II, Gudrun says "In the cup were runes of every kind / Written and reddened, I could not read them".[63][64]
There are several runestones where it is declared that they were originally painted. A runestone in Södermanland says "Here shall these stones stand, reddened with runes",[60][65] a second runestone in the same province says "Ásbjörn carved and Ulfr painted"[60][66] and a third runestone in Södermanland says "Ásbjôrn cut the stone, painted as a marker, bound with runes".[61][67] Sometimes, the original colours have been preserved unusually well, and especially if the runestones were used as construction material in churches not very long after they had been made. One runestone in the church of Köping on Öland was discovered to be painted all over, and the colour of the words was alternating between black and red.[60]
The most common paints were red ochre, red lead, soot, calcium carbonate, and other earth colours, which were bound with fat and water. It also appears that the Vikings imported white lead, green malachite and blue azurite from Continental Europe.[60] By using an electron microscope, chemists have been able to analyse traces of colours on runestones, and in one case, they discovered bright red vermilion, which was an imported luxury colour. However, the dominating colours were white and red lead.[68] There are even accounts where runes were reddened with blood as in Grettis saga, where the Völva Þuríðr cut runes on a tree root and coloured them with her own blood to kill Grettir, and in Egils saga where Egill Skallagrímsson cut ale runes on a drinking horn and painted them with his own blood to see if the drink was poisoned.[69]
Preservation and care
The exposed runestones face several threats to the inscribed rock surface.
In Sweden, lichen grows at approximately 2 mm (1⁄16 in) per year. In more ideal conditions it can grow considerably faster. Many runestones are placed alongside roads and road dust causes lichen to grow faster, making lichen a major problem. The lichen's small root strands break through the rock, and blast off tiny pieces, making the rock porous, and over time degrade the inscriptions. Algae and moss also cause the rock to become porous and crumble.[70]
Water entering the cracks and crevices of the stone can cause whole sections to fall off either by freezing or by a combination of dirt, organic matter, and moisture, which can cause a hollowing effect under the stone surface.[70]
Proper preservation techniques slow down the rate of degradation. One method to combat the lichen, algae and moss problem is to smear in fine-grained moist clay over the entire stone. This is then left to sit for a few weeks, which suffocates the organic matter and kills it.[70]
See also
- Alliterative verse
- Bautil
- Deer stone
- Eltang stone
- England Runestones
- Funeral
- Greece runestones
- Hero stone
- Ingvar runestones
- Jötunvillur
- Kudurru
- Kurgan stelae
- List of runestones
- Old Norse orthography
- Ovansjö Runestones
- Petroglyphs
- Picture stone
- Piraeus Lion
- Stele
- Valknut
- Varangian runestones
- Viking runestones
Notes
- ^ "Om lifvet i Sverige under hednatiden" by Oscar Montelius (1905), pp. 81–82.
- ^ a b c d e "Runsten", Nationalencyklopedin (1995), volume 16, pp. 91-92.
- ^ a b c d Zilmer 2005:38
- ^ Koesling, Jonas. 2021. “Memories Carved in Stones? Collective Memory Studies and Early Scandinavian Rune-Stones, or Remarks on the Banalities of ‘Burial-Stones’.” Scandinavian-Canadian Studies Journal / Études scandinaves au Canada 28: 38–77.
- ^ a b c Olstad, Lisa (2002-12-16). "Ein minnestein for å hedre seg sjølv". forskning.no. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ Ynglinga saga in English translation, at Northvegr.
- ^ Bellows 1936:44
- ^ a b c d e f g Harrison & Svensson 2007:192
- ^ Entry DR 42 in Rundata.
- ^ Page 1995: 207–44
- ^ Pritsak 1987:306
- ^ Sawyer, B. 2000:26
- ^ Zilmer 2005:39
- ^ Larsson 1999:176
- ^ a b c Harrison & Svensson 2007:195
- ^ Jansson 1987:120
- ^ Harrison & Svensson 2007:195ff
- ^ Jansson 1987:116
- ^ a b Jansson 1987:118
- ^ Jansson 1987:119
- ^ a b c d e f Harrison & Svensson 2007:196
- ^ The entry U 241 in Rundata.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Harrison & Svensson 2007:197
- ^ The entry Ög 8 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry Vg 184 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry Vg 197 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry Sö 65 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry Sö 171 in Rundata.
- ^ Harrison & Svensson 2007:197ff
- ^ a b c d e f g h Harrison & Svensson 2007:198
- ^ The entry Sö 260 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry U 344 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry U 668 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry Ög 111 in Rundata.
- ^ Harrison & Svensson 2007:198ff
- ^ The entry U 539 in Rundata.
- ^ a b c d e Harrison & Svensson 2007:199
- ^ The entry Sö 166 in Rundata.
- ^ a b c d e f Jansson 1987:113
- ^ a b Jansson 1987:112
- ^ Entry U 699 in Rundata.
- ^ The entry U 243 in Rundata.
- ^ A monk in the Abbey of St. Gall tells of a group of Norsemen who visited the court of the Frankish king Louis the Pious. They agreed to get baptized and were given valuable baptismal robes, but, as there were not enough robes, the robes were cut up and divided among the Norsemen. One of the Vikings then exclaimed that he had got baptized 20 times and he had always received beautiful potatoes, but this time he got rags that better fit a herdsman than a warrior. (Harrison & Svensson 2007:199)
- ^ Entry U 160 in Rundata.
- ^ Entry DR 399 in Rundata.
- ^ Jansson 1987:114
- ^ Entry U 170 in Rundata.
- ^ a b c Pritsak 1987:307
- ^ Sawyer, B. 2000:1
- ^ Pritsak 1987:308
- ^ Sawyer, B. 2000:3
- ^ Sawyer, P. 1997:139
- ^ Jansson 1987:144
- ^ a b Jansson 1987:145
- ^ Jansson 1987:146
- ^ Jansson 1987:149
- ^ Jansson 1987:150
- ^ Jansson 1987:151ff
- ^ a b c Jansson 1987:152
- ^ a b c d e f Harrison & Svensson 2007:208
- ^ a b Jansson 1987:156
- ^ Bellows 1936:67
- ^ Jansson 1987:153
- ^ Bellows 1936:459
- ^ Entry Sö 206 in Rundata.
- ^ Entry Sö 347 in Rundata.
- ^ Entry Sö 213 in Rundata.
- ^ Harrison & Svensson 2007:209
- ^ Jansson 1987:154
- ^ a b c Snaedal & Åhlen 2004:33-34
References
- Bellows, Henry A. (1936). The Poetic Edda. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New York.
- Harrison, D. & Svensson, K. (2007). Vikingaliv. Fälth & Hässler, Värnamo. ISBN 91-27-35725-2
- Nationalencyklopedin (1995), volume 16, pp. 91–92.
- Jansson, Sven B. F. (1987), Runes in Sweden, Gidlunds, ISBN 91-7844-067-X
- Koesling, Jonas. 2021. “Memories Carved in Stones? Collective Memory Studies and Early Scandinavian Rune-Stones, or Remarks on the Banalities of ‘Burial-Stones’.” Scandinavian-Canadian Studies Journal / Études scandinaves au Canada 28: 38–77.
- Larsson, Mats G. (1999). Svitjod – Resor till Sveriges Ursprung. Atlantis. ISBN 91-7486-421-1
- Page, Raymond I. (1995). Runes and Runic Inscriptions: Collected Essays on Anglo-Saxon and Viking Runes. Parsons, D. (ed). Woodbridge: Boydell Press. ISBN 978-0-85115-387-2
- Pritsak, O. (1987). The Origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Distributed by Harvard University Press for the Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute.
- Sawyer, Birgit. (2000). The Viking-Age Rune-Stones: Custom and Commemoration in Early Medieval Scandinavia. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-926221-7
- Sawyer, P. (1997). The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-285434-8
- Snaedal, T. & Åhlen, M. (2004). Svenska Runor. Riksantikvarieämbetet, 33 & 34. ISBN 91-7209-366-8
- Stocklund, Marie; et al., eds. (2006), Runes and Their Secrets: Studies in Runology, Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, ISBN 87-635-0428-6
- Zilmer, Kristel (2005), "He Drowned in Holmr's Sea": Baltic Traffic in Early Nordic Sources (PDF), Tartu University Press, (diss.), ISBN 9949-11-089-0
External links
- The Jelling Project – Information about Jelling and the runestones
- Photos of runestones and image stones from Gotland

![The Jelling stones which triggered the great runestone trend in Scandinavia[according to whom?]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/ef/Runenstein_Blauzahn_2.jpg/200px-Runenstein_Blauzahn_2.jpg)